Abstract
In this work, the behavior of new GO-based mixed matrix membranes was tested in view of their use as CO2-selective membrane in post combustion carbon capture applications. In particular, the new materials were obtained by mixing of Pebax® 2533 copolymer with different types of graphene oxide (GO). Pebax® 2533 has indeed lower selectivity, but higher permeability than Pebax® 1657, which is more commonly used for membranes, and it could therefore benefit from the addition of GO, which is endowed with very high selectivity of CO2 with respect to nitrogen. The mixed matrix membranes were obtained by adding different amounts of GO, from 0.02 to 1% by weight, to the commercial block copolymers. Porous graphene oxide (PGO) and GO functionalized with polyetheramine (PEAGO) were also considered in composites produced with similar procedure, with a loading of 0.02%wt. The obtained films were then characterized by using SEM, DSC, XPS analysis and permeability experiments. In particular, permeation tests with pure CO2 and N2 at 35°C and 1 bar of upstream pressure were conducted for the different materials to evaluate their separation performance. It has been discovered that adding these GO-based nanofillers to Pebax® 2533 matrix does not improve the ideal selectivity of the material, but it allows to increase CO2 permeability when a low filler content, not higher than 0.02 wt%, is considered. Among the different types of GO, then, porous GO seems the most promising as it shows CO2 permeability in the order of 400 barrer (with an increase of about 10% with respect to the unloaded block copolymer), obtained without reducing the CO2/N2 selectivity of the materials, which remained in the order of 25.
1. Introduction
In the last decades, the worldwide rise in energy demand has increased the consumption of fossil fuels, leading to remarkable and regular emissions of combustion products—most of all, carbon dioxide—which, in turn, have led to global warming issues. CO2 is indeed the most problematic among the greenhouse gases, not because of its global warming potential [1], but because of the huge amount emitted daily into the environment [2,3].
It is, today, well known that the CO2 concentration in the atmosphere has to be reduced to contain the temperature increase below +2 °C compared to the pre-industrial age, as needed to minimize the negative effects of global warming on the planet [4]. To reach this goal, however, the undergoing energy transition towards more green and sustainable sources has to be coupled with more immediate solutions such as the use of the so-called “carbon capture” technologies [5,6] which aim at recovering the emitted CO2 and to store it in safe places, thus reducing the CO2 emission in the medium–short term.
Nowadays, the most advanced and mature carbon capture technique is solvent absorption [7,8,9], but more environmentally friendly approaches have also been studied, such as mineralization [10], cryogenic separation [11] and, as in this work, membrane separation [12,13,14,15,16].
The main features of gas separation membranes are the permeability of the target compound, in the present case, CO2, and its selectivity with respect to other gases present in the stream to be treated. In case of the post combustion approach, where CO2 is recovered from flue gas, the main competitor is usually nitrogen.
The permeation through dense membranes is described by the solution-diffusion model, which considers the process as formed by a series of steps involving gas solubilization into the high-pressure side of the membrane, its diffusion across the thickness and, finally, the desorption at the opposite, low-pressure side of the system [17]. Polymer membranes can be very efficient in gas separation, but they present an intrinsic performance limitation as the higher selectivity is usually coupled with lower permeability and vice versa [18].
In order to overcome this tradeoff, several approaches have been considered, such as the use of “mixed matrix membranes” (MMM) which, indeed, have been intensively studied in recent years [16,19,20,21,22,23,24]. In MMMs, different types of organic or inorganic nanofillers are included in the main polymeric matrix in order to provide high selectivity and, possibly also, high permeability.
Among the different polymer considered as starting point, Pebax® materials have been often chosen for their good balance among mechanical resistance, processability, and separation performances [25,26,27,28,29]. Pebax® is the trade name of a series of block copolymers composed by polyamide and polyether blocks, produced with various types of each moiety and in different ratios [30,31,32,33]. They are widely used as a membrane matrix in carbon capture because some of them possess both good CO2 permeability and CO2/N2 selectivity, properties that can be tuned with chemical modification or by the use of fillers, as also reported in the very complete summary from Ho et al. [15].
While the type of Pebax® more commonly used in carbon capture membrane applications is Pebax® 1657, made of nylon-6 and PEO with a respective ratio of 40/60 in mass, other materials of the family also possess interesting performances, such as Pebax® 2533, which was employed in this work as matrix due to the higher CO2 permeability showed with respect to Pebax® 1657 (about 130–351 barrer against 45–80 barrer) although with lower CO2/N2 selectivity (about 25–34 against 43–80) in experiments conducted in mild conditions (pressure upstream of 1–2 bar and temperature from 20 to 35 °C) [27,28,29,34,35,36,37,38,39,40].
Among the many possible fillers usually considered, GO-based nanomaterials have recently attracted much interest and have been widely employed in carbon capture for their capability of enhancing membranes’ gas permselective properties and chemical tunability, with many examples already available in literature [41,42,43,44,45,46,47] and, also, described in reviews such as the one about 0D and 2D filler MMMs by Janakiram et al. [48], or the one specific for graphene and graphene oxide materials from Yoo et al. [49], or even the wider and more general review by Sun et al. [50]. Among the many available studies, one can recall the work from Anastasiou et al. [46], which increased both polysulfone’s CO2 permeability (from about 0.9 to 1.8 barrer) and CO2/N2 selectivity (from about 0.8 to 5) by using a combined system ZIF-8 plus graphene oxide as nanofiller. Similar results improvements were obtained by Dong et al. [44] who managed to increase both CO2 permeability (from about 60 to 120 barrer) and CO2/N2 selectivity (from about 60 to 100) of Pebax® 1657 employing high loadings of porous reduced graphene oxide, or Karunakaran et al., who increased CO2/N2 selectivity of a PEO–BPT matrix of almost 50%, from 52 to 73, by adding only 0.0625% graphene oxide [51].
As already investigated by Karunakaran et al., GO-loaded membranes tested did not follow the kinetic diameter trend in term of permeation, revealing that the improvement were not due to a physical sieving effect, but to a higher affinity and thus absorption of CO2 to GO, as also demonstrated by Shen et al. [52]. That considered, it has to be noted that, generally, the permeabilities of all gases tend to decrease with GO addition, and CO2/N2 selectivity was incremented by the smaller decrement of CO2 itself compared to nitrogen and other gases.
Based on these results and in view of the positive results obtained on Pebax® 1657, the present work aimed at developing a matrix–filler compatibilization procedure by using GO and Pebax® 2533 endowed with higher permeability, but lower selectivity, than Pebax® 1657, with the aim of increasing its selectivity. A recent and accurate economic analysis, provided by Roussanaly et al. [53], about membrane separation in carbon capture showed that a competitive post combustion membrane should to have high permeability coupled with a CO2/N2 selectivity of at least 100.
Following this idea, in the present work, a set of Pebax® 2533–GO mixed matrix membranes have been prepared and tested to study their potential application for CO2 separation in post combustion carbon capture. Different loadings of unmodified GO, used as benchmark filler, were initially considered to optimize the MMM composition. Afterwards, also, porous graphene oxide (PGO), which has similar structure of GO but is less polar and with higher surface/volume ratio [44,54], and graphene oxide functionalized with polyetheramine (PEAGO), which should have a better polymer and CO2 compatibility, were used [55].
2. Materials and Methods
Pebax® 2533, is a block copolymer of the Pebax® thermoplastic elastomer family produced and provided by Arkema S.r.l. It is made of two blocks: one of polyamide-12, which occupies 20% of the copolymer mass, while the remaining 80 wt% is polytetramethyleneoxide, as also confirmed by many studies found in the literature [56,57,58,59,60]. The structure of Pebax® 2533 is shown in Figure 1.
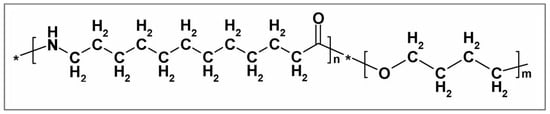
Figure 1.
Pebax® 2533 chemical structure.
During the procedure, different solutions and solvents have been used: ethanol, acetone, hydrochloric acid, and sodium hydroxide were provided by Dae-Jung Chemicals, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) by Sigma Aldrich (city, state abbr. if USA or CA, country), and graphite (used to prepare GO and the other GO-based materials) by Bay Carbon Inc. (Bay City, MI, USA).
2.1. Nanofiller Preparation
2.1.1. Graphene Oxide
Graphene oxide (GO), synthesized daily in the laboratory of professor Park, was prepared using modified Hummer’s method [61] by stirring 10 g of highly pure graphite powder in 380 mL of H2SO4 at 5 °C for 10 min, and adding 50 g of KMnO4 and stirring for 12 h at 35 °C. Then, the dispersion was highly diluted by adding first 500 mL at 5 °C while stirring for 1 h, then another 2 L of water. The last oxidative step was performed by adding H2O2 dropwise until the dispersion color changed from dark brown to golden yellow.
Immediately after the synthesis, the so-obtained GO was stirred for 30 min and then filtered, and washed multiple times with 10% HCl and acetone in order to remove any residual impurities [62].
2.1.2. Porous Graphene Oxide
Porous graphene oxide (PGO) was also available in the professor Park’s laboratory, where it is normally synthesized through the following standardized procedure. A 2 mg/mL GO dispersion in water is sonicated for 30 min to ensure high homogeneity. The dispersion was then heated up to 50 °C and NH4OH and H2O2 were added with a volume ratio of GO/NH4OH/H2O2 = 20/1/1. The solution was stirred at constant temperature for 5 h, and then cooled and centrifuged for 1 h at 12,000 rpm to recover the precipitated PGO. This was then redispersed in DI water and dialyzed for 3–4 days to eliminate any residual reagents or impurities. During the dialysis, the pH was continuously monitored, and the process was completed when the solution reached neutrality (pH = 7) [63].
2.1.3. Graphene Oxide Functionalized with Polyetheramine
Graphene oxide functionalized with polyetheramine (PEAGO) was prepared using the method designed by Yoo et al. [55]: 200 mg of 1 mg/mL GO/water dispersion was mixed with 150 mg of Jeffamine M-1000 and stirred for 24 h at room temperature, the pH was then adjusted to 4.5 using 1 M HCl, and 200 mg of EDC and NHS were added to the mixture. The solution was sonicated for 30 min and then stirred for 24 h to complete the modification. Dark brown PEAGO so-obtained was finally washed with HCl and then with acetone in order to remove any impurities.
The three GO-based structures are shown in Figure 2:
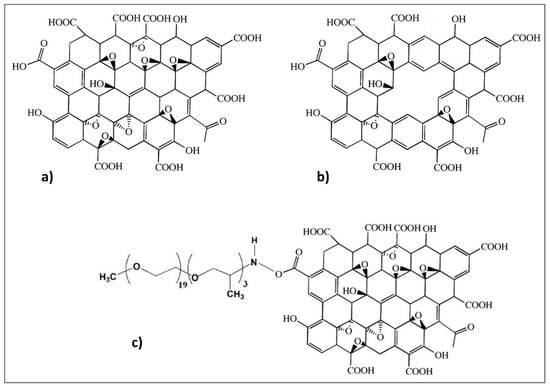
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of (a) GO [64], (b) PGO, and (c) PEAGO.
2.2. Membranes Preparation: “Double-Solvent Compatibilization”
Pebax® 2533 and graphene oxide are compatible in different solvents, the former in alcohols (ethanol and, even better, in butanol), the latter just in water. In order to mix them homogeneously and avoid phase segregation, a double-solvent solution has been developed as explained in this section, in order to compatibilize these incompatible materials.
In order to prepare polymeric solutions, Pebax® 2533 pellets have been solubilized in ethanol [26,65] with a concentration of 2 wt% of polymer/solvent by stirring at about 700 rpm upon a 150 °C hot plate for 5 h, and then letting it reach room temperature on 500 rpm stirring.
Water was instead used as dispersive solvent for graphene oxide, which readily precipitated when mixed with ethanol. The water–GO dispersions used in the present work were characterized by a concentration of 0.5 mg/mL and were produced by mixing the GO powder with the desired amount of water and then sonicating the solution for 2 h while maintaining the temperature below 35 °C. The same procedure was used also for the other two types of graphene considered in the present work namely PGO and PEAGO.
Once the aqueous dispersion of GO was ready, it was added to the Pebax® 2533/ethanol polymeric solution at 35 °C which was then vigorously stirred for 10 min before pouring it in a teflon petri dish. The solution was then left to evaporate at room temperature in order to obtain self-standing membranes. Four different loadings were considered for GO addition, namely 0.02, 0.1, 0.5 and 1 wt%, to study the influence of this parameters on the overall polymer permeability. In all cases, polymer + GO ethanol/H2O mixture resulted very homogeneous and allowed obtaining very smooth membranes with no sign of agglomerates even at the highest loading inspected, as shown in Figure 3a–c.
Figure 3.
Pebax® 2533 + graphene oxide composite casted membranes; loadings (a) 0.1 wt%, (b) 0.5 wt%, and (c) 1 wt%.
Unfortunately for the two other GO types considered, the dispersion in Pebax® 2533 resulted in more difficulties, and for both PGO and PEAGO, only the 0.02 wt% loaded films were obtained with good homogeneity and limited presence of GO aggregates (see Figure 4a,b) while increasing concentration always led to aggregation and heterogenous films as shown in Figure 4c.
Figure 4.
Pebax® 2533 loaded with (a) 0.02 wt% PGO, (b) 0.02 wt% PEAGO, and (c) 0.1 wt% PGO.
The thickness of different tested membranes ranged from 75 to 100 µm, and every resulting membrane was very homogeneous, with a variation in thickness of less than 2% on each sample, as determined from a minimum of 6 measurements on different part of the membranes.
2.3. Materials Characterization
2.3.1. XPS
XPS analysis was carried out to confirm that PEA groups were successfully grafted onto GO by monitoring the nitrogen peak of the material. The analysis was conducted using an Omicron ESCALAB (Omicron, Taunusstein, Germany) with a monochromatic Al Kα (1486.8 eV) 300 W X-ray source, and a flood gun to counter charging effects under ultra-high vacuum (UHV ≈ 1 × 10−9 torr) conditions.
2.3.2. SEM Analysis
In order to have more precise information about filler dispersion, SEM analysis has been conducted considering both planar and fracture surfaces of membranes of pristine Pebax® 2533 and of all composite samples.
To obtain information on membranes’ surface, flat pieces of every type of tested material was analyzed, while the fracture surfaces were realized by cutting the membranes in liquid nitrogen with scissors. Indeed, even after immersion, it was impossible to obtain a brittle fracture of the materials by simply bending the samples, which remained rather flexible and tough even when immersed in liquid nitrogen.
SEM images have been carried out using a Phenom ProX (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), with a voltage of 10 kV and a magnification range of 1000–5000×. Before the analysis, all samples have been metal-coated in a Quorum sputter SC7620 using an Au–Pd disc target.
2.3.3. DSC
To better understand how the filler may have affected the matrix structure and if there was preferential distribution within the two copolymer moieties, DSC analysis has been carried out as well. The program used was always made of four cycles, always with a heating rate of 10 °C/min:
- (1)
- Cooling from room temperature to −80 °C
- (2)
- Heating from −80 to 250 °C
- (3)
- Cooling from 250 to −80 °C
- (4)
- Heating from −80 to 250 °C
In this way, with cycles 1 and 2, the thermal history of the material was cancelled, and it was possible to obtain information on the tested material by analyzing cycles 3 and 4.
The apparatus employed was a DSC Q2000 (TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA), and the sample size was always between 5 and 25 mg.
2.3.4. Permeation Test
Permeation tests were carried out with the system shown in Figure 5, which has been designed to perform single gas permeability measurement using the so-called barometric technique [24,28]. All experiments have been conducted at 35 °C, with temperature maintained constant by using a heated water bath, which contained almost the entire system. In every experiment, the upstream pressure was maintained at 1 bar while the downstream side was under vacuum conditions.
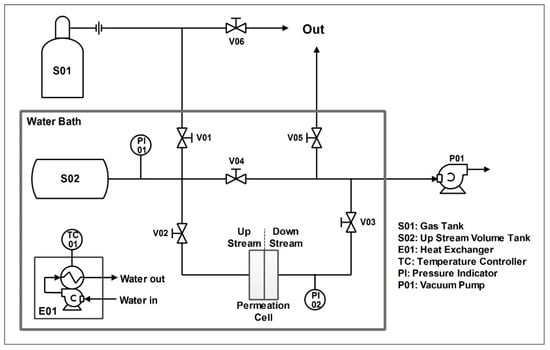
Figure 5.
Permeation system employed.
Technically, the test procedure started by placing the membrane sample into the cell, and then treating it under vacuum until pressure indicators PI01 and PI02 measured a steady value of upstream and downstream pressure. The permeating gas was then charged into the upstream volume (limited between valves V01, V02, and V04, including the tank S02) at the pressure of 1 bar.
Once the upstream pressure was stabilized, the test was started by opening valve V02 while keeping V01, V04, and V03 closed; during the tests, the downstream pressure was continuously monitored and saved to allow then the calculation of permeability (P) through Equation (1).
where pressure Δp indicates the pressure difference between upstream and downstream compartment, dPd/dt the rate of the downstream pressure increase, δ and A the membrane thickness and area, respectively, and Vd the downstream volume. All quantities were reported with correct units to obtain the permeability in Barrer (1 Barrer = 10−10 (cm3STP/(cmHg·s·cm)) or 3.35 × 10−16 (mol/Pa·s·m)).
All tests were set up to end when an increase of 10 torr in downstream was registered: this value is indeed high enough to allow the measurement of permeability, while not significantly decreasing the pressure driving force between upstream and downstream sections of the apparatus.
Since the system used allowed only one gas to be tested at once, in order to achieve information on membranes’ selectivity, ideal selectivity was calculated through the ratio between the permeability of the two different gases of interest, CO2 and N2, determined separately as shown in Equation (2):
Overall, the error on the results of gas permeation test, considering thickness variations, volume calibration uncertainty, and other sources of error, was in the order of 2%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XPS
To investigate PEAGO reaction and verify the success of grafting, XPS analysis was carried out, focusing on the signal related to nitrogen and carbon and obtaining the results shown in Figure 6.
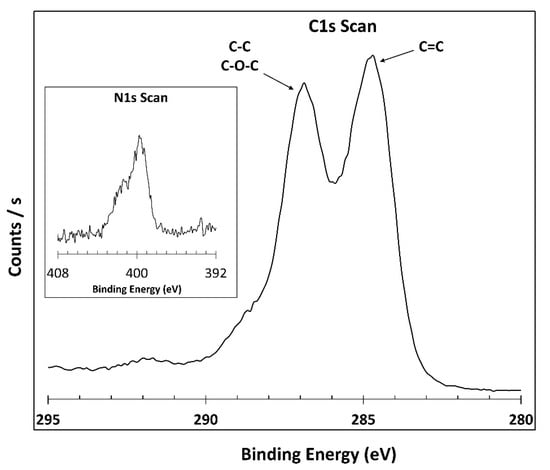
Figure 6.
C1s and N1s XPS scan of PEAGO.
From the XPS analysis, a small amount of nitrogen 1s was found into the structure, while almost negligible changes were present in the C1s region: PEA already carries a low amount of nitrogen itself, so a high amount of this atom is not expected after the reaction with a nitrogen-less material like GO. XPS confirmed the nitrogen presence and therefore ensured the success of the reaction with a conversion similar to the one obtained from Yoo et al. [55] which, indeed, also presented very similar XPS results.
3.2. SEM
Through the SEM images presented below, it has been possible to obtain information on the membrane microstructures, which may be helpful to understand material properties, including the permeation behavior.
Considering the fracture sections, reported in Figure 7, it is possible to notice from that the neat polymer fracture (7a) is the smoothest, while the amount of imperfections increases with the rise of the GO content (7b–e). Indeed, while neat Pebax® shows a very homogeneous structure, the fractured surface of the different mixed matrix membranes always present cracks likely related to nanometric defects, close to the polymer/GO interface, which were amplified during the fracture. Such defects and cracks clearly increase and become more pronounced by increasing the amount of the filler with the 7d and e images, referring respectively to 0.5 and 1% GO loading, that suggest the presence of layered structure on the membrane surface induced by the presence of the filler. These seemed to be characteristic of the lower surface of the membrane suggesting the tendency of the graphene to sediment during the casting procedure; this possibility, however, should be verified further with more specific analyses.
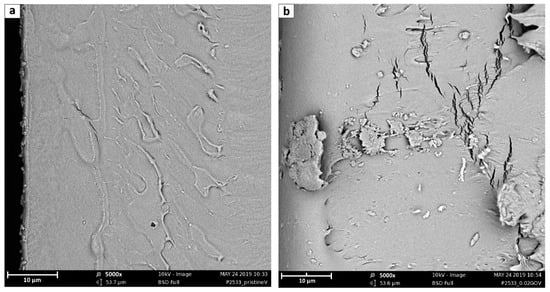
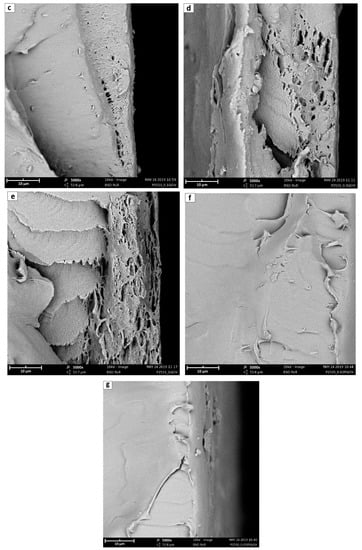
Figure 7.
Fracture sections 5000× SEM images of (a) neat Pebax® 2533; (b) + 0.02 wt% GO; (c) + 0.1 wt% GO; (d) + 0.5 wt% GO; (e) + 1 wt% GO; (f) + 0.02 wt% PGO; and (g) + 0.02 wt% PEAGO. The scale bar in the figure refers to 10 μm.
Considering the differences between different types of GO considered, it is worthwhile to note that comparing Figure 7b,f,g, which refer to GO, PGO, and PEAGO with 0.02%wt loading, the latter results have less cracks, suggesting a better interaction between the filler and the polymeric matrix.
SEM analysis of the membrane surfaces does not give the same amount of information as the images obtained for the different composites are indeed very similar and are not shown in detail for the sake of brevity. In general, however, they provide indirect information about platelet dimensions; indeed, on membrane surface, it is sometimes possible to see the presence of a high aspect ratio agglomerated GO flakes, partially covered by the polymer. The platelets shown in Figure 8, for example, have lateral dimensions in the order of 10–70 μm, although with the GO synthesis method described in Section 2.1, it is possible to obtain a wide range of GO sizes from hundreds of nanometers to some micrometers, as demonstrated by Cho et al. [66].
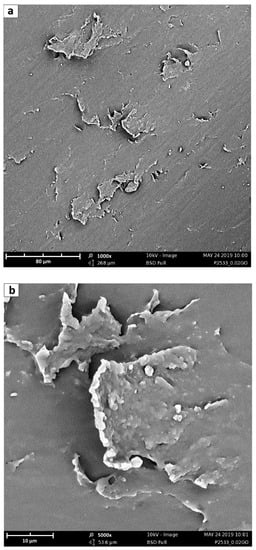
Figure 8.
SEM of GO sheets trapped in Pebax® 2533 matrix at (a) 1000× and (b) 5000×. The scale bars in the two figures (a,b) refer to 80 and 10 μm respectively.
3.3. DSC
DSC analysis was conducted through the four cycles explained in Section 2.3.3, and below are listed the full spectra of the 3rd cycle of heating (Figure 9) and, on the 4th cycle, of cooling (Figure 10), both with shifted lines for the sake of clarity.
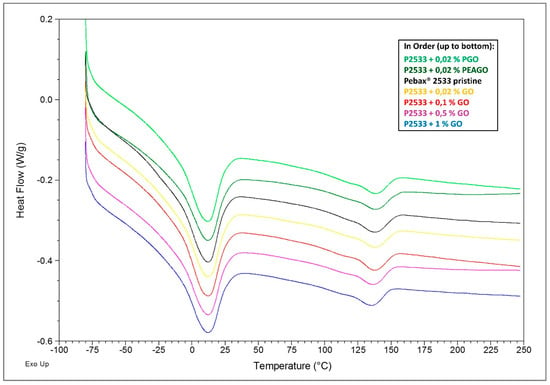
Figure 9.
DSC results—4th cycle, heating.
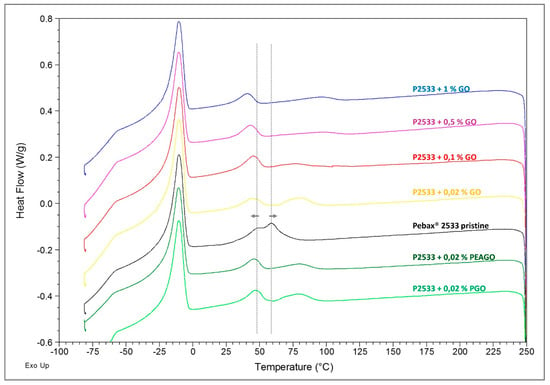
Figure 10.
DSC results—3rd cycle, cooling.
In Figure 9, the spectra of the last heating cycle are shown, where the results are quite clear in that all the inspected materials substantially present the same behavior. The two melting peaks (at about 130 °C for the polyamide-12 block and at about 10°C for polytetramethyleneoxide (PTMO) domains) are indeed very similar in all the different spectra, both for position and intensity. It seems, therefore, that the presence of GO nanofillers did not affect the amount or distribution of crystals within the copolymers.
However, looking at Figure 10, referring to the cooling cycle, some differences are clear. Indeed, while the crystallization peak of PTMO (at about −10 °C) remained substantially unaltered in every sample, the crystallization signal of nylon, made up of two partially overlapped peaks at about 50 and 60 °C, was subjected to a slight, but noticeable change. The two peaks indeed shifted respectively toward lower and higher temperatures, thus becoming more and more separated as the filler loading was increased. The shift was then independent of the chemical nature of the materials as in Pebax® 2533 loaded with 0.02% GO, two peaks moved at 45 and 80 °C in almost the same positions observed respectively for the PEAGO and PGO composites with the same filler loading.
Such results suggest that the filler was mainly dispersed into the nylon moiety, affecting its crystallization process. Nylon crystals indeed started to form at lower temperatures with respect to the unloaded polymer (as the GO was acting as nucleating agent) and completed their growth at higher temperature likely due to the increased rigidity of the loaded material, which slowed down the overall process. The platelet, however, did not compromise the completion of the crystallization, nor the structure of the crystals since, as stated above, the melting signals (Figure 9) remained substantially unchanged.
3.4. Permeation
All permeation data measured in the present work are reported in Table 1, which also shows permeability and selectivity variations with respect to pristine Pebax®. For a more detailed analysis, Figure 11 shows the results of the permeation tests in the Pebax® 2355 MMMs obtained with different loading of GO. The addition of graphene oxide seems to substantially decrease the permeability for both CO2 and N2. Indeed from 0.02 to 1 wt% GO, the Pebax®-based MMMs show lower and lower permeability with a decrease from 365 to 51 Barrer for CO2 and from 15 to 2 Barrer for nitrogen. The only exception in the observed trend is possibly represented by the composite with the lower loading, which indeed showed a very limited increase for CO2 permeability (371 Barrer with respect to the 365 Barrer measured for pristine Pebax®). Similar behavior was already observed in a previous work made by Lee et al. that were able to improve the permselective properties of polymer matrix Pebax® 1657 loaded with “ZPGO” (that is, ZIF-8 grown on porous graphene oxide), by employing such low filler concentrations [67]. In the present case, however, the difference observed is too limited, within 2%, to conclude that the observed increase is real and not due to an experimental uncertainty, which was also in the order of 2%, considering thickness variation in the membranes and uncertainty in the experimental tests.

Table 1.
Summary and variation in percentage of permeation results.
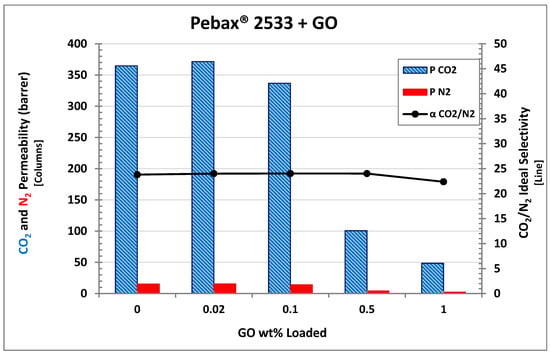
Figure 11.
CO2/N2 permeability and ideal selectivity of Pebax®2533 with different GO loadings.
The observed decrease in permeability at “high” loading, on the other hand, could be expected as GO platelets can increase the tortuosity of the diffusion path within the membrane, as schematized in Figure 12, due to their high aspect ratio and their low intrinsic permeability, as already reported by other authors [51]. This type of effect seems also confirmed by the SEM images analyzed, where layered structures were clearly visible when the graphene oxide concentration was increased within the matrix.
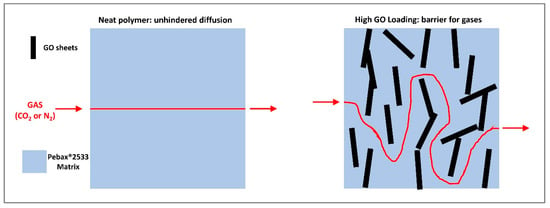
Figure 12.
Graphene oxide barrier behavior concept.
By comparing the CO2 and nitrogen permeability, membrane selectivity can be obtained which is also presented in Figure 11 as a black line. Interestingly, this parameter was substantially unaffected by the addition of the filler, somewhat in contrast with the expected behavior since GO is usually considered to be selective towards CO2 and already proved to be able to improve polymer selectivity when used to obtain mixed matrix membranes [41,42,43,44,45,46,47].
In the present case, instead, no substantial changes in CO2/N2 selectivity were observed, as this parameter indeed remained very close to 24 for all the materials tested, so that GO seemed to behave as an impermeable filler which reduced the permeability merely because of tortuosity effects without affecting the permselective behavior of the polymer.
In order to test different GO-based fillers behavior, Pebax® 2533 membrane mixed with PEAGO and PGO have been also tested, and all of them were compared with 0.02 wt% loading which, based on GO analyses, resulted in being the most promising in terms of permselective properties. The results are shown in Figure 13, where the permeability of CO2 and N2 in PGO and PEAGO nanofiller are reported together with those already discussed of pristine Pebax® and 0.02 wt% GO membrane that are repeated for the sake of clarity.
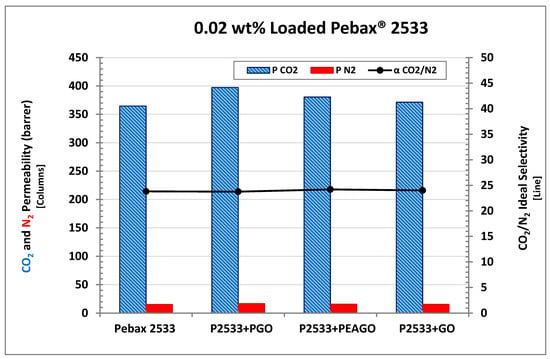
Figure 13.
CO2 permeability of Pebax® 2533 filled with 0.02 wt% of different GO-based materials.
Interestingly, both PEAGO and PGO slightly improved permselective properties with respect to the base polymer with differences between 4% and 8% (that is higher than the recognized experimental error). CO2 permeability, in particular, reached the value of 380 Barrer in the PEAGO-loaded sample, and increased even more in PGO-loaded Pebax®, where it reached 397 Barrer. CO2/N2 selectivity, on the other hand, was still unaltered, remaining very close to 24 also for the last two samples inspected.
Such an increase in permeability without any effect on selectivity cannot be explained by gas platelet interaction which would favor CO2 with respect to nitrogen, so that it seems to be related to the presence of a lower density region (possibly related to poor interfacial adhesion or less efficient polymer packing) at the polymer–filler interface where the permeating gases, both CO2 and N2, can permeate at a higher rate, thus reducing the time to cross the membranes without altering the relative selectivity, as already suggested by various authors [68,69,70,71]. A schematic concept of this hypothesis is displayed in Figure 14.
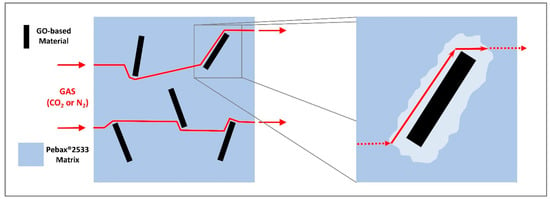
Figure 14.
GO material–Pebax® interface voids concept.
From this point of view, the performance differences among the three GO materials at the same low concentration (0.02 wt%) are probably related to the dispersion of the different types of GO have in the matrix, which influences both the increase in tortuosity and the properties of the interfacial region. These two processes indeed have opposite effects on permeability, and their balance gives the final materials properties. In the present case, the observed behavior could be explained by considering that, very likely, two modified GOs have lower aspect ratio with respect to the pristine one, due to the additional harsh treatment that the original materials had to undergo to be modified.
Porous graphene oxide is indeed well known to be have reduced area compared the pristine GO and also an higher amount of defects, which makes the nanofiller intrinsically more permeable: Lee et al. [67] demonstrated the formation of pores upon GO, and most likely, such treatment was also able to partially fracture the sheets themselves. On the other hand, fragmentation of GO platelet during PEAGO synthesis can likely be related to the presence of intensive mixing and sonication, which could produce mechanical stresses able to break GO and PEAGO sheets, as demonstrated also by Baig et al. [72].
The difference between PGO and PEAGO could be related to the presence of ether-based polymer chains grafted to the latter, which can lead to a better interaction with the Pebax® matrix, slightly decreasing the interfacial voids compared to PGO and thus causing a smaller effect on permeability.
Finally, the limited changes observed among different materials can be related to the fact that, as suggested by DSC results, the fillers were preferentially dispersed in the nylon moiety, which was less abundant and also less involved in gas permeation compared to PTMO; the features of the latter phase, which is also the main one responsible for the CO2/N2 selectivity, indeed remained substantially constant in the DSC chart. Thus, by analyzing both DSC and the interface theory previously explained, the obtained permeation results turned out to be consistent.
In general, however, even if slight improvements have actually been obtained, especially with the addition of PGO, the overall permeation properties of the Pebax® 2533-modified GO were not good enough to overcome current state-of-the-art materials, and remained below the 2008 Robeson’s upper bound which, for a CO2 permeability of 400 Barrer, requires a selectivity with respect to nitrogen above 50 to be overcome [18]. On the other hand, the results show the possibility to obtain homogeneous dispersion of nanofiller in the polymeric matrix, thus opening the path for further optimization aimed at increasing not only permeability but also CO2 selectivity of the obtained MMMs.
4. Conclusions
Nanocomposite membranes of Pebax® 2533 have been prepared through its mixing with GO-based materials to investigate the ability of this material to serve as a matrix for MMMs.
First of all, the behavior of graphene oxide loaded into the polymer at different concentrations was investigated, revealing that 0.02 wt% was the best composition in terms of improvements in properties. Higher loading indeed caused the permeability to drop from 364 barrer of pristine Pebax® 2533 to 50 barrer for the 1 wt% GO loaded sample. SEM analysis revealed indeed that at high concentration, GO platelet tends to aggregate, forming a layered structure with barrier behavior.
After this initial screening, PEAGO and PGO were also tested at a concentration of 0.02 wt%, showing a further improvement in permselective properties: ideal CO2/N2 selectivity still remained constant, but CO2 permeability increased, even if not dramatically, going from pristine Pebax® (364 Barrer) to the GO (371 Barrer) loaded and then to PEAGO (380 Barrer) and PGO (397 Barrer), which resulted in the most promising nanofiller.
The better performance of PGO may be due to both its sieving behavior, provided by holes on the layer itself, and by its better dispersion caused by the smaller dimensions and surface/volume ratio.
Despite the permeability improvements, the present MMMs still cannot compete with state-of-the-art membrane materials for post combustion carbon capture, and further optimization is needed to also obtain an improvement in the CO2/N2 selectivity. The current results, in particular, allowed determining the optimal graphene oxide loading, but more attention should be given toward controlling the GO dispersion; a proper control of the distance among platelets, indeed, would hinder the diffusion of nitrogen molecules without substantially affecting the CO2 permeability, thus obtaining a molecular sieving structure able to increase the overall membrane selectivity.
Author Contributions
Data Curation, R.C.; Investigation and methodology R.C., M.J.Y.; supervision, H.B.P., M.G.B.; writing-original draft preparation, R.C., M.G.B.; writing-review and editing, R.C., M.G.B.; Resources, L.G., H.B.P., M.G.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was performed in the framework of the European Project H2020 NANOMEMC 2 “NanoMaterials Enhanced Membranes for Carbon Capture”, funded by the Innovation and Networks Executive Agency (INEA) Grant Agreement Number: 727734.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Global Warming Potential Values. Available online: https://www.ghgprotocol.org/sites/default/files/ghgp/Global-Warming-Potential-Values%20%28Feb%2016%202016%29_1.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- IPCC, Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Global warming of 1.5 °C; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 9789291691517. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, A.; Gholami, R.; Rezaee, R.; Rasouli, V.; Rabiei, M. Significant aspects of carbon capture and storage–A review. Petroleum 2019, 5, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilberforce, T.; Baroutaji, A.; Soudan, B.; Al-alami, A.H.; Ghani, A. Science of the Total Environment Outlook of carbon capture technology and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, I.; Nahar, T.; Venugopal, A.; Srinivas, B. Carbon capture by absorption–Path covered and ahead. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1080–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Miller, D.C. Post-combustion CO2 capture technologies—A review of processes for solvent-based and sorbent-based CO2 capture. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017, 17, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardsen, I.M.; Knuutila, H.K. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control A review of potential amine solvents for CO2 absorption process: Absorption capacity, cyclic capacity and pKa. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 61, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraharisetti, P.K.; Yeo, T.Y.; Bu, J. New classification of CO2 mineralization processes and economic evaluation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 99, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, Q.; Deng, S.; Li, H.; Kitamura, Y. Cryogenic-based CO2 capture technologies: State-of-the-art developments and current challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalilpour, R.; Mumford, K.; Zhai, H.; Abbas, A.; Stevens, G.; Rubin, E.S. Membrane-based carbon capture from flue gas: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedhar, I.; Vaidhiswaran, R.; Kamani, B.M.; Venugopal, A. Process and engineering trends in membrane based carbon capture. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 659–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering Recent advances on the membrane processes for CO2 separation. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2280–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Ho, W.S. Recent advances in polymeric membranes for CO2 capture. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 2238–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Recent advances on mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1581–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.; Ying, L.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Ebadi, A. Progress in Polymer Science State-of-the-art membrane based CO2 separation using mixed matrix membranes (MMMs): An overview on current status and future directions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 817–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroon, M.A.; Ismail, A.F. Performance studies of mixed matrix membranes for gas separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Sanip, S.M.; Ng, B.C.; Aziz, M. Recent advances of inorganic fillers in mixed matrix membrane for gas separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoba, M.; Bhagiyalakshmi, M.; Alqaheem, Y.; Alomair, A.A.; Pérez, A.; Rana, M.S. Recent progress of fillers in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 188, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, D.; Chrysanthou, A.; Dhuiège, B.; Missoum, K.; Baschetti, M.G. Arginine/Nanocellulose membranes for carbon capture applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkat, S.; Kaliaguine, S.; Rodrigue, D. Enhancing CO2 separation performance of Pebax® MH-1657 with aromatic carboxylic acids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chan, S.; Kim, T.; Wook, S.; Soo, Y. Direct molecular interaction of CO2 with KTFSI dissolved in Pebax 2533 and their use in facilitated CO2 transport membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 548, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.; Ki, S.; Hoon, Y.; Bum, H. Effect of PEG-MEA and graphene oxide additives on the performance of Pebax®1657 mixed matrix membranes for CO2 separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 572, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Ding, R.; Yang, K.; Dai, Y.; Yan, X.; He, G. ZIF-8 nanoparticles with tunable size for enhanced CO2 capture of Pebax based MMMs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 214, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, V.; Hägg, M.B. Development of dual layer of ZIF-8/PEBAX-2533 mixed matrix membrane for CO2 capture. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 459, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkema ARKEMA Products Online Database. Available online: https://www.extremematerials-arkema.com/en/materials-database/products (accessed on 23 October 2019).
- Deluca, N. PEBA: TPE materials for high performance applications. In Proceedings of the Annual Technical Conference - ANTEC, Anaheim, CA, USA, 8–10 May 2017; pp. 2343–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, J.P.; Xu, J.; Wilkes, G.L. Solid state structure–property behavior of semicrystalline poly (ether-block-amide) PEBAX® thermoplastic elastomers. Polymer (Guildf.) 2003, 44, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkema, Arkema Reference Document 2018 Including the Annual Financial Report. Labrador Information Design: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–364.
- Rahman, M.M.; Filiz, V.; Shishatskiy, S.; Abetz, C.; Neumann, S.; Bolmer, S.; Khan, M.M.; Abetz, V. PEBAX® with PEG functionalized POSS as nanocomposite membranes for CO2 separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 437, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Shi, D.; Dong, W.; Li, X.; Bai, Y. Metal-organic framework-graphene oxide composites: A facile method to highly improve the CO2 separation performance of mixed matrix membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 520, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scofield, J.M.P.; Gurr, P.A.; Kim, J.; Fu, Q.; Kentish, S.E.; Qiao, G.G. Development of novel fluorinated additives for high performance CO2 separation thin-film composite membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 499, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, G.S.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, K.C.W.; Lin, C.H.; Tung, K.L. Characterization and molecular simulation of Pebax-1657-based mixed matrix membranes incorporating MoS2 nanosheets for carbon dioxide capture enhancement. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 582, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaeepur, H.; Ahmadi, R.; Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Ghanbari, D. A novel ternary mixed matrix membrane containing glycerol-modified poly(ether-block-amide) (Pebax 1657)/copper nanoparticles for CO2 separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 573, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, W.; Luo, J.; Gao, M.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Park, A.H.A. Selective separation of CO2 using novel mixed matrix membranes based on Pebax and liquid-like nanoparticle organic hybrid materials. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 584, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafisi, V.; Hägg, M.B. Development of nanocomposite membranes containing modified Si nanoparticles in PEBAX-2533 as a block copolymer and 6FDADurene diamine as a glassy polymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 15643–15652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koolivand, H.; Razzaghi-kashani, M.; Karimi, M.; Koolivand, M. Functionalized graphene oxide/polyimide nanocomposites as highly CO2-selective membranes. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Soyekwo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, C.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Q. Graphene oxide nanosheets to improve permeability and selectivity of PIM-1 membrane for carbon dioxide separation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, M.; Li, S.; Yu, M. Ultrathin graphene oxide-based hollow fiber membranes with brush-like CO2-philic agent for highly efficient CO2 capture. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V.; Liu, J. Enhanced CO2/N2 separation by porous reduced graphene oxide / Pebax mixed matrix membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 520, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xin, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, Z.; Su, F.; Zheng, Y. Carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide-based solvent-free hybrid nanofluids functionalized mixed-matrix membranes for efficient CO2/N2separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 221, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, S.; Bhoria, N.; Pokhrel, J.; Reddy, K.S.K.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Wang, K.; Karanikolos, G.N. Metal-organic framework / graphene oxide composite fillers in mixed-matrix membranes for CO2 separation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 212, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A.; Nasir, A.M.; Aziz, F.; Kumar, G.; Sallehhudin, W.; Jaafar, J.; Lau, W.J.; Yusof, N.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F. CO2/N2 selectivity enhancement of PEBAX MH 1657/Aminated Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide Mixed Matrix Composite Membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiram, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. Performance of nanocomposite membranes containing 0D to 2D nanofillers for CO2 separation: A review. Membranes 2018, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.M.; Shin, J.E.; Lee, H.D.; Park, H.B. Graphene and graphene oxide membranes for gas separation applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2017, 16, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Li, J. Graphene oxide membranes: Functional structures, preparation and environmental applications. Nano Today 2018, 20, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunakaran, M.; Shevate, R.; Kumar, M.; Peinemann, K.V. CO2-selective PEO-PBT (PolyActiveTM)/graphene oxide composite membranes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14187–14190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, G.; Huang, K.; Jin, W.; Lee, K.R.; Xu, N. Membranes with fast and selective gas-transport channels of laminar graphene oxide for efficient CO2 capture. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 578–582. [Google Scholar]
- Roussanaly, S.; Anantharaman, R.; Lindqvist, K.; Zhai, H.; Rubin, E. Membrane properties required for post-combustion CO2 capture at coal-fired power plants. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 511, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, B.; Yan, F.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Li, L. Engineering nano-porous graphene oxide by hydroxyl radicals. Carbon N. Y. 2019, 105, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.J.; Kim, H.W.; Yoo, B.M.; Park, H.B. Highly soluble polyetheramine-functionalized graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide both in aqueous and non-aqueous solvents. Carbon N. Y. 2014, 75, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-estévez, J.C.I.; Antônio, L.; de Almeida, S.; Schulte, K.; Bucio, E. PEBAX TM-Silanized Al2O3 Composite, Synthesis and Characterization. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2012, 2, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, S.; Freeman, B.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Gas permeability of melt-processed poly (ether block amide) copolymers and the effects of orientation. Polymer (Guildf.) 2012, 53, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Fang, C.; Li, Z.; Young, M. Separation of thiophene/n-heptane mixtures using PEBAX/PVDF-composited membranes via pervaporation. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 451, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, G.; Bernardo, P.; Gorrasi, G.; Zampino, D.; Carroccio, S.C. Influence of the Preparation Method and Mhoto-Oxidation Treatment on the Thermal and Gas Transport Properties of Dense Films Based on a Poly(ether-block-amide) Copolymer. Materials 2018, 11, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahab, M.S.A.; Sunarti, A.R. Development of PEBAX Based Membrane for Gas Separation: A Review. Int. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2015, 2, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dikin, D.A.; Stankovich, S.; Zimney, E.J.; Piner, R.D.; Dommett, G.H.B.; Evmenenko, G.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide paper. Nature 2007, 448, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, H.D.; Shin, J.E.; Yoo, B.M.; Park, H.B. Water and ion sorption, diffusion, and transport in graphene oxide membranes revisited. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 544, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, F.; Lee, T.H.; Park, I.; Park, H.B. Thermally annealed polyimide-based mixed matrix membrane containing ZIF-67 decorated porous graphene oxide nanosheets with enhanced propylene/propane selectivity. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 603, 118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; University of Manchester; Wilkinson, J.; AzoNano. Interview: Developing Graphene Oxide Membranes for the Purification of Water and Green Fuels. Available online: https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=4275 (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- Ehsani, A.; Pakizeh, M. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers Synthesis, characterization and gas permeation study of ZIF-11 / Pebax ® 2533 mixed matrix membranes. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 66, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, T.H.; Park, H.B.; Park, H.; Nam, S.; Park, Y. Sacrificial graphene oxide interlayer for highly permeable ceramic thin film composite membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 118442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.C.; Roh, J.S.; Moon, G.H.; Shin, J.E.; Kang, Y.S.; Park, H.B. Metal-organic frameworks grown on a porous planar template with an exceptionally high surface area: Promising nanofiller platforms for CO2 separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 22500–22505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, N.; Liao, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Relationship between polymer-filler interfaces in separation layers and gas transport properties of mixed matrix composite membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 495, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Paul, D.R. Gas permeation in poly(ether imide) nanocomposite membranes based on surface-treated silica. Part 1: Without chemical coupling to matrix. Polymer (Guildf.) 2006, 47, 7519–7534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.T.; Koros, W.J. Non-ideal effects in organic-inorganic materials for gas separation membranes. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 739, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinh-Thang, H.; Kaliaguine, S. Predictive models for mixed-matrix membrane performance: A review. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4980–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, Z.; Mamat, O.; Mustapha, M.; Mumtaz, A.; Munir, K.S.; Sarfraz, M. Investigation of tip sonication effects on structural quality of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) for superior solvent dispersion. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 45, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).