Identification of Anthocyanins and Their Fouling Mechanisms during Non-Thermal Nanofiltration of Blueberry Aqueous Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Blueberry Extracts
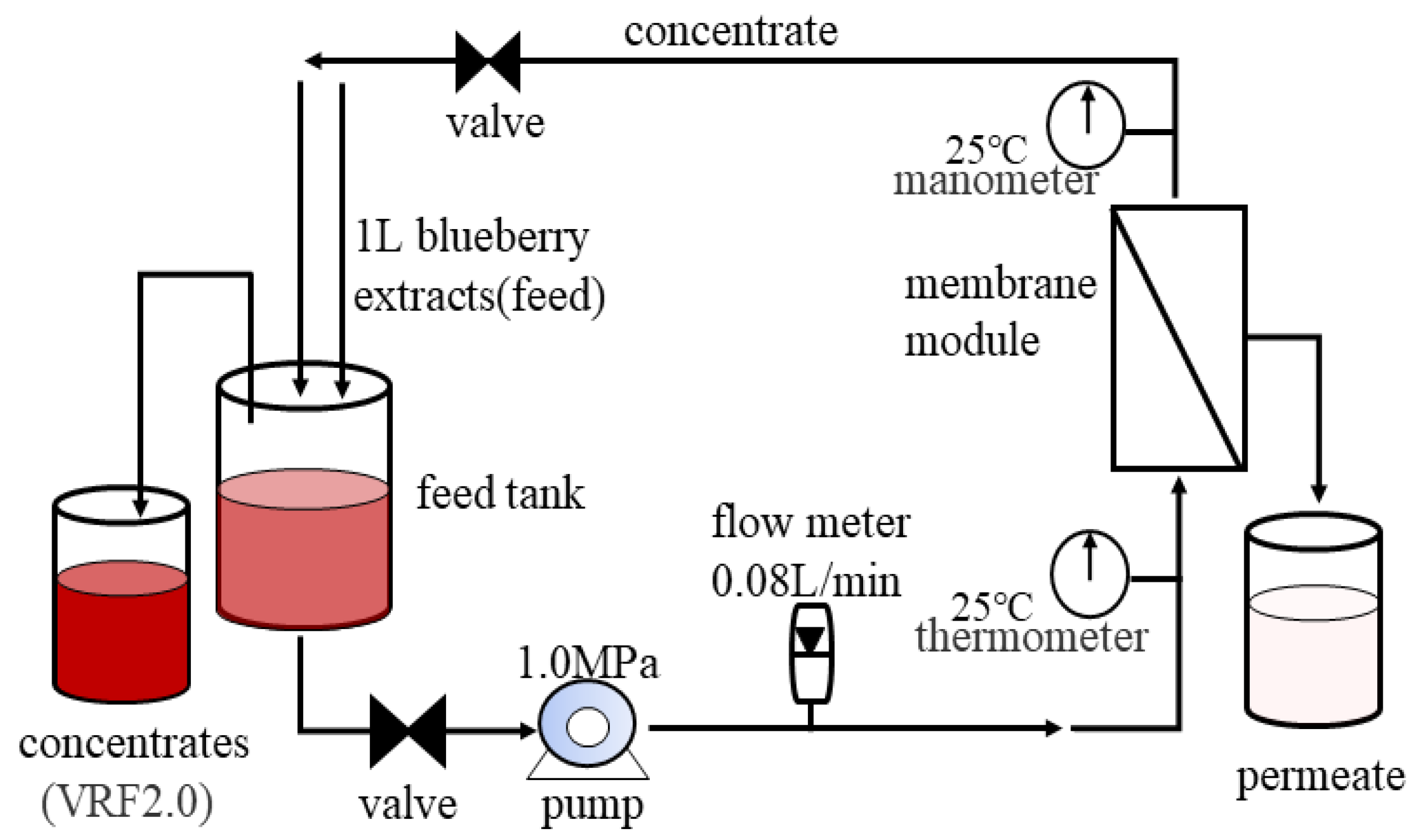
2.3. NF Concentration of Blueberry Extracts
2.4. Characterization of Membrane and Foulants
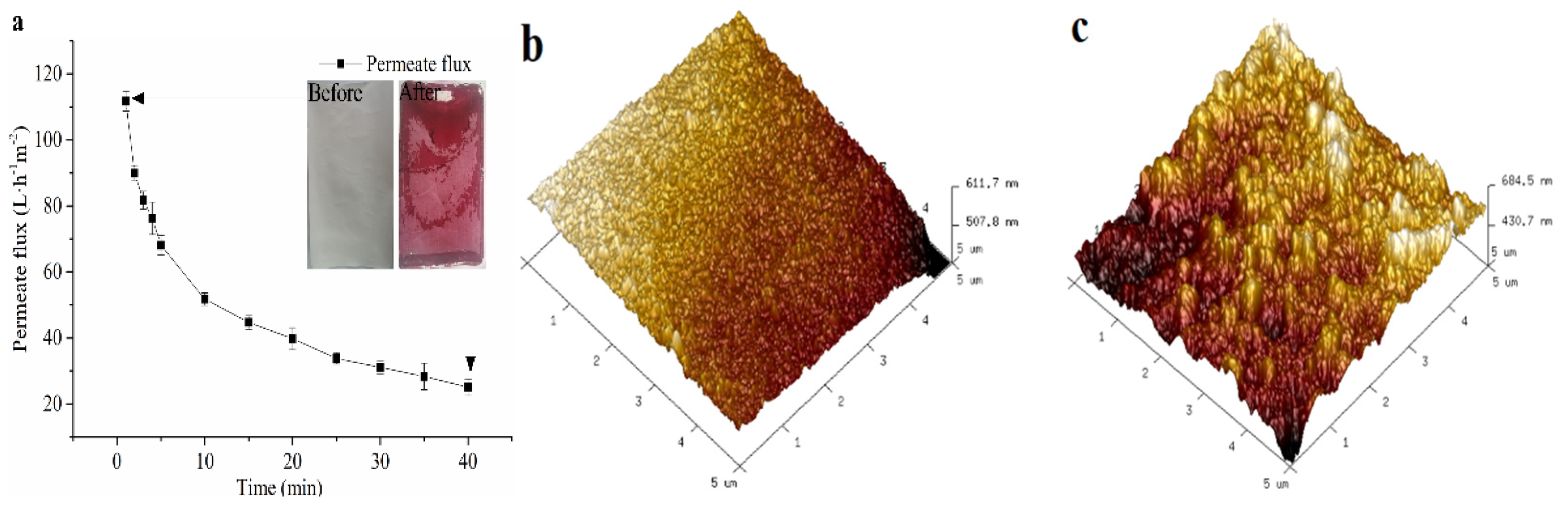
2.4.1. Permeate Flux
2.4.2. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
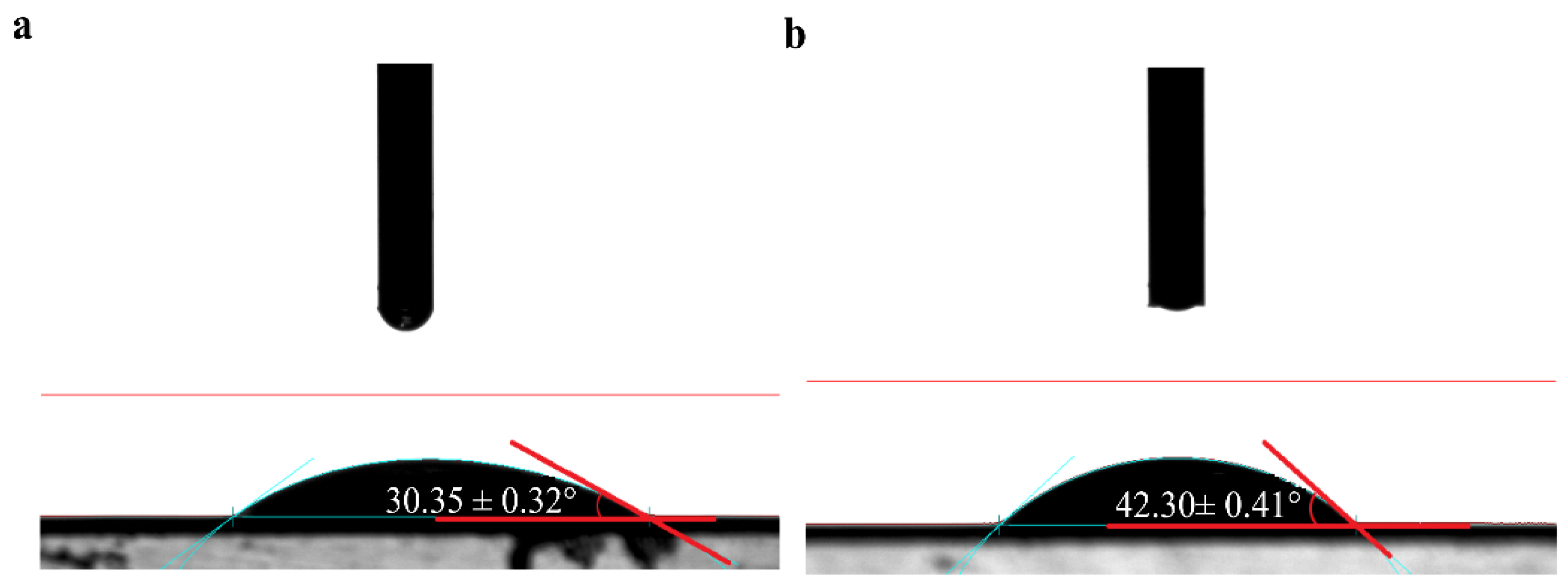
2.4.3. Contact Angle
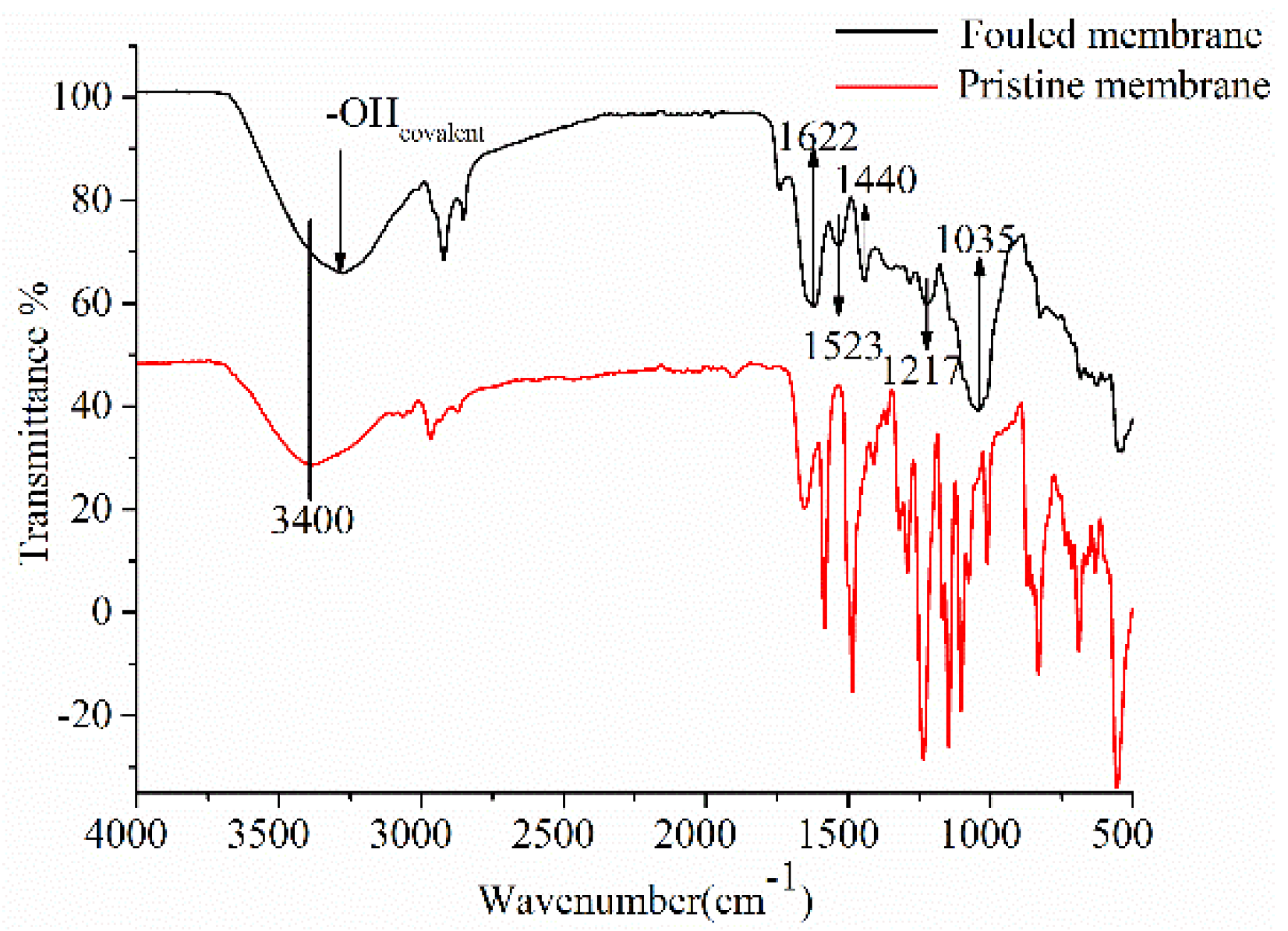
2.4.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.4.5. Extraction of Fouling Compounds
2.4.6. HPLC Analysis
2.4.7. HPLC-ESI-MS Analysis
2.4.8. Determination of Monomeric and Polymeric Anthocyanins
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Membrane Fouling in the NF Process
3.2. Characterization of Anthocyanins in the Fouled Membrane
3.2.1. Content of Anthocyanins on the Fouled Membrane
3.2.2. Identification of Anthocyanins in Foulants
3.3. Fouling Mechanisms between Anthocyanins and Membrane
3.3.1. Changes in Hydrophobic Characteristics of the Membrane Surface
3.3.2. Interaction between Anthocyanins and Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohideen, F.W.; Solval, K.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Chouljenko, A.; Chotiko, A.; Prudente, A.D.; Bankston, J.D.; Sathivel, S. Effect of continuous ultra-sonication on microbial counts and physico-chemical properties of blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum) juice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, T.J.; Ponce, A.G.; Alvarez, V.A. Nano-clays from natural and modified montmorillonite with and witout added blueberry extract for active and intelligent food nanopackaging materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 194, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, S.; Ji, T.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y. Development and optimization of dynamic gelatin/chitosan nanoparticles incorporated with blueberry anthocyanins for milk freshness monitoring. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhong, J.; Liu, X.H.; Gu, Z.P.; Li, Y.W. Natural Polyphenol Fluorescent Polymer Dots. Green Chem. 2021, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Le Phuong, H.A.; Blanford, C.F.; Szekely, G. Tailoring the performance of organic solvent nanofiltration membranes with biophenol coatings. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, X.L.; Chen, Q.L.; Song, H.L.; Yang, Y.L. Enhanced performance of microbial fuel cells with electron mediators from anthraquinone/polyphenol-abundant herbal plants. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 11263–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Bary, S.; Zhou, W. Changes in the color, chemical stability and antioxidant capacity of thermally treated anthocyanin aqueous solution over storage. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arend, G.D.; Adorno, W.T.; Rezzadori, K.; Di Luccio, M.; Chaves, V.C.; Reginatto, F.H.; Petrus, J.C.C. Concentration of phenolic compounds from strawberry (Fragaria X ananassa Duch) juice by nanofiltration membrane. J. Food Eng. 2017, 201, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voros, V.; Drioli, E.; Fonte, C.; Szekely, G. Process intensification via continuous and simultaneous isolation of antioxidants: An upcycling approach for olive leaf waste. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18444–18452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cissé, M.; Vaillant, F.; Pallet, D.; Dornier, M. Selecting ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes to concentrate anthocyanins from roselle extract (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conidi, C.; Cassano, A.; Caiazzo, F.; Drioli, E. Separation and purification of phenolic compounds from pomegranate juice by ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, T.; Mota, A.T.; Barbeitos, C.; Andrade, K.; Ferreira, F.C. A study on lupin beans process wastewater nanofiltration treatment and lupanine recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didaskalou, C.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Fonte, C.P.; Szekely, G. Valorisation of agricultural waste with an adsorption/nanofiltration hybrid process: From materials to sustainable process design. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3116–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeas, V.; Correia, A.C.; Jordão, A.M. Wine tartrate stabilization by different levels of cation exchange resin treatments: Impact on chemical composition, phenolic profile and organoleptic properties of red wines. Food Res. Int. 2015, 69, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Perreault, V.; Mikhaylin, S.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Bazinet, L.; Dammak, L. Identification of phenolic compounds and their fouling mechanisms in ion-exchange membranes used at an industrial scale for wine tartaric stabilization by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 233, 115995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernhet, A.; Moutounet, M. Fouling of organic microfiltration membranes by wine constituents: Importance, relative impact of wine polysccharides and polyphenols and incidence of membrane properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 201, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, A.; De Luca, G.; Conidi, C.; Drioli, E. Effect of polyphenols-membrane interactions on the performance of membrane-based processes. A review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 351, 45–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Araújo, P.A.; Correia, P.B.; Ramsey, M.M.; Kruithof, J.C.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Freeman, B.D.; Paul, D.R.; Whiteley, M.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S. Short-term adhesion and long-term biofouling testing of polydopamine and poly (ethylene glycol) surface modifications of membranes and feed spacers for biofouling control. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3737–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Santana Magalhães, F.; de Souza Martins Sá, M.; Cardoso, V.L.; Reis, M.H.M. Recovery of phenolic compounds from pequi (Caryocar brasiliense Camb.) fruit extract by membrane filtrations: Comparison of direct and sequential processes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 257, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, B.C.B.S.; Petrus, J.C.C.; Hubinger, M.D. Concentration of flavonoids and phenolic compounds in aqueous and ethanolic propolis extracts through nanofiltration. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.S.; Moreira, F.K.V.; Matsumoto, R.L.S.; Michelon, M.; Filho, F.M.; Hubinger, M.D. Influence of nanofiltration membrane features on enrichment of jussara ethanolic extract (Euterpe edulis) in anthocyanins. J. Food Eng. 2018, 226, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutabarat, R.P.; Xiao, Y.D.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, D.J.; Huang, W.Y. Identification of Anthocyanins and Optimization of Their Extraction from Rabbiteye Blueberry Fruits in Nanjing. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, A.M.; Morin, P.; Brownmiller, C.; Howard, L.R.; Sengupta, A.; Wickramasinghe, S.R. Concentrations of polyphenols from blueberry pomace extract using nanofiltration. Food Bioprod. Process. 2017, 106, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, M.; Korhummel, S.; Carle, R.; Kammerer, D.R. Impact of enzymatic mash maceration and storage on anthocyanin and color retention of pasteurized strawberry purées. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimpour, A.; Jahanshahi, M.; Mortazavian, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Mansourpanah, Y. Preparation and characterization of asymmetric polyethersulfone and thin-film composite polyamide nanofiltration membranes for water softening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, H.; Saikia, M.D. Structural and thermodynamic factors on adsorptive interaction of certain flavonoids onto polymeric resins and activated carbon. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 469, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeken, L.; Ramaekers, R.; Zhang, Y.; Maes, G.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Influence of hydrophobicity on retention in nanofiltration of aqueous solutions containing organic compounds. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 252, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-García, B.; Berrueta, L.A.; Garmón-Lobato, S.; Gallo, B.; Vicente, F. A general analytical strategy for the characterization of phenolic compounds in fruit juices by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection coupled to electrospray ionization and triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 5398–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, N.; Kimura, Y.; Ohno, T. Examination of molecular mechanism for the enhanced thermal stability of anthocyanins by metal cations and polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veberic, R.; Slatnar, A.; Bizjak, J.; Stampar, F.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M. Anthocyanin composition of different wild and cultivated berry species. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.; Jons, S.D. Chemistry and fabrication of polymeric nanofiltration membranes: A review. Polymer 2016, 103, 417–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Nebavskaya, X.; Kozmai, A.; Aleshkina, D.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N. Characterization of bulk and surface properties of anion-exchange membranes in initial stages of fouling by red wine. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 559, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Qi, B.; Cao, W.; Wan, Y. NOM fouling behavior during ultrafiltration: Effect of membrane hydrophilicity. J. Water Process Eng. 2015, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Porozhnyy, M.; Nevakshenova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V. Characterization and cleaning of anion-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis of polyphenol-containing food industry solutions; comparison with cation-exchange membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Chaabane, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Cleaning of cation-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis for food industry by chemical solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Huang, J.; Maan, O.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, H. Probing molecular interaction mechanisms of organic fouling on polyamide membrane using a surface forces apparatus: Implication for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, K.; Liu, S.; Luo, Q.; Xu, M. Adsorption properties of tea polyphenols onto three polymeric adsorbents with amide group. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 315, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| TAC | Polymeric Anthocyanins | |
|---|---|---|
| Foulants in membrane (mg/g) | 0.27 ± 0.03 b | 0.72 ± 0.01 a |
| Feed (mg/L) | 90.5 ± 0.14 d | 27.81 ± 0.04 c |
| Concentrate (mg/L) | 167.32 ± 0.22 a | 76.05 ± 0.00 a |
| Peak No. | tR(min) | MS/MS2 | Identification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18.00 | 465/303 | delphinidin-3-O-galactoside |
| 2 | 20.45 | 465/303 | delphinidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 3 | 23.10 | 435/303 | delphinidin-3-O-arabinoside |
| 4 | 24.78 | 449/287 | cyanidin-3-O-galactoside |
| 5 | 25.65 | 479/317 | petunidin-3-O-galactoside |
| 6 | 27.53 | 479/317 | petunidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 7 | 29.67 | 449/317 | petunidin-3-O-arabinoside |
| 8 | 31.21 | 493/331 | malvidin-3-O-galactoside |
| 9 | 31.21 | 463/301 | peonidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 10 | 33.06 | 493/331 | malvidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 11 | 34.87 | 463/331 | malvidin-3-O-glucoside |
| 12 | 37.04 | 465/303 | delphinidin-3-O-xyloside |
| 13 | 38.14 | 479/303 | delphinidin -3-O glucoside acid |
| 14 | 43.41 | 463/303 | delphinidin-3-O-rutin |
| (2) | 16.77 | 305 | chalcone |
| (3) | 30.06 | 319/273 | myricetin derivative |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, M.; Xie, C.; Zhong, H.; Tian, B.; Yang, K. Identification of Anthocyanins and Their Fouling Mechanisms during Non-Thermal Nanofiltration of Blueberry Aqueous Extracts. Membranes 2021, 11, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030200
Cai M, Xie C, Zhong H, Tian B, Yang K. Identification of Anthocyanins and Their Fouling Mechanisms during Non-Thermal Nanofiltration of Blueberry Aqueous Extracts. Membranes. 2021; 11(3):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030200
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ming, Chunfang Xie, Huazhao Zhong, Baoming Tian, and Kai Yang. 2021. "Identification of Anthocyanins and Their Fouling Mechanisms during Non-Thermal Nanofiltration of Blueberry Aqueous Extracts" Membranes 11, no. 3: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030200
APA StyleCai, M., Xie, C., Zhong, H., Tian, B., & Yang, K. (2021). Identification of Anthocyanins and Their Fouling Mechanisms during Non-Thermal Nanofiltration of Blueberry Aqueous Extracts. Membranes, 11(3), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11030200






