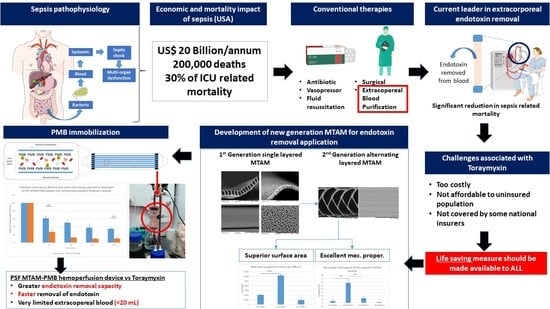
Ultra-High Packing Density Next Generation Microtube Array Membrane for Absorption Based Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
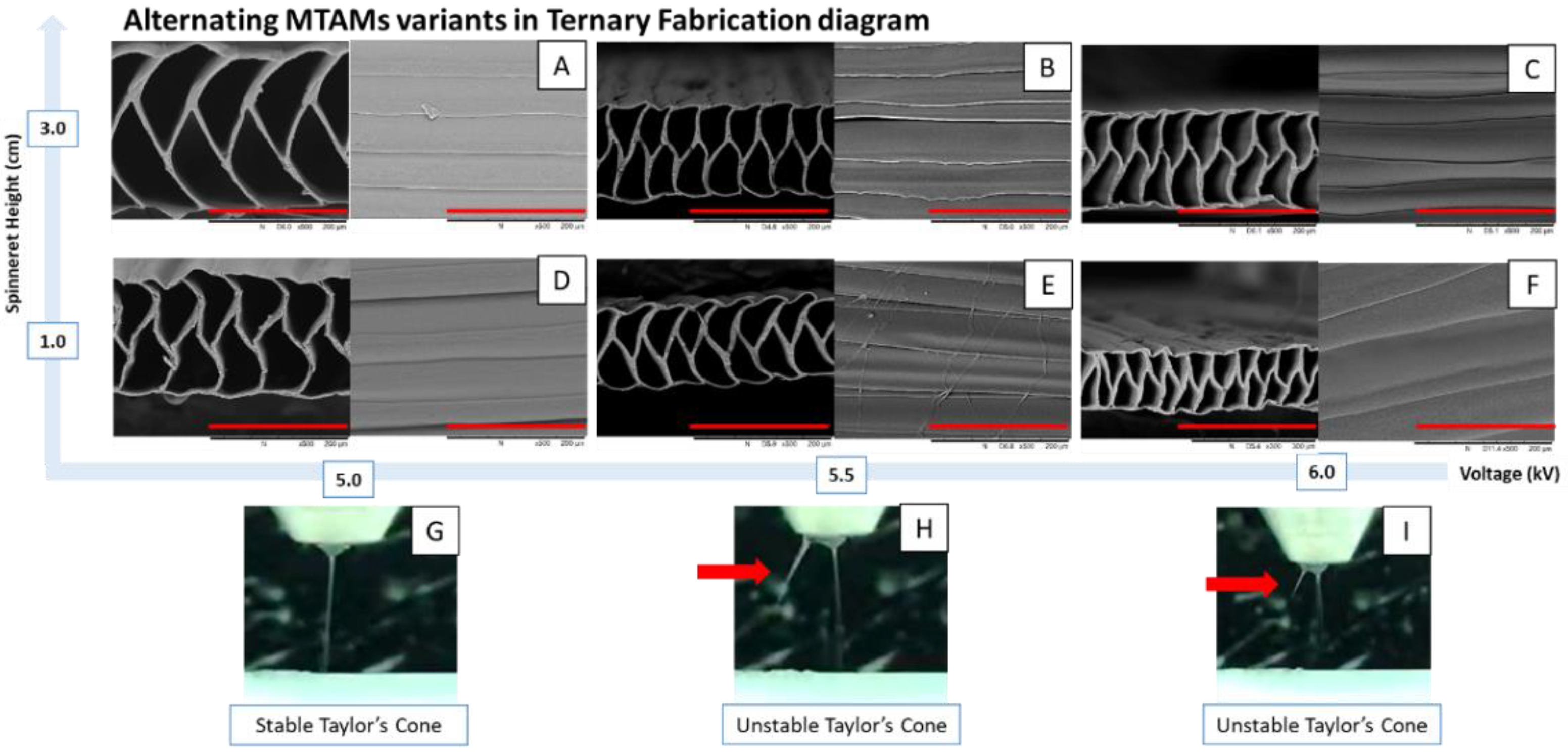
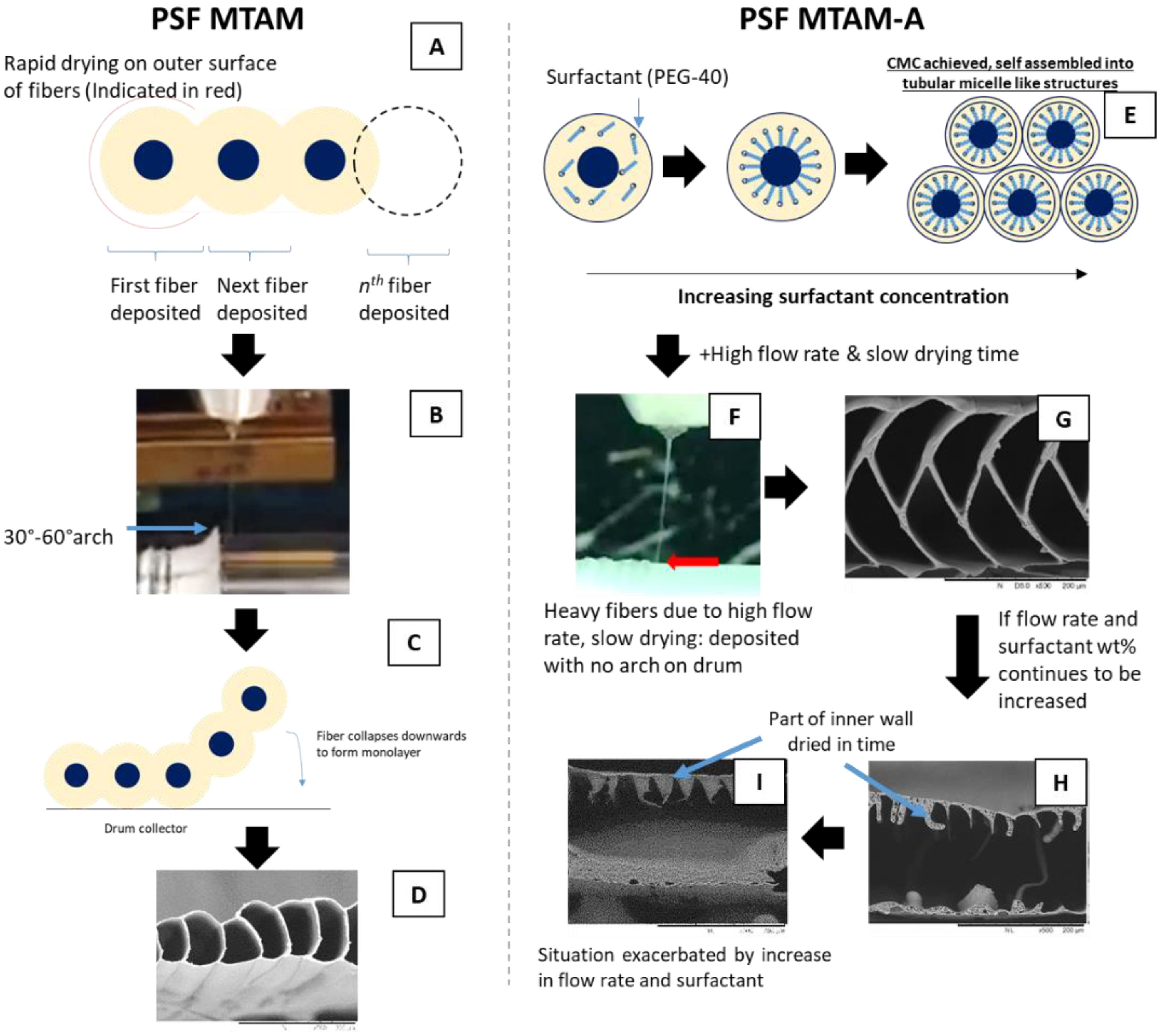
2.1. Tri-Axial Electrospinning of MTAM Variants
2.2. Microstructure Analysis of the Respective MTAM Variants
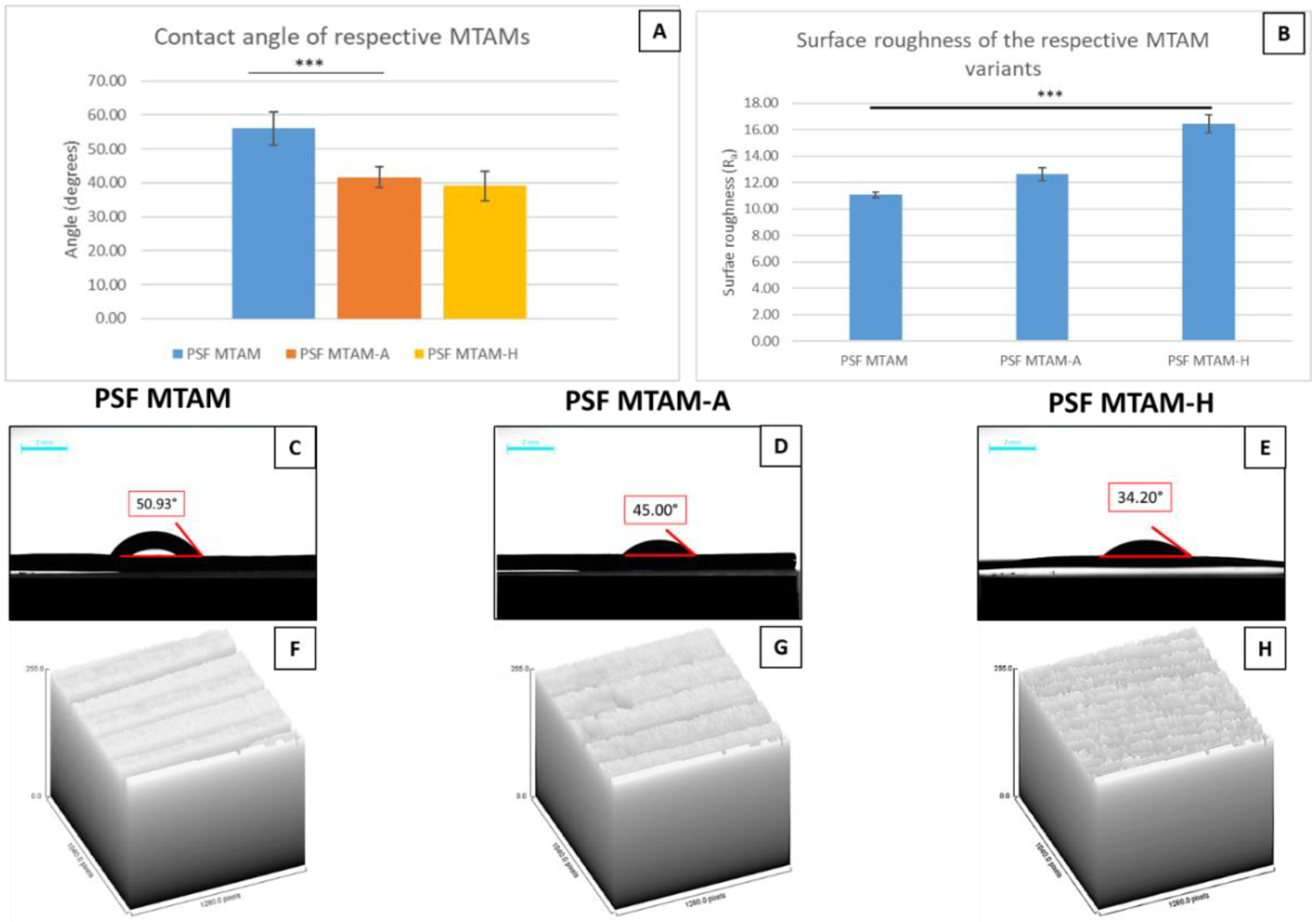
2.3. Contact Angle Determination of Double Distilled Water (ddH2O) on the Surfaces of the Respective MTAM Variants
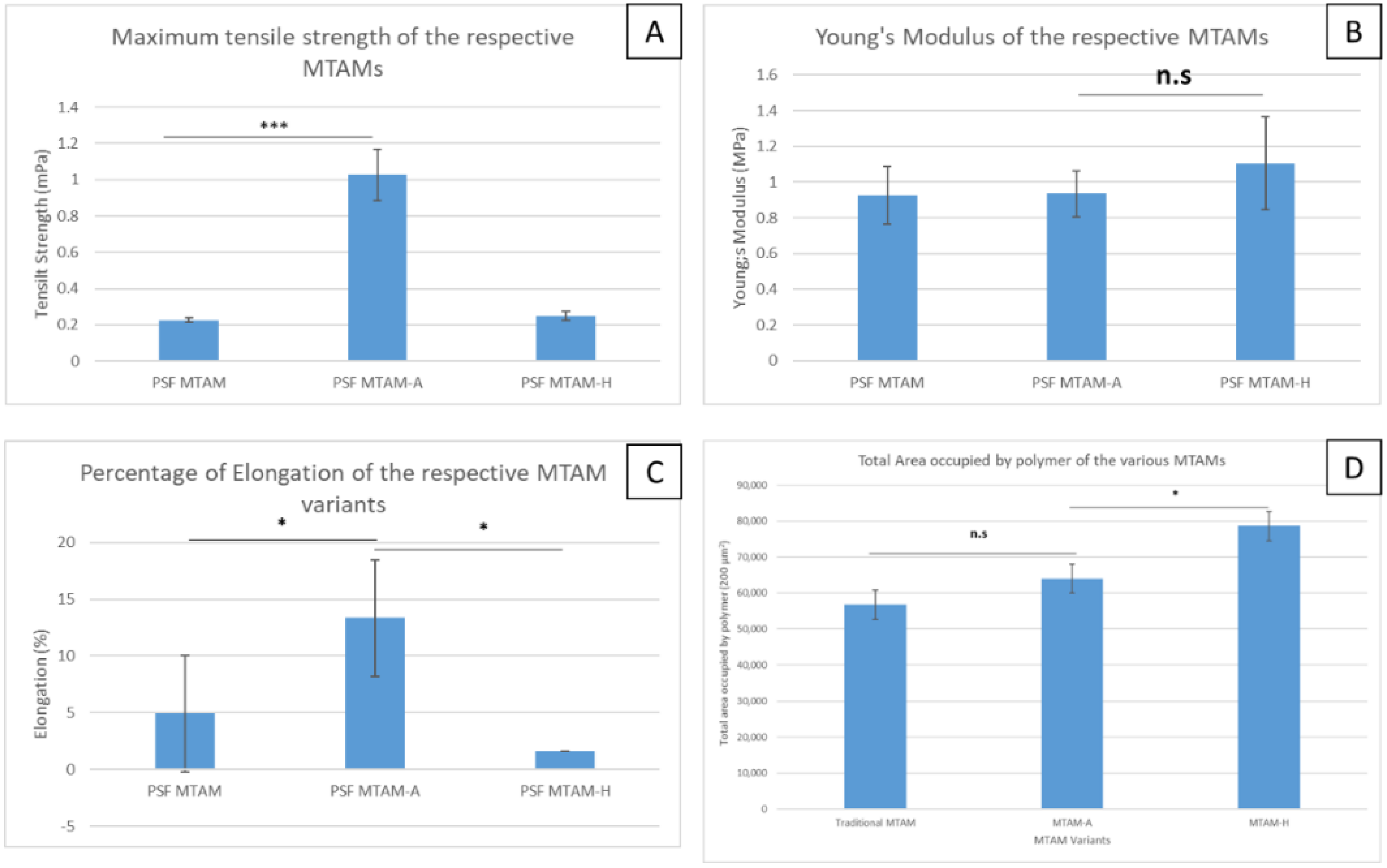
2.4. Mechanical Properties of the MTAM Variants
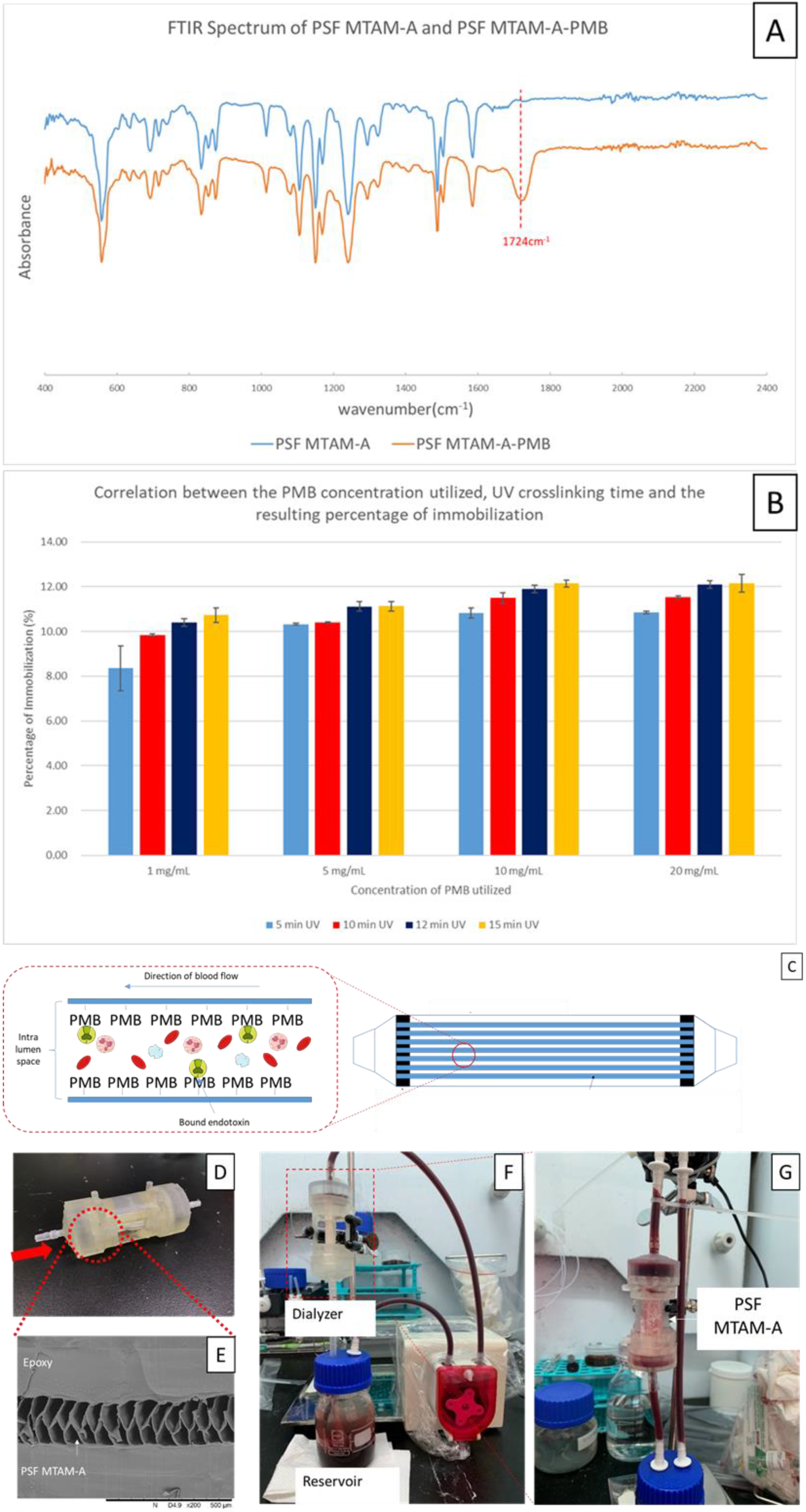
2.5. Immobilization of the Polymyxin B (PMB) onto the Surfaces of PSF MTAM-A and the Determination of Degree of Immobilization Rate of PMB
2.6. Design, Fabrication, and Assembly of the PSF MTAM-A-PMB Based Hemoperfusion Unit
2.7. Dynamic Adsorption Testing of the Removal of Endotoxin with the PSF MTAM-A-PMB Hemoperfusion Device
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chew, C.H.; Cheng, L.; Huang, W.; Wu, Y.M.; Lee, C.; Wu, M.; Chen, C. Ultrahigh packing density next generation microtube array membrane: A novel solution for absorption-based extracorporeal endotoxin removal device. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2020, 108, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Eng. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; Wax, R.S. Epidemiology of sepsis: An update. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, S109–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, D.; Wang, F.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, C. Polymyxin B immobilized nanofiber sponge for endotoxin adsorption. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 110, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolin, H.H.; Papadimos, T.J.; Stepkowski, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z.K. A Novel Combination of Biomarkers to Herald the Onset of Sepsis Prior to the Manifestation of Symptoms. Shock 2018, 49, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellhammar, L.; Wullt, S.; Lindberg, Å.; Lanbeck, P.; Christensson, B.; Linder, A. Sepsis Incidence: A Population-Based Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, E.; Lupia, E.; Bosco, O.; Vizio, B.; Montrucchio, G. Platelets and Multi-Organ Failure in Sepsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, J.L.; Kelly, M.S.; Benjamin, D.K.; Clark, R.H.; Greenberg, R.; Benjamin, D.K., Jr.; Smith, P.B. Timing of multi-organ dysfunction among hospitalized infants with fatal fulminant sepsis. Am. J. Perinatol. 2017, 34, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berto, P.; Ronco, C.; Cruz, D.; Melotti, R.M.; Antonelli, M. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Polymyxin-B Immobilized Fiber Column and Conventional Medical Therapy in the Management of Abdominal Septic Shock in Italy. Blood Purif. 2011, 32, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, J.; Leone, S.; Cascella, M.; Fiore, M. Should endotoxin be a research priority in Gram-negative sepsis and septic shock? Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 697–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Yamada, M.; Sohmiya, M.; Shibuya, K.; Maeda, N. Clinical effects of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column direct hemoperfusion for severe bacterial meningitis: A series of 10 cases. Clin. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.C.; Foster, D.M.; Vincent, J.; Cook, D.J.; Cohen, J.; Dellinger, R.P.; Opal, S.M.; Abraham, E.H.; Brett, S.J.; Smith, T.J.; et al. Diagnostic and Prognostic Implications of Endotoxemia in Critical Illness: Results of the MEDIC Study. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiroli, M.; Monti, G.; Pinciroli, R.; Vecchi, I.; Terzi, V.; Ortisi, G.; Casella, G.; Fumagalli, R. Prevalence and clinical significance of early high Endotoxin Activity in septic shock: An observational study. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbet, M.B.; Sefton, M.V. Review: Biomaterial-associated thrombosis: Roles of coagulation factors, complement, platelets and leukocytes. In The Biomaterials: Silver Jubilee Compendium; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 219–241. [Google Scholar]
- Seidel, J.; Haller, S.; Eckmanns, T.; Harder, T. Routine screening for colonization by Gram-negative bacteria in neonates at intensive care units for the prediction of sepsis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, V.S.; Shaw, C. Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid Dosages. In Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid Dosages; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 193–221. [Google Scholar]
- Sakr, Y.; Jaschinski, U.; Wittebole, X.; Szakmany, T.; Lipman, J.; Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Leone, M.; Lupu, M.-N.; Vincent, J.-L.; et al. Sepsis in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Worldwide Data from the Intensive Care over Nations Audit. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Shimizu, K.; Ogura, H.; Kurakawa, T.; Umemoto, E.; Motooka, D.; Nakamura, S.; Ichimaru, N.; Takeda, K.; Takahara, S.; et al. Hydrogen-Rich Saline Regulates Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, Dysbiosis, and Bacterial Translocation in a Murine Model of Sepsis. Shock 2018, 50, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Triantos, C.; Thomopoulos, K.; Fligou, F.; Maroulis, I.; Marangos, M.; Gogos, C.A. Gut-origin sepsis in the critically ill patient: Pathophysiology and treatment. Infection 2018, 46, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, J.A.; Bobba, C.; Baron, R.M. Integrating molecular pathogenesis and clinical translation in sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. JCI Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H.; Warkentin, T.E.; Thachil, J.; Van Der Poll, T.; Levi, M. Diagnosis and management of sepsis-induced coagulopathy and disseminated intravascular coagulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 1989–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzu, A.; Schorer, R.; Lopez-Delgado, J.C.; Cassina, T.; Landoni, G. Blood purification and mortality in sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedlowski, M.; Engler, H.; Grigoleit, J.-S. Endotoxin-induced experimental systemic inflammation in humans: A model to disentangle immune-to-brain communication. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiers, D.; Koch, R.M.; Hamers, L.; Gerretsen, J.; Thijs, E.J.M.; Van Ede, L.; Riksen, N.P.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Characterization of a model of systemic inflammation in humans in vivo elicited by continuous infusion of endotoxin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepper, P.; Held, T.; Schneider, E.; Bölke, E.; Gerlach, H.; Trautmann, M. Clinical implications of antibiotic-induced endotoxin release in septic shock. Intensiv. Care Med. 2002, 28, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.M.S.; Endo, Y.; Nikolaev, V.G.; Tani, T.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, W.-H. Hemoperfusion, Plasmaperfusion and Other Clinical Uses of General, Biospecific, Immuno and Leucocyte Adsorbents; World Scientific Pub Co Pte Lt: Singapore, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa, K.I.; Takakuwa, R.; Taya, K.; Wada, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Murata, M.; Hirata, K.; Masuno, T.; Yokota, H.; Ishii, F. Adsorption of various antimicrobial agents to endotoxin removal polymyxin-B immobilized fiber (Toraymyxin®). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, T.; Shimizu, T.; Tani, M.; Shoji, H.; Endo, Y. Anti-endotoxin Properties of Polymyxin B-immobilized Fibers. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1145, pp. 321–341. [Google Scholar]
- Shoji, H. Extracorporeal Endotoxin Removal For The Treatment of Sepsis:Endotoxin Adsorption Cartridge (Toraymyxin). Ther. Apher. Dial. 2003, 7, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, D.N.; Perazella, M.A.; Bellomo, R.; De Cal, M.; Polanco, N.; Corradi, V.; Lentini, P.; Nalesso, F.; Ueno, T.; Ranieri, V.M.; et al. Effectiveness of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column in sepsis: A systematic review. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawazoe, Y.; Sato, T.; Miyagawa, N.; Yokokawa, Y.; Kushimoto, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Ohta, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Yamamura, H. Mortality Effects of Prolonged Hemoperfusion Therapy Using a Polymyxin B-Immobilized Fiber Column for Patients with Septic Shock: A Sub-Analysis of the DESIRE Trial. Blood Purif. 2018, 46, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jason, N. Developing a Treatment for Septic Shock; Initiating coverage of Spectral Medical, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Xia, Y. An in vitro study of non-aligned or aligned electrospun poly(methyl methacrylate) nanofibers as primary rat astrocytes-loading scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.B.; Chainani, A.; Hippensteel, K.J.; Kishan, A.; Gilchrist, C.; Garrigues, N.W.; Ruch, D.S.; Guilak, F.; Little, D. Aligned multilayered electrospun scaffolds for rotator cuff tendon tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2015, 24, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-C.; Lee, S.-Y.; Tseng, W.-C.; Shu, Y.-C.; Lu, J.-C.; Shie, H.-S.; Chen, C.-C. Formation of Highly Aligned, Single-Layered, Hollow Fibrous Assemblies and the Fabrication of Large Pieces of PLLA Membranes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 297, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-C.; Shu, Y.-C.; Yang, J.-C.; Shie, H.-S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-C. Nano-porous Poly-L-lactic Acid Microtube Array Membranes. Curr. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Lin, L.-H.; Tsen, W.-C.; Shie, H.-S.; Chiu, H.-L.; Yang, T.C.; Chen, C.-C. Permeation of biological compounds through porous poly(l-lactic acid) (PLLA) microtube array membranes (MTAMs). Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Huang, W.-T.; Chew, C.H.; Lai, J.-K.; Tu, S.-H.; Wei, P.-L.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lai, G.-M.; Chen, C.-C. Electrospun Polylactic Acid (PLLA) Microtube Array Membrane (MTAM)—An Advanced Substrate for Anticancer Drug Screening. Materials 2019, 12, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, V.C.-H.; Chew, C.H.; Huang, W.-T.; Wang, Y.-K.; Chen, K.-S.; Chou, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-C. An Effective Cell Coculture Platform Based on the Electrospun Microtube Array Membrane for Nerve Regeneration. Cells Tissues Organs 2017, 204, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.; Piscioneri, A.; Salerno, S.; Chen, C.-C.; Chew, C.H.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E.; De Bartolo, L. Microtube array membrane bioreactor promotes neuronal differentiation and orientation. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 025018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, S.; Piscioneri, A.; Curcio, E.; Salerno, S.; Chen, C.-C.; De Bartolo, L. Membrane bioreactor for investigation of neurodegeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.; Wu, C.; Chen, C. A novel electrospun Microtube Array Membrane (MTAM) based low cost conceptual tubular Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC). Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 83, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.H.; Lee, C.-W.; Huang, W.-T.; Cheng, L.-W.; Chen, A.; Cheng, T.-M.; Liu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-C. Microtube Array Membrane (MTAM)-Based Encapsulated Cell Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Membrances 2020, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lan, C.-C.; Pan, C.-L.; Huang, M.-Y.; Chew, C.-H.; Hung, C.-C.; Chen, P.-H.; Lin, H.-T.V. Repeated-batch lactic acid fermentation using a novel bacterial immobilization technique based on a microtube array membrane. Process. Biochem. 2019, 87, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lin, H.-J.; Lu, W.-J.; Wu, J.-J.; Chew, C.-H.; Wong, C.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-T.V. Enhanced Repeated-Batch Bioethanol Fermentation of Red Seaweeds Hydrolysates Using Microtube Array Membrane-Encapsulated Yeast. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2020, 14, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Wu, C.-H.; Wu, J.-J.; Chiu, C.-C.; Wong, C.-H.; Tsai, M.-L.; Lin, H.-T.V. Accelerated bioethanol fermentation by using a novel yeast immobilization technique: Microtube array membrane. Process. Biochem. 2015, 50, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, R.H.; Gazzaniga, A.B.; Jefferies, M.R.; Huxtable, R.F.; Haiduc, N.J.; Fong, S.W. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) cardiopulmonary support in infancy. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Intern. Organs 1976, 22, 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Tiruvoipati, R.; Botha, J.; Peek, G. Effectiveness of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation when conventional ventilation fails: Valuable option or vague remedy? J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-H.; Tsai, J.-C.; Chen, T.-M.; Chen, K.-S.; Yang, J.-M.; Kang, P.-L.; Wu, T.-H. Fabrication and evaluation of auto-stripped tri-layer wound dressing for extensive burn injury. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 102, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-C.; Yan, T.-R.; Chen, K.-S.J.C.; Biointerfaces, S.B. Detecting cells on the surface of a silver electrode quartz crystal microbalance using plasma treatment and graft polymerization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarin, A.L. Coaxial electrospinning and emulsion electrospinning of core–shell fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Haider, A. Electrospinning and Electrospraying: Techniques and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pstras, L.; Waniewski, J.; Wojcik-Zaluska, A.; Zaluska, W. Relative blood volume changes during haemodialysis estimated from haemoconcentration markers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.C.; Lin, C.C.J.A.J. In vitro characterization of the occurrence of hemolysis during extracorporeal blood circulation using a mini hemodialyzer. Asaio J. 2000, 46, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Wachter, D.S.; Verdonck, P.R.; Verhoeven, R.F.; Hombrouckx, R.O. Red cell injury assessed in a numeric model of a peripheral dialysis needle. Asaio J. 1996, 42, M524–M529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beissinger, R.L.; Williams, M.C. A dual mechanism for low-stress hemolysis in laminar blood flow. AIChE J. 1984, 30, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Role of red blood cells in haemostasis and thrombosis. ISBT Sci. Ser. 2016, 12, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Red blood cells: The forgotten player in hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compendium, S. Solubility Enhancement with BASF Pharma Polymers; Pharma Ingredients & Services: Lampertheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Song, J.-C.; Yoon, K.-B. Controlled wall thickness and porosity of polymeric hollow nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, N.K.; Niu, H.; Ali, U.; Morsi, Y.S.; Lin, T. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Small-Diameter Blood Vessels: A Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; William Andrew, Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, P.P.; Pawar, V.S. Electrospun nanofiber scaffolds: Technology and applications. In Applications of Nanocomposite Materials in Drug Delivery; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 509–573. [Google Scholar]
- Şener, A.G.; Altay, A.S.; Altay, F. (Eds.) Effect of voltage on morphology of electrospun nanofibers. In Proceedings of the 2011 7th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 1–4 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, K.; Bowlin, G.L. Electrospinning jets and nanofibrous structures. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 013403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.G.; Stolojan, V.; Silva, S.R.P. Large area uniform electrospun polymer nanofibres by balancing of the electrostatic field. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 129, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanadam, G.; Chase, G.G. Modified electric fields to control the direction of electrospinning jets. Polymers 2013, 54, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Pavier, M.; Shterenlikht, A. Experimental study of modulus, strength and toughness of 2D triangular lattices. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 152, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Moroni, L.; Dijkstra, P.J. Influence of the solvent type on the morphology and mechanical properties of electrospun PLLA yarns. Biofabrication 2013, 5, 035014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.H.; Yoon, H.J.A.P.L. Effect of an auxiliary electrode on the crystalline morphology of electrospun nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 023127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.C. Hydrolytic degradation of polyglycolic acid: Tensile strength and crystallinity study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1981, 26, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, K.; Cho, K.; Park, C. Surface modification of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by oxygen plasma treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 199, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Hou, D.; Wei, Q. Morphology and Surface Properties of Poly (L-lactic acid)/Captopril Composite Nanofiber Membranes. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.T.; Imadojemu, H.; Webb, R. Effects of oxidation and surface roughness on contact angle. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 1994, 8, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Surface roughness and contact angle. J. Phys. Chem. 1949, 53, 1466–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Ao, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; et al. 3D hierarchical porous amidoxime fibers speed up uranium extraction from seawater. Energy Environ. Sci. 12.6 2019, 12, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromes, Y.; Gaillard, D.; Ponzio, O.; Chauffert, M.; Gerhardt, M.-F.; Deleuze, P.; Bical, O.M. Reduction of the inflammatory response following coronary bypass grafting with total minimal extracorporeal circulation. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2002, 22, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiore, Q.; Dattolo, P.; Piacenti, M.; Morales, M.A.; Pelosi, G.; Pizzarelli, F.; Cerrai, T. Thermal balance and dialysis hypotension. Int. J. Artif. Organs 1995, 18, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, E.E.; Gross, P. Anticomplementary power of heparin. J. Infect. Dis. 1929, 250, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Yuan, Q.; Huo, D.; Zheng, S.; Zhan, D. Investigation on clotting and hemolysis characteristics of heparin-immobilized polyether sulfones biomembrane. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 85, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesebro, J.H. Direct thrombin inhibition superior to heparin during and after thrombolysis: Dose, duration, and drug. Circulation 1997, 96, 2118–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzelmann, M.; Bosshart, H. Heparin Binds to Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Binding Protein, Facilitates the Transfer of LPS to CD14, and Enhances LPS-Induced Activation of Peripheral Blood Monocytes. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2280–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, H.; Tani, T.; Hanasawa, K.; Kodama, M. Extracorporeal Endotoxin Removal by Polymyxin B Immobilized Fiber Cartridge: Designing and Antiendotoxin Efficacy in the Clinical Application. Ther. Apher. 1998, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Zhao, J.; Du, H.C.; Tian, S.; Li, L.W. Removing endotoxin from plasmid samples by Triton X-114 isothermal extraction. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 424, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novelli, G.; Ferretti, G.; Poli, L.; Pretagostini, R.; Ruberto, F.; Perrella, S.; Levi, S.; Morabito, V.; Berloco, P. Clinical Results of Treatment of Postsurgical Endotoxin-Mediated Sepsis with Polymyxin-B Direct Hemoperfusion. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesentini, S.; Soncini, M.; Fiore, G.B.; Redaelli, A. Mechanisms of polymyxin B endotoxin removal from extracorporeal blood flow: Molecular interactions. Contrib. Nephrol. 2010, 167, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Deitch, E.A.; Ulloa, L. Novel Insights for Systemic Inflammation in Sepsis and Hemorrhage. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, P.; Jennewein, C.; Zacharowski, K. Biomarkers of endothelial dysfunction: Can they help us deciphering systemic inflammation and sepsis? Biomarkers 2011, 16, S11–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeerleder, S.; Hack, C.E.; Wuillemin, W.A. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation in Sepsis. Chest 2005, 128, 2864–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browdie, D.A.; Deane, R.; Shinozaki, T.; Morgan, J.; DeMeules, J.E.; Coffin, L.H.; Davis, J.H. Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). J. Traum. 1977, 17, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virzì, G.M.; Clementi, A.; Brocca, A.; Ronco, C. Endotoxin Effects on Cardiac and Renal Functions and Cardiorenal Syndromes. Blood Purif. 2017, 44, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, F.E.; Schollum, J.B.; Coulter, C.V.; Doyle, T.C.; Duffull, S.B.; Walker, R.J. Red Blood Cell Survival in Long-term Dialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, Y.A.; Abbas, A.; Khalil, A.; Mustafa, H.I.A.; Sciences, H. The effect of hemodialysis on hemoglobin concentration, platelets count and white blood cells count in end stage renal failure. Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2016, 5, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wenz, L.M.; Merritt, K.; Brown, S.A.; Moet, A.; Steffee, A.D. In vitro biocompatibility of polyetheretherketone and polysulfone composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Membrane Groupc | Polysulfone Concentration (wt%) | Surfactant Concentration (PEG 40, wt%) | Core Flow Rate (mL/h) | Total Shell Flow Rate (mL/h) | Core Flow Rate to Total Shell Flow Rate Ratio | Surfactant to Total Shell Flow Rate Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 20.0 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 17.0 | 1.0:2.43 | 1.0: 13.08 |
| B | 20.0 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 15.0 | 1.0:2.41 | 1.0:11.50 |
| C | 20.0 | 1.3 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 1.0:1.14 | 1.0:6.15 |
| D | 20.0 | 2.5 | 8.0 | 16.5 | 1.0:2.06 | 1.0:6.60 |
| E | 20.0 | 2.5 | 8.0 | 14.0 | 1.0:1.75 | 1.0:5.60 |
| F | 20.0 | 2.5 | 8.0 | 13.0 | 1.0:1.62 | 1.0:5.20 |
| G | 20.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 17.0 | 1.0:2.22 | 1.0:2.43 |
| H | 20.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 15.0 | 1.0:1.88 | 1.0:2.14 |
| I | 20.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 13.5 | 1.0:1.68 | 1.0:1.92 |
| J | 20.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 20.0 | 1.0:2.22 | 1.0:2.35 |
| K | 20.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 18.5 | 1.0:2.06 | 1.0:2.32 |
| L | 20.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 17.0 | 1.0:1.88 | 1.0:2.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chew, C.H.; Huang, W.-T.; Yang, T.-S.; Chen, A.; Wu, Y.M.; Wu, M.-S.; Chen, C.-C. Ultra-High Packing Density Next Generation Microtube Array Membrane for Absorption Based Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040273
Chew CH, Huang W-T, Yang T-S, Chen A, Wu YM, Wu M-S, Chen C-C. Ultra-High Packing Density Next Generation Microtube Array Membrane for Absorption Based Applications. Membranes. 2021; 11(4):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040273
Chicago/Turabian StyleChew, Chee Ho, Wan-Ting Huang, Tzu-Sen Yang, Amanda Chen, Yun Ming Wu, Mai-Szu Wu, and Chien-Chung Chen. 2021. "Ultra-High Packing Density Next Generation Microtube Array Membrane for Absorption Based Applications" Membranes 11, no. 4: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040273
APA StyleChew, C. H., Huang, W.-T., Yang, T.-S., Chen, A., Wu, Y. M., Wu, M.-S., & Chen, C.-C. (2021). Ultra-High Packing Density Next Generation Microtube Array Membrane for Absorption Based Applications. Membranes, 11(4), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11040273