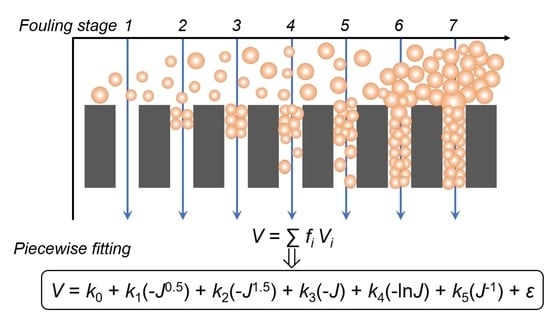
A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model
3. Experimental
3.1. Membrane and Model Foulant Solution
3.2. Filtration Test
3.3. Analytical Items
4. Results and Discussion
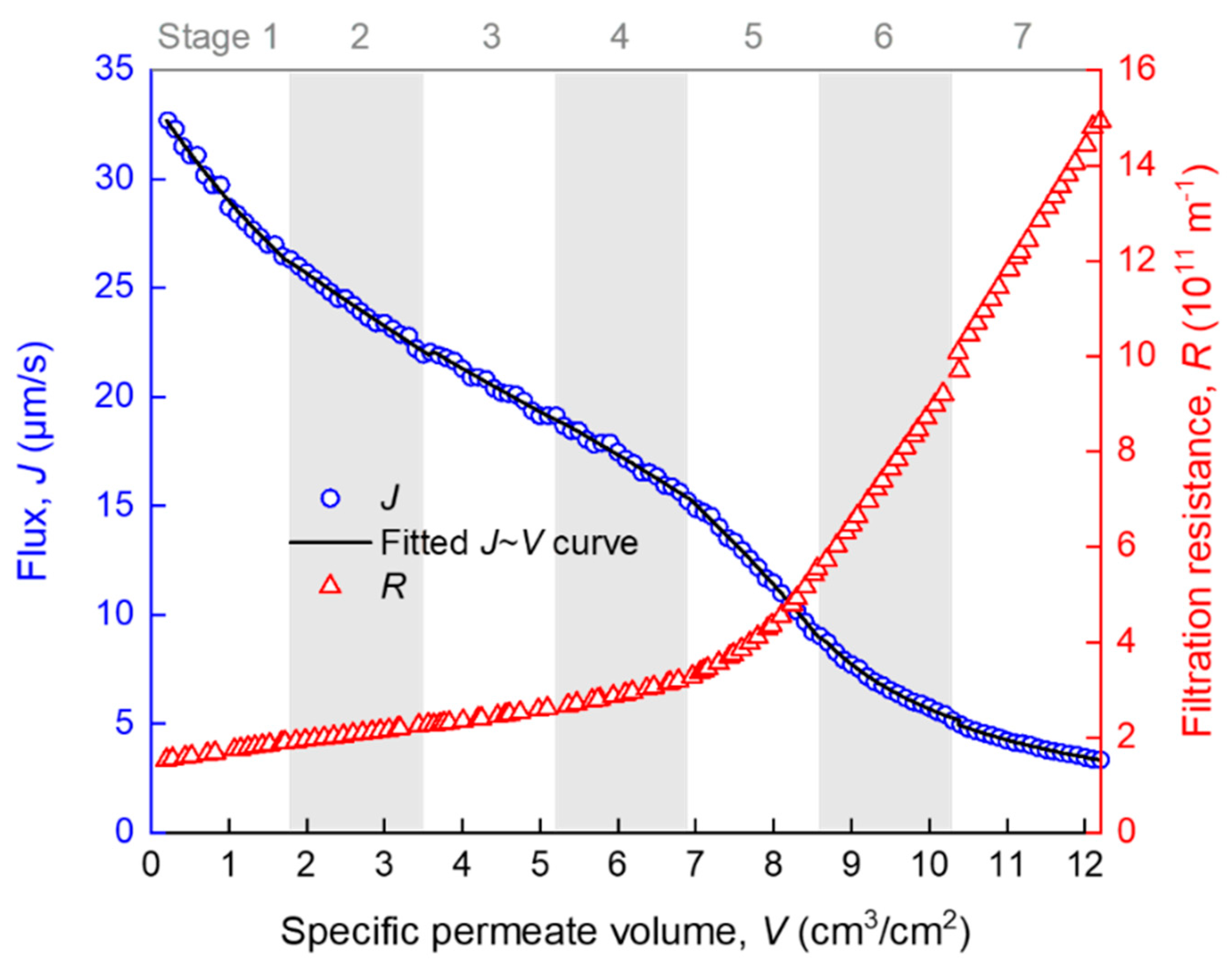
4.1. Overview of Fouling Evolution
4.2. Piecewise Fitting Results
4.3. Interpreting the Transition of Major Mechanisms According to Foulant Composition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. MATLAB Code for Automatically Calculating V, J, R and dR/dV from the Raw Data of Filtration
Appendix B. MATLAB Code for Piecewise Fitting of the Multiple Linear Model to the J~V Data
Appendix C. Abbreviation List
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| DOM | Dissolved organic matter |
| DW | Durbin–Watson |
| EEM | Excitation–emission matrix |
| FI | Fluorescence intensity |
| HA | Humic acid |
| J | Filtration flux |
| k | Model coefficient (Equations (1)–(4)) |
| MF | Microfiltration |
| N | Characteristic exponent |
| n | Number of segments of the filtration process |
| P | Trans-membrane pressure |
| pDW | p value of DW test |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| R | Filtration resistance |
| R.U. | Raman unit |
| SA | Sodium alginate |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| t | Filtration time |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| UV | Ultraviolet absorbance |
| V | Specific permeate volume |
| ε | Error term |
| μ | Dynamic viscosity of the permeate |
References
- Baker, R.W. Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tal, G.; Hankins, N.P.; Gitis, V. Fouling and cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 1, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Carlson, K.; Robbins, C.A.; Zhang, Z.; Du, X. Membrane-based treatment of shale oil and gas wastewater: The current state of knowledge. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: A review. Membranes (Basel) 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Monnot, M.; Ercolei, L.; Moulin, P. Membrane-based processes used in municipal wastewater treatment for water reuse: state-of-the-art and performance analysis. Membranes 2020, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zularisam, A.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, R. Behaviours of natural organic matter in membrane filtration for surface water treatment—A review. Desalination 2006, 194, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Wei, C.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. Outlining the roles of membrane-foulant and foulant-foulant Interactions in organic fouling during microfiltration and ultrafiltration: A mini-review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.G.; Zhang, S.Q.; Oh, Y.; Zhou, Z.B.; Shin, H.S.; Chae, S.R. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Res. 2017, 114, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Tarabara, V.V. Pore blocking mechanisms during early stages of membrane fouling by colloids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.S.; Ngo, H.H.; Li, J.X. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Mo, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, M.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Waite, T.D. An extended standard blocking filtration law for exploring membrane pore internal fouling due to rate-determining adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Zydney, A.L. A combined pore blockage and cake filtration model for protein fouling during microfiltration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Gu, H.; Xiao, K.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Fouling mechanisms analysis via combined fouling models for surface water ultrafiltration process. Membranes (Basel) 2020, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iritani, E.; Katagiri, N. Developments of blocking filtration model in membrane filtration. KONA Powder Part. J. 2016, 33, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglia, S.; Straeffer, G. Combined mechanism fouling model and method for optimization of series microfiltration performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 417, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, A.Y.; Cheng, Y.H.; Paul, D.R.; Field, R.W.; Freeman, B.D. Fouling mechanisms in constant flux crossflow ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufidou, K.; Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J. A study of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acids and flux recovery by backwashing: experiments and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 266, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, X.R.; Rosenthal, I.; Anlauf, H.; Nirschl, H. Experimental and analytical modeling of the filtration mechanisms of a paper stack candle filter. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 2776–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Orime, T.; Matsumoto, K. Response of zeta potential to cake formation and pore blocking during the microfiltration of latex particles. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401–402, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos Orsello, C.; Li, W.; Ho, C.C. A three mechanism model to describe fouling of microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sankararao, B.; Lee, S.; Yoo, C. Prediction and identification of membrane fouling mechanism in a membrane bioreactor using a combined mechanistic model. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 17198–17205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.C.; Docê, R.C.; de Barros, S.T.D. Clarification of passion fruit juice by microfiltration: analyses of operating parameters, study of membrane fouling and juice quality. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, M.C.V.; Blanco, S.Á.; García, J.L.; Rodríguez, E.B. Analysis of membrane pore blocking models applied to the ultrafiltration of PEG. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 62, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, A.; Abbasi, M.; Mohammadi, T. Permeate flux decline during UF of oily wastewater: experimental and modeling. Desalination 2010, 251, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Yoo, G.Y.; Yoo, C. Development of combined fouling model in a membrane bioreactor. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 6, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wang, Z.; Song, P. A precise combined complete blocking and cake filtration model for describing the flux variation in membrane filtration process with BSA solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofungwu, J. Statistical Applications for Environmental Analysis and Risk Assessment; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.; Ramarao, B.V. Revisiting the laws of filtration: an assessment of their use in identifying particle retention mechanisms in filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, Y.S.; Zydney, A.L. Ultrafiltration membrane performance: effects of pore blockage/constriction. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramarao, B.V.; Tien, C. Approximate analysis of fine-particle retention in the cake filtration of suspensions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, C.; Ramarao, B.V.; Yasarla, R. A blocking model of membrane filtration. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 111, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiao, K.; Liang, P.; Sun, J.; Sai, S.; Huang, X. Characterization of soluble microbial products in 10 large-scale membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment in China. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xiao, K.; Xue, W.; Shen, Y.; Tan, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X. Excitation-emission matrix (EEM) fluorescence spectroscopy for characterization of organic matter in membrane bioreactors: Principles, methods and applications. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2020, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; He, T.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, T. Removal of fluorescence and ultraviolet absorbance of dissolved organic matter in reclaimed water by solar light. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslanalaton, I.; Balcioglu, I.A. Biodegradability assessment of ozonated raw and biotreated pharmaceutical wastewater. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X.W.; Ye, Q.H.; Zhang, Z.T.; Kong, S.F.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.J. Dissolved metal(loid) concentrations and their relations with chromophoric and fluorescent dissolved organic matter in an urban river in Shenzhen, South China. Water 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; O’Melia, C.R. Protein and humic acid adsorption onto hydrophilic membrane surfaces: effects of pH and ionic strength. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Waite, T.D.; Wen, X. Analysis of polysaccharide, protein and humic acid retention by microfiltration membranes using Thomas’ dynamic adsorption model. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 342, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Kocic, A.; Zydney, A.L. Analysis of humic acid fouling during microfiltration using a pore blockage–cake filtration model. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutzkover Gutman, I.; Hasson, D.; Semiat, R. Humic substances fouling in ultrafiltration processes. Desalination 2010, 261, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Yu, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Wei, C.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression. Membranes 2020, 10, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080171
Xu H, Xiao K, Yu J, Huang B, Wang X, Liang S, Wei C, Wen X, Huang X. A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression. Membranes. 2020; 10(8):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080171
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hao, Kang Xiao, Jinlan Yu, Bin Huang, Xiaomao Wang, Shuai Liang, Chunhai Wei, Xianghua Wen, and Xia Huang. 2020. "A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression" Membranes 10, no. 8: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080171
APA StyleXu, H., Xiao, K., Yu, J., Huang, B., Wang, X., Liang, S., Wei, C., Wen, X., & Huang, X. (2020). A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression. Membranes, 10(8), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10080171