Oral Peptide Vaccine against Hookworm Infection: Correlation of Antibody Titers with Protective Efficacy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
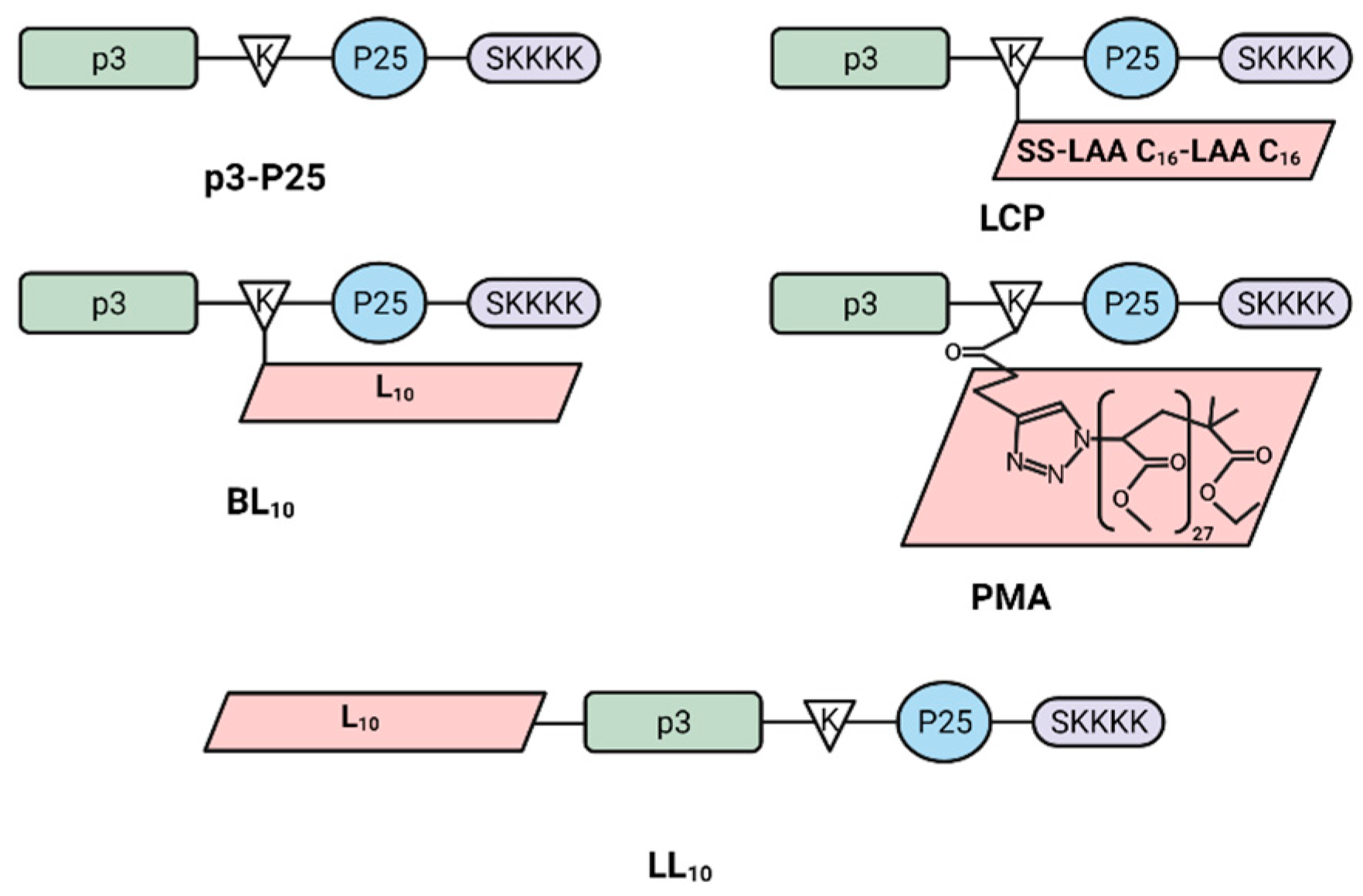
2.2. Synthesis of Peptide Vaccines
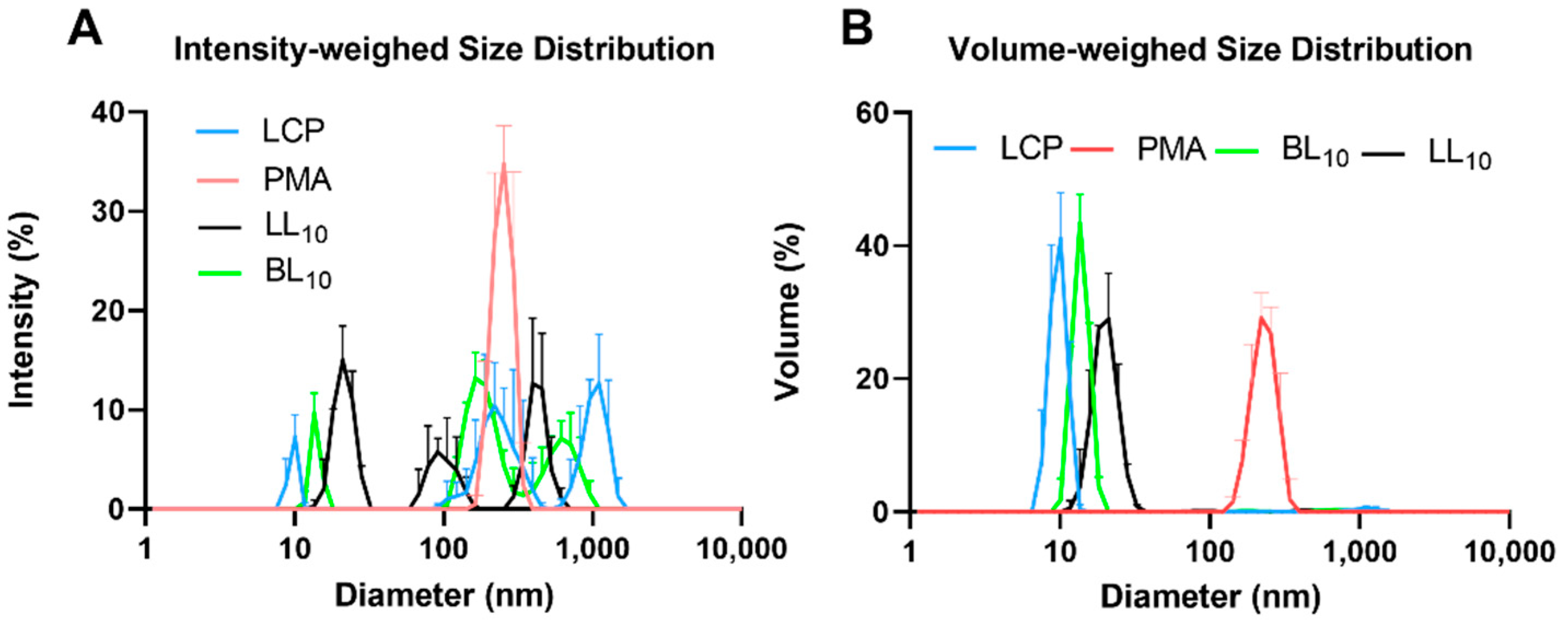
2.3. Peptide Vaccine Particle Size and Shape
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
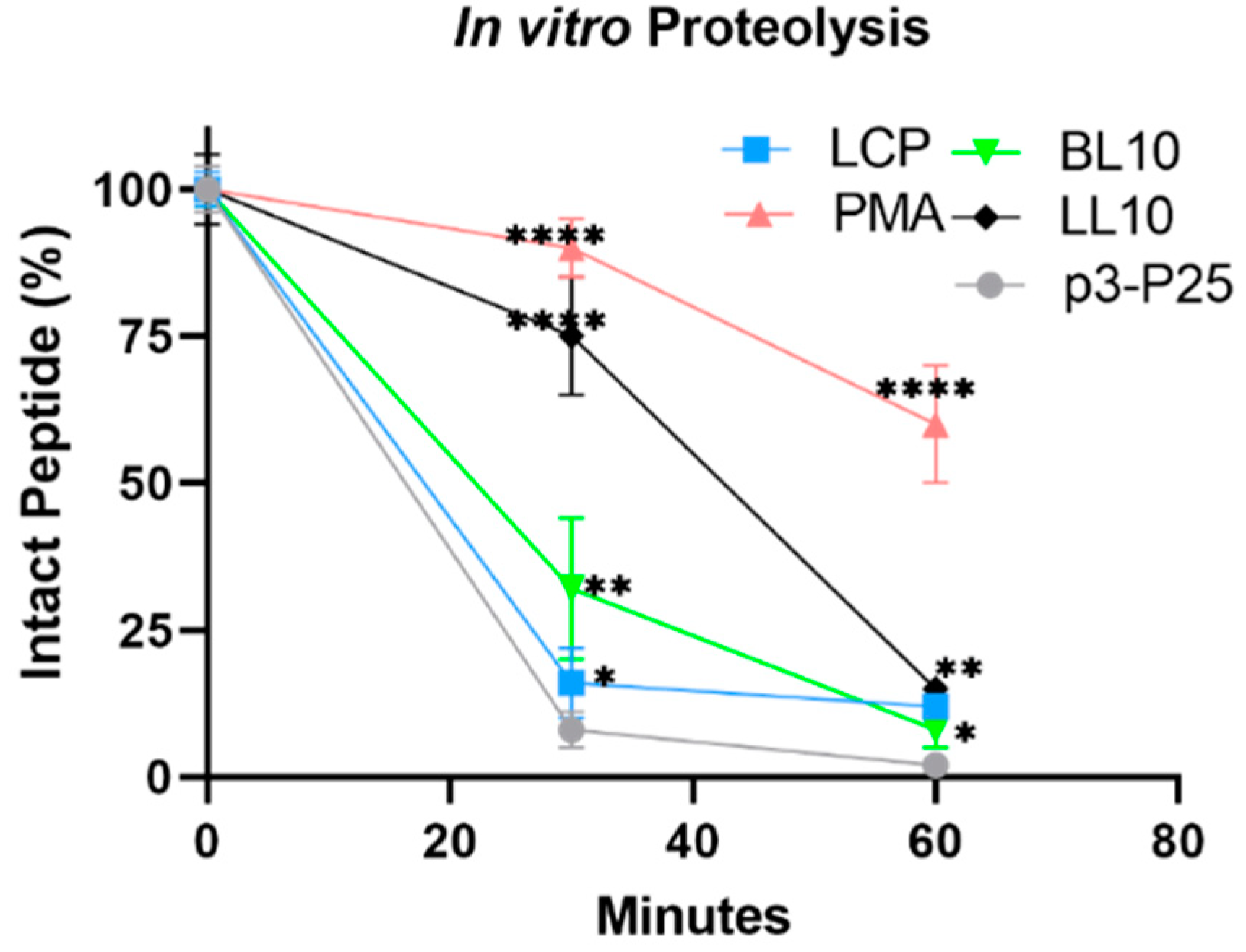
2.5. In Vitro Stability against Proteolysis
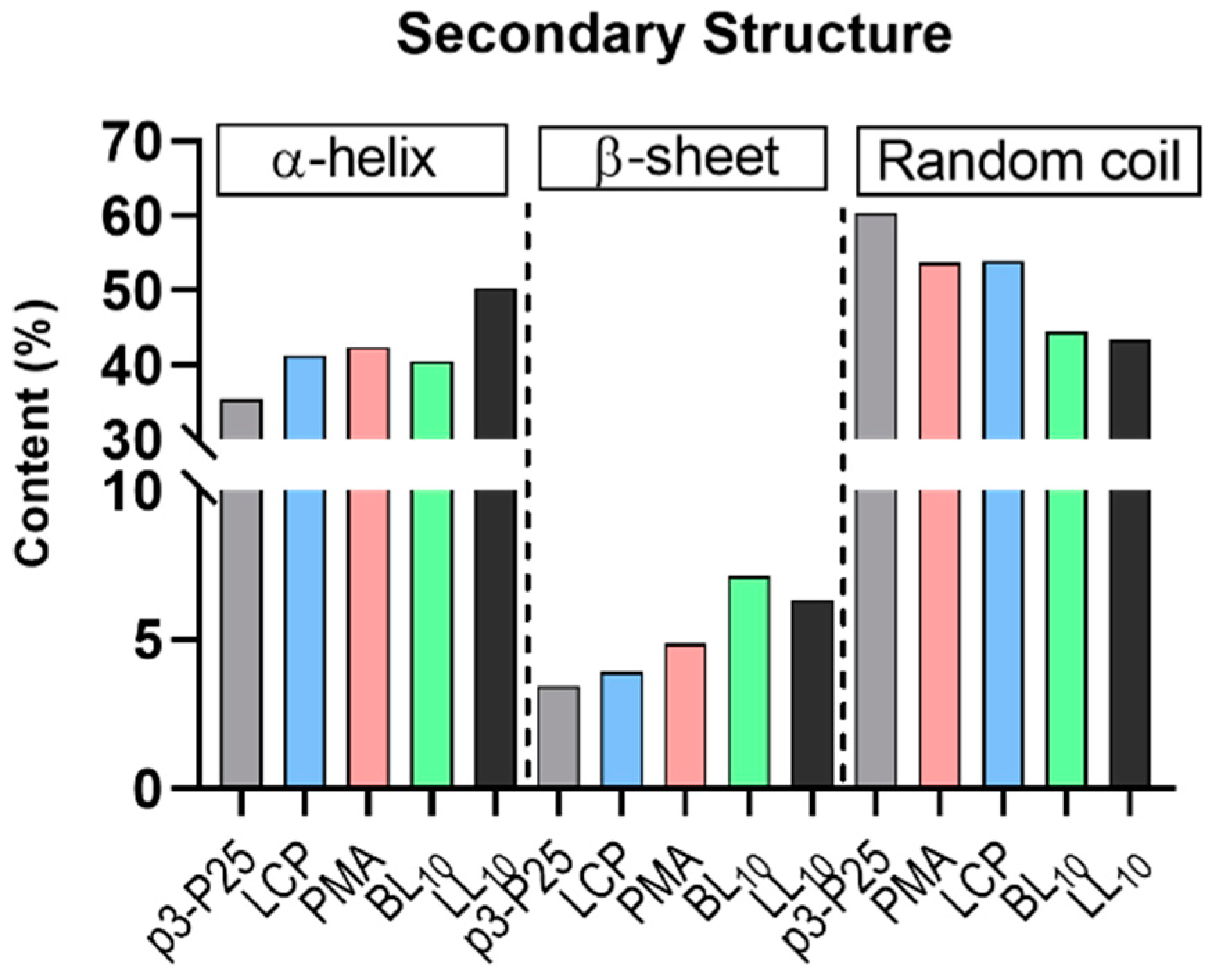
2.6. Secondary Structure of Peptide Vaccines
2.7. Oral Immunization of BALB/c Mice
2.8. Serological and Mucosal Immunogenicity Assays
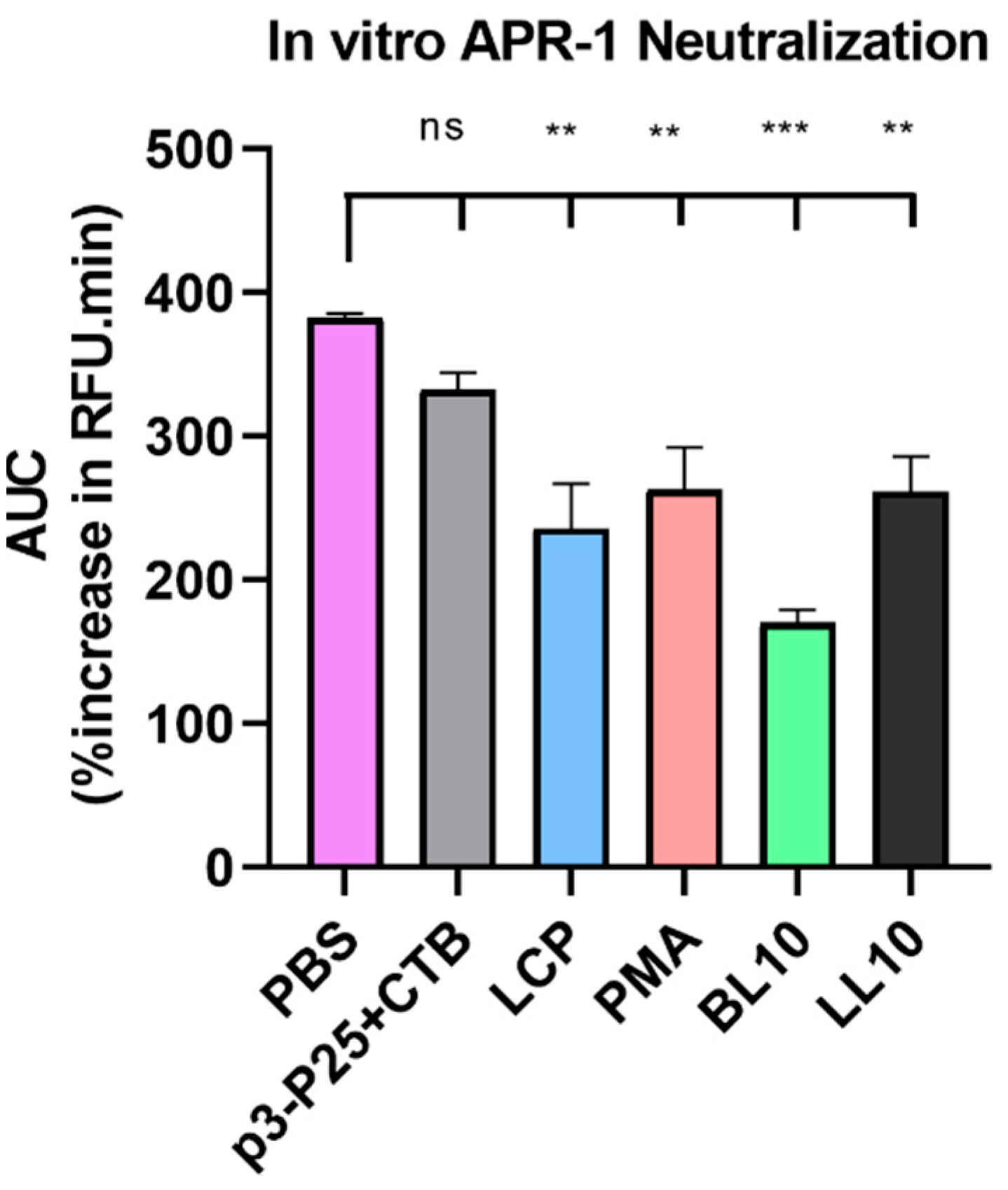
2.9. Enzyme Neutralization
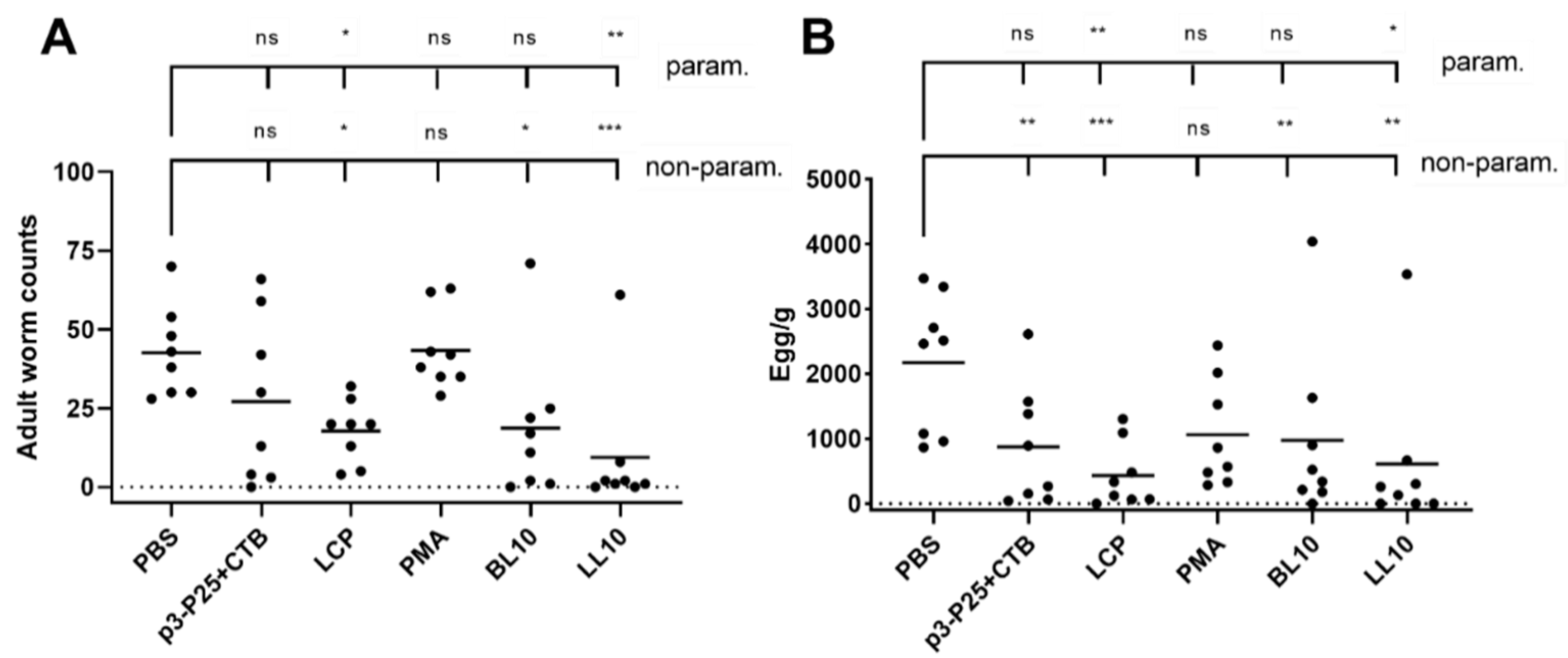
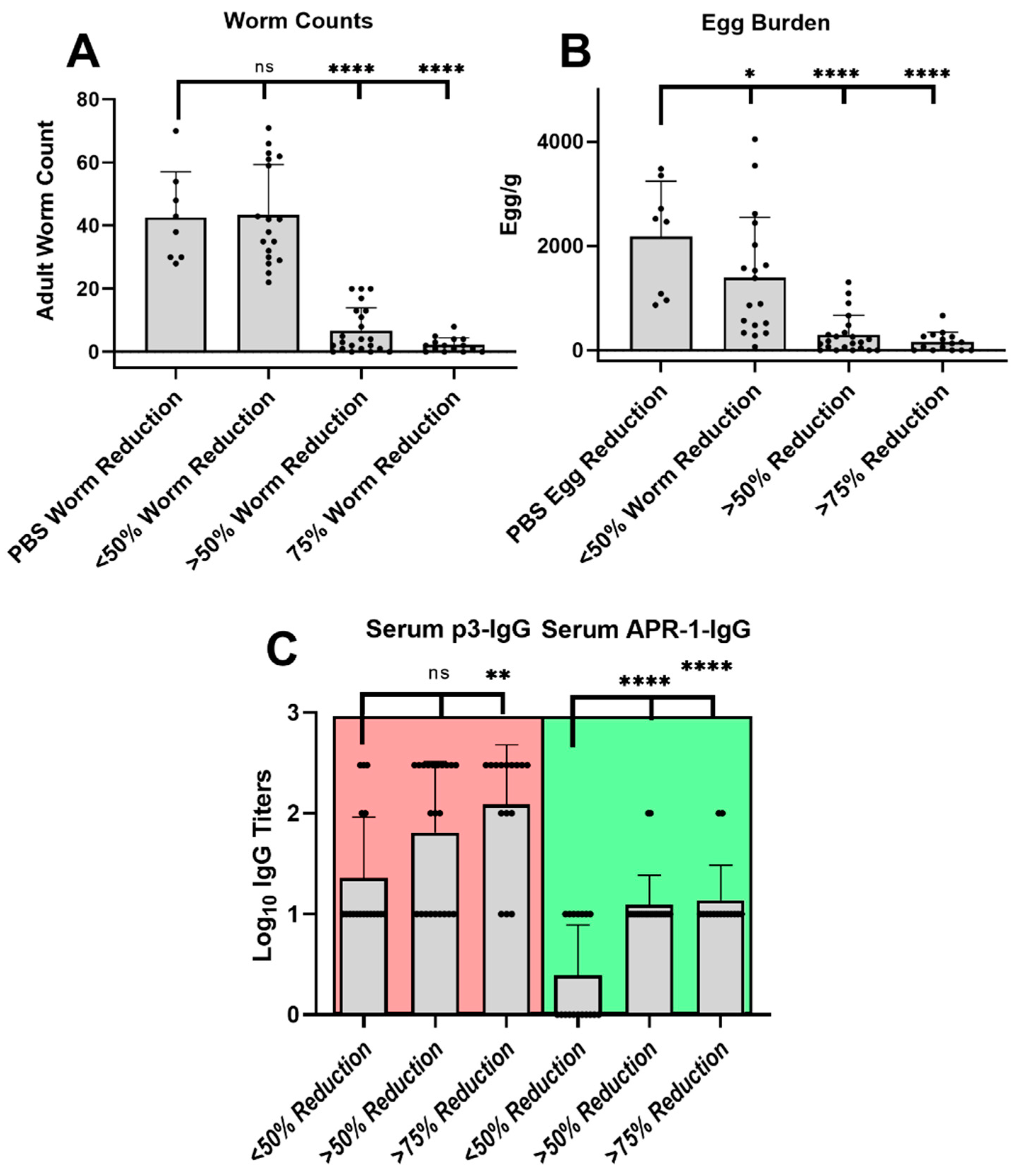
2.10. Challenge Infection
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. Secondary Structure
3.3. Enzymatic Stability In Vitro
3.4. Immunogenicity of the Conjugates
3.5. Infection Challenge
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hotez, P.J.; Zhan, B.; Bethony, J.M.; Loukas, A.; Williamson, A.; Goud, G.N.; Hawdon, J.M.; Dobardzic, A.; Dobardzic, R.; Ghosh, K.; et al. Progress in the development of a recombinant vaccine for human hookworm disease: The Human Hookworm Vaccine Initiative. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotez, P.; Bethony, J.M.; Diemert, D.; Pearson, M.; Loukas, A. Developing vaccines to combat hookworm infection and intestinal schistosomiasis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 8, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis. Progress report on number of children treated with anthelminthic drugs: An update towards the 2010 global target. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2008, 82, 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Behnke, J.M. Do hookworms elicit protective immunity in man? Parasitol. Today 1987, 3, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwenkenbecher, J.M.; Albonico, M.; Bickle, Q.; Kaplan, R.M. Characterization of beta-tubulin genes in hookworms and investigation of resistance-associated mutations using real-time PCR. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 156, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albonico, M.; Smith, P.G.; Hall, A.; Chwaya, H.M.; Alawi, K.S.; Savioli, L. A randomized controlled trial comparing mebendazole and albendazole against Ascaris, Trichuris and hookworm infections. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1994, 88, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemert, D.J.; Pinto, A.G.; Freire, J.; Jariwala, A.; Santiago, H.; Hamilton, R.G.; Periago, M.V.; Loukas, A.; Tribolet, L.; Mulvenna, J.; et al. Generalized urticaria induced by the Na-ASP-2 hookworm vaccine: Implications for the development of vaccines against helminths. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 169–176.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzsimmons, C.M.; Falcone, F.H.; Dunne, D.W. Helminth Allergens, Parasite-Specific IgE, and Its Protective Role in Human Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, T.A. Persistence of Immunity Following Double Vaccination of Pups with X-Irradiated Ancylostoma caninum Larvae. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, J.; Pearson, M.S.; Manda, S.S.; Choi, Y.-J.; Field, M.; Eichenberger, R.M.; Mulvenna, J.; Nagaraj, S.H.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Gazzinelli-Guimaraes, P.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the secreted proteome of adult Necator americanus hookworms. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, D. Proteases in Blood-Feeding Nematodes and Their Potential as Vaccine Candidates. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 712, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.S.; Bethony, J.M.; Pickering, D.A.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Jariwala, A.; Santiago, H.; Miles, A.P.; Zhan, B.; Jiang, D.; Ranjit, N.; et al. An enzymatically inactivated hemoglobinase from Necator americanus induces neutralizing antibodies against multiple hookworm species and protects dogs against heterologous hookworm infection. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pearson, M.S.; Jariwala, A.R.; Abbenante, G.; Plieskatt, J.L.; Wilson, D.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Hotez, P.; Keegan, B.; Bethony, J.M.; Loukas, A. New tools for NTD vaccines: A case study of quality control assays for product development of the human hookworm vaccineNa-APR-1M74. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, M.; Pickering, D.A.; Tribolet, L.; Cooper, L.; Mulvenna, J.; Oliveira, L.M.; Bethony, J.M.; Hotez, P.; Loukas, A. Neutralizing Antibodies to the Hookworm HemoglobinaseNa-APR-1: Implications for a Multivalent Vaccine against Hookworm Infection and Schistosomiasis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, S.; Zhan, B.; Xue, J.; Goud, G.N.; Loukas, A.; Liu, Y.; Williamson, A.; Liu, S.; Deumic, V.; Hotez, P. The evaluation of recombinant hookworm antigens as vaccines in hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) challenged with human hookworm, Necator americanus. Exp. Parasitol. 2008, 118, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Bethony, J.M.; Mendez, S.; Fujiwara, R.T.; Goud, G.N.; Ranjit, N.; Zhan, B.; Jones, K.; Bottazzi, M.E.; Hotez, P.J. Vaccination with Recombinant Aspartic Hemoglobinase Reduces Parasite Load and Blood Loss after Hookworm Infection in Dogs. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegnika, A.; De Vries, S.; Zinsou, F.J.; Honkpehedji, J.; Dejon, J.C.; Loembe, M.M.; Bache, B.; Pakker, N.; Van Leeuwen, R.; Hounkpatin, A.B.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of co-administered hookworm vaccine candidates na-gst-1 and na-apr-1 with alhydrogel® and glucopyranosyl-lipid a in gabonese adults: Interim results. BMJ Glob. Health 2017, 2, A12–A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hotez, P.J.; Beaumier, C.M.; Gillespie, P.M.; Strych, U.; Hayward, T.; Bottazzi, M.E. Advancing a vaccine to prevent hookworm disease and anemia. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3001–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuaad, A.A.A.; Pearson, M.S.; Pickering, D.A.; Becker, L.; Zhao, G.; Loukas, A.C.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Lipopeptide Nanoparticles: Development of Vaccines against Hookworm Parasite. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verity, C.K.; McManus, D.; Brindley, P.J. Vaccine efficacy of recombinant cathepsin D aspartic protease fromSchistosoma japonicum. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttiprapa, S.; Mulvenna, J.; Huong, N.T.; Pearson, M.; Brindley, P.J.; Laha, T.; Wongkham, S.; Kaewkes, S.; Sripa, B.; Loukas, A. Ov-APR-1, an aspartic protease from the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini: Functional expression, immunolocalization and subsite specificity. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouchery, T.; Filbey, K.; Shepherd, A.; Chandler, J.; Patel, D.; Schmidt, A.; Camberis, M.; Peignier, A.; Smith, A.A.T.; Johnston, K.; et al. A novel blood-feeding detoxification pathway in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis L3 reveals a potential checkpoint for arresting hookworm development. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Dougall, A.M.; Khoshnejad, M.; Chandrudu, S.; Pearson, M.; Loukas, A.; Toth, I. Peptide-Based Subunit Vaccine against Hookworm Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Recent advances in peptide-based subunit nanovaccines. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Peptide-based synthetic vaccines. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Non-invasive mucosal vaccine delivery: Advantages, challenges and the future. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marasini, N.; Giddam, A.K.; Khalil, Z.G.; Hussein, W.M.; Capon, R.J.; Batzloff, M.R.; Good, M.F.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. Double adjuvanting strategy for peptide-based vaccines: Trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles for lipopeptide delivery. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 3223–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faruck, M.O.; Zhao, L.; Hussein, W.M.; Khalil, Z.G.; Capon, R.J.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Polyacrylate–Peptide Antigen Conjugate as a Single-Dose Oral Vaccine against Group A Streptococcus. Vaccines 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrudu, S.; Bartlett, S.; Khalil, Z.G.; Jia, Z.; Hussein, W.M.; Capon, R.J.; Batzloff, M.R.; Good, M.F.; Monteiro, M.J.; Skwarczynski, M.; et al. Linear and branched polyacrylates as a delivery platform for peptide-based vaccines. Ther. Deliv. 2016, 7, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.S.A.I.T.S.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Lipids as Activators of Innate Immunity in Peptide Vaccine Delivery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2887–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuar, A.; Li, Z.; Shibu, M.A.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Y.; Shalash, A.O.; Khalil, Z.G.; Capon, R.J.; Hussein, W.M.; Toth, I.; et al. Poly(hydrophobic amino acid)-Based Self-Adjuvanting Nanoparticles for Group A Streptococcus Vaccine Delivery. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Zhao, G.; Boer, J.C.; Ozberk, V.; Azuar, A.; Cruz, J.G.; Giddam, A.K.; Khalil, Z.G.; Pandey, M.; Shibu, M.A.; et al. Poly(amino acids) as a potent self-adjuvanting delivery system for peptide-based nanovaccines. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, S.; Skwarczynski, M.; Xie, X.; Toth, I.; Loukas, A.; Eichenberger, R.M. Development of natural and unnatural amino acid delivery systems against hookworm infection. Precis. Nanomed. 2020, 3, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, S.; Eichenberger, R.M.; Nevagi, R.J.; Ghaffar, K.A.; Marasini, N.; Dai, Y.; Loukas, A.; Toth, I.; Skwarczynski, M. Lipopeptide-Based Oral Vaccine Against Hookworm Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 221, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Walker, J.; Jackson, D.C. Identification of canine helper T-cell epitopes from the fusion protein of canine distemper virus. Immunology 2001, 104, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberis, M.; Le Gros, G.; Urban, J., Jr. Animal model of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and Heligmosomoides polygyrus. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2003, 55, 19.12.1–19.12.27. [Google Scholar]
- Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Lipid-Core-Peptide System for Self-Adjuvanting Synthetic Vaccine Delivery. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 751, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, G.; Greindl, M.; Palmberger, T.F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Insulin-loaded poly(acrylic acid)-cysteine nanoparticles: Stability studies towards digestive enzymes of the intestine. Drug Deliv. 2009, 16, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.J.; Anwer, K.; Jamil, S.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Ali, B.E.; Ahmad, M.M. Enhanced oral bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: Pharmacokinetic bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in diabetic rats. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Yang, S.; Kong, J.; Dong, A.; Yu, S. Obtaining information about protein secondary structures in aqueous solution using Fourier transform IR spectroscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjit, N.; Zhan, B.; Hamilton, B.; Stenzel, D.; Lowther, J.; Pearson, M.; Gorman, J.; Hotez, P.; Loukas, A. Proteolytic Degradation of Hemoglobin in the Intestine of the Human HookwormNecator americanus. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.W.; Weaver, J.L. Secondary structure of substance P bound to liposomes in organic solvents and in solution from Raman and CD spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 2505–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Wallace, B.A. Circular dichroism spectroscopy of membrane proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4859–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerker, M.; Farone, W.A.; Matijevic, E. Applicability of Rayleigh-Gans Scattering to Spherical Particles. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1963, 53, 758–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A. Transfer of immunity to Ancylostoma caninum infection in pups by serum and lymphoid cells. Immunology 1967, 12, 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sarles, M.P.; Taliaferro, W.H. The local points of defense and the passive transfer of acquired immunity to Nippostrongylus muris in rats. J. Infect. Dis. 1936, 59, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalash, A.O.; Becker, L.; Yang, J.; Giacomin, P.; Pearson, M.; Hussein, W.M.; Loukas, A.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Oral Peptide Vaccine against Hookworm Infection: Correlation of Antibody Titers with Protective Efficacy. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091034
Shalash AO, Becker L, Yang J, Giacomin P, Pearson M, Hussein WM, Loukas A, Skwarczynski M, Toth I. Oral Peptide Vaccine against Hookworm Infection: Correlation of Antibody Titers with Protective Efficacy. Vaccines. 2021; 9(9):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091034
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalash, Ahmed O., Luke Becker, Jieru Yang, Paul Giacomin, Mark Pearson, Waleed M. Hussein, Alex Loukas, Mariusz Skwarczynski, and Istvan Toth. 2021. "Oral Peptide Vaccine against Hookworm Infection: Correlation of Antibody Titers with Protective Efficacy" Vaccines 9, no. 9: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091034
APA StyleShalash, A. O., Becker, L., Yang, J., Giacomin, P., Pearson, M., Hussein, W. M., Loukas, A., Skwarczynski, M., & Toth, I. (2021). Oral Peptide Vaccine against Hookworm Infection: Correlation of Antibody Titers with Protective Efficacy. Vaccines, 9(9), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9091034









