Abstract
Amylose of Phragmites Australis captures heavy metals in a box consisting of sugar chains. However, its absorption rate is low in the period of the month scale. Therefore, the electrochemical driving force was used to promote the absorption rate in this research. Amylose was doped with TiO2 porous graphite electrode. The composted absorbent was characterized using XRD(X-ray diffraction), SEM (Scanning Electrode Microscopy), Raman spectroscopy, and electrochemical methods. The affinity and maximum absorption amount were calculated using the isotherm method. In this study, Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Cr6+ were chosen to demonstrate because these heavy metals are significant pollutants in Japan’s surface water. It was found that the maximum absorption was Cu2+ (56.82-mg/L) > Pb2+ (55.89-mg/L) > Cr6+ (53.97-mg/L) > Cd2+ (52.83.68-mg/L) at −0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl. This is approximately the same order as the hydration radius of heavy metals. In other words, the absorption amounts were determined by the size of heavy metal ions. Subsequently, the mixed heavy metal standard solution was tested; the maximum absorption amount was 21.46 ± 10.03 mg/L. It was inferred that the electrochemical driving force could be shown as the ion size effect in the mixed solution. Despite there being no support for this hypothesis at this time, this study succeeded in showing that the electrochemical driving force can improve the ability of the absorbent.
1. Introduction
Rising population, factory expansion, urbanization, agricultural activities, and various chemicals usage have led to serious environmental issues [1,2]. Water contamination is the most important of these environmental issues to examine, as water quality has a direct link to human health, as hazardous substances are absorbed in bodily organisms through the food chain and drinking water [1]. Copper, chromium, cadmium, and lead are the most common heavy metal contaminants in Japan. Heavy metals are highly toxic, non-biodegradable, and easily accumulate in human organs, causing various diseases and health disorders [3,4,5,6]. After the investigation, it was discovered that the high concentration of copper discharged into the river and infiltrated into the surface of the soil due to copper mining in the Ashio Copper Mine upstream of the Watarase River killed numerous crops and fish died downstream of the Watarase River in Japan in 1890 [7]. In 1905, the Japanese government decided to build sedimentation ponds to remove the mining poison. Phragmites australis was planted in large quantities surrounded Watarase River to absorb harmful heavy metals from the water [8]. Phragmites australis is still used today to protect water safety and wildlife [7]. Heavy metal contamination in water bodies has resulted in numerous illnesses, such as ITAI-ITAI disease, lead poisoning, and skin fester [9]. Thus, regarding these illnesses, WHO stipulates the standard for different types of heavy metals in water bodies: the copper concentration should be less than 2 mg/L, chromium is set at 0.05 mg/L, cadmium must be less than 0.003 mg/L, and lead must be maintained below 0.01 mg/L [10]. In addition to complying with regulations, water treatment technology must be implemented to achieve water recycling.
Coagulation, chemical precipitation, oxidation, reverse osmosis, membranes, solid-phase extraction, electrochemical, and adsorption are some of the wastewater treatment technologies developed over the last few decades [11,12,13]. These technologies have some limitations; for example, chemical precipitation generates sludge, which needs further treatment and will eventually increase the cost [14,15,16]. Adsorption is the most widely used and recommended method for water treatment due to the adsorbent materials being possible to extract from natural resources, having a large quantity, being easily degradable, having the benefit of being highly efficient, and being less likely to cause secondary pollution to the environment [17,18,19]. Many materials are used as adsorbent materials for water treatment, such as zeolites, resins, polymeric membranes, and clays that can adsorb heavy metals [20,21]. However, some adsorbent materials showed limited capacity due to adsorption limitations, therefore many researchers are looking for various potential methods such as a modification to enlarge the capacity site [22,23,24].
Starch is a polysaccharide substance found in enormous quantities in nature, that is inexpensive, biocompatible, renewable, and degradable [25,26]. Amylose and amylopectin are two forms of semi-crystalline granules found in starch [27]. Amylose is less polymerized and has a higher water solubility than amylopectin. The focus of this study is on amylose as an adsorbent material in polymeric membranes. However, existing natural starch is not easily soluble in water; thus, changing the chemical and physical properties has become an approach for its wide use [28]. Most studies have demonstrated that modifying starch could change its response to pH value and temperature limitation [29,30]. There is also the possibility of adding specific functional groups to starch, such as amino, hydroxyl, and carboxyl groups to improve the adsorption affinity for heavy metal ions in water treatment. Various studies have succeeded in replacing the hydroxyl group of starch with different groups, such as carboxyl and acetyl group insertion [31]. There are many approaches to chemically altering starch like acid hydrolysis, cross-linking, and oxidation to replace the hydroxyl groups [32,33]. However, the hydroxyl group on the backbone of starch is one of the beneficial functional groups for heavy metal adsorption, and modifying its chemical properties does not essentially increase its adsorption surface area.
Therefore, in this study, we propose a new concept in which we use amylose in starch as a basic absorbent, and then add carboxyl functional groups at the periphery interface to increase its absorption surface area using the electrochemical driving force. Carbon materials are well known for having carboxyl functional groups surrounded by the backbone, low cost, and environmental friendliness, so they have become one of the common adsorbent materials [34,35]. Activated carbon is used as one of the common adsorbent materials because of its high surface area. However, it gradually loses its adsorption efficiency due to the limited sorption site [36]. Gang X. et al. suggested that graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets can adsorb cationic and anionic ions in wastewater because of the absorbents’ special shape and semi-conductivity properties [37]. Many studies have shown that the carbon materials are used as adsorbent materials; the pH value in the water body needs to be changed in most cases because the carboxyl groups are easily affected by different pH values [38,39]. Therefore, an adsorbent material that is not affected by the pH but has high absorption ability is requested.
We believe that a composite of graphite and starch amylose could be a new heavy metal absorption material in wastewater treatment. Different amylose concentrations were used to modify the graphite carbon plates to analyze the absorption efficiency hoping to find the optimized concentration of amylose usage. Then, the material was conducted with a negative charge to calculate the absorption efficiency and compared with the results of uncharged experiments to confirm if the efficiency was improved. We expected the new absorption material to absorb various heavy metal ions from contaminated water efficiently and quickly.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
All reagents used in this study were analytical grade. Standard solutions of copper (II) chloride, lead (II) chloride, cadmium (II) chloride, chromium (VI) oxide, potassium chloride, and amylose of starch were purchased from Wako, Japan. Potassium chloride was added as an electrolyte when the electrochemical method was applied. Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd. donated porous carbon plates.
2.2. Instruments
In this study, the characterization of graphite porous carbon plates was measured using Scanning Electrode Microscopy (SEM, Hitachi High-Tech Corporation, S4800, Tokyo, Japan), X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku Corporation, RINT2200V, Tokyo, Japan), Raman spectroscopy (JASCO Corporation, RMP500, Tokyo, Japan), and a digital multimeter (ADVANTEST, R6450, Tokyo, Japan). The amylose and graphite porous carbon plate was used in the vacuum system and new adsorbent materials were dried in an oven at 80 °C. The adsorption of heavy metals was performed using an Electrochemical Instrument (HOKUTO DENKO CORPORATION, HZ-7000, Tokyo, Japan), with three electrodes connected. The working electrode (WE), counter electrode (CE), and reference electrode (RE) were amylose/graphite porous carbon plate,/graphite porous carbon plate, and Ag/AgCl electrode, respectively. The concentration of heavy metal ions was measured using an Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer (AAS, Hitachi High-Tech Corporation Z-2000, Tokyo, Japan).
2.3. Characterization of Graphite Porous Carbon Plate
Two types of graphite carbon plate could be a potential material. Two types of graphite porous carbon plates were prepared; SEM was used to observe the appropriate porous size, for which samples were controlled in magnification: 4000, working distance: 17.4 mm, acceleration voltage: 5 KV, and emission current: 10 μA condition. SEM images (Figure 1a,b) show the pore size of the two types of graphite porous carbon plate; the cavity of the pore was measured at 5 μm. According to the SEM images, two graphite porous carbon plate exposed a similar pore size, and the multilayer sheets were also expressed.
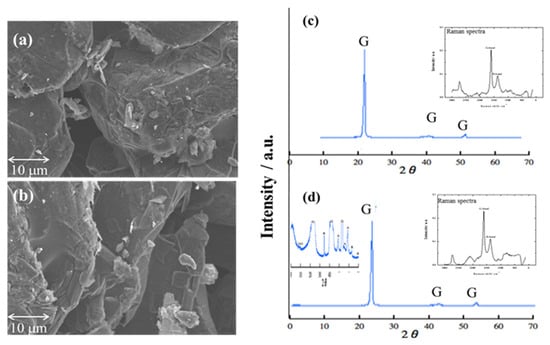
Figure 1.
SEM imagines of (a) porous carbon; (b) TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon. (I: 10 μA V:5 kV Mag: 4000 WD: 17.4 mm). XRD and Raman spectra of (c) porous carbon; (d) TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon.
However, XRD was used to identify the carbon components and detect the carbon crystal phase of two porous carbon plates using Cu-Ka radiation of 1.5405 Å wavelength and a scanning speed of 2° min−1. The surface property of porous carbon electrodes was investigated using Raman spectroscopy (JASCO, RMP 500, Tokyo, Japan). In carbon materials, Raman spectroscopy is used to detect bond strengths via lattice vibration. Figure 1c,d shows the XRD and Raman spectra of two types of porous carbon plates. As a result, two types of porous carbon showed a typical graphite peak in XRD patterns at 2θ = 26.7° [40]. In Raman spectra, the main features of the G-band and D-band appear at 1582 cm−1 and 1350 cm−1, respectively. The Raman peak around 1582 cm−1 is known as the G-band typical Raman peak of bulk crystalline graphite. This peak is the basic vibration mode of graphite crystals. The size of the crystal influences the intensity [41]. The vibration of the crystalline carbon edge of the graphite, known as the D-band, produces a peak value of 1350 cm−1.
Regarding the Raman spectra, graphite-dominated porous carbon was noticed because the high G-band value was exposed in both carbon electrodes. The high value of the G-band and D-band ratio means good electroconductivity property [42]. The ratio of G-band and D-band of two carbon electrodes were 0.45 and 0.48, respectively. Furthermore, anatase and rutile composite crystal phases was observed in Figure 1d after being added to the carbon graphite plate with anatase peaking at 2θ values of 47.6°, 53.5°, and 55.1°; and 2θ values peak of rutile were found at 35.6° and 61.0°, which coincided with crystal planes of anatase (200), (105), and (211), and rutile crystal planes of (101) and (310) [43]. Graphite carbon plates have good electroconductivity, but their hydrophobic characteristic makes them unsuitable for water mediation. Thus, anatase and rutile were added to the graphite carbon plate to change the surface of the graphite carbon plate for a hydrophilic property. TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon plate was used as a potential material for water mediation in this study.
2.4. Doping Amylose into Graphite Porous Carbon Plates
The vacuum pump was used to vacuumize TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon plates, which were subsequently immersed in 10g of amylose solutions and vacuumed for 120 min. The weights of amylose/TiO2 doped porous carbon plates were measured after they were removed from the solution and dried in an oven at 80 °C for 120 min. Figure 2 shows the dried weight of amylose/TiO2-doped porous carbon increased tendency. It shows that the weight of TiO2-doped porous carbon plate became saturated in 120 min of doping time. The lowest carbon area (1.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 0.2 cm) showed 0.1 g change and the biggest carbon plate area (9.0 cm × 15.0 cm × 0.2 cm) showed 0.9 g change; thus, the amylose of starch increased proportionally with the carbon plate area. Since the electrochemical method was to be used, the area of carbon plate was chosen to be 5.0 cm × 9.0 cm × 0.2 cm for ease of operation.
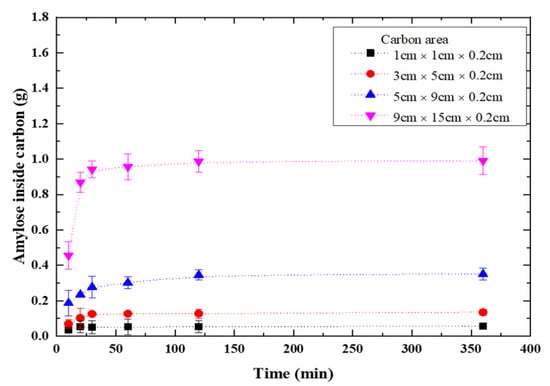
Figure 2.
Time dependence of amylose doped into TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon.
2.5. Absorption Isotherm
Absorption isotherms show how the absorbents interact with adsorbate and their distribution on the surface. It has also been used to compare the affinity of absorbents for the removing contaminants from the hydrosphere.
The Langmuir isotherm is the most common method for describing the absorption capacity, applied to real ions absorption processes in many studies. There are already several common isotherms to express the efficiency of adsorbents. However, in this study, amylose was doped into the graphite multilayer sheet plate; the common adsorption isotherm could not certainly be consistent in this study. Here, one new absorption isotherm was discussed based on the Langmuir sorption isotherm. It assumes that at first, adsorbates are uniformly distributed on a homogeneous monolayer absorbent. We also assumed that despite inside amylose being random distribution, the surface of amylose also shows a homogeneous monolayer. Therefore, the equation is given as follows:
[] means the free concentration of heavy metal ions in solution, [] means the amylose absorption site. [ exhibits the absorbed concentration of heavy metals in the new absorbent. Regarding the chemical equilibrium reaction, the affinity constant [K] can be written as follows:
The calculation of the concentration of [] can simply be considered the maximum absorption ability of [] subtraction.
Equation (4) is substituted from Equation (3), and the equation can be rewritten as follows:
Here, K and []max exhibit affinity of absorbent and the maximum absorption capacity, respectively. The heavy metal absorption isotherm analysis using amylose doped into graphite porous carbon electrode was described.
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metal Absorption Amount Analysis
This study on heavy metal ion absorption amount using amylose was conducted to verify heavy metal ion absorption ability. Then, the amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon was described at a given potential change for a 120 min heavy metal ion absorption process. Figure 3a shows the absorption amount of Pb2+ using amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon in 0.3 g at a −0.5 V charged potential applied. The absorption amount is 66.11 mg/L; approximately 26.4% of Pb2+ had been absorbed at the end of 120 min. However, at the initial concentration, 100 mg/L of Pb2+ exposed to approximately 47.52% of Pb2+ was absorbed in 120 min. According to the absorption rate for lead removal, 100 mg/L could be a critical initial concentration for the absorption equilibrium. Figure 3b shows the maximum absorption amount of 57.69 mg/L for 250 mg/L Cu2+ absorption using amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon in 0.3 g at a −0.5 V charged potential applied; however, the capacity of absorption in Cu2+ solution showed 40.76% at the initial 100 mg/Lof Cu2+. As a result, the absorption amount of the developed absorbent has the best absorption performance at 100 mg/L of Cu2+. Figure 3c shows the absorption amount of Cd2+, and the results show that even though absorption amount continued to grow as cadmium concentration increased, the absorption amount decreased over 200 mg/L of Cd2+ absorption, which is a similar phenomenon to Pb2+ and Cu2+. The maximum absorption amount and capacity were 47.81 mg/L and 42.65%, respectively. Cr6+ absorption amount is also described in Figure 3d, which shows the lowest absorption amount among these heavy metals. The maximum absorption amount value was shown 39.68 mg/L for an initial concentration of 150 mg/L Cr6+ absorption, and the maximum absorption capacity appeared on the 100 mg/L, which showed approximately 34.68% absorption capacity. The maximum absorption amount and capacity are summarized in Table 1. Amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon for removal of heavy metals exhibited the best absorption amount at the initial concentration of 100 mg/L individually, but it showed a different value of absorption amount and capacity. The size of the ionic radius of Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, and Cr6+ is 1.75 Å, 1.28 Å, 1.49 Å, and 1.25 Å, respectively. The size of heavy metal ions determined the absorption ability and the absorption affinity.
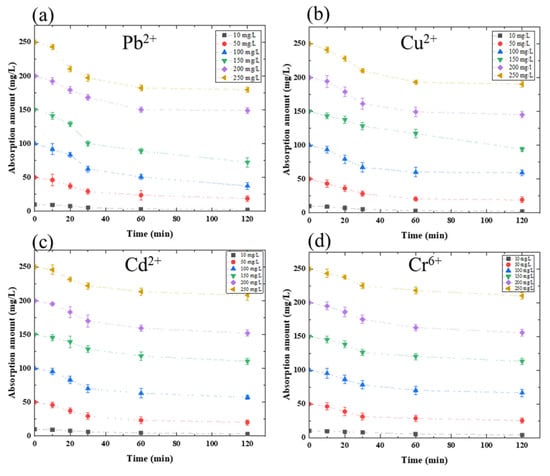
Figure 3.
Absorption amount in different heavy metal concentration solutions: (a) Pb2+; (b) Cu2+; (c) Cd2+; (d) Cr6+ using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.

Table 1.
The absorption amount and capacity for each heavy metal removal by using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.
3.2. Heavy Metal Absorption Isotherm of Amylose/TiO2 Doped Graphite Porous Carbon
In this study, amylose was fixed at a certain amount into TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon in each plate. To understand the absorption rate and how the electrochemical driving force method works for the removal of heavy metals, the affinity constant K and were calculated in Table 2 based on the established absorption isotherm. The new absorbent order of each heavy metal’s absorption ability is as follows: Cu2+ > Pb2+ > Cr6+ > Cd2+. The value of maximum absorption amount calculated from the absorption isotherms is similar to the results appeared in the experiments, the absorption amount of Cu2+ and Pb2+, and Cr6+ and Cd2+ were approximately at the same value. It is inferred that the ionic radius of Cu2+ and Pb2+ are close; Cr6+ and Cd2+ are at a similar value as well. Since the maximum absorption amount of the single component amylose absorbent showed that Pb2+(20.89-mg/L) > Cu2+ (19.15-mg/L) > Cd2+ (15.86-mg/L) > Cr6+ (13.29-mg L), the amylose-doped TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon absorbent had a higher absorption ability than the single component amylose absorbent.

Table 2.
The maximum absorption amount and affinity for each heavy metal absorption by using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.
Figure 4 showed that even if all of the heavy metal concentrations could not pass through the linear lines for every single point, most points are on the line. Therefore, the new absorbent could fix this new absorption isotherm. As previously mentioned, amylose does not show a homogeneous distribution on the surface of TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon. First, potential charges occurred with amylose covered by the carbon plate’s surface; subsequently, inside amylose acted as the charge potential continued.
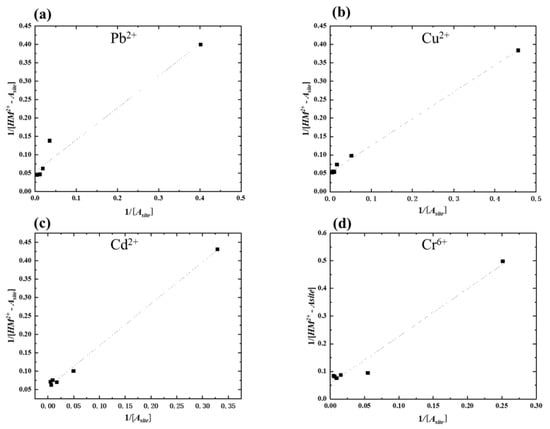
Figure 4.
The absorption isotherm fitting for each heavy metal absorption: (a) Pb2+; (b) Cu2+; (c) Cd2+; (d) Cr6+ using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.
3.3. Practical Application
As is well known, heavy metals contaminated with water have frequently co-existed with multi-species. The absorption of heavy metals in mixed water samples was investigated. Each heavy metal’s initial concentration ranged from 10 mg/L to 250 mg/L. The amount of absorbent was charged with the same potential as the individual experiment. Figure 5 shows each heavy metal absorption amount for 120 min absorption progress in a mixed solution. The absorption capacities for heavy metal removal are exhibited differently from a single ion absorption. The maximum absorption capacities occurred in the initial concentration of 100 mg/L of each ion, as with the individual heavy metal absorption results. The average of mixed heavy metal absorption was 21.46 mg/L. The maximum absorption amount value is shown in Table 3 for each heavy metal absorption based on the absorption isotherm. The order of maximum absorption for mixed heavy metals is Cd2+ > Cr6+ > Pb2+ > Cu2+. The maximum absorption amountsdeclined, and the order of the value expressed the opposite to the individual absorption value. However, this result can be considered to follow the ionic radius as well.
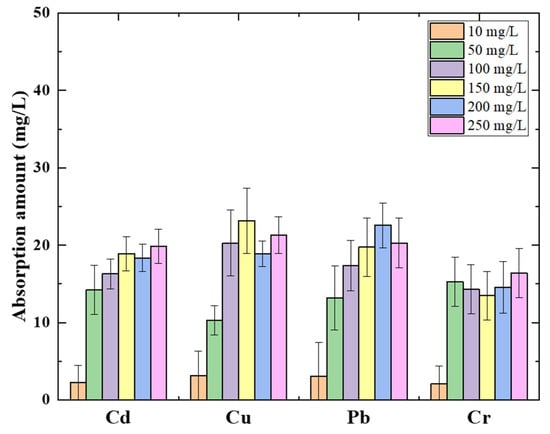
Figure 5.
Absorption amount in different commixture of heavy metals concentration solutions using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.

Table 3.
The maximum absorption amount and affinity for mixed heavy metal absorption using 0.3 g amylose/TiO2-graphite porous carbon at −0.5 V potential.
In the mixed solution, amylose on the surface absorbed the smaller size of ions making the inside of amylose unavailable for work, resulting in a two-fold decrease in average absorption levels. Despite an absorption competition in mixed solutions, the absorption amount is still as good as expected.
4. Conclusions
The electrochemical driving force approach was used to test a new absorbent using an amylose/TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon electrode for heavy metal absorption in this study. The performance of amylose-doped TiO2-doped graphite porous carbon absorption depended on the initial concentration of heavy metals, and the absorption equilibrium concentration was 100 mg/L. It was shown that the absorption amount and ability were advanced for single component amylose absorbent and single heavy metal absorption. Meanwhile, the devised absorption isotherm is in accordance with the absorption trend of the new absorbent material for heavy metals absorption, and the ionic radius determined the order of heavy metal maximum absorption. There is an opposite order compared to one heavy metal ion and mixed solution. In contrast, the electrochemical driving fore method for compositing porous carbon plate and amylose could drastically improve the absorbent ability compared to bulk amylose application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.K.; methodology, S.L. and T.K.; software, S.L.; validation, S.L., G.M., R.I. and T.K.; formal analysis, S.L. and T.K.; investigation, S.L. and T.K.; resources, S.L.; data curation, S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, T.K.; supervision, T.K.; project administration, T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Marques, P.A.S.S.; Rosa, M.F.; Pinheiro, H.M. pH effects on the removal of Cu2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solution by waste brewery biomass. Bioprocess Eng. 2000, 23, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, F.; Rizwi, S.J.; Haq, S.K.; Khan, R.H. Low dose mercury toxicity and human health. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 20, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoeurn, K.; Sakaguchi, A.; Tomiyama, S.; Igarashi, T. Long-term acid generation and heavy metal leaching from the tailings of Shimokawa mine, Hokkaido, Japan: Column study under natural condition. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 201, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Viraraghavan, T. Heavy metal removal in a biosorption column by immobilized M. rouxii biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 78, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Murakami, M.; Arao, T. Spatial Distribution and Risk Management of Heavy Metal Contamination in Japan; National Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences: Tsukuba, Japan, 2014; pp. 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Magee, D. Brett L. Walker, Toxic archipelago: A history of industrial disease in Japan (Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2010). J. Environ. Stud. Sci. 2011, 1, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, M. The World Whole: An Environmental History of Japanese Space Power. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Uetani, M.; Oishi, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Nogawa, K. Estimation of cumulative cadmium intake causing Itai-itai disease. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 159, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayato, Y. WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. Eisei Kagaku 1989, 35, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Pan, S.Y.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, H. Performance evaluation and optimization of flocculation process for removing heavy metal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, N.; Drogui, P.; Montané, C.; Hausler, R.; Blais, J.-F.; Mercier, G. Heavy metals removal from acidic and saline soil leachate using either electrochemical coagulation or chemical precipitation. J. Environ. Eng. 2006, 132, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; Sharma, S.; Joshi, R.; Tiwari, A.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Joshi, M.K. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.T.; Peng, L.; Reeder, W.S.; Moosavi, S.M.; Tiana, D.; Britt, D.K.; Oveisi, E.; Queen, W.L. Rapid, selective heavy metal removal from water by a metal-organic framework/polydopamine composite. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Strezov, V.; Kumar, R.; Weldekidan, H.; Jahan, S.; Dastjerdi, B.H.; Zhou, X.; Kan, T. Pyrolysis of heavy metal contaminated Avicennia marina biomass from phytoremediation: Characterization of biomass and pyrolysis products. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using carbon-based adsorbents: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Padilla, Á.; Moreno-Sader, K.A.; Realpe, Á.; Acevedo-Morantes, M.; Soares, J.B.P. Evaluation of adsorption capacities of nanocomposites prepared from bean starch and montmorillonite. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, J.; Gui, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, B.; Tan, C.; Fang, Y.; Cui, B. Porous starches modified with double enzymes: Structure and adsorption properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, B.M.; Fakhre, N.A. Crown ether modification of starch for adsorption of heavy metals from synthetic wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Tawfeek, A.M. Characterization of reactive amphiphilic montmorillonite nanogels and its application for removal of toxic cationic dye and heavy metals water pollutants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei Shirazani, M.; Bakhshi, H.; Rashidi, A.; Taghizadeh, M. Starch-based activated carbon micro-spheres for adsorption of methane with superior performance in ANG technology. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gao, B.; Li, A.; Yang, H. Evaluation of the selective adsorption of silica-sand/anionized-starch composite for removal of dyes and Cupper(II) from their aqueous mixtures. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.; Seib, P.A. Cross-linking of wheat starch and hydroxypropylated wheat starch in alkaline slurry with sodium trimetaphosphate. Carbohydr. Polym. 1997, 33, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Ma, Z.; Yin, X.; Hu, X.; Boye, J.I. Structural characteristics and physicochemical properties of field pea starch modified by physical, enzymatic, and acid treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, O.; Soto, D.; Antúnez, A.; Fernández, R.; González, J.; Piña, C.; Muñoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernandez-García, M. Hydrogels based on oxidized starches from different botanical sources for release of fertilizers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluru, S.S.; Agarwal, S.; Sireesha, S.; Sreedhar, I.; Kale, S.R. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using nanomaterials-process and engineering aspects. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 150, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Cai, L.; Liang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Z. Green synthesis of expanded graphite/layered double hydroxides nanocomposites and their application in adsorption removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Cheng, C.K.; Luque, R.; Thomas, S.; Banh, T.L.; Pham, V.V.; Nguyen, X.P. Heavy metal removal by biomass-derived carbon nanotubes as a greener environmental remediation: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2021, 287, 131959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossarutto, L.; Zimny, T.; Kaczmarczyk, J.; Siemieniewska, T.; Bimer, J.; Weber, J.V. Transport and sorption of water vapour in activated carbons. Carbon 2001, 39, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Li, P.; Yang, C.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Q.; Su, H. Superior adsorption performance of graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for both cationic and anionic heavy metals from wastewater. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrokhi-Shahraki, R.; Benally, C.; El-Din, M.G.; Park, J. High efficiency removal of heavy metals using tire-derived activated carbon vs commercial activated carbon: Insights into the adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Chiu, H. Adsorption of zinc(II) from water with purified carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashita, N.; Park, C.R.; Fujimoto, H.; Shiraishi, M.; Inagaki, M. Specification for a standard procedure of X-ray diffraction measurements on carbon materials. Carbon 2004, 42, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Li, L.H.; Hou, L.; Hu, X.; Zhou, S.; Peter, R.; Petravic, M.; Chen, Y. Disorder in ball-milled graphite revealed by Raman spectroscopy. Carbon 2013, 57, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.M.; Durães, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from anthropogenic activities and remediation strategies: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazi, H.A. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using agricultural and industrial wastes as adsorbents. HBRC J. 2013, 9, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Hu, S. ‘Smart’ materials based on cellulose: A review of the preparations, properties, and applications. Materials 2013, 6, 738–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.; Banat, F. Comparison of heavy metal ions removal from industrial lean amine solvent using ion exchange resins and sand coated with chitosan. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2014, 18, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusain, R.; Gupta, K.; Joshi, P.; Khatri, O.P. Adsorptive removal and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using metal oxides and their composites: A comprehensive review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 272, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tsai, H.-L.; Huang, C.-L. Effect of brookite phase on the anatase–rutile transition in titania nanoparticles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, M.; Piscanec, S.; Mauri, F.; Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Phonon linewidths and electron-phonon coupling in graphite and nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 73, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).