Solvent and pH Stability of Poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid) (PSaMA) Membranes Prepared by Aqueous Phase Separation (APS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
2.2. Membrane Preparation
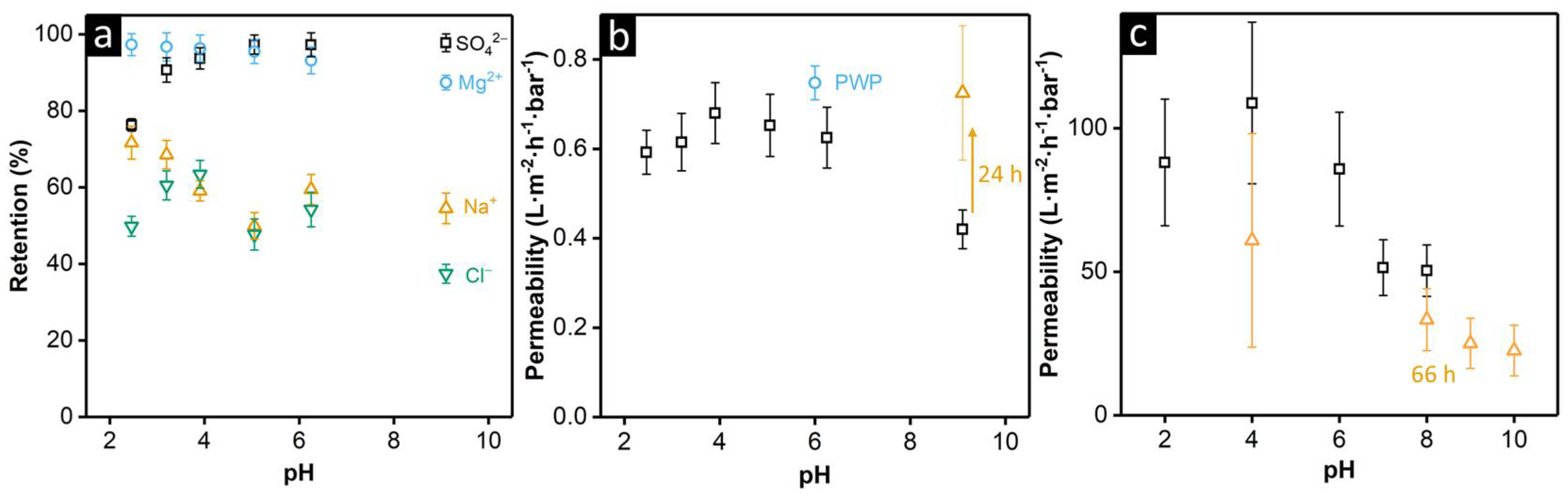
2.3. Membrane Performance Tests
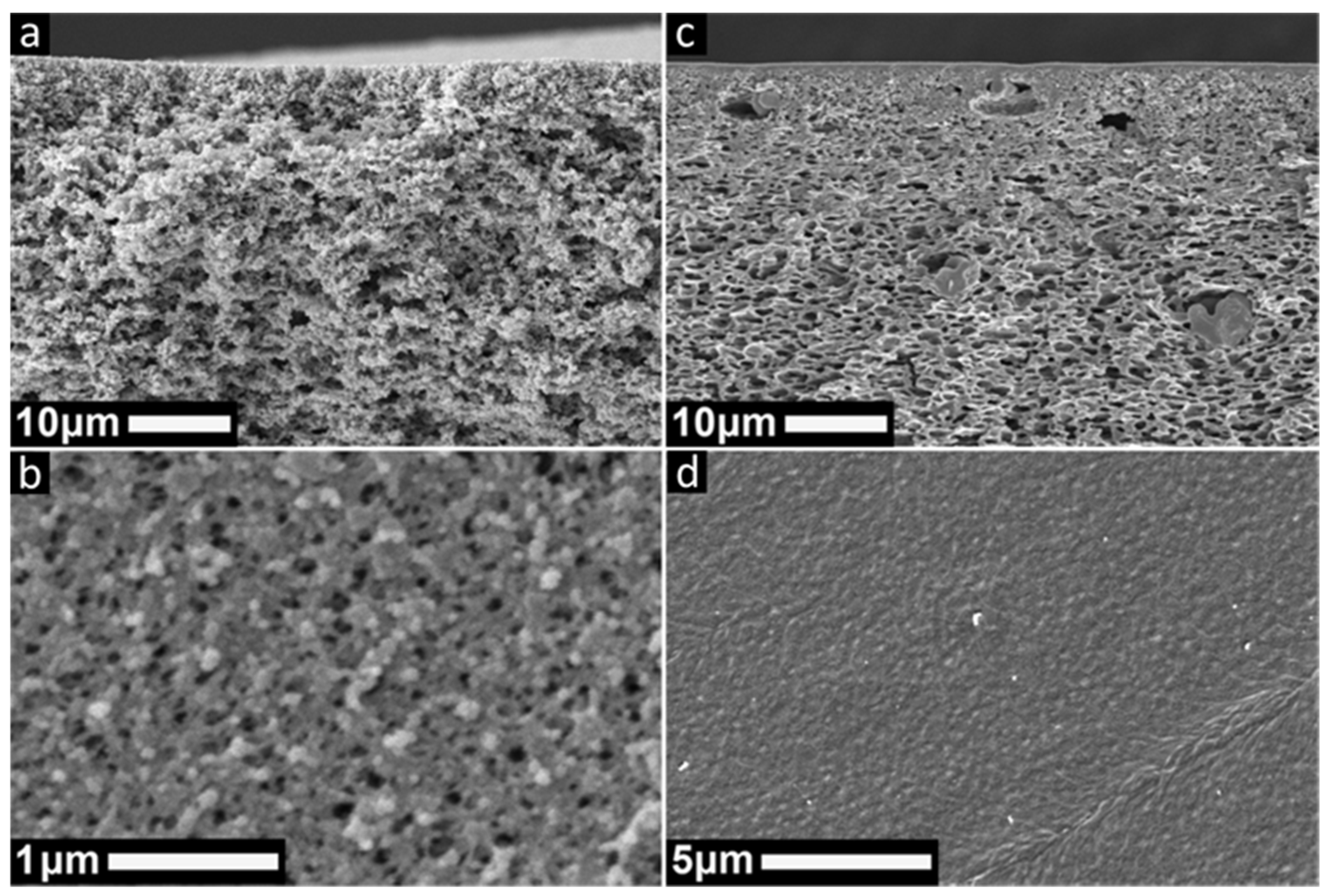
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
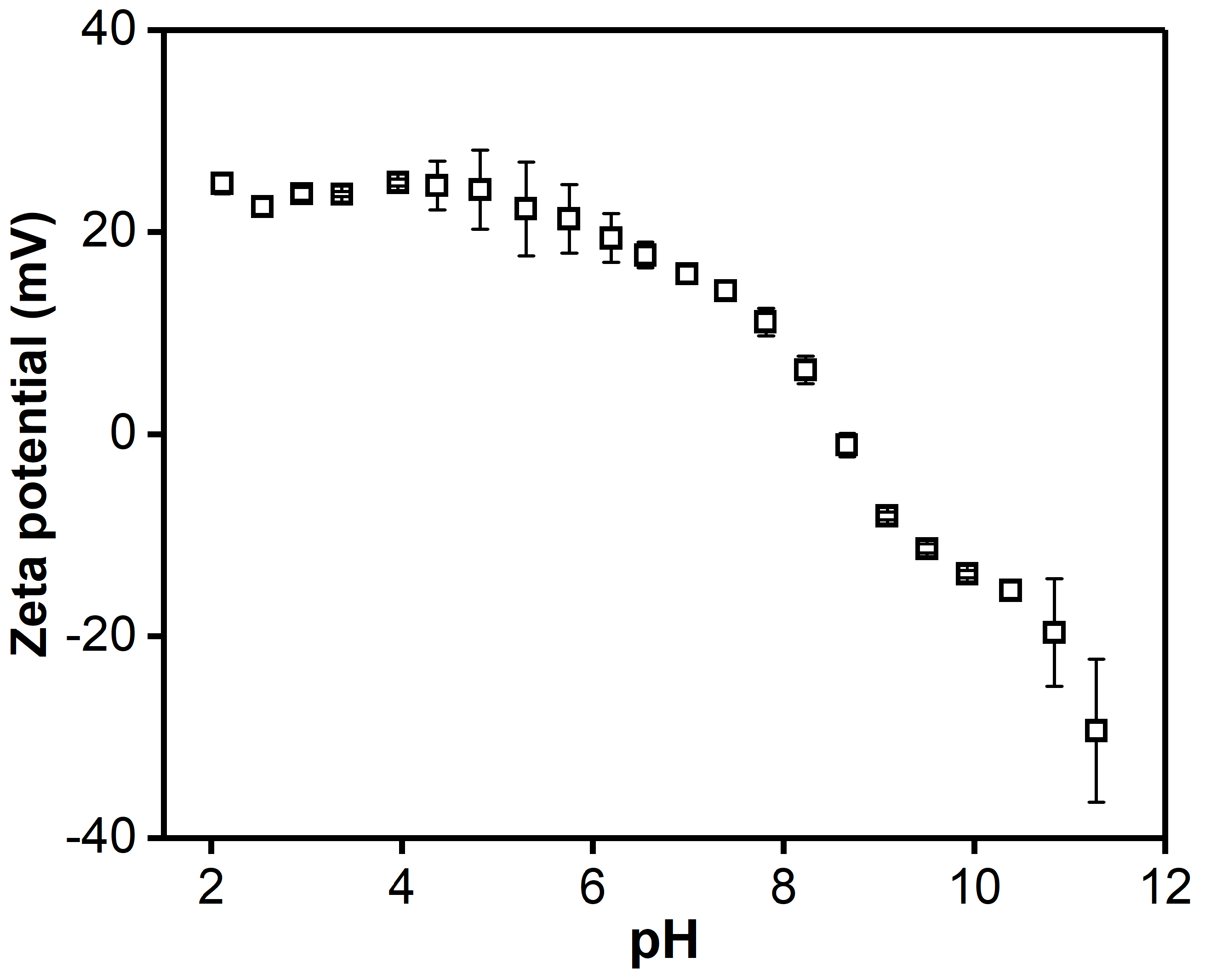
2.5. Zeta Potential
2.6. pH Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Organic Solvent Stability
3.2. pH Responsiveness and Stability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, J. Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strathmann, H.; Giorno, L.; Drioli, E. Introduction to Membrane Science and Technology; Wiley-VCH Weinheim: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The Challenge of Micropollutants in Aquatic Systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Lee, H.-S.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; McGrath, J.E.; Paul, D.R. Water purification by membranes: The role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1685–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Mariñas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. In Nanoscience and Technology; Co-Published with Macmillan Publishers Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Razali, M.; Kim, J.F.; Attfield, M.; Budd, P.M.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M.; Szekely, G. Sustainable wastewater treatment and recycling in membrane manufacturing. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5196–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, P.; Ismail, N.; Essalhi, M.; Tysklind, M.; Athanassiadis, D.; Tavajohi, N. Assessment of the environmental impact of polymeric membrane production. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 622, 118987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figoli, A.; Marino, T.; Simone, S.; Di Nicolo, E.; Li, X.M.; He, T.; Tornaghi, S.; Drioli, E. Towards non-toxic solvents for membrane preparation: A review. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nunes, S.P. Green solvents for membrane manufacture: Recent trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2020, 28, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, T.; Tiraferri, A.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A.; Crittenden, J.C.; Liu, B. Toward the Next Generation of Sustainable Membranes from Green Chemistry Principles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 50–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexowsky, C.; Bojarska, M.; Ulbricht, M. Porous poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes with tailored properties by fast and scalable non-solvent vapor induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 577, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Salazar, O.R.; Nunes, S.P. Membrane manufacture for peptide separation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, D.Y.; Peng, N.; Chung, T.-S. Formation of Cellulose Acetate Membranes via Phase Inversion Using Ionic Liquid, [BMIM]SCN, As the Solvent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 8761–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Gonzalez, Y.; Aimar, P.; Lahitte, J.F.; Remigy, J.C. Towards green membranes: Preparation of cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes using methyl lactate as a biosolvent. Int. J. Sustain. Eng. 2011, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marino, T.; Galiano, F.; Molino, A.; Figoli, A. New frontiers in sustainable membrane preparation: Cyrene™ as green bioderived solvent. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 580, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, T.; Blasi, E.; Tornaghi, S.; Di Nicolò, E.; Figoli, A. Polyethersulfone membranes prepared with Rhodiasolv® Polarclean as water soluble green solvent. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willott, J.D.; Nielen, W.M.; de Vos, W.M. Stimuli-Responsive Membranes through Sustainable Aqueous Phase Separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.I.; Durmaz, E.N.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Sustainable Membrane Production through Polyelectrolyte Complexation Induced Aqueous Phase Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrat, J.; Joanny, J. Theory of polyelectrolyte solutions. Adv. Chem. Phys. 1996, 94, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nielen, W.M.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Aqueous Phase Separation of Responsive Copolymers for Sustainable and Mechanically Stable Membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielen, W.M.; Willott, J.D.; Esguerra, Z.M.; de Vos, W.M. Ion specific effects on aqueous phase separation of responsive copolymers for sustainable membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielen, W.M.; Willott, J.D.; Galicia, J.A.R.; de Vos, W.M. Effect of Solution Viscosity on the Precipitation of PSaMA in Aqueous Phase Separation-Based Membrane Formation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Willott, J.D.; Fatima, A.; de Vos, W.M. Weak polyanion and strong polycation complex based membranes: Linking aqueous phase separation to traditional membrane fabrication. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 139, 110015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.I.; Sari, P.P.I.; Li, J.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Sustainable Aqueous Phase Separation membranes prepared through mild pH shift induced polyelectrolyte complexation of PSS and PEI. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 625, 119114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.I.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Tuning the structure and performance of polyelectrolyte complexation based aqueous phase separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 615, 118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamp, J.; Emonds, S.; Borowec, J.; Toro, M.A.R.; Wessling, M. On the organic solvent free preparation of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membranes using polyelectrolyte complexation in an all aqueous phase inversion process. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadman, K.; Delgado, D.E.; Won, Y.; Wang, Q.; Gray, K.A.; Shull, K.R. Versatile and High-throughput Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes via Phase Inversion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 16018–16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emonds, S.; Kamp, J.; Borowec, J.; Roth, H.; Wessling, M. Polyelectrolyte Complex Tubular Membranes via a Salt Dilution Induced Phase Inversion Process. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Van der Bruggen, B. Polyelectrolytes self-assembly: Versatile membrane fabrication strategy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 20870–20896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Baig, M.I.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Polyelectrolyte Complex Membranes via Salinity Change Induced Aqueous Phase Separation. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 2612–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, D.; Vijay, I.K. A method for the high efficiency of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated amidation. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 218, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanherck, K.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Crosslinking polyimides for membrane applications: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 874–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration: Separating on a molecular level. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Solomon, M.F.J.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A.G. Molecular Separation with Organic Solvent Nanofiltration: A Critical Review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbrother, F.; Mastin, H. CCCXII.—Studies in electro-endosmosis. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. Trans. 1924, 125, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybytek, J.T.; Krieger, P.A. High Purity Solvent Guide: Specifications, Applications, Physical Properties, Safety Data; Burdick Jackson Laboratories: Morristown, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, P.; Han, S.; Livingston, A.G. Solvent transport in organic solvent nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidelaar, S.; Koorengevel, M.C.; van Walree, C.A.; Dominguez, J.J.; Dörr, J.; Killian, J.A. Effect of Polymer Composition and pH on Membrane Solubilization by Styrene-Maleic Acid Copolymers. Biophys. J. 2016, 111, 1974–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Harpe, A.; Petersen, H.; Li, Y.; Kissel, T. Characterization of commercially available and synthesized polyethylenimines for gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2000, 69, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnan, F.G. Theory of membrane equilibria and membrane potentials in the presence of non-dialysing electrolytes. A contribution to physical-chemical physiology. J. Membr. Sci. 1995, 100, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroshchuk, A.E. Dielectric exclusion of ions from membranes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 85, 193–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agmon, N. The Grotthuss mechanism. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1995, 244, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nielen, W.M.; Willott, J.D.; de Vos, W.M. Solvent and pH Stability of Poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid) (PSaMA) Membranes Prepared by Aqueous Phase Separation (APS). Membranes 2021, 11, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110835
Nielen WM, Willott JD, de Vos WM. Solvent and pH Stability of Poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid) (PSaMA) Membranes Prepared by Aqueous Phase Separation (APS). Membranes. 2021; 11(11):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110835
Chicago/Turabian StyleNielen, Wouter M., Joshua D. Willott, and Wiebe M. de Vos. 2021. "Solvent and pH Stability of Poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid) (PSaMA) Membranes Prepared by Aqueous Phase Separation (APS)" Membranes 11, no. 11: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110835
APA StyleNielen, W. M., Willott, J. D., & de Vos, W. M. (2021). Solvent and pH Stability of Poly(styrene-alt-maleic acid) (PSaMA) Membranes Prepared by Aqueous Phase Separation (APS). Membranes, 11(11), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110835






