Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes in Wastewater Treatment: Filtration Behavior, Fouling and Prevention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Water Crisis
3. Membrane Technology and Applications
4. Filtration
4.1. Pressure Driven Membrane Processes
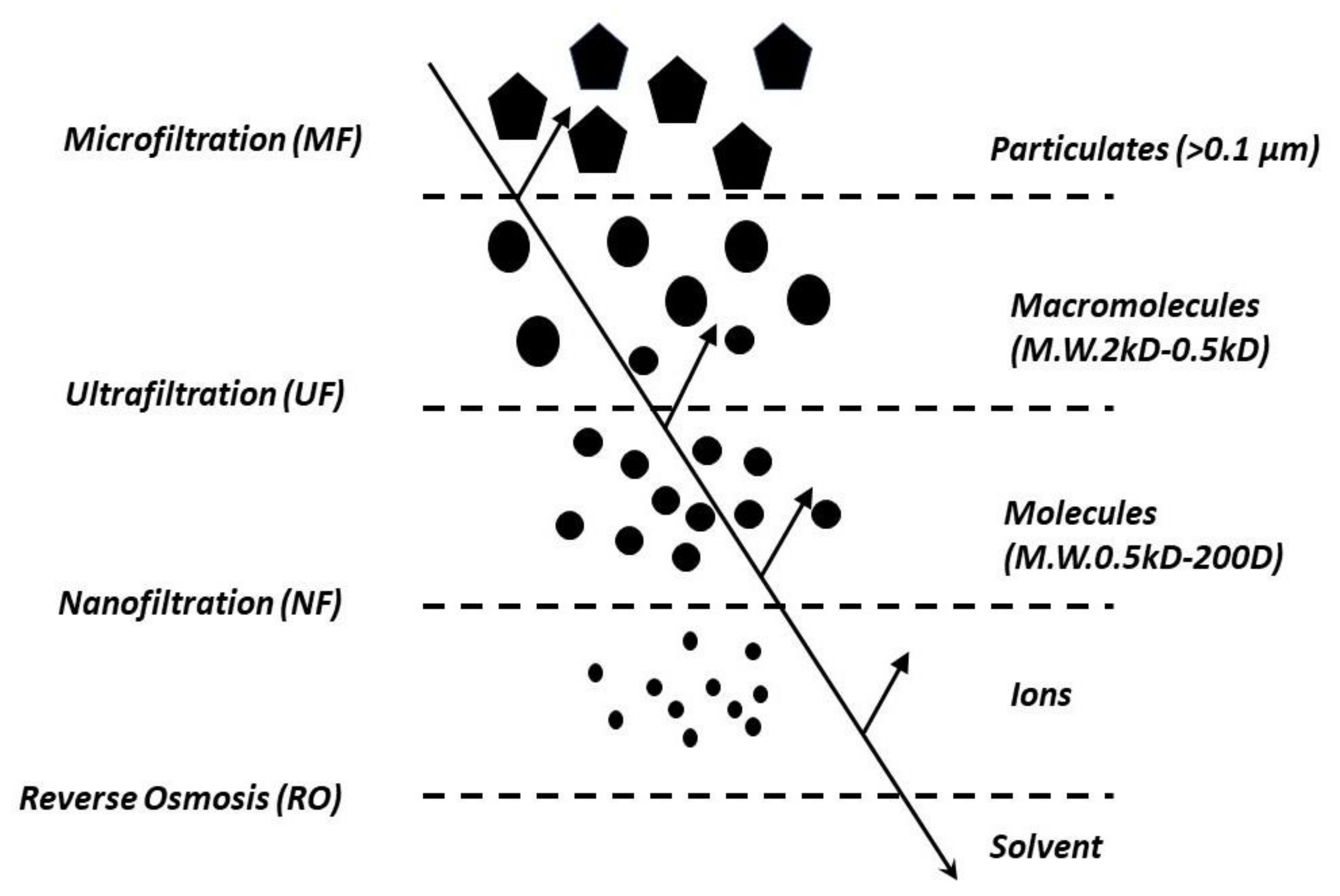
| Membrane Pores Size | MF | UF | NF | RO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typical separation mechanism | Sieving | Sieving | Sieving, charge effect, adsorption, solution diffusion | Solution–Diffusion (diffusion limitation), convection) |
| Pore size (nm) | 100–10,000 | 2–100 | 0.5–2 | Unknown |
| Pressure (bar) | 0.1–3 | 0.1–5 | 3–20 | 5–120 |
| Permeability (l/h·m2·bar) | >1000 | 10–1000 | 15–30 | 0.05–1.5 |
| Retention | ||||
| • Monovalent ions | – | – | – | + |
| • Multivalent ions | – | –/+ | + | + |
| • Small organic compounds | – | – | –/+ | + |
| • Macromolecules | – | + | + | + |
| • Particles | + | + | + | + |
| Energy consumption (kWh/m3) | 0.4 | 3.0 | 5.3 | 10.2 |
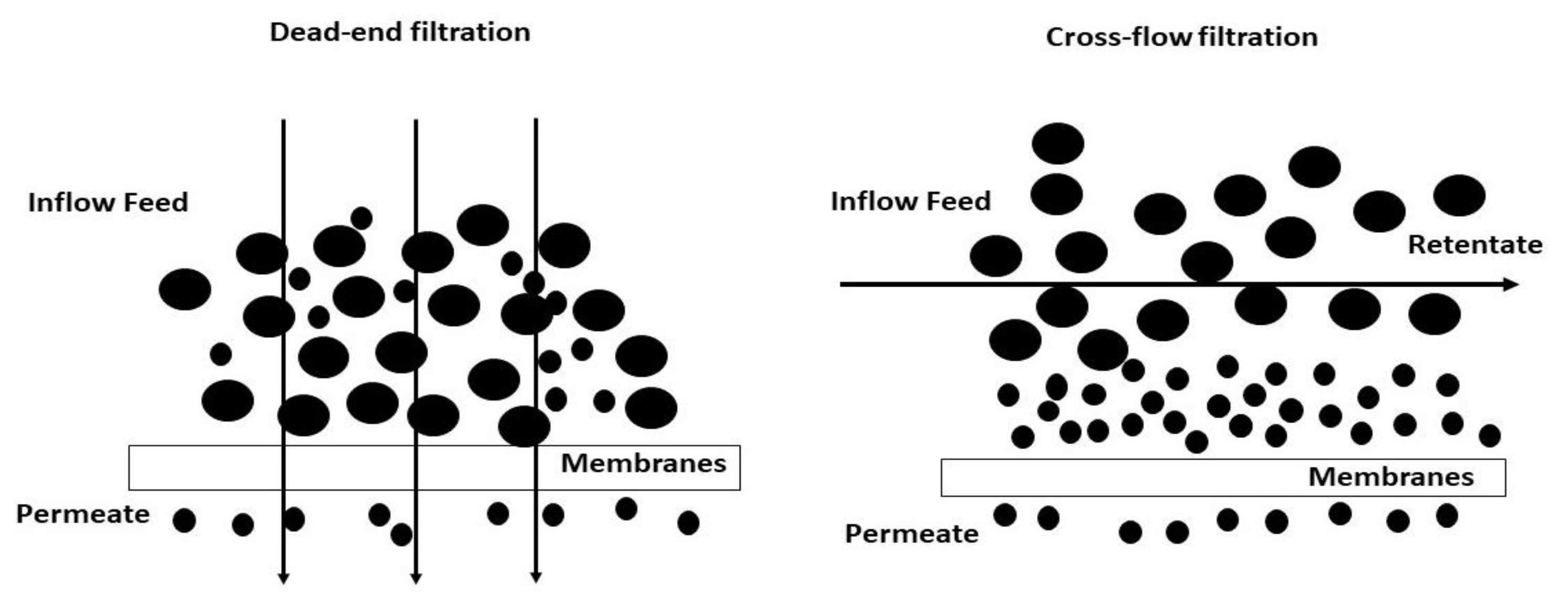
4.2. Filtration Mode
4.3. Dead-End Mode
4.4. Cross-Flow Mode
5. Microfiltration
5.1. Membranes for Microfiltration
5.2. Industrial Applications for Microfiltration
6. Membrane Manufacturing
| Membrane Materials | Manufacturing Procedure | Industrial Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Pressing, sintering of fine powders followed by sol-gel coating | MF, UF, aggressive (high concentration of acid and alkali chemicals for cleaning) and/or highly fouling media |
| Stretched polymers | Stretching of partially crystalline foil | MF, aggressive media, sterile filtration, medical technology |
| Track-etched polymers | Radiation followed by acid etching | MF, polycarbonate (PC) or polyethylene terephthalate (PET) materials. Analytical and medical chemistry, sterile filtration |
| Supported liquid | Formation of liquid film in inert polymer matrix | Gas separations, carrier-mediated transport |
| Integral asymmetric, microporous | Phase inversion | MF, UF, nanofiltration (NF), Gas transfer(GT) |
| Composite asymmetric, microporous | Application of thin film to integral asymmetric microporous membrane to produce TFC | NF, RO, pervaporation (PV) |
| Ion exchange | Functionalization of polymer material | Electrodialysis (ED) |
6.1. Inorganic Membranes
6.2. Recent Developments of Membrane Materials
7. Module Design and Configuration
- -
- High membrane area to module bulk volume ratio
- -
- High degree of turbulence for mass transfer promotion on the feed side
- -
- Low energy expenditure per unit product water volume
- -
- Low cost per unit membrane area
- -
- A design that facilitates cleaning
- -
- A design that also facilitates modularization
7.1. Tubular Modules
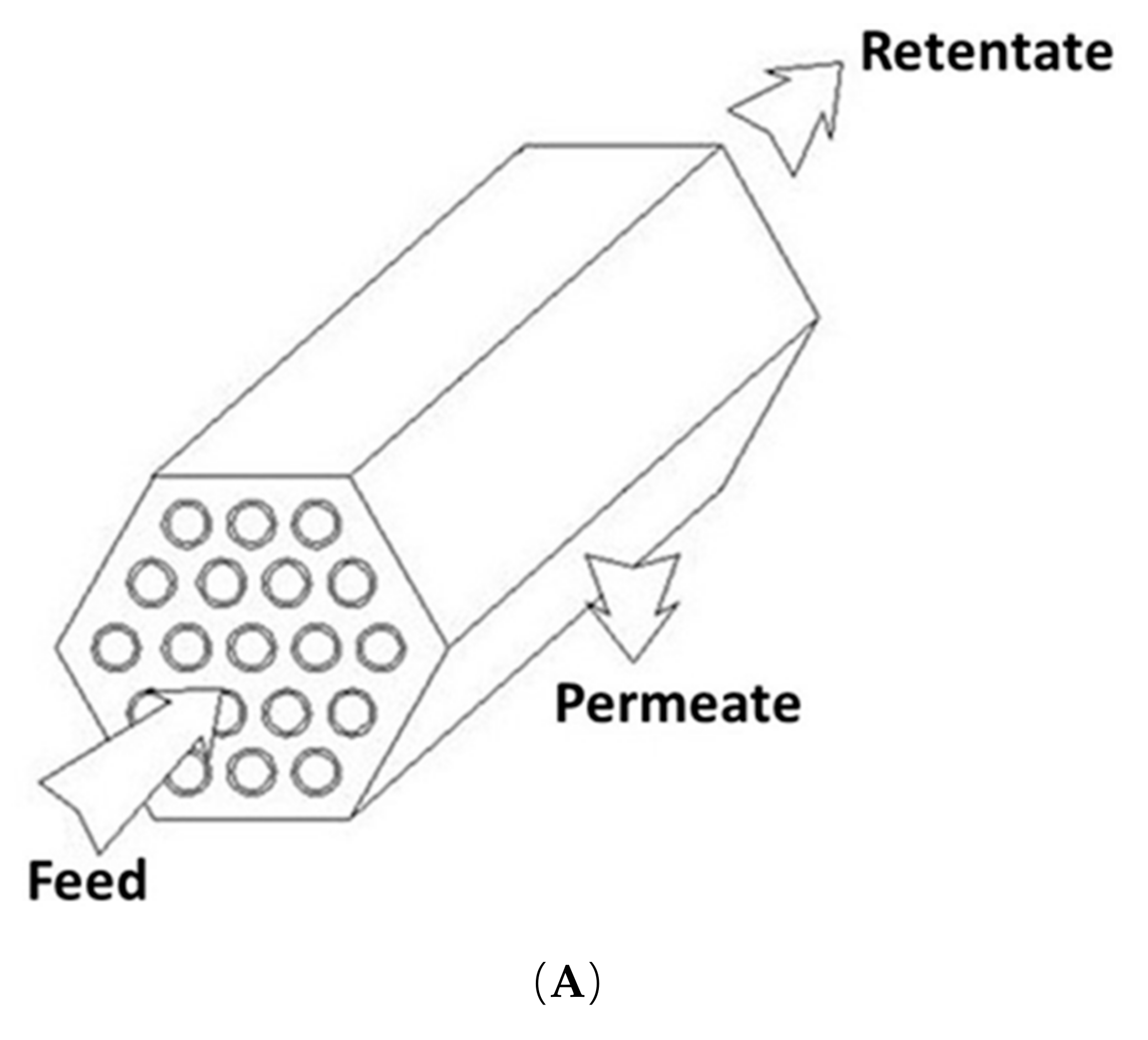
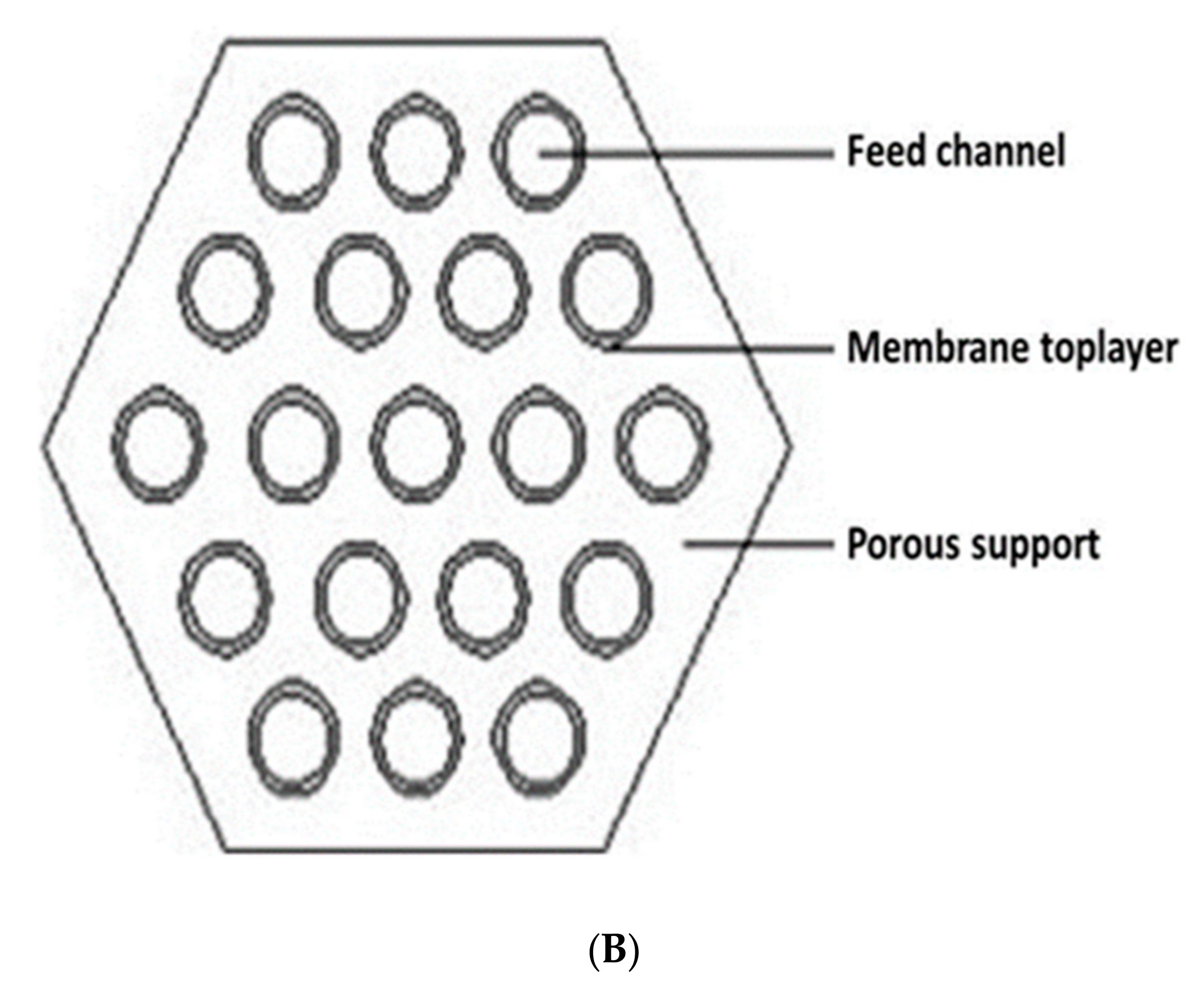
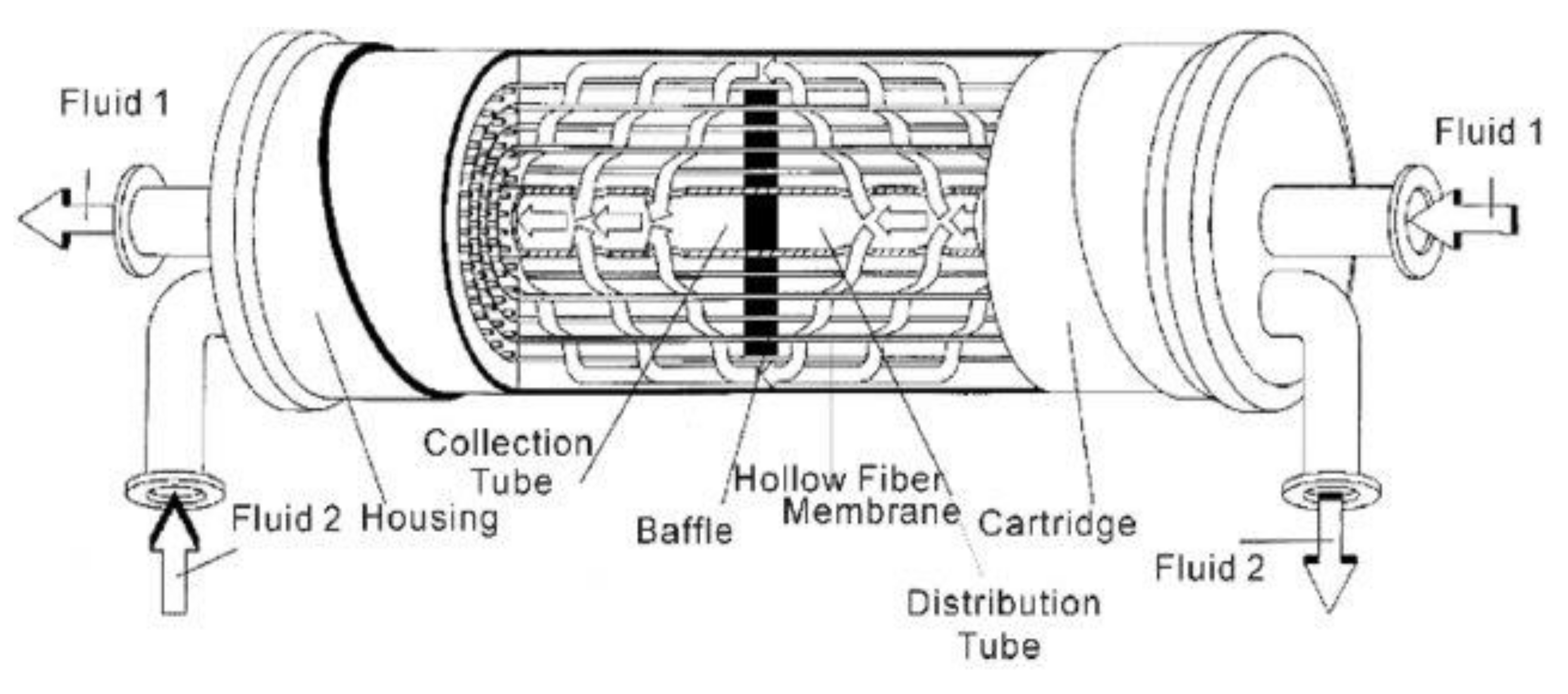
7.2. Hollow-Fiber Modules
8. Current Developments in Module Configurations
9. Properties of Ceramic Membranes
10. Preparation of Ceramic Membranes
11. Ceramic Membrane Microfiltration
11.1. Gel Layer Formation and Control
11.2. Technical Advances in Using Ceramic Membranes
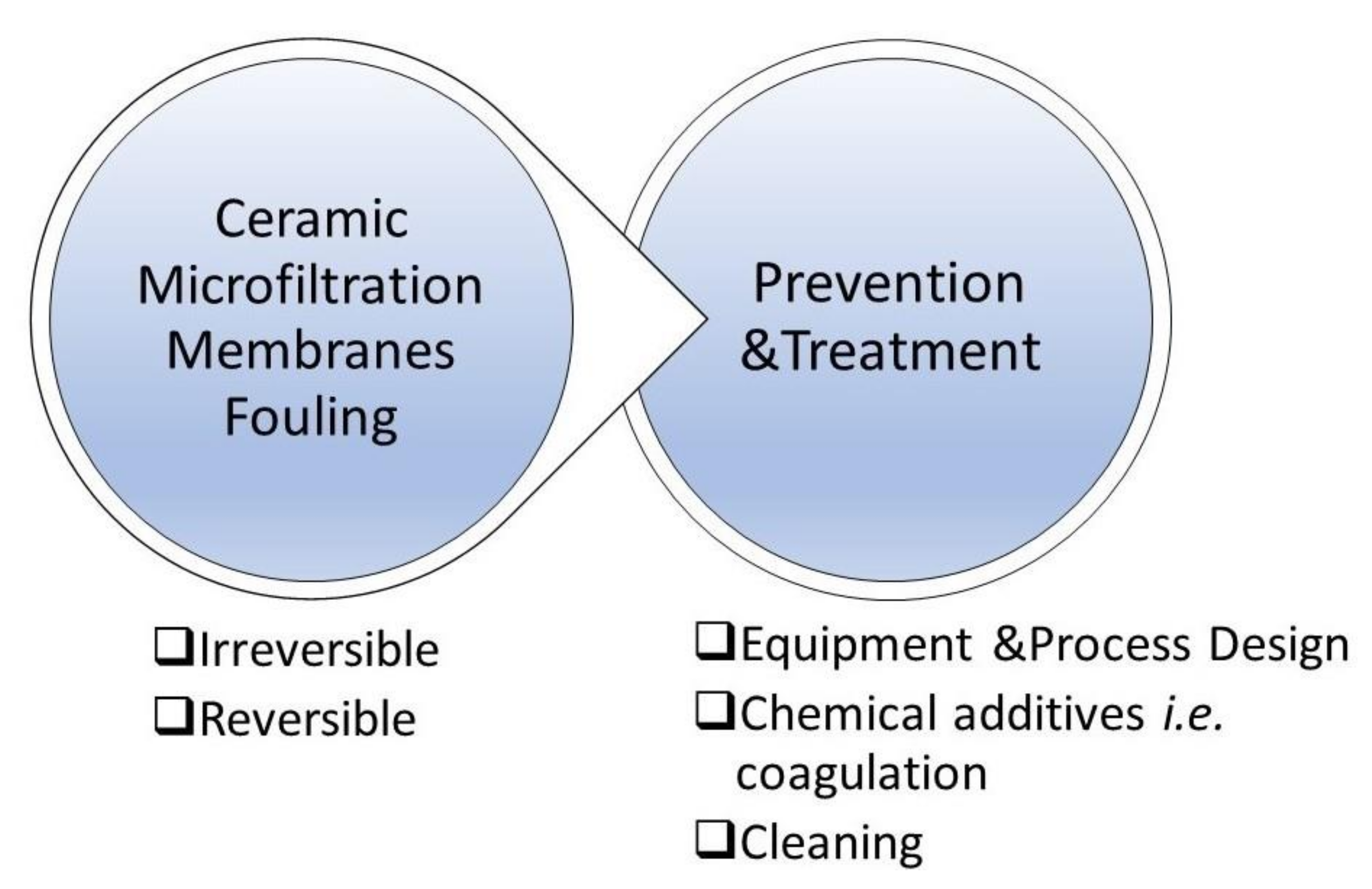
12. Ceramic Membrane Fouling
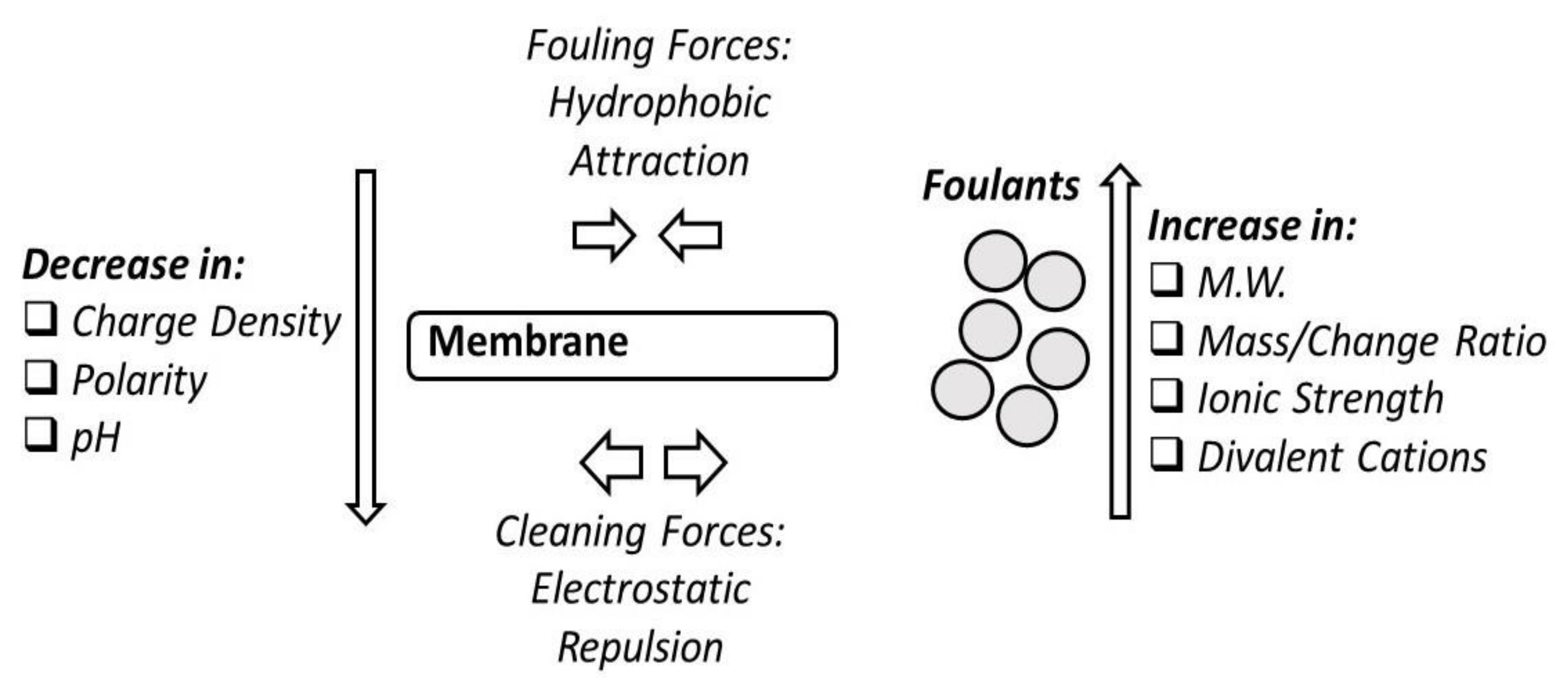
12.1. Fouling Phenomena
12.2. Concentration Polarization
12.3. Cake Layer
12.4. Fouling and Retention of Particles due to Natural Organic Matter (NOM)
13. Methods Employed to Increase Retention and Reduce Fouling
13.1. Integration of Coagulation with Membrane Filtration
13.2. Coagulation
13.3. Integration of Coagulation with Membrane Filtration
13.4. Turbulence Promoters
13.5. Electrical Field
13.6. Ultrasonic Field
13.7. Backwashing (Backflushing)
14. Membrane Cleaning
14.1. Cleaning Reagent Performance
- -
- Bulk reaction (hydrolysis and other) of cleaning reagent as the cleaning in place (CIP) is introduced.
- -
- Cleaning agent is transported to membrane surface.
- -
- Cleaning agent transits through foulant layers to membrane surface.
- -
- Cleaning reactions solubilise and detach foulants.
- -
- Waste cleaning agent with suspended foulants transported to interface.
- -
- Finally, transport of waste matter to the bulk solution from retentive side of membrane.
14.2. Caustic Soda
14.3. Oxidants
14.4. Acids
15. Conclusions
- Fouling remains the toughest hurdle regarding to the even greater use and implementation of the membranes in the industry.
- Fouling is a complex multifactorial phenomenon which although there is a much higher level of understanding today comparing to the past, further research is needed for its further alleviation.
- Numerous ways of addressing fouling are been investigated and implemented in the industry including hydrodynamics, testing different materials of fabrication, testing different pre-treatments, i.e., coagulation, hydrodynamics and cleaning with different agents and techniques.
- Although several other highly sophisticated methods for prevention of fouling such as ozonation have been tested, coagulation remains the widely applied option.
- As fouling prevention mechanisms such as intermittent cleaning with agents and other relevant cleaning strategies do remain the main method to address the occurring problem in industrial scale.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Www.Prb.Org. Available online: https://www.prb.org/Populationtrendsandchallengesinthemiddleeastandnorthafrica/ (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Agriculture & Water. Available online: https://www.saudiembassy.net/agriculture-water (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Water Resources. Available online: https://www.saudiembassy.net/water-resources (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.B.; Hilal, N. Analytical and Forecasting Study for Wastewater Treatment and Water Resources in Saudi Arabia. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghonemy, A.M.K. A small-scale brackish water reverse-osmosis desalination system used in northern Saudi Arabia: A case study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4597–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corominas, L.; Flores-Alsina, X.; Snip, L.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Comparison of different modeling approaches to better evaluate greenhouse gas emissions from whole wastewater treatment plants. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2854–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bis, M.; Montusiewicz, A.; Piotrowicz, A.; Łagód, G. Modeling of Wastewater Treatment Processes in Membrane Bioreactors Compared to Conventional Activated Sludge Systems. Processes 2019, 7, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zularisam, A.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, R. Behaviors of natural organic matter in membrane filtration for surface water treatment—A Review. Desalination 2006, 194, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, M.A. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Gestel, T.; Doyen, W.; Leysen, R. A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K. American Water Works Association (AWWA) Water Quality & Treatment: A Handbook on Drinking Water, 6th ed.; Europe, McGraw-Hill Professional; McGraw-Hill Education: Berkshire, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharof, M.P.; Lovitt, R.W. The filtration characteristics of anaerobic digester effluents employing cross flow ceramic membrane microfiltration for nutrient recovery. Desalination 2014, 341, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M.P.; Mandale, S.J.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.; Lovitt, R.W. Nutrient recovery and fractionation of anaerobic digester effluents employing pilot scale membrane technology. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Carbon Plan: Delivering our Low Carbon Future Presented to Parliament Pursuant to Sections 12 and 14 of the Climate Change Act 2008 Amended 2nd December 2011 from the Version Laid Before Parliament on 1st December 2011; Department of Energy & Climate Change, Ed.; HM Government: London, UK, 2011.
- DECC (Department of Energy and Climate Change Website). Increasing the Use of Low Carbon Technologies. 2014. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/policies/increasing-the-use-of-low-carbontechnologies (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Waste Management Plan for England; Department for Environment Food and Rural Affairs UK: London, UK, 2013.
- Wastewater Treatment in the United Kingdom—2012 Implementation of the European Union Urban Waste Water Treatment Directive—91/271/EEC; Department for Environment, FARA, Ed.; Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs: London, UK, 2012.
- Review of Waste Policy and Legislation EU Waste Framework Directive 2008/98/EC, the Landfill Directive 1999//31/EC and the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive 94/62/EC; Waste-Environment-European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2014.
- Rice, J.; Wutich, A.; Westerhoff, P. Assessment of De Facto Wastewater Reuse across the US: Trends between 1980 and 2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11099–11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, B. From a fossil-fuel to a biobased economy: The politics of industrial biotechnology. Environ. Plan. C Gov. Policy 2012, 30, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, S.R.H.; Sebzari, M.R.; Hemati, M.; Rekabdar, F.; Mohammadi, T. Ceramic membrane perfor-mance in microfiltration of oily wastewater. Desalination 2011, 265, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’souza, N.M.; Mawson, A.J. Membrane Cleaning in the Diary Industry: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chellam, S.; Clifford, D.A. Indirect evidence for deposit rearrangement during dead-end microfiltration of iron coagulated suspensions. J. Mem. Sci. 2004, 239, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, H. Artificial recharge of groundwater: Hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, Q.; Bahri, A.; Toshio Sato, T.; Al-Karadsheh, E. Wastewater production, treatment, and irrigation in Middle East and North Africa. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2010, 24, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Wichelns, D.; Raschid-Sally, L.; McCornick, P.G.; Drechsel, P.; Bahri, A.; Minhas, P.S. The Challenges of Wastewater Irrigation in Developing Countries. Water for Food Faculty Publications. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, J.; Wutich, A.; Westerhoff, P. Spatial and temporal variation in de facto wastewater reuse in drinking water systems across the U.S.A. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, G.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Hospido, A.; Hernandez-Sancho, F.; Moreira, M.T.; Feijoo, G. Environmental and economic profile of six typologies of wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5997–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M. Grape Winery Waste as Feedstock for Bioconversions: Applying the Biorefinery Concept. Waste Biomass Valor. 2017, 8, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M.-P.; Lovitt, R.W. Adding value to wastewater by resource recovery and reformulations growth media: Current prospects and potential. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2015, 5, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, A. Case studies in Middle Eastern and North African countries. In Water Reuse: An International Survey of Current Practice, Issues and Needs; Jimenez, B., Asano, T., Eds.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Keraita, B.; Jimenez, B.; Drechsel, P. Extent and implications of agricultural reuse of untreated, partly treated and diluted wastewater in developing countries. CAB Rev. Perspect. Agric. Vet. Sci. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2008, 58, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelessidis, A.; Stasinakis, A. Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Alsina, X.; Arnell, M.; Amerlinck, Y.; Corominas, L.; Gernaey, K.V.; Guo, L.; Lindblom, E.; Nopens, I.; Porro, J.; Shaw, A.; et al. Balancing effluent quality, economic cost and greenhouse gas emissions during the evaluation of (plant-wide) control/operational strategies in WWTPs. Sci. Total Envrion. 2014, 466, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Alsina, X.; Corominas, L.; Snip, L.; Vanrolleghem, P.A. Including greenhouse gas emissions during benchmarking of wastewater treatment plant control strategies. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4700–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foladori, P.; Andreottola, G.; Ziglio, G. Sludge Reduction Technologies in Wastewater Treatment Plants; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.-W.; Yu, H.-Q. From wastewater to bioenergy and biochemicals via two-stage bioconversion processes: A future paradigm. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, M.; Srinivasan, R.S.; Ries, R. Complementary life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment plants: An integrated approach to comprehensive upstream and downstream impact assessments and its extension to building-level wastewater generation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 23, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Minear, R.A. Removal of Low-Molecular Weight Dbps and Inorganic Ions for Characterization of High-Molecular Weight Dbps in Drinking Water. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.; Kwon, B.; Sun, M.; Ahn, H.; Kim, C.; Kwoak, C.; Lee, D.; Chae, S.; Hyung, H.; Cho, J. Application Of Various Membranes To Remove Nom Typically Occurring In Korea With Respect To Dbp, Aoc And Transport Parameters. Desalination 2005, 178, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domany, Z.; Galambos, I.; Vatai, G.; Bekassy-Molnar, E. Humic Substances Removal from Drinking Water by Membrane Filtration. Desalination 2002, 145, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abri, M.; Al Anezi, K.; Dakheel, A.; Hilal, N. Humic substance coagulation: Artificial neural network simulation. Desalination 2010, 253, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abri, M.; Dakheel, A.; Tizaoui, C.; Hilal, N. Combined humic substance and heavy metals coagula-tion, and membrane filtration under saline conditions. Desalination 2010, 253, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, N.; Al-Abri, M.; Al-Hinai, H.; Somerfield, C. Combined Humic Substance and Heavy Metals Agglomeration, and Membrane Filtration under Saline Conditions. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 1488–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakami, M.; Tizaoui, C.; Kochkodan, V.; Hilal, N. Effect of Hydrodynamic Operations, Salinity, and Heavy Metals on HA Removal by Microfiltration Ceramic Tubular Membrane. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Lay, H.T.; Li, W.; Chew, J.W. Effect of initial particle deposition rate on cake formation during dead-end microfiltration. J. Mem. Sci. 2021, 618, 118672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Stensel, H.D.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Burton, F.L.; Abu-Orf, M.; Bowden, G.; Pfrang, W. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment & Resource Recovery, 5th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Towler, G.R.; Sinnott, R. Chemical Engineering Design Principles, Practice and Economics of Plant and Process Design, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Clavreul, J.; Scheutz, C.; Christensen, T.H. Influence of data collection schemes on the Life Cycle Assessment of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 2014, 56, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Removal of Pollutants from Surface Water and Groundwater by Nanofiltration: Overview of Possible Applications In The Drinking Water Industry. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Bruggen, B.; Verberk, J.Q.J.C.; Verhack, J. Comparison of pressure-driven membrane processes and traditional processes for drinking water production in Europe based on specific impact criteria. Water SA 2004, 30, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baker, R. Membrane Technology and Applications, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, N. Membrane Separation Processes, 1st ed.; PHI Learning: Delhi, India, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- World Demand for Membranes to Reach $19.3 Bil. 2011. Available online: https://www.flowcontrolnetwork.com/world-demand-for-membranes-to-reach-19-3-bil-in-2015/ (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- J.E.T.O. (JETRO) Rapid Growth of the Global Water Treatment Business-Japan’s Public and Private Sectors Join Hands to Develop National Strategy. 2009. Available online: https://www.jetro.go.jp/en/reports/market/pdf/2009_01.pdf (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Scholz, W.; Lucas, M. Techno-Economic Evaluation of Membrane Filtration for the Recovery and Re-Use of Tanning Chemicals. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Huanga, X. Fouling Characteristics and Cleaning Strategies in a Coagulation-Microfiltration Combination Process for Water Purification. Desalination 2003, 159, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chegini, S. Removal of Potential Inhibitors from Hemicellulose Hydrolysate by Membrane Filtration. Master’s Thesis, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014. Available online: https://publications.polymtl.ca/1495/ (accessed on 29 August 2020).
- Zacharof, M.; Lovitt, R.W. Complex Effluent Streams as a Potential Source of Volatile Fatty Acids. Waste Biomass Valor. 2013, 4, 557–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajenthira, A.; Siddiqi, A.; Anadon, L.D. A new case for promoting wastewater reuse in Saudi Arabia: Bringing energy into the water equation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinčl, J.; Doleček, P.; Cakl, J. Filtration Model for Hollow Fiber Membranes with Compressible Cake Formation. Desalination 2009, 240, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ha, J.-H.; In-Hyuck Song, I.-H.; Shin, D.W. Enhanced fouling resistance of organosilane-grafted ceramic microfiltration membranes for water treatment. J. Ceramic Soc. Jpn. 2017, 125, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Analysis of Constant Permeate Flow Filtration Using Dead-End Hollow Fiber Membranes. J. Mem. Sci. 2006, 268, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, H.K.; Bennett, R.; Marshall, A. Influence of Operating Conditions On Membrane Fouling In Crossflow Microfiltration Of Particulate Suspensions. Int. Dairy J. 2000, 10, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Hawlader, M.; Malek, A. An Experiment with Different Pretreatment Methods. Desalination 2003, 156, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Alexakis, D. Karstic Spring Water Quality: The Effect of Groundwater Abstraction from the Recharge Area. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 52, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C. Membrane Processes in Biotechnology: An Overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M.-P.; Vouzelaud, C.; Lovitt, R.W. (Eds.) The Use of Membrane Technology for the Formulation of Spent Anaerobic Digester Effluents as Nutrient Source for Bacterial Growth; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vinoth Kumara, R.; Goswamib, L.; Pakshirajanb, K.; GPugazhenthi, G. Dairy wastewater treatment using a novel low cost tubular ceramic membrane and membrane fouling mechanism using pore blocking models. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 13, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Linhua Fan, L.; Roddick, F. Impact of the Interaction between Aquatic Humic Substances and Algal Organic Matter on the Fouling of a Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane. Membranes 2018, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.M.; Roshni, M.; Vasanth, D. Treatment of aqueous bacterial solution using ceramic membrane prepared from cheaper clays: A detailed investigation of fouling and cleaning. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 29, 100797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.-I.; Jeong, S.; Im, S.-J.; Jang, A. High turbidity water treatment by ceramic microfiltration membrane: Fouling identification and process optimization. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, L.; Peng, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z. Fenton cleaning strategy for ceramic membrane fouling in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 85, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ling, G.Q.; Huang, P.; Li, K.; Lu, H.Q.; Hang, F.X.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, C.F.; Lu, D.J.; Li, H.; et al. Performance of ceramic microfiltration membranes for treating carbonated and filtered remelt syrup in sugar refinery. J. Food Eng. 2016, 170, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Zhang, M.; Yao, M.; Qiu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Lan, W.; Xia, H.; Jin, X. Membrane Fouling and Performance of Flat Ceramic Membranes in the Application of Drinking Water Purification. Water 2019, 11, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi, M.; Arzani, M.; Mahdavi, H.R.; Mohammadi, T. Kaolinitic clay-based ceramic microfiltration membrane for oily wastewater treatment: Assessment of coagulant addition. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 17826–17836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.L.; Bram, M.V.; Pedersen, S.; Yang, Z. Membrane Fouling for Produced Water Treatment: A Review Study from a Process Control Perspective. Water 2018, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almojjly, A.; Johnson, D.; Mandale, S.; Hilal, N. Optimisation of the removal of oil in water emulsion by using ceramic microfiltration membrane and hybrid coagulation/sand filter-MF. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 27, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Microfiltration membrane processes: A review of research trends over the past decade. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummons, E.; Qi, H.; Tanudjaja, H.J.; Hejase, C.A.; Chew, J.W.; Tarabara, V.V. Membrane fouling by emulsified oil: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 116919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H.; Omura, T.; Asai, T.; Kanezashi, M.; Tsuru, T. Filtration of surfactant-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions with porous ceramic membranes: Effects of membrane pore size and surface charge on fouling behavior. J. Mem. Sci. 2020, 610, 118210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, D.; Nakada, N.; Kato, Y.; Aoki, M.; Tanaka, H. Pretreatment of ceramic membrane microfiltration in wastewater reuse: A comparison between ozonation and coagulation. Environ. Manag. J. 2019, 251, 109555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Willershausen, D.; Ashaghi, K.S.; Engel, L.; Placido, P.; Mund, P.; Bolduan, P.; Czermak, P. Investigations on the use of different ceramic membranes for efficient oil-field produced water treatment. Desalination 2010, 250, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanudjaja, H.J.; Hejase, C.A.; Tarabara, V.V.; Fane, A.G.; Chew, J.W. Membrane-based separation for oily wastewater: A practical Perspective. Water Res. 2019, 156, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmsiri, E.; Rasouli, Y.; Abbasi, M.; Izadpanah, A.A. Chemical cleaning of mullite ceramic microfiltration membranes which are fouled during oily wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaser Rasouli, Y.; Abbasi, M.; Hashemifard, S.A. Fabrication, characterization, fouling behavior and performance study of ceramic microfiltration membranes for oily wastewater treatment. Asian Ceram. Soc. J. 2019, 7, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xing, W. Clarification of raw rice wine by ceramic microfiltration membranes and membrane fouling analysis. Desalination 2010, 256, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankins, N.P.; Lu, N.; Hilal, N. Enhanced Removal of Heavy Metal Ions Bound To Humic Acid by Polyelectrolyte Flocculation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 51, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.-M.; Yeh, H.-H. Removal of Giardia and Cryptosporidium in Drinking Water Treatment: A Pilot-Scale Study. Water Res. 2003, 37, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, A.; Capannelli, C.; Del Borghi, A.; Colombino MConio, O. Water Treatment for Drinking Purpose: Ceramic Microfiltration Application. Desalination 2001, 141, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Basic Principles on Membrane Technology, 1st ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, M. The Use of Membrane Processes in Environmental Problems. An Introduction. Nato Asi Ser. E Appl. Sci. Adv. Study Inst. 1994, 272, 229–262. [Google Scholar]
- Nah, W.; Kang, Y.W.; Hwang, K.-Y.; Song, W.-K. Mechanical pre-treatment of waste activated sludge for anaerobic digestion process. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Sakai, H. Ceramic membrane development in NGK. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parameshwaran, K.; Fane, A.G.; Cho, B.D.; Kim, K.J. Analysis of microfiltration performance with constant flux processing of secondary effluent. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4349–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciora, R.J.; Liu, P.K.T. Ceramic membranes for enviromental related applications, Fluid Part. Sep. J. 2003, 15, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, I.-J.; Yoon, S.-H.; Lee, C.-H. Comparison of the filtration characteristics of organic and inorganic membranes in a membrane-coupled anaerobic bioreactor. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waeger, F.; Delhaye, T.; Fuchs, W. The use of ceramic microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes for particle removal from anaerobic digester effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-O.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, R.-H. Filtration performance of ceramic membrane for the recovery of volatile fatty acids from liquid organic sludge. Desalination 2010, 172, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosqueda-Jimenez, D.B.; Huck, P.M. Characterization of Membrane Foulants in Drinking Water Treatment. Desalination 2006, 198, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xing, W.; Xu, N.; Shi, J. Study on Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor with Turbulence Promoter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2003, 32, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiropoulou, S.; Gavalas, V.; Vamvakaki, V.; Chaniotakis, N. Novel Carbon Materials in Biosensor Systems. Biosens. Bioelectr. 2003, 18, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Yonetani, K. Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Membranes with Oligopeptide Tweezers for Optical Resolution. Desalination 2002, 149, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Na, K.; Bae, Y.H. Sulfonamide Based Ph-Sensitive Polymeric Micelles: Physicochemical Characteristics and pH-Dependent Aggregation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 214, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S.; Jefferson, B. Membranes for Industrial Wastewater Recovery and Re-Use; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, S.J.; Hillis, P. Optimisation of Combined Coagulation and Microfiltration for Water Treatment. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2895–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Tsang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chan, S.; Chua, H.; Sin, S. Performance Study of Ceramic Microfiltration Membrane For Oily Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 128, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Xing, W.; Xu, N.; Shi, J. Application of Turbulence Promoters in Ceramic Membrane Bioreactor Used for Municipal Wastewater Reclamation. Membr. Sci. J. 2002, 210, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, D.M.; Koris, A.K.; Tekić, M.N. Do Static Turbulence Promoters Have Potential in Crossflow Membrane Filtration Applications? Desalination 2006, 191, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. Sol-Gel Science: The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y. Modification of Ceramic Membranes for Pore Structure Tailoring: The Atomic Layer Deposition Route. Membr. Sci. J. 2012, 397, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, G.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, X. Treatment of river water by a hybrid coagulation and ceramic membrane process. Desalination 2011, 280, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, L.; Xing, W.; Xu, N. Coagulation-microfiltration for lake water purification using ceramic membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 18, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agashichev, S.P. Enhancement of Concentration Polarization Due to Gel Accumulated At Membrane Surface. Membr. Sci. J. 2006, 285, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchin, P.; Si-Hassen, D.; Starov, V.; Clifton, M.J.; Aimar, P. A Unifying Model for Concentration Polarization, Gel-Layer Formation and Particle Deposition in Cross-Flow Membrane Filtration of Colloidal Suspensions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2002, 57, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Xing, W.; Zhang, B. Fabrication of Ceramic Membranes with Controllable Surface Roughness and Their Applications in Oil/Water Separation. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 4355–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyn, T.; Leiknes, T. Comparison of optional process configurations and operating conditions for ceramic membrane MF coupled with coagulation/flocculation pre-treatment for the removal of NOM in drinking water production. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2010, 59, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, N. Recent Advances in Process-Engineering Oriented Preparation and Application of Ceramic Membranes. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. Soc. China 2009, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Del Colle, R.; Fortulan, C.A.; Fontes, S.R. Manufacture and Characterization of Ultra and Microfiltration Ceramic Membranes by Isostatic Pressing. Ceramics Int. 2011, 37, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.L.; Bai, R. Membrane Fouling and Cleaning In Microfiltration of Activated Sludge Wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 216, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Bowman, C.N.; Davis, R.H. Membrane Fouling Reduction by Backpulsing and Surface Modification. Membr. Sci. J. 2000, 173, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.M.; Hakim, L.F.; Bowman, C.N.; Davis, R.H. Factors Affecting Membrane Fouling Reduction by Surface Modification and Backpulsing. Membr. Sci. J. 2001, 189, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, W. Effectiveness of Ferrate (Vi) Preoxidation in Enhancing the Coagulation of Surface Waters. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4959–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmad, M.; Aleem, F.A.A.; Mutiri, A.; Ubaisy, A. Biofuoling in RO Membrane Systems Part 1: Fundamentals and Control. Desalination 2000, 132, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Mariadas, A. Baffled Microfiltration Membrane and Its Fouling Control for Feed Water of Desalination. Desalination 2004, 168, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Kilduff, J.E.; Belfort, G. Low Fouling Synthetic Membranes by UV-Assisted Graft Polymerization: Monomer Selection to Mitigate Fouling by Natural Organic Matter. Membr. Sci. J. 2003, 222, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Watanabe, Y. The Effect of Shear Rate on Controlling the Concentration Polarization and Membrane Fouling. Desalination 2000, 131, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Du, C.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, C. Preparation, Performances, and Mechanisms of Microbial Flocculants for Wastewater Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J. An Experimental Study of Humid Acid and Powdered Activated Carbon Deposition on UF Membranes and Their Removal by Backwashing. Desalination 2001, 140, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufidou, K.; Yiantsios, S.; Karabelas, A. An Experimental Study of UF Membrane Fouling By Humic Acid and Sodium Alginate Solutions: The Effect of Backwashing on Flux Recovery. Desalination 2008, 220, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Fouling Effects on Rejection in the Membrane Filtration of Natural Waters. Desalination 2000, 131, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Cost Factors and Chemical Pretreatment Effects in the Membrane Filtration of Waters Containing Natural Organic Matter. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Richards, B.S. Testing of a Hybrid Membrane System for Groundwater Desalination in an Australian National Park. Desalination 2005, 183, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.I.; Schwicker, U.; Fischer, M.M.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T.D. Microfiltration of Colloids and Natural Organic Matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 171, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.M.; Farooque, A.M.; Jamaluddin, A.T.M.; Al-Amoudi, A.S.; Al-Sofi, M.A.K.; Al-Rubaian, A.F.; Kither, N.M.; Al-Tisan, I.A.R.; Rowaili, A. A Demonstration Plant Based on The New NF—SWRO Process. Desalination 2000, 131, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehant, A.; Bonnelye, V.; Perez, M. Comparison of MF/UF Pretreatment with Conventional Filtration Prior To Ro Membranes for Surface Seawater Desalination. Desalination 2002, 144, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reis, R.; Zydney, A. Bioprocess membrane technology. Membr. Sci. J. 2007, 5, 16–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Protein and Humic Acid Adsorption onto Hydrophilic Membrane Surfaces: Effects of pH And Ionic Strength. Membr. Sci. J. 2000, 165, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterböck, B.; Nikolausz, M.; Lv, Z.; Baumgartner, M.; Liebhard, G.; Fuchs, W. Improvement of anaerobic digestion performance by continuous nitrogen removal with a membrane contactor treating a substrate rich in ammonia and sulfide. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zularisam, A.; Ismail, A.; Sakinah, M. Application and Challenges of Membrane in Surface Water Treatment. Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 10, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, A. Characterization of natural organic matter in drinking water: Sample preparation and analytical approaches. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2016, 12, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratby, J. Coagulation and Flocculation in Water and Wastewater Treatment; International Water Association: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by Hydrolyzing Metal Salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J. Particles in Water: Properties and Processes; Crc Press—IWA Publishing: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, J.; Yukselen, M. Break-Up and Re-Formation of Flocs Formed by Hydrolyzing Coagulants And Polymeric Flocculants. In Chemical Water and Wastewater Treatment Vii; Hahn, H., Hoffmann, E., Odegaard, H., Eds.; IWA: Cornwall, UK, 2002; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mutairi, N.Z.; Hamoda, M.F.; Al-Ghusain, I. Coagulant Selection and Sludge Conditioning in A Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment Plant. Biores. Technol. 2004, 95, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, S.-K.; Gregory, J. The Interaction of Humic Substances with Cationic Polyelectrolytes. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3557–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amy, G. Fundamental Understanding of Organic Matter Fouling of Membranes. Desalination 2008, 231, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaic, D.; Freese, S.; Thompson, P. Longterm Experience in the Use of Polymeric Coagulants at Umgeni Water. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2001, 1, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelich, C.J.; Yun, T.I.; Coffey, B.M.; Suffet, I.H.M. Effects of Aluminum Sulfate and Ferric Chloride Coagulant Residuals on Polyamide Membrane Performance. Desalination 2002, 150, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Gregory, J. Organic Polyelectrolytes in Water Treatment. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2301–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.A. Chapter 5: Coagulation and Flocculation with Organic Polyelectrolytes. In Interface Science and Technology; Gayle, N., David, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Prime, D.C.; Stapley, A.G.; Rielly, C.D.; Jones, J.R.; Leaper, M.C. Analysis of Powder Caking In Multicomponent Powders Using Atomic Force Microscopy To Examine Particle Properties. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, K.; Bodzek, M.; Rajca, M.A. Coagulation–MF System for Water Treatment Using Ceramic Membranes. Desalination 2006, 198, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, K.; Rajca, M.; Bodzek, M.; Kwiecińska, A. Water Treatment Using Hybrid Method of Coagulation and Low-Pressure Membrane Filtration. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2009, 35, 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, L.; Vieira, A.M.S.; Vieira, M.F.; Silva, G.F.; Bergamasco, R. Application of Hybrid Process of Coagulation/Flocculation and Membrane Filtration for The Removal of Protozoan Parasites from Water. Procedia Eng. 2012, 42, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesters, S.; Darton, E.; Gallego, S.; Vigo, F. The Safe Use of Cationic Flocculants with Reverse Osmosis Membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2009, 6, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, K.; Svrcek, C.; Guest, R.; Smith, D.W. A Review of the Impact of Chemical Pretreatment on Low-Pressure Water Treatment Membranes. Environ. Eng. Sci. J. 2004, 3, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayon, S.; Noor, M.M.M.; Ghani, L.A.; Ahmad, J. Influence of Cationic Polyelectrolyte Coagulant on Microfiltration Performance for Treatment of Oxidation Pond Effluent. Desalination 2005, 184, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayon, S.; Noor, M.M.M.; Tat, W.K.; Halim, G.A.; Thamer, A.M.; Badronisa, Y. Effect of Natural Coagulant Application on Microfiltration Performance in Treatment of Secondary Oxidation Pond Effluent. Desalination 2007, 204, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseoglu, H.; Yigit, N.O.; Iversen, V.; Drews, A.; Kitis, M.; Lesjean, B.; Kraume, M. Effects of Several Different Flux Enhancing Chemicals on Filterability and Fouling Reduction of Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Mixed Liquors. Membr. Sci. J. 2008, 320, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, T.; King, S.; Gray, S.R.; Bolto, B.A.; Booker, N.A. The Fouling of Microfiltration Membranes by NOM after Coagulation Treatment. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdessemed, D.; Nezzal, G. Treatment of Primary Effluent by Coagulation-Adsorption-Ultrafiltration for Reuse. Desalination 2003, 152, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaydardzhiev, S.; Karthikeyan, J.; Ay, P. Colour Removal from Model Solutions by Coagulation-Surface Charge and Floc Characterisation Aspects. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Gregory, J.; Parsons, S.A. A Review of Floc Strength and Breakage. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3121–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Crawshaw, J.; Liu, T.; Graham, N. Ultrafiltration and nanofiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter: Mechanisms and mitigation by pre-ozonation and pH. Water Res. 2018, 139, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, P.; Veyret, D.; Charbit, F. Dean Vortices: Comparison of Numerical Simulation of Shear Stress and Improvement of Mass Transfer in Membrane Processes at Low Permeation Fluxes. Membr. Sci. J. 2001, 183, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, R.; Moulin, P.; Veyret, D.; Charbit, F. Numerical Simulation of Dean Vortices: Fluid Trajectories. Membr. Sci. J. 2002, 197, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidossi, R.; Veyret, D.; Moulin, P. Computational Fluid Dynamics Applied to Membranes: State of The Art and Opportunities. Chem. Eng. Process. 2006, 45, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Judd, S.; Murrer, J. Fouling Characteristics of Membrane Filtration in Membrane Bioreactors. Membr. Technol. 2000, 2000, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, B.K.; Moparthi, A.; Uppaluri, R.; Purkait, M.K. Treatment of oily wastewater using low cost ceramic membrane: Comparative assessment of pore blocking and artificial neural network models. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2010, 88, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeman, R.J.; Williams, C.J. Additional Techniques to Improve Microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 26, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervov, A.G.; Andrianov, A.P.; Efremov, R.V.; Desyatov, A.V.; Baranov, A.E. A New Solution for the Caspian Sea Desalination: Low-Pressure Membranes. Desalination 2003, 157, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, N.; Judd, S. Chemical Cleaning of Potable Water Membranes: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 71, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffaj, N.; MPersin, M.; Younsi, S.A.; Albizane, M.; Cretin, A. Larbot, Elaboration and characterization of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes deposited on raw support prepared from natural moroccan clay: Application to filtration of solution containing dyes and salts. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 31, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, D.; Pugazhenthi, G.; Uppaluri, R. Fabrication and properties of low-cost ceramic microfiltration membranes for separation of oil and bacteria from its solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lyu, Z.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. Ceramic-based membranes for water and wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Amy, G.; Croué, J.-P.; Buisson, H. Identification and Understanding Of Fouling In Low-Pressure Membrane (MF/UF) Filtration By Natural Organic Matter (NOM). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4511–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kwon, B.; Sun, M.; Cho, J. Characterizations of Nom Included in NF and UF Membrane Permeates. Desalination 2005, 173, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling Strategies and the Cleaning System of NF Membranes and Factors Affecting Cleaning Efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Ghoshal, A.K.; Pugazhenthi, G. Elaboration of novel tubular ceramic membrane from inexpensive raw materials by extrusion method and its performance in microfiltration of synthetic oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.R.; Bartlett, M. Measuring and Modelling Flux Recovery During The Chemical Cleaning Of MF Membranes For The Processing Of Whey Protein Concentrate. J. Food Eng. 2002, 53, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strugholtz, S.; Sundaramoorthy, K.; Panglisch, S.; Lerch, A.; Brugger, A.; Gimbel, R. Evaluation of the Performance of Different Chemicals For Cleaning Capillary Membranes. Desalination 2005, 197, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zondervan, E.; Roffel, B. Evaluation of Different Cleaning Agents Used For Cleaning Ultra Filtration Membranes Fouled By Surface Water. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 304, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofs, J.; Ogier, D.; Vries, E.F.; Beerendonk, E.R. Cornelissen, Comparison of ceramic and polymeric membrane permeability and fouling using surface water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 79, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Bu, J.; Qiu, M.; Ding, D.; Chen, X.; Verweij, H.; Fan, Y. PZT/Ti composite piezoceramic membranes for liquid filtration: Fabrication and self-cleaning properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alresheedi, M.T.; Barbeau, B.; Basu, O.D. Comparisons of NOM fouling and cleaning of ceramic and polymeric membranes during water treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kim, A.S. Prediction of Permeate Flux Decline in Crossflow Membrane Filtration of Colloidal Suspension: A Radial Basis Function Neural Network Approach. Desalination 2006, 192, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.P. Comparison of Hydrolysis/Coagulation Behavior of Polymeric and Monomeric Iron Coagulants in Humic Acid Solution. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheryan, M. (Ed.) Fouling and Cleaning: Cleaning Membranes. In Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook; Technomic Publishing Company: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 276–291. [Google Scholar]
- Cheryan, M. Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hristov, A.; Djambazov, I.; Dimitrov, D. Preparation and characterization of porous ceramic membranes for micro-filtration from natural zeolite. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2012, 47, 476–480. [Google Scholar]
- Côté, P.; Siverns, S.; Monti, S. Comparison of Membrane-Based Solutions for Water Reclamation and Desalination. Desalination 2005, 182, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Curcio, S.; Calabrò, V.; Iorio, G. Reduction and Control of Flux Decline in Cross-Flow Membrane Processes Modeled By Artificial Neural Networks. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 286, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Di Trapani, D. A Brief Review on the Resistance-in-Series Model in Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs). Membranes 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Rubia, A.; Rodríguez, M.; León, V.M.; Prats, D. Removal of Natural Organic Matter and Thm Formation Potential by Ultra-and Nanofiltration of Surface Water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Ng, T.C.A.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Ng, H.Y.; Wang, J. Interfacial diffusion assisted chemical deposition (ID-CD) for confined surface modification of alumina microfiltration membranes toward high flux and anti-fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadnejad, M.; Haghshenas, S.M.S.; Tavakoli Targhi, V.; Ghafarian Zahmatkesh, H.; Naeimi, M. Utilization of Sustainable Energies for Purification of Water. Adv. J. Chem. A 2020, 3, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tabach, E.; Lancelot, L.; Shahrour, I.; Najjar, Y. Use of Artificial Neural Network Simulation Metamodelling To Assess Groundwater Contamination in A Road Project. Math. Comput. Model. 2007, 45, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Vidic, R.D. Application of microfiltration for the treatment of Marcellus Shale flow backwater: Influence of floc breakage on membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Rentschler, J.; Perrone, R.; Liu, K. Application of ceramic membrane and ion-exchange for the treatment of the flowback water from Marcellus Shale gas production. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Xing, W.; Wong, F.S. Resistance analysis for ceramic membrane microfiltration of raw soy sauce. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 299, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Roddick, F.A. Feed water coagulation to mitigate the fouling of a ceramic MF membrane caused by soluble algal organic matter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavins, M.; Ansone, L. Study of Interaction between humic Acids and Fullerene C 60 Using Fluorescence Quenching Approach. Ecol. Chem. Eng. 2010, 17, 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kloster, N.; Brigante, M.; Zanini, G.; Avena, M. Aggregation Kinetics of Humic Acids in The Presence Of Calcium Ions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 427, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zhou, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Cerneaux, S.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Dong, Y. Application of ceramic microfiltration membrane modified by nano-TiO2 coating in separation of a stable oil-in-water emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 456, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Zhou, J.E.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, G. Hydrophilic modification of Al2O3 microfiltration membrane with nano-sized γ-Al2O3 coating. Desalination 2010, 262, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machenbach, I. Drinking Water Production by Coagulation and Membrane Filtration. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; DLu, D.; Cao, Y.S.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, M.; CXu, C.; Ma, J. Interaction analysis between gravity-driven ceramic membrane and smaller organic matter: Implications for retention and fouling mechanism in ultralow pressure-driven filtration system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13718–13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, S.C.; Han, H.J.; Jin, W.X. Characteristics of a Vibration Membrane in Water Recovery from Fine Carbon-Loaded Wastewater. Desalination 2004, 160, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, O.O.; Miles, N.J.; Hilal, N. Comparison of Different Pitch Lengths on Static Promoters for Flux Enhancement in Tubular Ceramic Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2007, 42, 1945–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammari, S.B.; Bou-Hamad, S.; Al-Saffar, A.; Salman, M.; Al-Sairafi, A. Treatment of dairy processing wastewater using integrated submergedmembrane microfiltration system. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.J. Future Challenges to Asset Investment in the UK Water Industry: The Wastewater Asset Investment Risk Mitigation Offered By Minimizing Principal Operating Cost Risks. Water Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papić, S.; Koprivanac, N.; Lončarić Božić, A.; Meteš, A. Removal of Some Reactive Dyes from Synthetic Wastewater By Combined Al(Iii) Coagulation/Carbon Adsorption Process. Dye Pigment. 2004, 62, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prisciandaro, M.; Salladini, A.; Barba, D. Membrane Filtration of Surface Water for the Removal of humic Substances. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qdais, H.A.; Moussa, H. Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater by Membrane Processes: A Comparative Study. Desalination 2004, 164, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladner, D.A.; Vardon, D.R.; Clark, M.M. Effects of shear on microfiltration and ultrafiltration fouling by marine bloom-formingalgae. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 356, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Dilaver, M.; Park, P.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Comparative analysis of fouling characteristics of ceramic and polymeric microfiltration membranes using filtration models. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 432, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, J.J.; Vo, T.K.Q.; Kim, H.S. Application of physical and chemical enhanced backwashing to reduce membrane fouling in the water treatment process using ceramic membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohaus, J.; Stockmeier, F.; Surray, P.; Lölsberg, J.; Wessling, M. What are the microscopic events during membrane backwashing? J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 602, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Membrane Type | Industrial Wastewater Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Microfiltration | Marcellus shale flowback water | [69] |
| Dairy wastewater | [70] | |
| Aquatic humic substances and algal organic matter | [71] | |
| Aqueous bacterial cell debris | [72] | |
| High-turbidity water (overflow) | [73] | |
| Activated sludge | [74] | |
| Carbonated and filtered remelt syrup | [75] | |
| Oily wastewater treatment | [76] | |
| Municipal wastewater | [77] | |
| Oil-water emulsions | [78,79,80,81] |
| Cleaning Agents | Chemical | Reactions |
|---|---|---|
| Base | Caustic Soda (NaOH) | Hydrolysis and solubilisation, saponification |
| Oxidants | Hypochlorite (HOCl), Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) | Oxidation and disinfection |
| Acids | Hydrochloric Acid (HCl), Sulfuric Acid (H2SO4), Nitric Acid (HNO3) | Solubilisation |
| Acid chelate | Citric acid | Chelation |
| Alkaline chelate | EDTA | Chelation |
| Surfactants | Proprietary | Emulsifying, dispersion and surface conditioning |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hakami, M.W.; Alkhudhiri, A.; Al-Batty, S.; Zacharof, M.-P.; Maddy, J.; Hilal, N. Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes in Wastewater Treatment: Filtration Behavior, Fouling and Prevention. Membranes 2020, 10, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090248
Hakami MW, Alkhudhiri A, Al-Batty S, Zacharof M-P, Maddy J, Hilal N. Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes in Wastewater Treatment: Filtration Behavior, Fouling and Prevention. Membranes. 2020; 10(9):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090248
Chicago/Turabian StyleHakami, Mohammed Wali, Abdullah Alkhudhiri, Sirhan Al-Batty, Myrto-Panagiota Zacharof, Jon Maddy, and Nidal Hilal. 2020. "Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes in Wastewater Treatment: Filtration Behavior, Fouling and Prevention" Membranes 10, no. 9: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090248
APA StyleHakami, M. W., Alkhudhiri, A., Al-Batty, S., Zacharof, M.-P., Maddy, J., & Hilal, N. (2020). Ceramic Microfiltration Membranes in Wastewater Treatment: Filtration Behavior, Fouling and Prevention. Membranes, 10(9), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10090248