Further Development of Polyepichlorohydrin Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis by Tuning Cast Solution Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
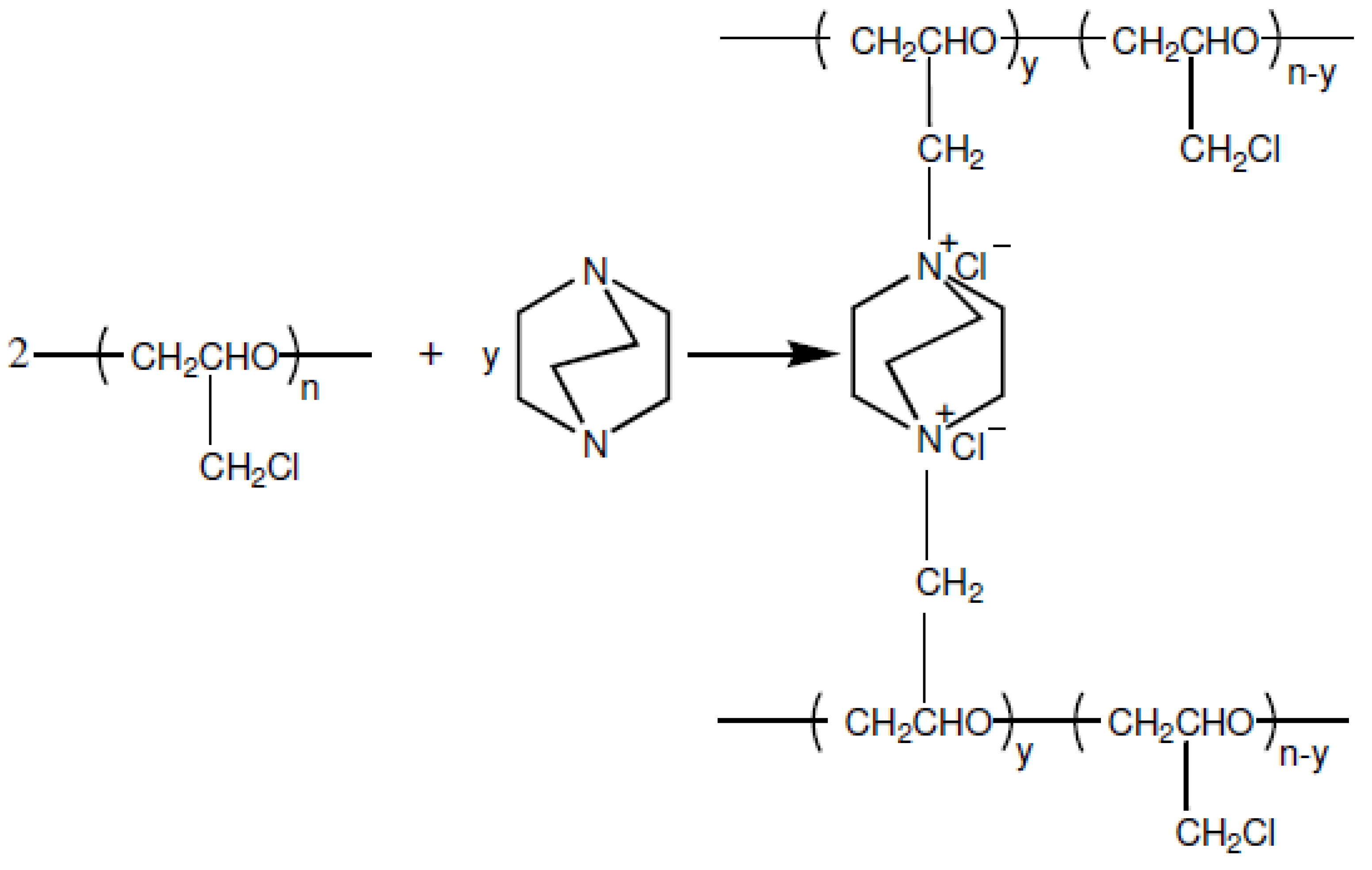
2.1. Synthesis of AEMs
2.2. Characterization of AEMs
2.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.3. Ion Exchange Capacity
2.2.4. Swelling Degree
2.2.5. Fixed Charge Density (FCD)
2.2.6. Electrical Conductivity and Area Resistance
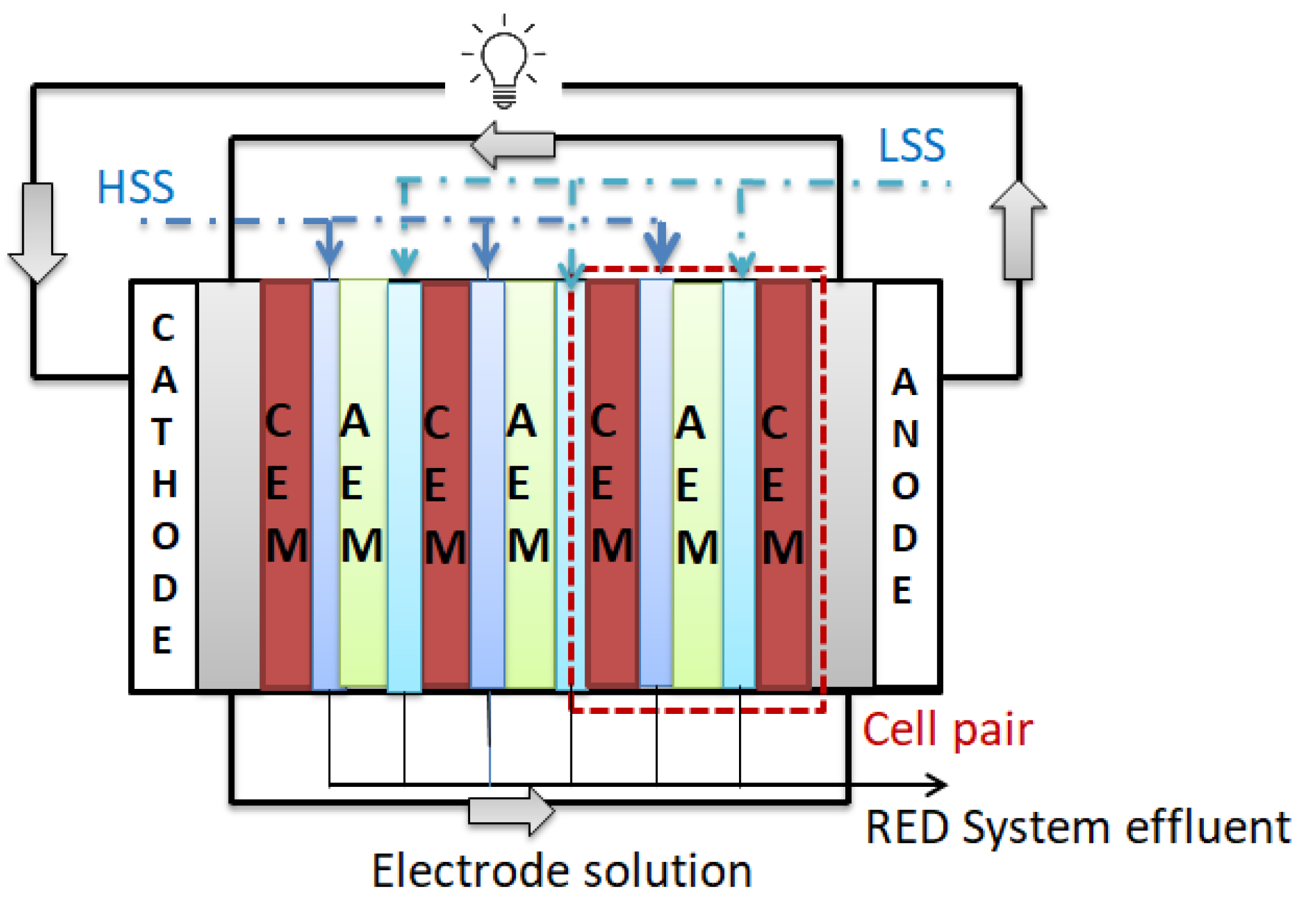
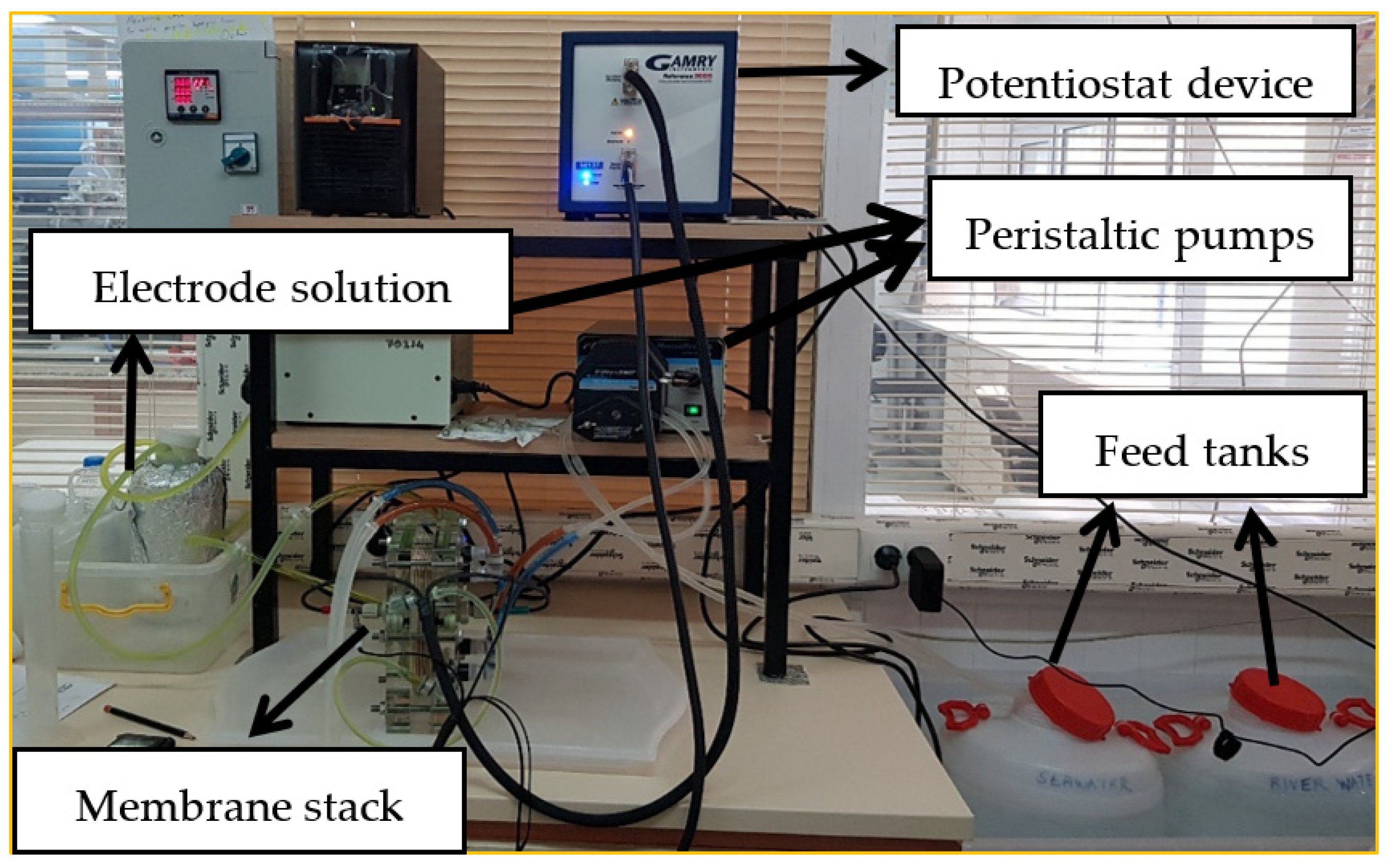
2.3. RED Tests
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Analysis
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Properties of AEMs
3.4. RED Performances of AEMs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Post, J.W.; Veerman, J.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Euverink, G.J.W.; Metz, S.J.; Nymeijer, K.; Buisman, C.J.N. Salinity-gradient power: Evaluation of pressure-retarded osmosis and reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 288, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, S. Experimental and Modeling Studies on Reverse Electrodialysis for Sustainable Power Generation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, C.; Pintossi, D.; Saakes, M.; Borneman, Z.; Brilman, W.; Nijmeijer, K. Electrode segmentation in reverse electrodialysis: Improved power and energy efficiency. Desalination 2020, 492, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerman, J.; Saakes, M.; Metz, S.J.; Harmsen, G.J. Reverse electrodialysis: Performance of a stack with 50 cells on the mixing of sea and river water. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tristán, C.; Fallanza, M.; Ibáñez, R.; Ortiz, I. Recovery of salinity gradient energy in desalination plants by reverse electrodialysis. Desalination 2020, 496, 114699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Crittenden, J.C. Unique applications and improvements of reverse electrodialysis: A review and outlook. Appl. Energy 2020, 262, 114482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Yip, N.Y. Elucidating conductivity-permselectivity tradeoffs in electrodialysis and reverse electrodialysis by structure-property analysis of ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Nijmeijer, K. Reverse electrodialysis for salinity gradient power generation: Challenges and future perspectives. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2018, 4, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eti, M.; Othman, N.H.; Güler, E.; Kabay, N. Ion exchange membranes for reverse electrodialysis (RED) applications-recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2021, 7, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidis, A.; Herber, R.; Vermaas, D.A. Upscale potential and financial feasibility of a reverse electrodialysis power plant. Appl. Energy 2014, 119, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Vermaas, D.A.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Performance-determining membrane properties in reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E.; Zhang, Y.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Tailor-made anion-exchange membranes for salinity gradient power generation using reverse electrodialysis. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 2262–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Park, S.H.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, Y.M. Effect of cationic groups in poly(arylene ether sulfone) membranes on reverse electrodialysis performance. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.L.; Nunes, S.P. Materials and membrane technologies for water and energy sustainability. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tufa, R.A.; Pawlowski, S.; Veerman, J.; Bouzek, K.; Fontananova, E.; di Profio, G.; Velizarov, S.; Goulão Crespo, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; Curcio, E. Progress and prospects in reverse electrodialysis for salinity gradient energy conversion and storage. Appl. Energy 2018, 225, 290–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Recent developments and future perspectives of reverse electrodialysis technology: A review. Desalination 2018, 425, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T.W.; Dhadake, Y. Property evaluation of custom-made ion exchange membranes for electrochemical performance in reverse electrodialysis application. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 850, 113437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.G.; Park, T.W. Electrochemical characterizations and reverse electrodialysis performance of hybrid anion exchange membranes for salinity gradient energy. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 817, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Geise, G.M.; Luo, X.; Hou, H.; Zhang, F.; Feng, Y.; Hickner, M.A.; Logan, B.E. Patterned ion exchange membranes for improved power production in microbial reverse-electrodialysis cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 271, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Hickner, M.A.; Logan, B.E. Ionic resistance and permselectivity tradeoffs in anion exchange membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10294–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Yang, S.; Jeong, N.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, W.S. Fabrication of an anion-exchange membrane by pore-filling using catechol-1,4-Diazabicyclo-[2,2,2]octane coating and its application to reverse electrodialysis. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10837–10846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.C.; Kim, W.S.; Choi, J.; Choi, Y.W.; Jeong, N.; Kim, H.; Nam, J.Y.; Jeong, H.; Kim, Y.H. Fabrication of photocured anion-exchange membranes using water-soluble siloxane resins as cross-linking agents and their application in reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Garcia, I.; Kotoka, F.; Portugal, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Characterization of poly(acrylic) acid-modified heterogenous anion exchange membranes with improved monovalent permselectivity for RED. Membranes 2020, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubenko, D.V.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Novel anion exchange membrane with low ionic resistance based on chloromethylated/quaternized-grafted polystyrene for energy efficient electromembrane processes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubenko, D.V.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Ion exchange membranes based on radiation-induced grafted functionalized polystyrene for high-performance reverse electrodialysis. J. Power Sources 2021, 511, 230460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güler, E.; Elizen, R.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Micro-structured membranes for electricity generation by reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, M.N.Z.; Nasef, M.M.; Veerman, J. Towards the development of new generation of ion exchange membranes for reverse electrodialysis: A review. Desalination 2022, 537, 115854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, E. Anion Exchange Membrane Design for Reverse Electrodialysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Universiteit Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Villafaña-López, L.; Reyes-Valadez, D.M.; González-Vargas, O.A.; Suárez-Toriello, V.A.; Jaime-Ferrer, J.S. Custom-made ion exchange membranes at laboratory scale for reverse electrodialysis. Membranes 2019, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karakoç, E.; Güler, E. Comparison of physicochemical properties of two types of polyepichlorohydrin-based anion exchange membranes for reverse electrodialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Długołecki, P.; Ogonowski, P.; Metz, S.J.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. On the resistances of membrane, diffusion boundary layer and double layer in ion exchange membrane transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mai, Z.; Shen, P.; Ortega, E.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Nanofiber based organic solvent anion exchange membranes for selective separation of monovalent anions. ACS Appl. Meter. Interfaces 2020, 12, 7539–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Mai, Z.; Shen, P.; Ortega, E.; Shen, J.; Gao, C.; Bruggen, B.V. Preparation of PVDF anionic exchange membrane by chemical grafting of GMA onto PVDF macromolecule. Solid State Ion. 2016, 293, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz, J.C.; Kamcev, J. Ionic conductivity of ion-exchange membranes: Measurement techniques and salt concentration dependence. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germer, W.; Harms, C.; Tullius, V.; Leppin, J.; Dyck, A. Comparison of conductivity measurement systems using the example of nafion and anion exchange membrane. Solid State Ion. 2015, 275, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, C.M.; Tinh, V.D.C.; Kim, D. Anion exchange membranes prepared from quaternized polyepichlorohydrin cross-linked with 1-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole grafted poly(arylene ether ketone) for enhancement of toughness and conductivity. Membranes 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarode, H.N. Understanding Ion and Solvent Transport in Anion Exchange mMembranes under Humidified Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, T.P.; Maes, A.M.; Sarode, H.N.; Peters, B.D.; Lavina, S.; Vezzù, K.; Yang, Y.; Poynton, S.D.; Varcoe, J.R.; Seifert, S.; et al. Interplay between water uptake, ion interactions, and conductivity in an e-beam grafted poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) anion exchange membrane. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandiver, A.M. Effect of Hydration on the Mechanical Properties of Anion Exchange Membranes. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rijnaarts, T.; Moreno, J.; Saakes, M.; de Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Role of anion exchange membrane fouling in reverse electrodialysis using natural feed waters. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 560, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raka, Y.D.; Bock, R.; Karoliussen, H.; Wilhelmsen, Ø.; Stokke Burheim, O. The Influence of concentration and temperature on the membrane resistance of ion exchange membranes and the levelised cost of hydrogen from reverse electrodialysis with ammonium bicarbonate. Membranes 2021, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altıok, E.; Kaya, T.Z.; Othman, N.H.; Kınalı, O.; Kitada, S.; Güler, E.; Kabay, N. Investigations on the effects of operational parameters in reverse electrodialysis system for salinity gradient power generation using central composite design (CCD). Desalination 2022, 525, 115508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample Code | Excess Diamine Ratio (ER) | Blend Ratio (BR) |
|---|---|---|
| ER1-BR1.07 | 1.00 | 1.07 |
| ER1.62-BR1.07 | 1.62 | 1.07 |
| ER2-BR1.07 | 2.00 | 1.07 |
| ER4-BR1.07 | 4.00 | 1.07 |
| ER1.62-BR1.23 | 1.62 | 1.23 |
| ER1.62-BR1.5 | 1.62 | 1.50 |
| ER1.62-BR2 | 1.62 | 2.00 |
| Parameter | Property |
|---|---|
| Active membrane/electrode area | 10 × 10 cm |
| Number of membranes | 3 membrane pairs |
| Electrodes (Anode and cathode) | Ti/Ru alloy mesh type |
| Membranes | Neosepta CMX |
|---|---|
| Membrane thickness (µm) | 181 ± 2 |
| Ion exchange capacity (mmol/g) | 1.64 ± 0.01 |
| Permselectivity (%) | 92.5 ± 0.6 |
| Swelling degree (%) | 21.5 ± 0.2 |
| Area resistance (Ω·cm2) | 3.43 ± 0.16 |
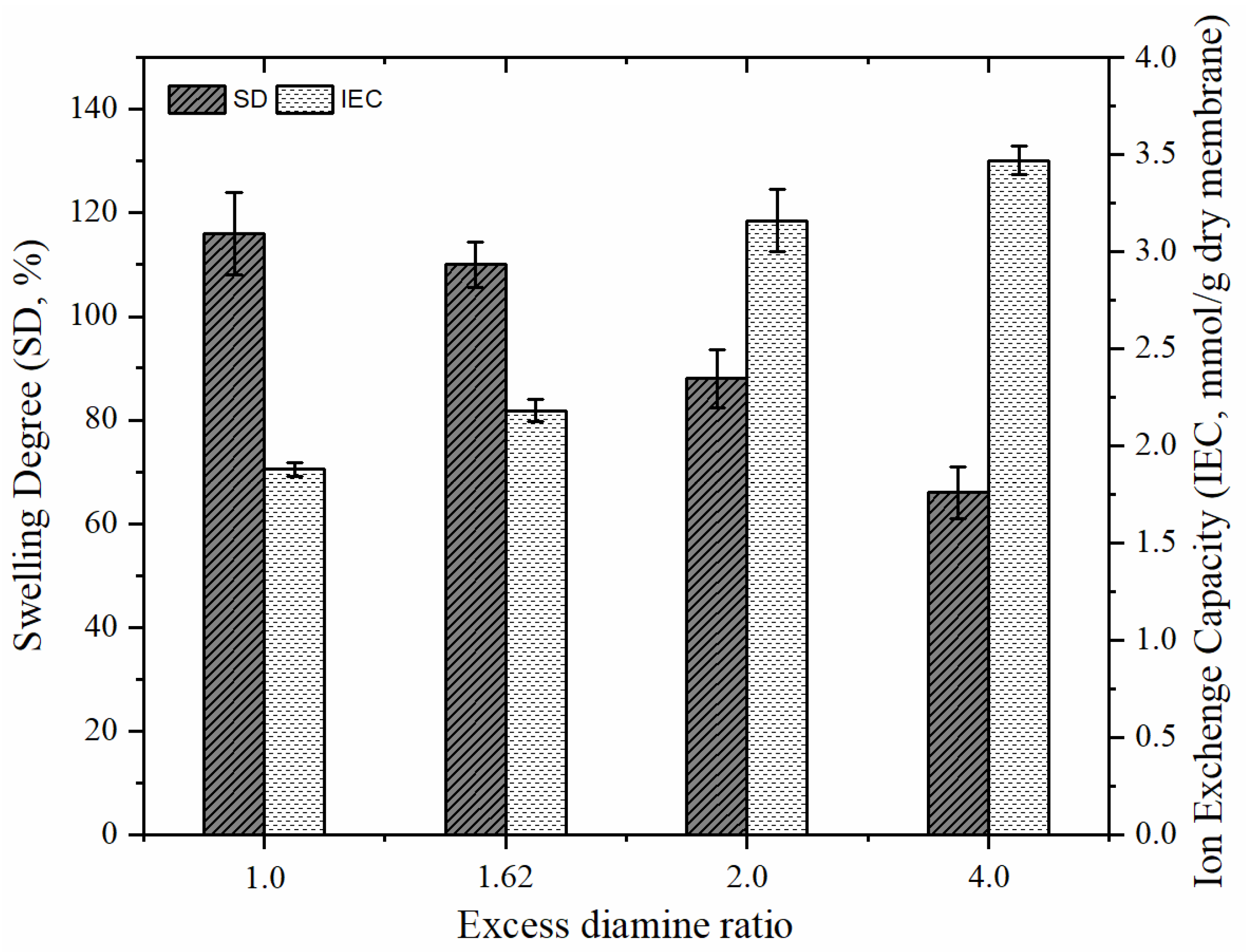
| Membrane | Thickness (µm) | ER-BR | SD (%) | IEC (mmol/g-Dry Membrane) | FCD (mmol/g H2O) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER1.62-BR1.23 | 132 | 1.62-1.23 | 119 | 2.32 | 1.95 | This study |
| ER1.62-BR1.07 | 135 | 1.62-1.07 | 110 | 2.18 | 1.98 | This study |
| ER2-BR1.07 | 132 | 2-1.07 | 88 | 3.16 | 3.59 | This study |
| ER4-BR1.07 | 139 | 4-1.07 | 66 | 3.47 | 5.25 | This study |
| PECH B-2 | 77 | 4.2-0.333 | 49 | 1.68 | 3.40 | [12] |
| ER4.2-BR1.04 | 77 | 4.2-1.04 | 120 | 2.80 | 1.46 | [12] |
| AEM | 77 | 5.5-3.33 | 30 | 1.40 | 4.68 | [30] |
| PECH-H | 120–160 | 2.0-0.6 | 20.88 | 2.02 | 9.70 | [34] |
| Membrane | Area Resistance (Ω·cm2) | Thickness (µm) | Electrical Conductivity (mS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER1.62-BR1.07 | 3.78 ± 0.16 | 134 | 3.55 ± 0.16 |
| ER1.62-BR1.23 | 3.48 ± 0.49 | 115 | 3.31 ± 0.49 |
| ER1.62-BR1.5 | 3.12 ± 0.10 | 149 | 4.77 ± 0.10 |
| ER1.62-BR2.0 | 2.85 ± 0.25 | 80 | 2.81 ± 0.25 |
| ER1-BR1.07 | 3.45 ± 0.19 | 155 | 4.50 ± 0.19 |
| ER2-BR1.07 | 3.83 ± 0.74 | 138 | 3.60 ± 0.73 |
| ER4-BR1.07 | 3.24 ± 0.10 | 209 | 6.44 ± 0.10 |
| Membrane | Membrane Structure | Thickness (µm) | IEC (mmol/g-Dry Membrane) | SD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER4-BR1.07 (Dia.: 55 mm) | Diamine ratio:4, Blend ratio:1.07 | 140 | 3.47 | 66 |
| ER4-BR1.07 (MS: 15 cm × 15 cm) | 250 | 3.42 | 90 |
| Parameter | Condition |
|---|---|
| Number of membrane pairs | 3 |
| Flow rates of feed solutions (mL/min) | 30, 75, 120 |
| Flow rate of electrode solution (mL/min) | 300 |
| Concentration of the feed solutions (g/L) | Dilute NaCl solution: 1 Concentrated NaCl solution: 30 |
| Salinity ratio (g/L low saline solution: g/L high saline solution) | 1:30 |
| Electrode solution | 0.25 M NaCl; 0.05 M K3Fe(CN)6; 0.05 M K4Fe(CN)6 |
| AEMs and CEMs | ER4-BR1.07; NEOSEPTA CMX |
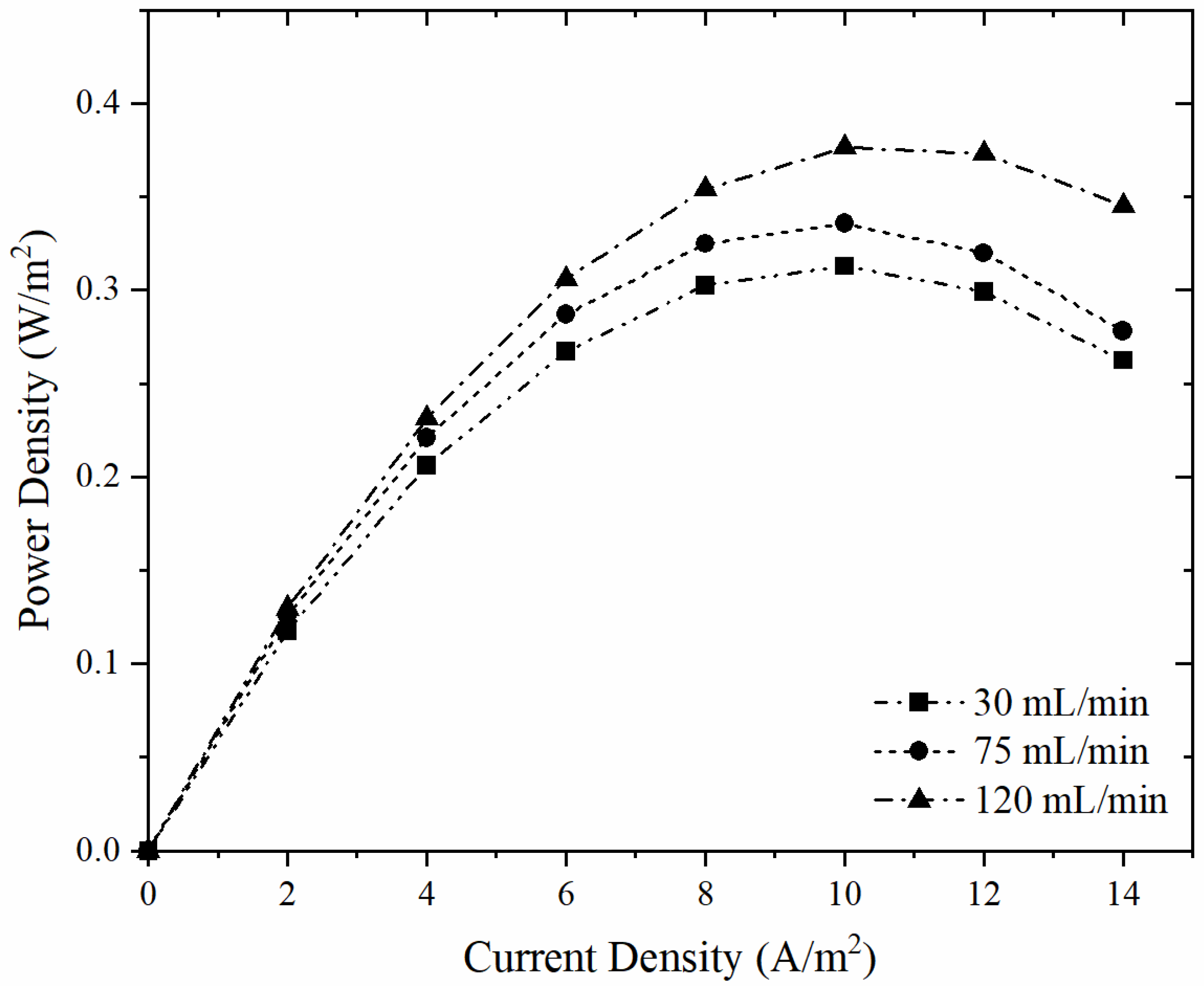
| Membrane | Volumetric Flow Rate (mL/min) | Open Circuit Voltage (V) | Maximum Power Density (W/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER4-BR1.07-NEOSEPTA CMX | 30 | 0.395 | 0.313 |
| 75 | 0.422 | 0.336 | |
| 120 | 0.431 | 0.376 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eti, M.; Cihanoğlu, A.; Güler, E.; Gomez-Coma, L.; Altıok, E.; Arda, M.; Ortiz, I.; Kabay, N. Further Development of Polyepichlorohydrin Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis by Tuning Cast Solution Properties. Membranes 2022, 12, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121192
Eti M, Cihanoğlu A, Güler E, Gomez-Coma L, Altıok E, Arda M, Ortiz I, Kabay N. Further Development of Polyepichlorohydrin Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis by Tuning Cast Solution Properties. Membranes. 2022; 12(12):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121192
Chicago/Turabian StyleEti, Mine, Aydın Cihanoğlu, Enver Güler, Lucia Gomez-Coma, Esra Altıok, Müşerref Arda, Inmaculada Ortiz, and Nalan Kabay. 2022. "Further Development of Polyepichlorohydrin Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis by Tuning Cast Solution Properties" Membranes 12, no. 12: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121192
APA StyleEti, M., Cihanoğlu, A., Güler, E., Gomez-Coma, L., Altıok, E., Arda, M., Ortiz, I., & Kabay, N. (2022). Further Development of Polyepichlorohydrin Based Anion Exchange Membranes for Reverse Electrodialysis by Tuning Cast Solution Properties. Membranes, 12(12), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12121192