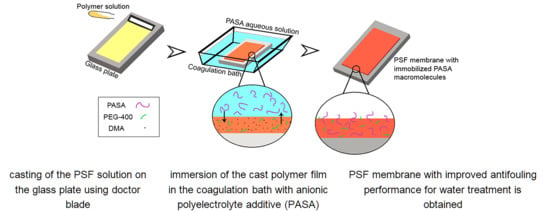
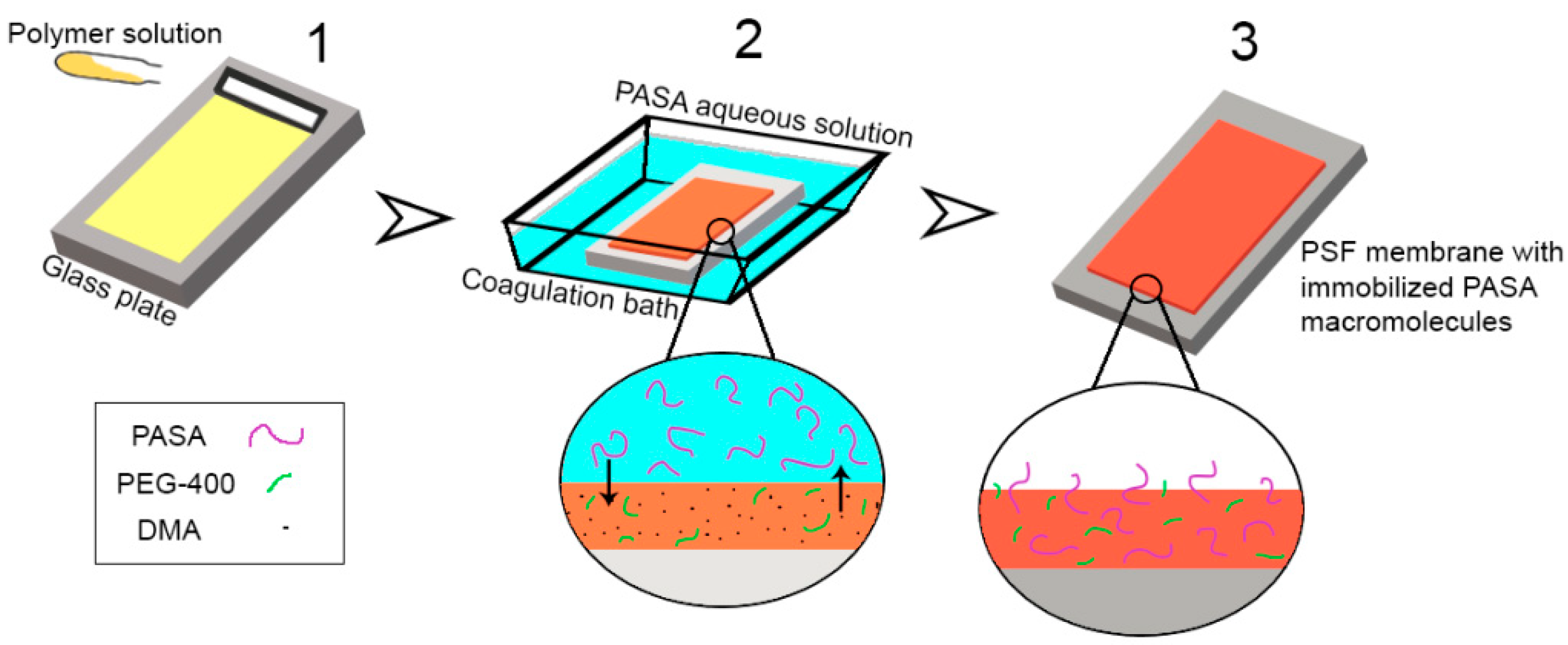
Modification of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Addition of Anionic Polyelectrolyte Based on Acrylamide and Sodium Acrylate to the Coagulation Bath to Improve Antifouling Performance in Water Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Casting Solution Preparation
2.3. Preparation of PASA Solutions for Coagulation Bath
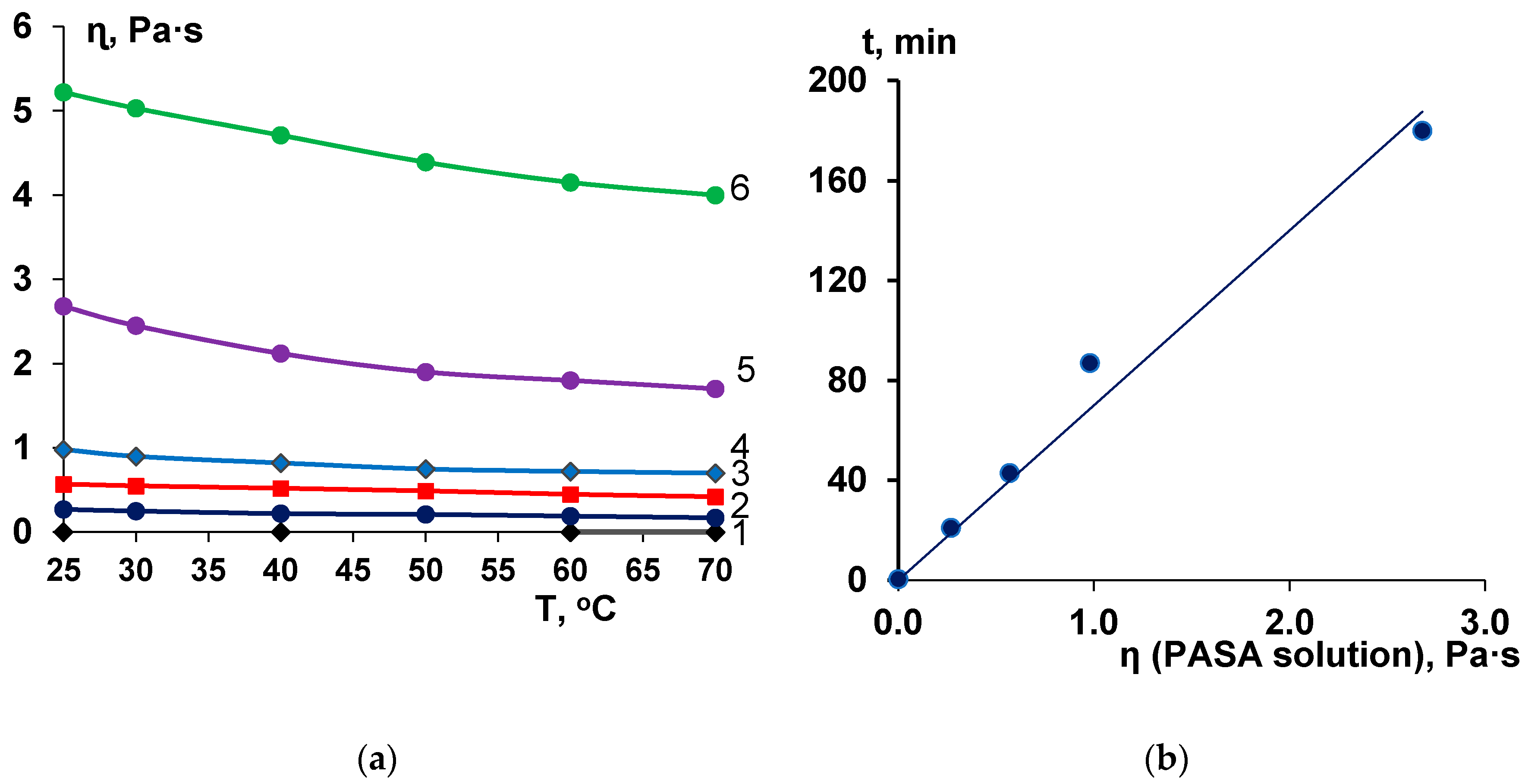
2.4. Measurements of the Viscosity
2.5. Precipitation Value of PASA Solutions
2.6. Preparation of Membranes
2.7. Membrane Formation Time
2.8. Determination of Flux and Separation in Ultrafiltration
2.9. Study of Membrane Resistance to Fouling
- (1)
- HA solution ultrafiltration for 60 min with flux measurements every 15 min;
- (2)
- distilled water ultrafiltration for 15 min (cleaning);
- (3)
- determination of PWF of the washed membranes (JWF).
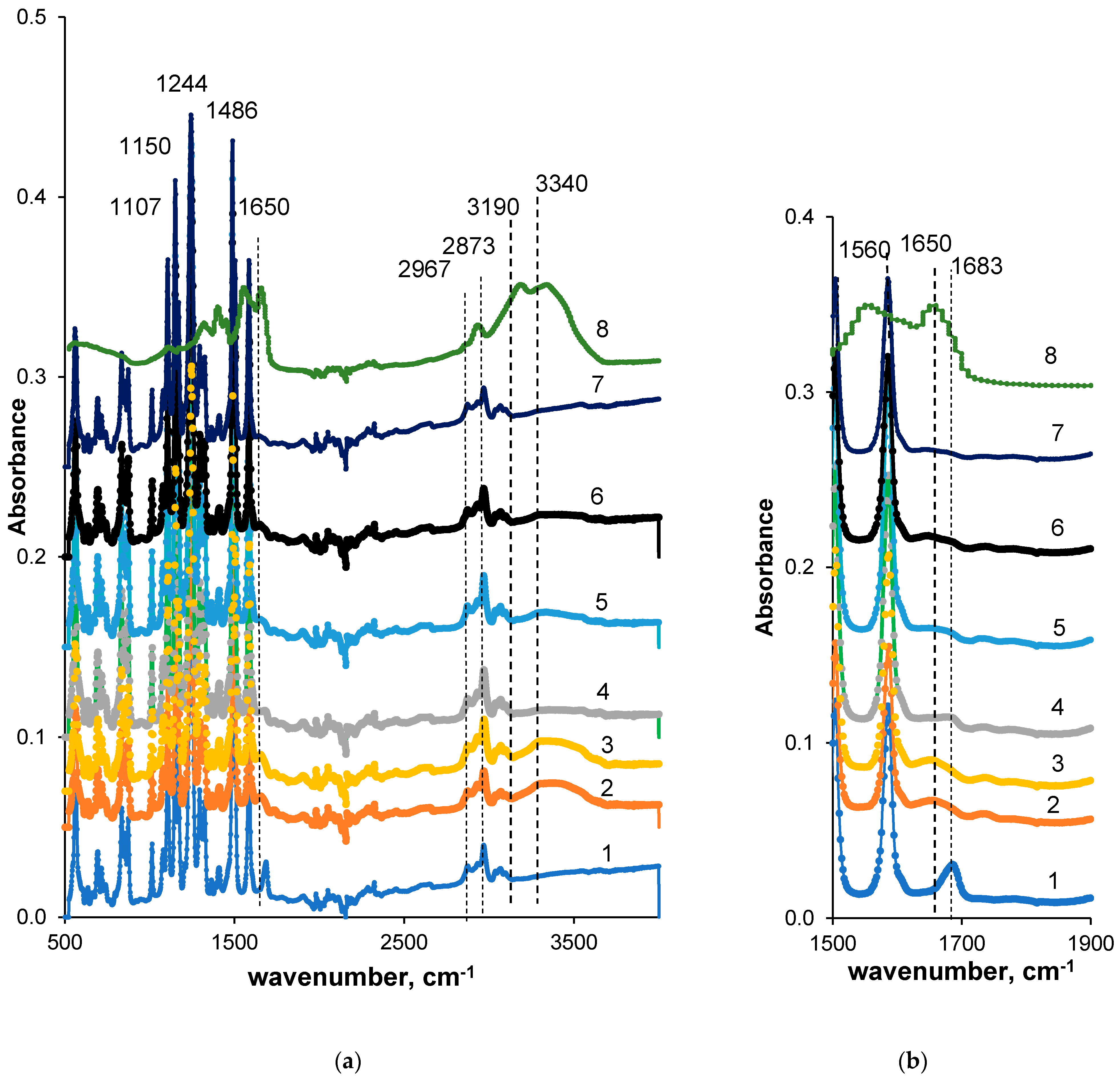
2.10. FTIR Studies
2.11. Investigation of the Morphology
2.12. Determination of Water Contact Angle
2.13. Zeta potential of the Skin Layer
2.14. Analysis of Surface Water and Humic Acid Solutions
2.15. Surface Water Ultrafiltration
3. Results
3.1. Effect of PASA Additive on Precipitation Value of PSF Solution in DMA
3.2. Effect of PASA Concentration and Temperature on Coagulation Bath Viscosity
3.3. Effect of PASA Concentration on Membrane Formation Time in NIPS
3.4. Effect of PASA Addition to the Coagulation Bath on Membrane Composition
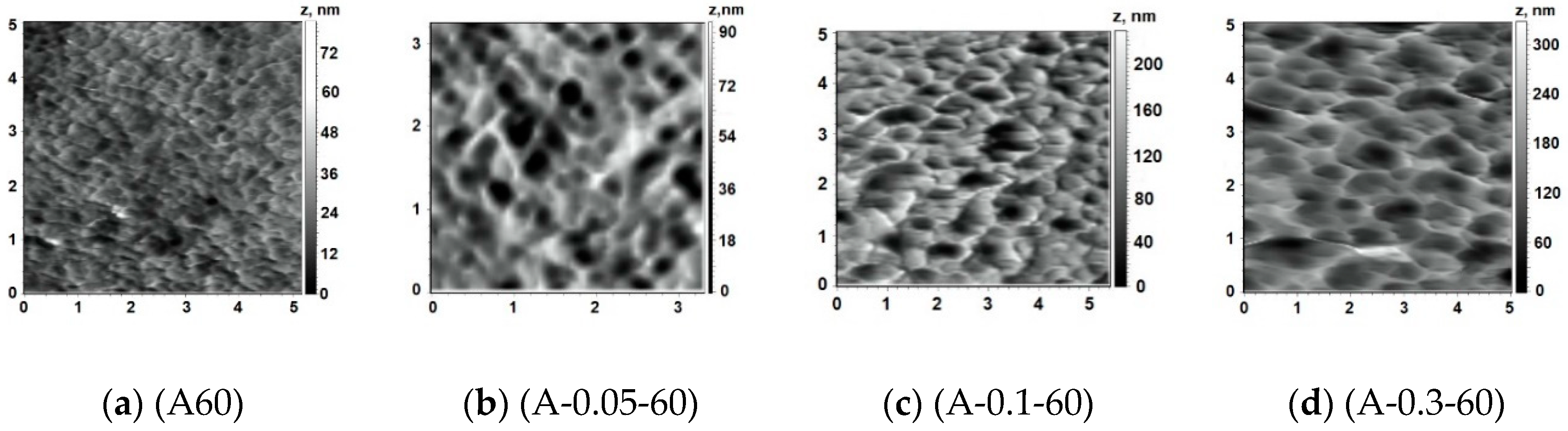
3.5. Effect of PASA Addition to the Coagulant on Membrane Morphology
3.5.1. SEM Investigations
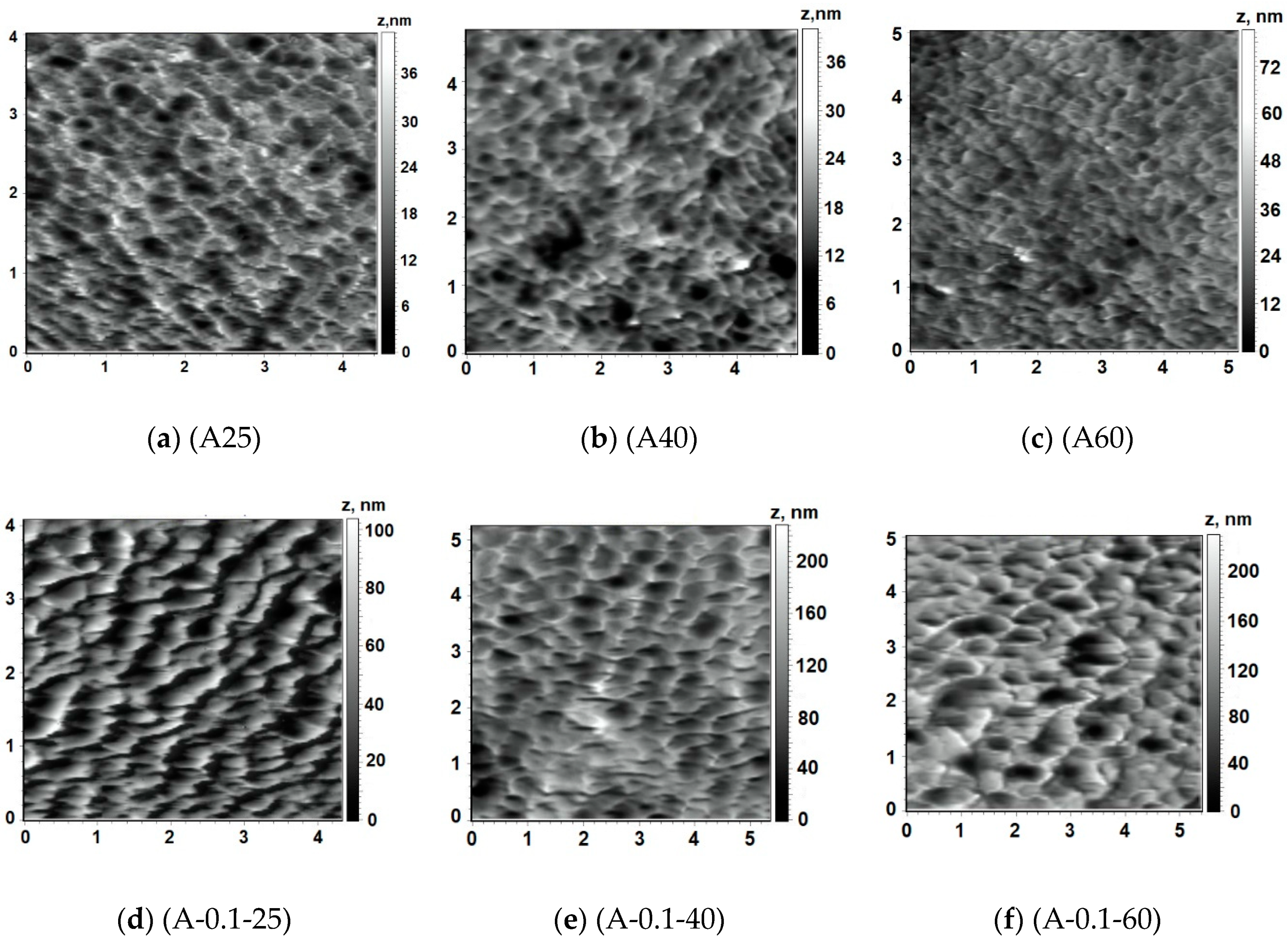
3.5.2. AFM Investigations
Influence of Coagulation Bath Temperature
3.6. Effect of PASA Addition to the Coagulant on Water Contact Angle of Membrane Skin Layer
3.7. Effect of PASA Addition to the Coagulant on Zeta Potential of Membrane Skin Layer
3.8. Membrane Barrier Properties
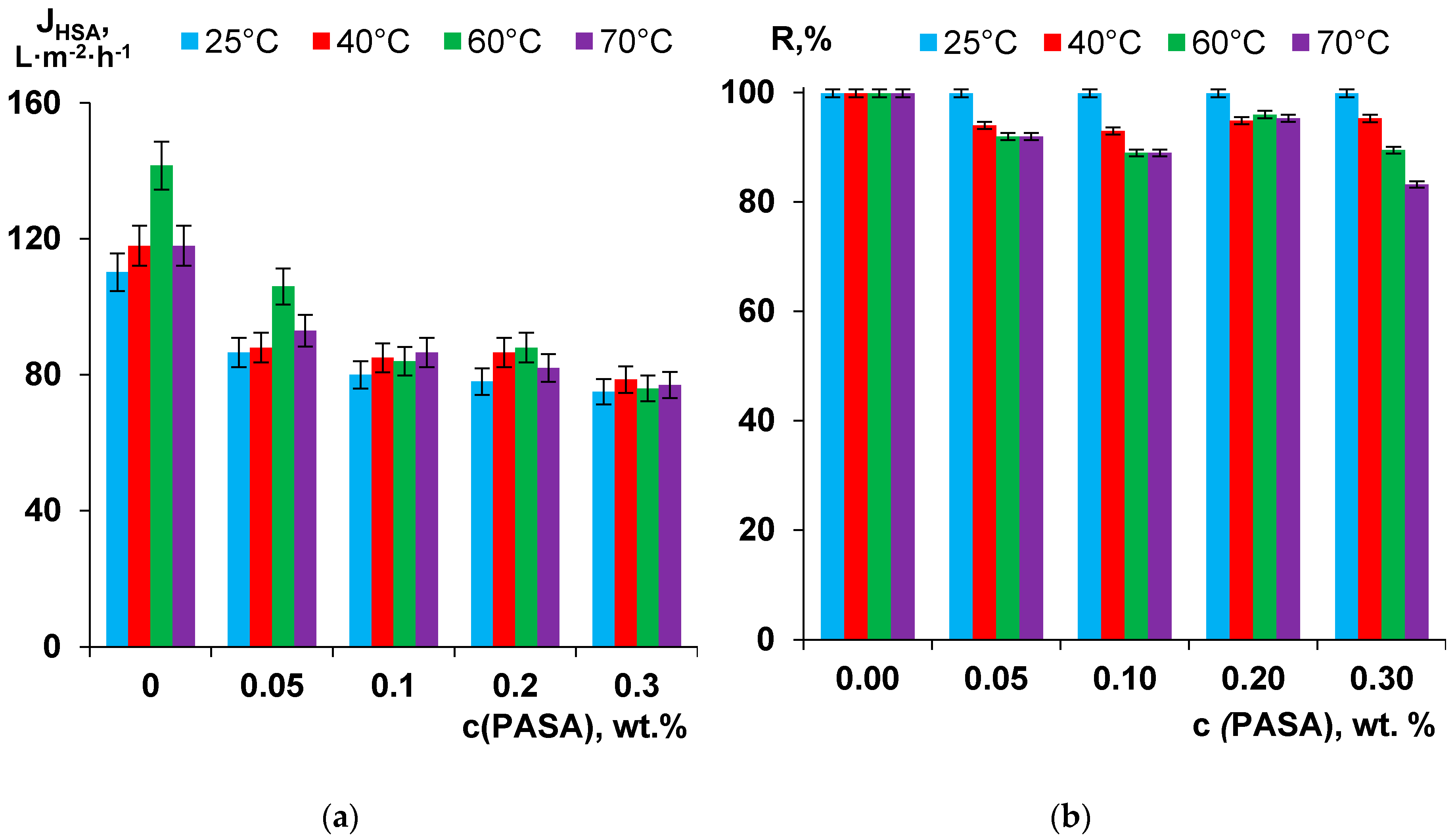
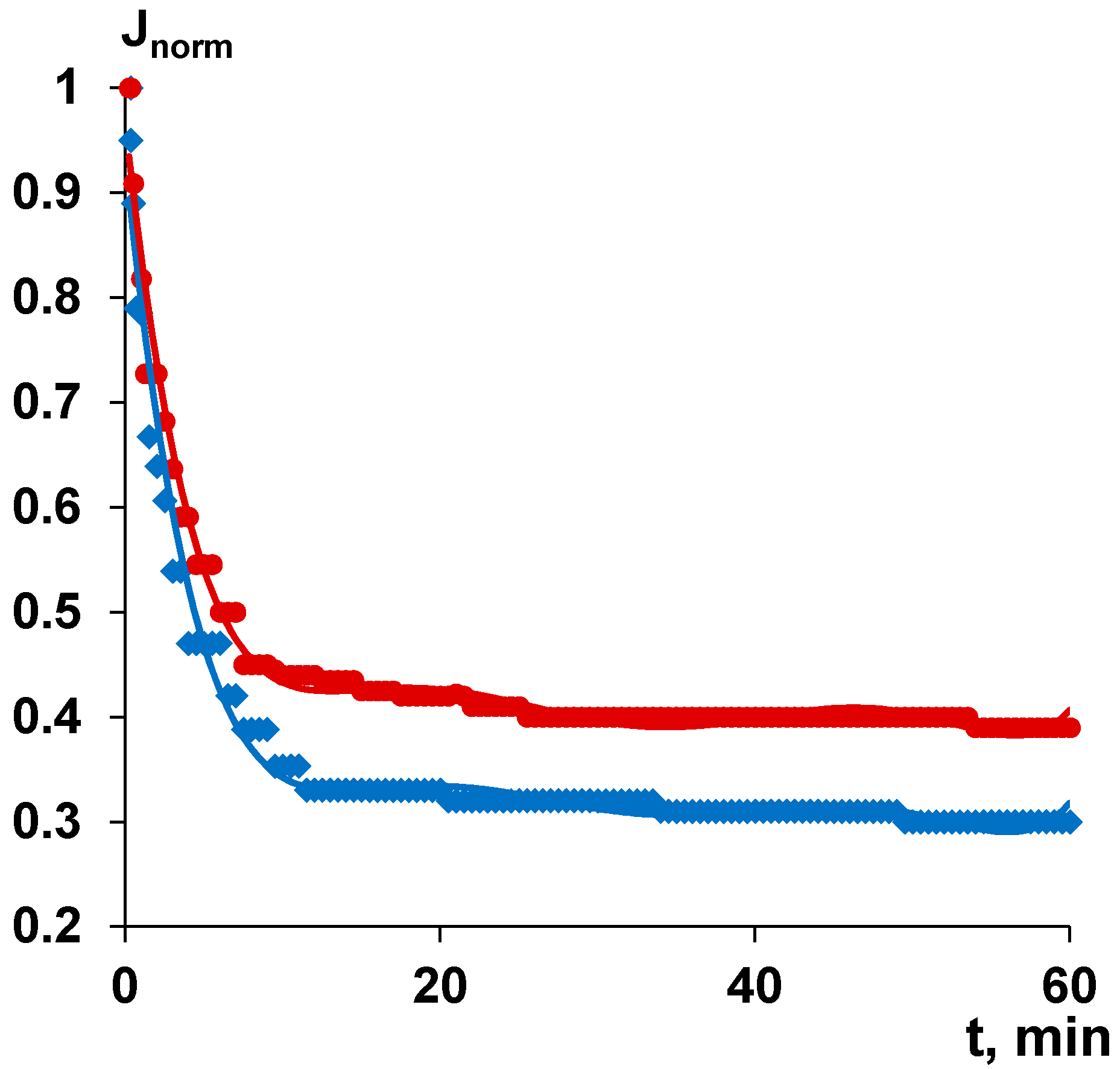
3.9. Separation and Antifouling Performance in Ultrafiltration of Humic Acids Model Solution and Surface Water
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Werber, J.R.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Materials for next-generation desalination and water purification membranes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Dreyer, D.R.; Bielawski, C.W.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Surface modification of water purification membranes. Angew. Chem Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4662–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bildyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Lipnizki, F.; Pratsenko, S.A. Correlation between membrane surface properties, polymer nature and fouling in skim milk ultrafiltration. Colloids Surf. A 2020, 605, 125387–125399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Schagerlöf, H.; Morkeberg Krogh, K.B.; Jönsson, A.S.; Lipnizki, F. Investigations of alkaline and enzymatic membrane cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes fouled by thermomechanical pulping process water. Membranes 2018, 8, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amy, G. Fundamental understanding of organic matter fouling of membranes. Desalination 2008, 231, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liang, H.; Bai, L.; Huang, K.; Xie, B.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Tang, X. Application of heat-activated peroxydisulfate pre-oxidation for degrading contaminants and mitigating ultrafiltration membrane fouling in the natural surface water treatment. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115905–115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Ncibi, M.; Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M. Removal of natural organic matter in drinking water treatment by coagulation: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 190, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Vepsäläinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Natural organic matter removal by coagulation during drinking water treatment: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 159, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shang, Y.; Zhuang, X. Photocatalysis-coagulation to control ultrafiltration membrane fouling caused by natural organic matter. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121790–121800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Shinde, D.B.; Sheng, G.; Lu, D.; Li, P.; Lai, Z. Tuning the Surface Structure of Polyamide Membranes Using Porous Carbon Nitride Nanoparticles for High-Performance Seawater Desalination. Membranes 2020, 10, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xiao, K.; Yu, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Wei, S.; Wen, X.; Huang, X. A Simple Method to Identify the Dominant Fouling Mechanisms during Membrane Filtration Based on Piecewise Multiple Linear Regression. Membranes 2020, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Gu, H.; Xiao, K.; Qu, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, C. Fouling mechanisms analysis via combined fouling models for surface water ultrafiltration process. Membranes 2020, 10, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Sun, X.; Gao, C.; Dong, M. Improved water flux and antifouling properties of cardo poly (aryl ether ketone) ultrafiltration membrane by novel sulfobetaine polyimides additive. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y. Upgrading polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by blending with amphiphilic block copolymers: Beyond surface segregation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, O.; Frost, I.; Ulbricht, M.; Shalmani, A.K.; Panglisch, S.; Grünig, L.; Handge, U.; Abetz, V.; Heijnen, M.; Weber, M. Hydrophilic poly (phenylene sulfone) membranes for ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117107–117117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Isaichykova, Y.A.; Ovcharova, A.A. Preparation of high-flux ultrafiltration polyphenylsulfone membranes. Pet. Chem. 2018, 58, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Usosky, V.V.; Volkov, V.V. Influence of the concentration and molecular weight of polyethylene glycol on the structure and permeability of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes. Pet. Chem. 2016, 56, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basri, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Aziz, M. Polyethersulfone (PES)–silver composite UF membrane: Effect of silver loading and PVP molecular weight on membrane morphology and antibacterial activity. Desalination 2011, 273, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Karslyan, Y.A.; Ovcharova, A.A.; Volkov, V.V. Development of high flux ultrafiltration polyphenylsulfone membranes applying the systems with upper and lower critical solution temperatures: Effect of polyethylene glycol molecular weight and coagulation bath temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.K. Characteristics of ultrafiltration membranes fabricated from polysulfone and polymer-grafted silica nanoparticles: Effects of the particle size and grafted polymer on the membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y. Improving the perm-selectivity and anti-fouling property of UF membrane through the micro-phase separation of PSf-b-PEG block copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117851–117859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, J.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Cui, F. Dopamine triggered one step polymerization and codeposition of reactive surfactant on PES membrane surface for antifouling modification. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 117148–117154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalani, D.V.; Bera, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Kumar, S.B.; Jewrajka, S.K. Multifunctionalization of Poly (vinylidene fluoride)/reactive copolymer blend membranes for broad spectrum applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3102–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahkaramipour, N.; Ramanan, S.N.; Fister, D.; Park, E.; Venna, S.R.; Sun, H.; Cheng, C.; Lin, H. Facile grafting of zwitterions onto the membrane surface to enhance antifouling properties for wastewater reuse. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9202–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, Y.; Feng, X.; Dai, F.; Yang, N.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L. A comprehensive description of the threshold flux during oil/water emulsion filtration to identify sustainable flux regimes for tannic acid (TA) dip-coated poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 563, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, F. Surface modification of polyacrylonitrile membrane by chemical reaction and physical coating: Comparison between static and pore-flowing procedures. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 4231–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Li, P.; Sun, H.; Niu, Q.J. Photo-Fenton assisted self-cleaning hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with high-efficient flux recovery for wastewater remediation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 249, 117159–117167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, W.; Jia, B.; Wang, P.; Sun, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhai, X.; Qi, J.; Liu, C. Micro fine particles deposition on gravity-driven ultrafiltration membrane to modify the surface properties and biofilm compositions: Water quality improvement and biofouling mitigation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 123270–123279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, T.R.; Patil, A.; Raza, B.G.; Reurink, D.; Van den Hengel, S.K.; Rutjes, S.A.; De Roda Husman, A.M.; Roesink, H.D.W.; De Vos, W.M. Cationically modified membranes using covalent layer-by-layer assembly for antiviral applications in drinking water. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzęcka, N.H.; Kozłowska, I.; Gac, J.M.; Bojarska, M. (Anti-fouling properties of poly (acrylic acid) grafted ultrafiltration membranes–experimental and theoretical study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144658–144665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Z.; Matsuyama, H. A comprehensively fouling-and solvent-resistant aliphatic polyketone membrane for high-flux filtration of difficult oil-in-water micro-and nanoemulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Single-step coating of polyethylenimine on gradient nanoporous phenolics for tight membranes with ultrahigh permeance. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 587, 117172–117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Van Loosdrecht, M. Hygienic water production in an innovative air lift bioreactor followed by high antifouling ultrafiltration membranes modified by layer-by-layer assembly. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 182, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaei, L.; Khorshidi, B.; Islam, M.A.; Sadrzadeh, M. Industrial waste lignin as an antifouling coating for the treatment of oily wastewater: Creating wealth from waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120304–120313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Li, X.; Omidvarkordshouli, M.; Sigurdardóttir, S.B.; Woodley, J.M.; Daugaard, A.E.; Luo, J.; Pinelo, M. Charge exclusion as a strategy to control retention of small proteins in polyelectrolyte-modified ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116936–116944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Miao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Fabricating a pH-responsive membrane through interfacial in-situ assembly of microgels for water gating and self-cleaning. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadifakhr, M.; Trzaskus, K.; Kemperman, A.J.B.; Roesink, H.D.W.; De Grooth, J. Increasing the success rate of interfacial polymerization on hollow fibers by the single-step addition of an intermediate layer. Desalination 2020, 491, 114581–114589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shen, X.; Sotto, A.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Polythyleneimine-modified original positive charged nanofiltration membrane: Removal of heavy metal ions and dyes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 222, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuChanois, R.M.; Epsztein, R.; Trivedi, J.A.; Elimelech, M. Controlling pore structure of polyelectrolyte multilayer nanofiltration membranes by tuning polyelectrolyte-salt interactions. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yin, W.; Chong, T.H.; Wang, R. Design and development of layer-by-layer based low-pressure antifouling nanofiltration membrane used for water reclamation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 584, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Fang, L.F.; Cheng, L.; Jeon, S.; Kato, N.; Matsuyama, H. Improved antifouling properties of membranes by simple introduction of zwitterionic copolymers via electrostatic adsorption. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Köser, J.; Wessling, M.; Wintgens, T. Phosphorus recovery in an acidic environment using layer-by-layer modified membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 582, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltrinieri, L.; Remmen, K.; Müller, B.; Chu, L.; Köser, J.; Wintgens, T.; Wessling, M.; de Smet, L.C.P.M.; Sudhölter, E.J. Improved phosphoric acid recovery from sewage sludge ash using layer-by-layer modified membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 587, 117162–117170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, F.; Moattari, R.M.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Bagheri, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Mohammadi, T.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of thin film composite nano-filtration membranes for brackish water softening based on the reaction between functionalized UF membranes and polyethyleneimine. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117207–117218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Xu, S.J.; Dong, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.Z.; Xu, Z.L.; Tang, C.Y. Polyethyleneimine modified carbohydrate doped thin film composite nanofiltration membrane for purification of drinking water. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118220–118230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Tang, X.; Xiong, C.; Tang, M.; Lu, Y. A dually charged nanofiltration membrane by pH-responsive polydopamine for pharmaceuticals and personal care products removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grooth, J.; Dong, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Building polyzwitterion-based multilayers for responsive membranes. Langmuir 2014, 30, 5152–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grooth, J.; Oborný, R.; Potreck, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; De Vos, W.M. The role of ionic strength and odd–even effects on the properties of polyelectrolyte multilayer nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, S.; De Grooth, J.; Nijmeijer, K.; De Vos, W.M. Multifunctional polyelectrolyte multilayers as nanofiltration membranes and as sacrificial layers for easy membrane cleaning. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 446, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhter, M.A.; Lakard, S.; Magnenet, C.; Euvrard, M.; Lakard, B. Preparation of polyelectrolyte-modified membranes for heavy metal ions removal. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2476–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabbatovskii, K.G.; Sergeeva, I.P.; Sobolev, V.D. The Effect of a Cationic Polyelectrolyte on the Electrokinetic Properties of a Nanofiltration Membrane and Retention of Ions by It. Colloid J. 2018, 80, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, O.; Sommerfeld, A.N.; Lee, I. Design of ultrathin nanostructured polyelectrolyte-based membranes with high perchlorate rejection and high permeability. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 145, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grooth, J.; Haakmeester, B.; Wever, C.; Potreck, J.; De Vos, W.M.; Nijmeijer, K. Long term physical and chemical stability of polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, H.; Alders, M.; Luelf, T.; Emonds, S.; Mueller, S.I.; Tepper, M.; Wessling, M. Chemistry in a spinneret—Sinusoidal-shaped composite hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 585, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.Y.; Xiong, S.W.; Zhang, P.; Fu, P.G.; Gai, J.G. Nanoscale polyelectrolyte/metal ion hydrogel modified RO membrane with dual anti-fouling mechanism and superhigh transport property. Desalination 2020, 488, 114510–114521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Yang, W.; Bucs, S.S.; Nava-Ocampo, M.F.; Vrouwenvelder, J.S.; Logan, B.E. Polyelectrolyte-based sacrificial protective layer for fouling control in reverse osmosis desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaileh, W.; Johnson, D.; Khodabakhshi, S.; Hilal, N. Superior cross-linking assisted layer by layer modification of forward osmosis membranes for brackish water desalination. Desalination 2019, 463, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwaileh, W.; Johnson, D.; Khodabakhshi, S.; Hilal, N. Development of forward osmosis membranes modified by cross-linked layer by layer assembly for brackish water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 583, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Zolotarev, A.; Plisko, T.; Burts, K.; Liamin, V.; Bildyukevich, A.; Ermakov, S.; Penkova, A. Effect of the Formation of Ultrathin Selective Layers on the Structure and Performance of Thin-Film Composite Chitosan/PAN Membranes for Pervaporation Dehydration. Membranes 2020, 10, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.E.; Penkova, A.V.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Morshed, M.; Larionov, M.I.; Alem, H.; Zolotarev, A.A.; Ermakov, S.S.; Roizard, D. Investigation of new modification strategies for PVA membranes to improve their dehydration properties by pervaporation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B. Defects reparation and surface hydrophilic modification of zeolite beta membranes with spherical polyelectrolyte complex nanoparticles via vacuum-wiping deposition technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 602, 117977–117986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Z. Evaluations of polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes assembled by a dynamic layer-by-layer technique. Desalination 2008, 234, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Wang, R. Enhanced hollow fiber membrane performance via semi-dynamic layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte inner surface deposition for nanofiltration and forward osmosis applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Song, X.; Ji, S.; Wang, N.; Liu, Z. Self-assembly of inner skin hollow fiber polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes by a dynamic negative pressure layer-by-layer technique. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Burts, K.S.; Ermakov, S.S.; Penkova, A.V.; Kuzminova, A.I.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Hliavitskaya, T.A.; Ulbricht, M. One-Step Preparation of Antifouling Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Modification by a Cationic Polyelectrolyte Based on Polyacrylamide. Polymers 2020, 12, 1017–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hliavitskaya, T.; Plisko, T.; Bildyukevich, A.; Lipnizki, F.; Rodrigues, G.; Sjölin, M. Modification of PES ultrafiltration membranes by cationic polyelectrolyte Praestol 859: Characterization, performance and application for purification of hemicellulose. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 162, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Guria, C.; Mandal, A. Kinetic modeling and simulation of non-solvent induced phase separation: Immersion precipitation of PVC-based casting solution in a finite salt coagulation bath. Polymer 2020, 199, 122527–122541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Enhanced permeation and antifouling performance of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) blend Pluronic F127 ultrafiltration membrane by using salt coagulation bath (SCB). J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H. Characteristics and performance of PVDF membrane prepared by using NaCl coagulation bath: Relationship between membrane polymorphous structure and organic fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, S.S.; Harun, Z.; Shohur, M.F. Effect of monovalent and divalent ions in non-solvent coagulation bath-induced phase inversion on the characterization of a porous polysulfone membrane. Polym. Bull. 2019, 76, 5957–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhu, B.K.; Xu, Y.Y. Effects of coagulant pH and ion strength on the dehydration and self-assembly of poly (N, N-dimethylamino-2-ethyl methacrylate) chains in the preparation of stimuli-responsive polyethersulfone blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. The effect of pH of coagulation bath on tailoring the morphology and separation performance of polysulfone/polyaniline ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.W.; Burford, R.P.; Fane, A.G.; Fell, C.J.D. Effect of coagulation conditions on structure and properties of membranes from aliphatic polyamides. J. Membr. Sci. 1988, 38, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baaij, J.P.B.; Smolders, C.A. The mechanism of formation of microporous or skinned membranes produced by immersion precipitation. J. Membr. Sci. 1983, 14, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barzin, J.; Sadatnia, B. Correlation between macrovoid formation and the ternary phase diagram for polyethersulfone membranes prepared from two nearly similar solvents. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayanandan, N.; Kapoor, A.; Karunanithi, S.; Sivaraman, P. Studies on the influence of coagulation bath composition on the preparation of PVDF membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 122, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Z. In-situ construction of antifouling separation layer via a reaction enhanced surface segregation method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 190, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mao, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S. In situ surface crosslinked tight ultrafiltration membrane prepared by one-step chemical reaction-involved phase inversion process between activated PAEK-COOH and PEI. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 538, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bildyukevich, A.V.; Plisko, T.V.; Liubimova, A.S.; Volkov, V.V.; Usosky, V.V. Hydrophilization of polysulfone hollow fiber membranes via addition of polyvinylpyrrolidone to the bore fluid. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbangaleeva, M.H. Studying the Effect of High Molecular Flocculants on Separation of Distillation Suspension-the Main Waste of Soda Ash Production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 272, 022022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvoruchko, A.P.; Yurlova, L.Y. Use of polyelectrolytes in ultra-and nanofiltration treatment of uranium-contaminated waters. Radiochemistry 2014, 56, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Loss, R.D.; Shields, D.; Pawlik, T.; Hochreiter, R.; Zydney, A.L.; Kumar, M. Polyacrylamide degradation and its implications in environmental systems. NPJ Clean Water 2018, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zydney, A.L. Humic acid fouling during microfiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 157, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoufidou, K.; Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J. A study of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acids and flux recovery by backwashing: Experiments and modelling. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 266, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zydney, A.L. Humic acid fouling during ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 5043–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolders, C.A.; Reuvers, A.J.; Boom, R.M.; Wienk, I.M. Microstructures in phase-inversion membranes. Part 1. Formation of macrovoids. J. Membr. Sci. 1992, 34, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKelvey, S.A.; Koros, W.J. Phase separation, vitrification and the manifestation of macrovoids in polymeric asymmetric membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1996, 112, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunos, M.Z.; Harun, Z.; Basri, H.; Ismail, A.F. Studies on fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) on polysulfone membranes: Effect of polyethyleneglycol (PEG). Desalination 2014, 333, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plisko, T.V.; Liubimova, A.S.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Penkova, A.V.; Dmitrenko, M.E.; Mikhailovskii, V.Y.; Melnikova, G.B.; Semenov, K.N.; Doroshkevich, N.V.; Kuzminova, A.I. Fabrication and characterization of polyamide-fullerenol thin film nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes with enhanced antifouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, F.; Cheng, S.; Wang, W. Synthesis of sodium acrylate and acrylamide copolymer/GO hydrogels and their effective adsorption for Pb2+ and Cd2+. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3948–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Wetting: Intrinsically robust hydrophobicity. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möckel, D.; Staude, E.; Dal-Cin, M.; Darcovich, K.; Guiver, M. Tangential flow streaming potential measurements: Hydrodynamic cell characterization and zeta potentials of carboxylated polysulfone membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 145, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Liao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sotto, A.; Zhu, J.; Bruggen, B.; Gao, C.; Shen, J. Bioinspired dual stimuli-responsive membranes with enhanced gating ratios and reversible performances for water gating. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 564, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klučáková, M. Conductometric study of the dissociation behavior of humic and fulvic acids. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 128, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

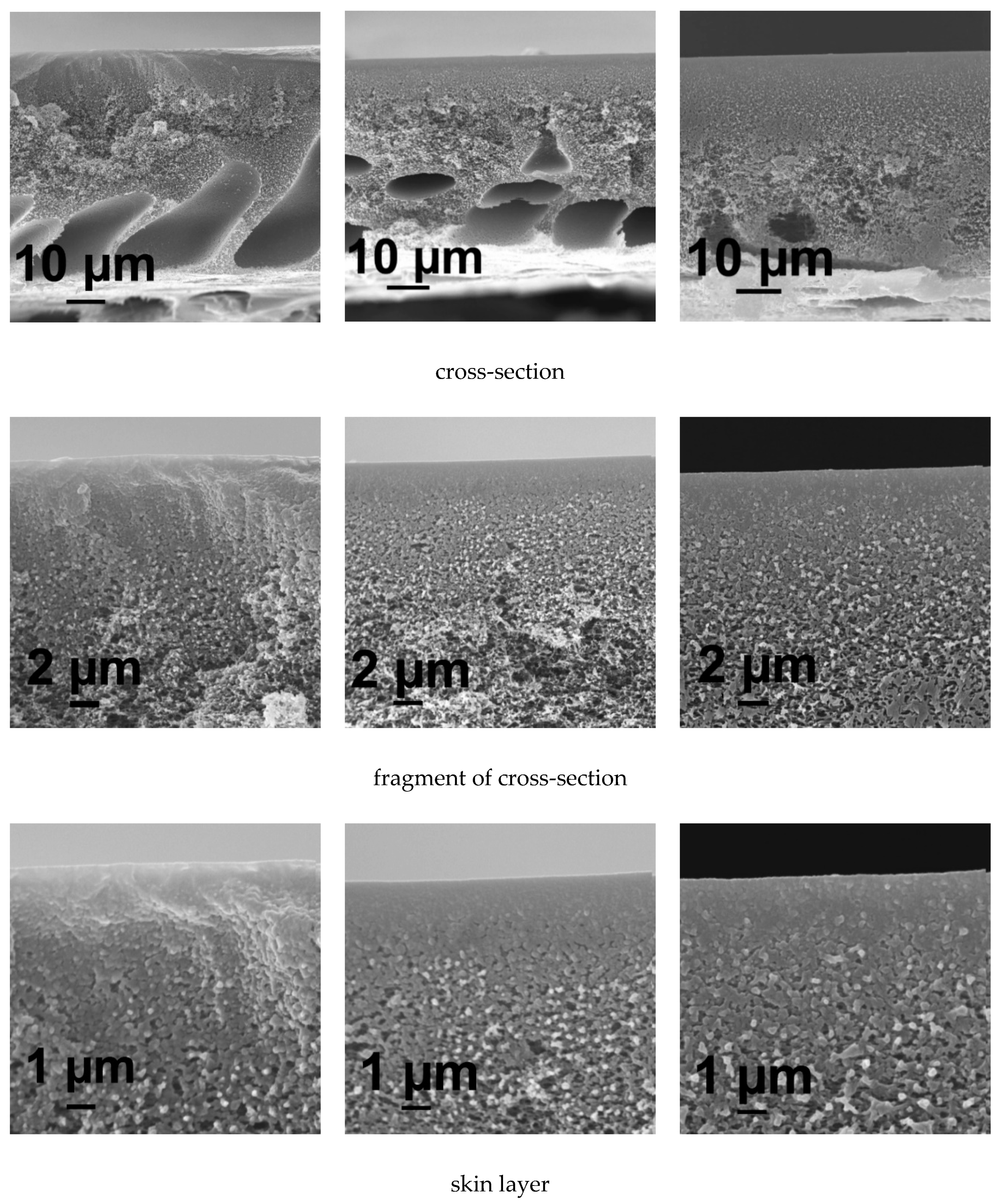
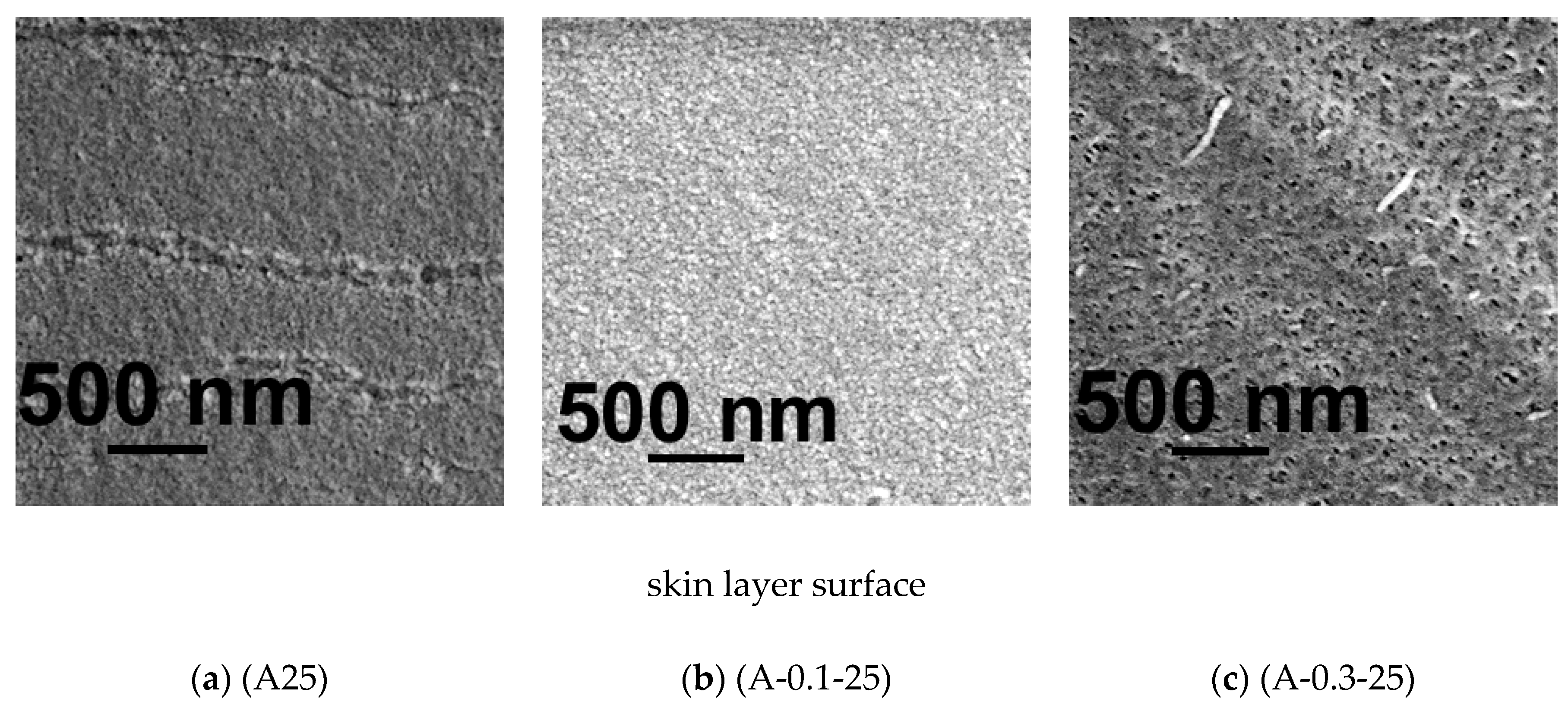
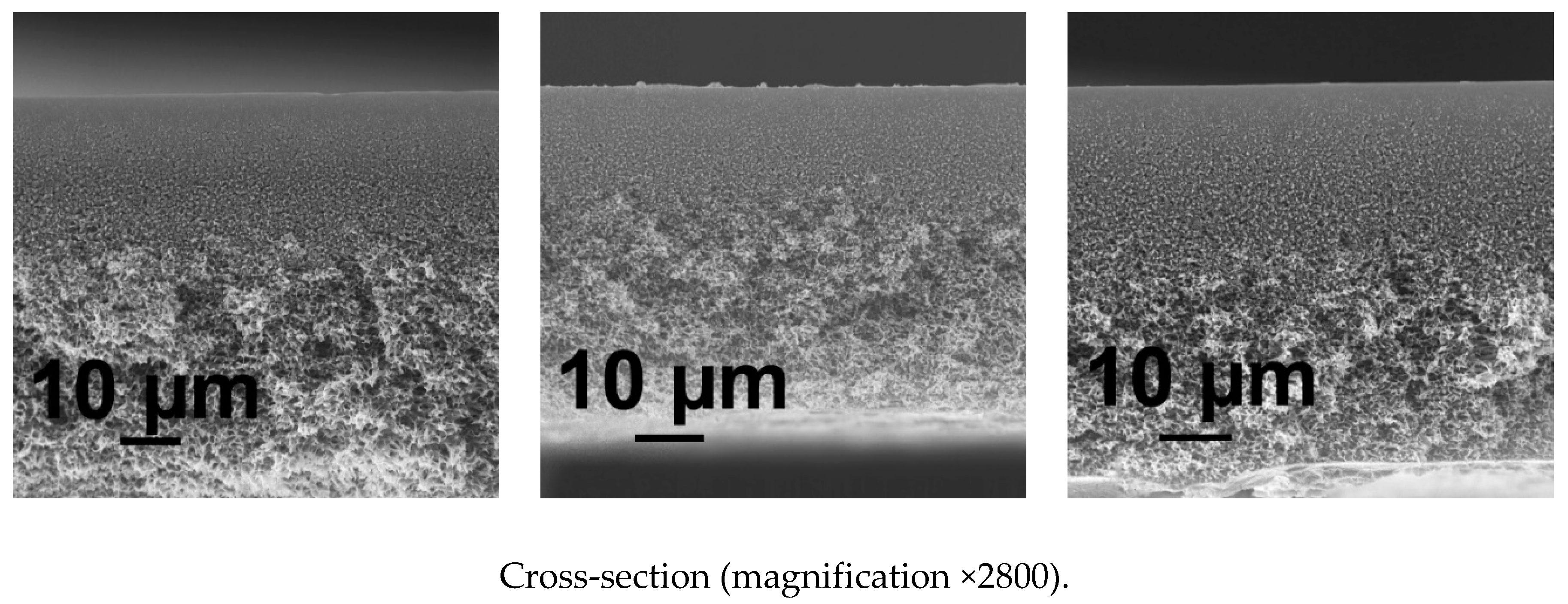




| Membrane | Composition of Coagulant | Coagulant Temperature, °C |
|---|---|---|
| c (PASA), wt % | ||
| A25 | 0 | 25 |
| A40 | 0 | 40 |
| A60 | 0 | 60 |
| A70 | 0 | 70 |
| A-0.05-25 | 0.05 | 25 |
| A-0.05-40 | 40 | |
| A-0.05-60 | 60 | |
| A-0.05-70 | 70 | |
| A-0.1-25 | 0.1 | 25 |
| A-0.1-40 | 40 | |
| A-0.1-60 | 60 | |
| A-0.1-70 | 70 | |
| A-0.2-25 | 0.2 | 25 |
| A-0.2-40 | 40 | |
| A-0.2-60 | 60 | |
| A-0.2-70 | 70 | |
| A-0.3-25 | 0.3 | 25 |
| A-0.3-40 | 40 | |
| A-0.3-60 | 60 | |
| A-0.3-70 | 70 |
| Membrane | Coagulation Bath | Ra, nm | Rq, nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| c (PASA), % | T, °C | |||
| A25 | 0 | 25 | 4.6 | 5.7 |
| A40 | 0 | 40 | 4.7 | 5.9 |
| A60 | 0 | 60 | 4.7 | 6.1 |
| A-0.05-60 | 0.05 | 60 | 11.2 | 14.1 |
| A-0.1-25 | 0.1 | 25 | 6.2 | 7.1 |
| A-0.1-40 | 0.1 | 40 | 20.7 | 26.3 |
| A-0.1-60 | 0.1 | 60 | 27.2 | 35.2 |
| A-0.3-60 | 0.3 | 60 | 20.9 | 25.4 |
| Membrane Abbreviation | Zeta Potential, mV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 3.2 | pH = 4.0 | pH = 4.6 | pH = 7.0 | pH = 9.5 | |
| A25 | 8 | 0 | −28 | −58 | −65 |
| A-0.3-25 | 28 | 0 | −18 | −88 | −95 |
| Characteristics | Feed 0.001 wt % HA Solution in Tap Water | Permeate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A25 | A-0.3-25 | ||
| Color (λ = 400 nm) | 0.10 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| pH | 8.4 | 8.4 | 8.4 |
| TOC, mg∙L−1 | 0.54 | 0 | 0 |
| c (Fe), µg∙L−1 | 156 | 0 | 0 |
| Characteristics | Feed Surface Water | Permeate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A60 | A-0.3-60 | ||
| Turbidity, NTU | 12.0 | 0.150 | 0.108 |
| pH | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.2 |
| Color (λ = 400 nm) | 0.128 | 0.017 | 0.017 |
| TOC, mg∙L−1 | 20.4 | 7.1 | 3.8 |
| c (Fe), µg∙L−1 | 410 | 0.70 | 0.38 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plisko, T.V.; Bildyukevich, A.V.; Burts, K.S.; Hliavitskaya, T.A.; Penkova, A.V.; Ermakov, S.S.; Ulbricht, M. Modification of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Addition of Anionic Polyelectrolyte Based on Acrylamide and Sodium Acrylate to the Coagulation Bath to Improve Antifouling Performance in Water Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100264
Plisko TV, Bildyukevich AV, Burts KS, Hliavitskaya TA, Penkova AV, Ermakov SS, Ulbricht M. Modification of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Addition of Anionic Polyelectrolyte Based on Acrylamide and Sodium Acrylate to the Coagulation Bath to Improve Antifouling Performance in Water Treatment. Membranes. 2020; 10(10):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100264
Chicago/Turabian StylePlisko, Tatiana V., Alexandr V. Bildyukevich, Katsiaryna S. Burts, Tatiana A. Hliavitskaya, Anastasia V. Penkova, Sergey S. Ermakov, and Mathias Ulbricht. 2020. "Modification of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Addition of Anionic Polyelectrolyte Based on Acrylamide and Sodium Acrylate to the Coagulation Bath to Improve Antifouling Performance in Water Treatment" Membranes 10, no. 10: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100264
APA StylePlisko, T. V., Bildyukevich, A. V., Burts, K. S., Hliavitskaya, T. A., Penkova, A. V., Ermakov, S. S., & Ulbricht, M. (2020). Modification of Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes via Addition of Anionic Polyelectrolyte Based on Acrylamide and Sodium Acrylate to the Coagulation Bath to Improve Antifouling Performance in Water Treatment. Membranes, 10(10), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100264