Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Feedwaters and Chemicals
2.2. PTFE Membrane Specifications
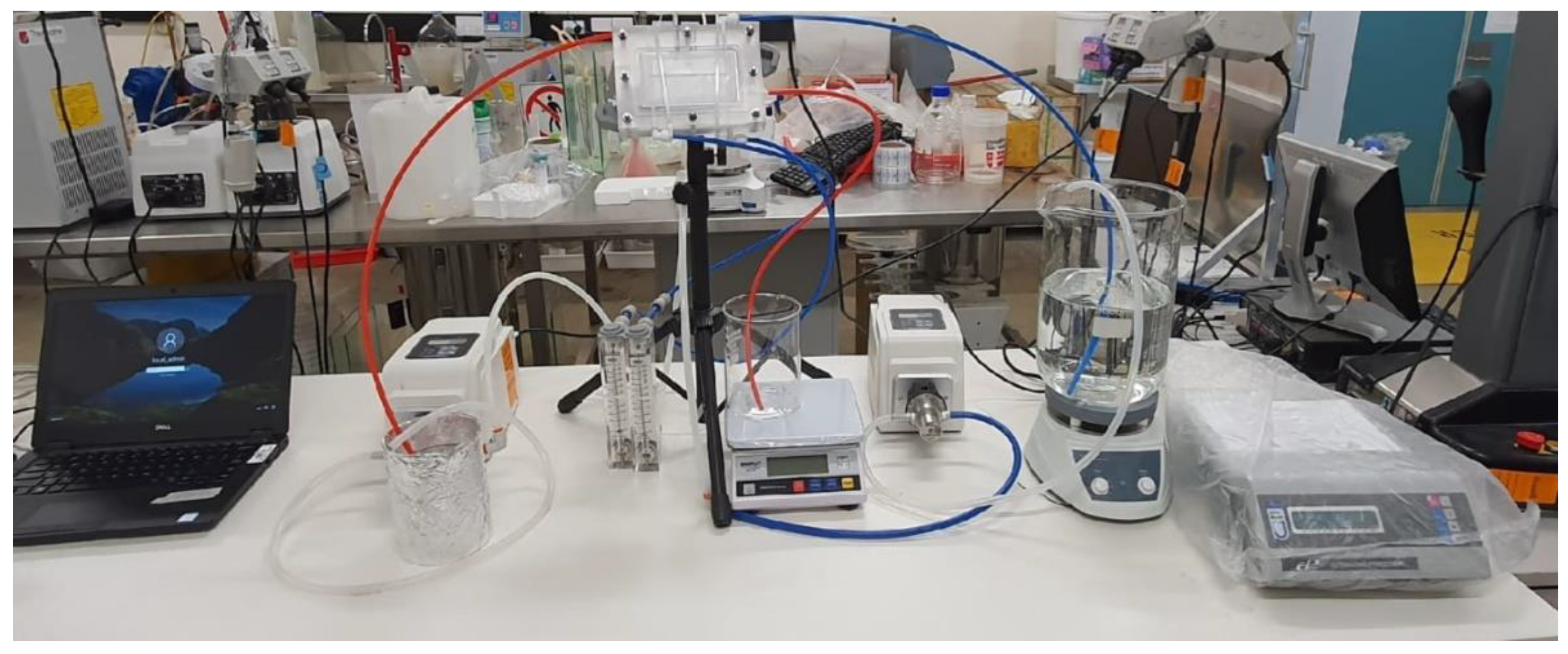
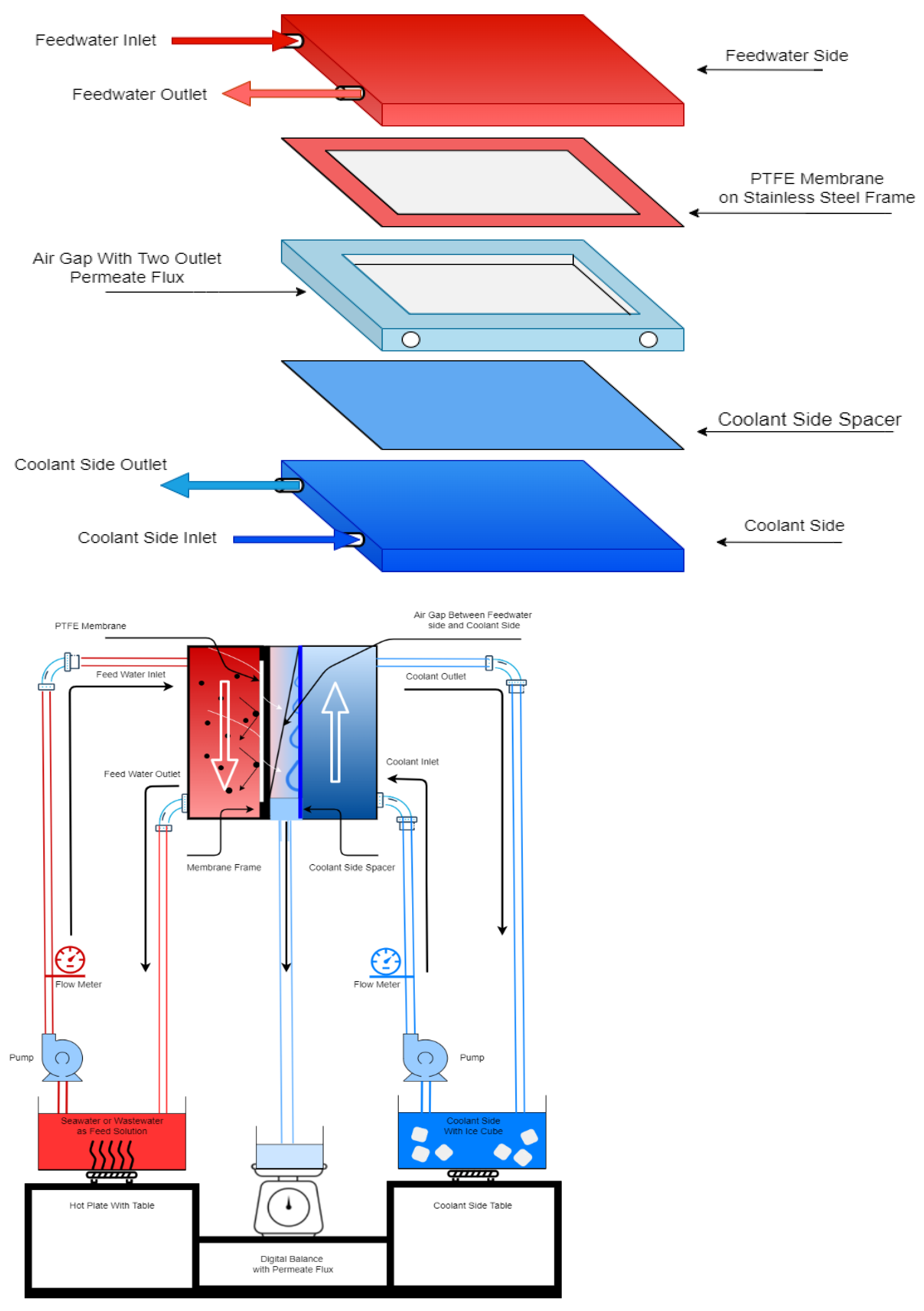
2.3. AGMD Module Setup and Experimental Methodology
2.4. Membrane Characterizations
2.4.1. FE-SEM and EDX Analysis
2.4.2. Pore Size and Contact Angle Analysis
2.4.3. FT-IR Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
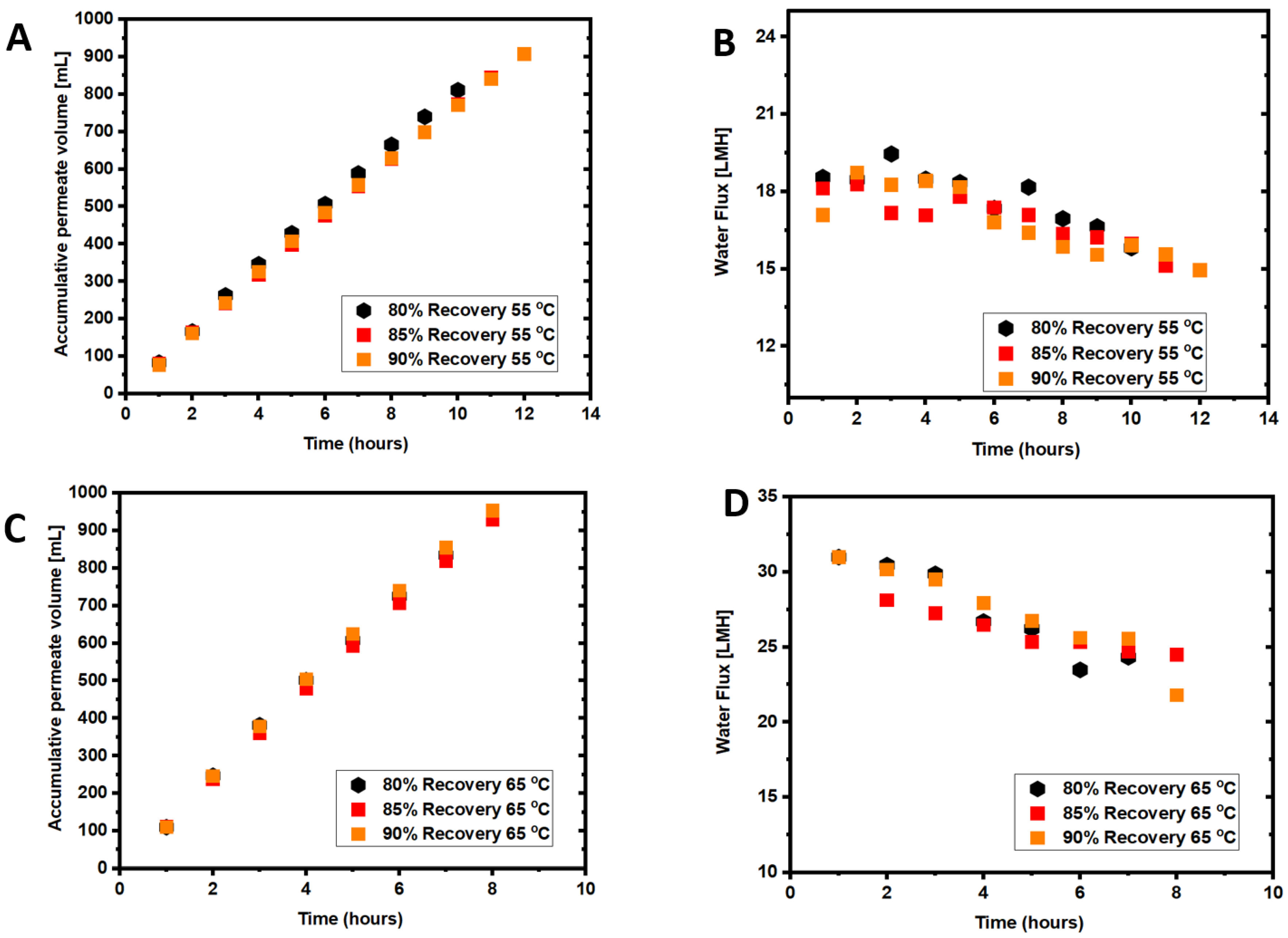
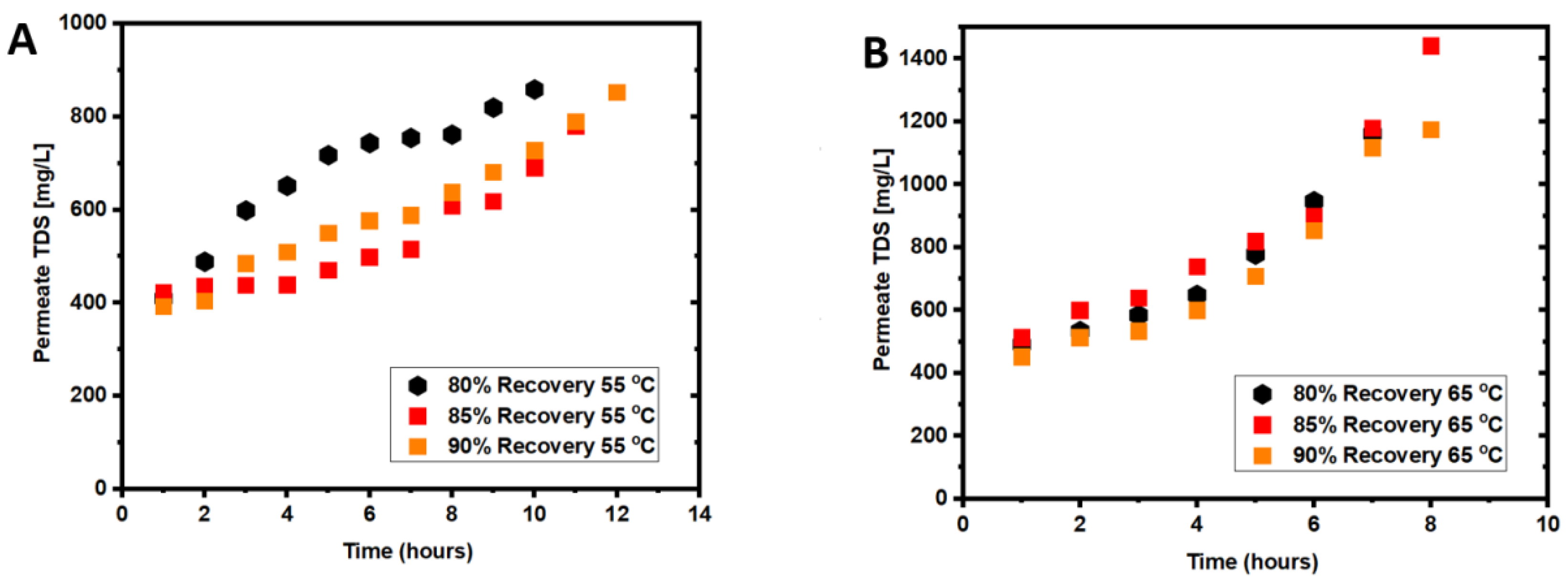
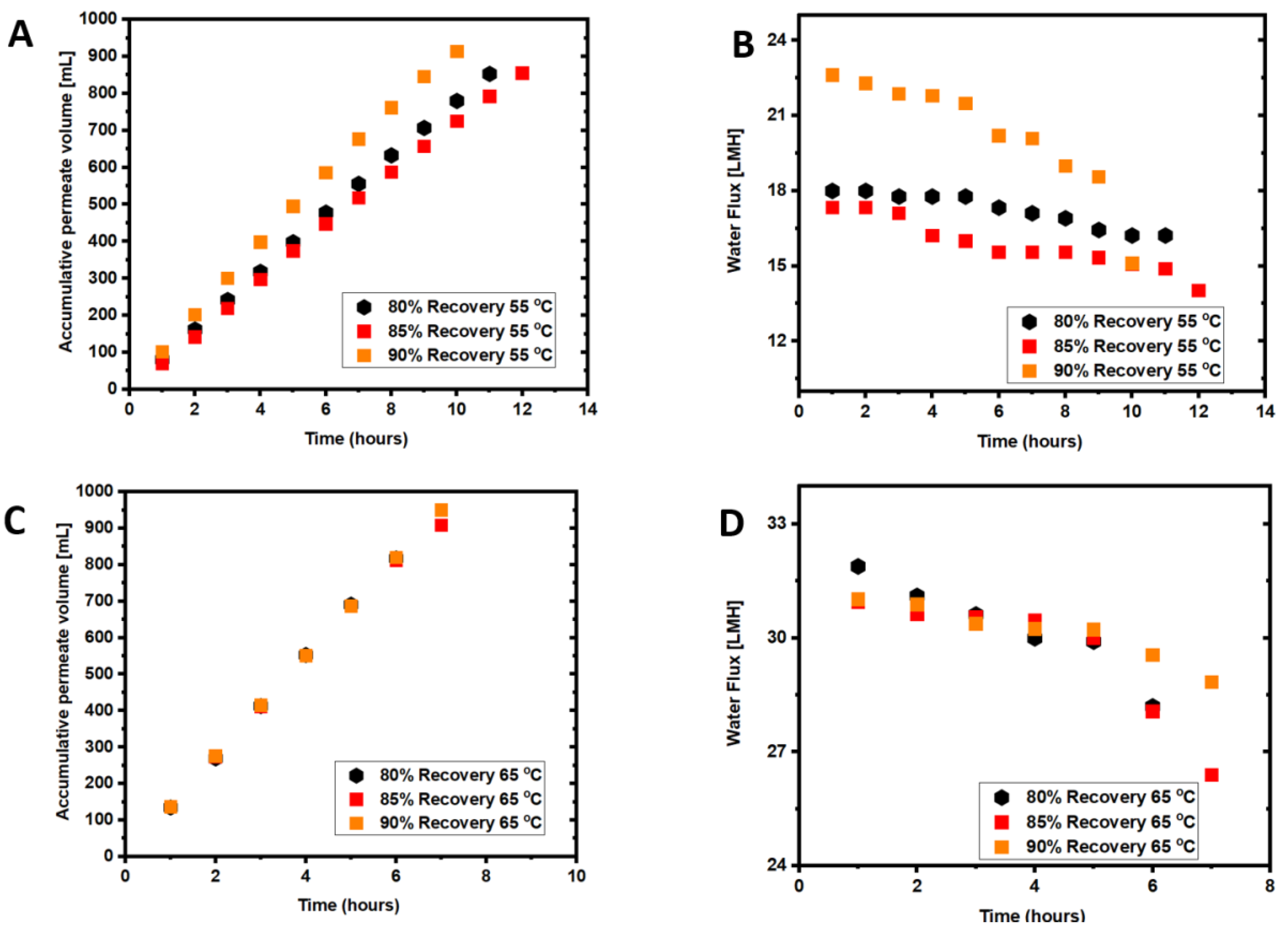
3.1. Coupled Effects of Temperature and Recovery on Seawater Treatment
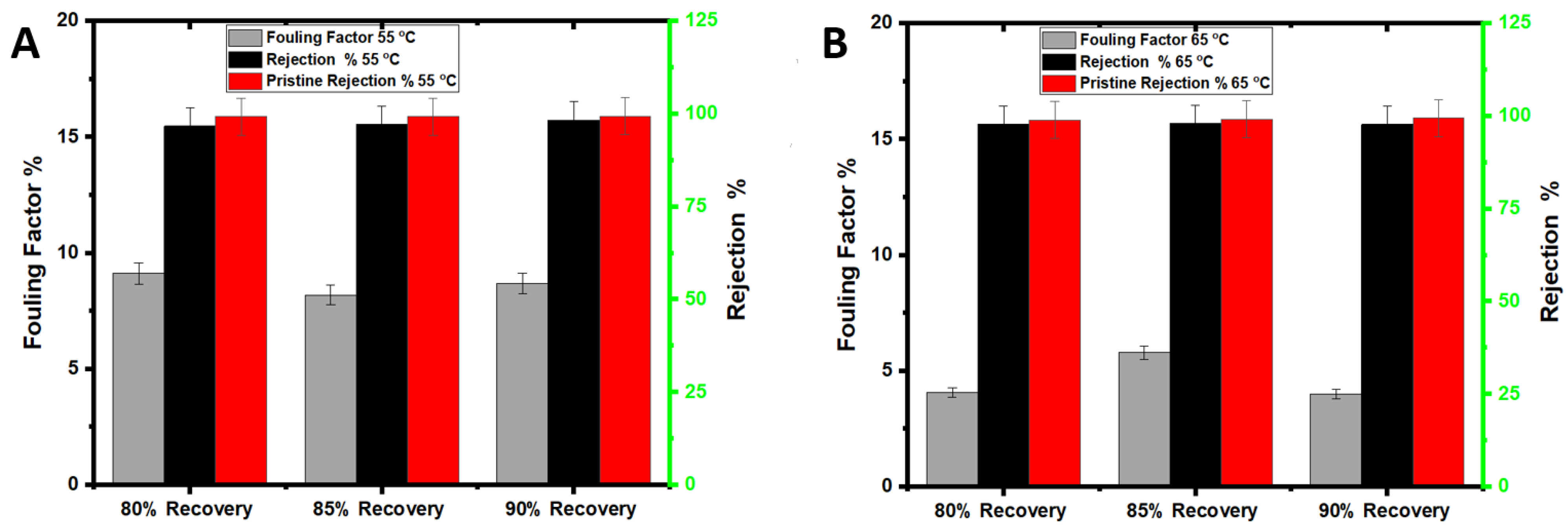
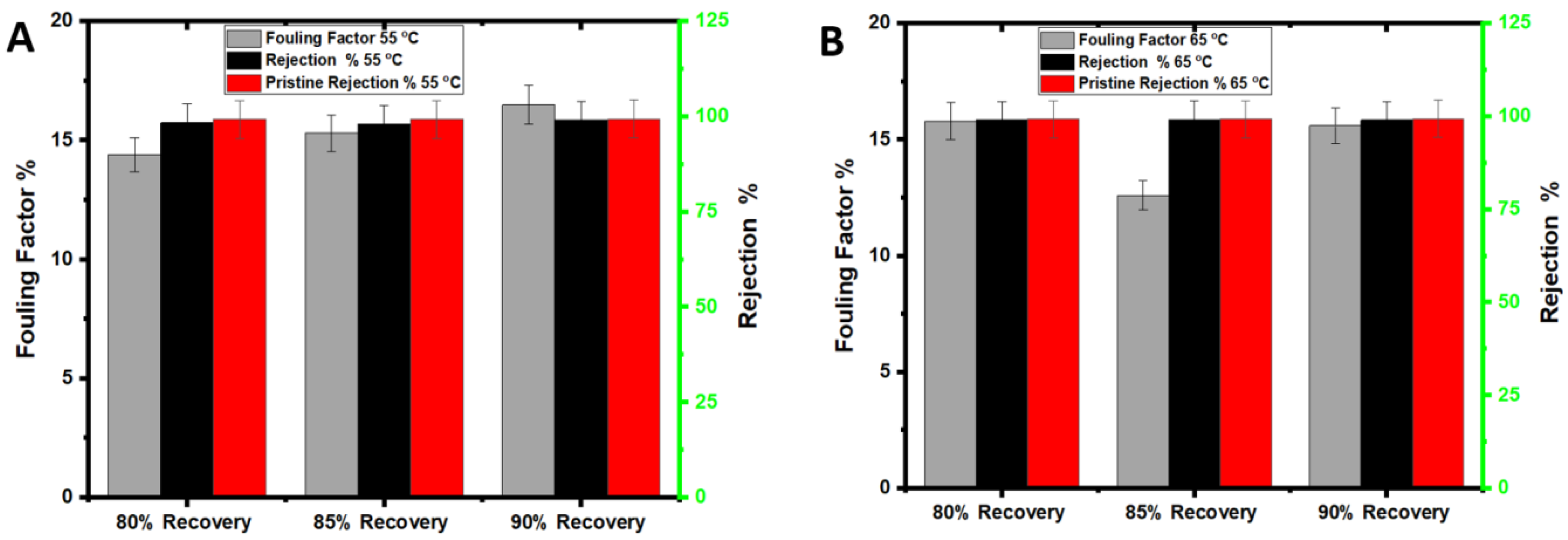
3.2. Membrane Fouling and Cleaning with Seawater Treatment
3.3. Coupled Effects of Temperature and Recovery on Wastewater Treatment
3.4. Membrane Fouling and Cleaning with Leachate Treatment
3.5. Membrane Characterization Tests
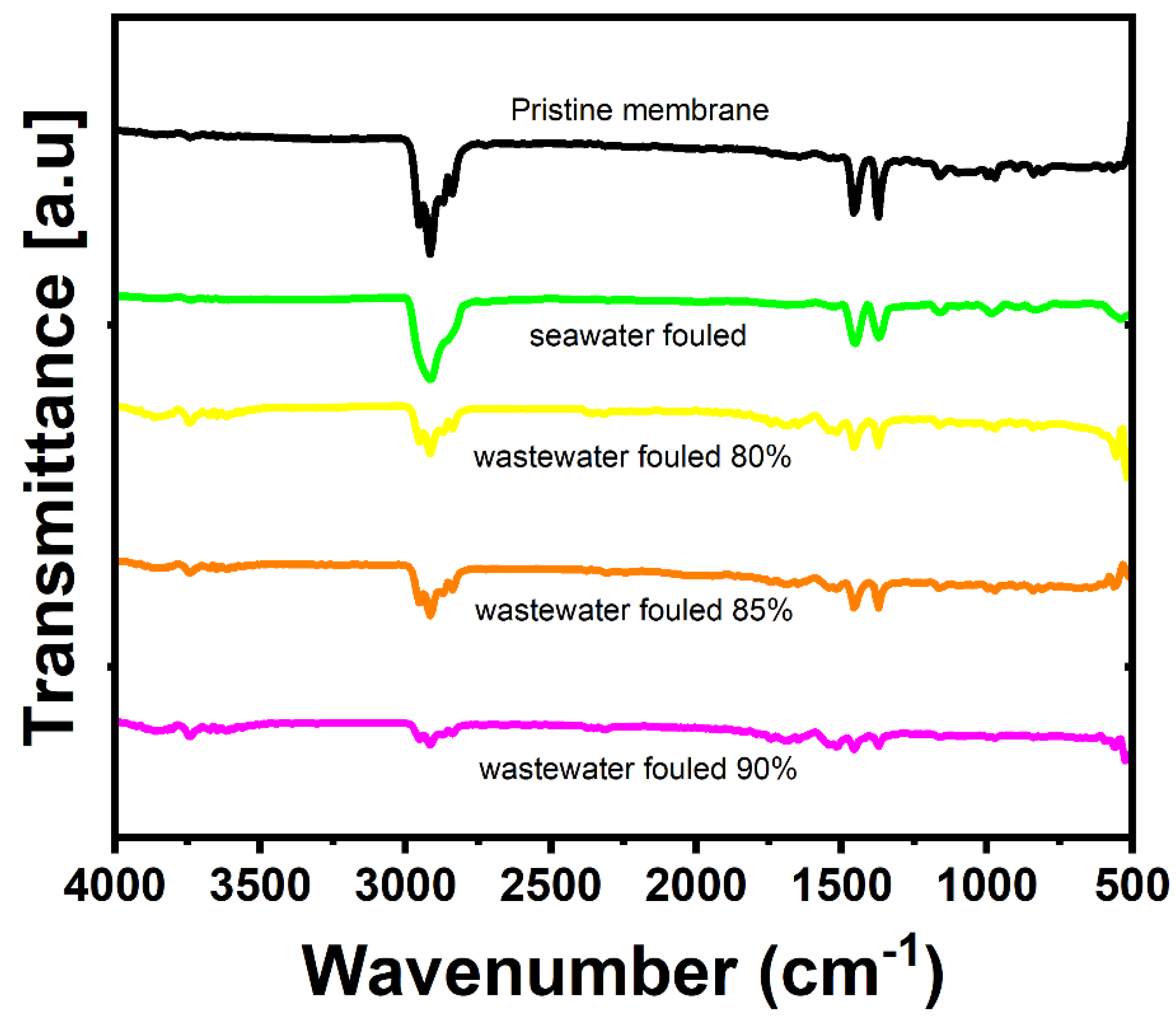
3.5.1. FE-SEM, EDX, and FT-IR Analysis
3.5.2. Pore Size and Contact Angle Analysis
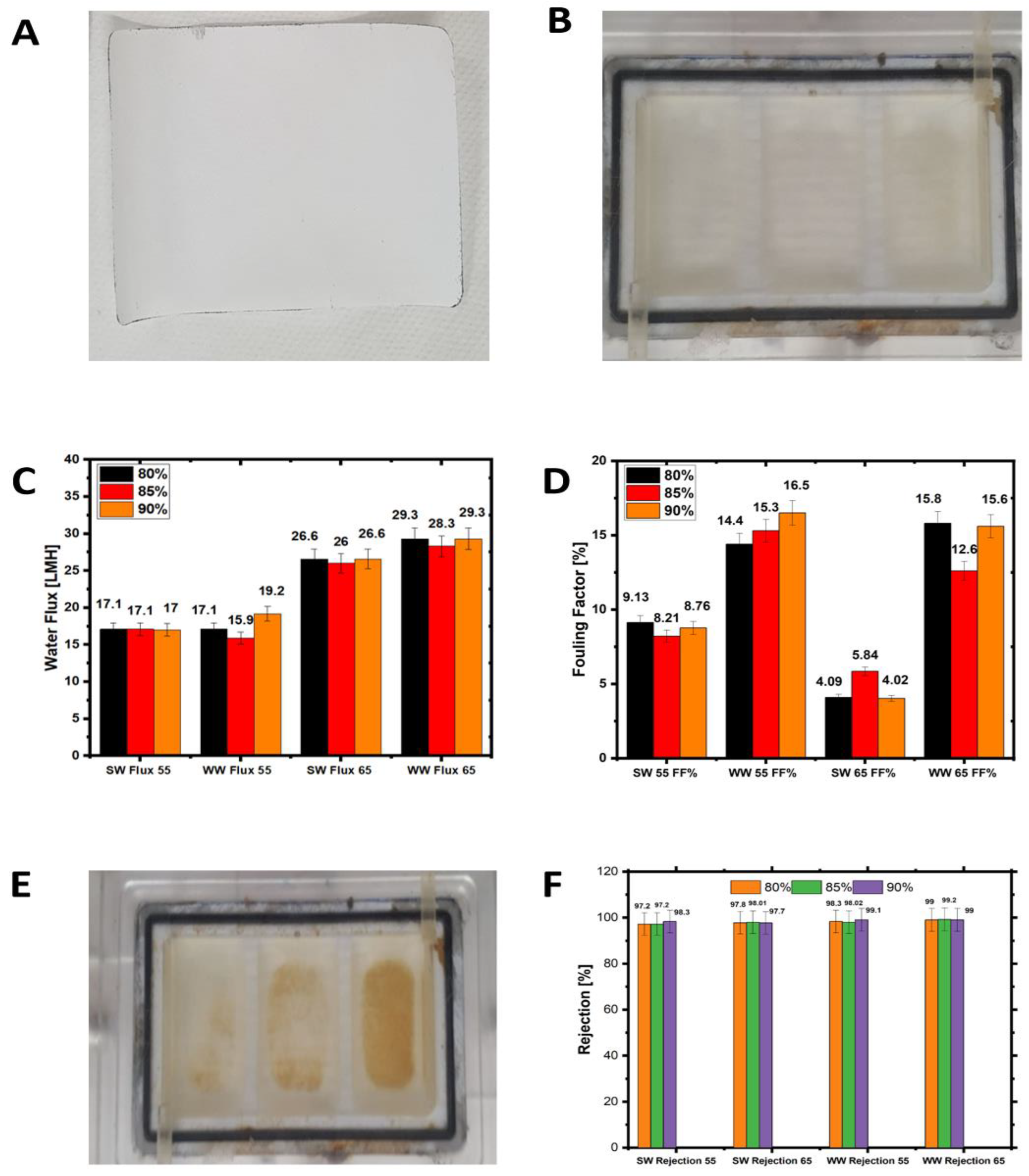
3.6. Comparison of Seawater and Wastewater Fouling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Pore Size Analysis
References
- Ibrar, I.; Yadav, S.; Braytee, A.; Altaee, A.; HosseinZadeh, A.; Samal, A.K.; Zhou, J.L.; Khan, J.A.; Bartocci, P.; Fantozzi, F. Evaluation of machine learning algorithms to predict internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 646, 120257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.; Yang, D.R.; Hong, S. A comprehensive review of energy consumption of seawater reverse osmosis desalination plants. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Batouti, M.; Al-Harby, N.F.; Elewa, M.M. A Review on Promising Membrane Technology Approaches for Heavy Metal Removal from Water and Wastewater to Solve Water Crisis. Water 2021, 13, 3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Reverse osmosis pretreatment technologies and future trends: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2019, 452, 159–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, L.A.; Phillip, W.A.; Tiraferri, A.; Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Forward with Osmosis: Emerging Applications for Greater Sustainability; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Vigneswaran, S.; Lee, S.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Experimental comparison of submerged membrane distillation configurations for concentrated brine treatment. Desalination 2017, 420, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Naidu, G.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Vigneswaran, S. Fractional-submerged membrane distillation crystallizer (F-SMDC) for treatment of high salinity solution. Desalination 2018, 440, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Batouti, M.; Alharby, N.F.; Elewa, M.M. Review of New Approaches for Fouling Mitigation in Membrane Separation Processes in Water Treatment Applications. Separations 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Han, X.; Shao, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, D. Effects of different pore sizes on membrane fouling and their performance in algae harvesting. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 641, 119916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.Z.; Askari, M.; Choong, L.T.; Chung, T.-S. Ultra-strong polymeric hollow fiber membranes for saline dewatering and desalination. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, G. UF/MF pre-treatment to RO in seawater and wastewater reuse applications: A comparison of energy costs. Desalination 2008, 222, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathan, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Bakly, S.; Khanafer, D.; Altaee, A.; Padmanaban, V.C.; Samal, A.K.; Hawari, A.H. Organic Fouling in Forward Osmosis: A Comprehensive Review. Water 2020, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Lienhard, J.H. How RO membrane permeability and other performance factors affect process cost and energy use: A review. Desalination 2019, 470, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Altaee, A.; Samal, A.K.; Zhou, J. Surface modification of nanofiltration membrane with kappa-carrageenan/graphene oxide for leachate wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.B.; Ji, B.; Maqbool, T.; Zhang, Z. Algogenic organic matter fouling alleviation in membrane distillation by peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Role of PMS con-centration and activation temperature. Desalination 2021, 516, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nthunya, L.N.; Bopape, M.F.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Quist-Jensen, C.A.; Richards, H. Fouling, performance and cost analysis of membrane-based water desalination technologies: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 301, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, H.; Nurgirisia, N.; Qiu, G.; Ting, Y.-P.; Wenten, I.G. Membrane distillation for wastewater treatment: Current trends, challenges and prospects of dense membrane distillation. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Alkaline scaling in the membrane distillation process. Desalination 2008, 228, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z.; Wei, Z.; Fan, G.; Liang, H.; Qu, F. Evaluation of applying membrane distillation for landfill leachate treatment. Desalination 2021, 520, 115358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, I.A.; Atherton, W.; Hashim, K.; Kot, P.; Alkhaddar, R.; Alo, B.I.; Shaw, A. An analyses of the status of landfill classification systems in developing countries: Sub Saharan Africa landfill expe-riences. Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righetto, I.; Al-Juboori, R.A.; Kaljunen, J.U.; Mikola, A. Multipurpose treatment of landfill leachate using natural coagulants–Pretreatment for nutrient recovery and re-moval of heavy metals and micropollutants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Galogahi, F.M.; Thiel, D.V.; Helfer, F.; Millar, G.; Soukane, S.; Ghaffour, N. Downstream variations of air-gap membrane distillation and comparative study with direct contact membrane distillation: A modelling approach. Desalination 2022, 526, 115539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Juboori, R.A.; Naji, O.; Bowtell, L.; Alpatova, A.; Soukane, S.; Ghaffour, N. Power effect of ultrasonically vibrated spacers in air gap membrane distillation: Theoretical and experimental investigations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Ghaffour, N.; Mahmoudi, H.; Goosen, M.; Mushtaq, S.; Hoinkis, J. Low-cost low-enthalpy geothermal heat for freshwater production: Innovative applications using thermal desalination processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.C.; Cooper, P.; Nelemans, B.; Cath, T.Y.; Nghiem, L.D. Optimizing thermal efficiency of direct contact membrane distillation by brine recycling for small-scale seawater desalination. Desalination 2015, 374, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, W.G. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, M.T.T.; Diep, B.Q.; Sano, H.; Nishimura, Y.; Boivin, S.; Kodamatani, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Sakti, S.C.W.; Fujioka, T. Membrane distillation for achieving high water recovery for potable water reuse. Chemosphere 2021, 288, 132610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, P.; Wang, S. Membrane fouling and wetting in a DCMD process for RO brine concentration. Desalination 2014, 344, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.A.; Vanneste, J.; Cath, T.Y. Membrane distillation for concentration of hypersaline brines from the Great Salt Lake: Effects of scaling and fouling on performance, efficiency, and salt rejection. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenky, A.C.; de Souza, N.G.; Nguyen, H.H.; Jeon, J.; Choi, H. Decomposition of Carboxylic PFAS by Persulfate Activated by Silver under Ambient Conditions. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 06020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrar, I.; Yadav, S.; Ganbat, N.; Samal, A.K.; Altaee, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Nguyen, T.V. Feasibility of H2O2 cleaning for forward osmosis membrane treating landfill leachate. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Aguirre, A.; Andrés-Mañas, J.A.; Zaragoza, G. Evaluation of permeate quality in pilot scale membrane distillation sys-tems. Membranes 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charfi, A.; Tibi, F.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.; Cho, J. Organic Fouling Impact in a Direct Contact Membrane Distillation System Treating Wastewater: Experimental Observations and Modeling Approach. Membranes 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, L.; Elcik, H.; Blankert, B.; Ghaffour, N.; Vrouwenvelder, J. Textile dye wastewater treatment by direct contact membrane distillation: Membrane performance and detailed fouling analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puro, L.; Kallioinen, M.; Mänttäri, M.; Nyström, M. Evaluation of behavior and fouling potential of wood extractives in ultrafiltration of pulp and paper mill process water. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 368, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, L.; Fan, G.; Chang, H.; Qu, F.; Liang, H. Membrane distillation treatment of landfill leachate: Characteristics and mechanism of membrane fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 289, 120787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebska, A.; Amor, C.; Ciurkot, K.; Karring, H.; Thygesen, O.; Andersen, T.; Hägg, M.-B.; Christensen, K.; Norddahl, B. Fouling mitigation in membrane distillation processes during ammonia stripping from pig manure. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 484, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-M.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S. Characteristics of membrane foulants at different degrees of SWRO brine concentration by membrane distillation. Desalination 2017, 409, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendra, D.; Yunus, W.W.; Haron, J.; Basri, M.; Silong, S. Enzymatic Synthesis of Fatty Hydroxamic Acids from Palm Oil. J. Oleo Sci. 2005, 54, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Chellam, S. Pre-chlorination effects on fouling during microfiltration of secondary municipal wastewater effluent. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Thomas, R.; Mansoor, B.; Johnson, D.; Hilal, N.; Arafat, H. Effect of dry-out on the fouling of PVDF and PTFE membranes under conditions simulating intermittent seawater membrane distillation (SWMD). J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 438, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrar, I.; Yadav, S.; Altaee, A.; Samal, A.K.; Zhou, J.L.; Nguyen, T.V.; Ganbat, N. Treatment of biologically treated landfill leachate with forward osmosis: Investigating membrane performance and cleaning protocols. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.C.; Duke, M.; Gray, S.; Cooper, P.; Nghiem, L.D. Membrane scaling and prevention techniques during seawater desalination by air gap membrane distillation. Desalination 2016, 397, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnajjar, H.; Tabatabai, A.; Alpatova, A.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N. Organic fouling control in reverse osmosis (RO) by effective membrane cleaning using saturated CO2 solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 264, 118410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayet, M.; Mengual, J. Effect of salt concentration during the treatment of humic acid solutions by membrane distillation. Desalination 2004, 168, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisurichan, S.; Jiraratananon, R.; Fane, A. Humic acid fouling in the membrane distillation process. Desalination 2005, 174, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Seawater | Landfill Leachate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) | Measuring Instrument | Parameter | Concentration (mg/L) | Measuring Instrument |
| Color | colorless | - | Color | Brown yellowish | - |
| pH | 7.7 | HQ40d multi (Hach, Sydney, Australia) | pH | 8.0 | HQ40d multi(Hach, Sydney, Australia) |
| Turbidity, NTU | 1.1 | 2100P Turbidimeter (Hach, Sydney, Australia) | Turbidity, NTU | 35.0 | 2100P Turbidimeter Hach, Sydney, Australia) |
| Conductivity mS/cm | 50.3 | HQ14d Conductivity Hach, Sydney, Australia) | Conductivity ms/cm | 12.1 | HQ14d Conductivity Hach, Sydney, Australia) |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) | 32,800 | - | TDS | 4500 | - |
| K+ | 505.8 | 7900 ICP-MS (Agilent, Auburn, United States) | Total organic carbon (TOC) | 145.1 ± 5 | TOC analyzer (Shimadzu CorporationTokyo, Japan) |
| Cl− | 7177.4 | 7900 ICP-MS (Agilent, Auburn, United States) | TSS | 27–117 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) |
| Na+ | 11,952.2 | 7900 ICP-MS (Agilent, Auburn, United States) | Total irons | 3.5–52 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) |
| Ca2+ | 624.3 | 7900 ICP-(Agilent, Auburn, United States) | Ammonia | <0.5 | 5051—Ammonium Flow Plus ISE |
| SO42− | 2315.3 | DIONEX AS-AP (ThermoFisher Sydney, Australia) | Ca2+ | 126 ± 5 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) |
| Mg2+ | 1383.6 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) | Mg2+ | 95.3 ± 5 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) |
| - | - | - | K+ | 47.87 | (Agilent, Auburn, United States) |
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Nominal pore size, µm | 0.45 |
| Thickness, µm | 184 ± 38.5 |
| Bubble point, psi | 12.3 ± 0.725 |
| Contact angle | 129° ± 2° |
| Element | Pristine Membrane | Seawater-Fouled | Landfill Leachate after 15 h of Fouling | Landfill Leachate after 30 h of Fouling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 93.7 | - | 70.42 | 44.01 |
| Na | 2.81 | 6.91 | 1.86 | 2.45 |
| Mg | 1.73 | 5.82 | 0.90 | 1.42 |
| Cl | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.19 | 0.29 |
| K | 0.33 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 0.29 |
| Ca | 0.26 | 3.6 | 0.20 | 0.39 |
| Fe | 0.57 | - | 0.66 | 2.06 |
| O | - | 73.54 | - | - |
| S | - | 12.29 | - | - |
| N | - | - | 24.27 | 50.39 |
| Membrane Type | Smallest Pore Diameter (μm) | Largest Pore Diameter (μm) | Mean Pore Diameter (μm) | Contact Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine membrane | 0.213 ± 0.010 | 0.296 ± 0.009 | 0.248 ± 0.008 | 129 ± 2 |
| Seawater-fouled 65 h | 0.201 ± 0.008 | 0.294 ± 0.008 | 0.231 ± 0.008 | 115 ± 3 |
| Landfill leachate-fouled 15 h | 0.182 ± 0.008 | 0.296 ± 0.007 | 0.194 ± 0.007 | 102 ± 3 |
| Landfill leachate-fouled 30 h | 0.166 ± 0.006 | 0.244 ± 0.007 | 0.170 ± 0.008 | 93 ± 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Al Juboori, R.A.; Razzak, S.A.; Deka, P.; Subbiah, S.; Shah, S. Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation. Membranes 2022, 12, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100951
Khan A, Yadav S, Ibrar I, Al Juboori RA, Razzak SA, Deka P, Subbiah S, Shah S. Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation. Membranes. 2022; 12(10):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100951
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Abdulaziz, Sudesh Yadav, Ibrar Ibrar, Raed A. Al Juboori, Sara Ali Razzak, Priyamjeet Deka, Senthilmurugan Subbiah, and Shreyansh Shah. 2022. "Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation" Membranes 12, no. 10: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100951
APA StyleKhan, A., Yadav, S., Ibrar, I., Al Juboori, R. A., Razzak, S. A., Deka, P., Subbiah, S., & Shah, S. (2022). Fouling and Performance Investigation of Membrane Distillation at Elevated Recoveries for Seawater Desalination and Wastewater Reclamation. Membranes, 12(10), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12100951









