Rush Hour of LATs towards Their Transport Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Information about the APC Family
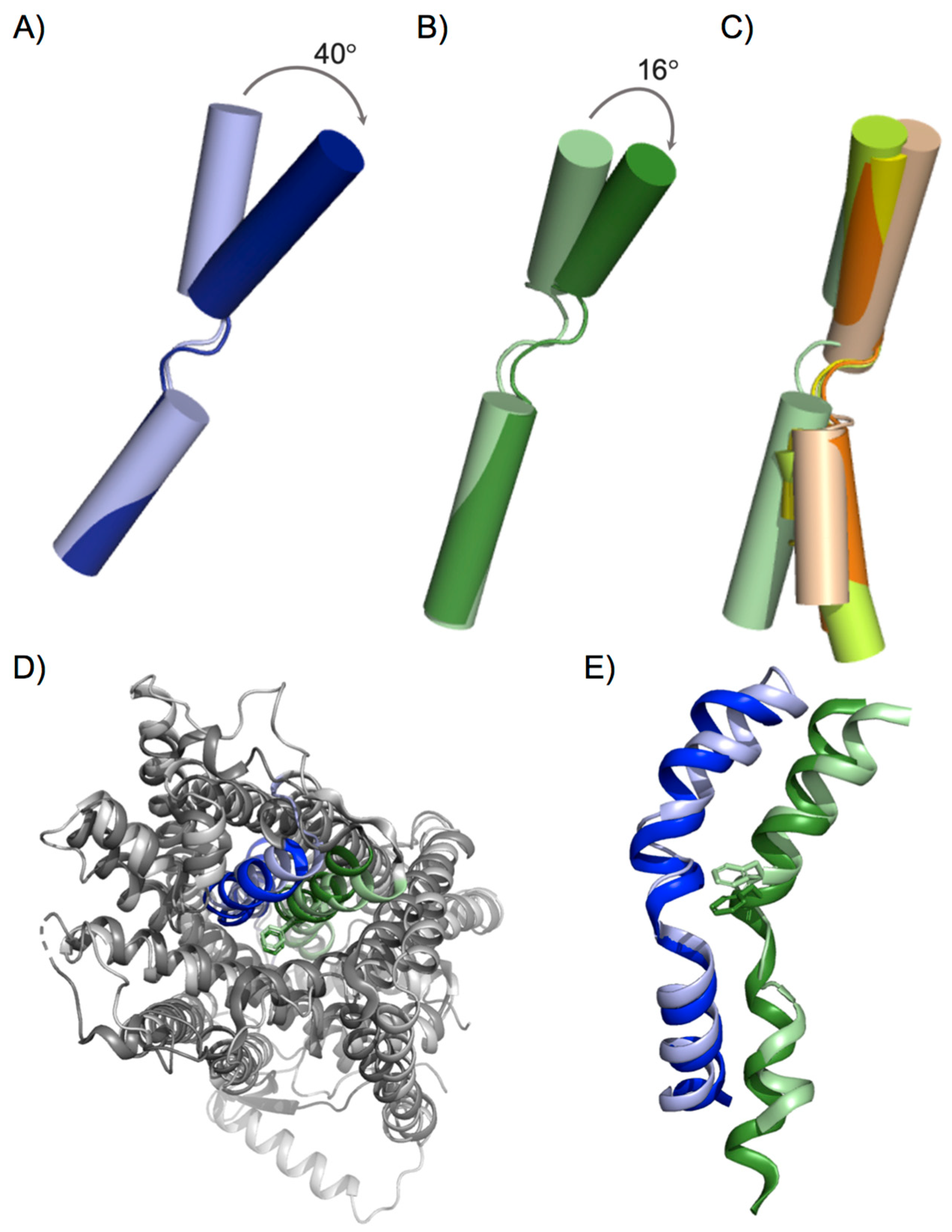
3. Conformation States in the Substrate Translocation Cycle of APC Transporters
4. Design of the Substrate-Binding Site
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almén, M.S.; Nordström, K.J.V.; Fredriksson, R.; Schiöth, H.B. Mapping the human membrane proteome: A majority of the human membrane proteins can be classified according to function and evolutionary origin. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overington, J.P.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hopkins, A.L. How many drug targets are there? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggin, P.C.; Aldeghi, M.; Bodkin, M.J.; Heifetz, A. Beyond membrane protein structure: Drug discovery, dynamics and difficulties. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 922, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Flynn, A.D. Drugging Membrane Protein Interactions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 18, 51–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröer, S.; Bröer, A. Amino acid homeostasis and signalling in mammalian cells and organisms. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1935–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiadis, D.; Kanai, Y.; Palacín, M. The SLC3 and SLC7 families of amino acid transporters. Mol. Asp. Med. 2013, 34, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vastermark, A.; Wollwage, S.; Houle, M.E.; Rio, R.; Saier, M.H. Expansion of the APC superfamily of secondary carriers. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2014, 82, 2797–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, P.; Gyimesi, G.; Kanai, Y.; Hediger, M.A. Amino acid transporters revisited: New views in health and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 2018, 43, 752–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliubadaló, L.; Font, M.; Purroy, J.; Rousaud, F.; Estivill, X.; Nunes, V.; Golomb, E.; Centola, M.; Aksentijevich, I.; Kreiss, Y.; et al. Non-type I cystinuria caused by mutations in SLC7A9, encoding a subunit (b0,+AT) of rBAT. Nat. Genet. 1999, 23, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonge, M.J.; Gasparini, P.; Chillarón, J.; Chillón, M.; Gallucci, M.; Rousaud, F.; Zelante, L.; Testar, X.; Dallapiccola, B.; Di Silverio, F.; et al. Cystinuria caused by mutations in rBAT, a gene involved in the transport of cystine. Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrents, D.; Mykkänen, J.; Pineda, M.; Feliubadaló, L.; Estévez, R.; De Rafael, C.; Sanjurjo, P.; Zorzano, A.; Nunes, V.; Huoponen, K.; et al. Identification of SLC7A7, encoding y+LAT-1, as the lysinuric protein intolerance gene. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino-Guarch, M.; Font-Llitjós, M.; Murillo-Cuesta, S.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Celaya, A.M.; Girotto, G.; Vuckovic, D.; Mezzavilla, M.; Vilches, C.; Bodoy, S.; et al. Mutations in L-type amino acid transporter-2 support SLC7A8 as a novel gene involved in age-related hearing loss. eLife 2018, 7, e31511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöpfel, E.B.; Vilches, C.; Camargo, S.M.R.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Stäubli, A.; Mayayo, C.; Munier, F.L.; Miroshnikova, N.; Poncet, N.; Junza, A.; et al. Dysfunctional LAT2 amino acid transporter is associated with cataract in mouse and humans. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tărlungeanu, D.C.; Deliu, E.; Dotter, C.P.; Kara, M.; Janiesch, P.C.; Scalise, M.; Galluccio, M.; Tesulov, M.; Morelli, E.; Sonmez, F.M.; et al. Impaired amino acid transport at the blood brain barrier is a cause of autism spectrum disorder. Cell 2016, 167, 1481–1494.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Noverr, M.C.; Parsons, C.; Kaleeba, J.A.R.; Qin, Z. xCT, not just an amino-acid transporter: A multi-functional regulator of microbial infection and associated diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sason, H.; Billard, J.M.; Smith, G.P.; Safory, H.; Neame, S.; Kaplan, E.; Rosenberg, D.; Zubedat, S.; Foltyn, V.N.; Christoffersen, C.T.; et al. Asc-1 Transporter regulation of synaptic activity via the tonic release of d-serine in the forebrain. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, M.; Ling, V.; Wang, Y.Z.; Gout, P.W. The xc− cystine/glutamate antiporter: A mediator of pancreatic cancer growth with a role in drug resistance. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ross, D.D.; Arakawa, H.; Ganapathy, V.; Tamai, I.; Nakanishi, T. Impact of system L amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) on proliferation of human ovarian cancer cells: A possible target for combination therapy with anti-proliferative aminopeptidase inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Singh, S.K.; Kawate, T.; Jin, Y.; Gouaux, E. Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of Na+/Cl−-dependent neurotransmitter transporters. Nature 2005, 437, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. The rocking bundle: A mechanism for ion-coupled solute flux by symmetrical transporters. Physiology 2009, 24, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmier, K.; Sharma, S.; Islam, S.M.; Roux, B.; Mchaourab, H.S.; Wright, E.M.; Geffen, D. Conformational cycle and ion-coupling mechanism of the Na+/hydantoin transporter Mhp1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14752–14757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, L.; Ratera, M.; Paladino, A.; Bartoccioni, P.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Valencia, E.; Portella, G.; Bial, S.; Zorzano, A.; Fita, I.; et al. Molecular basis of substrate-induced permeation by an amino acid antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3935–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Fort, J.; Bartoccioni, P.; Díaz, L.; Pardon, E.; Carpena, X.; Espino-Guarch, M.; Zorzano, A.; Ziegler, C.; Steyaert, J.; et al. L amino acid transporter structure and molecular bases for the asymmetry of substrate interaction. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungnickel, K.E.J.; Parker, J.L.; Newstead, S. Structural basis for amino acid transport by the CAT family of SLC7 transporters. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Jin, C.; Quan, L.; Ohgaki, R.; Okuda, S.; Kusakizako, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Oda, K.; Ishitani, R.; et al. Cryo-EM structure of the human L-type amino acid transporter 1 in complex with glycoprotein CD98hc. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhao, X.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q. Structure of the human LAT1–4F2hc heteromeric amino acid transporter complex. Nature 2019, 568, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.; Koshy, C.; Ressl, S.; Nicklisch, S.; Krämer, R.; Ziegler, C. Substrate specificity and ion coupling in the Na+/betaine symporter BetP. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, P.L.; Goehring, A.; Shankaranarayanan, A.; Gouaux, E. Structure and mechanism of a Na+-independent amino acid transporter. Science 2009, 325, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, L.; Jiao, X.; Lu, F.; Yan, C.; Zeng, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Mechanism of substrate recognition and transport by an amino acid antiporter. Nature 2010, 463, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Jayaram, H.; Shane, T.; Kolmakova-Partensky, L.; Wu, F.; Williams, C.; Xiong, Y.; Miller, C. Structure of a prokaryotic virtual proton pump at 3.2 Å resolution. Nature 2009, 460, 1040–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Lu, F.; Zhou, L.; Dang, S.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of an amino acid antiporter. Science 2009, 324, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Lu, P.; Yan, C.; Fan, C.; Yin, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of a glutamate-GABA antiporter. Nature 2012, 483, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Ecker, G.F. Insights into the structure, function, and ligand discovery of the large neutral amino acid transporter 1, LAT1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geier, E.G.; Schlessinger, A.; Fan, H.; Gable, J.E.; Irwin, J.J.; Sali, A.; Giacomini, K.M. Structure-based ligand discovery for the Large-neutral Amino Acid Transporter 1, LAT-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5480–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.; Meury, M.; Alvarez-Marimon, E.; Costa, M.; Perez-Cano, L.; Zorzano, A.; Fernandez-Recio, J.; Palacin, M.; Fotiadis, D. Structural bases for the interaction and stabilization of the human amino acid transporter LAT2 with its ancillary protein 4F2hc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2966–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrecillas, I.R.; Conde-Ceide, S.; De Lucas, A.I.; Garcĺa Molina, A.; Trabanco, A.A.; Lavreysen, H.; Pardo, L.; Tresadern, G. Inhibition of the alanine-serine-cysteine-1 transporter by BMS-466442. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2510–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Scalise, M.; Galluccio, M.; Wieder, M.; Seidel, T.; Langer, T.; Indiveri, C.; Ecker, G.F. Discovery of potent inhibitors for the large neutral amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) by structure-based methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Li, Y.; Müller, J.; Zhang, Y.; Singer, S.; Xia, L.; Zhong, X.; Gertsch, J.; Altmann, K.H.; Zhou, Q. Mechanism of substrate transport and inhibition of the human LAT1-4F2hc amino acid transporter. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, R.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lei, J.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q. Cryo-EM structure of the human heteromeric amino acid transporter b0,+AT-rBAT. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Grund, T.N.; Welsch, S.; Mills, D.J.; Michel, M.; Safarian, S.; Michel, H. Structural basis for amino acid exchange by a human heteromeric amino acid transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21281–21287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q. Structural insight into the substrate recognition and transport mechanism of the human LAT2–4F2hc complex. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilgü, H.; Jeckelmann, J.-M.; Gapsys, V.; Ucurum, Z.; de Groot, B.L.; Fotiadis, D. Insights into the molecular basis for substrate binding and specificity of the wild-type L-arginine/agmatine antiporter AdiC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10358–10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Rohithaswa, A.C. Atomic-level characterization of conformational transition and substrate binding of xCT transporter. bioRxiv 2018, 389643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Moriyama, S.; Mills, D.J.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Nagamori, S. Ca 2+-mediated higher-order assembly of b0,+ AT-rBAT is a key step for system b0,+ biogenesis and cystinuria. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Lee, Y.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Tanaka, Y.; Takemoto, M.; Yamashita, K.; Nagamori, S.; Nishizawa, T.; Nureki, O. Consensus mutagenesis approach improves the thermal stability of system xc− transporter, xCT, and enables cryo-EM analyses. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardetzky, O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature 1966, 211, 969–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, M. Transport viewed as a catalytic process. Biochimie 2007, 89, 1042–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, D.; Boudker, O. Shared Molecular Mechanisms of Membrane Transporters. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 543–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzenberg, S.; Li, Z.; Quick, M.; Malinauskaite, L.; Nissen, P.; Weinstein, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Shi, L. The role of transmembrane segment 5 (TM5) in Na2 release and the conformational transition of neurotransmitter:sodium symporters toward the inward-open state. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 7372–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-F.; Fang, Y.; Miller, C. Sided functions of an arginine-agmatine antiporter oriented in liposomes. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoulari, S.; Margheritis, E.; Nagarajan, A.; DeWitt, D.C.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Rosado, E.; Ravera, S.; Rhoades, E.; Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. Two Na+ sites control conformational change in a neurotransmitter transporter homolog. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, D.D.F.; Jiang, X.; Gorraitz, E.; Hirayama, B.A.; Wright, E.M. Functional identification and characterization of sodium binding sites in Na symporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E4557–E4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, K.M.; Meyer, K.; Kinne, A.; Schülein, R.; Köhrle, J.; Krause, G. Structural insights into thyroid hormone transport mechanisms of the L-type amino acid transporter 2. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, S.; Wiriyasermkul, P.; Okuda, S.; Kojima, N.; Hari, Y.; Kiyonaka, S.; Mori, Y.; Tominaga, H.; Ohgaki, R.; Kanai, Y. Structure-activity relations of leucine derivatives reveal critical moieties for cellular uptake and activation of mTORC1-mediated signaling. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zur, A.A.; Chien, H.-C.; Augustyn, E.; Flint, A.; Heeren, N.; Finke, K.; Hernandez, C.; Hansen, L.; Miller, S.; Lin, L.; et al. LAT1 activity of carboxylic acid bioisosteres: Evaluation of hydroxamic acids as substrates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5000–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoccioni, P.; Fort, J.; Zorzano, A.; Errasti-Murugarren, E.; Palacín, M. Functional characterization of the alanine-serine-cysteine exchanger of Carnobacterium sp AT7. J. Gen. Physiol. 2019, 151, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C. Activation of system L heterodimeric amino acid exchangers by intracellular substrates. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinauskaite, L.; Quick, M.; Reinhard, L.; Lyons, J.A.; Yano, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Nissen, P. A mechanism for intracellular release of Na+ by neurotransmitter/sodium symporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafizov, K.; Perez, C.; Koshy, C.; Quick, M.; Fendler, K.; Ziegler, C.; Forrest, L.R. Investigation of the sodium-binding sites in the sodium-coupled betaine transporter BetP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3035–E3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Albers, T.; Fiumera, H.L.; Gameiro, A.; Grewer, C. A conserved Na+ binding site of the sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 2 (SNAT2). J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 25314–25323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoccioni, P.; Del Rio, C.; Ratera, M.; Kowalczyk, L.; Baldwin, J.M.; Zorzano, A.; Quick, M.; Baldwin, S.A.; Vázquez-Ibar, J.L.; Palacín, M. Role of transmembrane domain 8 in substrate selectivity and translocation of SteT, a member of the L-Amino acid Transporter (LAT) family. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 28764–28776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, M.; Feliubadaló, L.; Estivill, X.; Nunes, V.; Golomb, E.; Kreiss, Y.; Pras, E.; Bisceglia, L.; d’Adamo, A.P.; Zelante, L.; et al. Functional analysis of mutations in SLC7A9, and genotype–phenotype correlation in non-Type I cystinuria. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rotoli, B.M.; Barilli, A.; Ingoglia, F.; Visigalli, R.; Bianchi, M.G.; Ferrari, F.; Martinelli, D.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Dall’Asta, V. Analysis of LPI-causing mutations on y+LAT1 function and localization. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandeo, M.P.; Andria, G.; Sebastio, G. Lysinuric protein intolerance: Update and extended mutation analysis of the SLC7A7 gene. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Font-Llitjós, M.; Jiménez-Vidal, M.; Bisceglia, L.; Di Perna, M.; De Sanctis, L.; Rousaud, F.; Zelante, L.; Palacín, M.; Nunes, V. New insights into cystinuria: 40 New mutations, genotype-phenotype correlation, and digenic inheritance causing partial phenotype. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closs, E.I.; Boissel, J.P.; Habermeier, A.; Rotmann, A. Structure and function of cationic amino acid transporters (CATs). J. Membr. Biol. 2006, 213, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Transporter | Conformational State | Structural Information | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbr. & Class | Name and Spp. | Facing | Opening | Substrate | Amph. | Å | PDB | Notes | |
| AdiC TC# 2.A.3.2.5 | Arginine:agmatine antiporter (E. coli) | Outward | Open | - | NG | 3.61 | 3LRB | [32] | |
| - | NG | 4.00 | 3LRC | [32] | |||||
| - | DM | 3.20 | 3NCY | (a) | [31] | ||||
| - | NG | 2.21 | 5J4I | N101A | [43] | ||||
| L-Arg | Cymal-6 | 3.00 | 3OB6 | [23] | |||||
| Agmatine | NG | 2.59 | 5J4N | [43] | |||||
| Occluded | L-Arg | NG | 3.00 | 3L1L | N22A | [30] | |||
| ApcT TC# 2.A.3.6.3 | Proton coupled amino acid transporter (M. jannaschii) | Inward | Occluded | OG | 2.32 | 3GIA | [29] | ||
| OG | 2.59 | 3GI8 | K158A (a) | [29] | |||||
| OG | 2.48 | 3GI9 | (a) | [29] | |||||
| GadC TC# 2.A.3.7.3 | Glutamate:GABA antiporter (E. coli) | Inward | Open | NG + LDAO | 3.10 | 4DJK | [33] | ||
| NG + LDAO | 3.19 | 4DJI | [33] | ||||||
| GkApcT TC# 2.A.3.3.n | Proton-coupled amino acid transporter (G. kaustophilus) | Inward | Occluded | L-Arg | DDM | 3.13 | 6F34 | (b) | [25] |
| L-Ala | DDM | 2.86 | 5OQT | (b) | [25] | ||||
| BasC TC# 2.A.3.8.n | Ala-Ser-Cys antiporter (Carnobacterium sp. AT7) | Inward | Open | DM | 2.92 | 6F2G | (c) | [24] | |
| 2-AIB * | DM | 3.40 | 6F2W | (c) | [24] | ||||
| LAT1 SLC7A5 TC# 2.A.3.8.25 | L-type amino acid transporter 1 (H. sapiens) | Inward | Open | BCH * | Digitonin | 3.50 | 6IRT | A36E | [27] |
| GDN | 3.30 | 6IRS | A36E | [27] | |||||
| Digitonin | 3.31 | 6JMQ | (a) | [26] | |||||
| Outward | Occluded | JX-075 * | GDN | 2.90 | 7DSK | [39] | |||
| JX-078 * | GDN | 2.90 | 7DSL | [39] | |||||
| JX-119 * | GDN | 3.10 | 7DSN | [39] | |||||
| Diiodo-Tyr * | GDN | 3.40 | 7DSQ | [39] | |||||
| b0,+AT SLC7A9 TC# 2.A.3.8.19 | b0,+-type amino acid transporter 1 (H. sapiens and Ovis sp.) | Inward | Open | L-Arg | GDN | 2.30 | 6LI9 | [40] | |
| GDN | 2.70 | 6LID | [40] | ||||||
| Digitonin | 2.90 | 6YUP | [41] | ||||||
| Digitonin | 3.40 | 6YV1 | [41] | ||||||
| Nanodisc | unreleased | [45] | |||||||
| Nanodisc | unreleased | [45] | |||||||
| LAT2 SLC7A8 TC# 2.A.3.8.20 | L-type amino acid transporter 2 (H. sapiens) | Inward | Open | L-Trp | GDN | 2.90 | 7CMH | [42] | |
| L-Leu | GDN | 3.40 | 7CMI | [42] | |||||
| xCT SLC7A9 TC# 2.A.3.8.19 | Cystine:glutamate antiporter (H. sapiens) | Inward | Open | Digitonin | 6.20 | 7CCS | [46] | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicolàs-Aragó, A.; Fort, J.; Palacín, M.; Errasti-Murugarren, E. Rush Hour of LATs towards Their Transport Cycle. Membranes 2021, 11, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080602
Nicolàs-Aragó A, Fort J, Palacín M, Errasti-Murugarren E. Rush Hour of LATs towards Their Transport Cycle. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080602
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicolàs-Aragó, Adrià, Joana Fort, Manuel Palacín, and Ekaitz Errasti-Murugarren. 2021. "Rush Hour of LATs towards Their Transport Cycle" Membranes 11, no. 8: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080602
APA StyleNicolàs-Aragó, A., Fort, J., Palacín, M., & Errasti-Murugarren, E. (2021). Rush Hour of LATs towards Their Transport Cycle. Membranes, 11(8), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080602









