Developing a Thin Film Composite Membrane with Hydrophilic Sulfonated Substrate on Nonwoven Backing Fabric Support for Forward Osmosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
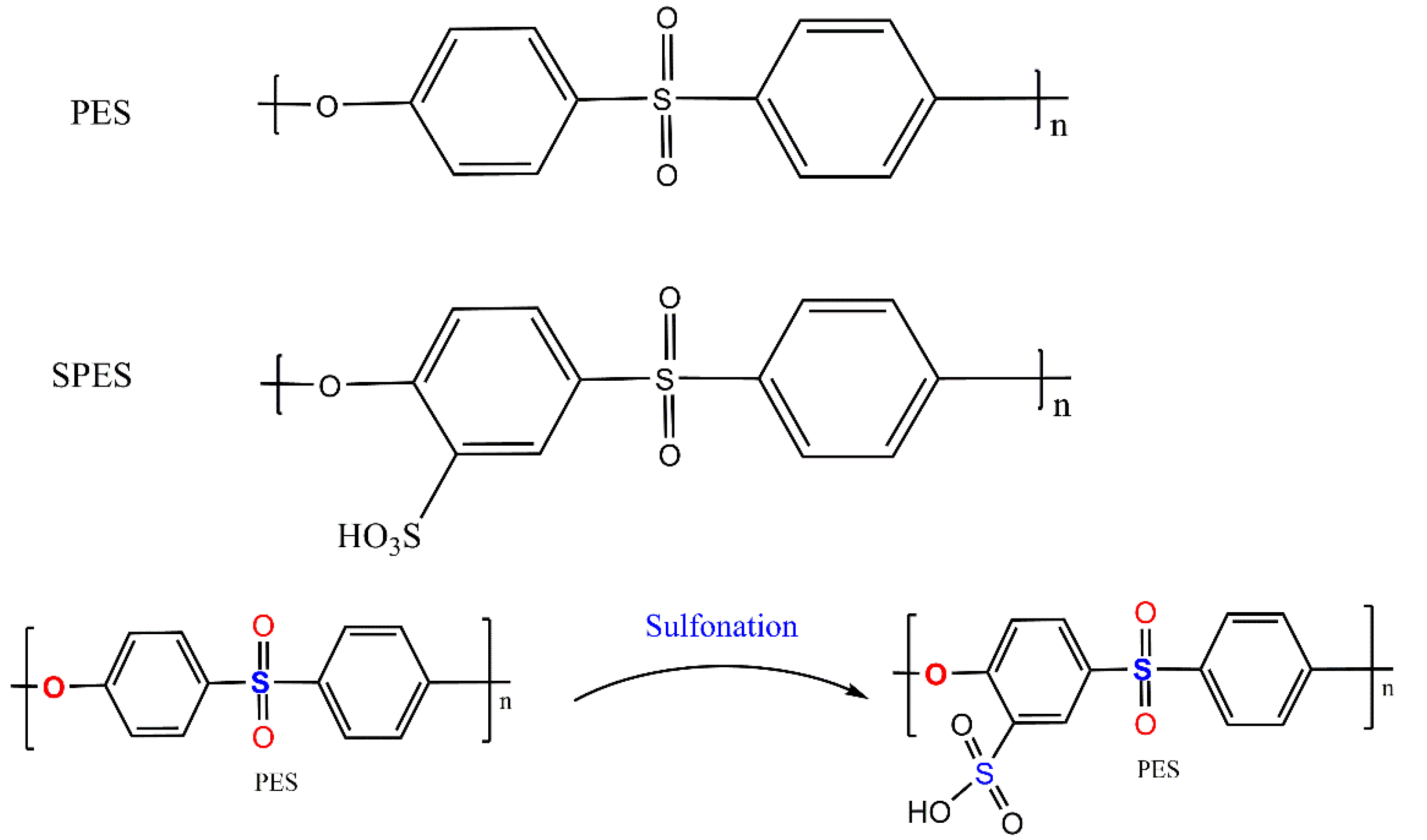
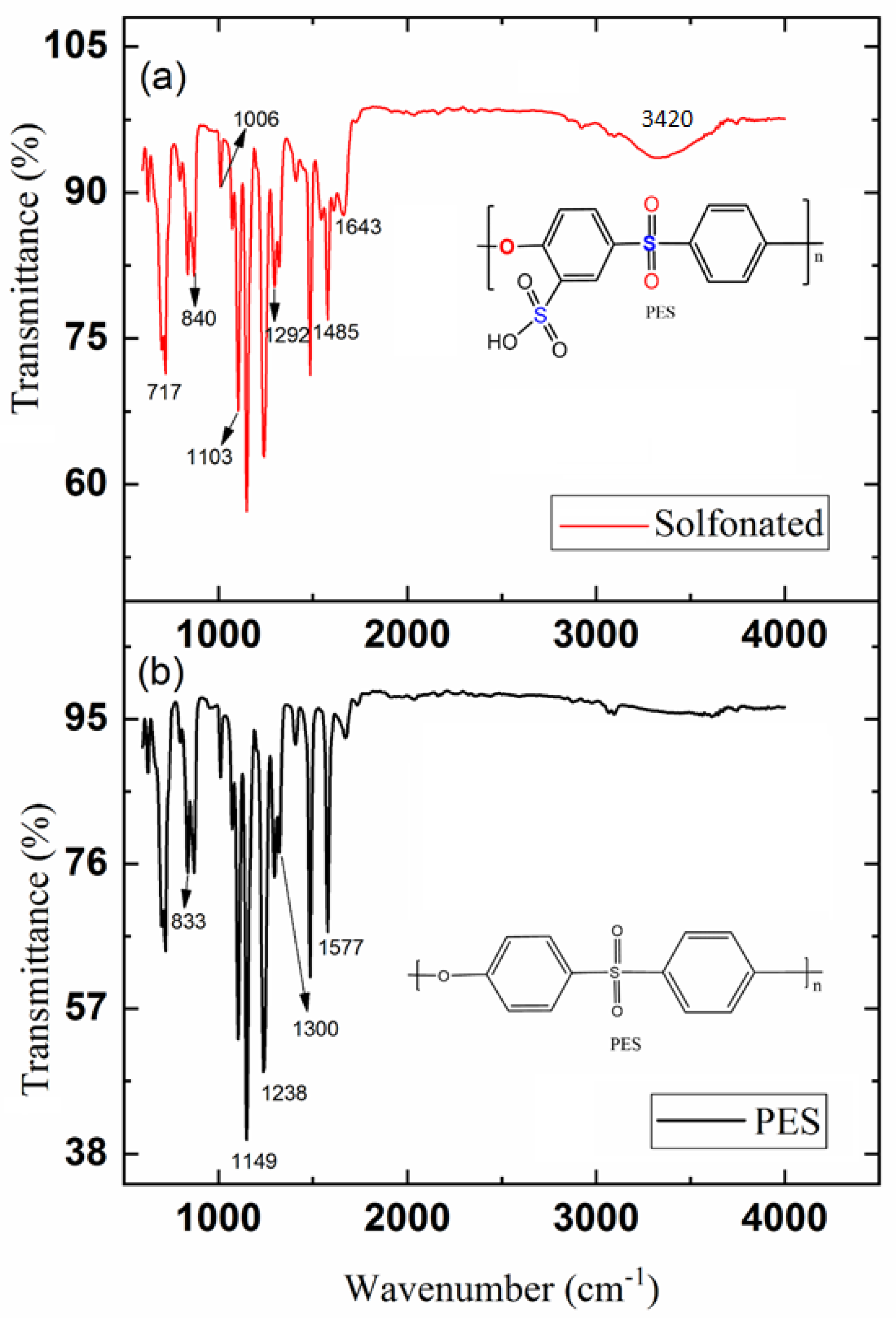
2.2. Preparing of Sulfonated Polyethersulfone (SPES)
2.3. FO membrane Substrates Fabrication via Phase Inversion
2.4. Fabrication of Polyamide (PA) Rejection Layer
2.5. Membrane Characterization
Thin-Film Composite Membrane Characterization
2.6. TFC-FO Performance Tests
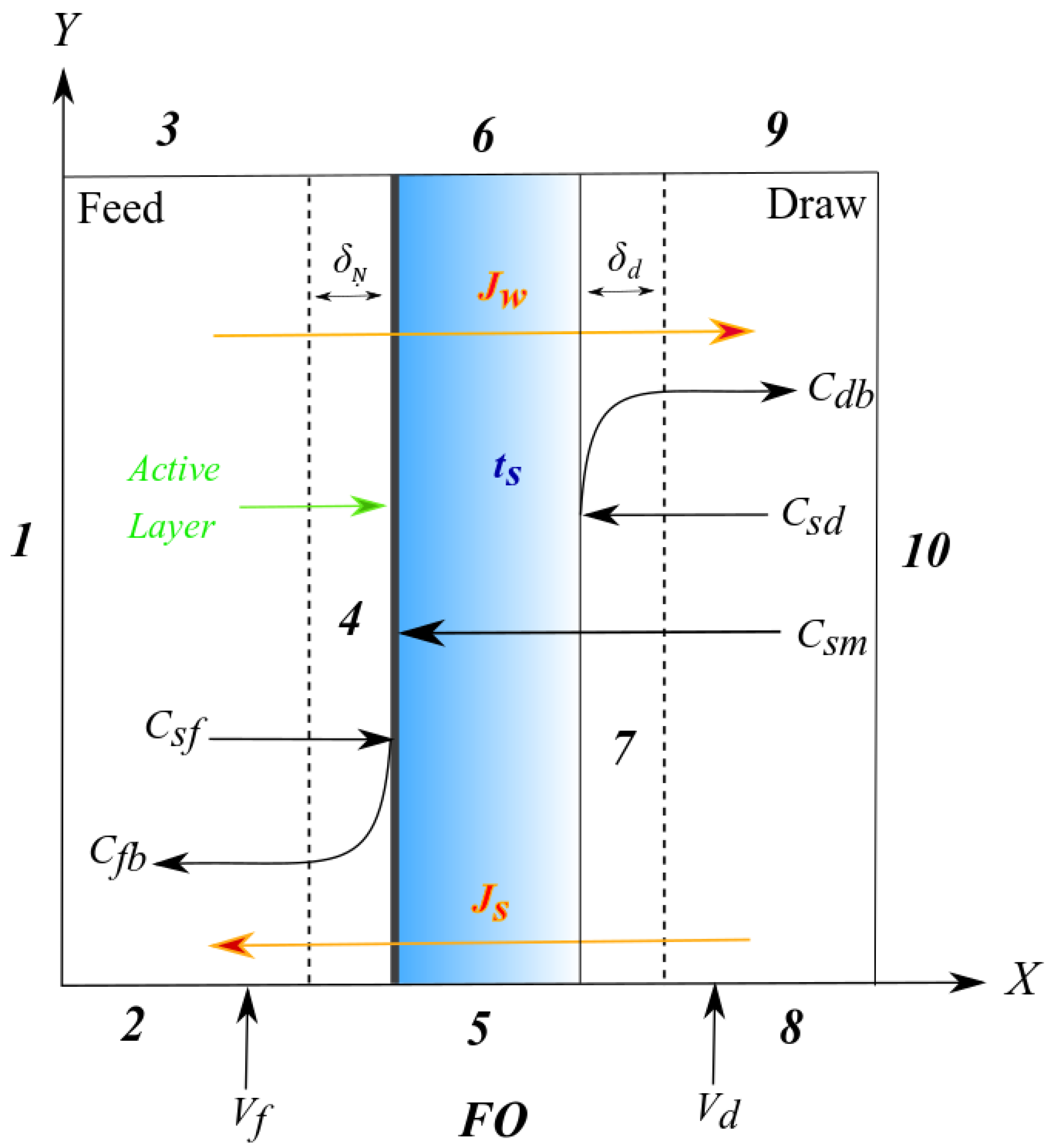
2.7. Model Development
Governing Equations
- Steady-state;
- Isothermal conditions;
- Flow is incompressible and the laminar flow on the draw and feed solution channels; and
- Thermodynamic equilibrium at the interface of the active layer.
3. Results and Discussion
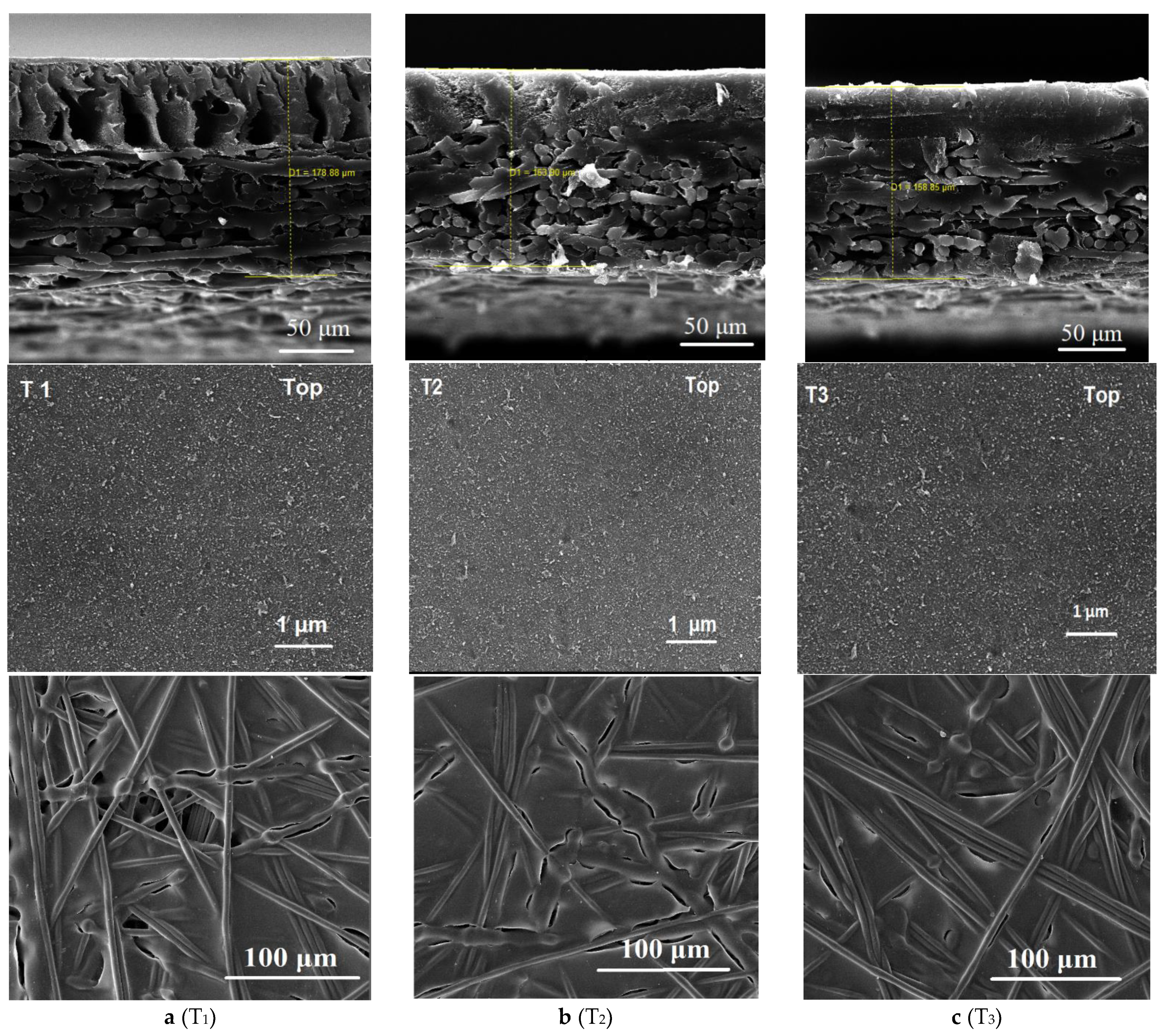
3.1. Sulfonated Membrane Substrate Characterization
3.2. Characterization of TFC FO Membranes
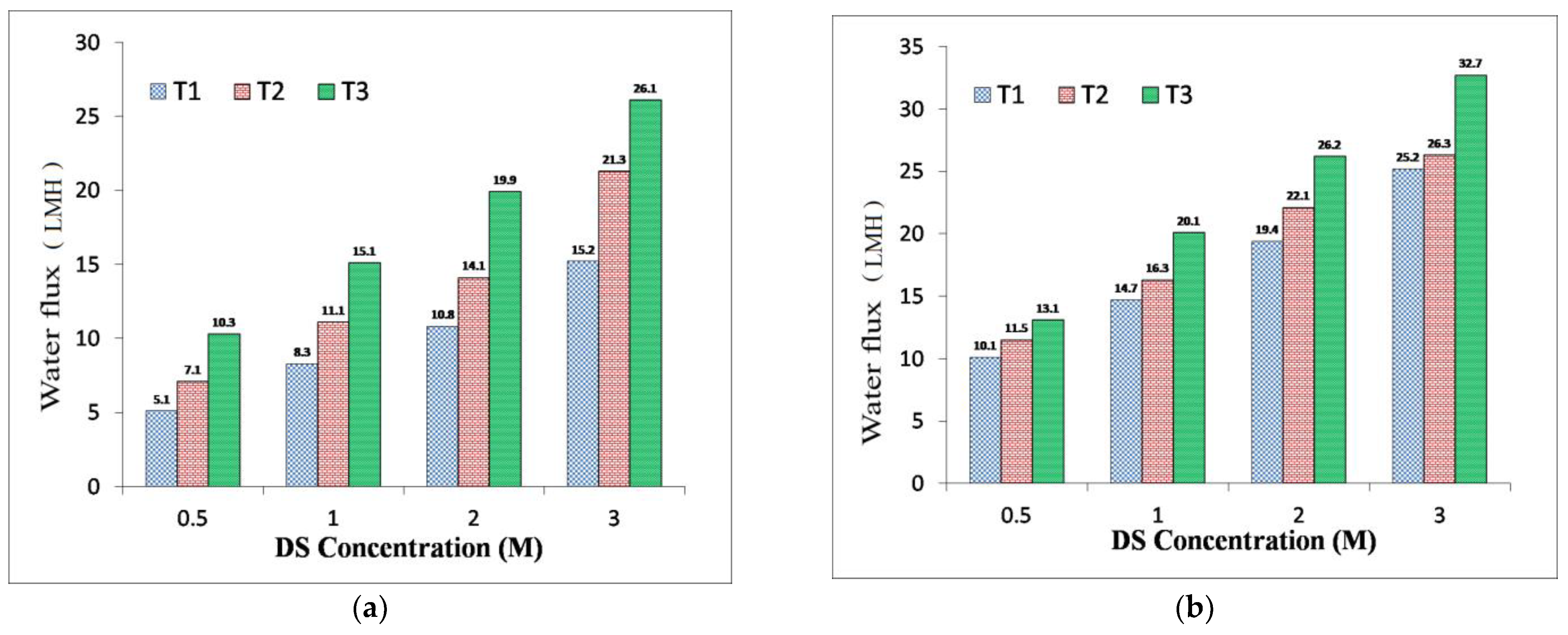
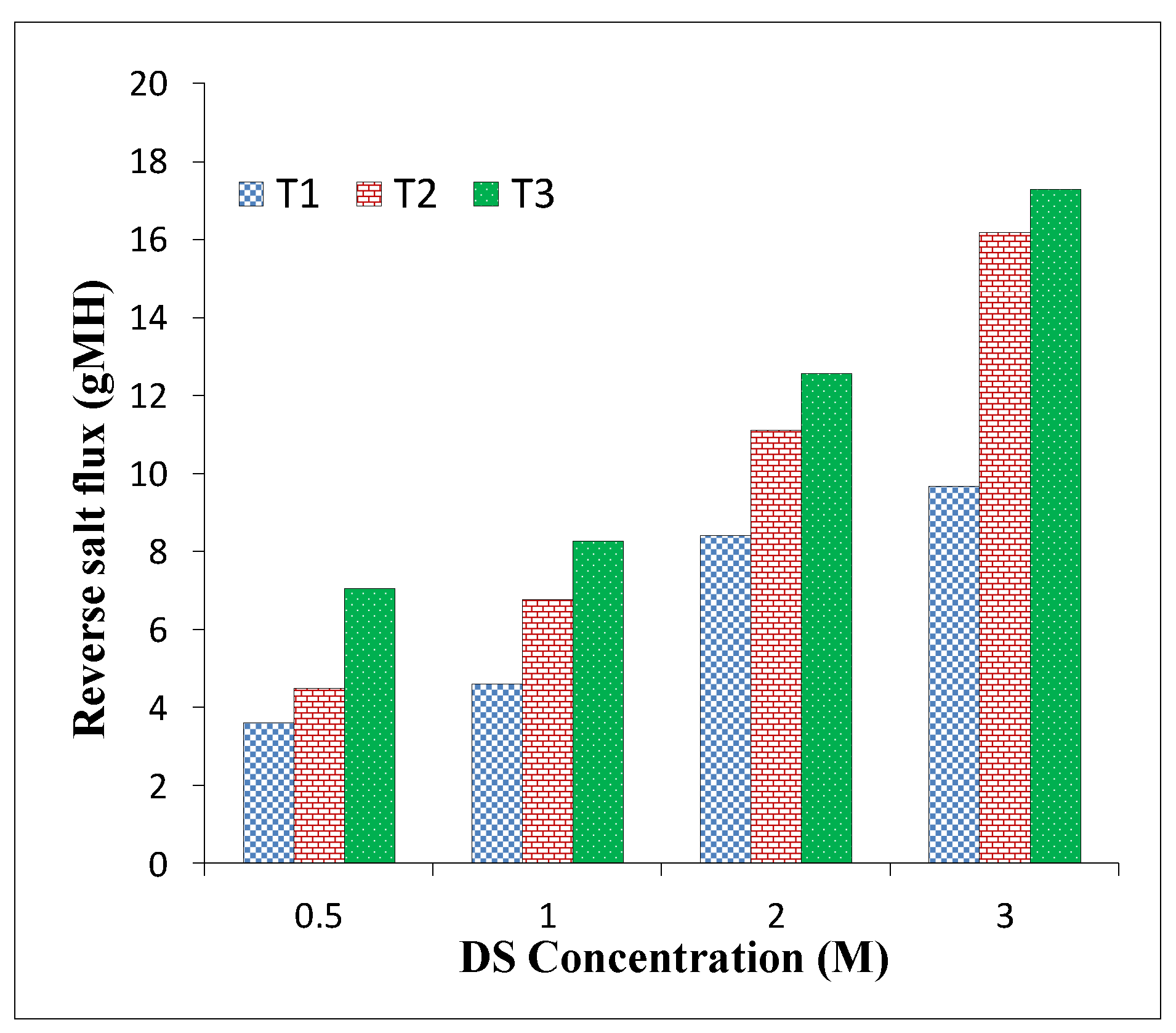
3.3. TFC FO Membranes Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuntsho, S.; Sahebi, S.; Majeed, T.; Lotfi, F.; Kim, J.E.; Shon, H.K. Assessing the major factors affecting the performances of forward osmosis and its implications on the desalination process. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.E.; Hong, S.; Shon, H.K. Pressure assisted fertiliser drawn osmosis process to enhance final dilution of the fertiliser draw solution beyond osmotic equilibrium. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M. Energy requirements of ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 207, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Adham, S.; Han, D.S.; Phuntsho, S.; Suwaileh, W.; Hilal, N.; Shon, H.K. Salinity gradient energy generation by pressure retarded osmosis: A review. Desalination 2021, 500, 114841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdali, Z.; Sahebi, S.; Mousazadeh, M.; Jamali, H.A. Optimization of the Forward Osmosis Process Using Aquaporin Membranes in Chromium Removal. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Tijing, L.; Han, G.; Han, D.S.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Shon, H.K. Thin-film composite membrane on a compacted woven backing fabric for pressure assisted osmosis. Desalination 2017, 406, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, M.J.; Gonzales, R.R.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Hydrophilic polyvinyl alcohol coating on hydrophobic electrospun nanofiber membrane for high performance thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2018, 426, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Darwish, N.A.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N. Water desalination by forward (direct) osmosis phenomenon: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2015, 374, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.T.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis: Role of membrane orientation. Desalination 2006, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C.; Warzelhan, V. The role of sulphonated polymer and macrovoid-free structure in the support layer for thin-film composite (TFC) forward osmosis (FO) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Synthesis and characterization of flat-sheet thin film composite forward osmosis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 372, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3812–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Tang, C.Y.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Characteristics and potential applications of a novel forward osmosis hollow fiber membrane. Desalination 2010, 261, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Chou, S.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Characterization of novel forward osmosis hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 355, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadpour, S.; Tavakol, I.; Shabani, Z.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A.; Sahebi, S.J.J.o.E.C.E. Synthesis and characterization of novel thin film composite forward osmosis membrane using charcoal-based carbon nanomaterials for desalination application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L. Relating solution physicochemical properties to internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Park, M.J.; Bae, T.-H.; Yang, Y.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Melamine-based covalent organic framework-incorporated thin film nanocomposite membrane for enhanced osmotic power generation. Desalination 2019, 459, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaileh, W.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Sarp, S.; Hilal, N.J.D. Advances in forward osmosis membranes: Altering the sub-layer structure via recent fabrication and chemical modification approaches. Desalination 2018, 436, 176–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadaie, N.; Sheikhi, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Tofighy, M.A.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Sahebi, S. Novel Plasma Functionalized Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNPs) incorporated in forward osmosis substrate with improved performance and tensile strength. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Wang, C.; Seo, D.H.; Gonzales, R.R.; Matsuyama, H.; Shon, H.K. Inkjet printed single walled carbon nanotube as an interlayer for high performance thin film composite nanofiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S.; Phuntsho, S.; Woo, Y.C.; Park, M.J.; Tijing, L.D.; Hong, S.; Shon, H.K. Effect of sulphonated polyethersulfone substrate for thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2016, 389, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, M.; Mirshekar, L.; Kamarehie, B.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Ramavandi, B.; Amini, F.; Fadaie, N.; Sahebi, S.J.C.E. Thin-Film Composite Forward-Osmosis Membranes Reinforced on Woven Mesh and Nonwoven Backing Fabric Supports. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Saleem, H.; Ibrar, I.; Naji, O.; Hawari, A.A.; Alanezi, A.A.; Zaidi, S.J.; Altaee, A.; Zhou, J. Recent developments in forward osmosis membranes using carbon-based nanomaterials. Desalination 2020, 482, 114375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Fang, Z.; Ng, D.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Thin-film composite membrane with interlayer decorated metal–organic framework UiO-66 toward enhanced forward osmosis performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhao, S.; Ng, D.; Xie, Z. Dopamine Incorporated Forward Osmosis Membranes with High Structural Stability and Chlorine Resistance. Processes 2018, 6, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Yang, Y.; Park, M.J.; Bae, T.-H.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Enhanced water permeability and osmotic power generation with sulfonate-functionalized porous polymer-incorporated thin film nanocomposite membranes. Desalination 2020, 496, 114756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liang, S.; Qiu, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Q. Thin film nanocomposite forward osmosis membranes based on layered double hydroxide nanoparticles blended substrates. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 504, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, R.R.; Zhang, L.; Sasaki, Y.; Kushida, W.; Matsuyama, H.; Shon, H.K. Facile development of comprehensively fouling-resistant reduced polyketone-based thin film composite forward osmosis membrane for treatment of oily wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 626, 119185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, J.; Shabani, Z.; Mohammadi, T.; Sahebi, S. Enhanced performance and fouling resistance of cellulose acetate forward osmosis membrane with the spatial distribution of TiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Seynaeve, M.; Bastin, M.; Davenport, D.M.; Eyley, S.; Thielemans, W.; Koeckelberghs, G.; Elimelech, M.; Vankelecom, I.F. The significant role of support layer solvent annealing in interfacial polymerization: The case of epoxide-based membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Gorgojo, P.; Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Livingston, A.G. Beneath the surface: Influence of supports on thin film composite membranes by interfacial polymerization for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Lau Jr, V.; Ji, Y.-L.; Huang, S.-H.; An, Q.-F.; Caparanga, A.R.; Tsai, H.-A.; Hung, W.-S.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.J.P. Correlating PSf support physicochemical properties with the formation of piperazine-based polyamide and evaluating the resultant nanofiltration membrane performance. Polymers 2017, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, S.; Shi, W.; Zhu, J.; Van der Bruggen, B.J.S.; Technology, P. Support membrane pore blockage (SMPB): An important phenomenon during the fabrication of thin film composite membrane via interfacial polymerization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.S.; Joshi, S.; Trivedi, J.; Devmurari, C.; Rao, A.P.; Ghosh, P.J. Probing the structural variations of thin film composite RO membranes obtained by coating polyamide over polysulfone membranes of different pore dimensions. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Chung, T.-S.; Toriida, M.; Tamai, S. Thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes with novel hydrophilic supports for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 423-424, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Krantz, W.B.; Chung, T.S. A novel primer to prevent nanoparticle agglomeration in mixed matrix membranes. AIChE J. 2007, 53, 2470–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chng, M.L.; Chung, T.-S.; Toriida, M.; Tamai, S.; Chen, H.; Jean, Y.J. Asymmetric structure and enhanced gas separation performance induced by in situ growth of silver nanoparticles in carbon membranes. Carbon 2010, 48, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiraferri, A.; Yip, N.Y.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M.J. Relating performance of thin-film composite forward osmosis membranes to support layer formation and structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 367, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukitpaneenit, P.; Chung, T.-S. Molecular elucidation of morphology and mechanical properties of PVDF hollow fiber membranes from aspects of phase inversion, crystallization and rheology. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 340, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, X. A low-cost and high-performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane based on an SPSU/PVC substrate. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeb, S.; Titelman, L.; Korngold, E.; Freiman, J. Effect of porous support fabric on osmosis through a Loeb-Sourirajan type asymmetric membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 129, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrizi, M.; Kasiri, N.; Mohammadi, T.; Zhao, S. Introducing sorption coefficient through extended UNIQAC and Flory-Huggins models for improved flux prediction in forward osmosis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 198, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, Z.; Kahrizi, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Kasiri, N.; Sahebi, S. A novel Thin film composite forward osmosis membrane using bio-inspired polydopamine coated polyvinyl chloride substrate: Experimental and computational fluid dynamics modelling. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 756–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Kant, J.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Smolders, C.A. Phase separation phenomena in solutions of polysulfone in mixtures of a solvent and a nonsolvent: Relationship with membrane formation. Polymer 1985, 26, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widjojo, N.; Chung, T.-S.; Weber, M.; Maletzko, C.; Warzelhan, V. A sulfonated polyphenylenesulfone (sPPSU) as the supporting substrate in thin film composite (TFC) membranes with enhanced performance for forward osmosis (FO). Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, M.; Bhattacharjee, S. Rational design of phase inversion membranes by tailoring thermodynamics and kinetics of casting solution using polymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 441, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, H.F.; Kroschwitz, J.I. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Engineering; Wiley: Hioboken, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.; Choi, J.; Tak, T. Sulfonated polyethersulfone by heterogeneous method and its membrane performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 2046–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.; Zou, H.; Lu, D.; Gong, C.; Liu, Y. Polyethersulfone sulfonated by chlorosulfonic acid and its membrane characteristics. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S.; Sheikhi, M.; Ramavandi, B. A new biomimetic aquaporin thin film composite membrane for forward osmosis: Characterization and performance assessment. Desalin. Water Treat 2019, 148, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, R.R.; Peyravi, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Amiri, A.A.Q. Decreasing ICP of forward osmosis (TFN-FO) membrane through modifying PES-Fe3O4 nanocomposite substrate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 2311–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrizi, M.; Lin, J.; Ji, G.; Kong, L.; Song, C.; Dumée, L.F.; Sahebi, S.; Zhao, S. Relating forward water and reverse salt fluxes to membrane porosity and tortuosity in forward osmosis: CFD modelling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S. Developing Thin Film Composite Membranes for Engineered Osmosis Processes. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sahebi, S.; Fadaie, N.; Mirshekar, L.; Kamarehie, B.; Mohammadi, T. Assessing biomimetic aquaporin membrane for forward osmosis desalination process: A dataset. Data Brief 2019, 26, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cath, T.Y.; Elimelech, M.; McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Achilli, A.; Anastasio, D.; Brady, A.R.; Childress, A.E.; Farr, I.V.; Hancock, N.T. Standard methodology for evaluating membrane performance in osmotically driven membrane processes. Desalination 2013, 312, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; McCutcheon, J.R. A new commercial thin film composite membrane for forward osmosis. Desalination 2014, 343, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, R.C.; Chung, T.-S.; de Wit, J.S.; Helmer, B.J. Novel cellulose ester substrates for high performance flat-sheet thin-film composite (TFC) forward osmosis (FO) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebi, S.; Sheikhi, M.; Ramavandi, B.; Zhao, S.; Baniasadi, J.; Fadaie, N.; Mohammadi, T.J.C.E.R. Developing novel thin film composite membrane on a permeate spacer backing fabric for forward osmosis. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 160, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; McGinnis, R.L.; Elimelech, M.J. Desalination by ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis: Influence of draw and feed solution concentrations on process performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.H.; Ng, H.Y. Modified models to predict flux behavior in forward osmosis in consideration of external and internal concentration polarizations. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | Solution Composition | Sulfonated Polymer Content (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES (wt %) | NMP (wt %) | SPES (wt %) | ||
| T1 | 15 | 85 | 0 | 0 |
| T2 | 10 | 85 | 5 | 25 |
| T3 | 7.5 | 85 | 7.5 | 50 |
| BC No. | NS–Feed | CD–Feed | Brinkman—Porous | CD–Porous | NS–Draw | CD–Draw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 3 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 4 | - | - | ||||
| 5 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 6 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 7 | - | - | ||||
| 8 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 9 | - | - | - | - | ||
| 10 | - | - | - | - |
| Membrane ID | Thickness (µm) | Porosity (%) | Contact Angle (°) | Mechanical Properties (with Backing Fabric) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Modulus (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | ||||
| T1 | 178 ± 2.0 | 71 ± 2 | 65 ± 1 | 42.1 | 115.2 | 39.2 |
| T2 | 163 ± 3.0 | 77 ± 3 | 45 ± 1 | 36.1 | 82.2 | 36.2 |
| T3 | 158 ± 2.0 | 82 ± 2 | 35 ± 2 | 33.2 | 55.6 | 43.3 |
| Sample ID | a Water permeability (A) | b Salt Permeability B (10−7 m/s) | NaCl Rejection (%) | c S (×10−4 m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMH bar−1 | ×10−12 m/s Pa | ||||
| T1 | 1.62 ± 0.15 | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 96.5 | 10.9 |
| T2 | 2.21 ±0.1 | 6.13 ± 0.5 | 3.59 ± 0.1 | 94.1 | 7.84 |
| T3 | 3.15 ±0.15 | 8.75 ± 0.5 | 6.25 ± 0.15 | 92.8 | 5.91 |
| Membrane ID | FO Mode | PRO Mode | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Flux (LMH) | RSF (gMH) | SRSF (g/L) | Water Flux (LMH) | RSF (gMH) | SRSF (g/L) | |
| T1 | 10.8 | 8.4 | 0.65 | 19.4 | 11.1 | 0.57 |
| T2 | 14.1 | 11.1 | 0.78 | 22.1 | 14.7 | 0.66 |
| T3 | 19.9 | 12.55 | 0.63 | 26.2 | 16.8 | 0.64 |
| Membrane Types/Materials/Support Fabric | Water Flux (LMH) | Specific Reverse Salt Flux (g/L) | DS NaCl (M) | FS | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FO Mode | PRO Mode | FO Mode | PRO Mode | ||||||
| TFC flat-sheet (HTI) | Psf | Polyester mesh | 16.8 | 33.1 | 0.44 | 0.55 | 1.0 | DI | [59] |
| TFC flat-sheet (HTI) | Psf | Polyester mesh | 13.0 | N/A | 0.81 | N/A | 2.0 | DI | [14] |
| TFC flat-sheet membrane | CE 1 | N/A | 37.6 | N/A | 0.17 | N/A | 1.0 | DI | [60] |
| TFC flat-sheet membrane | Psf | N/A | 12.0 | 20.5 | 0.40 | 0.31 | 1.0 | 10 mM NaCl | [13] |
| TFC flat-sheet membrane | Psf | PET nonwoven | 15.1 | N/A | - | - | 1.0 | DI | [14] |
| * TFC PAO 2 | PES | Compacted woven mesh | 16.1 | - | 0.43 | - | 0.5 | DI | [8] |
| TFC FO | PES | Permeate spacer fabric | 17.1 | 21.0 | 0.47 | 0.46 | 2.0 | DI | [61] |
| TFC FO | PES | Nonwoven PET fabric | 19.9 | 26.2 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 2.0 | DI | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sahebi, S.; Kahrizi, M.; Fadaie, N.; Hadadpour, S.; Ramavandi, B.; Gonzales, R.R. Developing a Thin Film Composite Membrane with Hydrophilic Sulfonated Substrate on Nonwoven Backing Fabric Support for Forward Osmosis. Membranes 2021, 11, 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110813
Sahebi S, Kahrizi M, Fadaie N, Hadadpour S, Ramavandi B, Gonzales RR. Developing a Thin Film Composite Membrane with Hydrophilic Sulfonated Substrate on Nonwoven Backing Fabric Support for Forward Osmosis. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):813. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110813
Chicago/Turabian StyleSahebi, Soleyman, Mohammad Kahrizi, Nasim Fadaie, Soheil Hadadpour, Bahman Ramavandi, and Ralph Rolly Gonzales. 2021. "Developing a Thin Film Composite Membrane with Hydrophilic Sulfonated Substrate on Nonwoven Backing Fabric Support for Forward Osmosis" Membranes 11, no. 11: 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110813
APA StyleSahebi, S., Kahrizi, M., Fadaie, N., Hadadpour, S., Ramavandi, B., & Gonzales, R. R. (2021). Developing a Thin Film Composite Membrane with Hydrophilic Sulfonated Substrate on Nonwoven Backing Fabric Support for Forward Osmosis. Membranes, 11(11), 813. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110813







