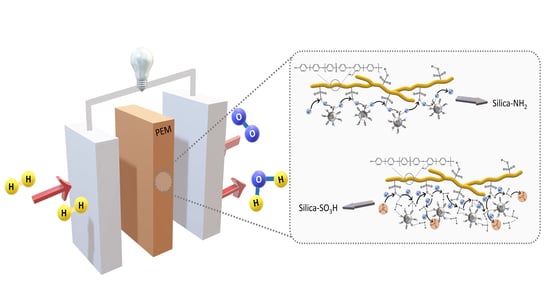
Composite Membranes Based on Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foam Particles and Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) with Potential Application in Fuel Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Sulfonated Poly(ether ether sulfone) (sPEES)
2.3. Synthesis MCF Silica
2.4. Modifications of Silanol Groups with APTES
2.5. Modifications of Silanol Groups with MPTMS
2.6. Characterization of Polymers and Silica
2.7. Preparation and Characterization of Composite Membranes
2.8. Water Uptake
2.9. Ion Exchange Capacity (IEC)
2.10. Protonic Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
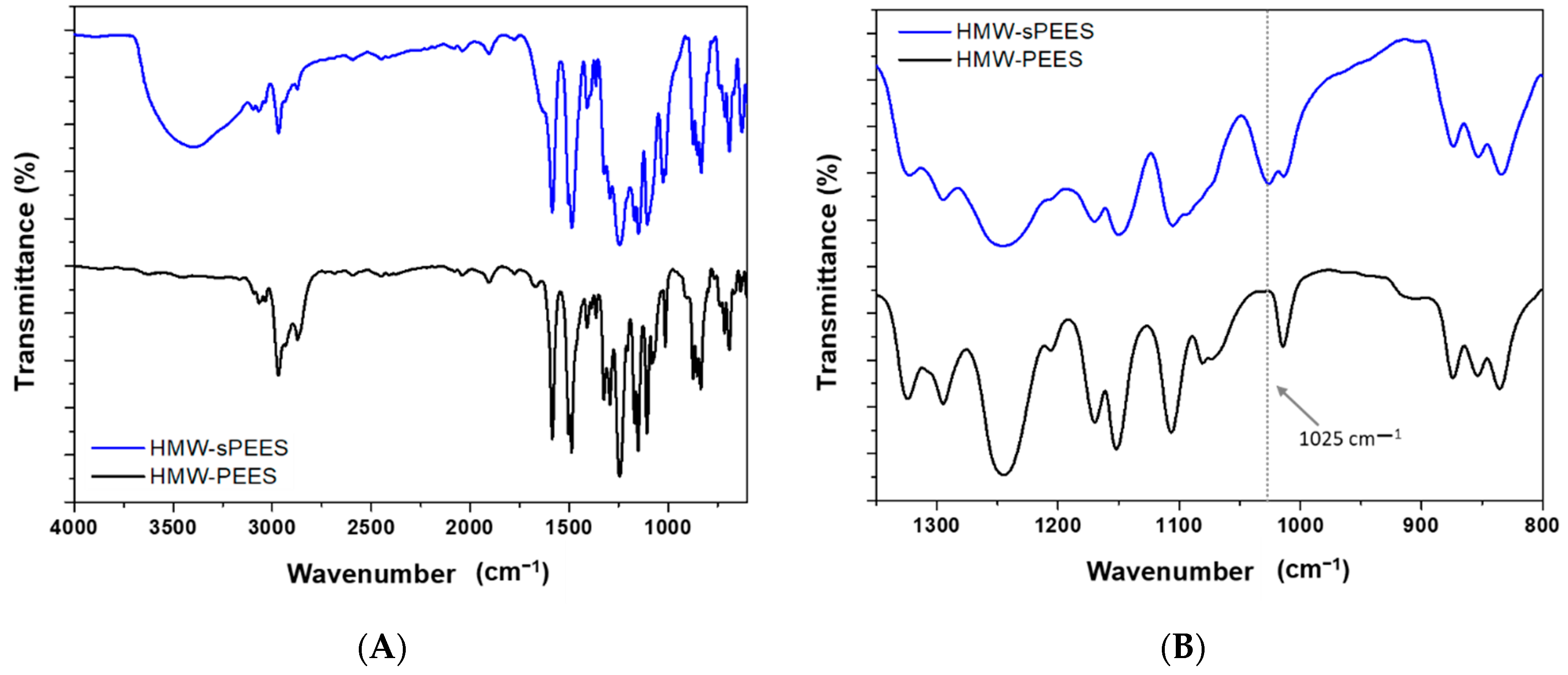
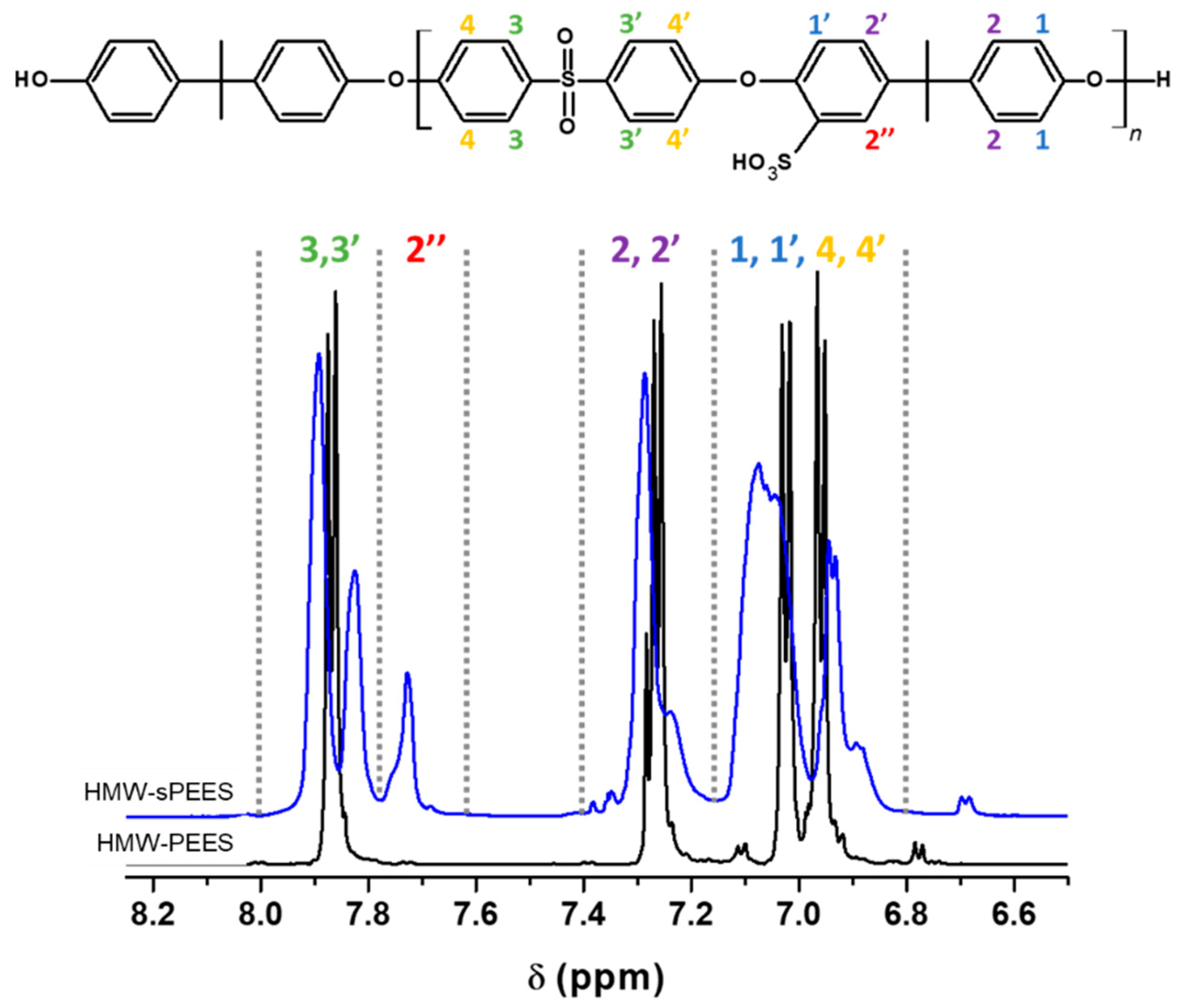
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Sulfonated Poly(ether ether sulfone) (sPEES)
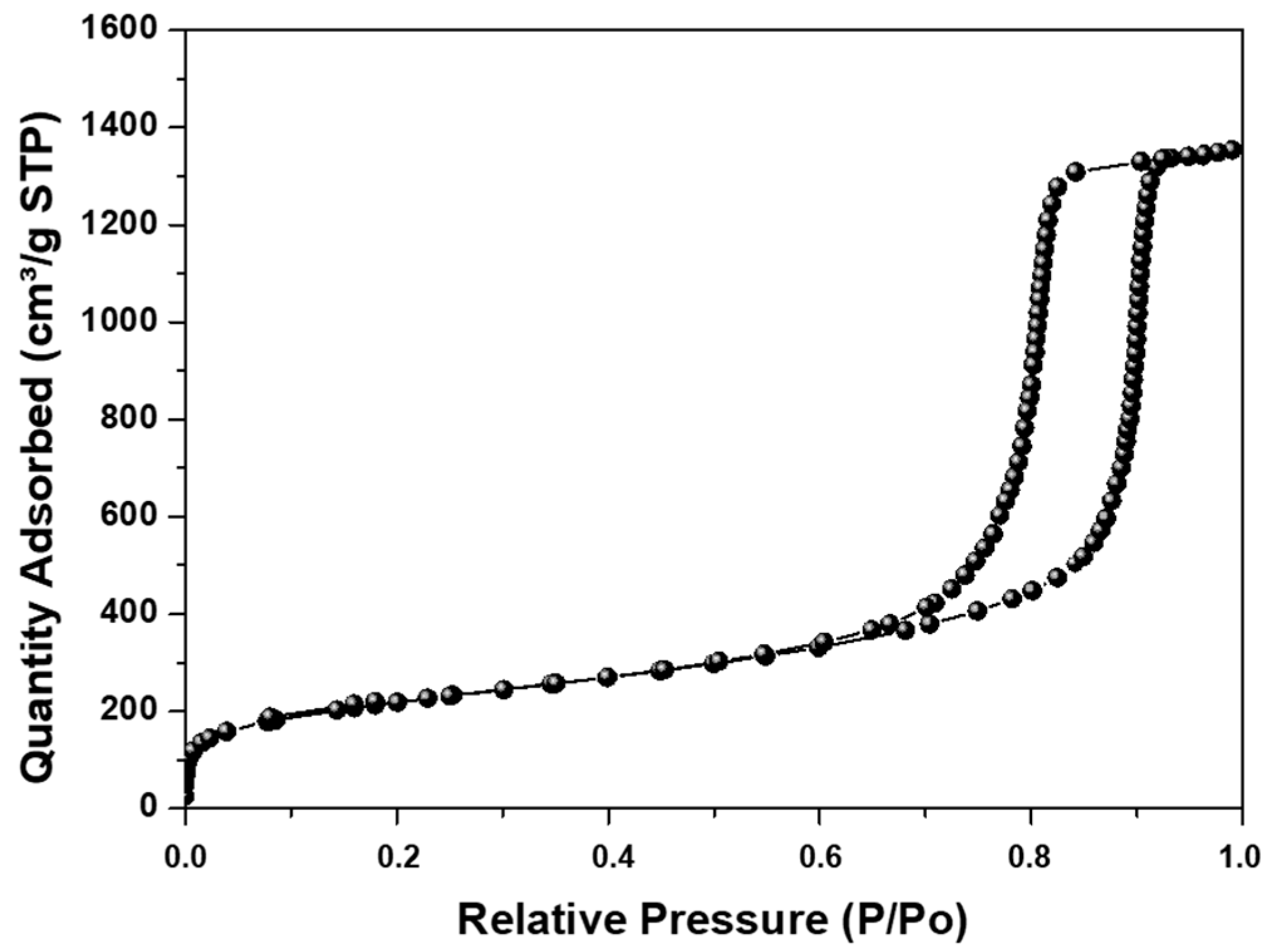
3.2. Synthesis of MCF Silica
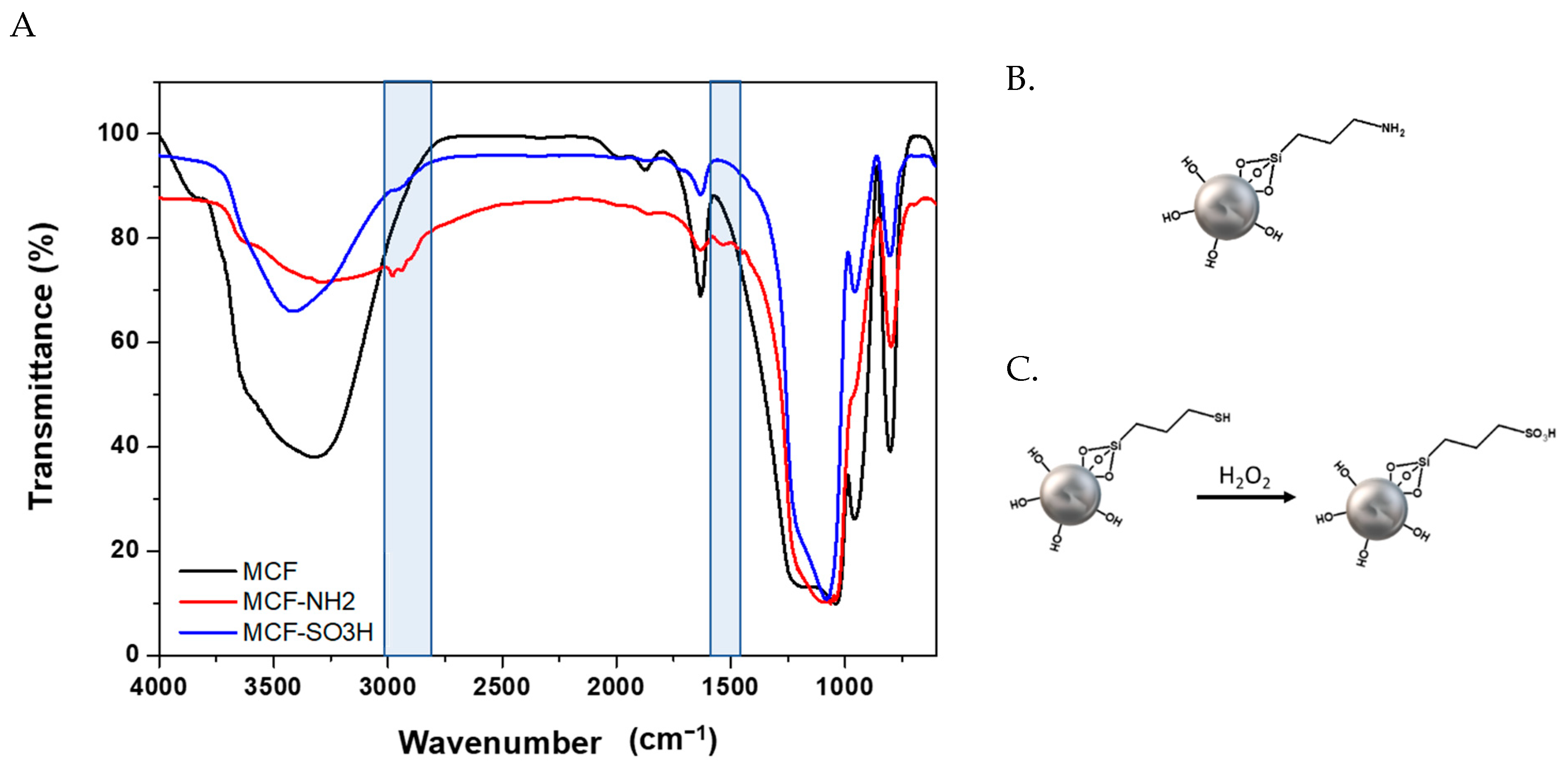
3.3. Modifications of Silanol Groups with APTES and MPTMS
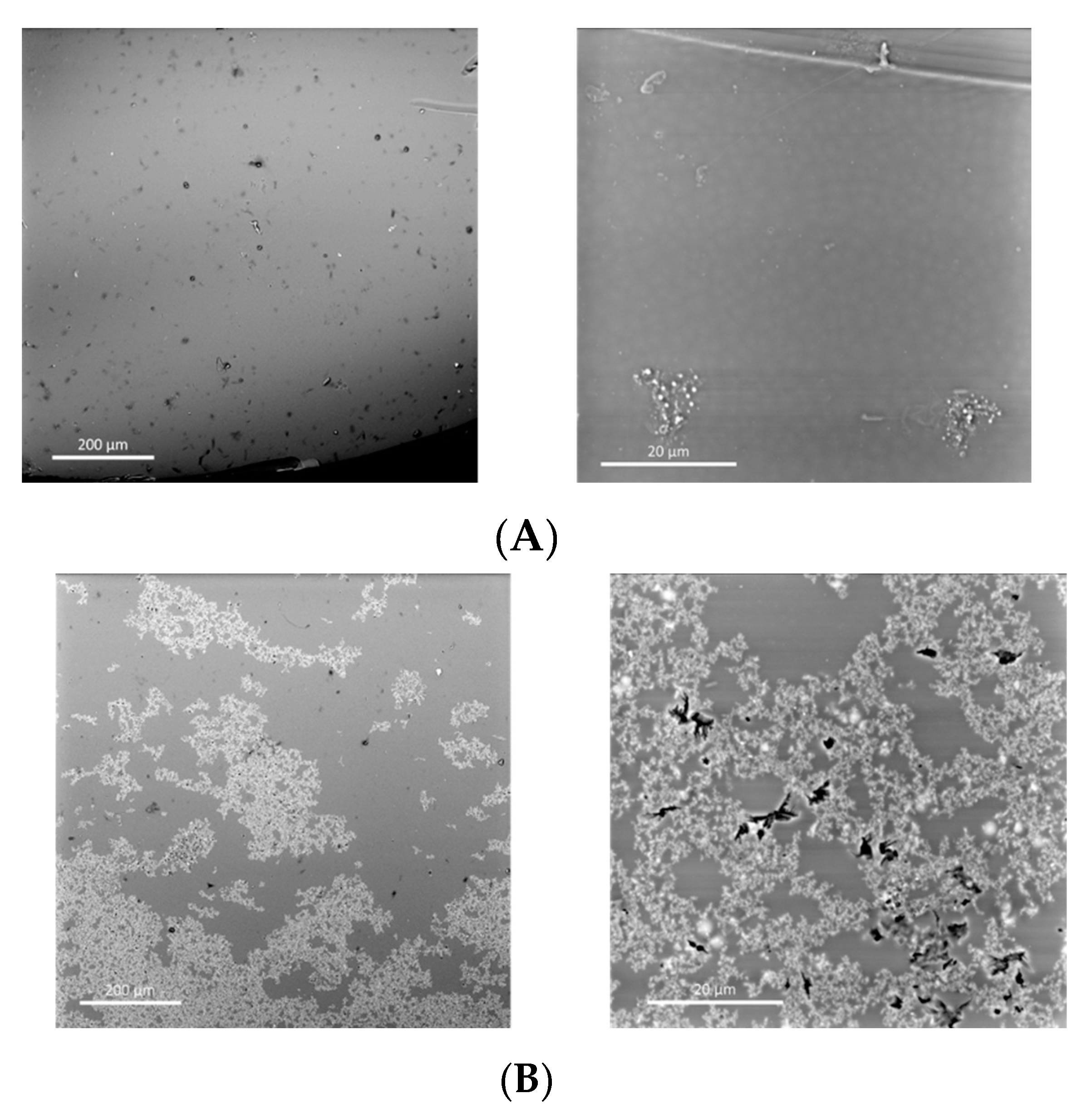
3.4. Preparation and Characterization of Composite Membranes
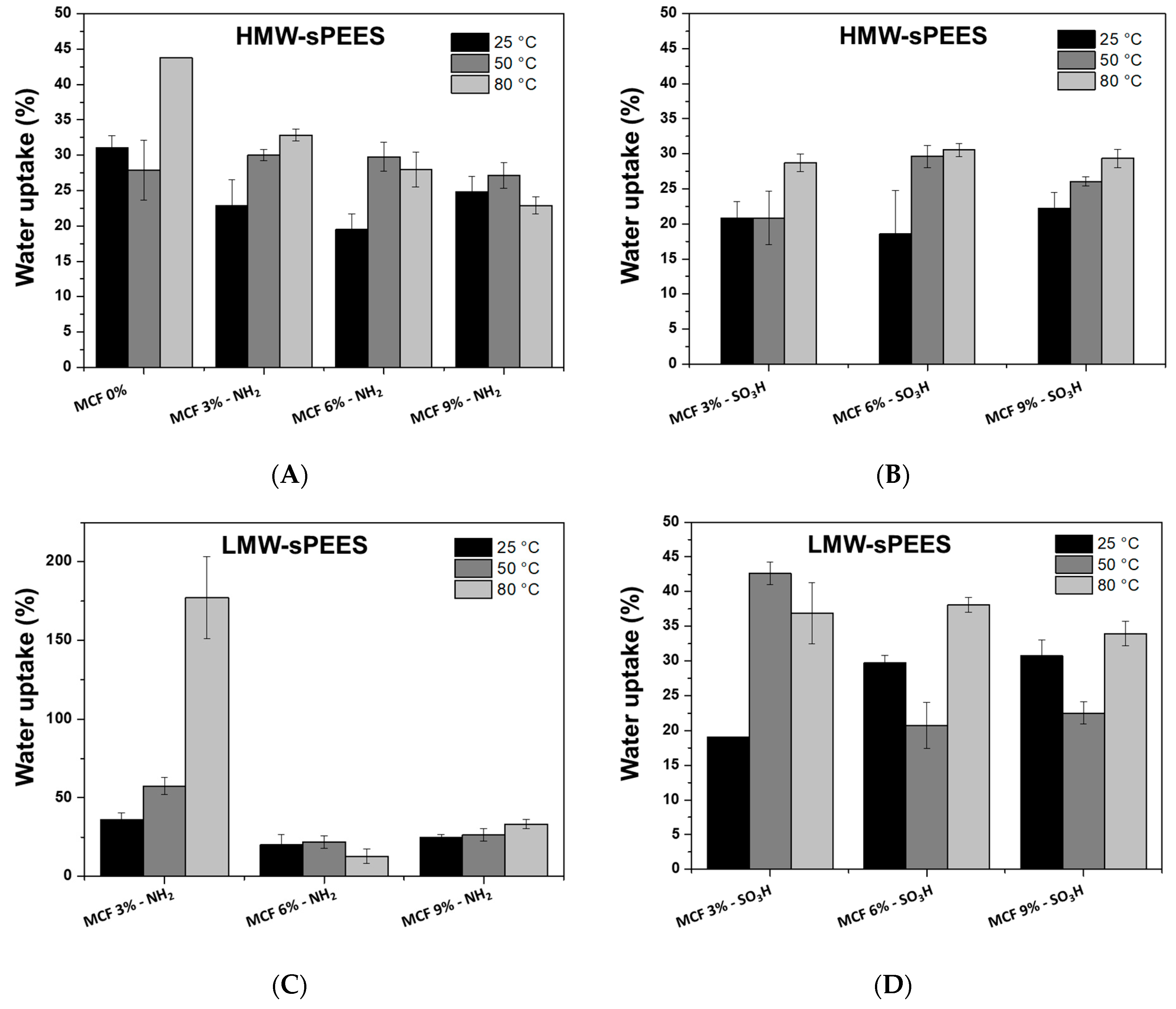
3.5. Water Uptake (WU)
3.6. Ionic Exchange Capacity (IEC)
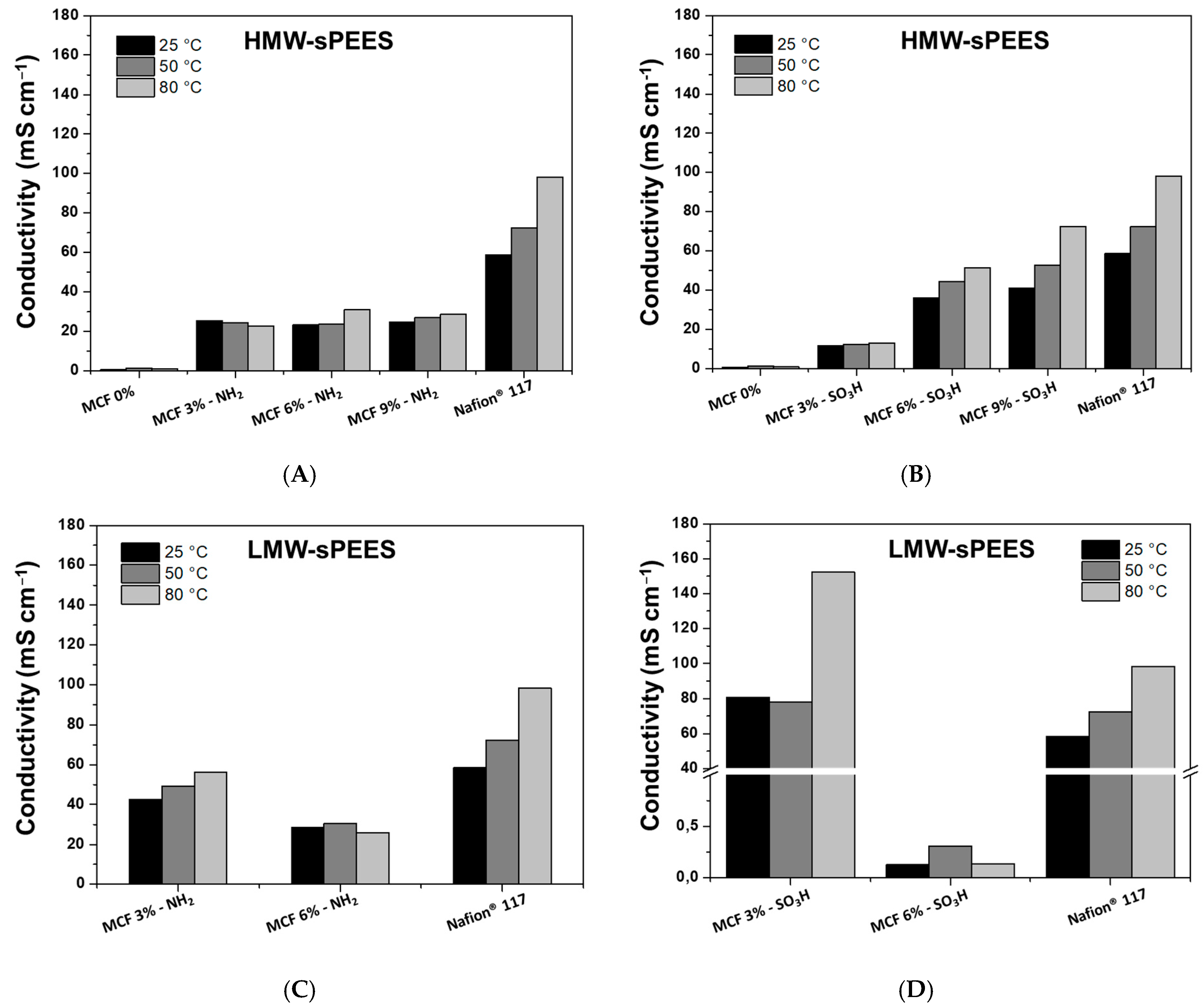
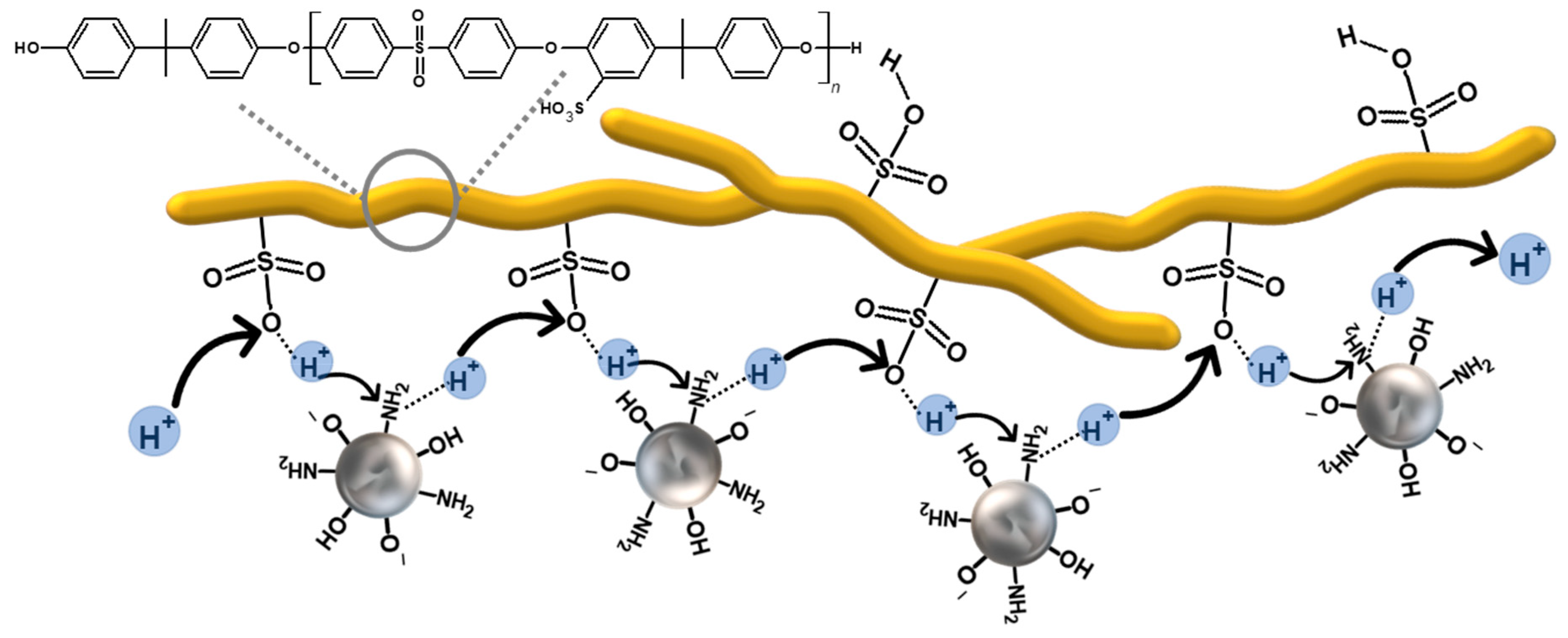
3.7. Proton Conductivity (σ)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prykhodko, Y.; Fatyeyeva, K.; Hespel, L.; Marais, S. Progress in Hybrid Composite Nafion®-Based Membranes for Proton Exchange Fuel Cell Application. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 409, 127329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souzy, R.; Ameduri, B. Functional Fluoropolymers for Fuel Cell Membranes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2005, 30, 644–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chae, S.R.; Hendren, Z.; Park, J.S.; Wiesner, M.R. Recent Advances in Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204–206, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, H.A.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. A Review of Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Protic Ionic Liquid/Polymer Blends for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2021, 484, 229197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Martinez, A.; Hong, P.; Xu, H.; Bockmiller, F.R. Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Station Networks for Automobiles: Status, Technology, and Perspectives. Adv. Appl. Energy 2021, 2, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ko, H.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, K. Study on Control of Polymeric Architecture of Sulfonated Hydrocarbon-Based Polymers for High-Performance Polymer Electrolyte Membranes in Fuel Cell Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, N.; Ray, S.S. Recent Progress on Nafion-Based Nanocomposite Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Macromol. Mater Eng. 2009, 294, 719–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauman Javed, R.M.; Al-Othman, A.; Tawalbeh, M.; Olabi, A.G. Recent Developments in Graphene and Graphene Oxide Materials for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrette, L.; Friedrich, K.A.; Stimming, U. Fuel Cells - Fundamentals and Applications. Fuel Cells 2001, 1, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrette, L.; Friedrich, K.A.; Stimming, U. Fuel Cells: Principles, Types, Fuels, and Applications. Chemphyschem 2000, 1, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A Review of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Technology, Applications, and Needs on Fundamental Research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiam, H.S.; Daud, W.R.W.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Mohammad, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Loh, K.S.; Majlan, E.H. Overview on Nanostructured Membrane in Fuel Cell Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen. Energy 2011, 36, 3187–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, J. On the Role of Fuel Cells and Hydrogen in a More Sustainable and Renewable Energy Future. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2010, 10, S9–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Nguyen, T.X.H.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.T.; Lee, J.H. Polymer Membranes for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell: Recent Advances and Challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashkar, A.; Al-Othman, A.; Tawalbeh, M.; Qasim, M. A Critical Review on the Use of Ionic Liquids in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Membranes 2022, 12, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooshyari, K.; Amini Horri, B.; Abdoli, H.; Fallah Vostakola, M.; Kakavand, P.; Salarizadeh, P. A Review of Recent Developments and Advanced Applications of High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Pem Fuel Cells. Energies 2021, 14, 5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyari, K.; Heydari, S.; Beydaghi, H.; Rajabi, H.R. New Nanocomposite Membranes Based on Sulfonated Poly (Phthalazinone Ether Ketone) and Fe3O4@SiO2@ Resorcinol–Aldehyde–SO3H for PEMFCs. Renew Energy 2022, 186, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of Advanced Materials for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peighambardoust, S.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Amjadi, M. Review of the Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications; Elsevier Ltd.: Singapore, 2010; Volume 35, ISBN 2177491223. [Google Scholar]
- Smitha, B.; Sridhar, S.; Khan, A.A. Solid Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications - A Review. J. Memb. Sci. 2005, 259, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devanathan, R. Recent Developments in Proton Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2008, 1, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P.N.; Park, J.W. New Developments in Proton Conducting Membranes for Fuel Cells. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2014, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J.; Matsuura, T.; Junoh, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A. Functionalization of Polymeric Materials as a High Performance Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cell: A Review. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Shahi, V.K. Organic-Inorganic Nanocomposite Polymer Electrolyte Membranes for Fuel Cell Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 945–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Pan, C.; Li, C.; Zhao, J. A Review of Membranes in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Transport Phenomena, Performance and Durability. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 141, 110771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyjaszewski, K.M.M. Polymers for a Sustainable Environment and Green Energy. In Polymer science: A comprehensive referencie; Elsevier: Singapore, 2013; Volume 10, ISBN 9780444533494. [Google Scholar]
- Jutemar, E.P. Proton-Conducting Sulfonated Aromatic Ionomers and Membranes by Chemical Modifications and Polycondensations. Doctoral. Ph.D. Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.C. Highly Sulfonated Polymer-Grafted Graphene Oxide Composite Membranes for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 74, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Yan, X.; He, G.; Wu, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y. SPEEK Proton Exchange Membranes Modified with Silica Sulfuric Acid Nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 11853–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Na, H.; Jeon, Y.; Jung Hwang, H.; Kim, H.J.; Mochida, I.; Yoon, S.H.; Park, J.I.; Shul, Y.G. Poly(Ether Imide) Nanofibrous Web Composite Membrane with SiO2/Heteropolyacid Ionomer for Durable and High-Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cells. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 74, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, I.; Oh, K.H.; Yun, M.; Kang, M.K.; Song, H.H.; Kim, H. Nanostructured Composite Membrane with Cross-Linked Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Ketone)/Silica for High-Performance Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells under Low Relative Humidity. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 549, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Chu, J.Y.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Effect of Functionalized SiO2 toward Proton Conductivity of Composite Membranes for PEMFC Application. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 5333–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, G.; Ibrahim, A.; Borello, D.; El-Kharouf, A. Composite Polymers Development and Application for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Technologies—A Review Enhanced Reader. Molecules 2020, 25, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lim, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, Y.T.; Lee, S.Y. Anomalous Behavior of Proton Transport and Dimensional Stability of Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) Nonwoven/Silicate Composite Proton Exchange Membrane with Dual Phase Co-Continuous Morphology. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 450, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangyang, J.; Tang, H.; Pan, M. Well-Ordered Sulfonated Silica Electrolyte with High Proton Conductivity and Enhanced Selectivity at Elevated Temperature for DMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 4612–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, K.S.; Hong, Y.T.; Lee, S.Y. Sulfonated SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica-Incorporated Sulfonated Poly(Phenylsulfone) Composite Membranes for Low-Humidity Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Anomalous Behavior of Humidity-Dependent Proton Conductivity. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9202–9211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Salarizadeh, P.; Sabooni Asre Hazer, M.; Hosseinabadi, P.; Kashefi, S.; Beydaghi, H. The Effect of Adding Sulfonated SiO2 Nanoparticles and Polymer Blending on Properties and Performance of Sulfonated Poly Ether Sulfone Membrane: Fabrication and Optimization. Electrochim Acta 2019, 295, 875–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabalizadeh Mojarrad, N.; Iskandarani, B.; Taşdemir, A.; Yürüm, A.; Alkan Gürsel, S.; Yarar Kaplan, B. Nanofiber Based Hybrid Sulfonated Silica/P(VDF-TrFE) Membranes for PEM Fuel Cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13583–13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigwadi, R.; Mokrani, T.; Dhlamini, M.S.; Nonjola, P.; Msomi, P.F. Nafion®/ Sulfated Zirconia Oxide-Nanocomposite Membrane: The Effects of Ammonia Sulfate on Fuel Permeability. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, R.; Ahamed, Z.; Charradi, K.; Beji, Z.; ben Assaker, I.; ben Naceur, J.; Auvity, B.; Squadrito, G.; Chtourou, R. Elaboration and Characterization of Hybrid Polymer Electrolytes Nafion-TiO2 for PEMFCs. Proc. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 11583–11590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Nam, K.; Kim, D.W. Composite Proton Conducting Membranes Based on Nafion and Sulfonated SiO 2 Nanoparticles. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 415–416, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domhoff, A.; Wang, X.; Silva, M.; Creager, S.; Martin, T.B.; Davis, E.M. Role of Nanoparticle Size and Surface Chemistry on Ion Transport and Nanostructure of Perfluorosulfonic Acid Ionomer Nanocomposites. Soft. Matter 2022, 18, 3342–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; García-Bernabé, A.; Montero, A.; Andrio, A.; Sahuquillo, Ó.; Gimenez, E.; Compañ, V. Proton Conductivity through Polybenzimidazole Composite Membranes Containing Silica Nanofiber Mats. Polymers 2019, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhuang, X.; Cheng, B.; Wang, W.; Kang, W.; Shi, L.; Li, H. Modification of Nafion Membrane with Biofunctional SiO2 Nanofiber for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 340, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. Anhydrous Proton Exchange Membrane of Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Ketone) Enabled by Polydopamine-Modified Silica Nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 152, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fu, Y.; Geng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lü, C. A Facile Route to Enhance the Properties of Polymer Electrolyte-Based Organic-Inorganic Hybrid Proton Exchange Membranes. Solid. State Ion. 2015, 283, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Yang, L.; Ding, M. Synthesis of Large-Pore Mesostructured Cellular Foam Silica Spheres for the Adsorption of Biomolecules. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 2411–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Wan, W.; Ding, M. Preparation and Retention Mechanism Exploration of Mesostructured Cellular Foam Silica as Stationary Phase for High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Talanta 2016, 149, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Desch, R.J.; Thiel, S.W.; Guliants, V.V.; Pinto, N.G. Adsorption of Biomolecules on Mesostructured Cellular Foam Silica: Effect of Acid Concentration and Aging Time in Synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 149, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, G.; Ding, Y.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Pu, X. Amino-Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foams as Carriers of Glucose Oxidase. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, N.A.; Elsen, A.M.; He, H.; Lõpez, B.L.; Matyjaszewski, K. ABA Triblock Copolymers from Two Mechanistic Techniques: Polycondensation and Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 2015, 53, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, N.A.; Palacio, J.; López, B.L. Sulfonation of Poly(Arylene Ethers) and ABA Triblock Copolymers with a Mild Sulfonation Agent. Macromol. Symp. 2016, 365, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, N.A.; Escobar, S.; Tejada, J.C.; López, B.L. Understanding of the Formation of Mesocellular-like Silica Foam Particles of Nano Size and Its Chemical Surface to Immobilization of Thermomyces Lanuginosus Lipase. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 294, 109948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.; Lopez, B.L.; Sierra, L. Study of the Acidic Sites and Their Modifications in Mesoporous Silica Synthesized in Acidic Medium under Quiescent Conditions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9275–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Hickner, M.; Kim, Y.S.; Zawodzinski, T.A.; Mcgrath, J.E. Direct Polymerization of Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) Random (Statistical) Copolymers: Candidates for New Proton Exchange Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2002, 197, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Yu, X.; Dunn, S.; McGrath, J.E. Influence of Microstructure and Chemical Composition on Proton Exchange Membrane Properties of Sulfonated-Fluorinated, Hydrophilic-Hydrophobic Multiblock Copolymers. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 327, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D. Electrochemical Analysis of Polymer Membrane with Inorganic Nanoparticles for High-Temperature PEM Fuel Cells. Membranes (Basel) 2022, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.K.; Maier, G.; Andreaus, B.; Scherer, G.G. Block Copolymer Ionomers for Ion Conductive Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 245, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Choi, Y.J.; Choi, I.J.; Yoon, T.H.; Moon, S.H. Electrochemical Characterization of Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) (S-PES) Cation-Exchange Membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2003, 216, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Zhu, B. Amphiphilic ABA Copolymers Used for Surface Modification of Polysulfone Membranes, Part 1: Molecular Design, Synthesis, and Characterization. Polymer 2008, 49, 3256–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Im, S.C.; Huang, J.; Matyjaszewski, K.; Pakula, T. Structure and Properties of Poly(Butyl Acrylate-Block-Sulfone-Block-Butyl Acrylate) Triblock Copolymers Prepared by ATRP. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2005, 206, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oréfice, R.L.; Brennan, A. Evaluation of the Interactions between Polymeric Chains and Surfaces with Different Structures Performed by an Atomic Force Microscope. Mater. Res. 1998, 1, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Komber, H.; Chakraborty, S.; Voit, B.; Banerjee, S. Degree of Sulfonation and Microstructure of Post-Sulfonated Polyethersulfone Studied by NMR Spectroscopy. Polymer 2012, 53, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iojoiu, C.; Genova-Dimitrova, P.; Maréchal, M.; Sanchez, J.Y. Chemical and Physicochemical Characterizations of Ionomers. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 4789–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Chan, J.C.C. Propylsulfonic Acid-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Synthesized by in Situ Oxidation of Thiol Groups under Template-Free Condition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 2156–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Hello, K.M.; Osman, H. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Immobilized with 3-[(Mercapto or Amino)Propyl]Trialkoxysilane by a Simple One-Pot Reaction. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawicka, K.; Trejda, M.; Ziolek, M. The Production of Biofuels Additives on Sulphonated MCF Materials Modified with Nb and Ta - Towards Efficient Solid Catalysts of Esterification. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 467, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, B.; Wang, T.J.; Gao, H.; Jin, Y. High Density Silanization of Nano-Silica Particles Using γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Serrano, E.; Blanco-Brieva, G.; Campos-Martin, J.M.; Fierro, J.L.G. Acid-Functionalized Amorphous Silica by Chemical Grafting-Quantitative Oxidation of Thiol Groups. Langmuir 2003, 19, 7621–7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscianska, J.; Olejnik, A.; Nowak, I. APTES-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica as a Vehicle for Antipyrine – Adsorption and Release Studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 533, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xiang, H.; Kim, T.; Chun, M.S.; Lee, K. Surface Properties of Submicrometer Silica Spheres Modified with Aminopropyltriethoxysilane and Phenyltriethoxysilane. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2006, 304, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odian, G. Principles of Polymerization Engineering. Available online: https://unpa.edu.mx/~aramirez/Principles%20of%20polymerization.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- Vijayakumar, V.; Khastgir, D. Hybrid Composite Membranes of Chitosan/Sulfonated Polyaniline/Silica as Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for Fuel Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnian, M.J.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Alipour Moghaddam, J. Investigation of Physicochemical and Electrochemical Properties of Recast Nafion Nanocomposite Membranes Using Different Loading of Zirconia Nanoparticles for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Applications. Mater Sci. Energy Technol. 2018, 1, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Chung, W.J.; Pinnau, I.; Guiver, M.D. Polysulfone/Silica Nanoparticle Mixed-Matrix Membranes for Gas Separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 314, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A. The Development of Speek/Pva/Teos Blend Membrane for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.R.; Park, C.J.; Vinothkannan, M.; Yoo, D.J. Sulfonated Poly Ether Sulfone/Heteropoly Acid Composite Membranes as Electrolytes for the Improved Power Generation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Compos. B Eng. 2018, 155, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, F.; Gill, R.; Batool, R.; Drexler, M.; Alamgir, F.; Abbas, G.; Jacob, K. Proton Conductivity and Methanol Permeability Study of Polymer Electrolyte Membranes with Range of Functionalized Clay Content for Fuel Cell Application. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.C. Organic/Inorganic Composite Membranes Comprising of Sulfonated Poly(Arylene Ether Sulfone) and Core-Shell Silica Particles Having Acidic and Basic Polymer Shells. Polymer 2015, 71, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian-Alam, L.; Mahdavi, H. A Novel Polysulfone-Based Ternary Nanocomposite Membrane Consisting of Metal-Organic Framework and Silica Nanoparticles: As Proton Exchange Membrane for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. Renew Energy 2018, 126, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Proton Conductivity | Ionic Exchange Capacity | Methanol Permeability | Water Retention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion 117 | 0.113 S/cm at 25 °C | 0.93 meq/g | 8.84 × 10−7 cm2/s (60 °C 5M) | 30% at 30 °C | [39] |
| F-GO/Nafion membrane: functionalized GO nanosheets (F-GO) with a sulfonic acid functional group (3-mercaptopropyl trimethoxysilane) | 0.012–0.047 S/cm at 120 °C | 0.96 meq/g (5% F-GO) and 0.93 meq/g (10% F-GO), | ~25% (5% F-GO) and ~29% (10% F-GO) | [8] | |
| Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) (SPAES) composite membranes with graphene oxide (GO) and sulfonated poly(arylene thioether sulfone)-grafted graphene oxide (SATS-GO) as fillers | 131.43 mS/cm SPAES/ SATS-GO-2.0 at 80 °C and 90% RH | 77.7% at 80 °C | [28] | ||
| Nafion–TiO2 (9%) | 0.1–0.15 (*10−2 S/cm) (50–130 °C) | 7.91% (2 M) and Nafion 9.9% | 17.77% | [33,40] | |
| Nafion CS-SiO2 6% | 0.17 S/cm at 80 °C | Around 0.96 meq/g | Around 6 (*10−7 cm2/s) (1 M) | 30% | [33,41] |
| Sulfonated SBA-15 mesoporous silica (SM-SiO2)-incorporated sulfonated poly(- phenylsulfone) (SPPSU) composite membranes | 5.9 mS/m 80 °C and 50% RH | 252% at 80 °C | [36] | ||
| Sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) doped with silica sulfuric acid (SSA) | 0.13 S/cm at 80 °C (5 wt.% SSA) (Nafion 0.12 S/cm) | 1.25 mmol/g | 0.56% at 80 °C | [29] | |
| Cross-linked sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) with silica nanoparticles (CL-SPAEK/silica) | 3.06 mS/cm, (SPAEK: 0.32 mS/cm) at 70 °C under 30% RH | 1.75 meq/g | Around 56% at 90 °C | [31] |
| Position | 2 + 2′ | 2″ | 3 + 3′ |
| Proton number | 4-DS | DS | 4 |
| Sample Name | Surface Area 1 (m2/g) | Mesoporous Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size 2 (nm) | Particle Size 3 (nm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dc | Dw | ||||
| MCF silica | 797.6 | 2.17 | 21.95 | 10.90 | 610.5 |
| Sample | BET Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Cell Size (nm) | Window Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF | 774.98 | 2.08 | 20.39 | 10.63 |
| MCF-NH2 | 560.65 | 1.70 | 20.64 | 9.86 |
| MCF-SO3H | 649.47 | 1.64 | 19.77 | 9.89 |
| Sample | Proton Conductivity | Ionic Exchange Capacity | Water Retention | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion® 117 | 113 mS/cm at 25 °C | 0.93 meq/g | 30% at 30 °C | [39] |
| LMW-sPEES + MCF 3%-SO3H | 80 mS/cm at 25 °C 80 mS/cm at 50 °C 160 mS/cm at 80 °C | 0.08 mmol/g | 20% at 25 °C 42% at 50 °C 36% at 80 °C | This work |
| Nafion® 117 | 60 mS/cm at 25 °C 70 mS/cm at 50 °C 100 mS/cm at 80 °C | --- | --- | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agudelo, N.A.; Echeverri-Cuartas, C.E.; López, B.L. Composite Membranes Based on Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foam Particles and Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) with Potential Application in Fuel Cells. Membranes 2022, 12, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111075
Agudelo NA, Echeverri-Cuartas CE, López BL. Composite Membranes Based on Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foam Particles and Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) with Potential Application in Fuel Cells. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111075
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgudelo, Natalia A., Claudia E. Echeverri-Cuartas, and Betty L. López. 2022. "Composite Membranes Based on Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foam Particles and Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) with Potential Application in Fuel Cells" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111075
APA StyleAgudelo, N. A., Echeverri-Cuartas, C. E., & López, B. L. (2022). Composite Membranes Based on Functionalized Mesostructured Cellular Foam Particles and Sulfonated Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) with Potential Application in Fuel Cells. Membranes, 12(11), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111075