Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications
Abstract
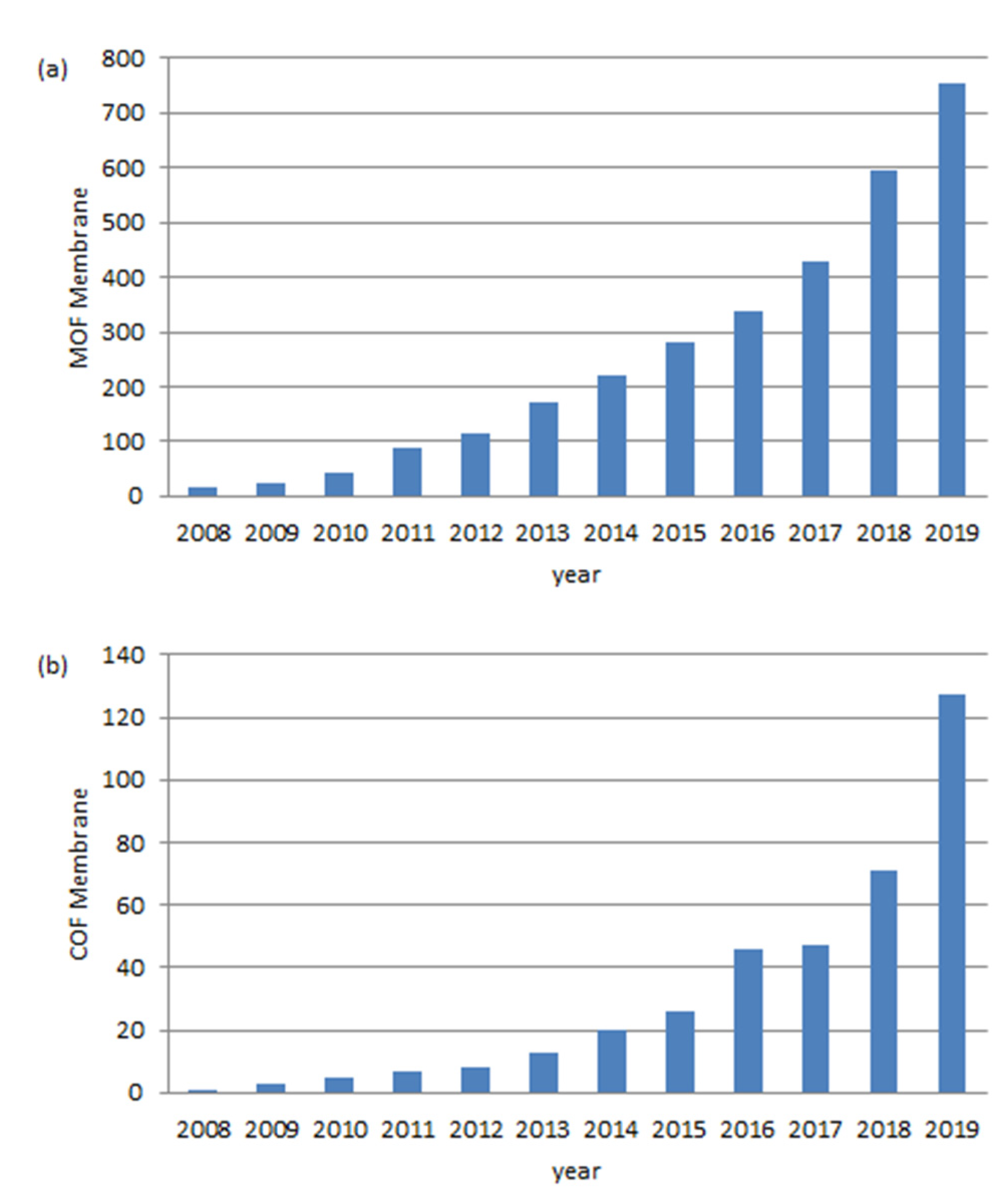
1. Introduction
2. Preparation Methods
2.1. MOF Membranes
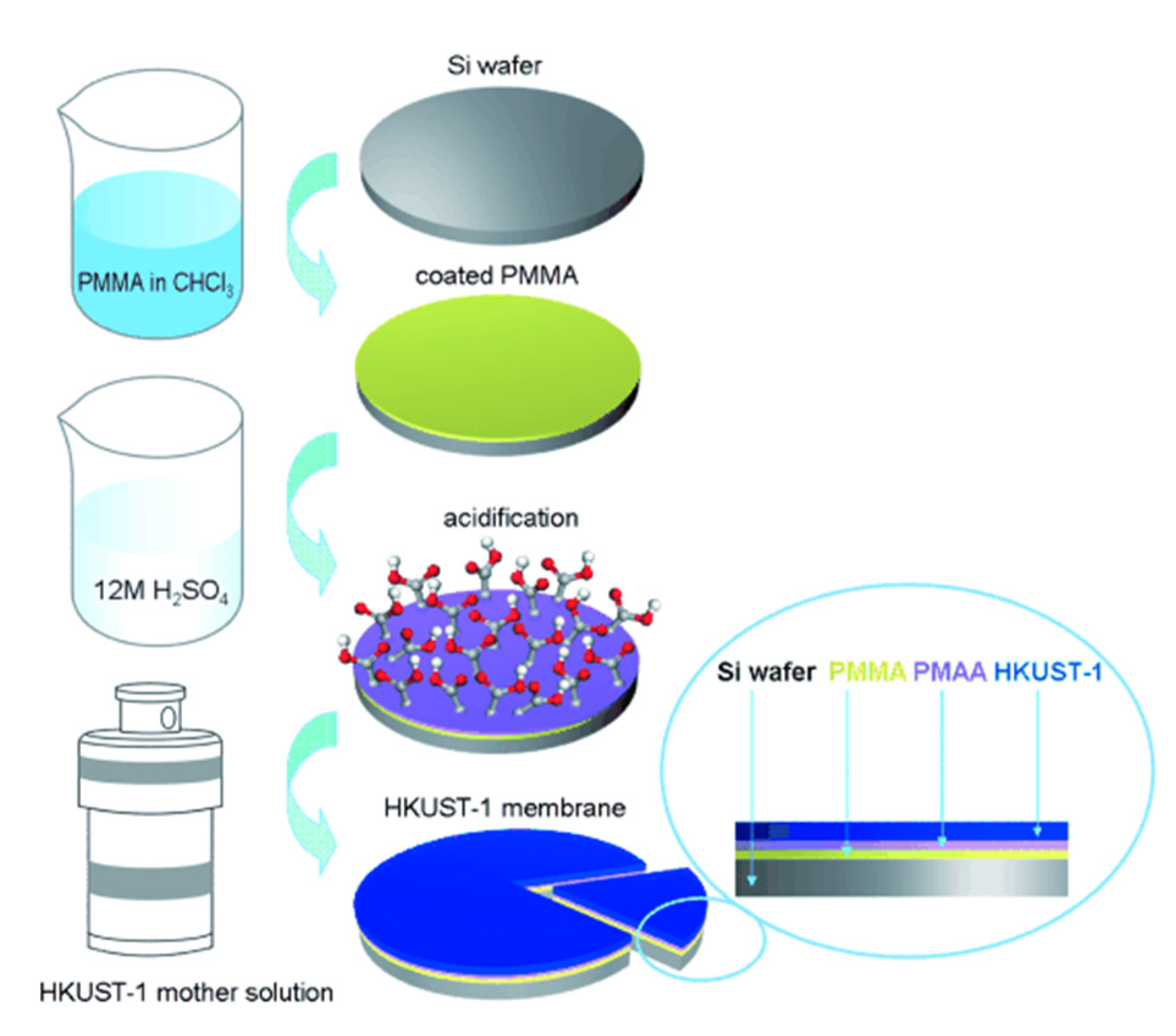
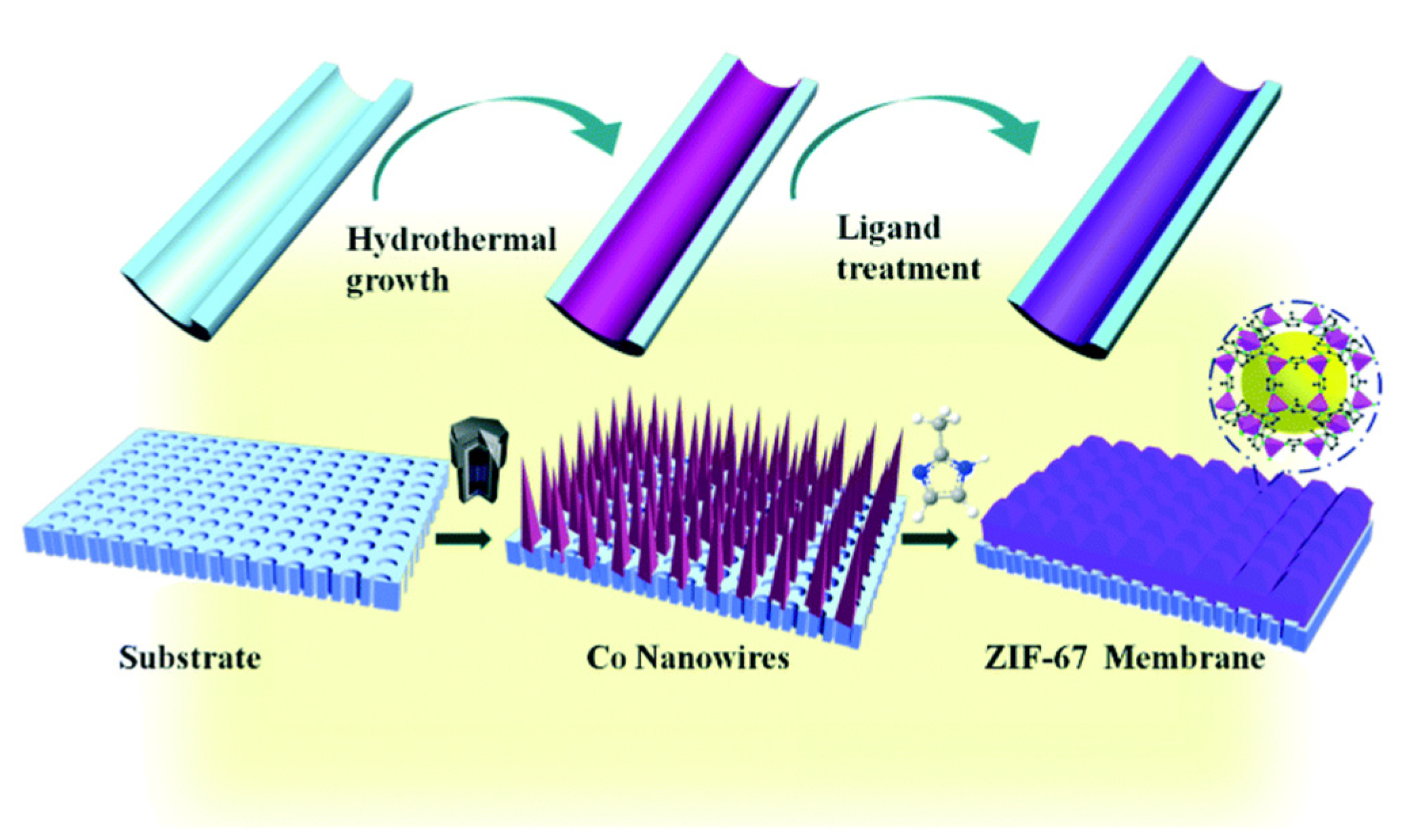
2.1.1. In Situ Growth
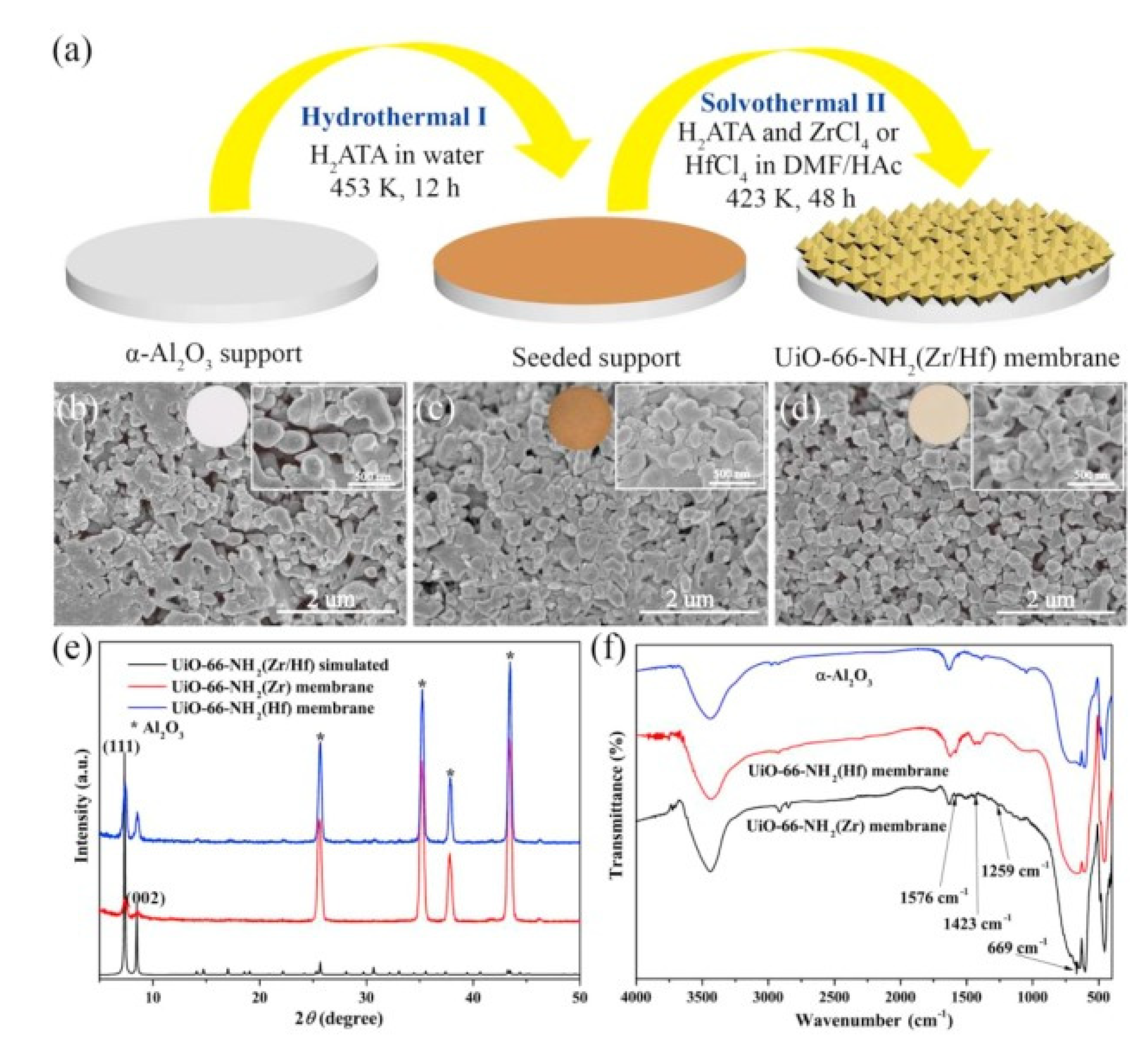
2.1.2. Seeded Assisted or Secondary Growth
2.1.3. Layer-by-Layer Assembly
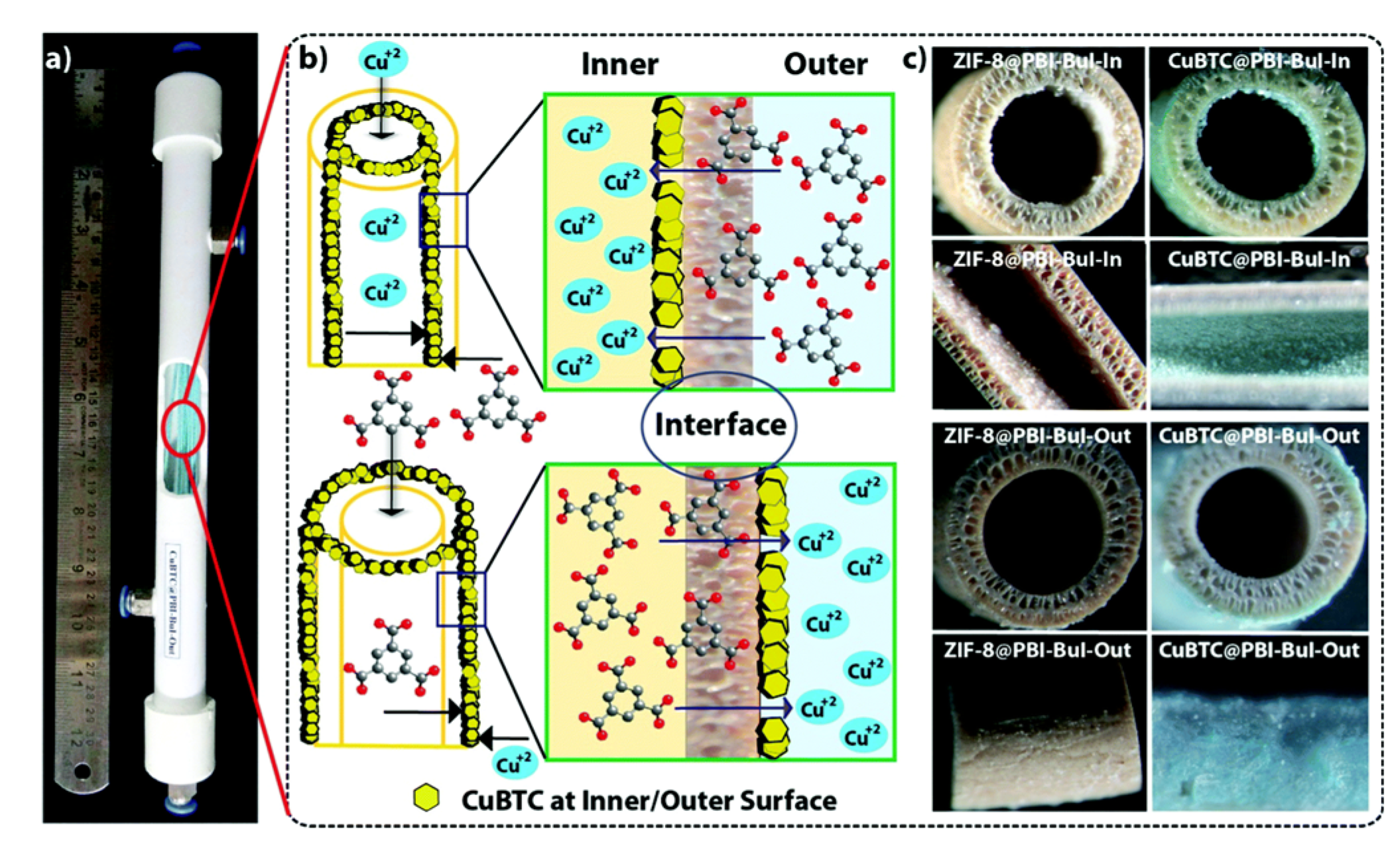
2.1.4. Contra-Diffusion or Interfacial Method
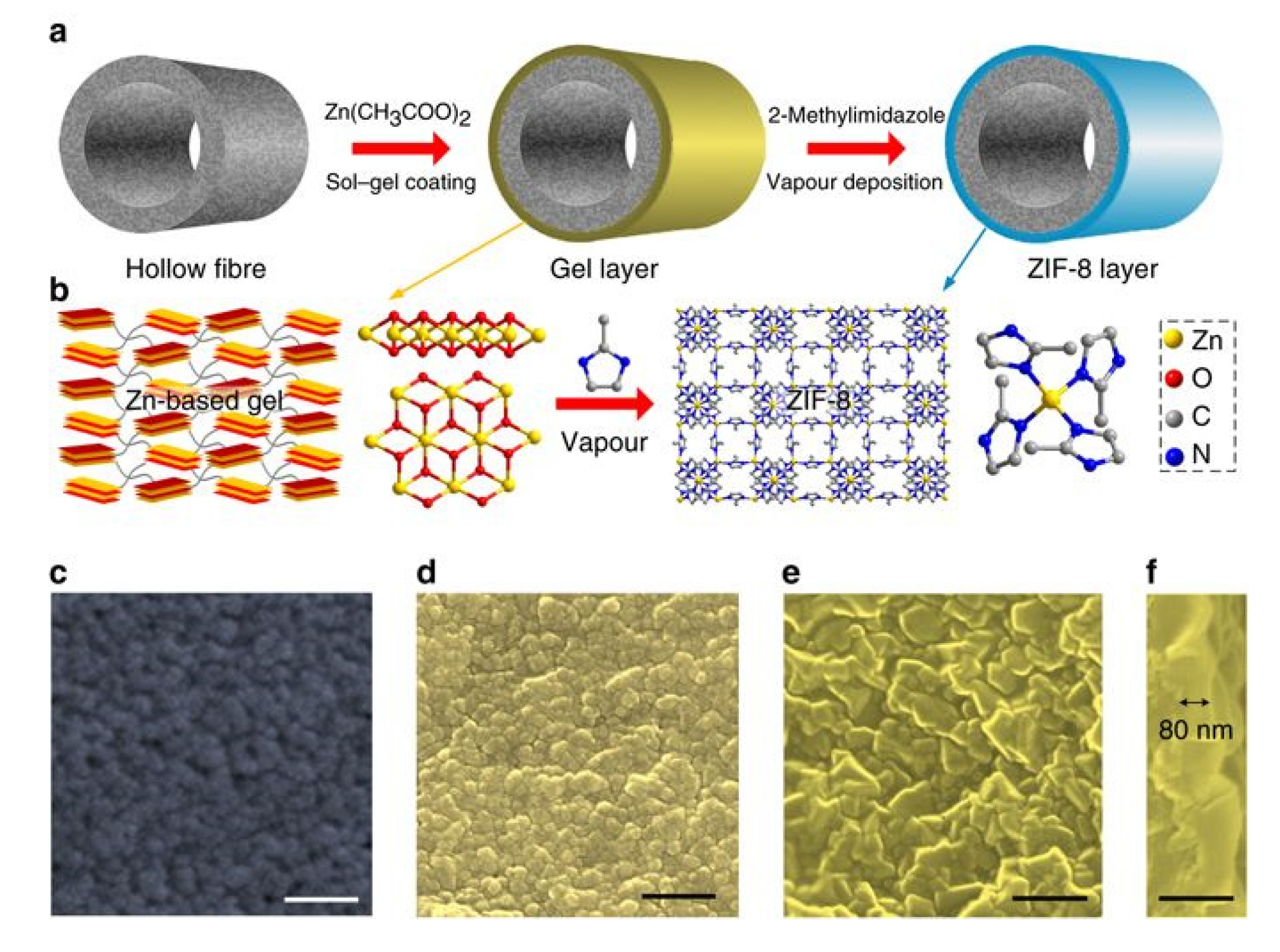
2.1.5. Vapour Deposition
2.2. COF Membranes
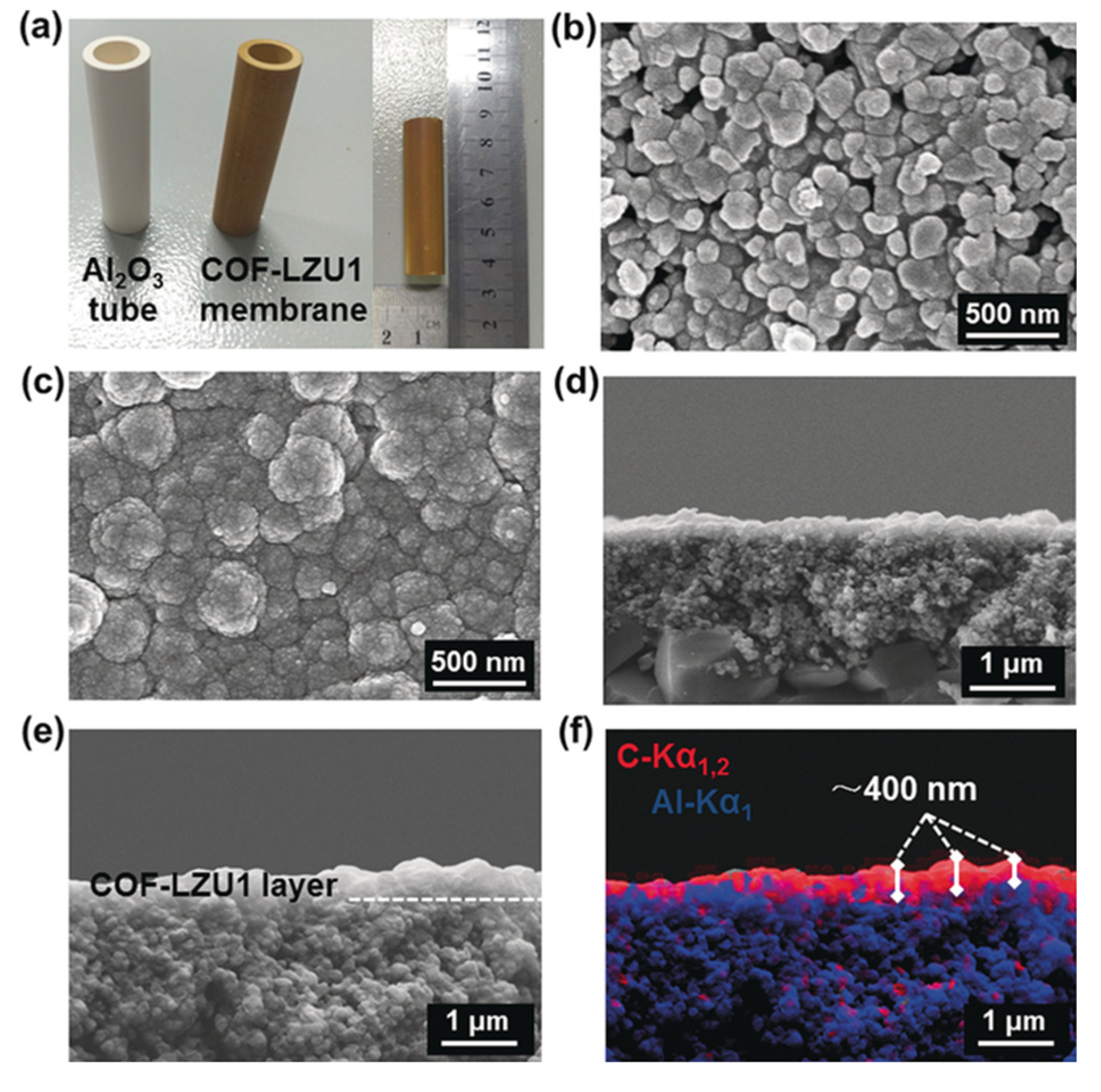
2.2.1. In Situ Growth
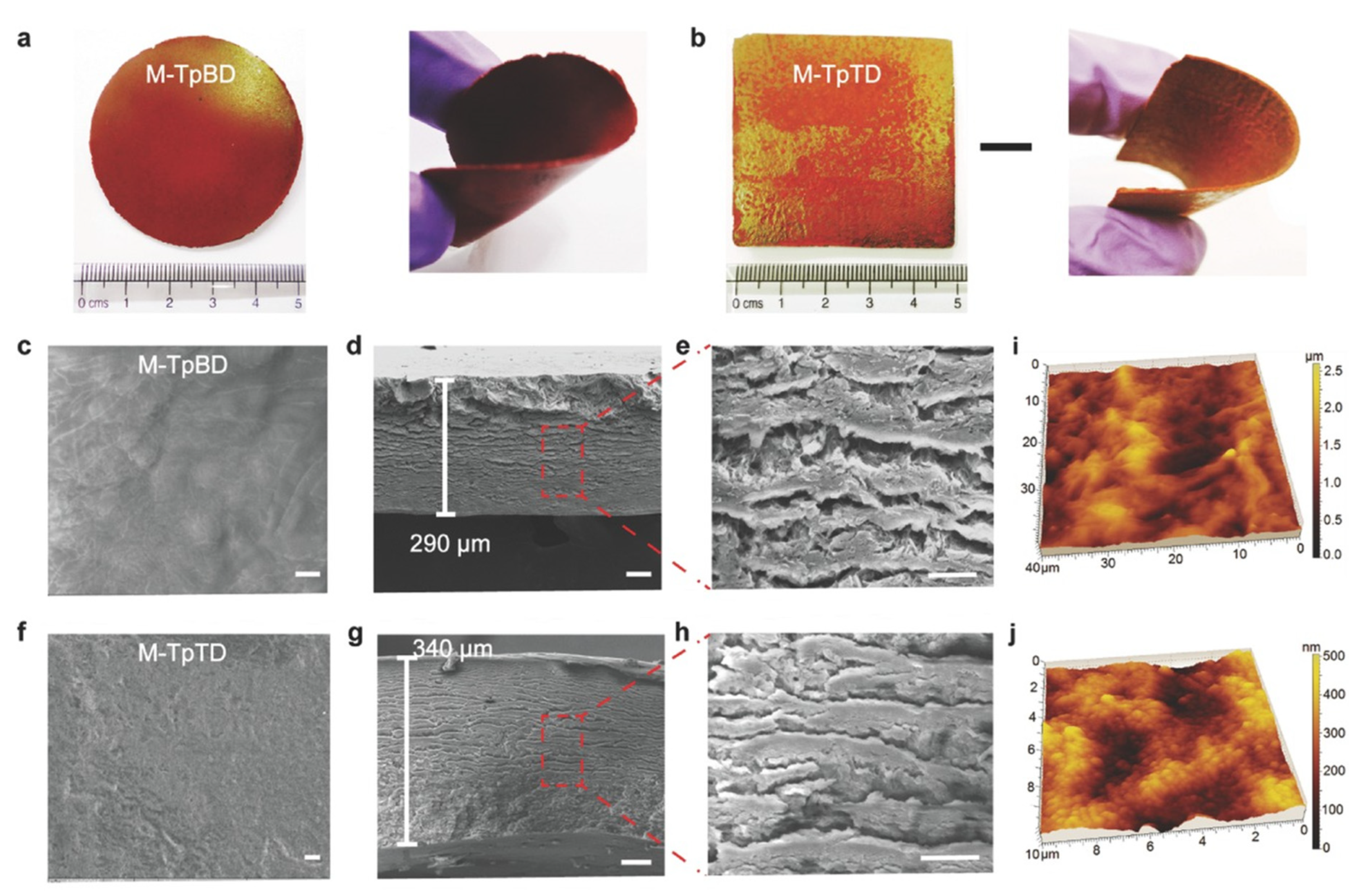
2.2.2. Solution Casting
2.2.3. Layer-by-Layer Assembly
2.2.4. Interfacial Polymerisation (IP)
2.2.5. Langmuir−Blodgett (LB) Method
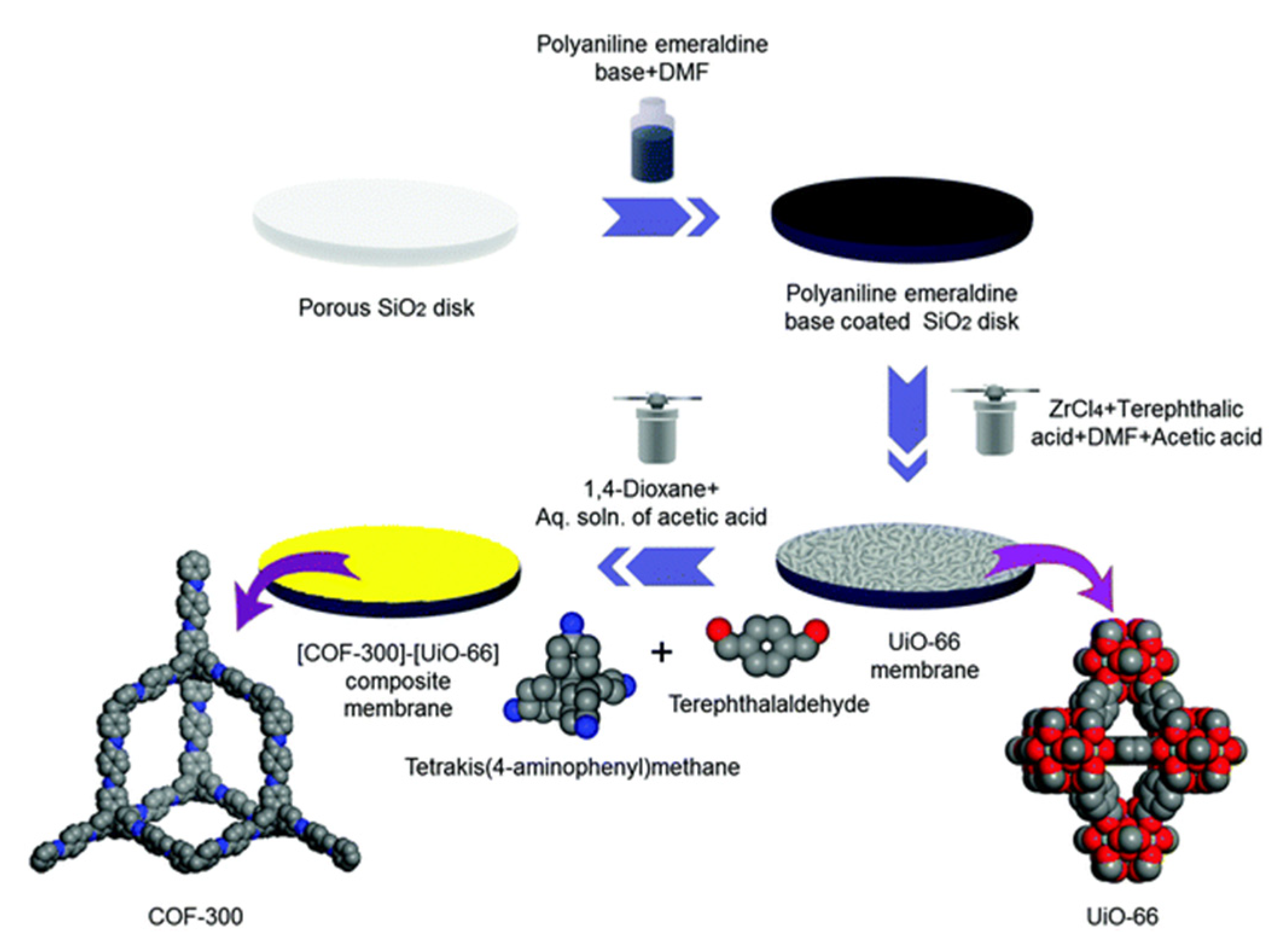
2.3. COF-MOF Composite Membranes
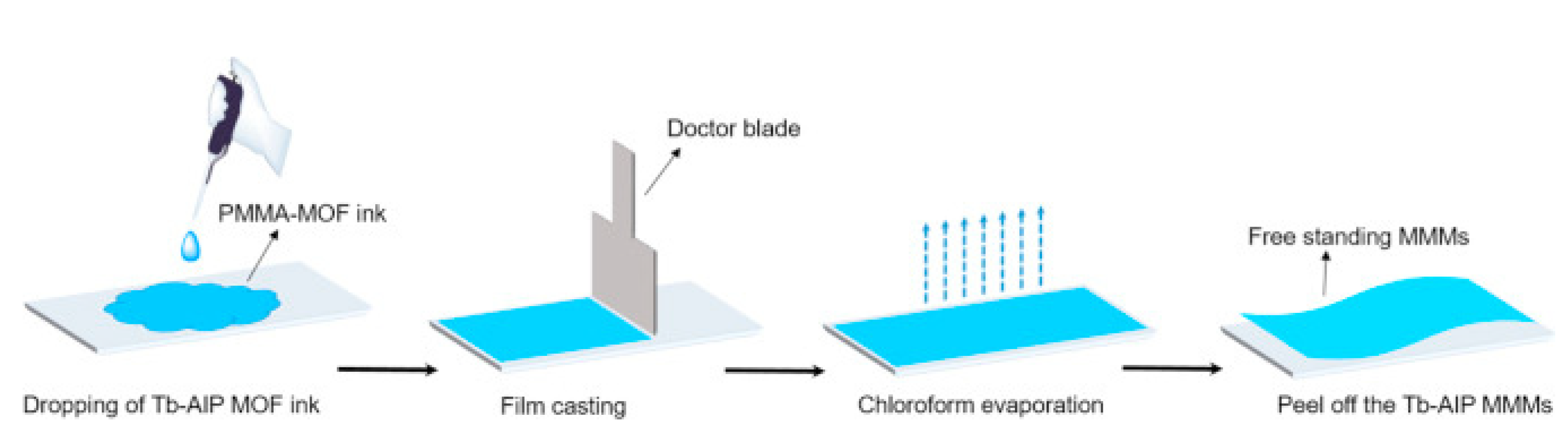
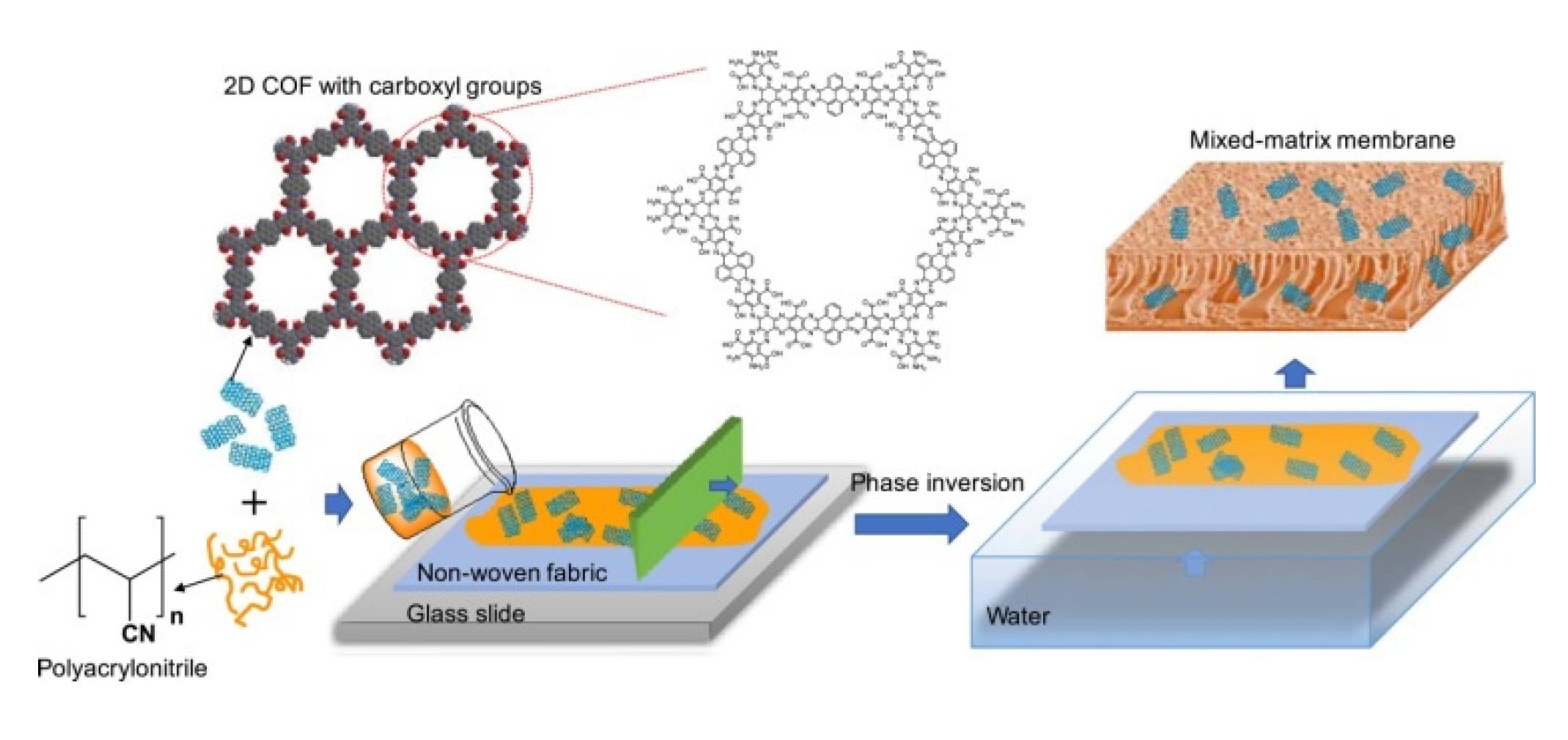
2.4. Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) Based on MOFs and COFs
3. Properties and Characterisation of MOF and COF Membranes
3.1. Characterisation of Structural Properties
3.2. Characterisation of Chemical Properties
3.3. Characterisation of Thermal and Mechanical Properties
3.4. Textural Characterisation of the Membrane Surface
3.5. Membrane Functional Characterisation
3.5.1. Gas Permeation Capacity
3.5.2. Liquid Permeation and Rejection Capacity
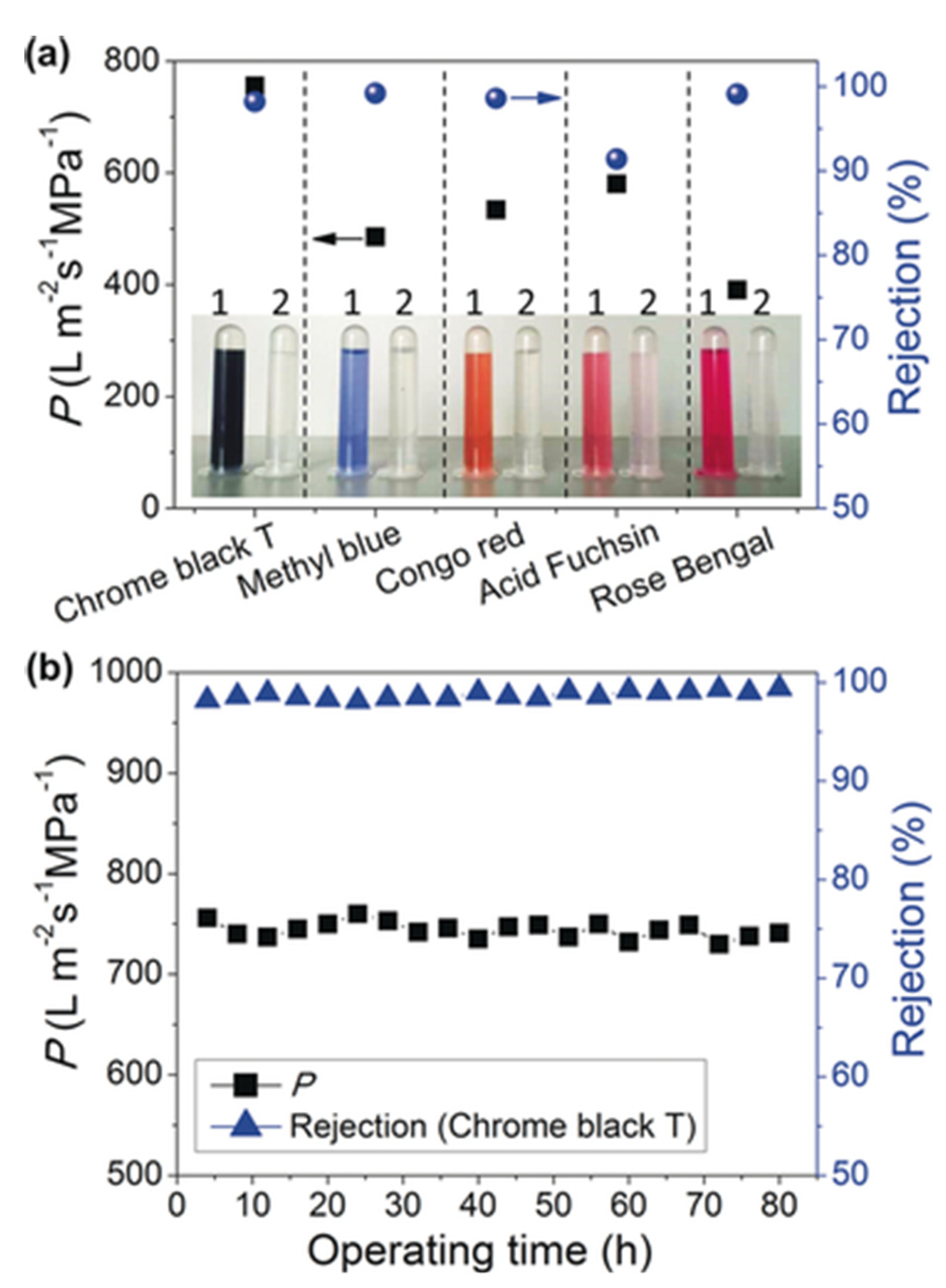
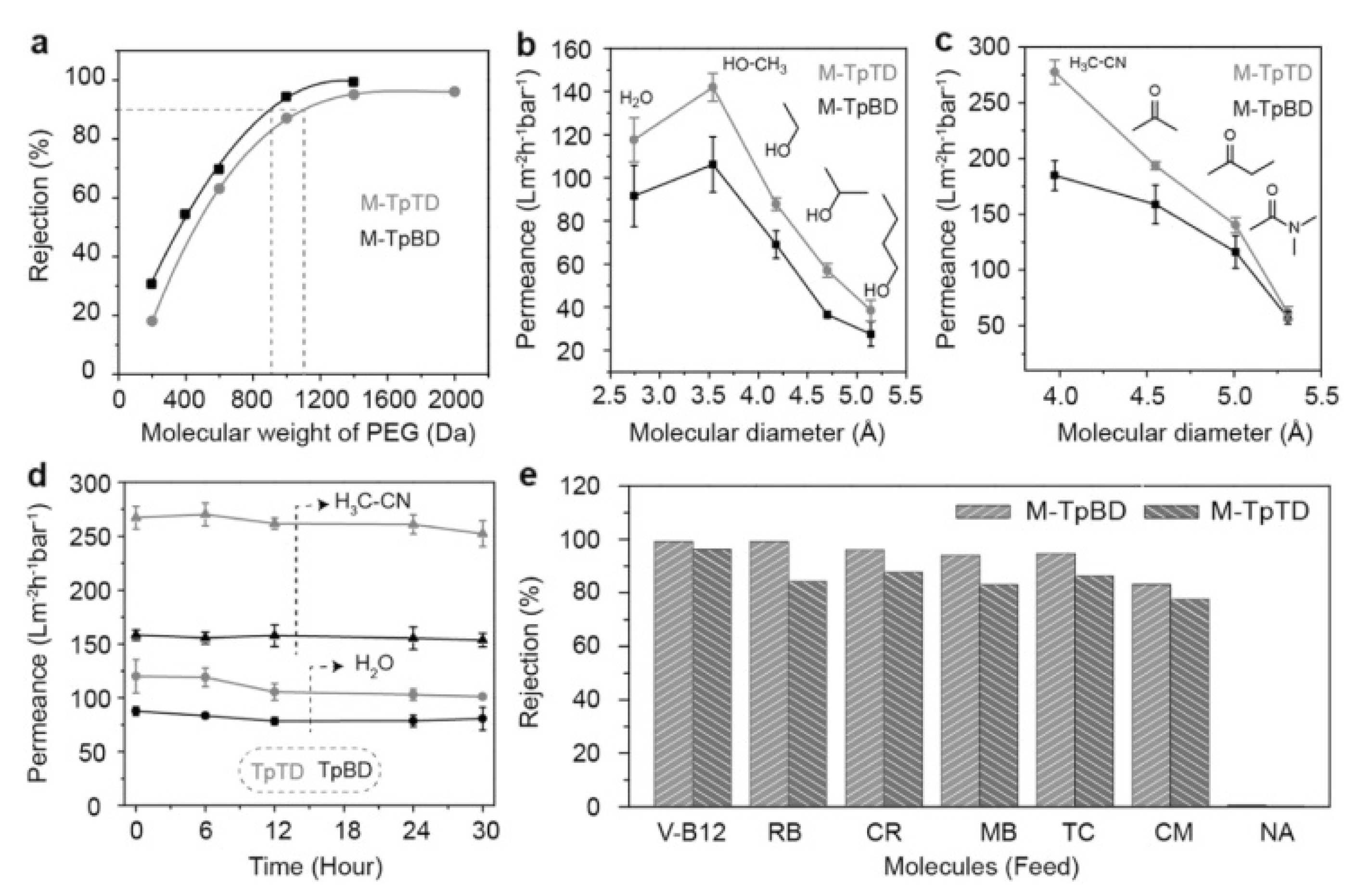
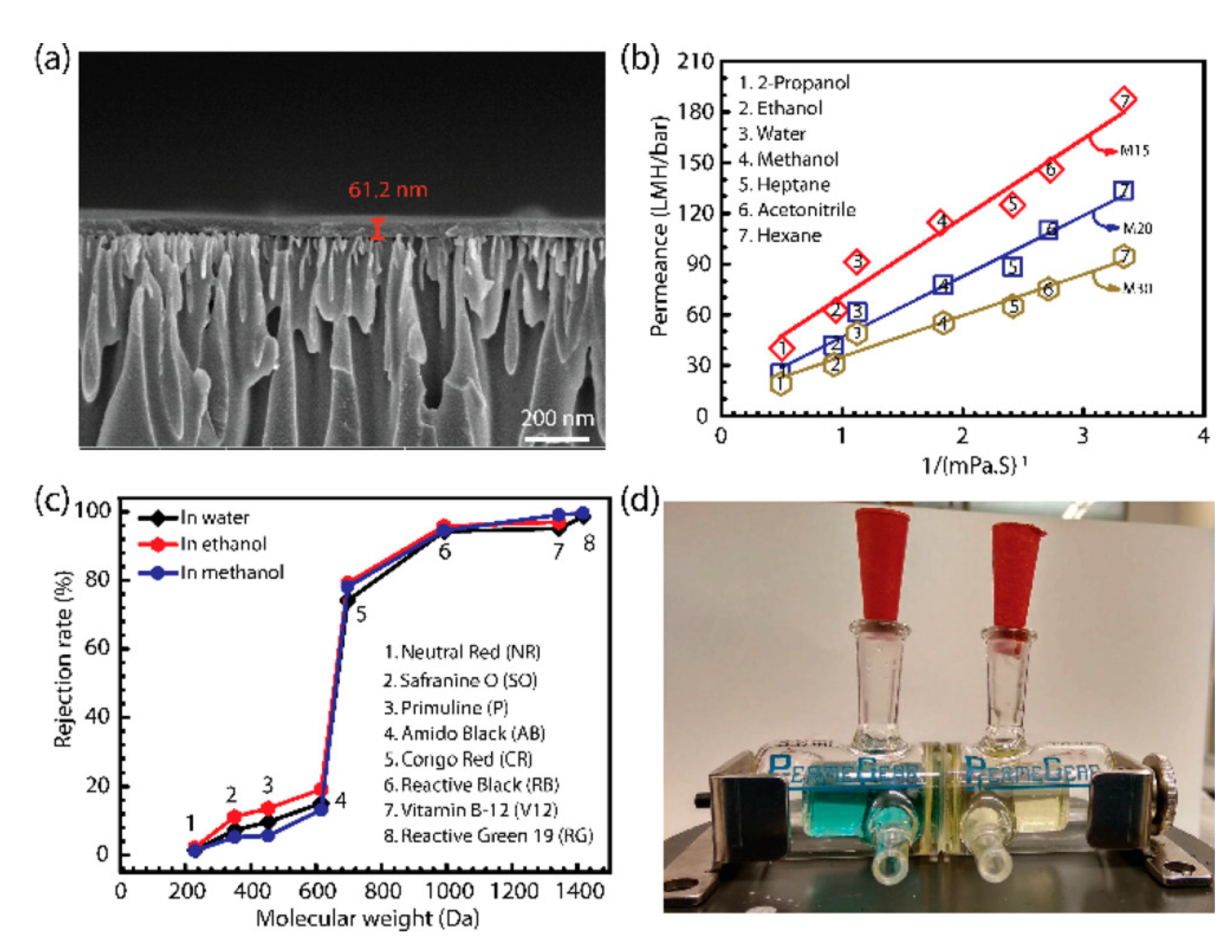
3.5.3. Solute Permeation and Rejection Capacity
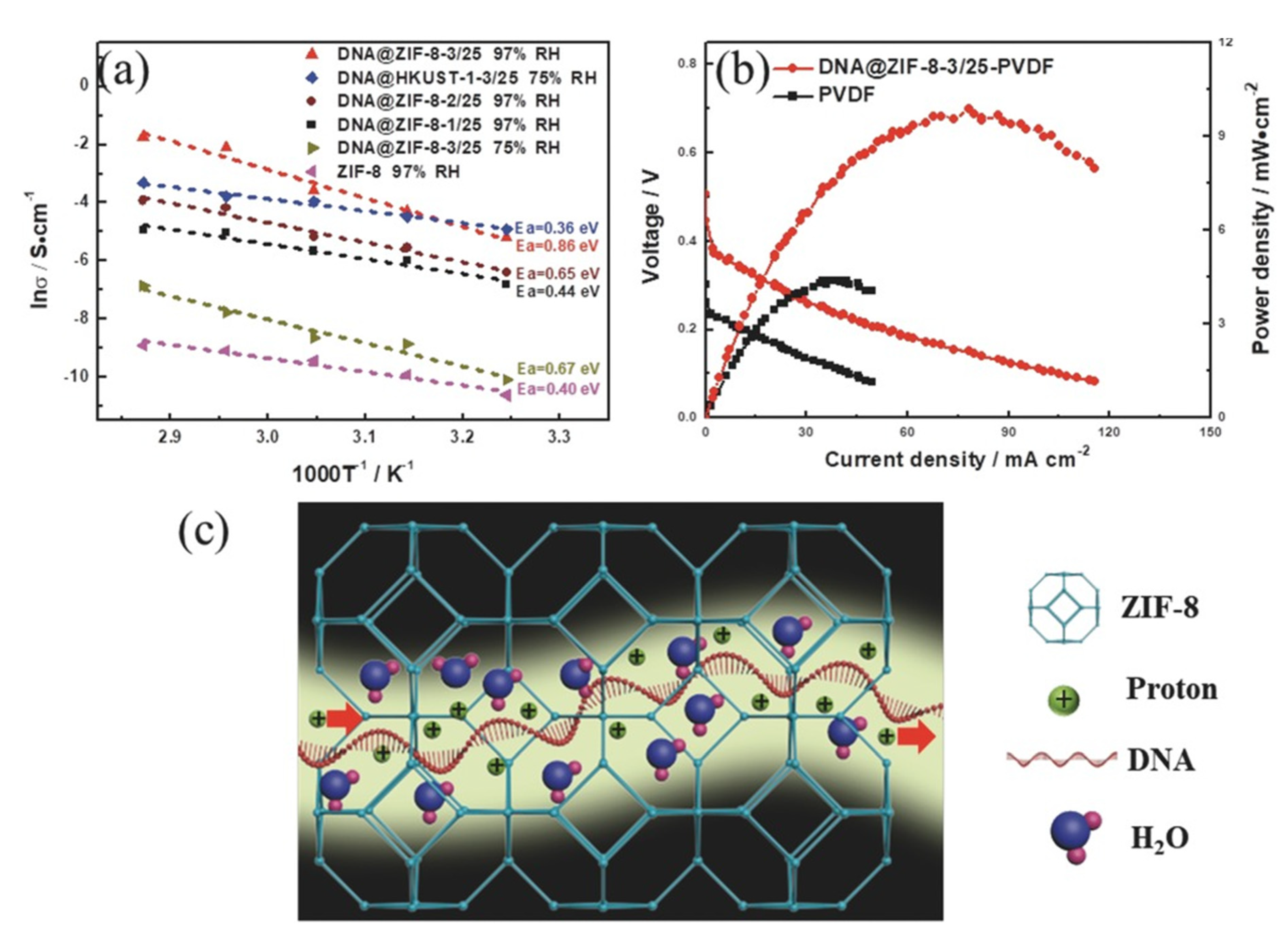
3.5.4. Proton Conductivity Properties
4. Applications of MOF and COF Membranes
4.1. Gas Separation
4.1.1. CO2 Recovery
4.1.2. H2 Purification and Recovery
4.1.3. Hydrocarbon Separation
4.2. Liquid Separation
4.2.1. Water Treatment
4.2.2. Organic Solvent Nanofiltration
4.2.3. Pervaporation
4.3. Fuel Cells
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aptel, P.; Armor, J.; Audinos, R.; Baker, R.W.; Bakish, R.; Belfort, G.; Bikson, B.; Brown, R.G.; Bryk, M.; Burke, J.J.; et al. Terminology for membranes and membrane processes (IUPAC Recommendations 1996). J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 120, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Minassian-Saraga, L.; Adler, M.; Barraud, A.; Churaev, N.V.; Eaton, D.F.; Kuhn, H.; Misono, M.; Platikanov, D.; Ralston, J.; Silberberg, A.; et al. Thin films including layers: Terminology in relation to their preparation and characterization. IUPAC recommendations 1994. Thin Solid Films 1996, 277, 7–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Based, C.; Based, C. Membrane Classification and Membrane Operations. In Nanomaterial and Polymer Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 55–82. ISBN 9780128047033. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, J.; Mulder, M. Basic Principles of Membrane; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Berlin, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pinnau, I. Membrane Preparation. Encycl. Sep. Sci. 2000, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Liu, J.; Fischer, R.A.; Wöll, C. MOF thin films: Existing and future applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1081–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M. Reticular Chemistry—Construction, Properties, and Precision Reactions of Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15507–15509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science (80) 2013, 341, 1230444–1230456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockwig, N.W.; Delgado-Friedrichs, O.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Reticular Chemistry: Occurrence and Taxonomy of Nets and Grammar for the Design of Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Ockwig, N.W.; Chae, H.K.; Eddaoudi, M.; Kim, J. Reticular synthesis and the design of new materials. Nature 2003, 423, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Li, G.; Li, H. Selective binding and removal of guests in a microporous metal-organic framework. Nature 1995, 378, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchon, A.; Feng, L.; Drake, H.F.; Joseph, E.A.; Zhou, H.C. From fundamentals to applications: A toolbox for robust and multifunctional MOF materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 8611–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, A.P.; Benin, A.I.; Ockwig, N.W.; O’Keeffe, M.; Matzger, A.J.; Yaghi, O.M. Porous, Crystalline, Covalent Organic Frameworks. Science (80) 2005, 310, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to Metal−Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, P.Z.; Li, A.; Wiggin, S.B.; Tao, A.; Maloney, A.G.P.; Wood, P.A.; Ward, S.C.; Fairen-Jimenez, D. Development of a Cambridge Structural Database Subset: A Collection of Metal-Organic Frameworks for Past, Present, and Future. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Martinez, M.; Avci-Camur, C.; Thornton, A.W.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D.; Hill, M.R. New synthetic routes towards MOF production at scale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3453–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.Y.; Wang, W. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 548–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohse, M.S.; Bein, T. Covalent Organic Frameworks: Structures, Synthesis, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumida, K.; Rogow, D.L.; Mason, J.A.; Mcdonald, T.M.; Bloch, E.D.; Herm, Z.R.; Bae, T.; Long, R. Carbon Dioxide Capture in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 2, 724–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujie, K.; Kitagawa, H. Ionic liquid transported into metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wu, X.T.; Zhu, Q.L. Pore surface engineering of metal–organic frameworks for heterogeneous catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 248–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Xue, H.; Pang, H. Metal-organic frameworks for direct electrochemical applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 376, 292–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sachdeva, S.; Lee, A.K.; Jeong, H.K. Current status of metal-organic framework membranes for gas separations: Promises and challenges. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2179–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Deibert, B.J.; Li, J. Luminescent metal-organic frameworks for chemical sensing and explosive detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5815–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, F.; Chen, D.; Wu, M.; Han, L.; Jiang, H. Chemical Sensors Based on Metal – Organic Frameworks. Chempluschem 2016, 81, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Qian, R.; Ling, P.; Cui, L.; Ju, H. Design and sensing applications of metal – organic framework composites. Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 58, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Marqués, M.; Hidalgo, T.; Serre, C.; Horcajada, P. Nanostructured metal-organic frameworks and their bio-related applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Zamora, F. Processing of covalent organic frameworks: An ingredient for a material to succeed. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 4375–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Metal–organic framework membranes: Production, modification, and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 100, 21–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M.; Deng, B. Metal-organic frameworks ( MOFs ) in water filtration membranes for desalination and other applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 11, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Fan, L.; Sun, D. Recent advances and challenges of metal-organic framework membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 10073–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gascon, J.; Li, J.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Metal-organic frameworks based membranes for liquid separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 7124–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ban, Y.; Yang, W. Microstructural Engineering and Architectural Design of Metal–Organic Framework Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, B.; Coronas, J.; Gascon, I.; Benavides, M.E.; Karvan, O.; Caro, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Metal-organic framework based mixed matrix membranes: A solution for highly efficient CO2 capture? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2421–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Van Puyvelde, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Covalent organic frameworks for membrane separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, B.-H.; Ma, M.-Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.-K. Ultrathin metal/covalent–organic framework membranes towards ultimate separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ng, Z.; Khan, E.A.; Jeong, H.K.; Ching, C.; Lai, Z. Synthesis of continuous MOF-5 membranes on porous α-alumina substrates. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 118, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Xue, M.; Zhu, G. Metal-organic framework membranes: From synthesis to separation application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6116–6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bux, H.; Liang, F.; Li, Y.; Cravillon, J.; Wiebcke, M.; Caro, J. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membrane with Molecular Sieving Properties by Microwave-Assisted Solvothermal Synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 16000–16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-S.; Liang, F.-Y.; Bux, H.; Feldhoff, A.; Yang, W.-S.; Caro, J. Molecular Sieve Membrane: Supported Metal-Organic Framework with High Hydrogen Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 548–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Dou, W.; Caro, J. Steam-stable zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-90 membrane with hydrogen selectivity through covalent functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 15562–15564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Bux, H.; Steinbach, F.; Caro, J. Molecular-Sieve Membrane with Hydrogen Permselectivity: ZIF-22 in LTA Topology Prepared with 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane as Covalent Linker. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4958–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Diestel, L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, A.; Caro, J. Polydopamine-based synthesis of a zeolite imidazolate framework ZIF-100 membrane with high H2/CO2 selectivity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4722–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Liu, Q.; Wang, N.; Caro, J. Highly hydrogen permselective ZIF-8 membranes supported on polydopamine functionalized macroporous stainless-steel-nets. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8246–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, T.; Lu, C.; Pei, C.; Xu, S.; Qiu, S. Polymer-supported and free-standing metal-organic framework membrane. Chem. A Eur. J. 2012, 18, 10250–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.C.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; Barnett, G.V.; Jeong, H.-K. Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Films and Membranes with Controlled Microstructures. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14636–14641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Xue, M.; Fan, L.; Ding, J.; Guo, L.; Gao, L.; Qiu, S. Single nickel source in situ fabrication of a stable homochiral MOF membrane with chiral resolution properties. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10569–10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Z.; Xue, M.; Fan, L.; Huang, L.; Guo, L.; Wei, G.; Chen, B.; Qiu, S. Highly selective sieving of small gas molecules by using an ultra-microporous metal-organic framework membrane. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 4053–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, G.; Hewitt, I.J.; Qiu, S. “Twin Copper Source” Growth of Metal-Organic Framework Membrane: Cu3(BTC)2 with High Permeability and Selectivity for Recycling H2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-Q.; Xie, L.-H.; Qin, X.; Sun, Y.-X.; Xie, Y.-B.; Li, J.-R. Continuous Crystalline Membranes of a Ni(II)-Based Pillared-Layer Metal-Organic Framework In Situ Grown on Nickel Foam with Two Orientations. Crystals 2018, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakanda, P.; Barankova, E.; Peinemann, K.V. Polymer supported ZIF-8 membranes by conversion of sputtered zinc oxide layers. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 220, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Kong, L.; Liu, H.; Qiu, J.; Han, W.; Weng, L.T.; Yeung, K.L.; Zhu, W. A simple and scalable method for preparing low-defect ZIF-8 tubular membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 10635–10638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, P.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Preparation of a pure ZIF-67 membrane by self-conversion of cobalt carbonate hydroxide nanowires for H2 separation. CrystEngComm 2018, 20, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, S.; Lercher, A.J.; Zhang, H. Coordination modulation induced synthesis of nanoscale Eu 1- Tb x metal-organic frameworks for luminescent thin films. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4190–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Seshimo, M.; Matsukata, M. Chapter 8. Membrane Technology: How, where, and why. In Zeolites and Metal-Organic Frameworks From Lab to Industry; Blay, V., Bobadilla, L.F., Cabrera-García, A., Eds.; Amsterdam University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 209–233. ISBN 9789462985568. [Google Scholar]
- Ramu, G.; Lee, M.; Jeong, H.K. Effects of zinc salts on the microstructure and performance of zeolitic-imidazolate framework ZIF-8 membranes for propylene/propane separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Caro, J.; Guo, X.; Song, C.; Liu, Y. In-Plane Epitaxial Growth of Highly c-Oriented NH2-MIL-125(Ti) Membranes with Superior H2/CO2 Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16088–16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, R.; Tsapatsis, M. Microporous Metal Organic Framework Membrane on Porous Support Using the Seeded Growth Method. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4920–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Xue, M.; Kang, Z.; Li, H.; Qiu, S. Electrospinning technology applied in zeolitic imidazolate framework membrane synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 25272–25276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceituno Melgar, V.M.; Kwon, H.T.; Kim, J. Direct spraying approach for synthesis of ZIF-7 membranes by electrospray deposition. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 459, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Dong, X.; Wang, W.; Jin, W.; Xu, N. Step-by-step seeding procedure for preparing HKUST-1 membrane on porous α-alumina support. Langmuir 2011, 27, 4309–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, X.; Nan, J.; Jin, W.; Ren, X.; Xu, N.; Lee, Y.M. Metal-organic framework membranes fabricated via reactive seeding. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Yi, X.; Wang, P.; Zheng, W.; Deng, J.; Wang, C. Robust photocatalytic reduction of Cr ( VI ) on UiO-66-NH 2 (Zr/Hf) metal- organic framework membrane under sunlight irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Wang, H.; Kowarik, S.; Schreiber, F.; Paulus, M.; Tolan, M.; Sternemann, C.; Evers, F.; Zacher, D.; Fischer, R.A.; et al. Step-by-Step Route for the Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15118–15119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhah, O.; Swaidan, R.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Du Plessis, M.; Jacobs, T.; Barbour, L.J.; Pinnau, I.; Eddaoudi, M. The liquid phase epitaxy approach for the successful construction of ultra-thin and defect-free ZIF-8 membranes: Pure and mixed gas transport study. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 2089–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jomekian, A.; Behbahani, R.M.; Mohammadi, T.; Kargari, A. Innovative layer by layer and continuous growth methods for synthesis of ZIF-8 membrane on porous polymeric support using poly(ether-block-amide) as structure directing agent for gas separation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 234, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Song, M.; Zhou, J.; Fang, Q.; Xue, M.; Qiu, S. Solvent-Free Crystallization of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membrane via Layer-by-Layer Deposition. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 4158–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, H.M.; Japip, S.; Hua, D.; Chung, T.S. Green Layer-by-Layer Method for the Preparation of Polyacrylonitrile-Supported Zinc Benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic Acid Membranes. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 2612–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Dong, D.; Li, D.; He, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, H. Contra-diffusion synthesis of ZIF-8 films on a polymer substrate. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2559–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Shen, J.; Guan, K.; Jin, W. A ZIF-71 Hollow Fiber Membrane Fabricated by Contra-Diffusion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16157–16160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.P.; Bhaskar, A.; Banerjee, R.; Kharul, U.K. Selective interfacial synthesis of metal–organic frameworks on a polybenzimidazole hollow fiber membrane for gas separation. Nanos 2015, 7, 7291–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Su, P.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, F.; Ou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, E. Ultrathin metal-organic framework membrane production by gel-vapour deposition. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Xia, Y. Sol-gel asynchronous crystallization of ultra-selective metal-organic framework membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16333–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Kumar, P.; Mittal, N.; Khlyustova, A.; Daoutidis, P.; Mkhoyan, K.A.; Tsapatsis, M. Zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes made by ligand-induced permselectivation. Science (80) 2018, 361, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, P.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Bottom-up fabrication of two-dimensional Co-based zeolitic imidazolate framework tubular membranes consisting of nanosheets by vapor phase transformation of Co-based gel for H2/CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Zhang, J.; Lu, H.; Leng, W.; Ge, R.; Dai, X.; Gao, Y. Fabrication of a COF-5 membrane on a functionalized α-Al 2O3 ceramic support using a microwave irradiation method. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1462–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Ge, R.; Leng, W.; Dong, B.; Huang, J.; Gao, Y. A novel 3D covalent organic framework membrane grown on a porous α-Al2O3 substrate under solvothermal conditions. Chem. Commun. (Cambridge, United Kingdom) 2015, 51, 15562–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Knebel, A.; Caro, J. High-Flux Membranes Based on the Covalent Organic Framework COF-LZU1 for Selective Dye Separation by Nanofiltration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandambeth, S.; Biswal, B.P.; Chaudhari, H.D.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu, H.S.; Mitra, S.; Karak, S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; et al. Selective Molecular Sieving in Self-Standing Porous Covalent-Organic-Framework Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603945–1603954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, H.S.; Aiyappa, H.B.; Bhange, S.N.; Karak, S.; Halder, A.; Kurungot, S.; Banerjee, R. Superprotonic Conductivity in Flexible Porous Covalent Organic Framework Membranes. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10894–10898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Tsuru, T. Two-Dimensional Covalent Organic Framework (COF) Membranes Fabricated via the Assembly of Exfoliated COF Nanosheets. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8433–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, J.; Tong, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, C. A GO-assisted method for the preparation of ultrathin covalent organic framework membranes for gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13444–13449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Feng, S.; Fan, L.; Pang, J.; Fan, W.; Kong, G.; Kang, Z. Separation and Puri fi cation Technology Covalent organic frameworks combined with graphene oxide to fabricate membranes for H2/CO2 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 223, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Pan, F. High-efficiency water-selective membranes from the solution-diffusion synergy of calcium alginate layer and covalent organic framework (COF) layer. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Livingston, A.G.; Santanu, K. Sub-10 nm polyamide nanofilms with ultrafast solvent transport for molecular separation. Science (80) 2015, 348, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Solomon, M.F.; Song, Q.; Jelfs, K.E.; Munoz-Ibanez, M.; Livingston, A.G. Polymer nanofilms with enhanced microporosity by interfacial polymerization. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, H. Covalent organic framework modified polyamide nanofiltration membrane with enhanced performance for desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, K.; Pal, M.; Rout, K.C.; Kunjattu, S.S.; Das, A.; Mukherjee, R.; Kharul, U.K.; Banerjee, R. Selective Molecular Separation by Interfacially Crystallized Covalent Organic Framework Thin Films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13083–13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, L.; Matsumoto, M.; Dichtel, W.R.; Marinas, B.J. Development and Performance Characterization of a Polyimine Covalent Organic Framework Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 14352–14359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Valentino, L.; Stiehl, G.M.; Balch, H.B.; Corcos, A.R.; Wang, F.; Ralph, D.C.; Mariñas, B.J.; Dichtel, W.R. Lewis-Acid-Catalyzed Interfacial Polymerization of Covalent Organic Framework Films. Chem 2018, 4, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, X.; Xiao, A.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y. Interfacial polymerization of covalent organic frameworks (COFs) on polymeric substrates for molecular separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Sheng, G.; Li, X.; Ostwal, M.; Emwas, A.-H.; Huang, K.-W.; Lai, Z. Crystalline 2D Covalent Organic Framework Membranes for High-Flux Organic Solvent Nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14342–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Das, S.; Xing, G.; Ben, T.; Valtchev, V.; Qiu, S. Fabrication of COF-MOF Composite Membranes and Their Highly Selective Separation of H2/CO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7673–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ben, T. A [COF-300]-[UiO-66] composite membrane with remarkably high permeability and H2/CO2 separation selectivity. Dalt. Trans. 2018, 47, 7206–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Japip, S.; Jiang, S.D.; Chung, T.S.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, D. Advanced Porous Materials in Mixed Matrix Membranes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechnik, J.; Gascon, J.; Doonan, C.J.; Janiak, C.; Sumby, C.J. Mixed-Matrix Membranes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9292–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kitagawa, S.; Wang, B.; Uemura, T. Hybridization of MOFs and polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3108–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Gracia-Guillén, I.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Thin supported MOF based mixed matrix membranes of Pebax® 1657 for biogas upgrade. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, P.H.H.; Kuehl, V.A.; Mastorovich, B.; Hoberg, J.O.; Parkinson, B.A.; Li-Oakey, K.D. Carboxyl-functionalized covalent organic framework as a two-dimensional nanofiller for mixed-matrix ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Y. Mixed matrix membranes incorporated with Ln-MOF for selective and sensitive detection of nitrofuran antibiotics based on inner filter effect. Talanta 2017, 174, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xiang, L.; Chang, H.; Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Rational matching between MOFs and polymers in mixed matrix membranes for propylene/propane separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 204, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinov, N.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Hensen, E.J.M. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, L.M.; Kuperman, A.; Kustov, A. Chapter 8 - Further Steps of Zeolites Toward Industrial Applications: A Short-Range Outlook. In Zeolites and Zeolite-Like Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 309–369. ISBN 9780444635068. [Google Scholar]
- Kiesow, I.; Marczewski, D.; Reinhardt, L.; Mühlmann, M.; Possiwan, M.; Goedel, W.A. Bicontinuous zeolite polymer composite membranes prepared via float casting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4380–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, R.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, C.; Xin, Q.; Lu, X. Facilitated transport mixed matrix membranes incorporated with amine functionalized MCM-41 for enhanced gas separation properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 465, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.; Mohammadi, T.; Behbahani, R.M. Synthesis of a PEBAX-1074/ZnO nanocomposite membrane with improved CO2 separation performance. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.F.; Goh, P.S.; Sanip, S.M.; Aziz, M. Transport and separation properties of carbon nanotube-mixed matrix membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 70, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattia, D.; Leese, H.; Lee, K.P. Carbon nanotube membranes: From flow enhancement to permeability. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Jawad, Z.A.; Low, S.C.; Zein, S.H.S. A cellulose acetate/multi-walled carbon nanotube mixed matrix membrane for CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 451, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Chowdhury, S. Recent advances and progress in the development of graphene-based adsorbents for CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21968–21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, R.; Wu, H. Efficient CO2 capture by functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets as fillers to fabricate multi-permselective mixed matrix membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 5528–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Goh, K.; Weerachanchai, P.; Bae, T.-H. 3D covalent organic framework for morphologically induced high-performance membranes with strong resistance toward physical aging. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, J.E.; Long, J.R. Plasticization-resistant Ni2(dobdc)/polyimide composite membranes for the removal of CO2 from natural gas. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Nataraj, S.K.; Roussenova, M.V.; Tan, J.C.; Hughes, D.J.; Li, W.; Bourgoin, P.; Alam, M.A.; Cheetham, A.K.; Al-Muhtaseb, S.A.; et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) based polymer nanocomposite membranes for gas separation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8359–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, B.; Martinez-Joaristi, A.; Serra-Crespo, P.; Tellez, C.; Coronas, J.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Functionalized flexible MOFs as fillers in mixed matrix membranes for highly selective separation of CO2 from CH4 at elevated pressures. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9522–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Zornoza, B.; Friebe, S.; Caro, J.; Cao, S.; Sabetghadam, A.; Seoane, B.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F.; Le Guillouzer, C.; et al. Influence of ZIF-8 particle size in the performance of polybenzimidazole mixed matrix membranes for pre-combustion CO2 capture and its validation through interlaboratory test. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 515, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Zornoza, B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. On the chemical filler-polymer interaction of nano- and micro-sized ZIF-11 in PBI mixed matrix membranes and their application for H2/CO2 separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14334–14341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, Y.; Bentz, K.C.; Cohen, S.M. Defect-Free MOF-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes Obtained by Corona Cross-Linking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 13029–13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Ebadi Amooghin, A.; Montazer-Rahmati, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. State-of-the-art membrane based CO2 separation using mixed matrix membranes (MMMs): An overview on current status and future directions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 817–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, H.; Pisklak, T.J.; Ferraris, J.P.; Balkus, K.J.; Musselman, I.H. Methane Facilitated Transport Using Copper(II) Biphenyl Dicarboxylate-Triethylenediamine/Poly (3-Acetoxyethylthiophene) Mixed Matrix Membranes. Polym. Prepr. 2004, 45, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Li, K. Novel Organic-Dehydration Membranes Prepared from Zirconium Metal-Organic Frameworks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechnik, J.; Sumby, C.J.; Janiak, C. Enhancing Mixed-Matrix Membrane Performance with Metal-Organic Framework Additives. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4467–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Villacorta Hernandez, B.; Ge, L.; Zhu, Z. Metal organic framework based mixed matrix membranes: An overview on filler/polymer interfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Enhanced performance of mixed matrix membrane by incorporating a highly compatible covalent organic framework into poly(vinylamine) for hydrogen purification. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 9167–9174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Seoane, B.; Andres-Garcia, E.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Mixed-matrix membranes containing an azine-linked covalent organic framework: Influence of the polymeric matrix on post-combustion CO2-capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Xu, G.; Hu, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Chi, C.; Yuan, D.; Cheng, H.; Zhao, D. Mechanoassisted Synthesis of Sulfonated Covalent Organic Frameworks with High Intrinsic Proton Conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18505–18512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, M.; Seoane, B.; Rozhko, E.; Dikhtiarenko, A.; Clet, G.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Azine-Linked Covalent Organic Framework (COF)-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Hu, L.; Jin, J. Interfacial Design of Mixed Matrix Membranes for Improved Gas Separation Performance. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3399–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien-Binh, N.; Vinh-Thang, H.; Chen, X.Y.; Rodrigue, D.; Kaliaguine, S. Polymer functionalization to enhance interface quality of mixed matrix membranes for high CO2/CH4 gas separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15202–15213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Nijmeijer, K.; Nehache, S.; Vankelecom, I.; Deratani, A.; Quemener, D. MOF-mixed matrix membranes: Precise dispersion of MOF particles with better compatibility via a particle fusion approach for enhanced gas separation properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.D.; Ladewig, B.P.; Hill, A.J.; Lau, C.H.; Hill, M.R. Post-synthetic Ti Exchanged UiO-66 Metal-Organic Frameworks that Deliver Exceptional Gas Permeability in Mixed Matrix Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maythalony, B.A.; Alloush, A.M.; Faizan, M.; Dafallah, H.; Elgzoly, M.A.A.; Seliman, A.A.A.; Al-Ahmed, A.; Yamani, Z.H.; Habib, M.A.M.; Cordova, K.E.; et al. Tuning the interplay between selectivity and permeability of ZIF-7 mixed matrix membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 33401–33407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Sheng, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y. Amino-Functionalized ZIF-7 Nanocrystals: Improved Intrinsic Separation Ability and Interfacial Compatibility in Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2/CH4 Separation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Maes, M.; Cano-Odena, A.; Alaerts, L.; De Vos, D.E.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration (SRNF) membranes based on metal-organic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 344, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venna, S.R.; Lartey, M.; Li, T.; Spore, A.; Kumar, S.; Nulwala, H.B.; Luebke, D.R.; Rosi, N.L.; Albenze, E. Fabrication of MMMs with improved gas separation properties using externally-functionalized MOF particles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 5014–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Ge, L.; Diao, H.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Ionic liquids as the MOFs/polymer interfacial binder for efficient membrane separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32041–32049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Jie, X.; Liu, D.; Cao, Y. Improved Interfacial Affinity and CO2 Separation Performance of Asymmetric Mixed Matrix Membranes by Incorporating Postmodified MIL-53(Al). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22696–22704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Fu, Q.; Kim, J.; Lu, H.; He, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Scofield, J.; Webley, P.A.; Qiao, G.G. Increasing both selectivity and permeability of mixed-matrix membranes: Sealing the external surface of porous MOF nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 535, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Shojaei, A.; Mousavib, S.A. Improving mixed-matrix membrane performance via PMMA grafting from functionalized NH2–UiO-66. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 2775–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, S.; Qin, X.; Li, C.; Li, T. Interfacial Engineering in Metal-Organic Framework-Based Mixed Matrix Membranes Using Covalently Grafted Polyimide Brushes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 17203–17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.P.; Chaudhari, H.D.; Banerjee, R.; Kharul, U.K. Chemically Stable Covalent Organic Framework (COF)-Polybenzimidazole Hybrid Membranes: Enhanced Gas Separation through Pore Modulation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 4695–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
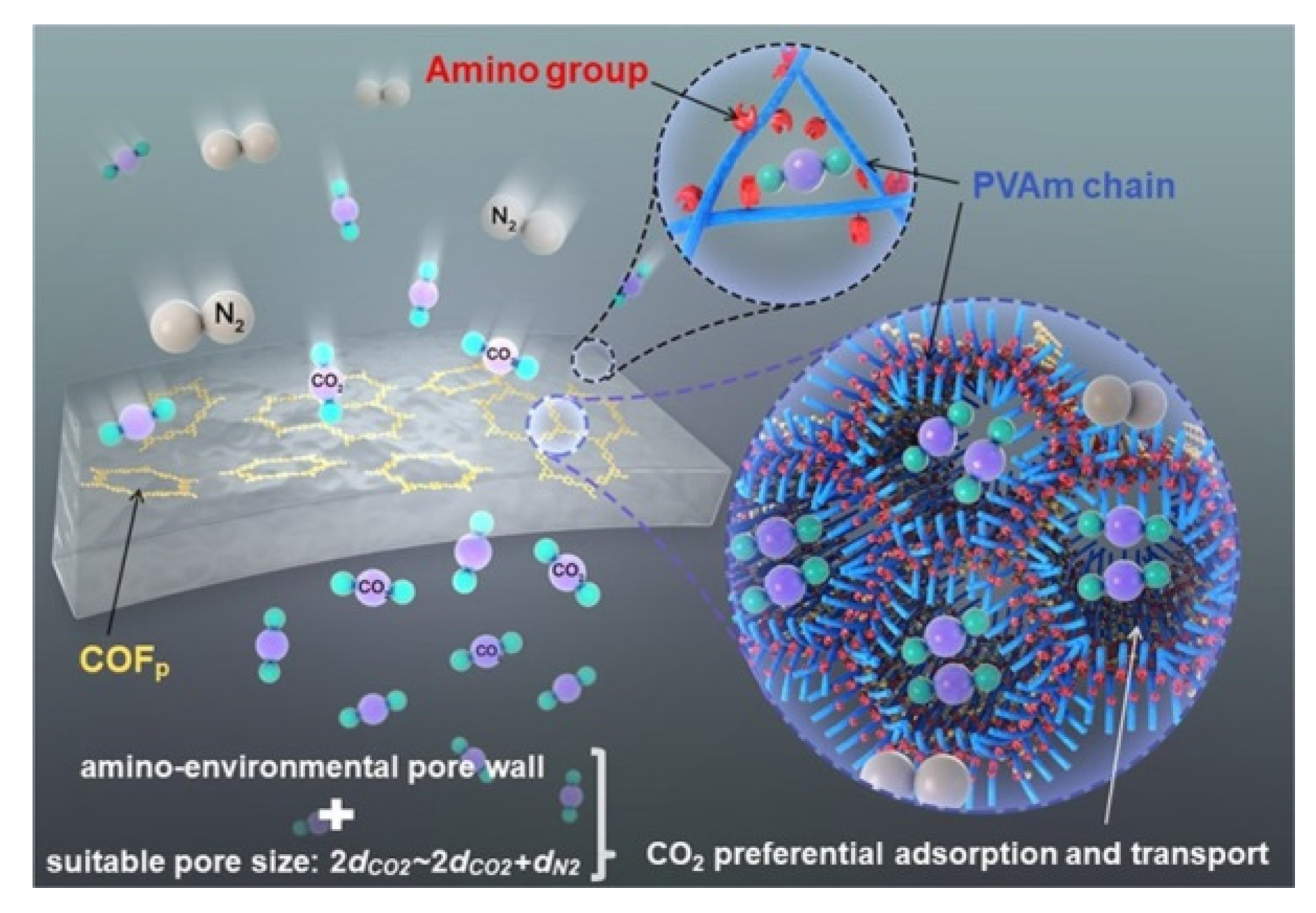
- Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J. Penetrated COF Channels: Amino Environment and Suitable Size for CO2 Preferential Adsorption and Transport in Mixed Matrix Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5306–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Khan, A.L.; Cano-Odena, A.; Liu, C.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Membrane-based technologies for biogas separations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenas, T.; Luz, I.; Prieto, G.; Seoane, B.; Miro, H.; Corma, A.; Kapteijn, F.; Llabrés i Xamena, F.X.; Gascon, J. Metal–organic framework nanosheets in polymer composite materials for gas separation. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, A.; Liu, X.; Gottmer, S.; Chu, L.; Gascon, J.; Kapteijn, F. Thin mixed matrix and dual layer membranes containing metal-organic framework nanosheets and PolyactiveTM for CO2 capture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.S.; Moreton, J.C.; Benz, L.; Cohen, S.M. Metal-organic frameworks for membrane-based separations. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16078–16095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Chernikova, V.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Shekhah, O.; Zhang, C.; Yi, S.; Eddaoudi, M.; Koros, W.J. Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzaqui, M.; Semino, R.; Carn, F.; Tavares, S.R.; Menguy, N.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Bellido, E.; Horcajada, P.; Berthelot, T.; Kuzminova, A.; et al. Covalent and Selective Grafting of PEG Brushes at the Surface of ZIF-8 for the Processing of Membranes for Pervaporation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6629–6639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Qian, Y.; Yuan, D.; Addicoat, M.A.; Heine, T.; Hu, Z.; Tee, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, D. Mixed Matrix Membranes (MMMs) Comprising Exfoliated 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) for Efficient CO2 Separation. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, Q.; Hua, Y.; Zhou, B.; Duan, J.; Jin, W. Mechanical Synthesis of COF Nanosheet Cluster and Its Mixed Matrix Membrane for Efficient CO2 Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29093–29100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) functionalized mixed matrix membrane for effective CO2/N2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ying, Y.; Zhai, L.; Liu, G.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Christopher, M.P.; Long, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. Mixed matrix membranes containing MOF@COF hybrid fillers for efficient CO2/CH4 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic Covalent Modification of a Neutral Metal-Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12368–12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Tuning the moisture stability of metal-organic frameworks by incorporating hydrophobic functional groups at different positions of ligands. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7377–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, A.J.; Peters, A.W.; Vermeulen, N.A.; Wang, T.C.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Best Practices for the Synthesis, Activation, and Characterization of Metal—Organic Frameworks. Chem. Mater. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bétard, A.; Fischer, R.A. Metal-organic framework thin films: From fundamentals to applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1055–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wöll, C. Surface-supported metal-organic framework thin films: Fabrication methods, applications, and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5730–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsubo, K.; Kitagawa, H. Metal-organic framework thin films with well-controlled growth directions confirmed by x-ray study. APL Mater. 2014, 2, 124105–124116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.H.; Bragg, W.L.; James, R.W.; Lipson, H. The crystalline state; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, G.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. Mixed-matrix hollow fiber composite membranes comprising of PEBA and MOF for pervaporation separation of ethanol/water mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 214, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Nasir, N.; Song, Y.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; et al. Covalent organic framework membranes through a mixed-dimensional assembly for molecular separations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumée, L.; He, L.; Hill, M.; Zhu, B.; Duke, M.; Schütz, J.; She, F.; Wang, H.; Gray, S.; Hodgson, P.; et al. Seeded growth of ZIF-8 on the surface of carbon nanotubes towards self-supporting gas separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9208–9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Du, H.; Cao, C.; Ren, Y.; Wu, Y.; Pan, F.; et al. Brønsted acid mediated covalent organic framework membranes for efficient molecular separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 20317–20324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Parent, L.R.; Overholts, A.C.; Beaucage, P.A.; Bisbey, R.P.; Chavez, A.D.; Hwang, N.; Park, C.; Evans, A.M.; Gianneschi, N.C.; et al. Colloidal Covalent Organic Frameworks. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, B. Introduction to Membrane Science and Technology. By Heinrich Strathmann. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, R.; Kaufman, Y.; Freger, V. Membrane Characterization. Encycl. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2013, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, F.; Marti, A.M.; Hopkinson, D.P. Layer-by-layer assembled polymer/MOF membrane for H2/CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, G. Ultra-high selectivity COF-based membranes for biobutanol production. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2018, 6, 17602–17611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Mundstock, A.; Feldhoff, A.; Knebel, A.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Caro, J. Covalent Organic Framework-Covalent Organic Framework Bilayer Membranes for Highly Selective Gas Separation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10094–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, F.; Feng, W.; Zou, X.; Zhao, C.; Na, H.; Liu, C.; Sun, F.; Zhu, G. From metal-organic framework (MOF) to MOF-polymer composite membrane: Enhancement of low-humidity proton conductivity. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.; Burgal, J.D.S.; Szekely, G.; Davies, R.P.; Braddock, D.C.; Livingston, A. Hybrid polymer/MOF membranes for Organic Solvent Nanofiltration (OSN): Chemical modification and the quest for perfection. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 503, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Varela-guerrero, V.; Jeong, H. Isoreticular Metal - Organic Frameworks and Their Membranes with Enhanced Crack Resistance and Moisture Stability by Surfactant-Assisted Drying. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2652–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Pan, F.; Wu, H.; Liu, G.; Song, Y.; Cao, X.; Jiang, Z. Highly water-selective membranes based on hollow covalent organic frameworks with fast transport pathways. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denny, M.S.; Cohen, S.M. In Situ Modification of Metal-Organic Frameworks in Mixed-Matrix Membranes. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9029–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidley, D.W.; Peng, H.; Vallery, R.S. Positron annihilation as amethod to characterize porous materials. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kwak, S.Y.; Suzuki, T. Positron annihilation spectroscopic evidence to demonstrate the flux-enhancement mechanism in morphology-controlled thin-film-composite (TFC) membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1764–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; Li, Z.; Ding, H.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; Wang, B. Highly water-permeable and stable hybrid membrane with asymmetric covalent organic framework distribution. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hung, W.S.; Zhu, H.; Guan, K.; Ji, Y.; Mao, Y.; Liu, G.; Lee, K.R.; Jin, W. Fabrication of ZIF-300 membrane and its application for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, X.; Guo, S.; Tang, L.; Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Pan, F.; Zhang, P.; Cao, X.; et al. Bimetallic metal-organic frameworks nanocages as multi-functional fillers for water-selective membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, V.; Shekhah, O.; Eddaoudi, M. Advanced Fabrication Method for the Preparation of MOF Thin Films: Liquid-Phase Epitaxy Approach Meets Spin Coating Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20459–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Li, X.; Ji, S.; An, Q.-F. Covalent organic frameworks hybird membrane with optimized mass transport nanochannel for aromatic/aliphatic mixture pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 117652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revol, P.; Perret, D.; Bertin, F.; Fusalba, F.; Rouessac, V.; Chabli, A.; Passemard, G.; Ayral, A. Porosimetry measurements on low dielectric constant-thin layers by coupling spectroscopic ellipsometry and solvent adsorption-desorption. J. Porous Mater. 2005, 12, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, P.; Jimenez Solomon, M.F.; Szekely, G.; Livingston, A.G. Molecular Separation with Organic Solvent Nanofiltration: A Critical Review. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10735–10806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeson, L.M. The upper bound revisited. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, M. Robeson Correlation of separation factor versus permeability for polymeric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1991, 62, 165–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An Essay on Cohesion of Fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc 1804, 95, 65.
- Yuan, Y.; Lee, R. Chapter 1 Contact Angle and Wetting Properties, Surface Science Techniques; Bracco, G., Holst, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; ISBN 9783642342431. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Guo, W.; Su, Y.; Khan, N.A.; Yang, H.; Jiang, Z. Direct growth of covalent organic framework nanofiltration membranes on modified porous substrates for dyes separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, C.; Rodríguez-San-Miguel, D.; Polo, E.; Escudero-Cid, R.; Ruiz-González, M.L.; Navarro, J.A.R.; Ocón, P.; Zamora, F. Ionic Conductivity and Potential Application for Fuel Cell of a Modified Imine-Based Covalent Organic Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10079–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of Nafion composite membrane by incorporating phosphoric acid-loaded covalent organic framework. J. Power Sources 2016, 332, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; He, X.; Shi, B.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of Nafion/zwitterion-functionalized covalent organic framework composite membranes with improved proton conductivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 568, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Aiyappa, H.B.; Bhadra, M.; Biswal, B.P.; Wadge, P.; Kandambeth, S.; Garai, B.; Kundu, T.; Kurungot, S.; Banerjee, R. A mechanochemically synthesized covalent organic framework as a proton-conducting solid electrolyte. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2016, 4, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, H.N.; Song, S.Y.; Zhang, H.J. Proton-conducting crystalline porous materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 464–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.S.; Bu, X.; Feng, P. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Separation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705189–1705223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wang, H. Zeolitic imidazolate framework composite membranes and thin films: Synthesis and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4470–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhah, O.; Chernikova, V.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Eddaoudi, M. Metal–Organic Framework Membranes: From Fabrication to Gas Separation. Crystals 2018, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Carson, C.; Ward, J.; Tannenbaum, R.; Koros, W. Metal organic framework mixed matrix membranes for gas separations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 131, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Feng, X.; Yuan, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B. Challenges and recent advances in MOF-polymer composite membranes for gas separation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gurr, P.A.; Fu, Q.; Webley, P.A.; Qiao, G.G. Two-dimensional nanosheet-based gas separation membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 23169–23196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, J.; Yang, L.; Nasir, N.; Wu, H.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z. 110 th Anniversary: Mixed Matrix Membranes with Fillers of Intrinsic Nanopores for Gas Separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, D.J.; He, G.; Villalobos, L.F.; Agrawal, K.V. Crystal Engineering of Metal-Organic Framework Thin Films for Gas Separations. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhu, G. Microporous Organic Materials for Membrane-Based Gas Separation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, A.; Cao, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y. Post-Synthesized Method on Amine-Functionalized MOF Membrane for CO2/CH4 Separation. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 9499–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venna, S.R.; Carreon, M.A. Metal organic framework membranes for carbon dioxide separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 124, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
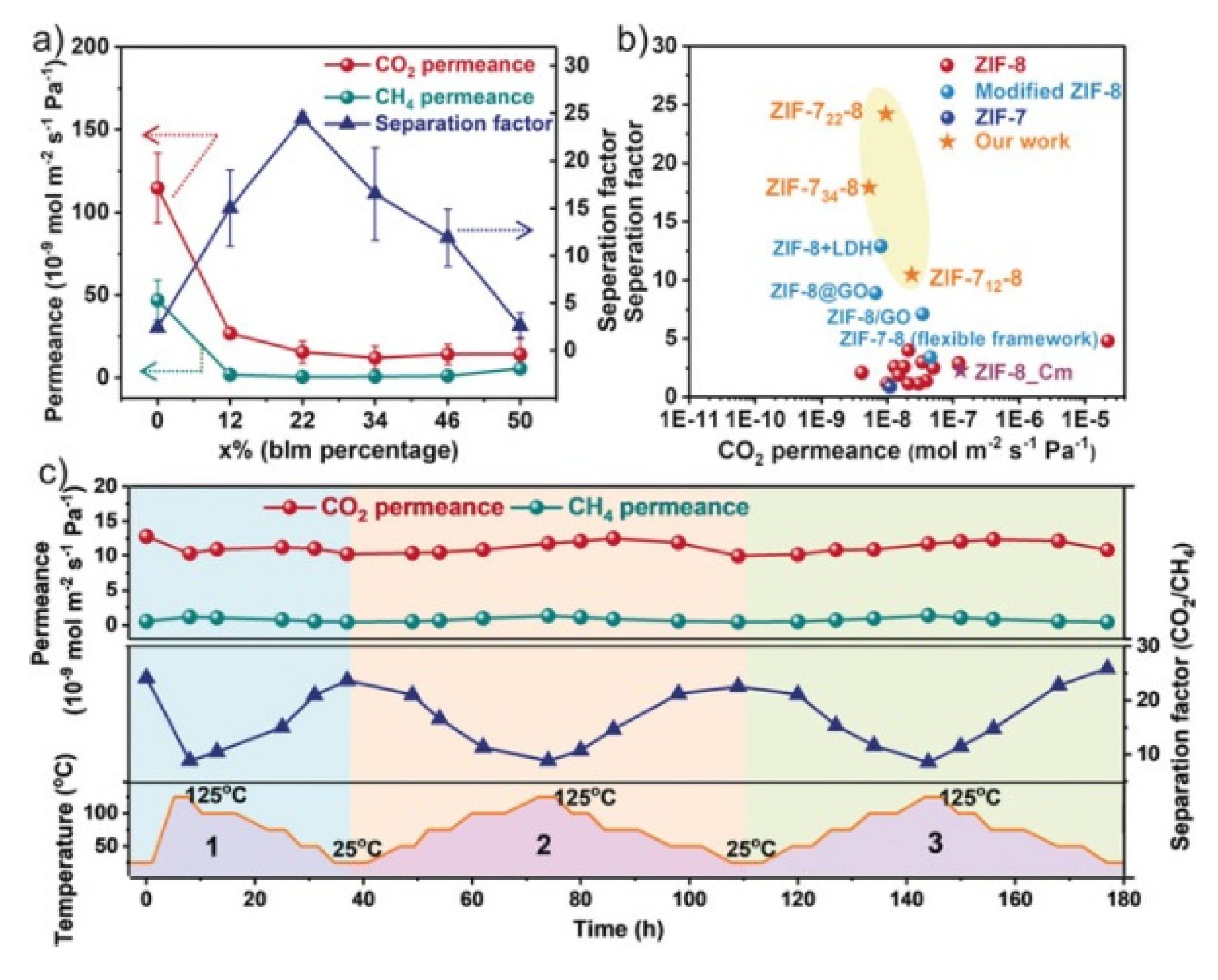
- Hou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wei, Y.; Caro, J.; Wang, H. Ultra-Tuning of the Aperture Size in Stiffened ZIF-8_Cm Frameworks with Mixed-Linker Strategy for Enhanced CO2/CH4 Separation. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Janakiram, S.; Dai, Z.; Ansaloni, L.; Deng, L. Performance of Mixed Matrix Membranes Containing Porous Two-Dimensional (2D) and Three-Dimensional (3D) Fillers for CO2 Separation: A Review. Membranes 2018, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xie, L.H.; Li, J.R.; Ma, Y.; Seminario, J.M.; Balbuena, P.B. CO2 Capture and Separations Using MOFs: Computational and Experimental Studies. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9674–9754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, D.J.; He, G.; Hao, J.; Vahdat, M.T.; Schouwink, P.A.; Mensi, M.; Agrawal, K.V. Restricting Lattice Flexibility in Polycrystalline Metal-Organic Framework Membranes for Carbon Capture. Adv. Mater. 2019, 1900855, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, J.H.; Wang, N.; Steinbach, F.; Liu, X.; Caro, J. Remarkably enhanced gas separation by partial self-conversion of a laminated membrane to metal-organic frameworks. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3028–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacho-Bailo, F.; Catalán-Aguirre, S.; Etxeberría-Benavides, M.; Karvan, O.; Sebastian, V.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Metal-organic framework membranes on the inner-side of a polymeric hollow fiber by microfluidic synthesis. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 476, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Mundstock, A.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Caro, J. An azine-linked covalent organic framework ACOF-1 membrane for highly selective CO2/CH4 separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 16849–16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Ding, R.; Yang, K.; Dai, Y.; Yan, X.; He, G. ZIF-8 nanoparticles with tunable size for enhanced CO2 capture of Pebax based MMMs. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 214, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.H.; Zhuang, G.L.; Tseng, H.H.; Wey, M.Y. Creation of tiny defects in ZIF-8 by thermal annealing to improve the CO2/N2 separation of mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, H.A.; Mohshim, D.F.; Mukhtar, H.; Murugesan, T.; Man, Z.; Bustam, M.A. Synthesis, characterization, and CO2 separation performance of polyether sulfone/[EMIM][Tf2N] ionic liquid-polymeric membranes (ILPMs). J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Ban, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, W. Metal-organic framework-based mixed matrix membranes: Synergetic e ff ect of adsorption and di ff usion for CO2/CH4 separation. J. Membr. 2018, 562, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarasinghe, S.A.S.C.; Chuah, C.Y.; Yang, Y.; Bae, T.H. Tailoring CO2/CH4 separation properties of mixed-matrix membranes via combined use of two- and three-dimensional metal-organic frameworks. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 557, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Laínez, J.; Pardillos-Ruiz, A.; Carta, M.; Malpass-Evans, R.; McKeown, N.B.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. Polymer engineering by blending PIM-1 and 6FDA-DAM for ZIF-8 containing mixed matrix membranes applied to CO2 separations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khdhayyer, M.; Bushell, A.F.; Budd, P.M.; Attfield, M.P.; Jiang, D.; Burrows, A.D.; Esposito, E.; Bernardo, P.; Monteleone, M.; Fuoco, A.; et al. Mixed matrix membranes based on MIL-101 metal–organic frameworks in polymer of intrinsic microporosity PIM-1. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, G.; Duan, J.; Liu, G.; Jin, W. MOF-801 incorporated PEBA mixed-matrix composite membranes for CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 217, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thür, R.; Van Velthoven, N.; Slootmaekers, S.; Didden, J.; Verbeke, R.; Smolders, S.; Dickmann, M.; Egger, W.; De Vos, D.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Bipyridine-based UiO-67 as novel filler in mixed-matrix membranes for CO2-selective gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, X.F.; Yao, J. Amine-functionalized MOFs@GO as filler in mixed matrix membrane for selective CO2 separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zou, X.; Sun, L.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, G. Constructing Connected Paths between UiO-66 and PIM-1 to Improve Membrane CO2 Separation with Crystal-Like Gas Selectivity. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Caro, J.; Huang, A. A new UiO-66-NH2 based mixed-matrix membranes with high CO2/CH4 separation performance. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 274, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabetghadam, A.; Liu, X.; Benzaqui, M.; Gkaniatsou, E.; Orsi, A.; Lozinska, M.M.; Sicard, C.; Johnson, T.; Steunou, N.; Wright, P.A.; et al. Influence of Filler Pore Structure and Polymer on the Performance of MOF-Based Mixed-Matrix Membranes for CO2 Capture. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7949–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, D.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Xin, Q.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Mixed matrix membranes comprising polymers of intrinsic microporosity and covalent organic framework for gas separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 528, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhai, L.; Ying, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Dong, J.; Ng, D.Z.L.; Khan, S.A.; Zhao, D. Highly efficient CO2 capture by mixed matrix membranes containing three-dimensional covalent organic framework fillers. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2019, 7, 4549–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ockwig, N.W.; Nenoff, T.M. Membranes for Hydrogen Separation. Chem. Rev. 2009, 110, 2573–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sutrisna, P.D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, V. Formation of Ultrathin, Continuous Metal-Organic Framework Membranes on Flexible Polymer Substrates. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3947–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, Y.; Jin, H.; Jiao, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, W. Metal-Organic Framework Nanosheets as Building Blocks for Molecular Sieving Membranes. Science (80) 2014, 346, 1356–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, Y.; Yang, W. Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets for Membrane-Based Gas Separation. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9757–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Howarth, A.J.; Nian, P.; Farha, O.K.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tu, M. Growth of ZnO self-converted 2D nanosheet zeolitic imidazolate framework membranes by an ammonia-assisted strategy. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, X. GO-guided direct growth of highly oriented metal-organic framework nanosheet membranes for H2/CO2 separation. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacho-Bailo, F.; Matito-Martos, I.; Perez-Carbajo, J.; Etxeberría-Benavides, M.; Karvan, O.; Sebastián, V.; Calero, S.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J. On the molecular mechanisms for the H2/CO2 separation performance of zeolite imidazolate framework two-layered membranes. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Urban, J.J. Hydrogen-Bonded Polyimide/Metal-Organic Framework Hybrid Membranes for Ultrafast Separations of Multiple Gas Pairs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, D.; Kong, C.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, T.; Chen, L. Design of thin and tubular MOFs-polymer mixed matrix membranes for highly selective separation of H2 and CO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 220, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, E.V.; Kalaw, G.J.D.; Ferraris, J.P.; Balkus, K.J.; Musselman, I.H. Amine-functionalized (Al) MIL-53/VTECTM mixed-matrix membranes for H2/CO2 mixture separations at high pressure and high temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 530, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, B.R.; Gonzalez, M.I.; Long, J.R. Recent Progress Towards Light Hydrocarbon Separations Using Metal–Organic Frameworks. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, D. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes for Light Olefin/Paraffin Separation. Crystals 2018, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, T.; Lestari, G.; Lai, Z. Effective separation of propylene/propane binary mixtures by ZIF-8 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 390–391, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K. Defect-dependent stability of highly propylene-selective zeolitic-imidazolate framework ZIF-8 membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.T.; Jeong, H.K.; Lee, A.S.; An, H.S.; Lee, J.S. Heteroepitaxially Grown Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Membranes with Unprecedented Propylene/Propane Separation Performances. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 12304–12311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Kim, J.; Othman, M.R. Microporous ZIF-8 membrane prepared from secondary growth for improved propylene permeance and selectivity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 285, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Shin, H.; Yoo, S.J.; Kwon, H.T.; Kim, J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8 films by ZnO to ZIF-8 conversion and their usage as seed layers for propylene-selective ZIF-8 membranes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Duan, Y.; Caro, J.; Wang, H.; Hou, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wei, Y.; Ding, L.-X.; Xue, J. Paralyzed membrane: Current-driven synthesis of a metal-organic framework with sharpened propene/propane separation. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Ge, L.; Diao, H.; Rudolph, V.; Zhu, Z. Propylene/propane selective mixed matrix membranes with grape-branched MOF/CNT filler. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 6084–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, F.; Leisen, J.; Kim, S.J.; Rownaghi, A.A.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. All-Nanoporous Hybrid Membranes: Redefining Upper Limits on Molecular Separation Properties. Angew. Chemie - Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, J.E.; Smith, Z.P.; Li, T.; Xu, T.; Long, J.R. Enhanced ethylene separation and plasticization resistance in polymer membranes incorporating metal-organic framework nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswal, B.P.; Kunjattu, S.H.; Kaur, T.; Banerjee, R.; Kharul, U.K. Transforming covalent organic framework into thin-film composite membranes for hydrocarbon recovery. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Demir, N.K.; Chen, J.P.; Li, K. Applications of Water Stable Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5107–5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.L.; Nunes, S.P. Materials and membrane technologies for water and energy sustainability. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2016, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, A.; Colombi Ciacchi, L.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in Nanoporous Membranes for Water Purification. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Huo, F. Fabrication of porous matrix membrane (PMM) using metal-organic framework as green template for water treatment. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paseta, L.; Antorán, D.; Coronas, J.; Téllez, C. 110th Anniversary: Polyamide/Metal-Organic Framework Bilayered Thin Film Composite Membranes for the Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 4222–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. In-situ grown covalent organic framework nanosheets on graphene for membrane-based dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xiao, A.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Growing covalent organic frameworks on porous substrates for molecule-sieving membranes with pores tunable from ultra- to nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Shan, B.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. TpPa-2-incorporated mixed matrix membranes for efficient water purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 526, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandezande, P.; Gevers, L.E.M.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Solvent resistant nanofiltration: Separating on a molecular level. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 365–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.K.; Goh, K.; Bae, T.H.; Wang, R. Polymer-based membranes for solvent-resistant nanofiltration: A review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1653–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorribas, S.; Gorgojo, P.; Téllez, C.; Coronas, J.; Livingston, A.G. High flux thin film nanocomposite membranes based on metal-organic frameworks for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15201–15208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarango, L.; Paseta, L.; Navarro, M.; Zornoza, B.; Coronas, J. Controlled deposition of MOFs by dip-coating in thin film nanocomposite membranes for organic solvent nanofiltration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 59, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, S.; Tian, L.; Zhang, J.; Su, B.; Hu, M.Z. Covalent organic frameworks (COFs)-incorporated thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membranes for high-flux organic solvent nanofiltration (OSN). J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Manchanda, P.; Peinemann, K.V. Solvent-resistant triazine-piperazine linked porous covalent organic polymer thin-film nanofiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Lu, X.; Jia, Z. Adjustable pervaporation performance of Zr-MOF/poly(vinyl alcohol) mixed matrix membranes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diestel, L.; Bux, H.; Wachsmuth, D.; Caro, J. Pervaporation studies of n-hexane, benzene, mesitylene and their mixtures on zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2012, 164, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Lin, Y.S. Pervaporation Separation of Organic Mixtures by MOF-5 Membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8652–8658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, H.; Yao, Z.; Shi, B.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Pan, F.; Liu, G.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, X. Functionally graded membranes from nanoporous covalent organic frameworks for highly selective water permeation. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2018, 6, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Geng, Y.; Jia, Z. In situ preparation of COF-LZU1 in poly(ether-block-amide) membranes for efficient pervaporation of n-butanol/water mixture. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Wang, M.; Ding, H.; Song, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, B.; Cao, X. Embedding Ag+@COFs within Pebax membrane to confer mass transport channels and facilitated transport sites for elevated desulfurization performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 552, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7303–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, D.E.; Spry, D.B.; Fayer, M.D. Water dynamics and proton transfer in nafion fuel cell membranes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3690–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritz, K.A.; Moore, R.B. State of Understanding of Nafion. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4535–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierke, T.D.; Munn, G.E.; Wilson, F.C. The morphology in nafion perfluorinated membrane products, as determined by wide- and small-angle x-ray studies. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 2003, 19, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Wong, N.E.; Shimizu, G.K.H. MOFs as proton conductors - challenges and opportunities crossover architectures and proton conduction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5913–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppei, Y.; Kazuya, O.; Rie, M.; Hiroshi, K. Designer coordination polymers: Dimensional. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6655–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.; Suh, K.; Natarajan, S.; Kim, K. Proton Conduction in Metal–Organic Frameworks and Related Modularly Built Porous Solids. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 2688–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; Elahi, S.M.; Pal, A.; Das, M.C. Metal–Organic Frameworks and Other Crystalline Materials for Ultrahigh Superprotonic Conductivities of 10 −2 S cm −1 or Higher. Chem. A Eur. J. 2019, 6259–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Kundu, T.; Kandambeth, S.; BabaRao, R.; Marathe, Y.; Kunjir, S.M.; Banerjee, R. Phosphoric Acid Loaded Azo (−N═N−) Based Covalent Organic Framework for Proton Conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6570–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, B.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.G.; Tan, H.Q.; Zang, H.Y.; Zhu, G. Cationic Covalent Organic Frameworks: A Simple Platform of Anionic Exchange for Porosity Tuning and Proton Conduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5897–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Tao, S.; Jiang, D. Proton conduction in crystalline and porous covalent organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakangura, E.; Wu, L.; Ge, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T. Mixed matrix proton exchange membranes for fuel cells: State of the art and perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 57, 103–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Ying, W.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.J.; Chen, B.; Peng, X. A DNA-Threaded ZIF-8 Membrane with High Proton Conductivity and Low Methanol Permeability. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Metal-organic framework-graphene oxide composites: A facile method to highly improve the proton conductivity of PEMs operated under low humidity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15838–15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Narducci, R.; Compañ, V.; Costantino, F. Proton Conductivity of Composite Polyelectrolyte Membranes with Metal-Organic Frameworks for Fuel Cell Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 6, 1801146–1801176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Zhang, B.; Cao, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Tiantian, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of nafion hybrid membrane under different humidities by incorporating metal-organic frameworks with high phytic acid loading. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9799–9807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; He, X.; Jiang, Z. Proton exchange nanohybrid membranes with high phosphotungstic acid loading within metal-organic frameworks for PEMFC applications. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 240, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced proton conductivity of proton exchange membranes by incorporating sulfonated metal-organic frameworks. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, J.; Sahuquillo, Ó.; García-Bernabé, A.; Giménez, E.; Compañ, V. Phosphoric Acid Doped Polybenzimidazole (PBI)/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Composite Membranes with Significantly Enhanced Proton Conductivity under Low Humidity Conditions. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Y.; Li, J.J.; Han, Z.; Duan, P.G.; Li, L.K.; Zang, S.Q. Tuning the functional substituent group and guest of metal-organic frameworks in hybrid membranes for improved interface compatibility and proton conduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3464–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Rational Design of S-UiO-66@GO Hybrid Nanosheets for Proton Exchange Membranes with Significantly Enhanced Transport Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26077–26087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Proton Conductivity of Proton Exchange Membrane Synergistically Promoted by Different Functionalized Metal-Organic Frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22597–22603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnadio, A.; Narducci, R.; Casciola, M.; Marmottini, F.; D’Amato, R.; Jazestani, M.; Chiniforoshan, H.; Costantino, F. Mixed Membrane Matrices Based on Nafion/UiO-66/SO3H-UiO-66 Nano-MOFs: Revealing the Effect of Crystal Size, Sulfonation, and Filler Loading on the Mechanical and Conductivity Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42239–42246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, H.J.; Ren, Q.; Luo, H.B.; Ren, X.M.; Tian, Z.F.; Lu, S. Extra Water- and Acid-Stable MOF-801 with High Proton Conductivity and Its Composite Membrane for Proton-Exchange Membrane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28656–28663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, P. Two-Dimensional Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Networks Modified Proton Exchange Membranes for Improving Transport Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35075–35085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, U.; Erkartal, M.; Kung, C.W.; Ramani, V.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Proton conducting self-assembled metal-organic framework/polyelectrolyte hollow hybrid nanostructures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 23015–23021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Chen-Yang, Y.W. Enhancing performance of Nafion ® -based PEMFC by 1-D channel metal-organic frameworks as PEM filler. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 15696–15705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian-Alam, L.; Mahdavi, H. A novel polysulfone-based ternary nanocomposite membrane consisting of metal-organic framework and silica nanoparticles: As proton exchange membrane for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
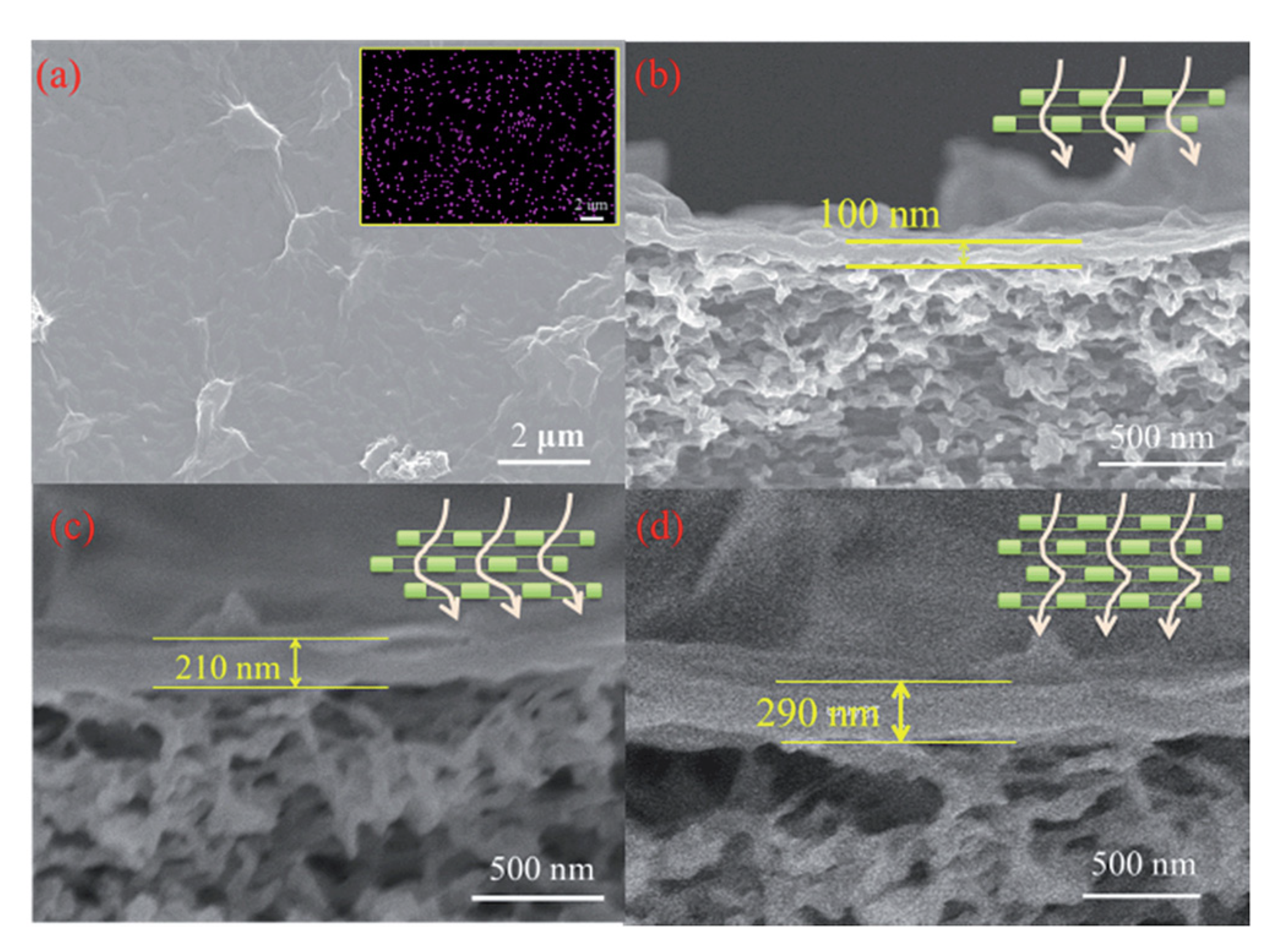
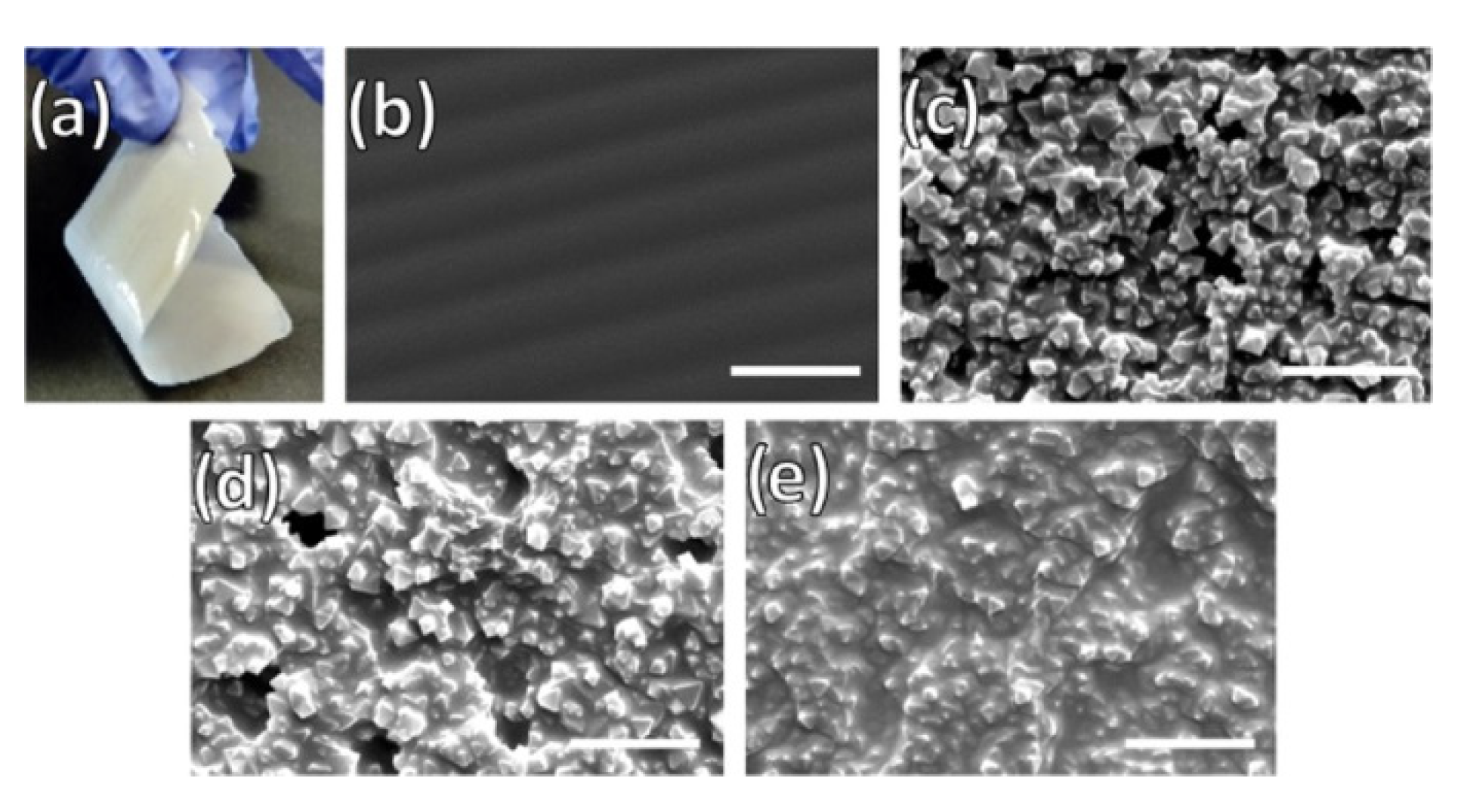
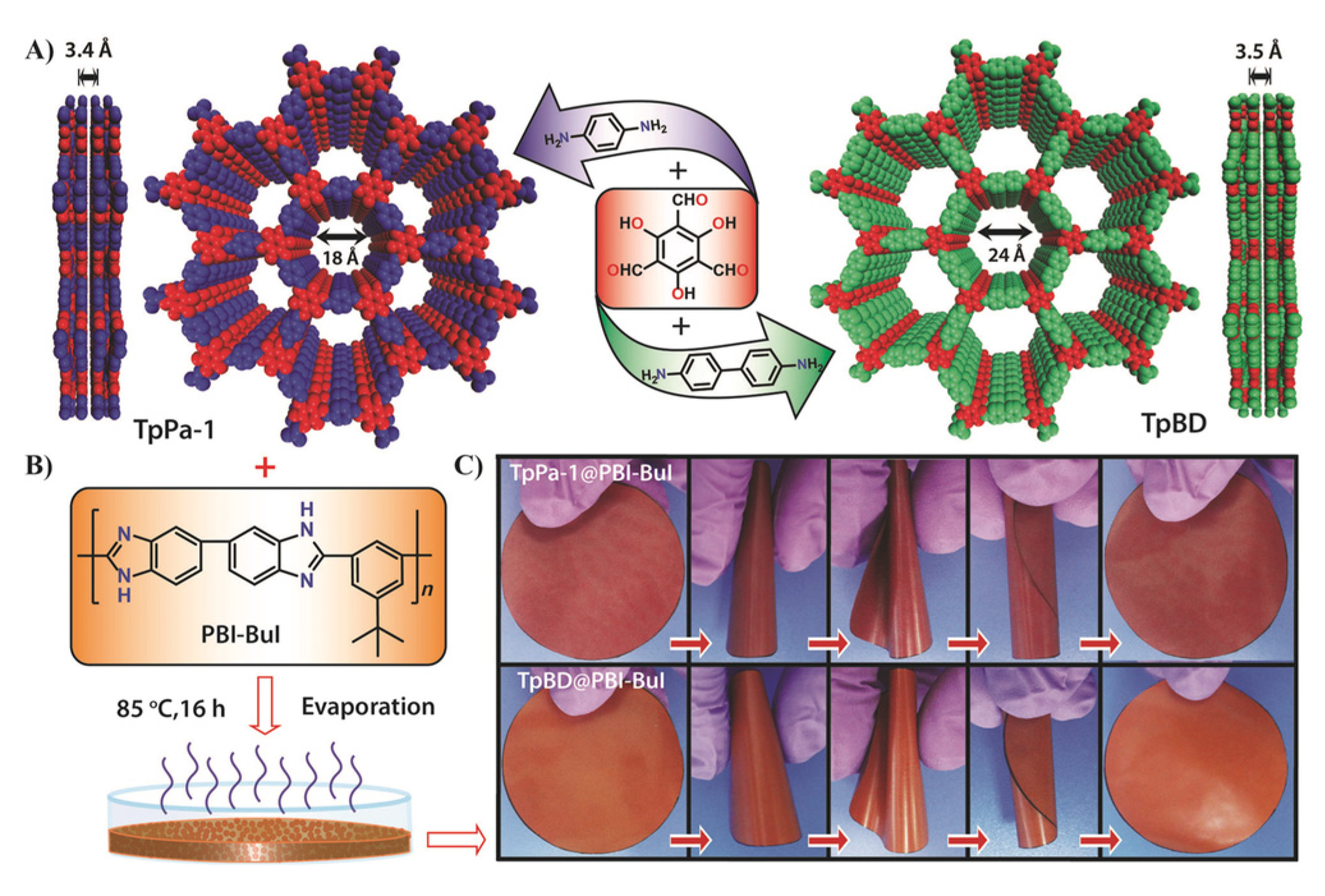
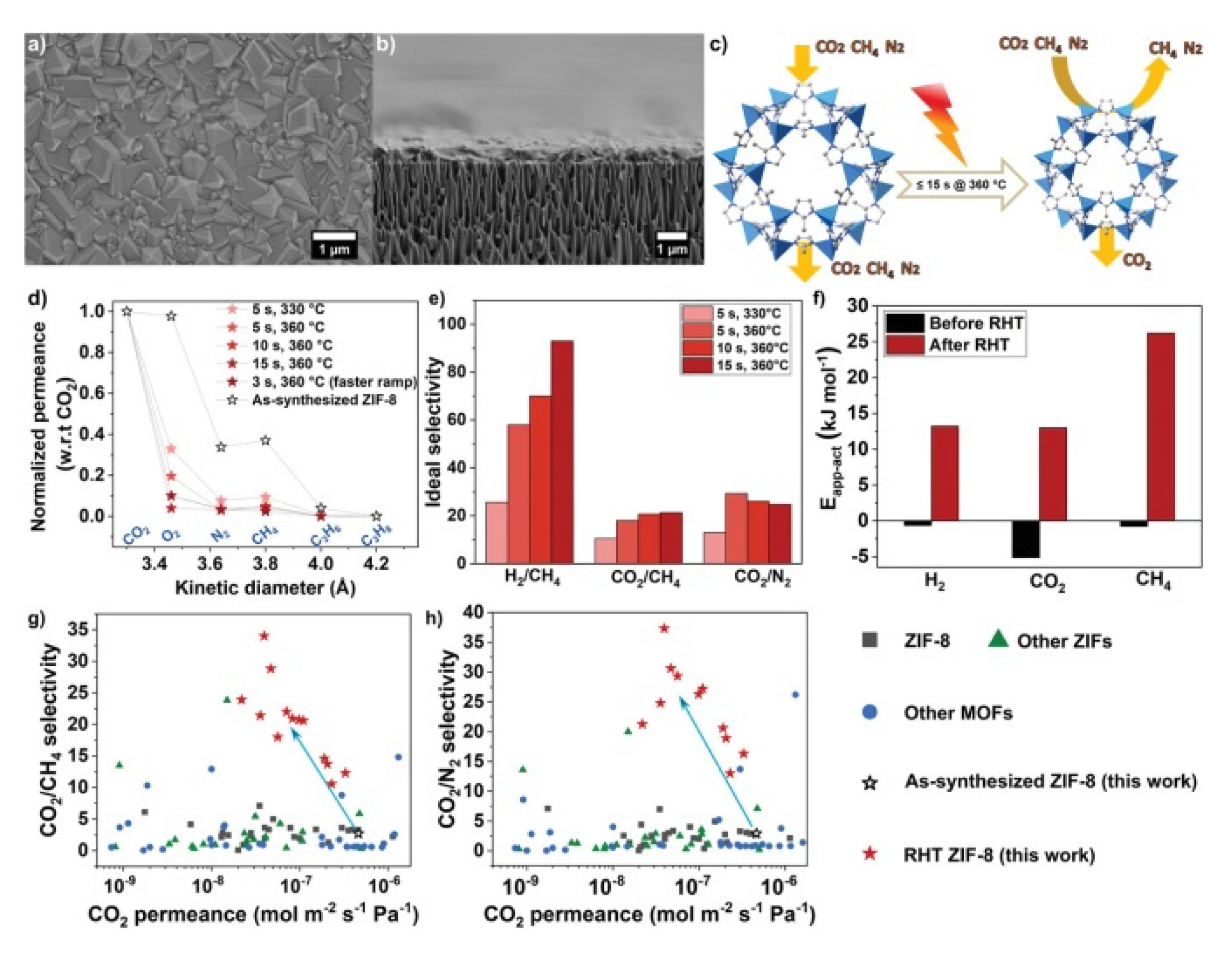

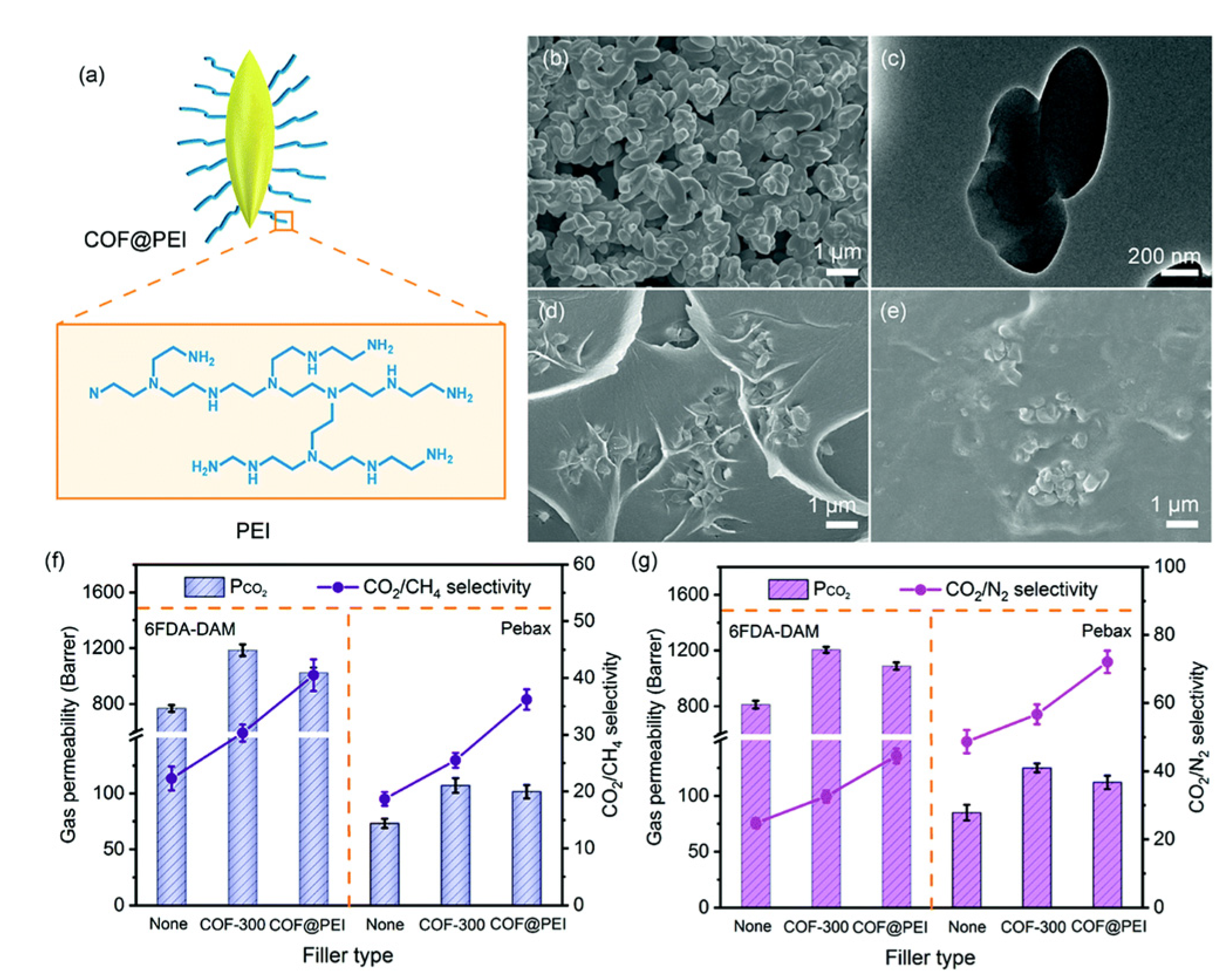
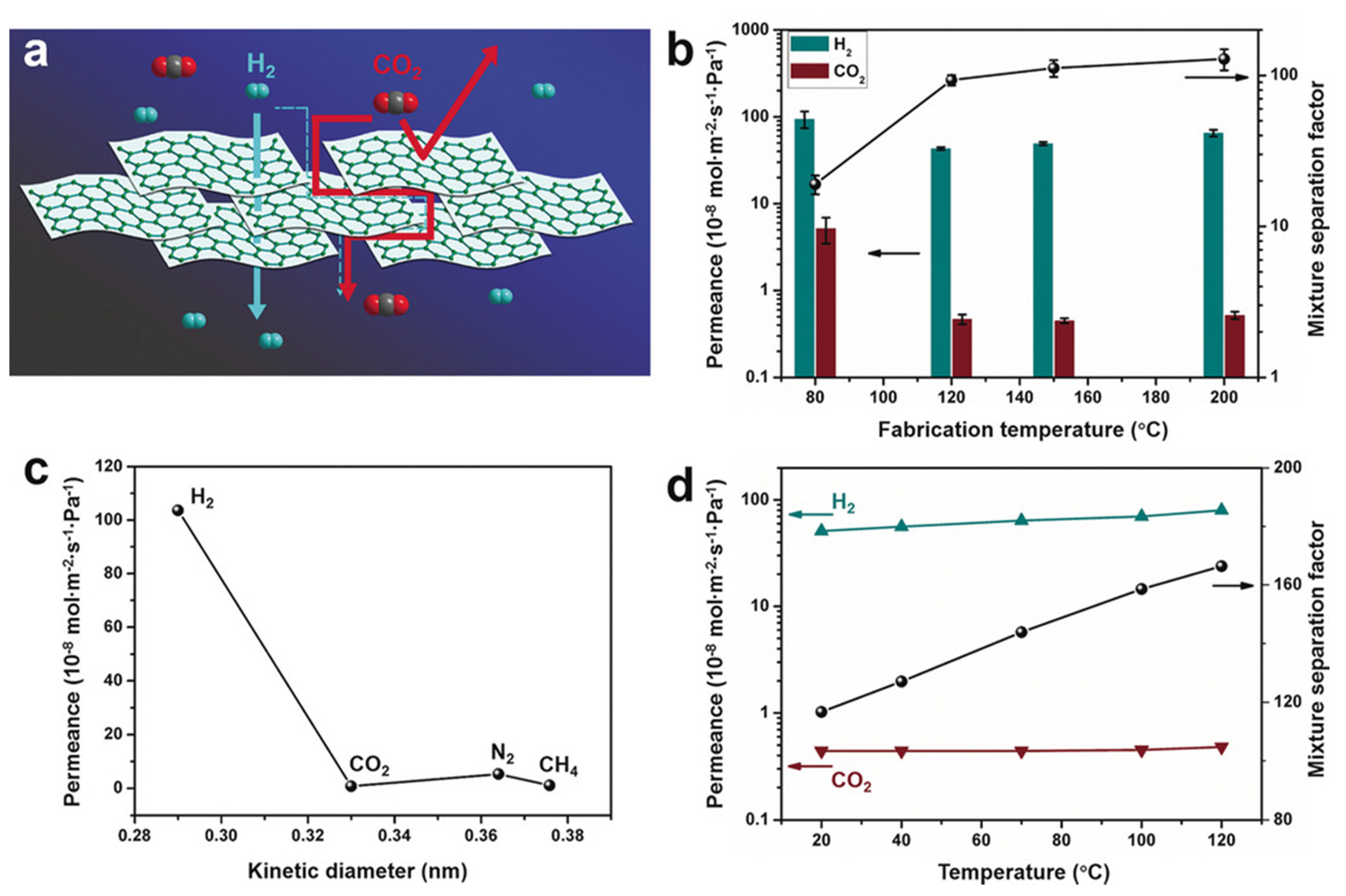
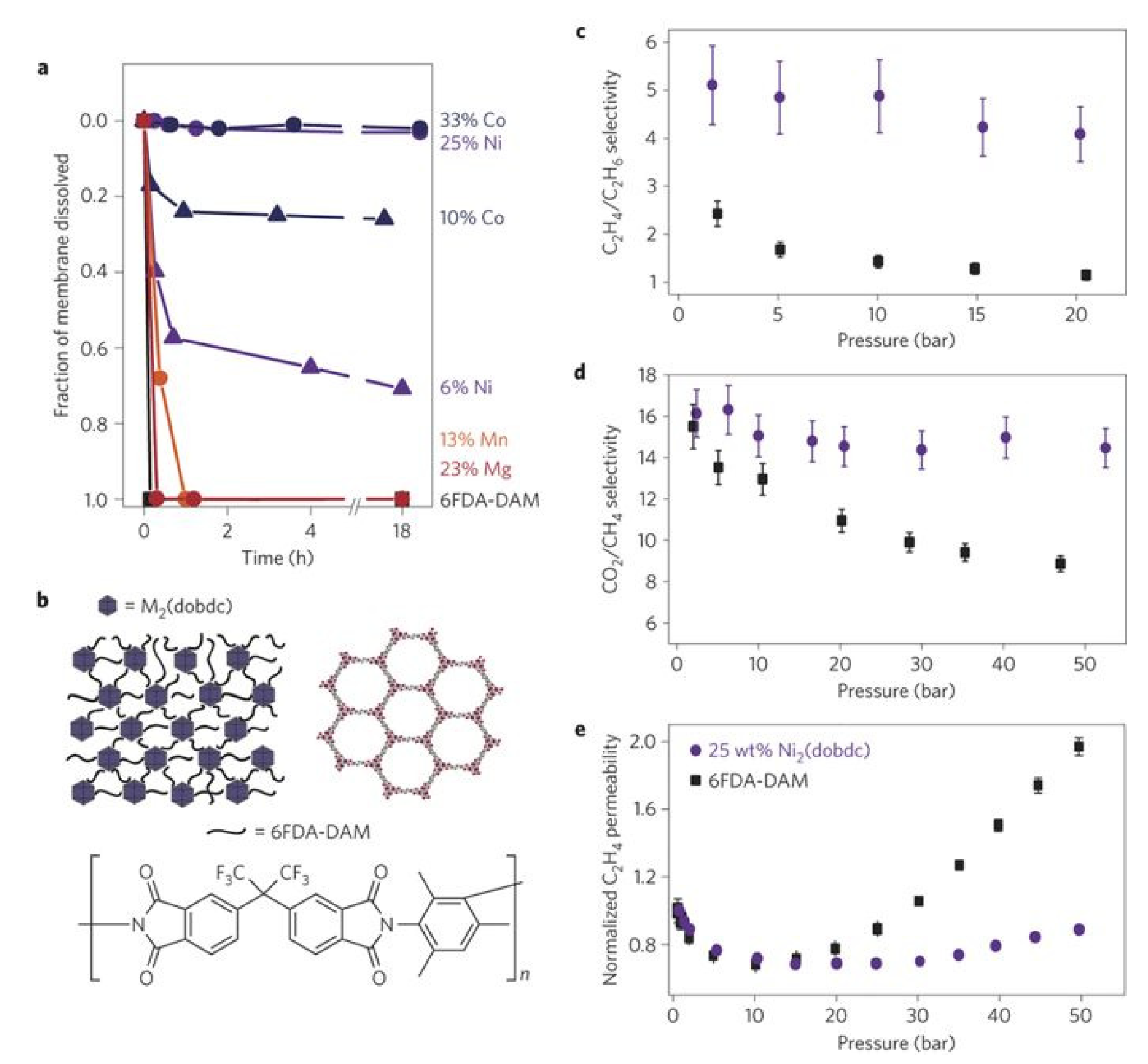
| Preparation Method | Thickness | Advantages | Limitations | Applications | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOF | In situ or direct growth | 300 nm–100 µm | Simple and universal Tunable thickness | Functional substrate surface required Poor heterogeneous nucleation site on the support | Gas separation | [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53] |
| Pervaporation | ||||||
| OSN | ||||||
| Seeded assisted or secondary growth | 1–25 µm | Better control of nucleation and crystallinity Various types of supports | Complex procedure Fix small nanosize MOF seeds to the support surface Thicker thickness | Gas separation Water treatment Pervaporation | [54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] | |
| Layer-by-layer assembly | 500 nm–2 µm/up to 10 µm | Controllable thickness | Rough surface | Gas separation | [64,65,66,67,68] | |
| Ultra-thin layer | Small-scale | |||||
| Contra-diffusion or interfacial method | 2–25 µm | Various types of supports | Gas separation | [69,70,71] | ||
| Fit for fast reaction | Pervaporation | |||||
| Controllable thickness | OSN | |||||
| Vapour deposition | 10–150 nm | Environmentally friendly Time-saving Controllable thickness/Ultra-thin layer | Small-scale | Gas separation | [72,73,74,75] | |
| COF | In situ growth | 400 nm–4 µm | Simple Tunable thickness | Functional substrate surface required | Gas storage and separation | [76,77,78] |
| (support the initial growth of COFs on the surface) | Water treatment | |||||
| Solution casting | 100–700 nm | Simple and scalable | Thicker thickness Less controllable | Water treatment | [79,80] | |
| OSN | ||||||
| Fuel cell (PEM) | ||||||
| Layer-by-layer assembly | 100–500 nm | Controllable thickness | Extra steps (exfoliation) | Gas separation | [81,82,83] | |
| Ultra-thin layer | ||||||
| Interfacial polymerisation (IP) | 2–300 nm / up to 100 µm | Directly forming and scalable Tunable thinkness | Water treatment | [87,88,89,90,91] | ||
| OSN | ||||||
| Langmuir−Blodgett (LB) method | 3–100 nm | Few COF layers of depostion feasible | Small-scale | Water treatment | [92] | |
| Can be tranformed to different substrats | ||||||
| Turnable thinkness |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, M.; Montoro, C.; Semsarilar, M. Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications. Membranes 2020, 10, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050107
Fang M, Montoro C, Semsarilar M. Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications. Membranes. 2020; 10(5):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050107
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Mingyuan, Carmen Montoro, and Mona Semsarilar. 2020. "Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications" Membranes 10, no. 5: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050107
APA StyleFang, M., Montoro, C., & Semsarilar, M. (2020). Metal and Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Applications. Membranes, 10(5), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10050107







