Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation and Production of AAV-HBV WT and AAV-HBV-E(−)
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. AAV-HBV Transduction
2.4. Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination
2.5. Isolation of Lymphocytes from Spleen and Liver
2.6. Detection of HBV-Specific CD8 T Cells by Multimer and Intracellular Cytokine Staining
2.7. Serological and vVirological Analyses
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
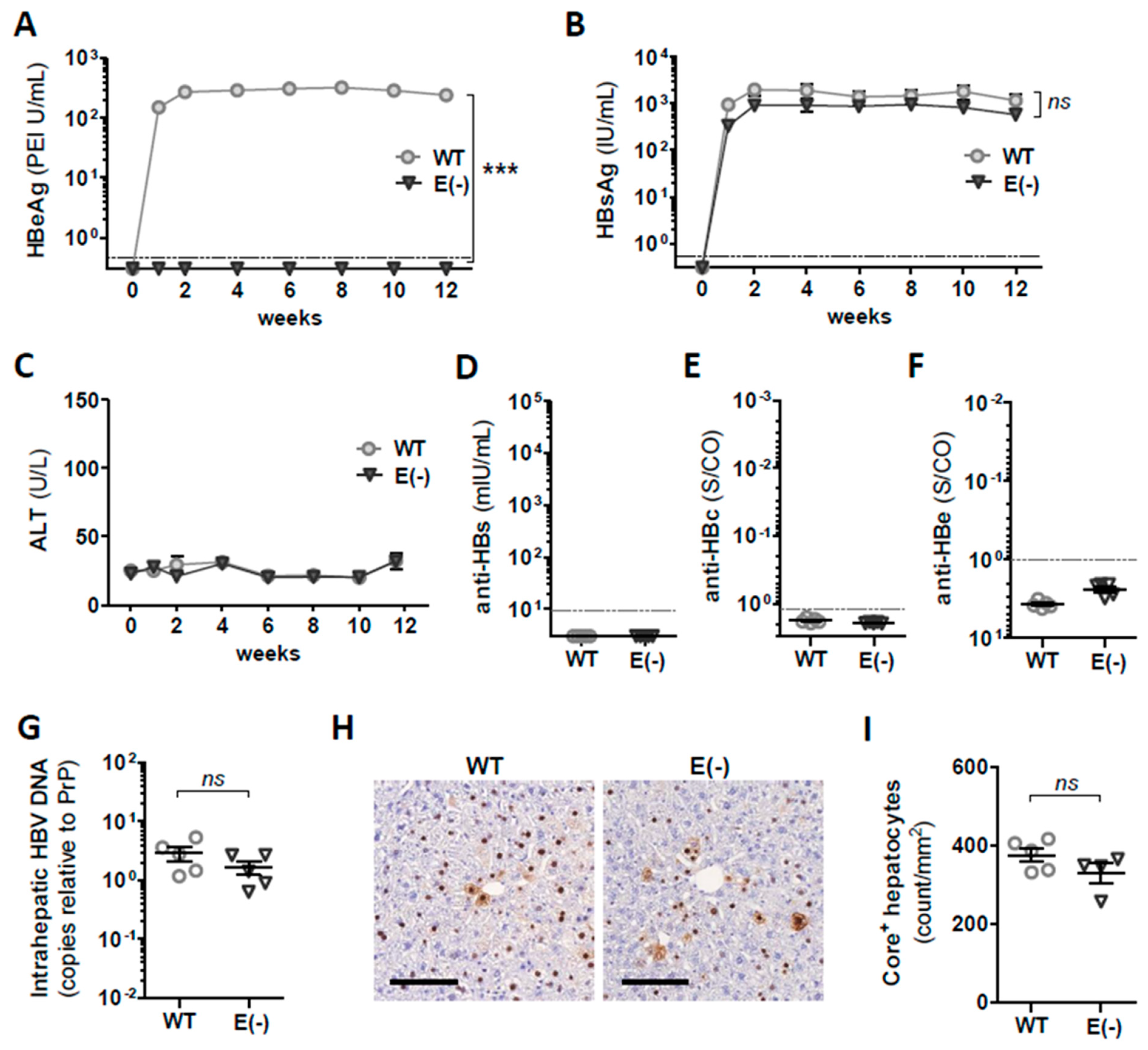
3.1. Generation and In Vivo Characterization of AAV Vectors Encoding 1.3 Overlength WT HBV Genome and Corresponding HBeAg(−) Variant
3.2. TherVacB-Mediated Immunogenicity and Antiviral Efficacy in AAV-HBV Mice Deficient for HBeAg
3.3. TherVacB Induces T Cell Responses in Mice Replicating HBeAg(+) and HBeAg(−) HBV
3.4. Vaccine-Induced T Cell Function Differs in Mice Replicating HBeAg(+) and HBeAg(−) HBV
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hepatitis B Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Liaw, Y.F.; Sheen, I.S.; Chen, T.J.; Chu, C.M.; Pao, C.C. Incidence, determinants and significance of delayed clearance of serum HBsAg in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A prospective study. Hepatology 1991, 13, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; McMahon, B.J.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Wong, J.B.; Ahmed, A.T.; Farah, W.; Almasri, J.; Alahdab, F.; Benkhadra, K.; Mouchli, M.A.; et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2016, 63, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, A.J.; Protzer, U. Targeting Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Cure Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Reignat, S.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Webster, G.J.; McMichael, A.J.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of hepatitis B virus-specific CD8(+) T cells associated with the control of infection. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B.; Ferrari, C.; Pasquinelli, C.; Chisari, F.V. The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients’ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Amadei, B.; Di Vincenzo, P.; Giuberti, T.; Laccabue, D.; Zerbini, A.; Cavalli, A.; Missale, G.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-specific T-cell dysfunction in chronic HBV infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4215–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burton, A.R.; Pallett, L.J.; McCoy, L.E.; Suveizdyte, K.; Amin, O.E.; Swadling, L.; Alberts, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Kennedy, P.T.; Gill, U.S.; et al. Circulating and intrahepatic antiviral B cells are defective in hepatitis B. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4588–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webster, G.J.; Reignat, S.; Brown, D.; Ogg, G.S.; Jones, L.; Seneviratne, S.L.; Williams, R.; Dusheiko, G.; Bertoletti, A. Longitudinal analysis of CD8+ T cells specific for structural and nonstructural hepatitis B virus proteins in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Implications for immunotherapy. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5707–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Bauer, T.; Protzer, U. Therapeutic vaccination for chronic hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Tai, D.I.; Chu, C.M.; Pao, C.C.; Chen, T.J. Acute exacerbation in chronic type B hepatitis: Comparison between HBeAg and antibody-positive patients. Hepatology 1987, 7, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, S.; Jager, C.; Dembek, C.J.; Kosinska, A.D.; Bauer, T.; Stephan, A.S.; Dislers, A.; Mutwiri, G.; Busch, D.H.; Babiuk, L.A.; et al. Protein-prime/modified vaccinia virus Ankara vector-boost vaccination overcomes tolerance in high-antigenemic HBV-transgenic mice. Vaccine 2016, 34, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Kosinska, A.D.; Festag, J.; Bunse, T.; Su, J.; Ringelhan, M.; Imhof, H.; Grimm, D.; Steiger, K.; Mogler, C.; et al. Knockdown of Virus Antigen Expression Increases Therapeutic Vaccine Efficacy in High-Titer Hepatitis B Virus Carrier Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Billaud, J.N.; Sallberg, M.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, J.; Hughes, J.; Milich, D.R. A function of the hepatitis B virus precore protein is to regulate the immune response to the core antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14913–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Kuo, C.F.; Akbari, O.; Ou, J.H. Maternal-Derived Hepatitis B Virus e Antigen Alters Macrophage Function in Offspring to Drive Viral Persistence after Vertical Transmission. Immunity 2016, 44, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liaw, Y.F.; Pao, C.C.; Chu, C.M.; Sheen, I.S.; Huang, M.J. Changes of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in two types of clinical events preceding spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology 1987, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.S.; Chien, R.N.; Yeh, C.T.; Sheen, I.S.; Chiou, H.Y.; Chu, C.M.; Liaw, Y.F. Long-term outcome after spontaneous HBeAg seroconversion in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1522–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carman, W.F.; Jacyna, M.R.; Hadziyannis, S.; Karayiannis, P.; McGarvey, M.J.; Makris, A.; Thomas, H.C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet 1989, 2, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Akarca, U.; Greene, S. Mutations in the pre-core region of hepatitis B virus serve to enhance the stability of the secondary structure of the pre-genome encapsidation signal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4077–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, K.; Huang, J.K.; Wands, J.R.; Obata, H.; Liang, T.J. Association of hepatitis B viral precore mutations with fulminant hepatitis B in Japan. Virology 1991, 185, 460–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Ehata, T.; Yokosuka, O.; Hosoda, K.; Ohto, M. Mutations in the precore region of hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with fulminant and severe hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1699–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, J.; Yuen, L.; Rosenberg, G.; Wong, D.; Littlejohn, M.; Jackson, K.; Gaggar, A.; Kitrinos, K.M.; Subramanian, G.M.; Marcellin, P.; et al. Deep sequencing shows that HBV basal core promoter and precore variants reduce the likelihood of HBsAg loss following tenofovir disoproxil fumarate therapy in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2017, 66, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetto, M.R.; Giarin, M.; Saracco, G.; Oliveri, F.; Calvo, P.; Capra, G.; Randone, A.; Abate, M.L.; Manzini, P.; Capalbo, M.; et al. Hepatitis B virus unable to secrete e antigen and response to interferon in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, M.W.; Piratvisuth, T.; Lau, G.K.; Marcellin, P.; Chow, W.C.; Cooksley, G.; Luo, K.X.; Paik, S.W.; Liaw, Y.F.; Button, P.; et al. HBeAg and hepatitis B virus DNA as outcome predictors during therapy with peginterferon alfa-2a for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2008, 47, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penaud-Budloo, M.; Francois, A.; Clement, N.; Ayuso, E. Pharmacology of Recombinant Adeno-associated Virus Production. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2018, 8, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Moeed, A.; Kallin, N.; Festag, J.; Su, J.; Steiger, K.; Michel, M.L.; Protzer, U.; Knolle, P.A. Synergy of therapeutic heterologous prime-boost hepatitis B vaccination with CpG-application to improve immune control of persistent HBV infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.C.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, C.L.; Yang, W.T.; Tsai, C.S.; Kuo, S.F.; Verbree, F.C.; Su, T.H.; Wang, C.C.; et al. Higher proportion of viral basal core promoter mutant increases the risk of liver cirrhosis in hepatitis B carriers. Gut 2015, 64, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, G.M.; Lee, Y.I.; Suh, D.J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, Y.I. Gradual accumulation of mutations in precore core region of HBV in patients with chronic active hepatitis: Implications of clustering changes in a small region of the HBV core region. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 48, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Stadler, D.; Lucifora, J.; Reisinger, F.; Webb, D.; Hosel, M.; Michler, T.; Wisskirchen, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. Interferon-gamma and Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Produced by T Cells Reduce the HBV Persistence Form, cccDNA, Without Cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogawa, M.; Furuichi, Y.; Chisari, F.V. Oscillating CD8(+) T cell effector functions after antigen recognition in the liver. Immunity 2005, 23, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wherry, E.J.; Jin, B.; Xu, B.; Zou, Z.S.; Zhang, S.Y.; Li, B.S.; Wang, H.F.; Wu, H.; et al. Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus-specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1938–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallett, L.J.; Davies, J.; Colbeck, E.J.; Robertson, F.; Hansi, N.; Easom, N.J.W.; Burton, A.R.; Stegmann, K.A.; Schurich, A.; Swadling, L.; et al. IL-2(high) tissue-resident T cells in the human liver: Sentinels for hepatotropic infection. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1567–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosinska, A.D.; Festag, J.; Mück-Häusl, M.; Festag, M.M.; Asen, T.; Protzer, U. Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080841
Kosinska AD, Festag J, Mück-Häusl M, Festag MM, Asen T, Protzer U. Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection. Vaccines. 2021; 9(8):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080841
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosinska, Anna D., Julia Festag, Martin Mück-Häusl, Marvin M. Festag, Theresa Asen, and Ulrike Protzer. 2021. "Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection" Vaccines 9, no. 8: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080841
APA StyleKosinska, A. D., Festag, J., Mück-Häusl, M., Festag, M. M., Asen, T., & Protzer, U. (2021). Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection. Vaccines, 9(8), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9080841






