Catalytic Efficiency of Carbon-Cementitious Microfiltration Membrane on the Ozonation-Based Oxidation of Small Molecule Organic Compounds and Its Alkaline Buffering Effect in Aqueous Solution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Characterization of CCM
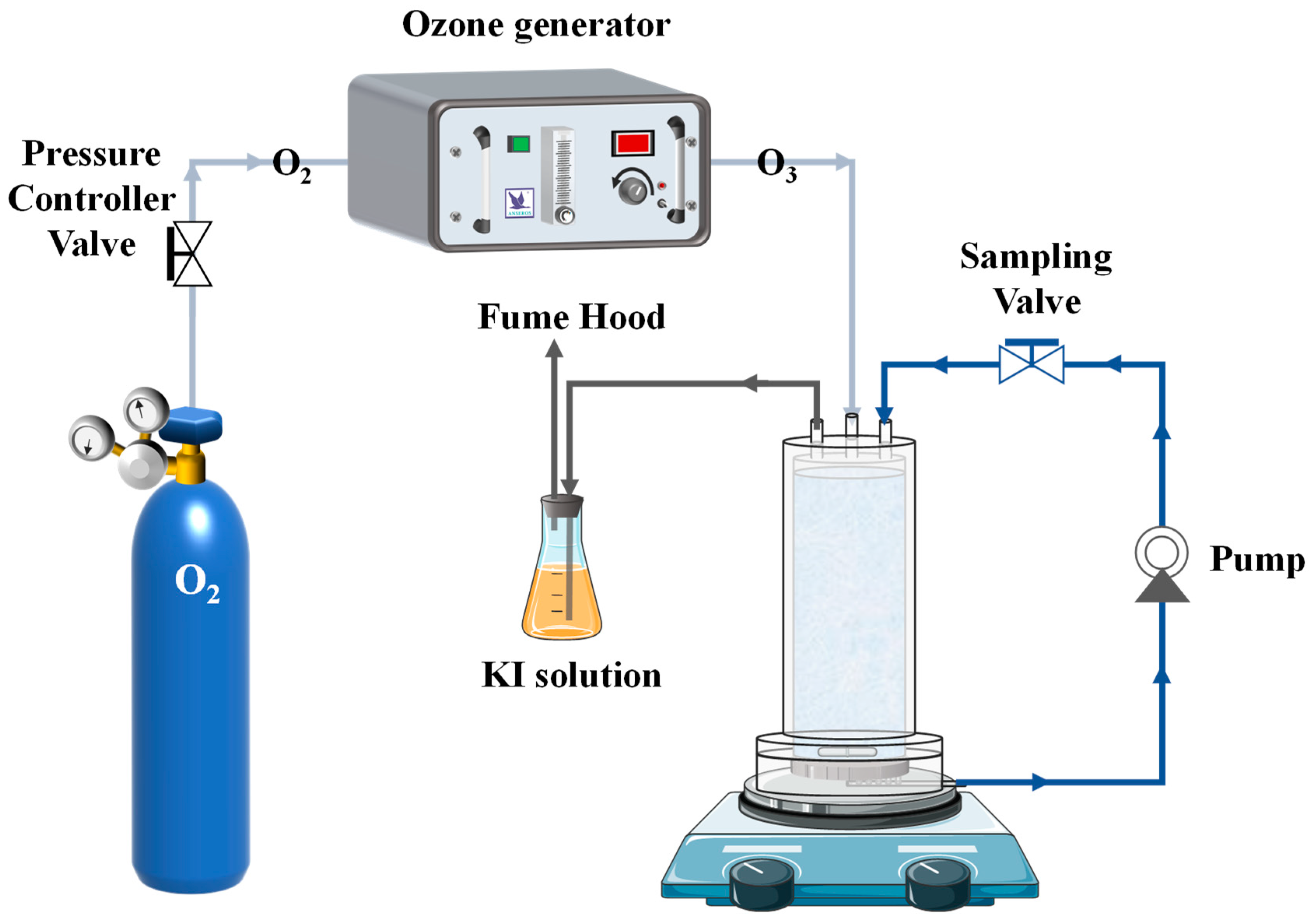
2.3. CCM Catalytic Ozonation Process
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
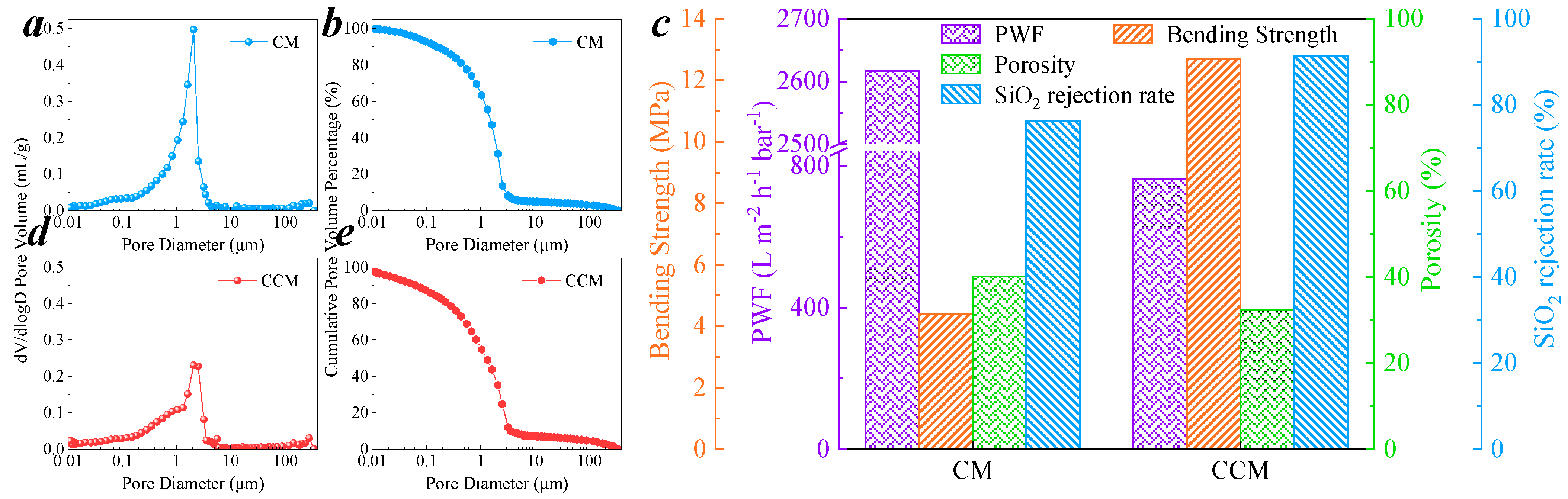
3.1. Characterization of CCM
3.2. Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Membrane-Catalyzed Ozone
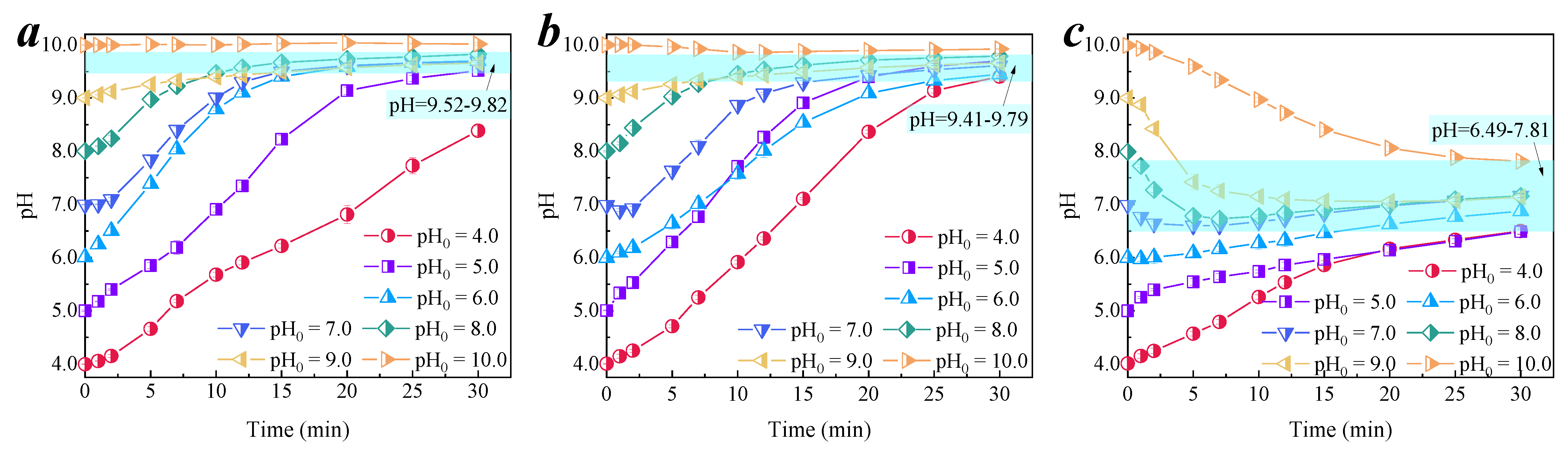
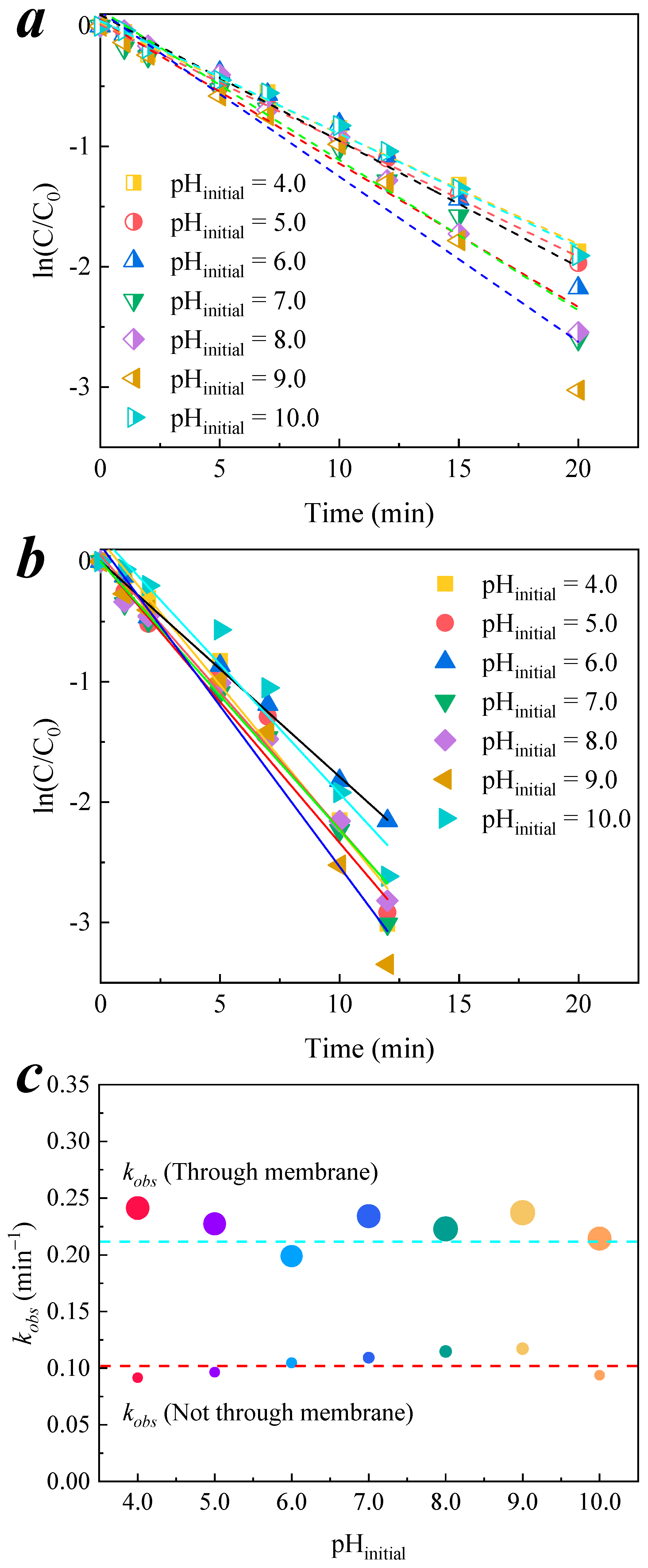
3.3. Effect of pH on Membrane Catalytic Ozonation
3.3.1. Change Trend of pH in the Degradation Process
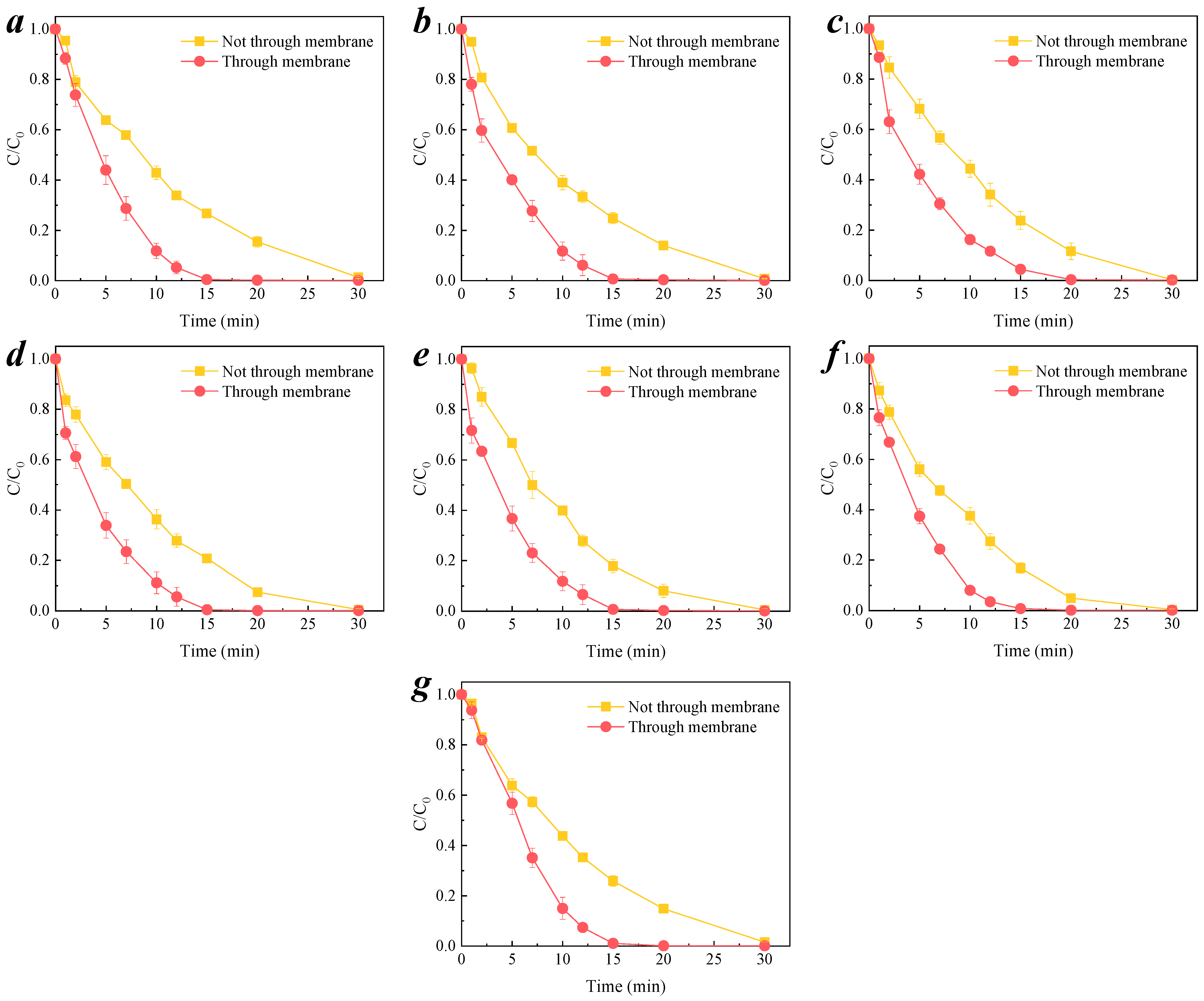
3.3.2. Transmembrane Removal of Organic Compound
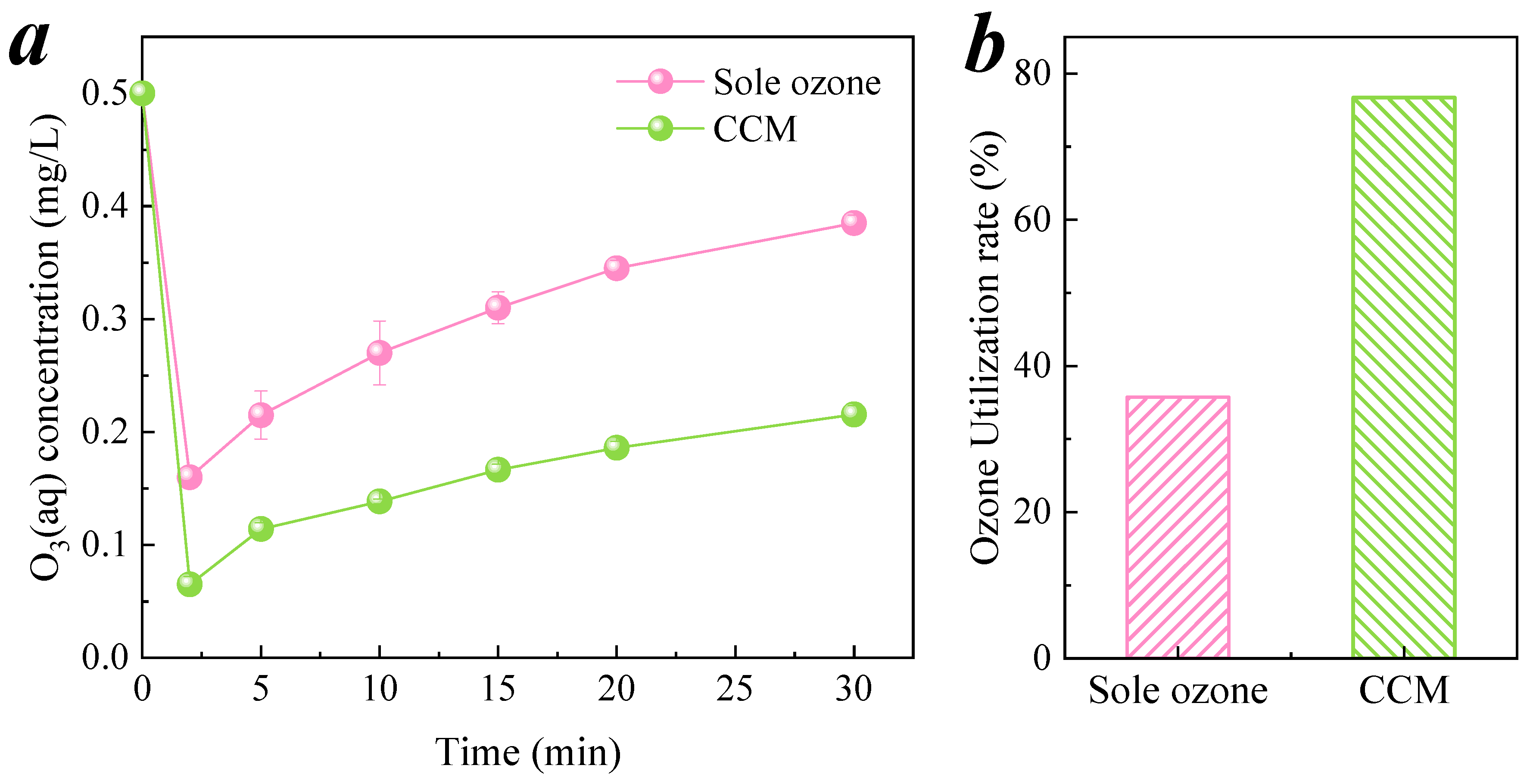
3.3.3. Decomposition and Utilization of Ozone
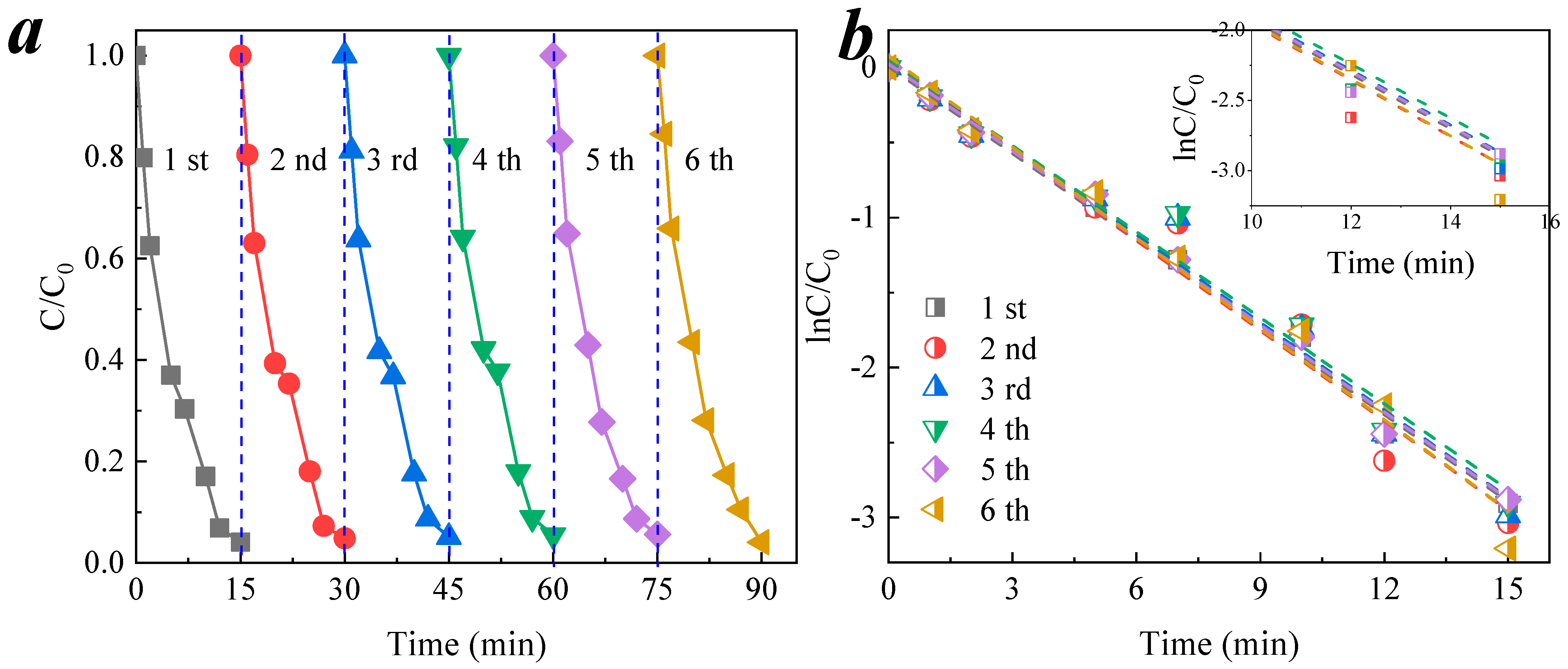
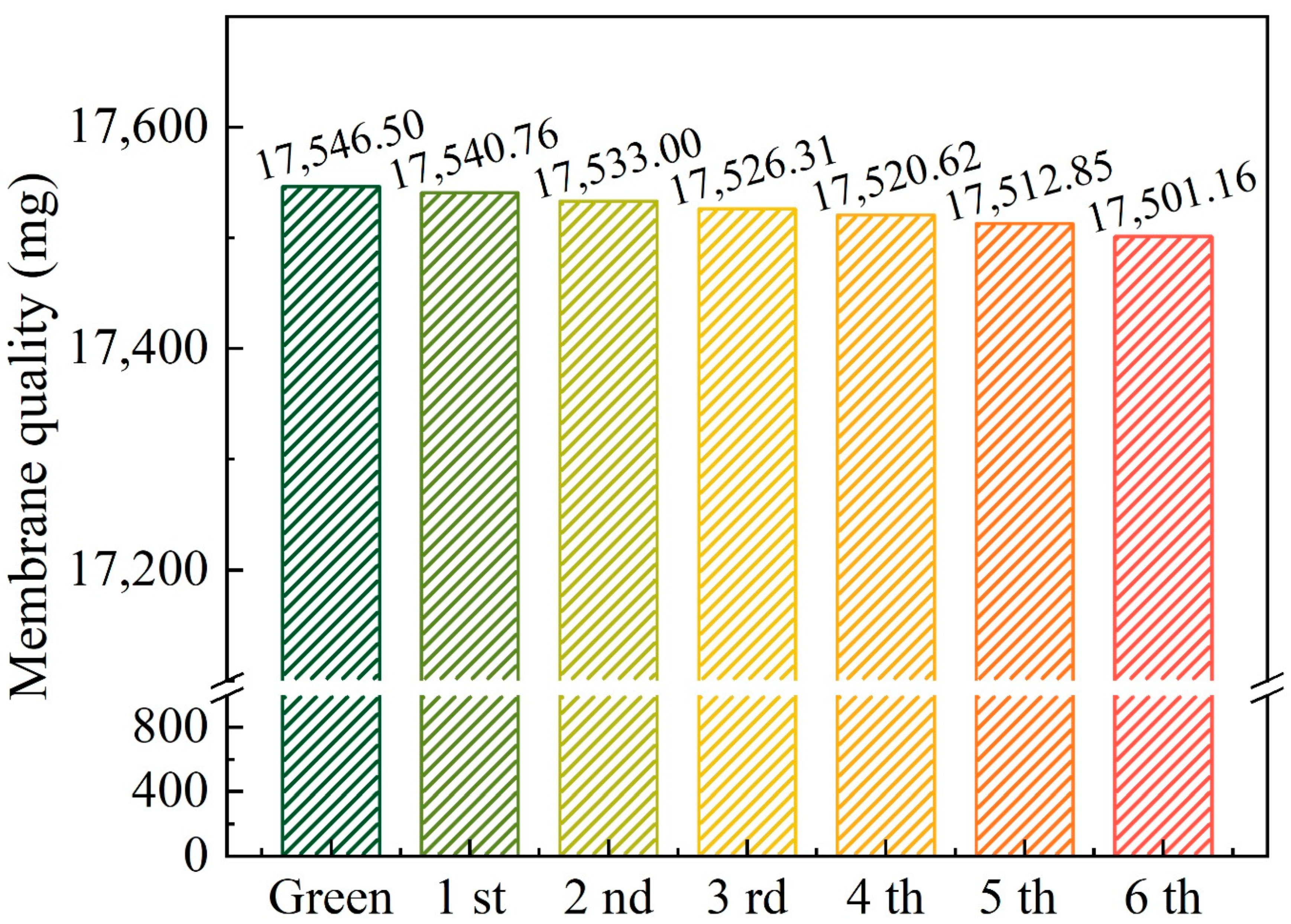
3.4. Reusability of CCM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luukkonen, T.; Heponiemi, A.; Runtti, H.; Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Lassi, U. Application of alkali-activated materials for water and wastewater treatment: A review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2019, 18, 271–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Camões, A.F.; Jamshidi, M.; Ding, Y. Durability of alkali-activated binders: A clear advantage over Portland cement or an unproven issue? Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, C.; Colombo, P. Processing, properties and applications of highly porous geopolymers: A review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 16103–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Abdollahnejad, Z.; Yliniemi, J.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Comparison of alkali and silica sources in one-part alkali-activated blast furnace slag mortar. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, K.; He, Y.; Cui, X. Preparation of geopolymer-based inorganic membrane for removing Ni2+ from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilla, M.S.; de Mello Innocentini, M.D.; Morelli, M.R.; Colombo, P. Geopolymer foams obtained by the saponification/peroxide/gelcasting combined route using different soap foam precursors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, N.; Alghoul, M.; Mohammad, M.; Amin, M.H.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Amin, N.; Sopian, K. Emerging sustainable solutions for depollution: Geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 199, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Seabra, M.P.; Labrincha, J.A. Porous geopolymer spheres as novel pH buffering materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, R.M.; Buruberri, L.H.; Seabra, M.P.; Bajare, D.; Labrincha, J.A. Novel porous fly ash-containing geopolymers for pH buffering applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 124, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liang, H.; Qu, F.; Ding, A.; Chang, H.; Liu, B.; Tang, X.; Wu, D.; Li, G. Fabrication of Mn oxide incorporated ceramic membranes for membrane fouling control and enhanced catalytic ozonation of p-chloronitrobenzene. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, F.; Croue, J.; Yuan, D. A novel catalytic ceramic membrane fabricated with CuMn2O4 particles for emerging UV absorbers degradation from aqueous and membrane fouling elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. A novel ceramic membrane coated with MnO2–Co3O4 nanoparticles catalytic ozonation for benzophenone-3 degradation in aqueous solution: Fabrication, characterization and performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hedtke, T.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, M.; Weon, S.; Zhao, Y.; Stavitski, E.; Elimelech, M.; Kim, J. Membrane-Confined Iron Oxychloride Nanocatalysts for Highly Efficient Heterogeneous Fenton Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 13, 9266–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chang, J.; Shen, J.; Kang, J.; Chen, Q. Fabrication of a low-cost cementitious catalytic membrane for p-chloronitrobenzene degradation using a hybrid ozonation-membrane filtration system. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, P.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Kang, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Tong, Y. Catalytic ozonation with silicate-based microfiltration membrane for the removal of iopamidol in aqueous solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Shen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, W.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kang, J. Improvement of the fabricated and application of aluminosilicate-based microfiltration membrane. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makar, J.M.; Chan, G.W. Growth of Cement Hydration Products on Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 92, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babak, F.; Abolfazl, H.; Alimorad, R.; Parviz, G. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Graphene Oxide: Cement Nanocomposites. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, J. The Effect of SWCNT and Other Nanomaterials on Cement Hydration and Reinforcement; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 103–130. [Google Scholar]
- Real, F.J.; Benitez, F.J.; Acero, J.L.; Casas, F. Adsorption of selected emerging contaminants onto PAC and GAC: Equilibrium isotherms, kinetics, and effect of the water matrix. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Ozonation of aniline promoted by activated carbon. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, C.; Bulushev, D.A.; Kiwi-Minsker, L. Dynamic behaviour of activated carbon catalysts during ozone decomposition at room temperature. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 61, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.J.; García-Araya, J.F.; Giráldez, I. Gallic acid water ozonation using activated carbon. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2006, 63, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhariyah, A.S.; Pradyasti, A.; Dianty, A.G.; Bismo, S. Comparative study of activated carbon, natural zeolite, and green sand supports for CuOX and ZnO sites as ozone decomposition catalyst. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 334, 12075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. Stable synergistic decontamination and self-cleaning performance of powerful N-rGO catalytic ozonation membrane: Clustering effect of free electrons and role of interface properties. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 283, 119662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C.; Cho, S.W.; Wang, L.C. The relationship between pore structure and chloride diffusivity from ponding test in cement-based materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 100, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kua, H.W. Carbonaceous micro-filler for cement: Effect of particle size and dosage of biochar on fresh and hardened properties of cement mortar. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Tang, L.; Fung, J.; Rahman, M.; Sillars, F.; Liggat, J.; Zhou, X. Graphene/fly ash geopolymeric composites as self-sensing structural materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 065006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Jana, S.; Mohanty, K. Synthesis of low-cost hydrophilic ceramic–polymeric composite membrane for treatment of oily wastewater. Desalination 2011, 282, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Lü, X.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; Cui, R.; Hu, S. Microfiltration of kiwifruit juice and fouling mechanism using fly-ash-based ceramic membranes. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekle-Röttering, A.; von Sonntag, C.; Reisz, E.; Eyser, C.V.; Lutze, H.V.; Türk, J.; Naumov, S.; Schmidt, W.; Schmidt, T.C. Ozonation of anilines: Kinetics, stoichiometry, product identification and elucidation of pathways. Water Res. 2016, 98, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Song, Y.; Ding, H.; Liu, Z.; Baldwin, A.; Wong, I.; Li, H.; Zhao, C. Insight into synergies between ozone and in-situ regenerated granular activated carbon particle electrodes in a three-dimensional electrochemical reactor for highly efficient nitrobenzene degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tian, S.; Kong, L.; Tu, Y.; Lu, J.; Xiong, Y. Efficient degradation of nitrobenzene by an integrated heterogeneous catalytic ozonation and membrane separation system with active MgO(111) catalyst. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 56, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, B.; Qi, F.; Yuan, D.; Pu, S. Insight into ·OH and O2·− formation in heterogeneous catalytic ozonation by delocalized electrons and surface oxygen-containing functional groups in layered-structure nanocarbons. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 357, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhai, X. Degradation of nitrobenzene by nano-TiO2 catalyzed ozonation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2007, 267, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, H. Enhancement Mechanism of Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation by Cordierite-Supported Copper for the Degradation of Nitrobenzene in Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2047–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. Insights into Heteroatom-Doped Graphene for Catalytic Ozonation: Active Centers, Reactive Oxygen Species Evolution, and Catalytic Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 5337–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Xi, S.; Miao, S.; Ding, J.; Cai, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; et al. Single Cobalt Atoms Anchored on Porous N-Doped Graphene with Dual Reaction Sites for Efficient Fenton-like Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12469–12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tuan, N.; Ye, G.; van Breugel, K.; Copuroglu, O. Hydration and microstructure of ultra high performance concrete incorporating rice husk ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, X. Effect of Nano-SiO2 on the Early Hydration of Alite-Sulphoaluminate Cement. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y. Effects of amorphous-zinc-silicate-catalyzed ozonation on the degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in drinking water. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 403, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene in drinking water by manganese silicate catalyzed ozonation. Desalination 2011, 279, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | CM/Ozone | CCM/Ozone | Ozone Alone | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kobs (min−1) | R2 | kobs (min−1) | R2 | kobs (min−1) | R2 | |
| Nitrobenzene | 0.1837 | 0.996 | 0.1934 | 0.995 | 0.0861 | 0.995 |
| p-CA | 0.7331 | 0.998 | 0.7907 | 0.998 | 0.9521 | 0.991 |
| BP-4 | 0.2849 | 0.998 | 0.3932 | 0.994 | 0.0964 | 0.999 |
| p-CP | 0.6836 | 0.995 | 1.0053 | 0.999 | 0.2664 | 0.964 |
| p-CNB | 0.1406 | 0.996 | 0.1622 | 0.988 | 0.0834 | 0.978 |
| p-CBA | 0.2039 | 0.998 | 0.2117 | 0.997 | 0.1286 | 0.986 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Kang, J.; Guo, Y.; Cai, L.; Shen, J.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Song, Z. Catalytic Efficiency of Carbon-Cementitious Microfiltration Membrane on the Ozonation-Based Oxidation of Small Molecule Organic Compounds and Its Alkaline Buffering Effect in Aqueous Solution. Membranes 2021, 11, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080601
Sun J, Chen Z, Liu S, Kang J, Guo Y, Cai L, Shen J, Wang B, Zhao S, Song Z. Catalytic Efficiency of Carbon-Cementitious Microfiltration Membrane on the Ozonation-Based Oxidation of Small Molecule Organic Compounds and Its Alkaline Buffering Effect in Aqueous Solution. Membranes. 2021; 11(8):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080601
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingyi, Zhonglin Chen, Shan Liu, Jing Kang, Yuhao Guo, Liming Cai, Jimin Shen, Binyuan Wang, Shengxin Zhao, and Zilong Song. 2021. "Catalytic Efficiency of Carbon-Cementitious Microfiltration Membrane on the Ozonation-Based Oxidation of Small Molecule Organic Compounds and Its Alkaline Buffering Effect in Aqueous Solution" Membranes 11, no. 8: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080601
APA StyleSun, J., Chen, Z., Liu, S., Kang, J., Guo, Y., Cai, L., Shen, J., Wang, B., Zhao, S., & Song, Z. (2021). Catalytic Efficiency of Carbon-Cementitious Microfiltration Membrane on the Ozonation-Based Oxidation of Small Molecule Organic Compounds and Its Alkaline Buffering Effect in Aqueous Solution. Membranes, 11(8), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11080601







