Rational Design and Porosity of Porous Alumina Ceramic Membrane for Air Bearing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
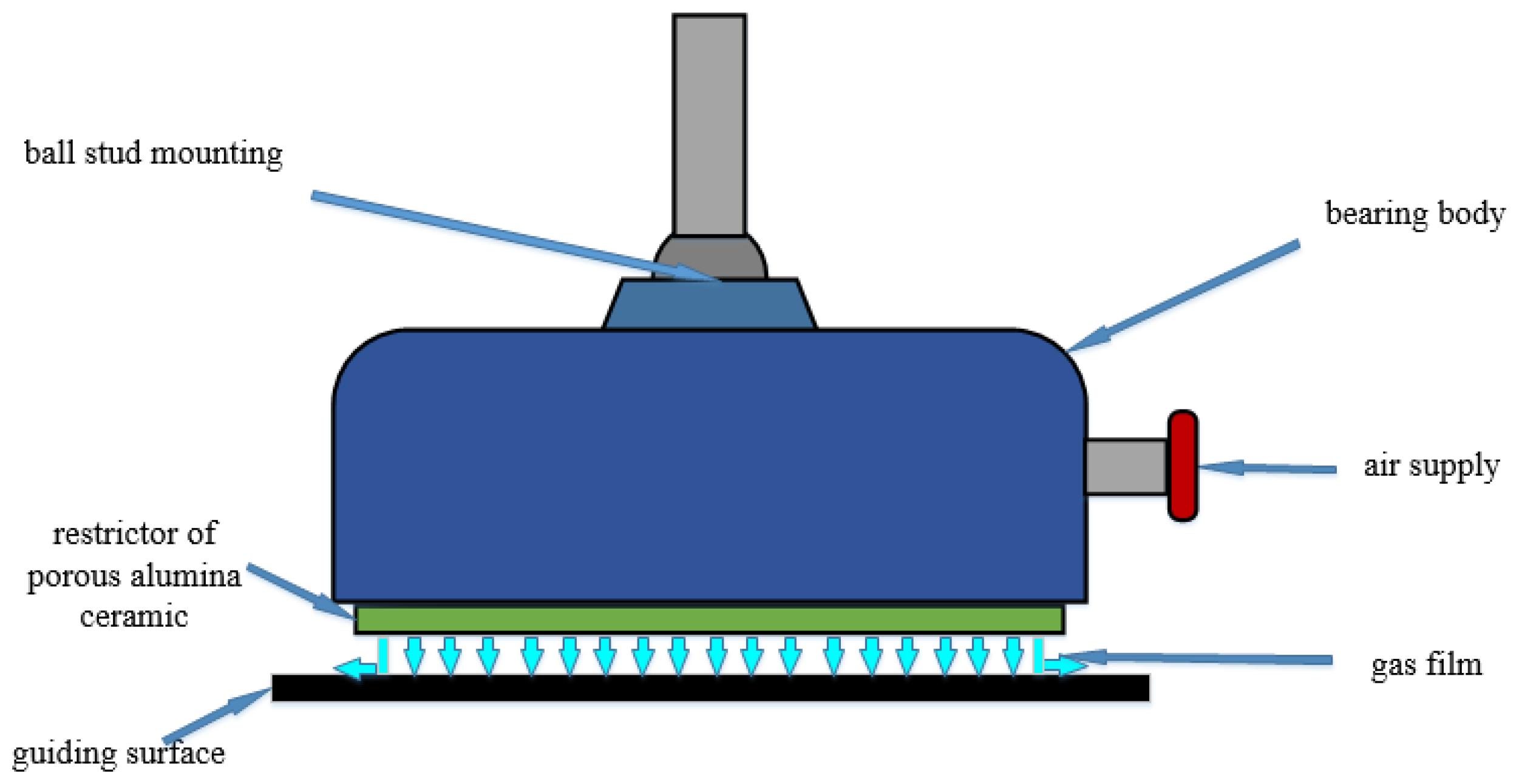
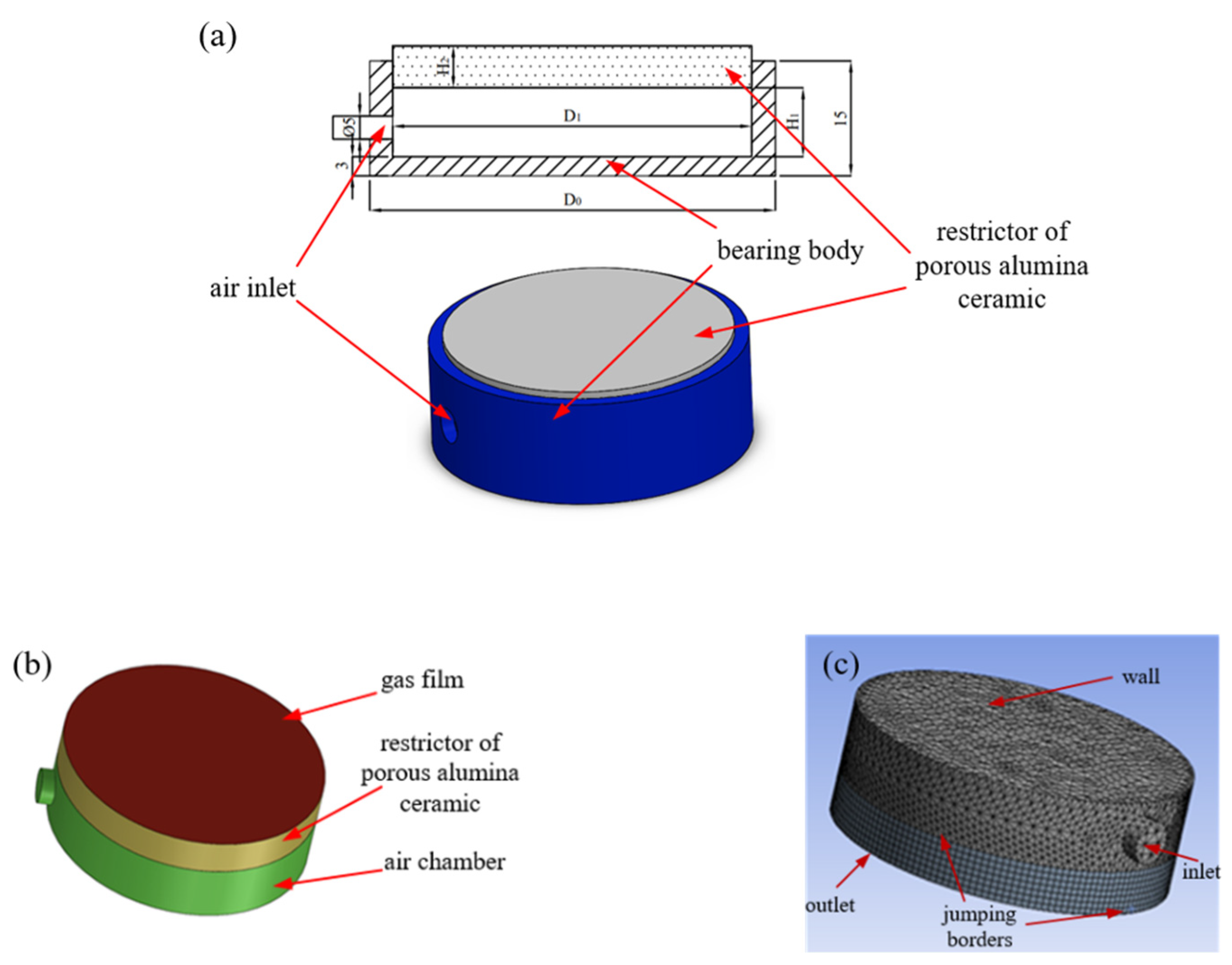
2.1. Model Configuration and Grid Meshing
- The flowing air in this simulation is a kind of ideal gas.
- The flowing gas between the air bearing and the guiding surface is laminar.
- All walls are smooth, and their damping effect on air is ignored.
- The porous alumina ceramic is isotropic, with the same permeability coefficient in all directions.
2.2. Fabrication of Porous Alumina Ceramics Membrane
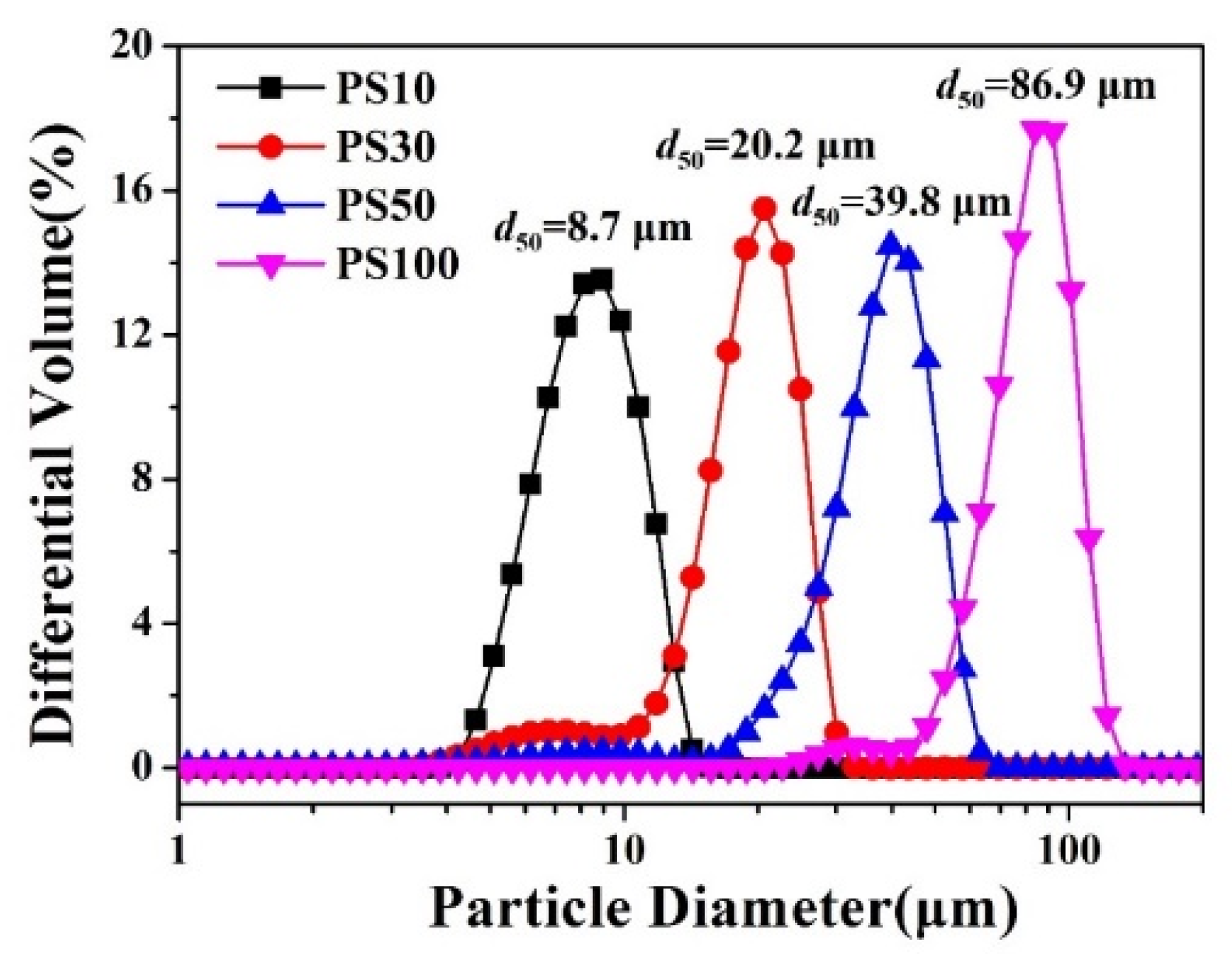
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation Analysis of Porosity
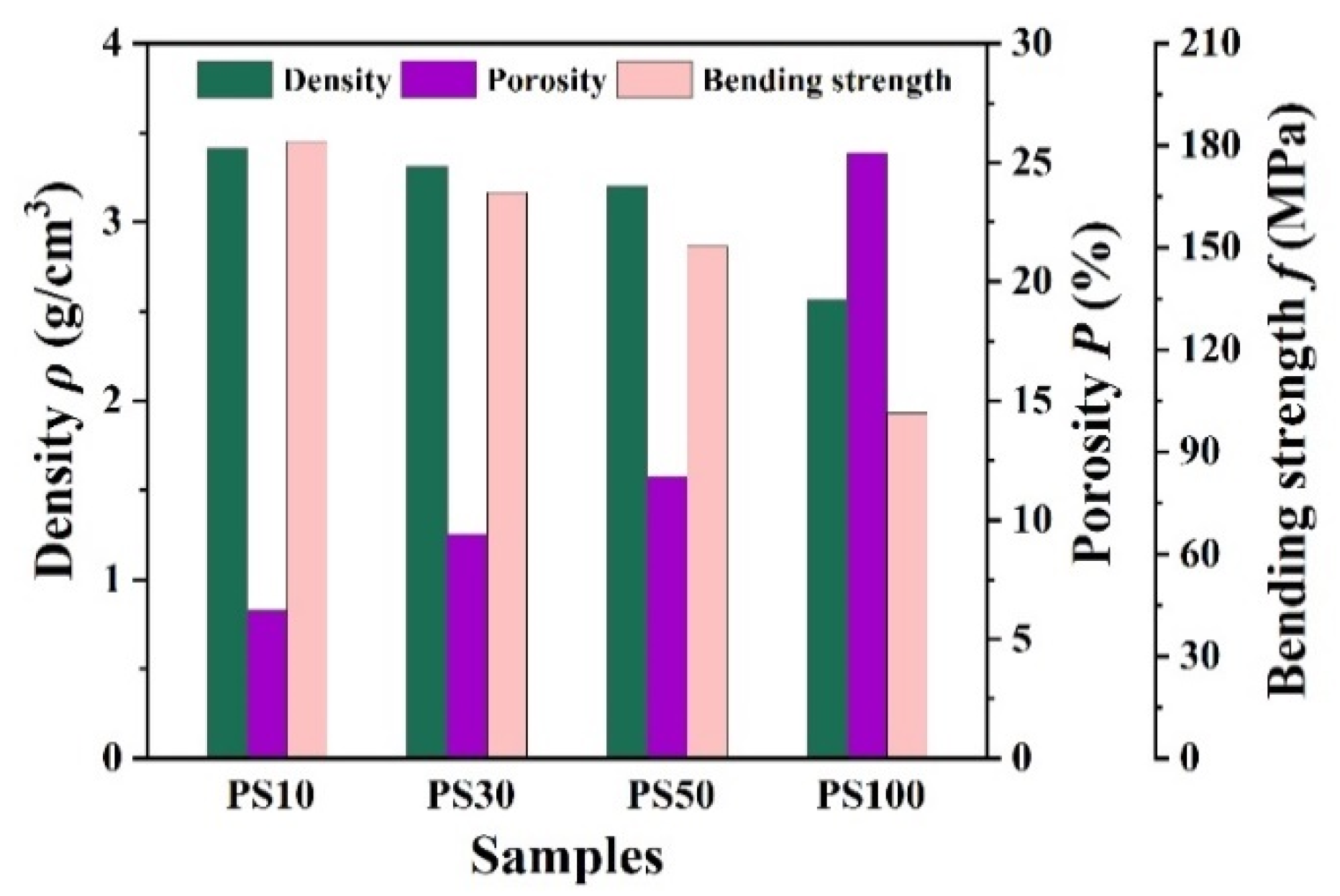
3.2. Microstructure and Performance
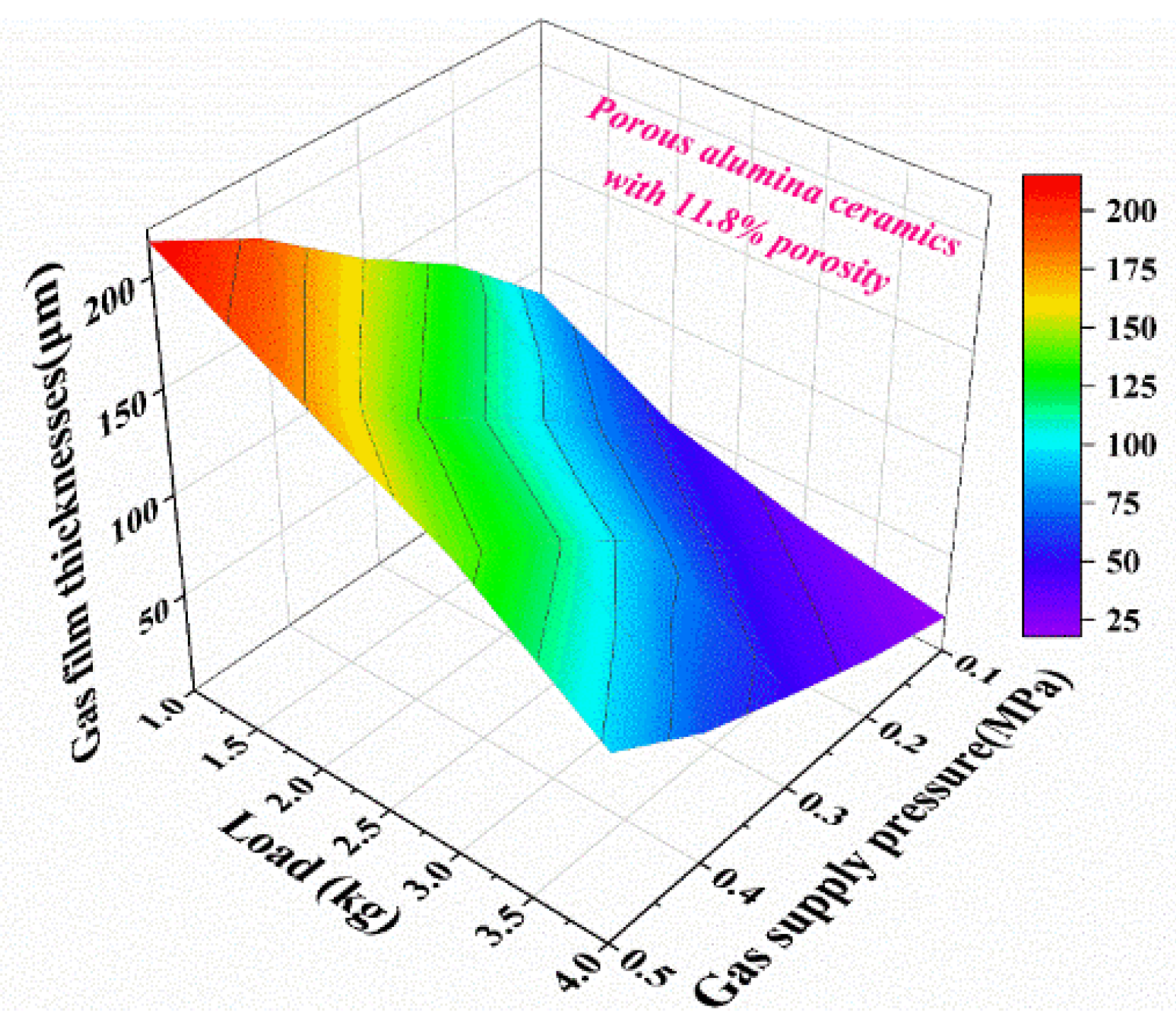
3.3. Simulation Analysis and Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, P. Accuracy prediction model of an orifice-compensated aerostatic bearing. Precis. Eng. 2021, 72, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ju, B.; Fang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yu, N.; Wan, Y. Air bearing: Academic insights and trend analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 106, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybus, T.; Seweryn, K.; Oleś, J.; Basmadji, F.L.; Tarenko, K.; Moczydłowski, R.; Barciński, T.; Kindracki, J.; Mężyk, Ł.; Paszkiewicz, P.; et al. Application of a planar air-bearing microgravity simulator for demonstration of operations required for an orbital capture with a manipulator. Acta Astronaut. 2019, 155, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.-P.; Wu, J.-W.; Tan, J.-B. An adaptive modeling method for multi-throttle aerostatic thrust bearing. Tribol. Int. 2020, 149, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Gong, W.; Cui, H. Effect of the deformation of porous materials on the performance of aerostatic bearings by fluid-solid interaction method. Tribol. Int. 2020, 150, 106391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, W. Theoretical investigation on porous tilting pad bearings considering tilting pad motion and porous material restriction. Precis. Eng. 2018, 53, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodsiyeh, D.; Colombo, F.; Lentini, L.; Raparelli, T.; Trivella, A.; Viktorov, V. An infinite stiffness aerostatic pad with a diaphragm valve. Tribol. Int. 2020, 141, 105964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zha, J. Dynamic accuracy model of porous journal air bearing considering rotational speed. Tribol. Int. 2021, 161, 107064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. A fractal method to calculate the permeability for compressible gas flow through a porous restrictor in aerostatic bearings. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 121, 437–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuyang, D.; Mingming, X. Study on static performance of gas-lubricated thrust bearing based on multi-microporous stainless steel plate. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. 2021, 43, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, R.; Cui, H. Three-dimensional flow state analysis of microstructures of porous graphite restrictor in aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 106955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, R.; de Moraes Purquerio, B.; de Castro Silveira, Z. The effect of permeability distribution on the numerical analysis of aerostatic ceramic porous bearings. Lubr. Sci. 2013, 25, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Kotobuki, M.; Kirk, C.H.; He, M.; Lim, G.J.H.; Ng, T.C.A.; Zhang, L.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, J. Overcoming the trade-off between water permeation and mechanical strength of ceramic membrane supports by interfacial engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 29199–29211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Zou, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, X.; Qiu, M.; Fan, Y. Enhanced Performance of fly ash-based supports for low-cost ceramic membranes with the addition of bauxite. Membranes 2021, 11, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X. A comparative study on the addition methods of TiO2 sintering aid to the properties of porous alumina membrane support. Membranes 2018, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishibashi, K.; Kondo, A.; Kawada, S.; Miyatake, M.; Yoshimoto, S.; Stolarski, T. Static and dynamic characteristics of a downsized aerostatic circular thrust bearing with a single feed hole. Precis. Eng. 2019, 60, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. Numerical analysis and experimental research on the angular stiffness of aerostatic bearings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, D.; Song, M.; Xie, Z.; Rao, Z.; Zou, D. Theoretical and experimental investigation on the effect of supply pressure on the nonlinear behaviors of the aerostatic bearing-rotor system. Mech. Syst. Signal Pract. 2021, 158, 107775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifei, L.; Yihui, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xinen, L.; Jun, M.; Hailong, C. Modeling for optimization of circular flat pad aerostatic bearing with a single central orifice-type restrictor based on CFD simulation. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z. Permeability of the porous Al2O3 ceramic with bimodal pore size distribution. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 5952–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee, S.; Ranjbar, K.; Kiasat, A.R. Characterization and strengthening of porous alumina-20 wt% zirconia ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, G.C.; Fortes, B.A.; Silva, L.d.; Castro, J.A.; Ribeiro, S. Evaluation of mechanical properties of porous alumina ceramics obtained using rice husk as a porogenic agent. Cerâmica 2019, 65, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, M.; Yin, X.; Cheng, L.; Ren, S.; Li, Z. Effect of core-shell microspheres as pore-forming agent on the properties of porous alumina ceramics. Mater. Des. 2017, 113, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybus, T.; Seweryn, K. Planar air-bearing microgravity simulators: Review of applications, existing solutions and design parameters. Acta Astronaut. 2016, 120, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Chen, W.; Lu, L.; Huo, D.; Cheng, K. Aerostatic bearings design and analysis with the application to precision engineering: State-of-the-art and future perspectives. Tribol. Int. 2019, 135, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raparelli, T.; Viktorov, V.; Colombo, F.; Lentini, L. Aerostatic thrust bearings active compensation: Critical review. Precis. Eng. 2016, 44, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Ng, T.C.A.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, L.; He, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, J. Highly permeable Al2O3 microfiltration membranes with holey interior structure achieved through sacrificial C particles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 103, 3361–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ng, T.C.A.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, J. Ultrathin TiO2 microfiltration membranes supported on a holey intermediate layer to raise filtration performance. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1622–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.-E.; Wang, X.; Cerneaux, S.; Zhu, L.; Dong, Y. Effect of particle size distribution of raw powders on pore size distribution and bending strength of Al2O3 microfiltration membrane supports. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



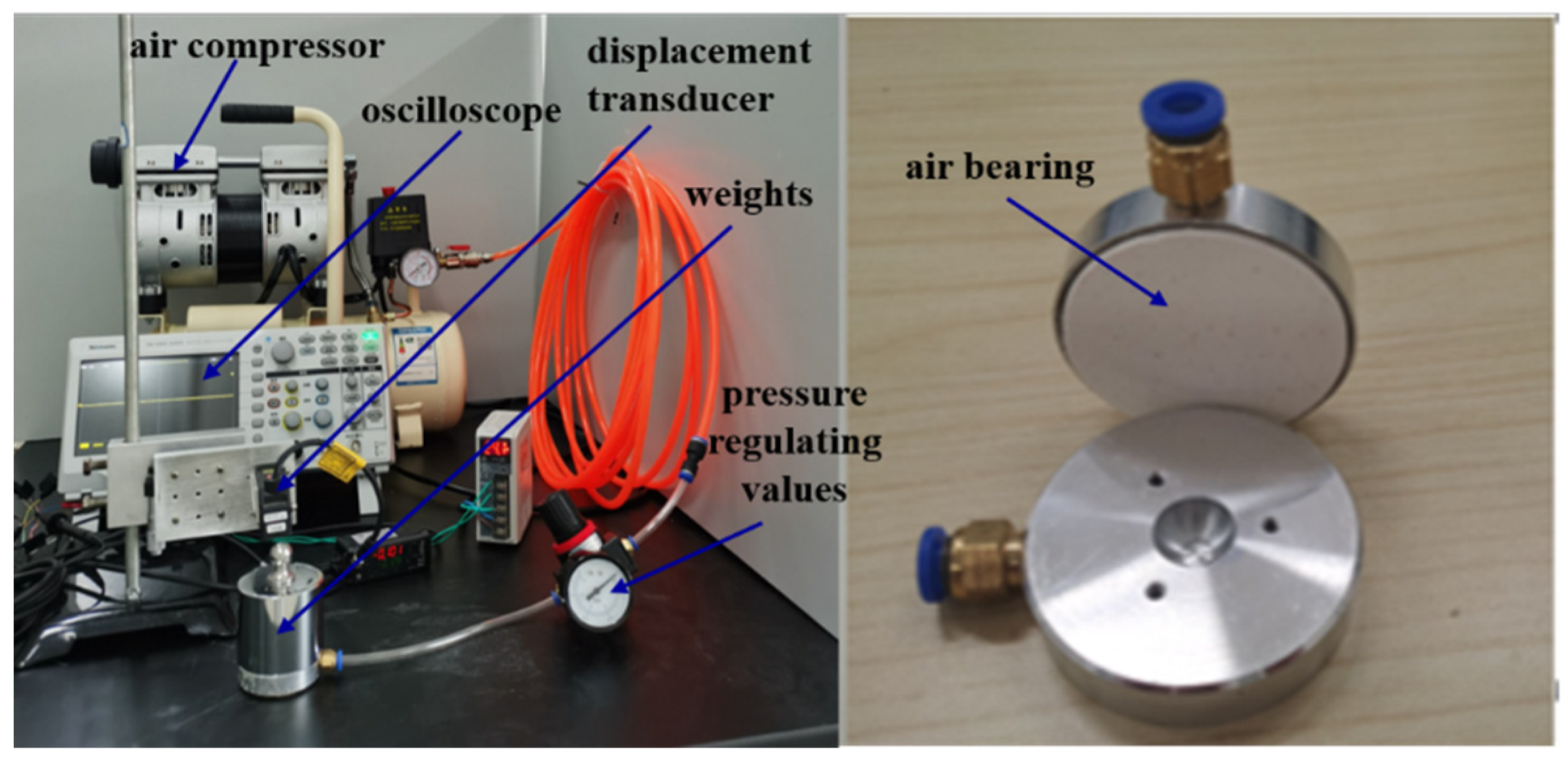
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bearing body diameter, D0 (mm) | 44 |
| Gas space depth, H1 (mm) | 8 |
| Porous medium diameter, D1 (mm) | 40 |
| Porous medium thickness, H2 (mm) | 5 |
| Film thickness, h (μm) | 25 |
| Environment temperature, T (K) | 300 |
| Gas supply pressure, Ps (MPa) | 0.5 |
| Environment stress, Po (MPa) | 0.1 |
| Dynamic viscosity of air, η (Ns/m2) | 1.7894 × 10−5 |
| Density of air, ρ (kg/m3) | 1.225 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Porous medium diameter, D1 (mm) | 40 |
| Porous medium thickness, H2 (mm) | 5 |
| Porosity, P (%) | 11.8 |
| Environment stress, Po (MPa) | 0.1 |
| Gas supply pressure, Ps (MPa) | 0.1~0.5 |
| Load, M (kg) | 1~4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, J.; Ai, D.; Xiao, X.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, K. Rational Design and Porosity of Porous Alumina Ceramic Membrane for Air Bearing. Membranes 2021, 11, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110872
Du J, Ai D, Xiao X, Song J, Li Y, Chen Y, Wang L, Zhu K. Rational Design and Porosity of Porous Alumina Ceramic Membrane for Air Bearing. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110872
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Jianzhou, Duomei Ai, Xin Xiao, Jiming Song, Yunping Li, Yuansheng Chen, Luming Wang, and Kongjun Zhu. 2021. "Rational Design and Porosity of Porous Alumina Ceramic Membrane for Air Bearing" Membranes 11, no. 11: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110872
APA StyleDu, J., Ai, D., Xiao, X., Song, J., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, L., & Zhu, K. (2021). Rational Design and Porosity of Porous Alumina Ceramic Membrane for Air Bearing. Membranes, 11(11), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110872













