Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Evaluation of Efflux Pump Inhibition by Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Reduction of Ethidium Bromide (EtBr)
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Evaluation of Efflux Pump Inhibition by MIC Reduction of Ethidium Bromide
2.5. Evaluation of Pump Inhibition by Fluorescence Emission of Ethidium Bromide
2.6. Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking
2.7. Sample Preparation for the Real-Time PCR Assay
2.8. Gene Expression Evaluation
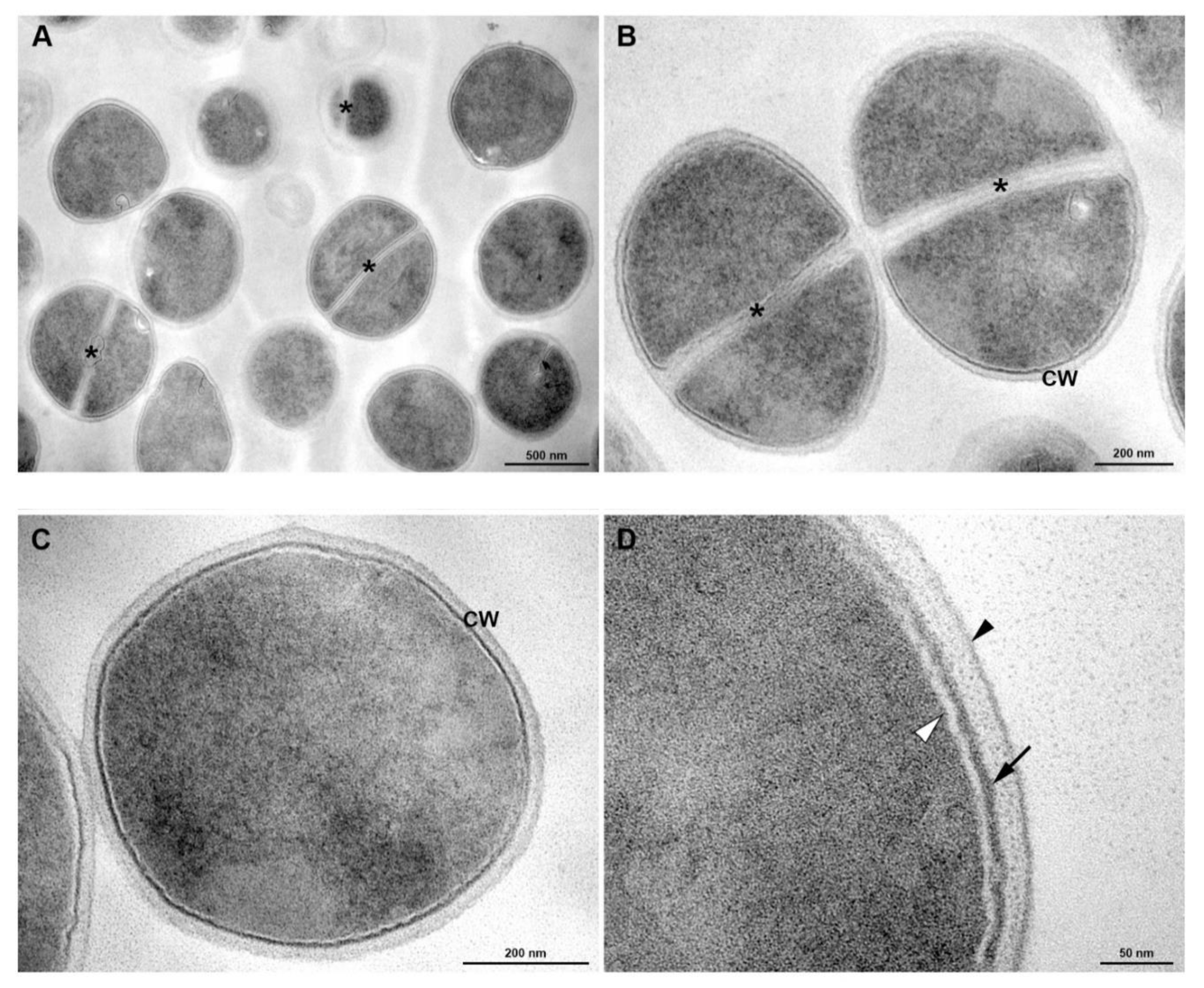
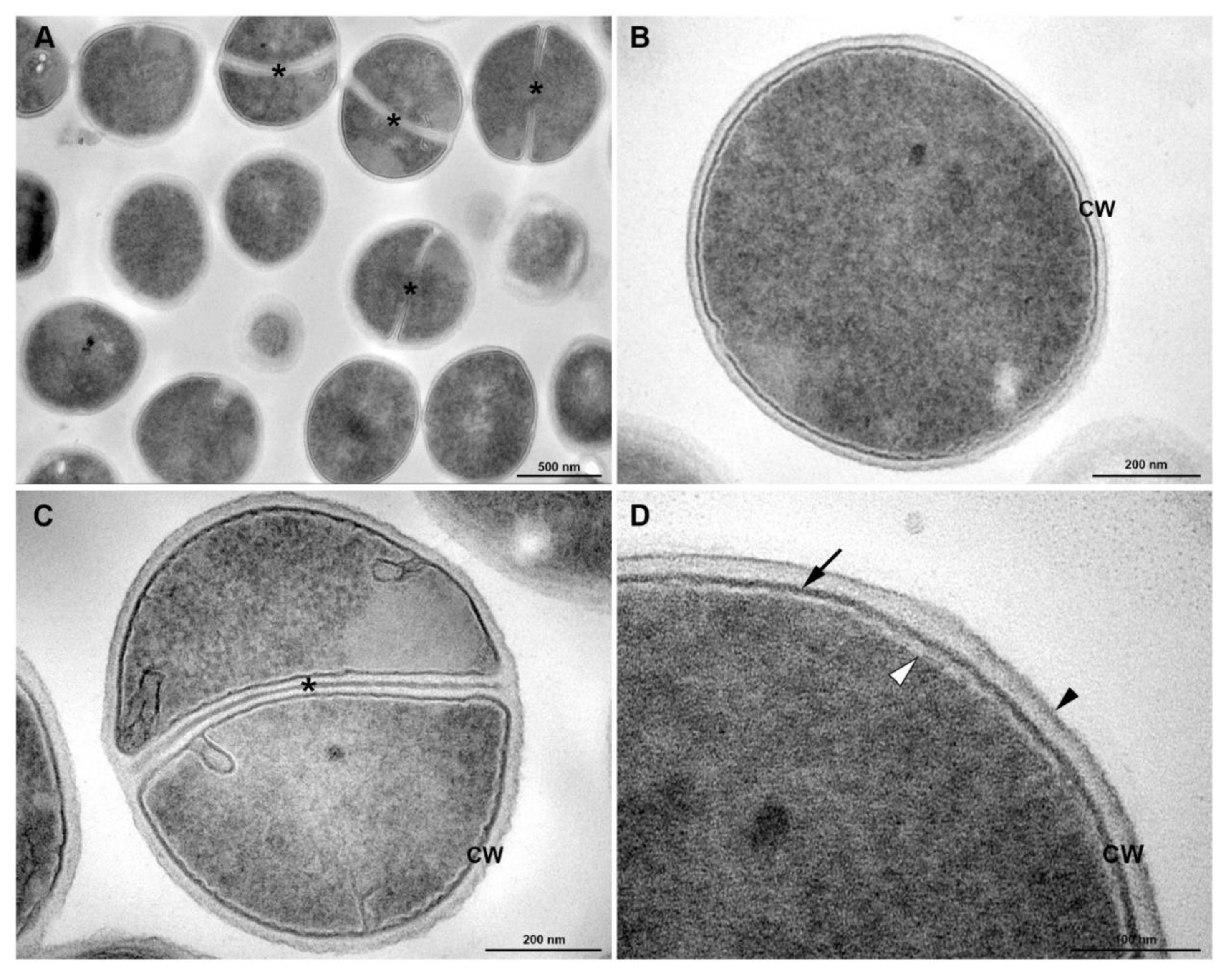
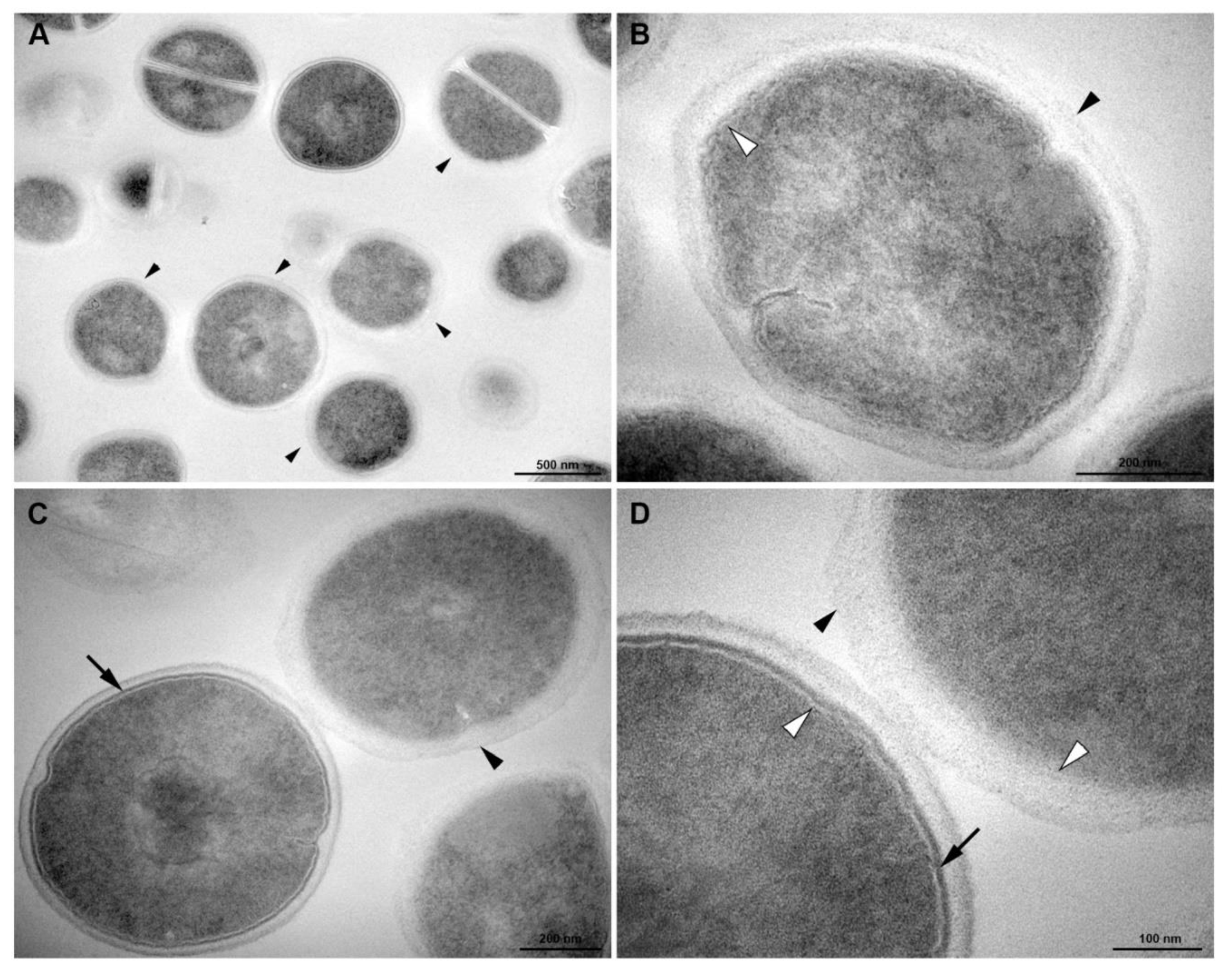
2.9. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.10. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3. Results
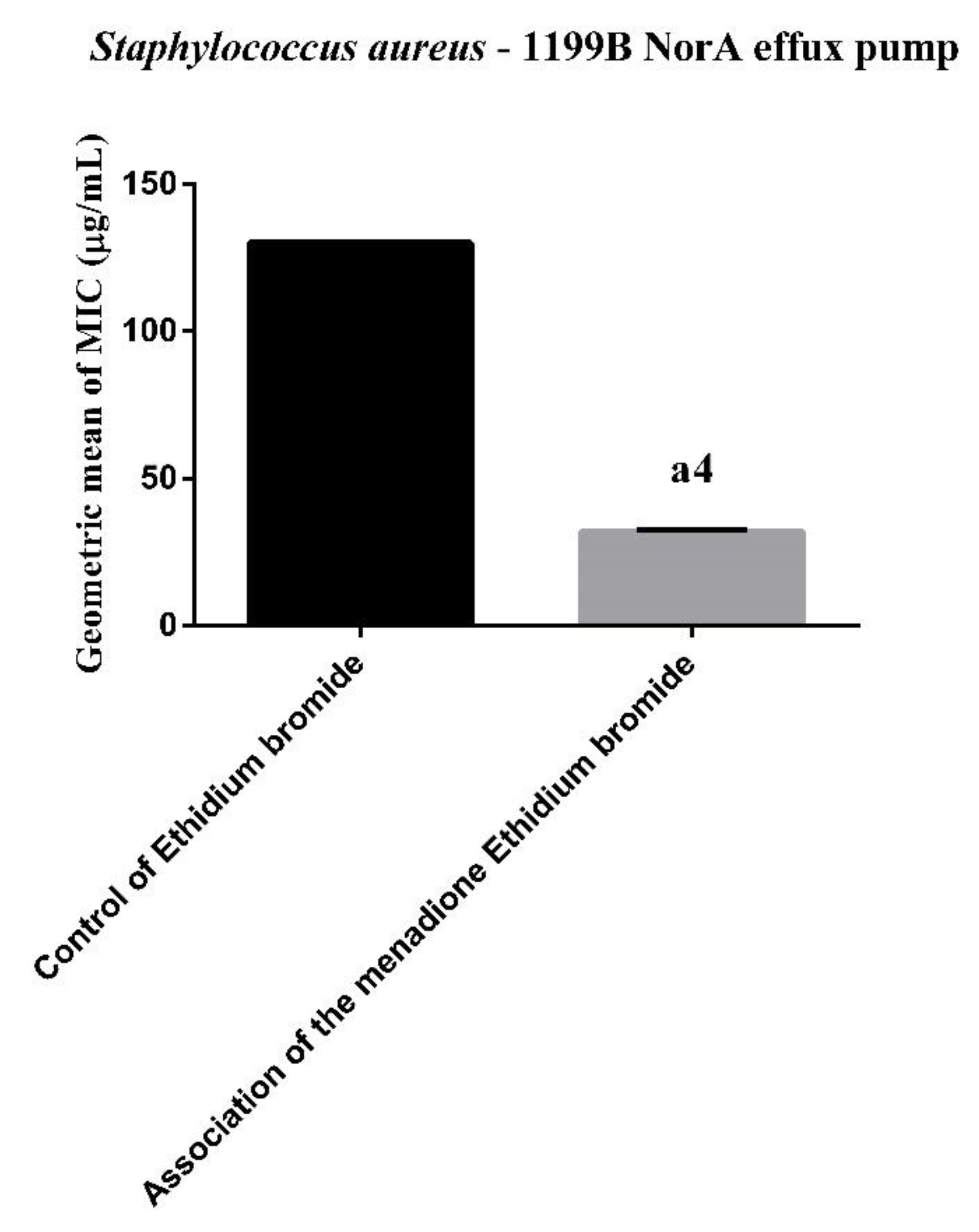
3.1. Efflux Pump Inhibition by MIC Reduction of Ethidium Bromide (EtBr)
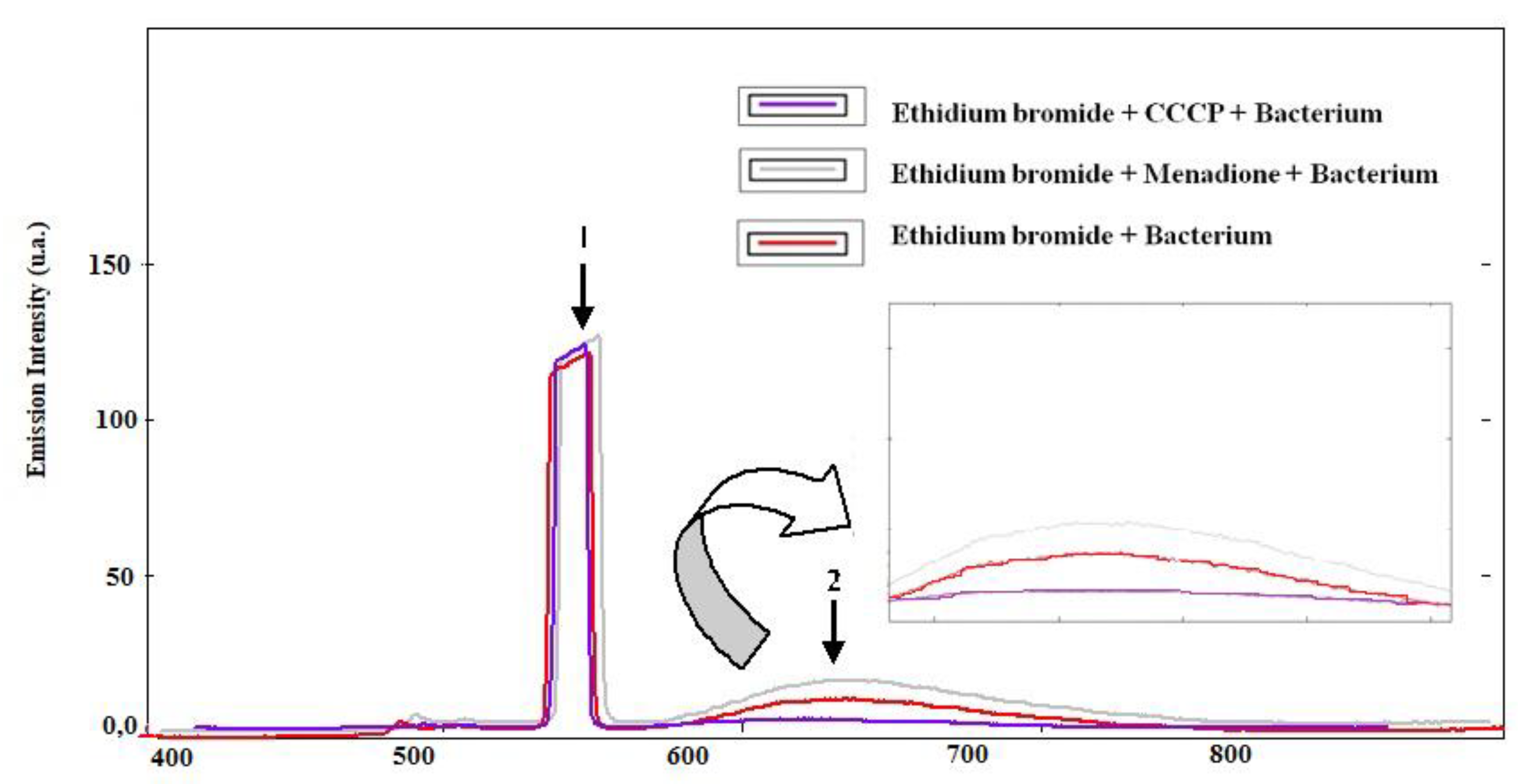
3.2. Evaluation of Pump Inhibition by Fluorescence Emission of Ethidium Bromide
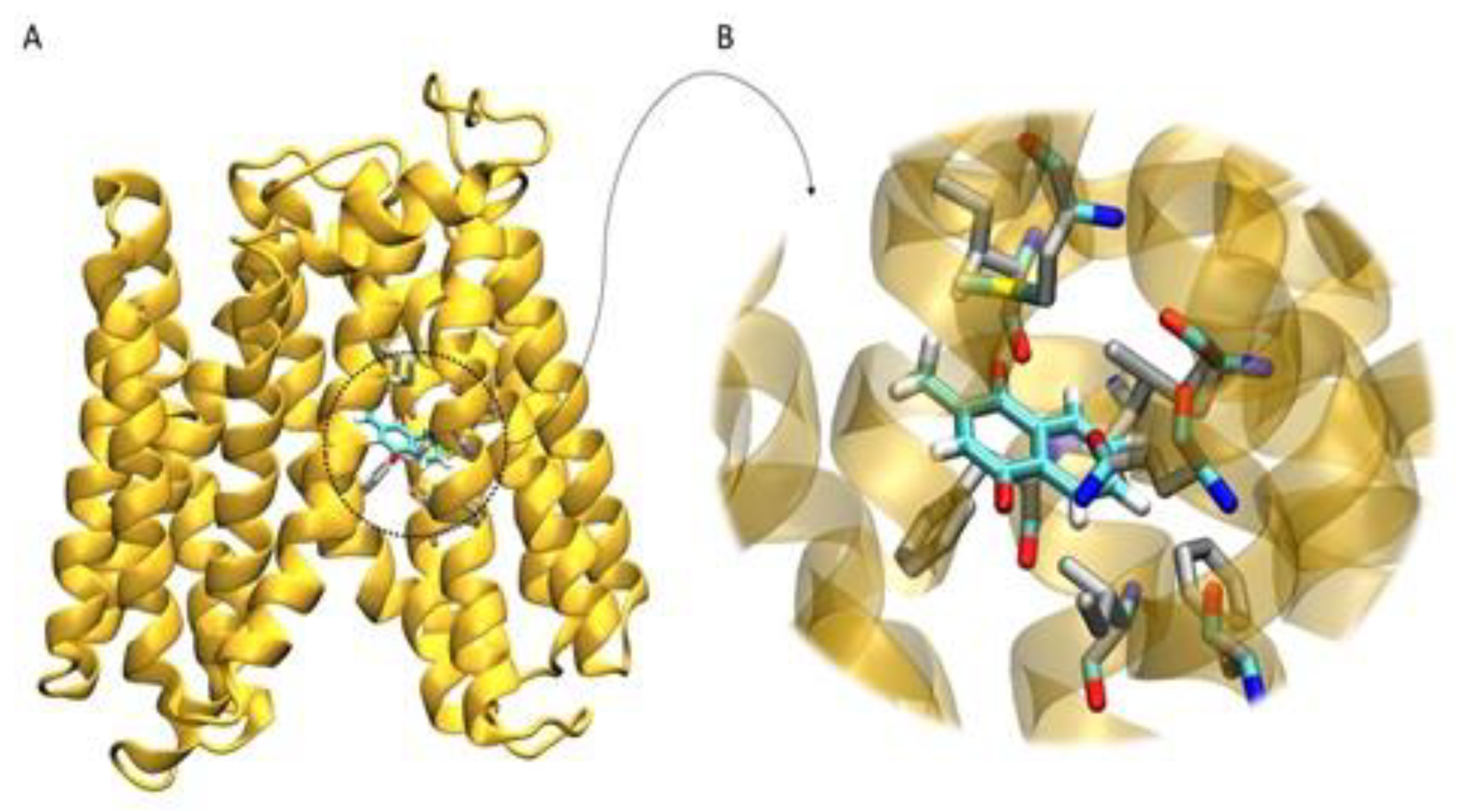
3.3. Homology Modeling and Molecular Docking
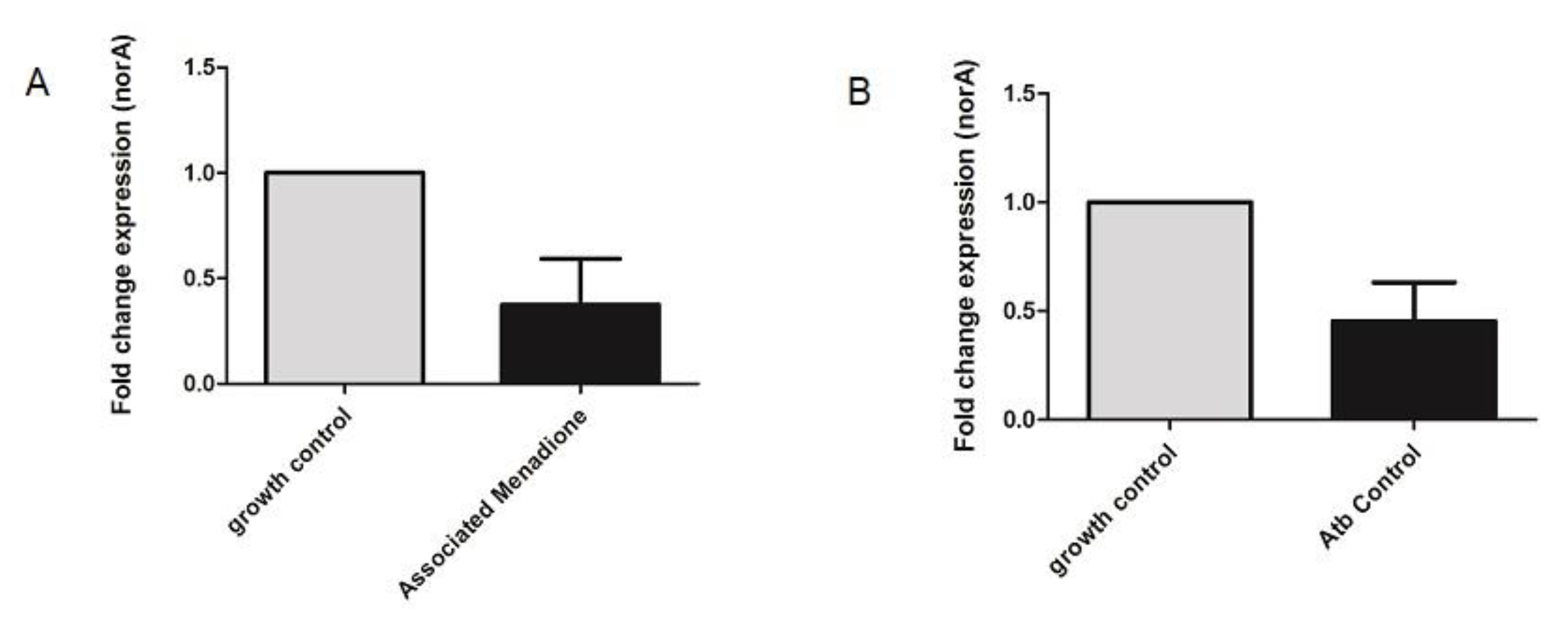
3.4. NorA Quantitative Real-Time PCR
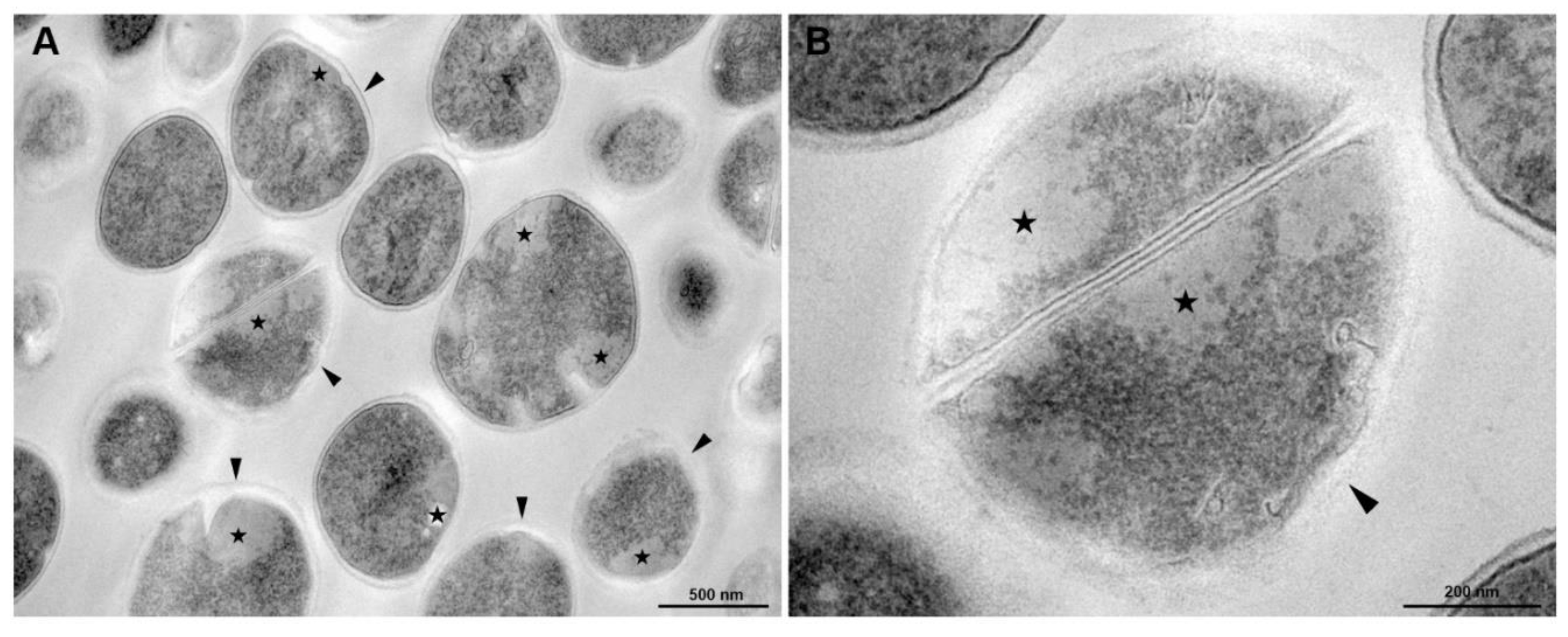
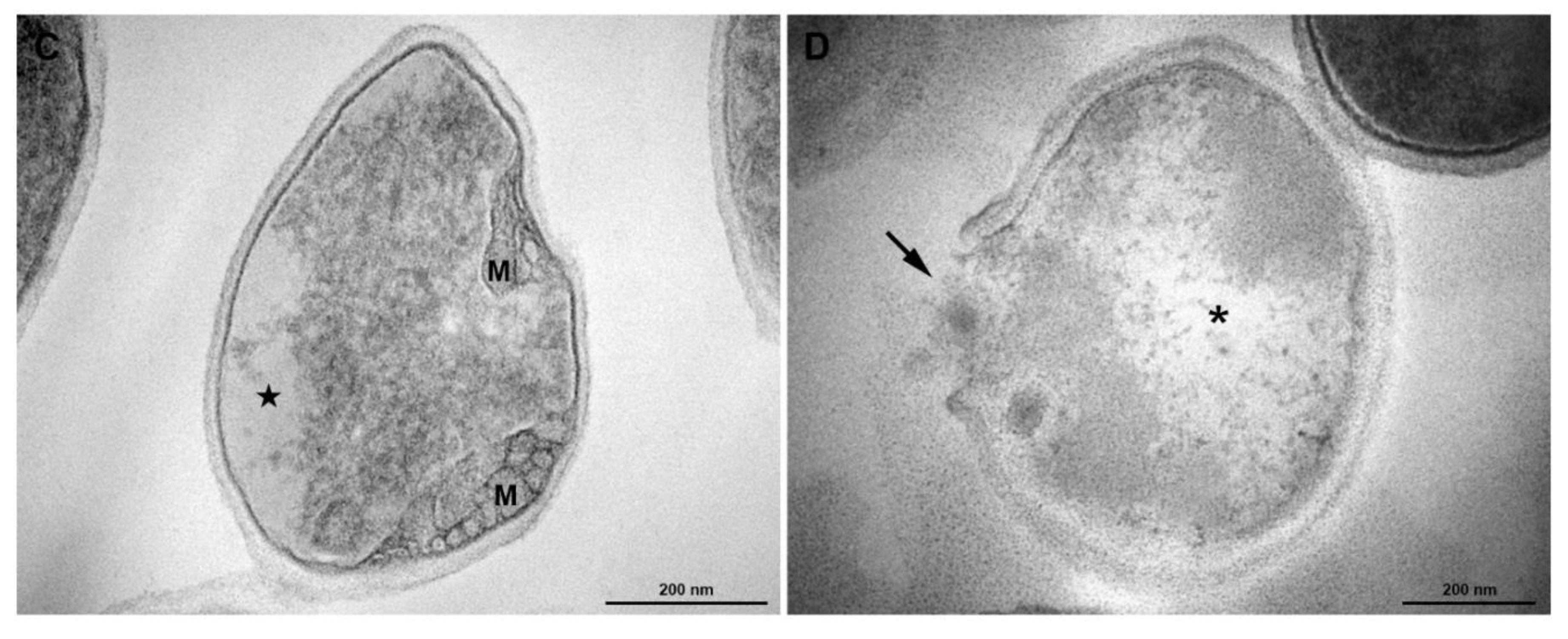
3.5. Transmission Electronic Microscopy
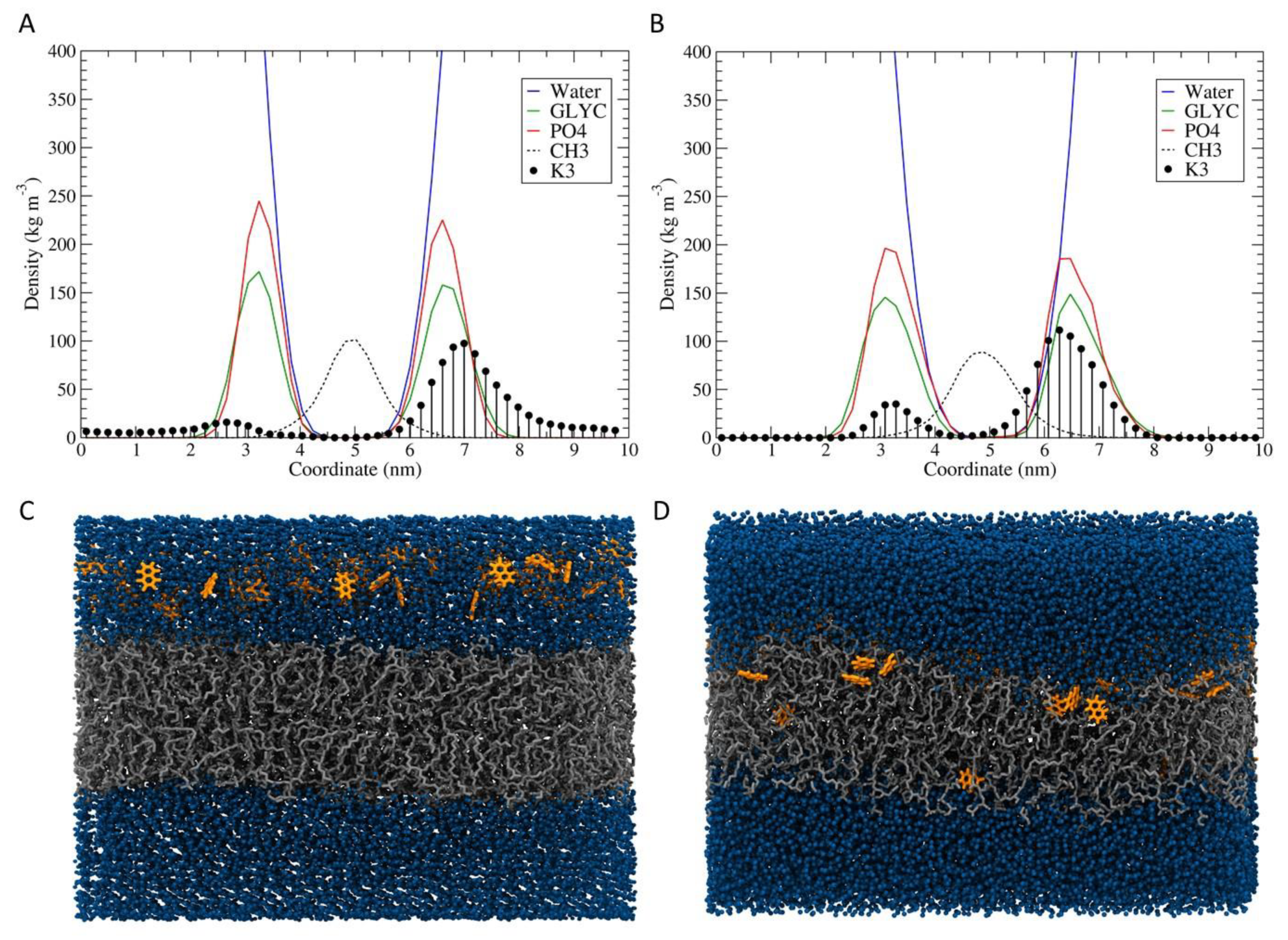
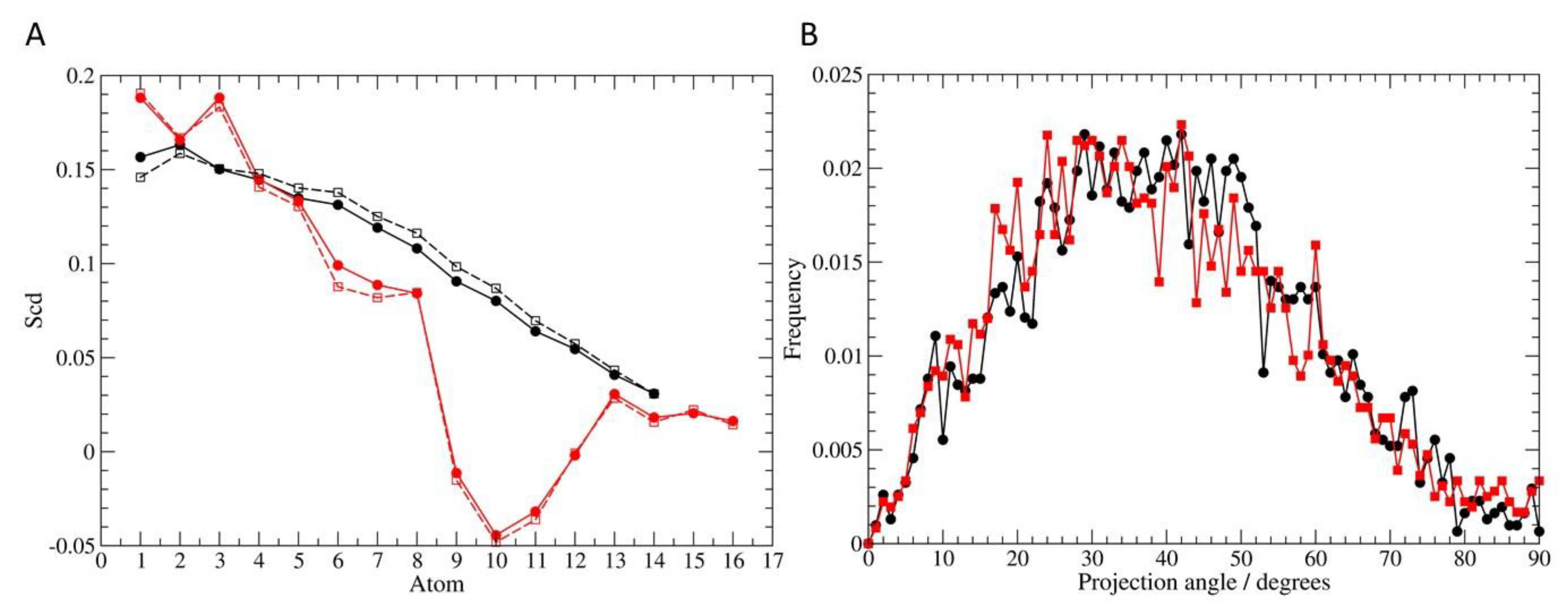
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2004, 430, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wertheim, H.F.; Melles, D.C.; Vos, M.C.; van Leeuwen, W.; van Belkum, A.; Verbrugh, H.A.; Nouwen, J.L. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, R.L.; Jensen, K.S. Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a cause of hospital-acquired infections. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmerson, A.M. The quinolones: Decades of development and use. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance in the 21st Century. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2014, 6, PMC.S14459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando-Amado, S.; Blanco, P.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Corona, F.; Reales-Calderón, J.A.; Sánchez, M.B.; Martínez, J.L. Multidrug efflux pumps as main players in intrinsic and acquired resistance to antimicrobials. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 28, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, M.A. The importance of efflux pumps in bacterial antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, A.; Martínez-Martín, N.; Mercadillo, M.; Galán, J.C.; Ghysels, B.; Matthijs, S.; Cornelis, P.; Wiehlmann, L.; Tümmler, B.; Baquero, F.; et al. The Neglected Intrinsic Resistome of Bacterial Pathogens. PLoS ONE. 2008, 3, e1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.Y.; Trucksis, W.M.; Hooper, D.C. Quinolone resistance mediated by norA: Physiologic characterization and relationship to flqB, a quinolone resistance locus on the Staphylococcus aureus chromosome. Antimicrob. Agen. Chemother. 1994, 38, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Kumana, C.R. Clinical Role of β-Lactam/ β -Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations. Drugs 2003, 63, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, K. Efflux pumps as antimicrobial resistance mechanisms. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, B.D.; Jacinto, P.; Kaatz, G.W. Inhibition of drug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: Current status of potentiating existing antibiotics. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, J.T.; Booth, S.L. Emerging Issues in Vitamin K Research. J. Evid. Based. Complementary Altern. Med. 2011, 16, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, K.B.; Speridiao, P.G.; Fagundes-Neto, U. Ácidos graxos poli-insaturados de cadeia longa. Electron. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. Liver Dis. 2006, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tintino, S.R.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.M.; Campina, F.F.; Weslley Limaverde, P.; Pereira, P.S.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; da Silva, T.G.; Leal-Balbino, T.C.; et al. Vitamin K enhances the effect of antibiotics inhibiting the efflux pumps of Staphylococcus aureus strains. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, J.; Heng, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, W.; Kang, X.; Huang, B.; Liu, J.; et al. Structure of the YajR transporter suggests a transport mechanism based on the conserved motif A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14664–14669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroet, M.; Caron, B.; Visscher, K.M.; Geerke, D.P.; Malde, A.K.; Mark, A.E. Automated Topology Builder Version 3.0: Prediction of Solvation Free Enthalpies in Water and Hexane. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 5834–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodford, P.J. A computational procedure for determining energetically favorable binding sites on biologically important macromolecules. J. Med. Chem. 1985, 28, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A programming language for software integration and development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, J.; Marsili, M. Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity—A rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 1980, 36, 3219–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.J.; Kollman, P.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Case, D.A. An all atom force field for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids. J. Comput. Chem. 1986, 7, 230–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, I.; Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Martins, M.; Amaral, L. Efflux-mediated response of Staphylococcus aureus exposed to ethidium bromide. J. Antim Chemoth. 2008, 62, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, C.M.; Vega, O.A.; Osorio, M.M.; Tapia, J.C.; Antonelli, M.; Stein, G.S.; Galindo, M.A. The cancer-related transcription factor Runx2 modulates cell proliferation in human osteosarcoma cell lines. J. Cell Physiol. 2013, 228, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Hora, G.C.A.; Archilha, N.L.; Lopes, J.L.S.; Müller, D.M.; Coutinho, K.; Itri, R.; Soares, T.A. Membrane negative curvature induced by a hybrid peptide from pediocin PA-1 and plantaricin 149 as revealed by atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 8884–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukol, A. Lipid Models for United-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2009, 5, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, N.; Eichenberger, A.P.; Choutko, A.; Riniker, S.; Winger, M.; Mark, A.E.; van Gunsteren, W.F. Definition and testing of the GROMOS force-field versions 54A7 and 54B7. Eur. Biophys. J. 2011, 40, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oostenbrink, C.; Soares, T.A.; van der Vegt, N.F.A.; van Gunsteren, W.F. Validation of the 53A6 GROMOS force field. Eur. Biophys. J. 2005, 34, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N ⋅log( N ) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tironi, I.G.; Sperb, R.; Smith, P.E.; van Gunsteren, W.F. A generalized reaction field method for molecular dynamics simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 102, 5451–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, F.J.S.; Rusu, V.H.; Soares, T.A.; Lins, R.D. The Effect of Temperature, Cations, and Number of Acyl Chains on the Lamellar to Non-Lamellar Transition in Lipid-A Membranes: A Microscopic View. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3830–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kalia, N.P.; Joshi, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.R.; Kumar, A.; Bharate, S.B.; Khan, I.A.; Boeravinone, B. A Novel Dual Inhibitor of NorA Bacterial Efflux Pump of Staphylococcus aureus and Human P-Glycoprotein, Reduces the Biofilm Formation and Intracellular Invasion of Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.M.; de Macedo, E.V.; Oliveira, F.A.A.; Ferreira, J.H.L.; Gutierrez, S.J.C.; Peláez, W.J.; Lima, F.C.A.; de Siqueira Júnior, J.P.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Kaatz, G.W.; et al. Inhibition of the NorA efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus by synthetic riparins. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, B.V.; Babu, T.M.C.; Reddy, N.V.; Rajendra, W. Homology modeling, molecular dynamics, and virtual screening of NorA efflux pump inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Wright, G.D. Bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, D.P.; Greenstock, C.L. Fluorescence lifetime analysis of DNA intercalated ethidium bromide and quenching by free dye. Biophys. Chem. 1994, 50, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viveiros, M.; Martins, A.; Paixão, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Martins, M.; Couto, I.; Fähnrich, E.; Kern, W.V.; Amaral, L. Demonstration of intrinsic efflux activity of Escherichia coli K-12 AG100 by an automated ethidium bromide method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2008, 31, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, K.A.; Mohanty, P. Bacterial Efflux Pumps Involved in Multidrug Resistance and their Inhibitors: Rejuvinating the Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Zhang, X.; Hooper, D.C. Characterization of NorR protein, a multifunctional regulator of norA expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3127–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbs, M.D.; Gupta, R.B. Solubility of Vitamin E (α-Tocopherol) and Vitamin K 3 (Menadione) in Ethanol−Water Mixture. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1998, 43, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, B.; Hooper, D.C. A New Two-Component Regulatory System Involved in Adhesion, Autolysis, and Extracellular Proteolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3955–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.L.; Kohlbrenner, W.E.; Weigl, D.; Baranowski, J. Mechanism of quinolone inhibition of DNA gyrase. Appearance of unique norfloxacin binding sites in enzyme-DNA complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 2973–2978. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, J.C.; Morais Braga, M.F.B.; Guedes, G.M.M.; Tintino, S.R.; Freitas, M.A.; Quintans, L.J.; Menezes, I.R.A.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Menadione (vitamin K) enhances the antibiotic activity of drugs by cell membrane permeabilization mechanism. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, T.-J.; Zhang, J.; Ferrans, V.J.; Tzeng, W.-F. Cardiac and renal toxicity of menadione in rat. Toxicology 1997, 124, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, J.; De Bont, J.A.M.; Poolman, B. Interactions of cyclic hydrocarbons with biological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 8022–8028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turina, A.d.V.; Nolan, M.V.; Zygadlo, J.A.; Perillo, M.A. Natural terpenes: Self-assembly and membrane partitioning. Biophys. Chem. 2006, 122, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamson, D.W.; Plaza, S.M. The anticancer effects of vitamin K. Altern. Med. Rev. 2003, 8, 303–318. [Google Scholar]
- Piddock, L.J.V. Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps —Not just for resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primers | Sequence (5′-3′) | Size (bp) * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| norA | NorA-Fw | 5′-TTCACCAAGCCATCAAAAAG-3′ | 620 | Couto et al. [26] |
| NorA-Rv | 5′-CTTGCCTTTCTCCAGCAATA-3′ | |||
| 16S | 16S-Fw | 5′-GTAGGTGGCAAGCGTTATGCC-3′ | 228 | Lucero et al. [27] |
| 16S-Rv | 5′-CGCACATCAGCGTCAG-3′ |
| Control | Menadione + Norfloxacin | |
|---|---|---|
| TC mean-16S | 31,907 | 31,209 |
| * TC mean-norA | 26,623 | 27,903 |
| ∆∆TC (Mean + SD) | 1 | 0.4534 ± 0.3567 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tintino, S.R.; Souza, V.C.A.d.; Silva, J.M.A.d.; Oliveira-Tintino, C.D.d.M.; Pereira, P.S.; Leal-Balbino, T.C.; Pereira-Neves, A.; Siqueira-Junior, J.P.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Rodrigues, F.F.G.; et al. Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus. Membranes 2020, 10, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060130
Tintino SR, Souza VCAd, Silva JMAd, Oliveira-Tintino CDdM, Pereira PS, Leal-Balbino TC, Pereira-Neves A, Siqueira-Junior JP, da Costa JGM, Rodrigues FFG, et al. Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus. Membranes. 2020; 10(6):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060130
Chicago/Turabian StyleTintino, Saulo R., Veruska C. A. de Souza, Julia M. A. da Silva, Cícera Datiane de M. Oliveira-Tintino, Pedro S. Pereira, Tereza C. Leal-Balbino, Antonio Pereira-Neves, José P. Siqueira-Junior, José G. M. da Costa, Fabíola F. G. Rodrigues, and et al. 2020. "Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus" Membranes 10, no. 6: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060130
APA StyleTintino, S. R., Souza, V. C. A. d., Silva, J. M. A. d., Oliveira-Tintino, C. D. d. M., Pereira, P. S., Leal-Balbino, T. C., Pereira-Neves, A., Siqueira-Junior, J. P., da Costa, J. G. M., Rodrigues, F. F. G., Menezes, I. R. A., da Hora, G. C. A., Lima, M. C. P., Coutinho, H. D. M., & Balbino, V. Q. (2020). Effect of Vitamin K3 Inhibiting the Function of NorA Efflux Pump and Its Gene Expression on Staphylococcus aureus. Membranes, 10(6), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10060130