Toward Suppressing Charge Trapping Based on a Combined Driving Waveform with an AC Reset Signal for Electro-Fluidic Displays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods
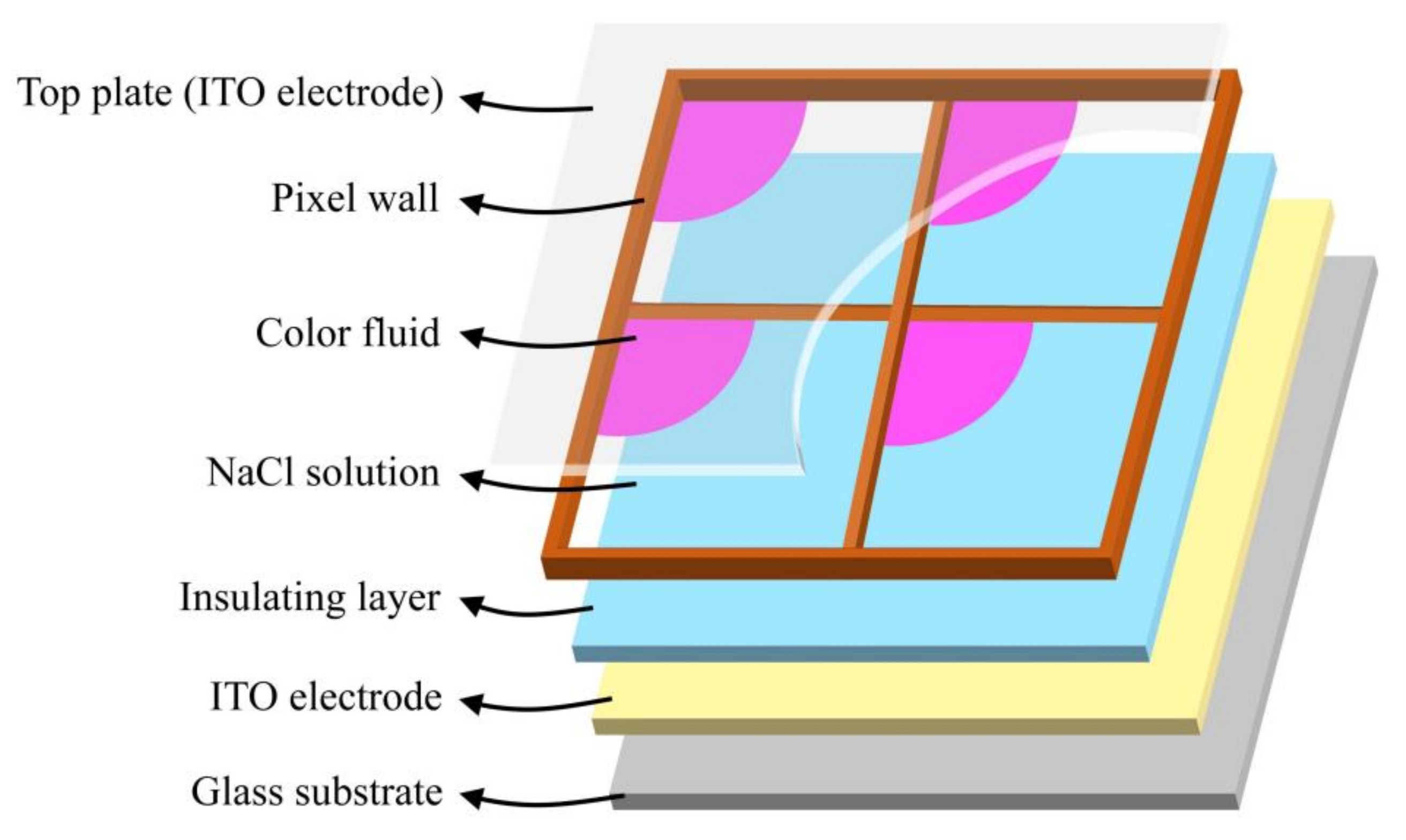
2.1. Principle of EFDs
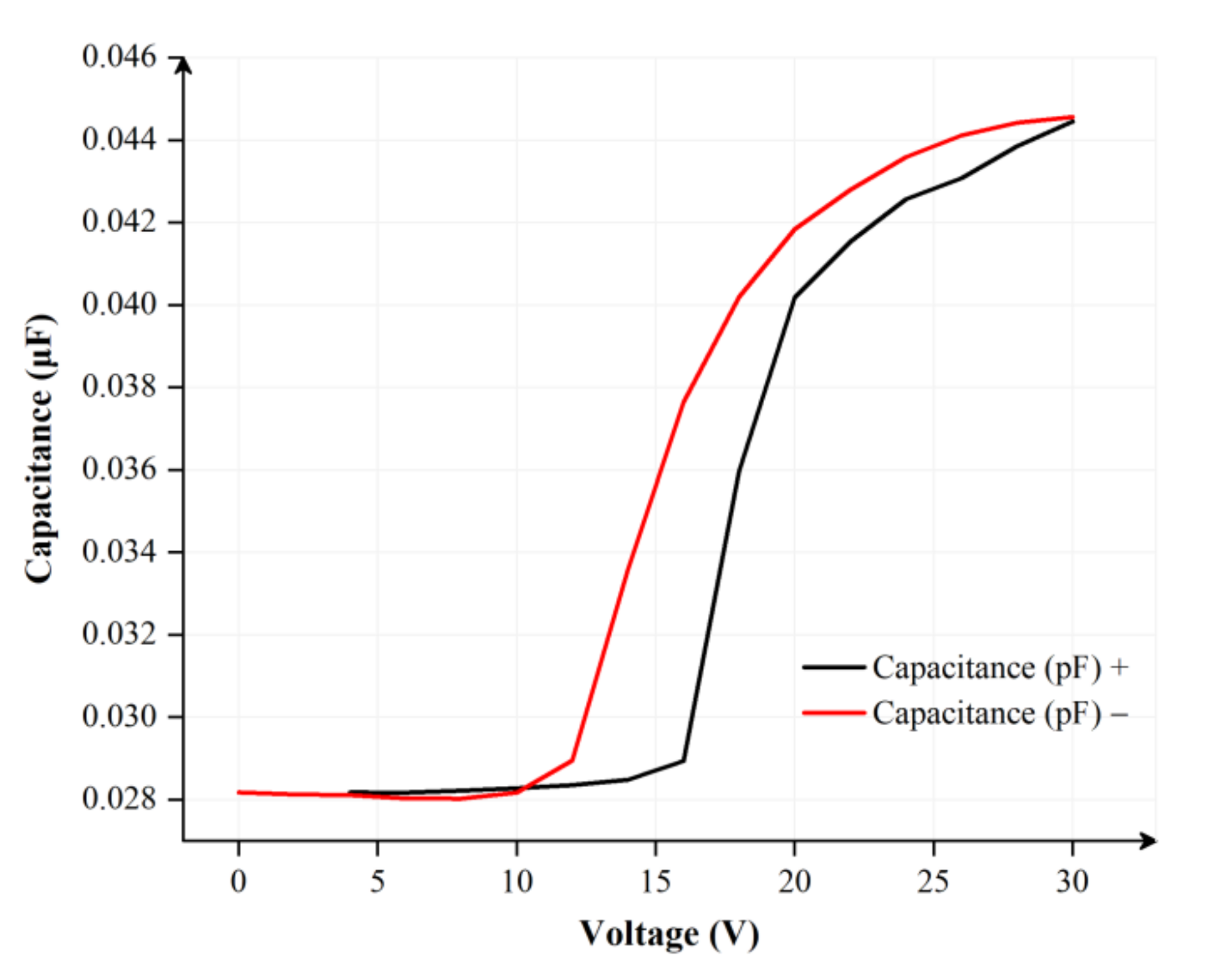
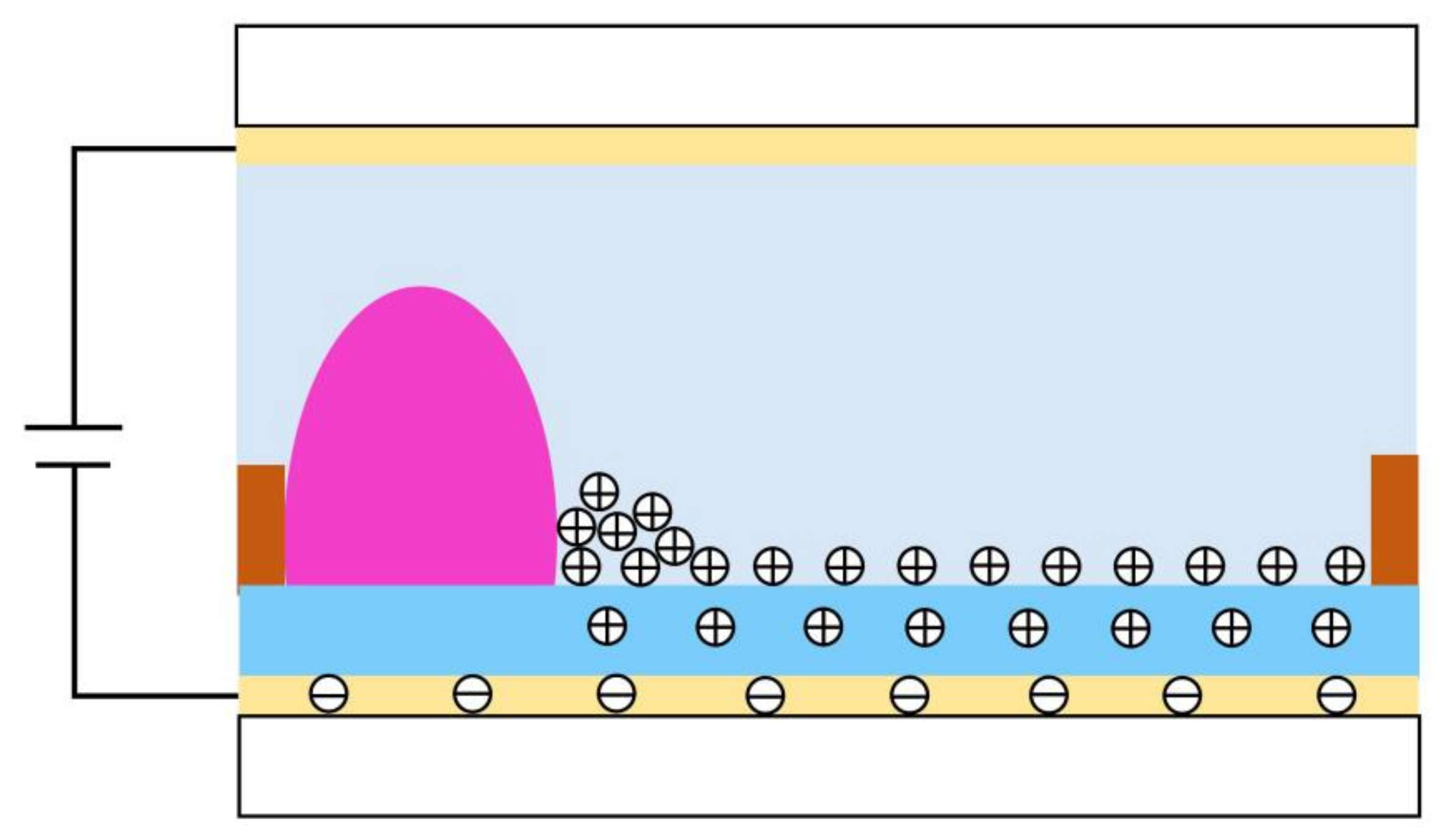
2.2. Charge Trapping of EFDs
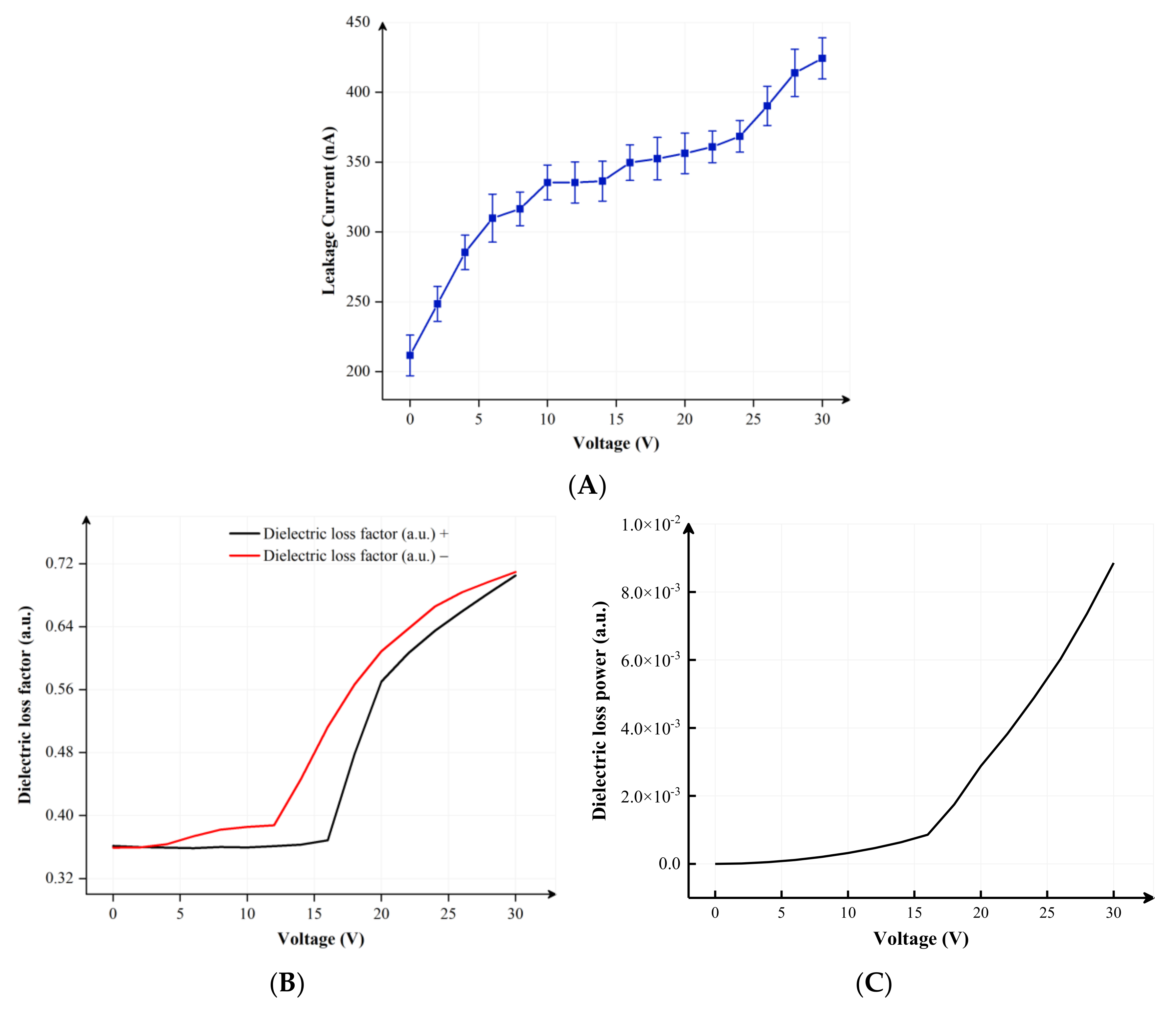
2.3. Leakage Current of EFDs
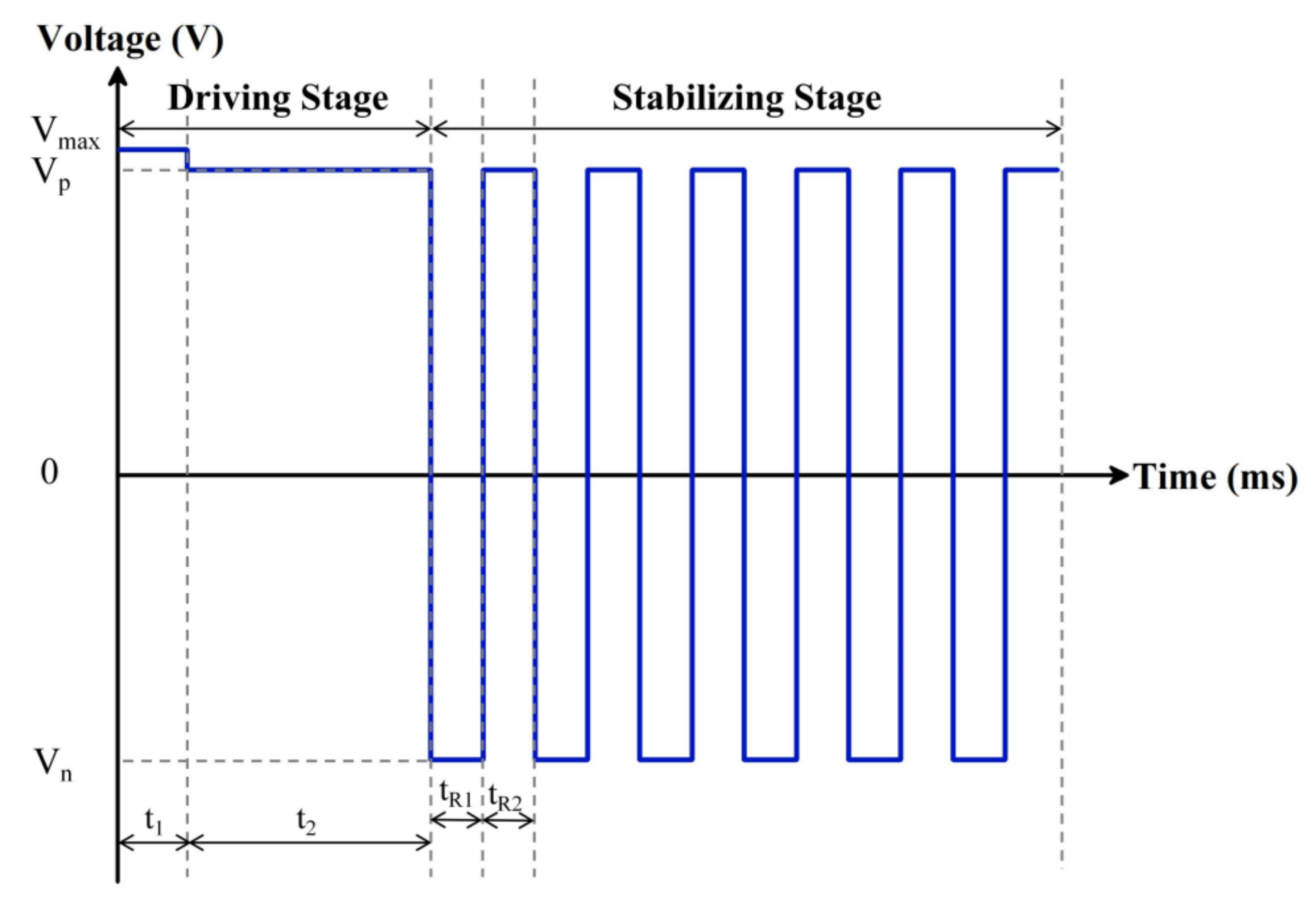
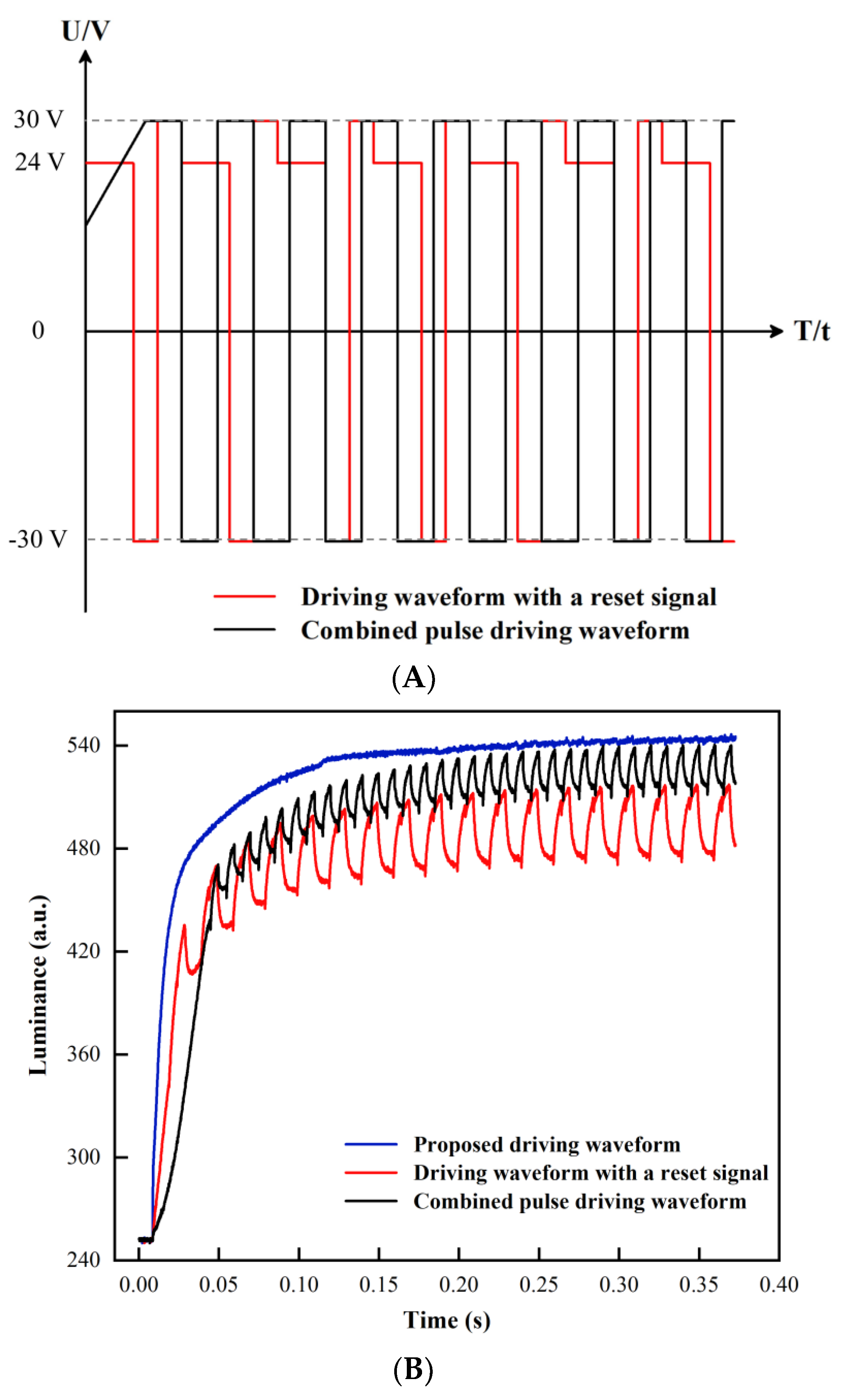
2.4. Design of Driving Waveforms
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Platform
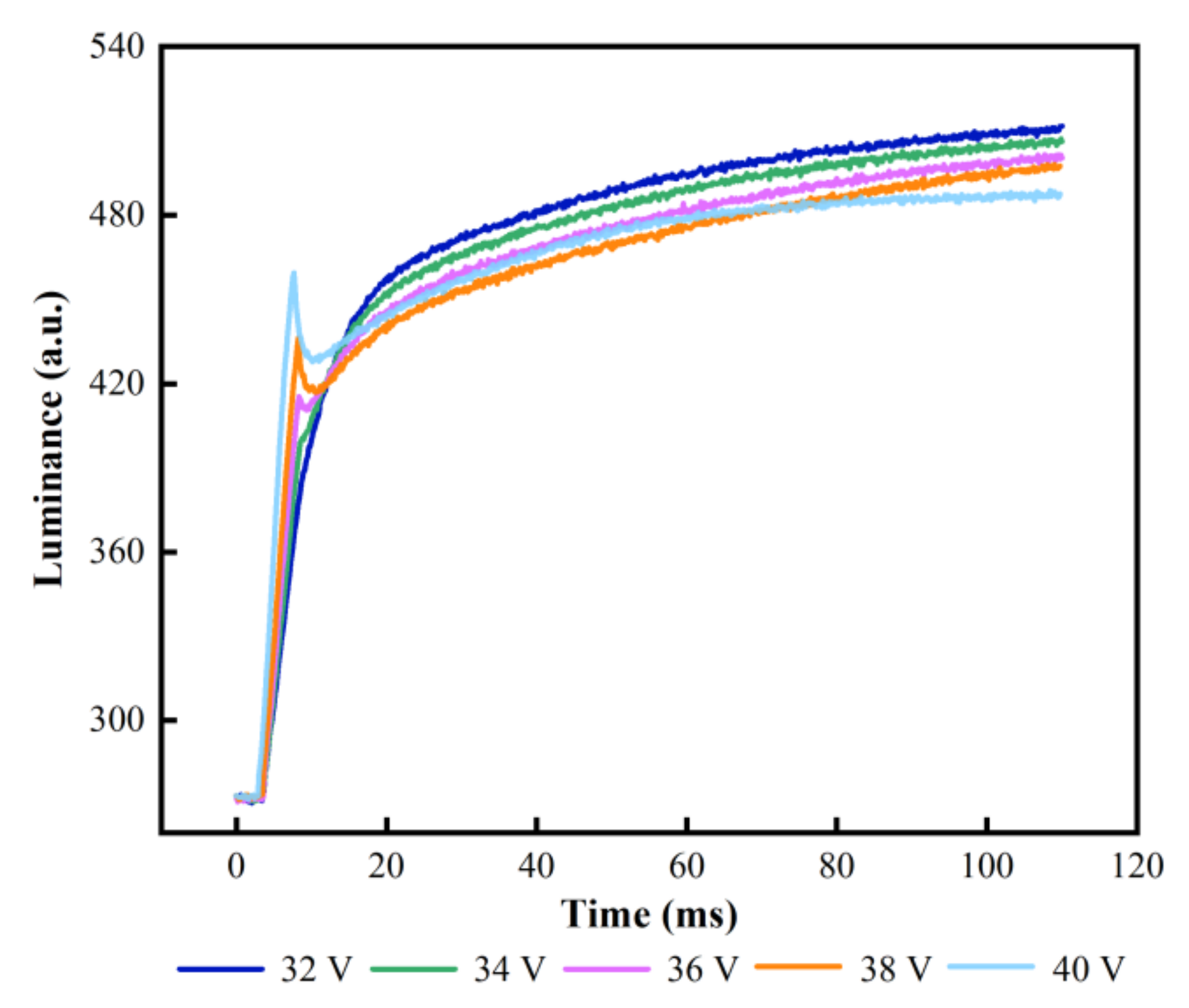
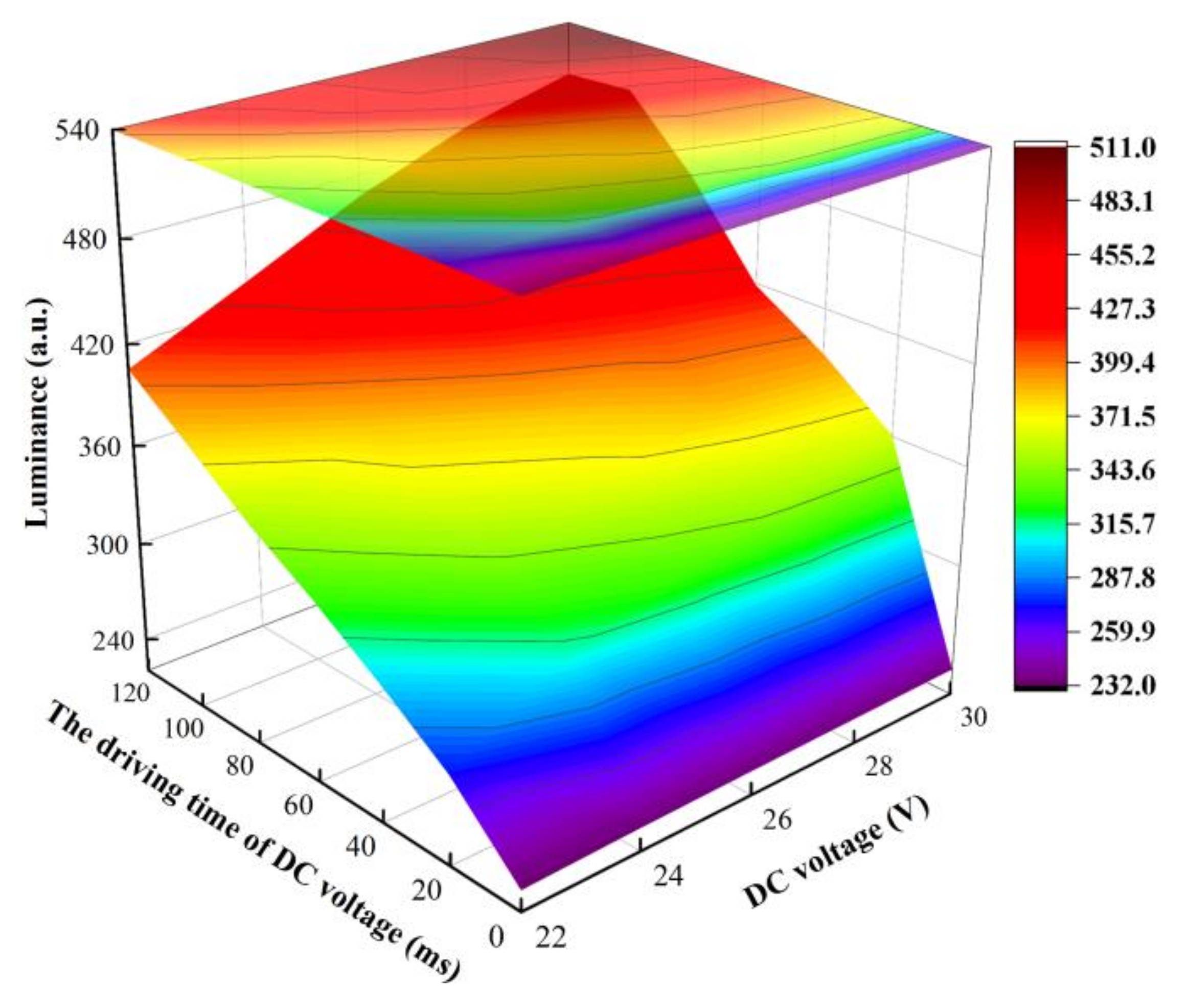
3.2. Testing of the Driving Stage
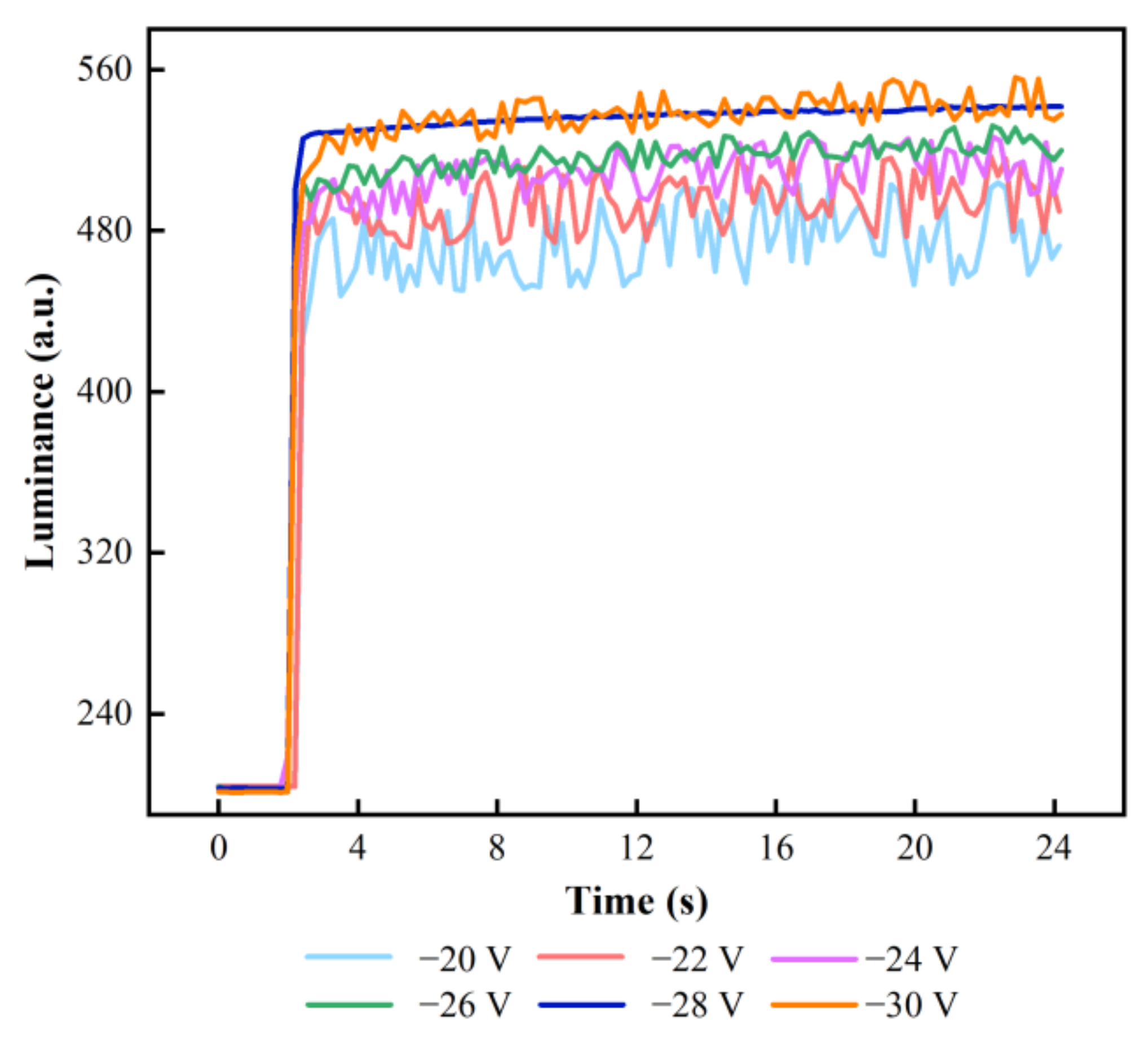
3.3. Testing of the Stabilizing Stage
3.4. Performance Comparison
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaik, F.A.; Cathcart, G.; Ihida, S.; Lereau-Bernier, M.; Leclerc, E.; Sakai, Y.; Toshiyoshi, H.; Tixier-Mita, A. Thin-film-transistor array: An exploratory attempt for high throughput cell manipulation using electrowetting principle. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Ya, L.; Shu, X.; Zhi, L.; Shi, S.; Zhi, Y.; Ming, J.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Intelligent droplet manipulation in electrowetting devices via capacitance-based sensing and actuation for self-adaptive digital microfluidics. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2020, 24, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Jin, M.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Two-phase microfluidics in electrowetting displays and its effect on optical performance. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 011908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikenfeld, J.; Zhou, K.; Kreit, E.; Raj, B.; Yang, S.; Sun, B.; Milarcik, A.; Clapp, L.; Schwartz, R. Electrofluidic displays using Young–Laplace transposition of brilliant pigment dispersions. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.; Lin, S.; Zeng, S.; Lin, Z.; Guo, T.; Tang, B. Real–time dynamic driving system implementation of electrowetting display. Opto–Electron. Eng. 2019, 46, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Lai, S.; Liu, L.; He, W.; Zhou, G.; Yi, Z. Driving waveform design with rising gradient and sawtooth wave of electrowetting displays for ultra–low power consumption. Micromachines 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivelu, S.; Surjya, S. Display Applications of Electrowetting. J. Adhes. Sci. Tech. 2012, 26, 1947–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Yi, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Ma, S.; Zhou, X.; Feng, H.; Liu, L.; Shui, L.; Zhang, C.; et al. Design of Driving Waveform Based on Overdriving Voltage for Shortening Response Time in Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 642682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zeng, W.; Ma, S.; Feng, H.; Zeng, W.; Shen, S.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, C. Design of Driving Waveform Based on a Damping Oscillation for Optimizing Red Saturation in Three–Color Electrophoretic Displays. Micromachines 2021, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.A.; Feenstra, B.J. Video–speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 2003, 425, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.N. An algorithm for selecting the most accurate protocol for contact angle measurement by drop shape analysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 125107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Mugele, F. How to make sticky surfaces slippery: Contact angle hysteresis in electrowetting with alternating voltage. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 244108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sur, A.; Liu, D.; Pascente, C.; Ruchhoeft, P. Dynamics of droplet motion induced by Electrowetting. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer. 2017, 106, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, P.; Hayes, R.; Shui, L.; Jin, M.; Tang, B.; Zhou, G. Novel Driving Methods for Manipulating Oil Motion in Electrofluidic Display Pixels. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Bai, P. A Combined Pulse Driving Waveform with Rising Gradient for Improving the Aperture Ratio of Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 709151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, Y. Driving Waveform Design of Electrowetting Displays Based on a Reset Signal for Suppressing Charge Trapping Effect. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 672541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Bai, P.; Yi, Z.; Zhou, G. A separated reset waveform design for suppressing oil backflow in active matrix electrowetting displays. Micromachines 2021, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zeng, S.; Qian, M.; Lin, Z.; Guo, T.; Tang, B. Improvement of display performance of electrowetting displays by optimized waveforms and error diffusion. J. Soc. Inf. Display. 2019, 27, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques–Carmes, T.; Hayes, R.; Feenstra, B.; Schlangen, L. Liquid behavior inside a reflective display pixel based on electrowetting. J. Appl. Physics. 2004, 95, 4389–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhou, X.; Shui, L. Design of an Open Electrowetting on Dielectric Device Based on Printed Circuit Board by Using a Parafilm M. Front Phys. 2020, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Seo, J.H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, J. Active energy–controlling windows incorporating transparent photovoltaics and an integrated transparent heater. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2021, 2, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kim, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Kim, J.; Wong, C. Transparent sustainable energy platform: Closed–loop energy chain of solar–electric–hydrogen by transparent photovoltaics, photo–electro–chemical cells and fuel system. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, R.; Li, F.; Henzen, A.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G. Influence of fluoropolymer surface wettability on electrowetting display performance. Displays 2018, 53, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Heikenfeld, J.; Dean, K.; Howard, E.; Johnson, M. A full description of a simple and scalable fabrication process for electrowetting displays. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 065029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, K.; Lao, Y.; Heikenfeld, J.; Cheng, W. Scalable fabrication of electrowetting displays with self–assembled oil dosing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 011106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Tang, B.; Hayes, R.; Dou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, G. Coating and patterning functional materials for large area electrofluidic arrays. Materials 2016, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zeng, W.; Ma, C.; Feng, H.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, C. A real–time touch control system design based on field–programmable gate array via optimizing Bresenham algorithm for electrowetting displays. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2021, 29, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Lai, S.; Bai, P. Design of an AC driving waveform based on characteristics of electrowetting stability for electrowetting displays. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 618752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, L.; Henzen, A. A Multi Waveform Adaptive Driving Scheme for Reducing Hysteresis Effect of Electrowetting Displays. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 618811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Mendel, N.; van Der Ham, S.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Mugele, F. Charge trapping based electricity generator (CTEG): An ultrarobust and high efficiency nanogenerator for energy harvesting from water droplets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, H.; Prins, M. Reversible electrowetting and trapping of charge: Model and experiments. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6616–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Dey, R.; Siretanu, I.; van den Ende, D.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Mugele, F. Electrically controlled localized charge trapping at amorphous fluoropolymer–electrolyte interfaces. Small 2019, 16, 1905726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, C.A.; Lourdudoss, S.; Martinsson, H. Analysis of leakage current in GaAs/AlGaAs buried–heterostructure lasers with a semi–insulating GaInP: Fe burying layer. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Tang, B.; Barman, J.; Groenewold, J.; Zhou, G. Approximately symmetric electrowetting pm an oil–lubricated surface. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 20257–20263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, S. Standards for standardized logistic regression coefficients. Soc. Forces 2011, 89, 1409–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, Z.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Shui, L. Toward Suppressing Charge Trapping Based on a Combined Driving Waveform with an AC Reset Signal for Electro-Fluidic Displays. Membranes 2022, 12, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111072
Long Z, Yi Z, Zhang H, Liu L, Shui L. Toward Suppressing Charge Trapping Based on a Combined Driving Waveform with an AC Reset Signal for Electro-Fluidic Displays. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111072
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Zhengxing, Zichuan Yi, Hu Zhang, Liming Liu, and Lingling Shui. 2022. "Toward Suppressing Charge Trapping Based on a Combined Driving Waveform with an AC Reset Signal for Electro-Fluidic Displays" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111072
APA StyleLong, Z., Yi, Z., Zhang, H., Liu, L., & Shui, L. (2022). Toward Suppressing Charge Trapping Based on a Combined Driving Waveform with an AC Reset Signal for Electro-Fluidic Displays. Membranes, 12(11), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111072





