Boron Removal by Membrane Distillation: A Comparison Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Membrane Technology
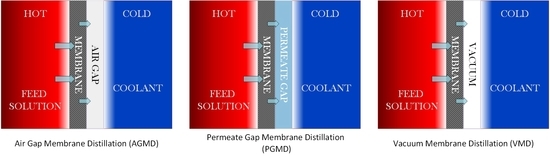
1.2. Membrane Distillation (MD)
2. Experimental Procedure and Material
2.1. Equipment and Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Operating Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
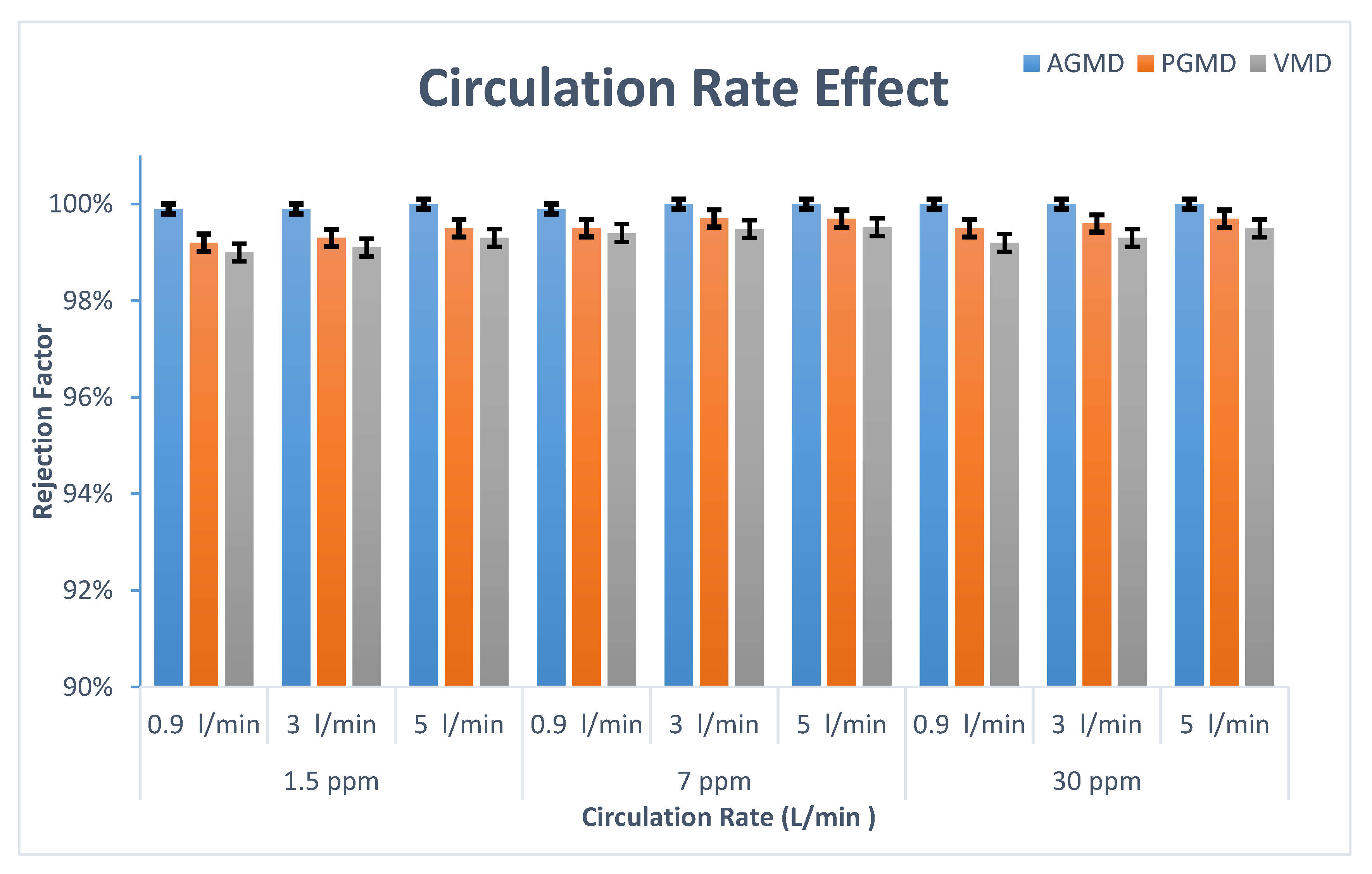
3.1. Influence of Circulation Rate
3.2. Impact of Feed Temperature
3.3. Synthetic Seawater
4. Conclusions
- MD is a worthy technology for boron removal and seawater desalination (which varied between 99.3–100%).
- Boron removal for AGMD was excellent and stable over a wide variety of concentrations, temperature range, and flow rate, while taking note that PGMD and VMD show better permeate fluxes.
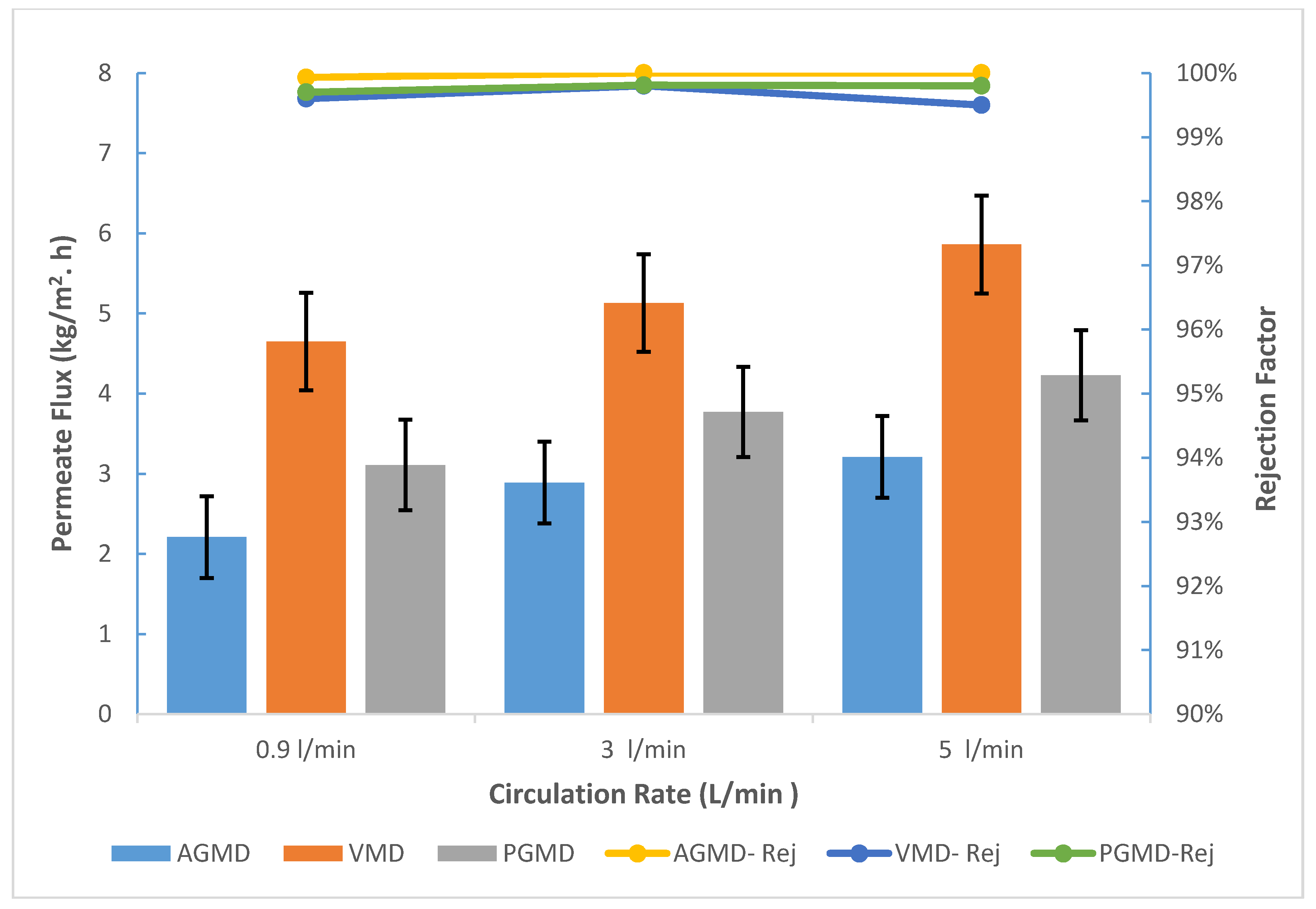
- The permeate fluxes of AGMD, PGMD, and VMD for synthetic seawater at 60 °C and 5 L/min were 3.21, 4.23, and 5.86 kg/m2·h. Additionally, the boron concentration was about 0.01 ppm.
- When the feed circulation rate increased, the boron rejection for AGMD, PGMD, and VMD increased no matter the concentration.
- For better boron removal by MD, it is recommended not to exceed 70 °C in the feed side to prevent membrane wetting.
- AGMD is proposed to be an alternative solution to the second-pass RO for boron removal. In addition, VMD is proposed to be an alternative technology for seawater desalination
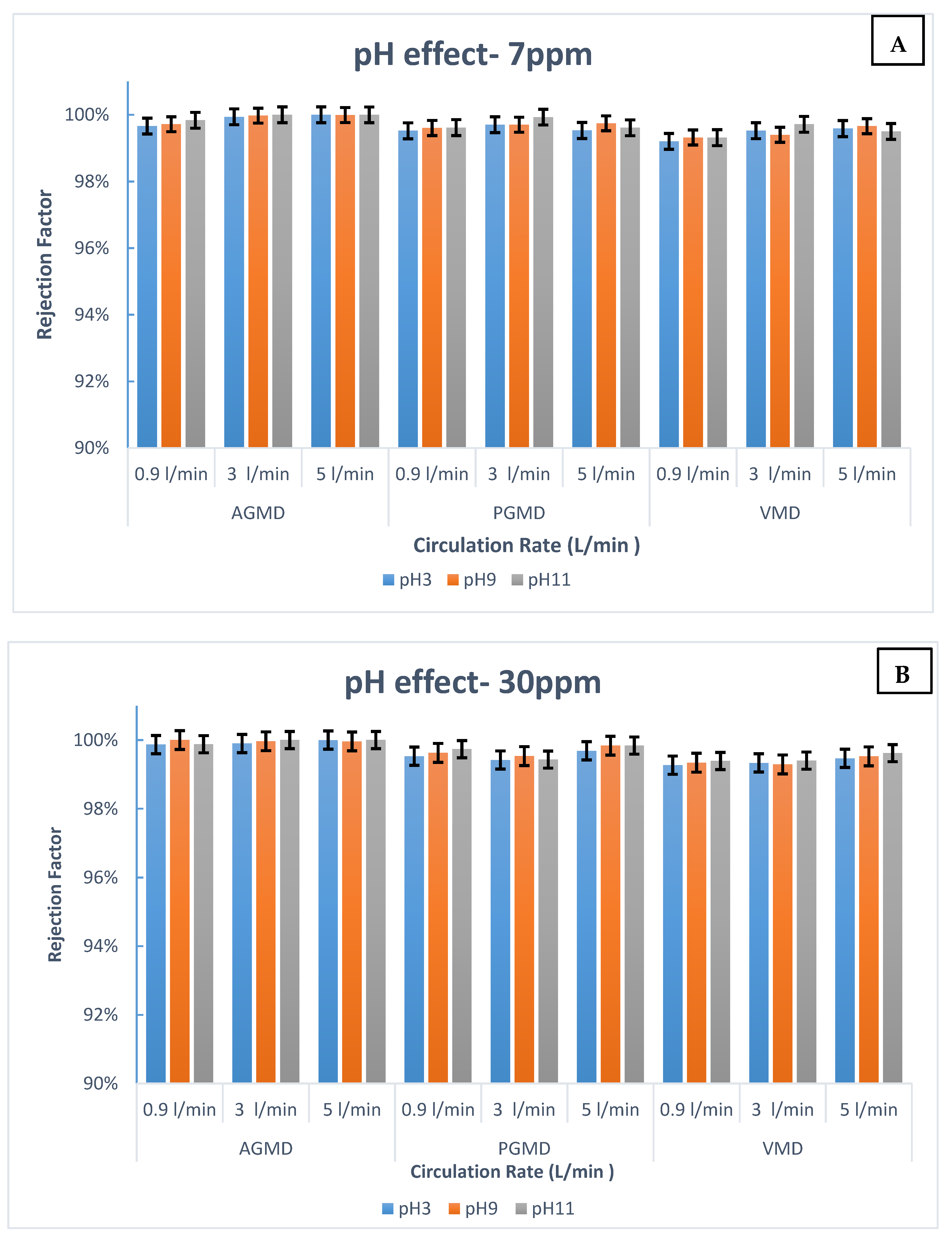
- There is no noteworthy impact on boron removal from the high acidity of the feed solution (PH value), which can be considered an attractive feature. Whereas the traditional membrane filtration depends highly on the pH feed solution.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochkodan, V.; Darwish, N.B.; Hilal, N. Chapter 2—The Chemistry of Boron in Water, in Boron Separation Processes; Kabay, N., Bryjak, M., Hilal, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 35–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hilal, N.; Kim, G.J.; Somerfield, C. Boron removal from saline water: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 273, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, A.; Ahmad, F.; Arafat, H. Analytical techniques for boron quantification supporting desalination processes: A review. Desalination 2013, 310, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats, D.; Chillon-Arias, M.F.; Rodriguez-Pastor, M. Analysis of the influence of pH and pressure on the elimination of boron in reverse osmosis. Desalination 2000, 128, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeebe, R.E.; Sanyal, A.; Ortiz, J.D.; Wolf-Gladrow, D.A. A theoretical study of the kinetics of the boric acid–borate equilibrium in seawater. Mar. Chem. 2001, 73, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baransi-Karkaby, K.; Bass, M.; Freger, V. In Situ Modification of Reverse Osmosis Membrane Elements for Enhanced Removal of Multiple Micropollutants. Membranes 2019, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ezechi, E.H.; Isa, M.H.; Kutty, S.R.B.M. Boron in Produced Water: Challenges and Improvements: A Comprehensive Review. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Gao, X.; Chen, G.; Zou, L.; Gao, C. High performance boron removal from seawater by two-pass SWRO system with different membranes. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2010, 10, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magara, Y.; Aizawa, T.; Kunikane, S.; Itoh, M.; Kohki, M.; Kawasaki, M.; Takeuti, H. The behavior of inorganic constituents and disinfection by products in reverse osmosis water desalination process. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 34, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hyung, H.; Wilf, M. Boron Rejection By Reverse Osmosis Membranes: National Reconnaissance and Mechanism Study; U.S. Department of the Interior Bureau of Reclamationmation: Denver, CO, USA, 2009.
- Rahmawati, K. Boron Removal in Seawater Reverse Osmosis System. Master’s Thesis, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, Thuwal, Saudi Arabia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Redondo, J.; Busch, M.; de Witte, J.-P. Boron removal from seawater using FILMTECTM high rejection SWRO membranes. Desalination 2003, 156, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, D.; Shemer, H.; Brook, I.; Zaslavschi, I.; Semiat, R.; Bartels, C.; Wilf, M. Scaling propensity of seawater in RO boron removal processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 384, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska, J.; Bryjak, A.M. Methods for boron removal from aqueous solutions—A review. Desalination 2013, 310, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Hilal, N. Air gap membrane distillation: A detailed study of high saline solution. Desalination 2017, 403, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Aguirre, A.; Andrés-Mañas, J.A.; Zaragoza, G. Evaluation of Permeate Quality in Pilot Scale Membrane Distillation Systems. Membranes 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, X.; Xu, Z.; Bai, A.-P.; Resina, M.; Ji, Z.-G. Separation and Recycling of Concentrated Heavy Metal Wastewater by Tube Membrane Distillation Integrated with Crystallization. Membranes 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Hakami, M.; Zacharof, M.-P.; Homod, H.; Alsadun, A. Mercury, Arsenic and Lead Removal by Air Gap Membrane Distillation: Experimental Study. Water 2020, 12, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eryildiz, B.; Yuksekdag, A.; Korkut, S.; Zeytuncu, B.; Pasaoglu, M.E.; Koyuncu, I. Effect of operating parameters on removal of boron from wastewater containing high boron concentration by vacuum assisted air gap membrane distillation. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Darwish, N.; Hilal, N. Membrane distillation: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2012, 287, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhudhiri, A.; Hilal, N. 3-Membrane distillation—Principles, applications, configurations, design, and implementation. In Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Desalination Handbook; Gude, V.G., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 55–106. [Google Scholar]
- Franken, A.C.M.; Nolten, J.A.M.; Mulder, M.H.V.; Bargeman, D.; Smolders, C.A. Wetting criteria for the applicability of membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 1987, 33, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eykens, L.; de Sitter, K.; Dotremont, C.; de Schepper, W.; Pinoy, L.; van der Bruggen, B. Wetting Resistance of Commercial Membrane Distillation Membranes in Waste Streams Containing Surfactants and Oil. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Duke, M.C.; Matsuura, T.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: Mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res. 2018, 139, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floros, I.; Kouvelos, E.; Pilatos, G.; Hadjigeorgiou, P.; Gotzias, A.; Favvas, E.; Sapalidis, A. Enhancement of Flux Performance in PTFE Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Polymers 2020, 12, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gryta, M. Mitigation of Membrane Wetting by Applying a Low Temperature Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Dai, G.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Luan, Z.; Fu, C. Boron removal and desalination from seawater by PVDF flat-sheet membrane through direct contact membrane distillation. Desalination 2013, 326, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Bouguecha, S.A.-T.; Dhaouadi, I.; Hafiane, A. Effect of operating parameters on boron removal from seawater using membrane distillation process. Desalination 2015, 373, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Luan, Z.; Zhao, C.; Ren, X. Boron removal from aqueous solution by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifa, A.E. Water and air gap membrane distillation for water desalination–An experimental comparative study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 141, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, N.; Kavak, D.; Köse, T.E. Boron removal from aqueous solution by reverse osmosis. Desalination 2008, 223, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutaz, I. Water desalination in the Arabian Gulf region. Water Purif. 2000, 2, 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Fu, K.; Cui, Z.; Fan, Y.; Drioli, E. Ceramic nanofiltration and membrane distillation hybrid membrane processes for the purification and recycling of boric acid from simulative radioactive waste water. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarini, R.; Arafat, H.; Thomas, R. Influence of pore structure on membrane wetting in membrane distillation. In Proceedings of the The Sixth Jordan International Chemical Engineering Conference (JIChEC 06), Amman, Jordan, 12–14 March 2012. [Google Scholar]





| Salt Component | Concentration (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Chloride, Cl− | 23,000 |
| Sodium, Na+ | 15,850 |
| Sulfate, SO42− | 3200 |
| Magnesium, Mg2+ | 1765 |
| Calcium, Ca2+ | 500 |
| Potassium, K+ | 460 |
| Boron, B | 7 |
| pH | 7.3 |
| Total dissolved solids, TDS | 45,000 |
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Material | PTFE |
| Commercial name | TF200 |
| Mean pore size | 0.2 µm |
| Liquid entry pressure (LEP) | 2.55 bar |
| Thickness | 175 µm |
| Membrane support | Polypropylene |
| Manufacturer | Sterlitech corporation |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkhudhiri, A.; Bin Darwish, N.; Hakami, M.W.; Abdullah, A.; Alsadun, A.; Abu Homod, H. Boron Removal by Membrane Distillation: A Comparison Study. Membranes 2020, 10, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100263
Alkhudhiri A, Bin Darwish N, Hakami MW, Abdullah A, Alsadun A, Abu Homod H. Boron Removal by Membrane Distillation: A Comparison Study. Membranes. 2020; 10(10):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100263
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkhudhiri, Abdullah, Nawaf Bin Darwish, Mohammed Wali Hakami, AbdelKader Abdullah, Ahmed Alsadun, and Hosam Abu Homod. 2020. "Boron Removal by Membrane Distillation: A Comparison Study" Membranes 10, no. 10: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100263
APA StyleAlkhudhiri, A., Bin Darwish, N., Hakami, M. W., Abdullah, A., Alsadun, A., & Abu Homod, H. (2020). Boron Removal by Membrane Distillation: A Comparison Study. Membranes, 10(10), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10100263