Recovery of Biologically Treated Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Subsequent Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process
Abstract
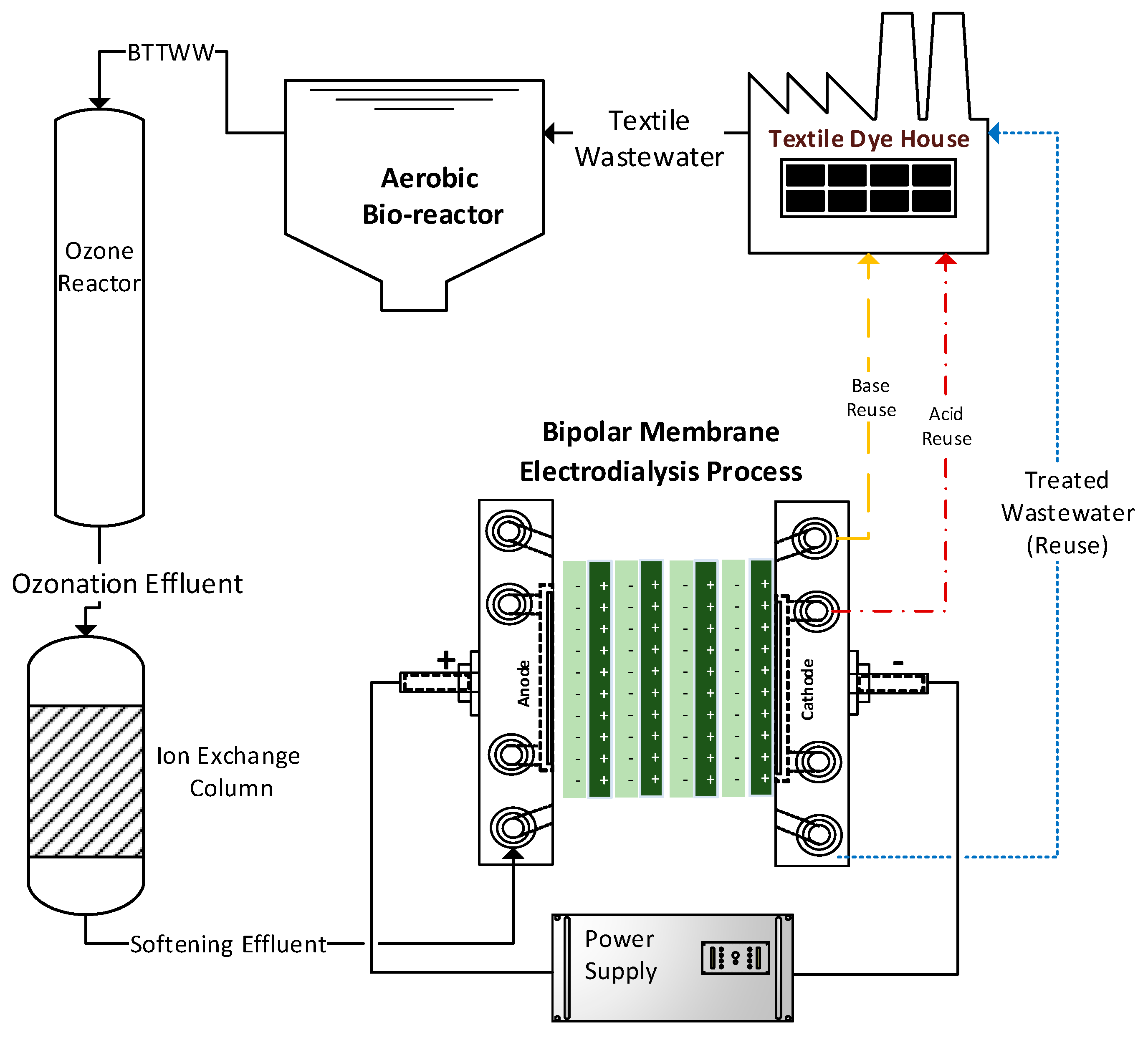
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Textile Wastewater
2.2. Ozonation Process
2.3. Water Softening via Ion-Exchange Resins
2.4. Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process
3.2. Fate and Transport of Organic Matter
3.3. Acid and Base Production via Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bener, S.; Bulca, Ö.; Palas, B.; Tekin, G.; Atalay, S.; Ersöz, G. Electrocoagulation process for the treatment of real textile wastewater: Effect of operative conditions on the organic carbon removal and kinetic study. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 129, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, R.; Khan, S.J.; Jamal, Y. Hybrid anaerobic-aerobic biological treatment for real textile wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 29, 100804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Syed, Z.; Brighu, U.; Gupta, A.B.; Ram, C. Adsorption of textile wastewater on alkali-activated sand. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lares, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Sillanpää, M.; Sillanpää, M. Occurrence, identification and removal of microplastic particles and fibers in conventional activated sludge process and advanced MBR technology. Water Res. 2018, 133, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedinzadeh, N.; Shariat, M.; Monavari, S.M.; Pendashteh, A. Evaluation of color and COD removal by Fenton from biologically (SBR) pre-treated pulp and paper wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoriya, S.; Bargole, S.; George, S.; Saharan, V.K. Treatment of textile dyeing industry effluent using hydrodynamic cavitation in combination with advanced oxidation reagents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobya, M.; Gengec, E.; Demirbas, E. Operating parameters and costs assessments of a real dyehouse wastewater effluent treated by a continuous electrocoagulation process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 101, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, W.; Han, H.; Xu, C.; Han, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, W.; Zhu, H. Selective recovery of salt from coal gasification brine by nanofiltration membranes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinkaya, E.; Tuncman, S.; Koc, I.; Guner, A.R.; Ciftci, S.; Aygun, A.; Sengul, S. Performance of a pilot-scale reverse osmosis process for water recovery from biologically-treated textile wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura Bernardes, A.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S. Electrodialysis in Water Treatment. In Electrodialysis and Water Reuse; Bernardes, A., Rodrigues, M.A.S., Ferreira, J.Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 63–75. ISBN 9783642402494. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Chapter 6 Ion-Exchange Membrane Processes in Water Treatment. In Sustainability Science and Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 141–199. ISBN 1871-2711. [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badruzzaman, M.; Oppenheimer, J.; Adham, S.; Kumar, M. Innovative beneficial reuse of reverse osmosis concentrate using bipolar membrane electrodialysis and electrochlorination processes. J. Memb. Sci. 2009, 326, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan Readi, O.M.; Kuenen, H.J.; Zwijnenberg, H.J.; Nijmeijer, K. Novel membrane concept for internal pH control in electrodialysis of amino acids using a segmented bipolar membrane (sBPM). J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 443, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, O.; Iwaszczuk, N.; Kharebava, T.; Bejanidze, I.; Pohrebennyk, V.; Nakashidze, N.; Petrov, A. Neutralization of Industrial Water by Electrodialysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Luo, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Malic acid production using a biological electrodialysis with bipolar membrane. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 471, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; Jin, J.; Wu, K.; Meng, W.; Wang, K. Recycling Lithium from Waste Lithium Bromide to Produce Lithium Hydroxide. Membranes 2021, 11, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuldeep; Badenhorst, W.D.; Kauranen, P.; Pajari, H.; Ruismäki, R.; Mannela, P.; Murtomäki, L. Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis for Sulfate Recycling in the Metallurgical Industries. Membranes 2021, 11, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurreri, L.; Tamburini, A.; Cipollina, A.; Micale, G. Electrodialysis Applications in Wastewater Treatment for Environmental Protection and Resources Recovery: A Systematic Review on Progress and Perspectives. Membranes 2020, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansima, M.A.C.K.; Makehelwala, M.; Jinadasa, K.B.S.N.; Wei, Y.; Nanayakkara, K.G.N.; Herath, A.C.; Weerasooriya, R. Fouling of ion exchange membranes used in the electrodialysis reversal advanced water treatment: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkessa, Y.W.; Lang, Q.; Yan, B.; Kuang, S.; Mao, D.; Shu, L.; Zhang, Y. Anion exchange membrane organic fouling and mitigation in salt valorization process from high salinity textile wastewater by bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Desalination 2019, 465, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Huang, J.; Ricard, B.; Baltaru, M.C.; Greydanus, B.; Balta, S.; Shen, J.; Vlad, M.; Sotto, A.; et al. Toward Resource Recovery from Textile Wastewater: Dye Extraction, Water and Base/Acid Regeneration Using a Hybrid NF-BMED Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wen, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, J. Zero discharge process for dyeing wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 11, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, R.; Gzara, L.; Lajimi, R.H.; Hafiane, A. Treatment of textile wastewater by a hybrid ultrafiltration/electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 132, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Catalytic ozone pretreatment of complex textile effluent using Fe2+ and zero valent iron nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Hybrid ozonation process for industrial wastewater treatment: Principles and applications: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Zeng, S.; Ouyang, Y.; Sang, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.-T.; Zhang, N. An intensified ozonation system in a tank reactor with foam block stirrer: Synthetic textile wastewater treatment and mass transfer modeling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilińska, L.; Gmurek, M. Novel trends in AOPs for textile wastewater treatment. Enhanced dye by-products removal by catalytic and synergistic actions. Water Resour. Ind. 2021, 26, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morali, E.K.; Uzal, N.; Yetis, U. Ozonation pre and post-treatment of denim textile mill effluents: Effect of cleaner production measures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmani, K.; Kherroub, D.E.; Boucherdoud, A.; Bestani, B. Removal of Ca(II) and Mg(II) hardness by ion exchange resins and soda ash for seawater pretreatment to reduce scale formation in evaporators multi-stage flash desalination. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 221, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, F.; Kabuk, H.A.; Kurt, U.; Avsar, Y.; Sari, H.; Gonullu, M.T. Evaluation of treatment and recovery of leachate by bipolar membrane electrodialysis process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 75, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzer, B. Wastewater Treatment by Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process and Evaluation of Reuse Alternatives. Ph.D. Thesis, Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa, İstanbul, Turkey, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 5–16, ISBN 10: 0875530133. [Google Scholar]
- Aydin, M.I.; Yuzer, B.; Ongen, A.; Okten, H.E.; Selcuk, H. Comparison of ozonation and coagulation decolorization methods in real textile wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 103, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properties of the Ion-Exchange Resin (Purolite C100). Available online: https://www.purolite.com/product/c100 (accessed on 11 October 2021).
- Hyder, A.G.; Morales, B.A.; Cappelle, M.A.; Percival, S.J.; Small, L.J.; Spoerke, E.D.; Rempe, S.B.; Walker, W.S. Evaluation of electrodialysis desalination performance of novel bioinspired and conventional ion exchange membranes with sodium chloride feed solutions. Membranes 2021, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Ersahin, M.E.; Ozgun, H.; Koyuncu, I. Pilot and full-scale applications of membrane processes for textile wastewater treatment: A critical review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathmann, H. Ion-Exchange Membrane Separation Processes, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 9, pp. 268–269. [Google Scholar]
- Chandramowleeswaran, M.; Palanivelu, K. Treatability studies on textile effluent for total dissolved solids reduction using electrodialysis. Desalination 2006, 201, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeman, J.J. Evaluation of electrodialysis for the treatment of a hazardous leachate. Desalination 2008, 224, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Wu, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z. Bipolar membrane electrodialysis for treatment of sodium acetate waste residue. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 154, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L.; Savadogo, O.; Paris, J. Electrochemical acidification of Kraft black liquor by electrodialysis with bipolar membrane: Ion exchange membrane fouling identification and mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 488, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Xu, X.; Tesfai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, P. Nanocomposite cation-exchange membranes for wastewater electrodialysis: Organic fouling, desalination performance, and toxicity testing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Polymer Structure | Gel Polystyrene Crosslinked with Divinylbenzene |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Spherical Beads |
| Functional Group | Sulfonic Acid |
| Ionic Form | Na+ form |
| Total Capacity (min.) | 2.0 eq/L (Na+ form) |
| Reversible Swelling, Na+ → H+ (max.) | 9% |
| Specific Gravity | 1.29 |
| Temperature Limit | 120 °C |
| Anode | Pt/Ir–Coated Titanium | |
|---|---|---|
| Cathode | V4A Steel | |
| Electrode housing material | Polypropylene | |
| Maximum current | 5A | |
| Maximum voltage | 30 V/cell | |
| Nominal flow rate | 4–8 L/h | |
| Membrane Type | Anion exchange | Cation exchange |
| Functional group | Strong basic | Strong acidic |
| Ammonium | Sulfonic acid | |
| Permselectivity KCl (0.1/0.5 N) Acid (0.7/3 N) | >0.95 | >0.95 |
| Resistivity, W.cm2 | ≈1.8 | ≈2.5 |
| Active membrane area, cm2 | 64 | 64 |
| Water content, (wt. %) | ≈14 | ≈9 |
| Max operational temperature, °C | 60 | 50 |
| Thickness, µm | 180–220 | 160–200 |
| Membrane size, mm | 110 × 110 | 110 × 110 |
| Ionic form | Cl− | Na+ |
| Parameter | Influent | BTTWW | Ozonation | BPMED |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.7 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 2.9–5.5 |
| Conductivity, mS/cm | 8.5 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 0.3–0.7 |
| Color, PtCo | 330 | 210 | 20 | 5–10 |
| COD, mg/L | 550 | 155 | 98 | 58–73 |
| TOC, mg/L | 230 | 38.5 | 32.8 | 20 |
| Alkalinity, mg/L | 1220 | 1420 | 1390 | - |
| Total Hardness, mg CaCO3/L | 570 | 550 | 545 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuzer, B.; Selcuk, H. Recovery of Biologically Treated Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Subsequent Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process. Membranes 2021, 11, 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110900
Yuzer B, Selcuk H. Recovery of Biologically Treated Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Subsequent Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):900. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110900
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuzer, Burak, and Huseyin Selcuk. 2021. "Recovery of Biologically Treated Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Subsequent Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process" Membranes 11, no. 11: 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110900
APA StyleYuzer, B., & Selcuk, H. (2021). Recovery of Biologically Treated Textile Wastewater by Ozonation and Subsequent Bipolar Membrane Electrodialysis Process. Membranes, 11(11), 900. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110900






