Abstract
Chronic hepatitis B affects more than 250 million individuals worldwide, putting them at risk of developing liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. While antiviral immune responses are key to eliminating hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections, insufficient antiviral immunity characterized by failure to eliminate HBV-infected hepatocytes is associated with chronic hepatitis B. Prophylactic vaccination against hepatitis B successfully established protective immunity against infection with the hepatitis B virus and has been instrumental in controlling hepatitis B. However, prophylactic vaccination schemes have not been successful in mounting protective immunity to eliminate HBV infections in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Here, we discuss the current knowledge on the development and efficacy of therapeutic vaccination strategies against chronic hepatitis B with particular emphasis on the pathogenetic understanding of dysfunctional anti-viral immunity. We explore the development of additional immune stimulation measures within tissues, in particular activation of immunogenic myeloid cell populations, and their use for combination with therapeutic vaccination strategies to improve the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination against chronic hepatitis B.
1. The Challenge of Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) infection affects almost one-third of the world’s population, and in most cases, is cleared by host anti-viral immunity [1,2]. However, more than 250 million individuals suffer from chronic hepatitis B [1], which puts them in danger of developing liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Dysfunctional anti-viral immunity is considered the cause of persistent viral infection with virus-specific effector immune cells lacking the capacity to eliminate HBV infected hepatocytes, which is characterized by failure to achieve seroconversion to anti-HBs and the establishment of broad and strong HBV-specific T cell response [2,3]. Nevertheless, liver damage during acute and chronic hepatitis B is caused by the host´s immune response against HBV [2,4]. This suggests that a delicate balance exists between mechanisms promoting persistent infection of hepatocytes with HBV and the host´s HBV-specific immune response. Along this line, spontaneous clearance of persistent HBV infection is observed in some patients with chronic hepatitis B [5], which supports the notion that persistent HBV infection and chronic hepatitis B may be therapeutically targeted by strengthening HBV-specific immunity.
Currently, however, efficient direct antiviral therapies using nucleoside inhibitors are used for treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B, which inhibit HBV replication but fail to induce protective HBV-specific immunity. The main reason for direct antiviral therapies to fail to achieve a cure from chronic hepatitis B, is the establishment of a persistent form in HBV-infected hepatocytes, the so-called covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) that serves as an extrachromosomal template for viral replication [6,7]. Despite successful control of HBV replication by direct antiviral drugs, treatment interruption is accompanied by re-activating cccDNA and initiation of viral replication, leading again to chronic viral hepatitis. In contrast, chronic hepatitis C is successfully treated by direct acting antiviral agents [8], but this sensitivity towards antiviral therapy is based on the strict requirement of the hepatitis C virus, as an RNA virus, to continuously replicate [9]. This is not the case for HBV, which can persist via its cccDNA without replicating at all. However, HBV cccDNA is sensitive to the anti-viral activity of cytokines, such as interferons and lymphotoxin [10], but these mediators fail to eliminate all HBV cccDNA from infected hepatocytes for reasons that remain to be discovered [6,11,12]. Current direct antiviral treatment options were recently addressed in expert reviews [13,14,15].
The only way to achieve control of persistent HBV infection and cure patients from chronic hepatitis B is to eliminate HBV-infected hepatocytes or at least eradicate the HBV cccDNA pool from the liver. Thus, an urgent medical need exists to develop novel immune therapies to strengthen HBV-specific effector responses in order to cure patients with chronic hepatitis B from the virus. A successful therapeutic vaccination against HBV would also provide a cure from infection with the more pathogenic hepatitis delta virus, which requires HBV coinfection to replicate, and against which few therapeutic options exist [16]. Furthermore, therapeutic vaccinations could prevent the occurrence of the sincere sequelae of continuous immune-mediated liver damage during chronic viral hepatitis that can result in liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
2. Immunopathogenesis of HBV Infection and Chronic Viral Hepatitis
Understanding the immunopathogenesis of chronic hepatitis B is key for a rationale development of novel immune-based therapies. HBV is a strictly hepatotropic virus that selective targets hepatocytes and selectively replicates within hepatocytes [2]. This strict hepatotropism of HBV is most likely one of the reasons why mounting of protective immunity poses particular challenges for the host´s immune response. Successful immunity against HBV infection is characterized by induction of a strong CD4 and CD8 T cell response, specific for many different viral epitopes and presence of effector CD8 T cells, as well as induction of B cell immunity against HBV that is characterized by neutralizing antibodies against HBV surface antigens [17,18,19]. In contrast, development of a persistent HBV infection is associated with a dysfunctional immune response against HBV [2,20]. Several factors have been associated with induction of persistent HBV infection (see Figure 1).
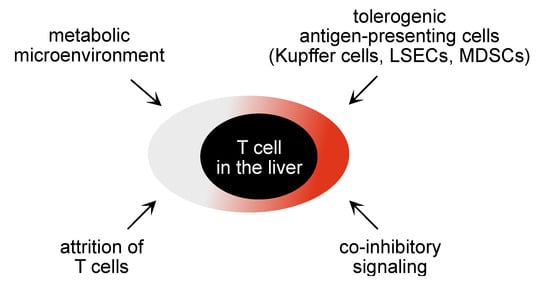
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of factors locally influencing T cell function in the liver.
First, HBV infection fails to elicit strong innate immunity and inflammation, which is necessary for maturation of antigen-presenting cells to induce protective immunity and for virus-specific immune effector cell populations to selectively localize to the site of infection. Lacking pattern recognition and lacking induction of cell-intrinsic immunity by HBV has been recognized as a major obstacle in raising anti-viral immunity [21,22,23,24], since inflammation is required for functional maturation of antigen presenting cells to mount protective immunity [25]. Activation of pattern-recognition pathways and induction of an inflammatory environment is therefore likely to play an important role in the generation of strong antiviral immunity in the liver.
Second, the restriction of HBV replication and gene expression to hepatocytes requires cells that use endocytosis for antigen acquisition and present HBV antigens on MHC molecules to virus-specific T cells. While antigen-uptake via receptor-mediated endocytosis is well established for induction of MHC-II restricted CD4 T cell immunity, presentation of endocytosed antigens on MHC-I molecules to CD8 T cells requires special competence of the antigen-presenting cell for a process called cross-presentation [26]. Thus, only certain professional antigen-presenting cells, such as functionally matured monocytes, can execute this cross-presentation of antigens released from virus-infected hepatocytes [27]. Furthermore, a complex interaction between different immune cell populations in distinct micro-anatomic niches within lymphoid tissues is required to generate antigen-specific CD8 T cells through cross-presenting dendritic cells [28]. Overall, this is believed to cause a failure to properly prime HBV-specific immunity, which then results in a dysfunctional HBV-specific immune response.
Third, the liver microenvironment is known for its tolerogenic function and contributes to down-tuning of effector T cell responses in the liver [29]. Liver-resident tolerogenic antigen presenting cells, such as liver dendritic cells and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), render CD4 and CD8 T cells dysfunctional, thereby attenuating anti-viral T cell immunity locally in the liver [30,31,32,33]. Antigen-presentation by hepatocytes themselves lead to clonal elimination of antigen-specific T cells and may thereby contribute to the attrition of T cell responses [34,35]. Hepatic stellate cells engage in veto function preventing local activation of specific T cells through professional antigen-presenting cells in the liver, and liver macrophages may further contribute to development of T cell dysfunction [36,37].
Fourth, regulatory immune cell populations in the liver such as regulatory T cells, but also myeloid-cell derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are present in the liver microenvironment and contribute to local inhibition of T cell immunity [38,39,40,41]. Fifth, the liver micromilieu is particularly rich in regulatory mediators, such as IL-10 or TGF-β, derived from local immune cell populations in the liver, such as Kupffer cells, dendritic cells, or hepatic stellate cells, and may contribute to local skewing of virus-specific immune effector functions [42,43,44].
Fifth, the continuous exposure to antigen appears to be a key driver of T cell dysfunction. For experimental viral infections, such as lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, the mechanisms mediating this dysfunction of virus-specific T cells have been described as a state of exhaustion that is determined by the exhaustion promoting transcription factor TOX [45,46,47,48]. In chronic hepatitis B, virus-specific T cells are also dysfunctional, but the mechanisms determining their dysfunction remain to be discovered. Recently it was found that HBV-specific T cells in chronic hepatitis suffer from metabolic disturbances that can affect their effector functions [49,50]. Thus, cell-intrinsic regulation of effector function of virus-specific T cells may also contribute to the lack of immune control of HBV infection.
Thus, a large number of immune inhibitory mechanisms operate locally in the liver to control immune effector cell functions and will have to be taken into account when developing novel immune therapies that aim to increase immune effector functions in the liver. Moreover, target cell killing in the liver also seems to be subject to regulation by target cells themselves. Expression of antigens at low levels on MHC-I molecules by hepatocytes and a lack of MHC-II on hepatocytes unless there is significant inflammation protects them from effector cell killing [51], and may thus establish a further level of T cell dysfunction in the liver. Finally, continuous exposure towards antigens expressed in the liver for prolonged periods of time is associated with development of immune tolerance, which includes generation of regulatory immune cell populations [52]. Taken together, numerous mechanisms impede generation as well as execution of virus-specific effector T cells.
Beyond alterations in T cell immunity, there are also contributions of HBV itself to persistence of infection. As already mentioned, the establishment of the extrachromosomal persistence form, the covalently, closed circular HBV DNA is associated with viral persistence. HBV cccDNA is extraordinarily stable and may serve as template for viral gene expression and initiate a virus rebound even long time after the active HBV replication has ceased [6]. It remains an open question whether a shut-down of HBV gene expression upon cytokine exposure may help infected hepatocytes to escape from killing by virus-specific effector T cells [53]. Presentation of antigens on MHC I molecules is typically related to ongoing gene expression and processing of defective ribosomal products for presentation on MCH-I molecules [54,55], so the consequences of stalling HBV gene expression for subsequent recognition by virus-specific effector T cells remains unclear. Furthermore, under immune pressure HBsAg-escape mutations develop, that can contribute to the failure of immune control against HBV infection even after vaccination [56]. Since depletion of B cells by anti-CD20 therapy leads to reactivation of HBV infection [57], continuous virus control by virus-specific B cells appears to be an important part of immune control of HBV infection. However, recent studies identified broadly neutralizing antibodies that can overcome these escape mutants and provide protection [58].
On the other hand, there is a large amount of viral antigens expressed in hepatocytes upon active viral replication. Recent studies indicate that expression of these viral antigens in the liver rather that secretion of viral antigens and presentation on non-hepatic antigen presenting cells induces antigen-specific immune tolerance [59,60].
Finally, mutated viral proteins may contribute to a viral immune escape if T cell recognition of infected hepatocytes is impaired. Although HBV is a DNA virus, it replicates via reverse transcription allowing mutations in the viral genome. Due to the very compact viral genome with largely overlapping open reading frames, however, most of the resulting variants are defective and immune escape variants remain rare.
Thus, a combination of factors influences the immune response to infection with HBV, generation of virus-specific effector T cells and elimination of HBV-infected hepatocytes. It is worth noting that clearance of HBV in a natural host, i.e., chimpanzees, requires several months [61,62], which is clearly distinct from the immune response to other viruses like influenza targeting lung tissue where rapid immune responses are observed [63]. This requirement for a prolonged time period to clear infected hepatocytes from the liver not only after HBV, but also after HAV or HCV infection points towards particular obstacles that have to be overcome by the host´s immune response, to mount virus-specific immunity and eliminate virus-infected hepatocytes.
3. Strategies for Therapeutic Vaccination against Chronic Hepatitis B
Different approaches have been used to establish a therapeutic vaccination against chronic hepatitis B. These were most often based on novel insights into the immunopathogenesis of HBV infection and novel technologies to improve the strengths of virus-specific immunity. However, one of the major problems in developing immune therapies against chronic hepatitis B is the lack of a suitable animal model that faithfully reflects all features of HBV infection in humans [64]. Human HBV shows strict species restriction. Only chimpanzees are susceptible for HBV infection, and important discoveries were made on HBV infectiousness and anti-viral immune responses in this model [4,62,65], before research was stopped for ethical reasons. While infection models exist for individual animal species with their particular hepatitis B viruses, such as, e.g., the duck and duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV), the woodchuck and woodchuck hepatitis B virus (WHBV), these models are restricted by important differences between the viruses and human HBV, with antigen being non-compatible as well as marked differences in immune responses and a lack of tools to study virus-specific immunity. Mice, as preferred preclinical animal models to study immune pathogenesis, are also employed for the study of HBV pathogenesis. However, to deliver HBV into hepatocytes in a species were infection is not possible, different strategies have been developed: first, genetic manipulation (transgenic mice expressing the HBV genome); second, hydrodynamic injection of HBV genomes or third, viral carriers for delivery of HBV genomes into hepatocytes [66,67]. Thus, most of our knowledge on the immunopathogenesis in persistent HBV infection and experimental approaches targeting particular immune mechanisms to control persistent infection have been generated in non-optimal models of HBV infection.
Numerous clinical trials have been performed in patients with chronic hepatitis B to explore the importance of particular concepts how to re-install protective immunity once persistent HBV infection had established [68,69,70]. In prophylactic vaccines, an emphasis is on the induction of immunity against the surface antigens of HBV in order to elicit neutralizing anti-HBs antibodies and prevent infection. The induction of HBs-specific CD8 T cells that target and eliminate HBsAg-expressing infected hepatocytes is less important. In contrast, in therapeutic vaccination also other viral antigens, in particular, HBcore antigen and the viral polymerase are targeted to increase the breadth of the virus-specific effector T cell response and a focus is on the induction of potent CD4 and CD8 T cell responses. In general, all strategies for developing therapeutic vaccination against chronic hepatitis B included a lowering of viral replication.
In the following, we will review the different strategies used for development of therapeutic vaccination for chronic hepatitis B and their outcome.
4. Strengthening the Immunogenicity of Vaccination against Chronic Hepatitis B
The conceptual idea behind the strategy for therapeutic vaccination lies in the assumption that a defective induction of HBV-specific B and T cell immunity is responsible for the lack of virus clearance [69,71,72,73]. Numerous approaches have been taken to increase the immunogenicity of vaccines against chronic hepatitis B, and thereby mount strong virus-specific immunity against the surface, nucleocapsid, or polymerase antigens of HBV that should then control HBV infection by induction of virus-specific neutralizing antibodies and elimination of virus-infected hepatocytes through effector T cells. The first attempts to establish therapeutic vaccination against chronic hepatitis B in patients were undertaken by increasing the number of administrations of vaccines, which were originally developed for use as prophylactic vaccines and, therefore, targeted HBsAg. Most vaccines contain alum as adjuvant, which has been shown to involve induction of innate immunity through still rather ill-defined pathways [74] and induces a strong Th2 bias. In an attempt to increase immunogenicity, prophylactic vaccines were injected at different sites and in particular intradermally, because local intradermal activation of immune responses is considered to be superior [75]. In addition, T cell-targeted vaccines or combinations of HBsAg and HBcAg as immunogens were investigated for their efficacy of therapeutic vaccination [76,77,78]. However, all these approaches failed to achieve a cure in patients with chronic hepatitis B [59,70,71].
The key for the success of prophylactic recombinant vaccines is the use of adjuvants [74] that are the basis for providing signal 3 to antigen presenting cells and induction of local inflammation and, therefore, properly prime T cell immunity. Hereby alum, by inducing a strong Th2 bias, prevents the induction of effector T cell responses. Using other adjuvants, in combination with particulate HBV antigens, have shown promising results at least in preclinical models [79]. The discovery of ligands for immune sensory molecules, such as ligands for TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, and cyclic-di-AMP as a ligand for the cGAS/STING pathway, as well as ligands for the cytosolic RNA-recognition receptor RIG-I or MDA-5, triggered substantial interest in their therapeutic use for chronic hepatitis B. Adjuvants serve the purpose of triggering inflammation and, more specifically, functional maturation of dendritic cells, thereby increasing the strength of the immune response against recombinant antigens. For instance, TLR9 is expressed on professional antigen-presenting B and dendritic cells, and ligands of TLR9 used as an adjuvant may therefore have a positive effect on the immunogenicity against antigens included in a vaccine [74,80]. Recently, a new prophylactic vaccine against hepatitis B was brought to the market that includes a TLR9-ligand as adjuvant showing superiority to alum-based vaccines [81]. It will be interesting to see whether it will show efficacy in a therapeutic setting against chronic hepatitis B.
Given the constant exposure of the persistently infected host to HBV antigens, in particular high levels of circulating HBsAg, it was reasoned that application of adjuvants might suffice to trigger HBV-specific immunity [74]. Along this line, oral delivery of TLR-ligands, considered to lead through the portal venous drainage of the gut to delivery of TLR-ligands to the liver, was evaluated as a treatment option for chronic hepatitis B [82,83]. Moreover, ligands for cytosolic immune sensory receptors, such as for the helicase RIG-I, were shown to be effective in controlling experimental HBV infection [84,85,86]. In clinical trials, neither control of HBV nor cure from chronic hepatitis B has been achieved using TLR agonists so far, indicating that the application of a TLR agonist may not result in induction of HBV-specific immunity, and triggering innate immunity and inflammation alone may not be sufficient to overcome immune tolerance and achieve control of chronic hepatitis B. However, alternative pattern-recognition receptor agonists triggering TLR8, Rig-I, or STING are currently evaluated in clinical trials; it will be interesting to see the outcome.
The choice of the immunogen in a vaccine is also of key importance. Whereas prophylactic vaccines only need to elicit neutralizing antibodies directed against the HBV envelop proteins, therapeutic vaccines most likely need to induce a broad T cell response and, thus, should include other HBV antigens, such as HBV core and polymerase [70]. An interesting approach identified the HBV X protein as a valuable target for vaccinations using a preclinical model of persistent HBV infection [87]. The HBV X protein is expressed at much lower levels than other viral proteins and its low abundance in the infected liver may provide a better target for a vaccination, since high antigen expression levels of model viruses are often associated with development of T cell exhaustion [88]. However, hepatocytes with their low-level MHC-I expression may also fail to present any peptide from this small X protein.
A further approach to increase immunogenicity of vaccines in the setting of chronic hepatitis B is the development of heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategies [70]. The combinations of adjuvanted protein-based vaccines, DNA vaccination, and vector-based immunizations have been tested in various preclinical models of persistent HBV infections, and have yielded promising results [89,90,91]. Conceptually, development of vaccines using viral vectors to deliver HBV antigens and to elicit strong anti-viral immunity provides an interesting approach for development of a therapeutic vaccine. Viral vectors employed for this purpose include adenoviral vectors (mostly non-human adenoviral vectors e.g., from chimpanzee), yellow fever virus vectors, and modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA)-based vectors [89,91,92]. The combination of a protein prime followed by an MVA-boost, referred to as TherVacB, has proven to be very successful in different preclinical models of persistent HBV infection [59,91,93], making it an excellent candidate for a therapeutic vaccination strategy to cure HBV. A key advantage of heterologous prime-boost vaccination is the induction of both, CD8 and CD4 T cell responses. Since CD4 T cells are instrumental for overcoming experimental chronic infection and have been shown to be associated with clearance of chronic hepatitis B in patients [18,94], the concomitant induction of anti-viral CD8 and CD4 T cell immunity may be critical for vaccine efficacy. Different combinations of prime and boost vaccinations are currently tested in clinical trials for efficacy in overcoming HBV-specific immune tolerance and control of chronic hepatitis B (Table 1).

Table 1.
List of current clinical trials investigating heterologous prime boost therapeutic vaccines against chronic hepatitis B.
The necessity for induction of potent HBV-specific immunity to overcome HBV-specific tolerance in the setting of chronic hepatitis B [2,95] may be best addressed by heterologous vaccination strategies. Such heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategies have proven beneficial for increasing immunity in other viral infection, such as SARS-CoV-2 [96,97]. The ongoing clinical trials will provide us with important information on the potency of heterologous prime-boost therapeutic vaccination in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
5. Local Support for T Cell Immunity in the Liver to Increase Efficacy of Therapeutic Vaccination
The liver has unique functions of as tolerogenic organ [2,29,71,98], and may curtail the effector function of T cells generated by a therapeutic vaccination, once they recognize their antigen in the liver. Such a threat of reducing the efficiency of therapeutic vaccination might not be possible to address by increasing the immunogenicity of therapeutic vaccination, but may require additional measures to enable effector T cells locally in the liver to control viral replication and to eliminate virus-infected cells. Three different approaches have surfaced over the last years that have the potential to increase the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination
Combination of therapeutic vaccination with inhibition of co-inhibitory receptor signaling in T cells may be an option to increase efficacy of vaccination. Expression of PD1 was shown to be increased in virus-specific T cells during persistent infection with different viruses and blockade of PD-1 was shown to increase the effector function of HBV-specific T cells from patients with chronic hepatitis B or in preclinical models [99,100,101,102,103]. However, anti-PD-1 treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma did not reveal an effect of checkpoint inhibition on restoration of HBV-specific immunity and consequent reduction in viral replication [104]. Notwithstanding this lack of an immunity-restoring effect of anti-PD-1 therapy, the combination of therapeutic vaccination with checkpoint inhibition may be beneficial to overcome the local tolerogenic microenvironment of the liver, where high expression levels of PD-L1 are observed [33,105]. Currently, one clinical trial explores the potential of an anti-PD-1 antibody in the context of therapeutic vaccination in chronic hepatitis B patients (Table 1).
High-level antigen expression has been identified as a key factor in reducing the efficacy of effector T cell responses [88,106] and has been suspected to play a role in attenuating HBV-specific immunity during chronic infection [95,106,107]. Recently, we have demonstrated that reduction of HBV-replication and gene expression through an siRNA or shRNA approach before therapeutic vaccination in two different models of persistent HBV infection in mice increased the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination, to eliminate HBV-expressing hepatocytes and achieve control of persistent infection [59]. Of note, neither induction of neutralizing antibodies reducing circulating HBsAg levels nor siRNA/shRNA-mediated knockdown of HBV gene expression alone was able to restore HBV-specific immunity [59]. This strengthens the notion that local inhibition of T cell effector function in the liver adds a separate hurdle to T cells generated by therapeutic vaccination to achieve control over persistent infection.
Although the liver is known for its tolerogenic function and has the capacity to curtail T cell effector functions, strong immunity can be built in the liver against pathogens, which seems to be strongly linked to the composition of myeloid cells in the liver [108]. In particular, replacement of tolerogenic liver macrophages (Kupffer cells), through pro-inflammatory monocytes, is correlated to the induction of immunity in the liver [109]. Recently, a distinct population of Kupffer cells was identified that is capable of cross-presenting hepatocyte-derived antigens to CD8 T cells upon stimulation by IL-2 and, thereby, increase HBV-specific immunity against infected hepatocytes [110].
Importantly, the accumulation of inflammatory monocytes in the liver as a consequence of TLR-induced inflammation leads to a massive expansion of T cells in the liver within dedicated anatomic niches termed iMATEs (intrahepatic myeloid cell aggregates associated with T cell expansion) [111]. The T cells expanding within iMATEs have potent effector potential and are capable of rapidly eliminating virus-infected hepatocytes [111]. Such TLR-induced and myeloid cell-mediated increase in effector T cell numbers in the liver also triggers elimination of hepatocytes expressing transgenes and establishes memory responses [112]. Recently, we have combined therapeutic vaccination and iMATE-induction in a model of persistent HBV infection in mice. The combination of heterologous prime-boost vaccination (HBV antigen prime vaccination followed by MVA-HBV boost vaccination) with iMATE induction leads to increased numbers of HBV-specific effector T cells in the liver [113]. Furthermore, it also improves the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination to eliminate HBV-expressing hepatocytes from the liver and clearing persistent infection [113]. This demonstrates a synergistic activity of therapeutic vaccination followed by local amplification of T cell immunity in the liver (see Figure 2). High numbers of HBV-expressing hepatocytes limit the efficacy of the heterologous prime-boost therapeutic vaccination [91]. The ability of the combination of therapeutic vaccination with iMATE-induced T cell expansion in the liver to control infection, higher levels of HBV infection than that controlled by therapeutic vaccination alone, further strengthens the notion that therapeutic vaccination to generate high numbers of virus-specific effector T cells, presumably in secondary lymphoid tissues and local expansion of T cells in the liver, are two separate mechanisms that synergize to increase the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination against virus-infected hepatocytes in the liver.
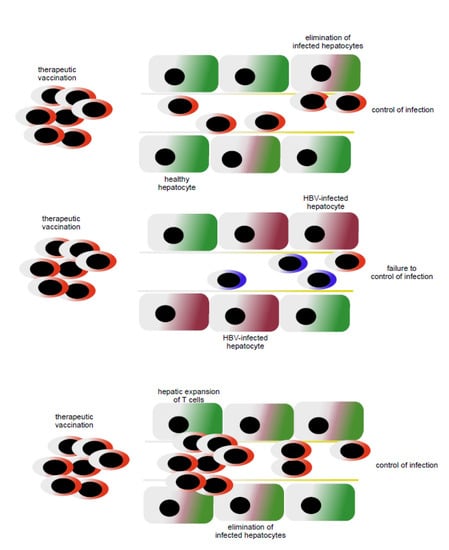
Figure 2.
Virus-specific T cells generated by therapeutic vaccination in lymphoid tissues recognize virus-infected hepatocytes and eliminate infection if the numbers of hepatocytes are limited (upper panel), whereas therapeutic vac-cination fails to control viral infection if the numbers of hepatocytes are too high (middle panel). Combination of in-duction of virus-specific T cells in lymphoid tissue through therapeutic vaccination and local expansion of T cells in the liver acts synergistically to achieve control of infection (bottom panel).
In summary, heterologous prime-boost vaccination strategies employ synergistic principles to increase the efficacy of vaccinations against chronic viral infections. Opportunities for a further increase in vaccine efficacy may lay in the combination of local amplification of vaccine-induced immune responses, such as the above-mentioned boosting of vaccine-induced T cell immunity by increasing the strength of T cell immunity locally in the liver. Furthermore, improvement of hepatic targeting and delivery strategies for molecules boosting T cell immunity in the liver may provide further benefits for overcoming immune tolerance during chronic inflammation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.A.K. and U.P.; writing—original draft preparation, P.A.K.; writing—review and editing, L.-R.H., A.K., D.W. and U.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), grant number 272983813-TRR179.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- MacLachlan, J.H.; Cowie, B.C. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U.; Maini, M.K.; Knolle, P.A. Living in the liver: Hepatic infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Thimme, R. Hepatic immune regulation and its involvement in viral hepatitis infection. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.I.; Lee, M.H.; Lu, S.N.; Jen, C.L.; Wang, L.Y.; You, S.L.; Iloeje, U.H.; Chen, C.J.; Group, R.-H.S. Incidence and determinants of spontaneous hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance: A community-based follow-up study. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ploss, A. Mechanism of Hepatitis B Virus cccDNA Formation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.; Negro, F.; Aghemo, A.; Berenguer, M.; Dalgard, O.; Dusheiko, G.; Marra, F.; Puoti, M.; Wedemeyer, H. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C: Final update of the series. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1170–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. Unravelling hepatitis C virus replication from genome to function. Nature 2005, 436, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucifora, J.; Xia, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Zhang, K.; Stadler, D.; Cheng, X.; Sprinzl, M.F.; Koppensteiner, H.; Makowska, Z.; Volz, T.; et al. Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA. Science 2014, 343, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M. The Role of cccDNA in HBV Maintenance. Viruses 2017, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucifora, J.; Protzer, U. Attacking hepatitis B virus cccDNA--The holy grail to hepatitis B cure. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsounis, E.P.; Tourkochristou, E.; Mouzaki, A.; Triantos, C. Toward a new era of hepatitis B virus therapeutics: The pursuit of a functional cure. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2727–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.G.; Villeret, F.; Testoni, B.; Zoulim, F. Can we cure hepatitis B virus with novel direct-acting antivirals? Liver Int. 2020, 40 (Suppl. 1), 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggie, S.; Lok, A.S. New Therapeutics for Hepatitis B: The Road to Cure. Annu. Rev. Med. 2021, 72, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Neumann-Haefelin, C.; Lampertico, P. Hepatitis D virus in 2021: Virology, immunology and new treatment approaches for a difficult-to-treat disease. Gut 2021, 70, 1782–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B.; Nascimbeni, M. Immunology of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Wan, X.; Fu, X.; Mao, Q.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma profile of HBV-specific CD4 T cells is associated with liver damage and viral clearance in chronic HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, U.S.; McCarthy, N.E. CD4 T cells in hepatitis B virus: "You don’t have to be cytotoxic to work here and help". J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehermann, B. Pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis: Differential roles of T cells and NK cells. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.F.; Chisari, F.V. Stealth and cunning: Hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Isogawa, M.; Chisari, F.V. Host-virus interactions in hepatitis B virus infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 36, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosel, M.; Quasdorff, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Webb, D.; Zedler, U.; Broxtermann, M.; Tedjokusumo, R.; Esser, K.; Arzberger, S.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xia, Y.; Serti, E.; Block, P.D.; Chung, M.; Chayama, K.; Rehermann, B.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B virus evades innate immunity of hepatocytes but activates cytokine production by macrophages. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1779–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shortman, K.; Naik, S.H. Steady-state and inflammatory dendritic-cell development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurts, C.; Robinson, B.W.; Knolle, P.A. Cross-priming in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.J.; Haniffa, M.; Kennedy, P.T.; Ho, Z.Z.; Boni, C.; Shin, A.; Banu, N.; Chia, A.; Lim, S.G.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Mobilizing monocytes to cross-present circulating viral antigen in chronic infection. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 3766–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickhoff, S.; Brewitz, A.; Gerner, M.Y.; Klauschen, F.; Komander, K.; Hemmi, H.; Garbi, N.; Kaisho, T.; Germain, R.N.; Kastenmuller, W. Robust Anti-viral Immunity Requires Multiple Distinct T Cell-Dendritic Cell Interactions. Cell 2015, 162, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.W.; Knolle, P.A. Antigen-presenting cell function in the tolerogenic liver environment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 753–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Creus, A.; Abe, M.; Lau, A.H.; Hackstein, H.; Raimondi, G.; Thomson, A.W. Low TLR4 expression by liver dendritic cells correlates with reduced capacity to activate allogeneic T cells in response to endotoxin. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carambia, A.; Frenzel, C.; Bruns, O.T.; Schwinge, D.; Reimer, R.; Hohenberg, H.; Huber, S.; Tiegs, G.; Schramm, C.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. Inhibition of inflammatory CD4 T cell activity by murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limmer, A.; Ohl, J.; Kurts, C.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Reiss, Y.; Groettrup, M.; Momburg, F.; Arnold, B.; Knolle, P.A. Efficient presentation of exogenous antigen by liver endothelial cells to CD8+ T cells results in antigen-specific T-cell tolerance. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, L.; Schurich, A.; Grochtmann, R.; Hegenbarth, S.; Chen, L.; Knolle, P.A. Tolerogenic maturation of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells promotes B7-homolog 1-dependent CD8+ T cell tolerance. Hepatology 2008, 47, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.G.; Zen, M.; Holz, L.; Davis, T.; McCaughan, G.W.; Bertolino, P. The site of primary T cell activation is a determinant of the balance between intrahepatic tolerance and immunity. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, L.E.; Benseler, V.; Bowen, D.G.; Bouillet, P.; Strasser, A.; O’Reilly, L.; d’Avigdor, W.M.; Bishop, A.G.; McCaughan, G.W.; Bertolino, P. Intrahepatic murine CD8 T-cell activation associates with a distinct phenotype leading to Bim-dependent death. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schildberg, F.A.; Wojtalla, A.; Siegmund, S.V.; Endl, E.; Diehl, L.; Abdullah, Z.; Kurts, C.; Knolle, P.A. Murine hepatic stellate cells veto CD8 T cell activation by a CD54-dependent mechanism. Hepatology 2011, 54, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Cheng, L.; Kedl, R.M.; Ju, C. Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2008, 48, 978–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luth, S.; Huber, S.; Schramm, C.; Buch, T.; Zander, S.; Stadelmann, C.; Bruck, W.; Wraith, D.C.; Herkel, J.; Lohse, A.W. Ectopic expression of neural autoantigen in mouse liver suppresses experimental autoimmune neuroinflammation by inducing antigen-specific Tregs. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallett, L.J.; Gill, U.S.; Quaglia, A.; Sinclair, L.V.; Jover-Cobos, M.; Schurich, A.; Singh, K.P.; Thomas, N.; Das, A.; Chen, A.; et al. Metabolic regulation of hepatitis B immunopathology by myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, T.; Dunkel, A.; Schmid, C.; Schmitt, S.; Hiltensperger, M.; Lohr, K.; Laketa, V.; Donakonda, S.; Ahting, U.; Lorenz-Depiereux, B.; et al. Regulatory myeloid cells paralyze T cells through cell–cell transfer of the metabolite methylglyoxal. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stross, L.; Gunther, J.; Gasteiger, G.; Asen, T.; Graf, S.; Aichler, M.; Esposito, I.; Busch, D.H.; Knolle, P.; Sparwasser, T.; et al. Foxp3+ regulatory T cells protect the liver from immune damage and compromise virus control during acute experimental hepatitis B virus infection in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knolle, P.A.; Uhrig, A.; Protzer, U.; Trippler, M.; Duchmann, R.; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, K.H.; Gerken, G. Interleukin-10 expression is autoregulated at the transcriptional level in human and murine Kupffer cells. Hepatology 1998, 27, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bissell, D.M.; Wang, S.S.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Roll, F.J. Cell-specific expression of transforming growth factor-beta in rat liver. Evidence for autocrine regulation of hepatocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 96, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carambia, A.; Freund, B.; Schwinge, D.; Heine, M.; Laschtowitz, A.; Huber, S.; Wraith, D.C.; Korn, T.; Schramm, C.; Lohse, A.W.; et al. TGF-beta-dependent induction of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) Tregs by liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J. T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, F.; Kanev, K.; Hofmann, M.; Wu, M.; Ghoneim, H.E.; Roelli, P.; Utzschneider, D.T.; von Hosslin, M.; Cullen, J.G.; Fan, Y.; et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature 2019, 571, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, O.; Giles, J.R.; McDonald, S.; Manne, S.; Ngiow, S.F.; Patel, K.P.; Werner, M.T.; Huang, A.C.; Alexander, K.A.; Wu, J.E.; et al. TOX transcriptionally and epigenetically programs CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Nature 2019, 571, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Legat, A.; Fuertes Marraco, S.A.; Carrie, L.; Luescher, I.; Speiser, D.E.; Zehn, D. T cells maintain an exhausted phenotype after antigen withdrawal and population reexpansion. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Barili, V.; Montanini, B.; Acerbi, G.; Ferracin, M.; Guerrieri, F.; Salerno, D.; Boni, C.; Massari, M.; Cavallo, M.C.; et al. Targeting mitochondrial dysfunction can restore antiviral activity of exhausted HBV-specific CD8 T cells in chronic hepatitis B. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, C.; Barili, V.; Acerbi, G.; Rossi, M.; Vecchi, A.; Laccabue, D.; Penna, A.; Missale, G.; Ferrari, C.; Fisicaro, P. HBV Immune-Therapy: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manske, K.; Kallin, N.; Konig, V.; Schneider, A.; Kurz, S.; Bosch, M.; Welz, M.; Cheng, R.L.; Bengsch, B.; Steiger, K.; et al. Outcome of Antiviral Immunity in the Liver Is Shaped by the Level of Antigen Expressed in Infected Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2018, 68, 2089–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingozzi, F.; Liu, Y.L.; Dobrzynski, E.; Kaufhold, A.; Liu, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Arruda, V.R.; High, K.A.; Herzog, R.W. Induction of immune tolerance to coagulation factor IX antigen by in vivo hepatic gene transfer. J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 111, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Protzer, U. Control of Hepatitis B Virus by Cytokines. Viruses 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yewdell, J.W.; Reits, E.; Neefjes, J. Making sense of mass destruction: Quantitating MHC class I antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, L.C.; Yewdell, J.W. Translating DRiPs: MHC class I immunosurveillance of pathogens and tumors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2014, 95, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, W.F.; Zanetti, A.R.; Karayiannis, P.; Waters, J.; Manzillo, G.; Tanzi, E.; Zuckerman, A.J.; Thomas, H.C. Vaccine-induced escape mutant of hepatitis B virus. Lancet 1990, 336, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J. Hepatitis B Reactivation Associated With Immune Suppressive and Biological Modifier Therapies: Current Concepts, Management Strategies, and Future Directions. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Michailidis, E.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hurley, A.M.; Oren, D.A.; Mayer, C.T.; Gazumyan, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; et al. A Combination of Human Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies against Hepatitis B Virus HBsAg with Distinct Epitopes Suppresses Escape Mutations. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 335–349.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michler, T.; Kosinska, A.D.; Festag, J.; Bunse, T.; Su, J.; Ringelhan, M.; Imhof, H.; Grimm, D.; Steiger, K.; Mogler, C.; et al. Knockdown of Virus Antigen Expression Increases Therapeutic Vaccine Efficacy in High-Titer Hepatitis B Virus Carrier Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1762–1775.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, V.; Di Lucia, P.; Venzin, V.; Bono, E.B.; Jordan, R.; Frey, C.R.; Delaney, W.; Chisari, F.V.; Guidotti, L.G.; Iannacone, M. Serum HBsAg clearance has minimal impact on CD8+ T cell responses in mouse models of HBV infection. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.; Thimme, R.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. Genomic analysis of the host response to hepatitis B virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6669–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, A.; Pillai, P.S. Innate immunity to influenza virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.; Liang, T.J. Experimental models of hepatitis B and C-new insights and progress. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Rochford, R.; Chung, J.; Shapiro, M.; Purcell, R.; Chisari, F.V. Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999, 284, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannacone, M.; Guidotti, L.G. Mouse Models of Hepatitis B Virus Pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzer, U. Viral hepatitis: The bumpy road to animal models for HBV infection. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.L.; Deng, Q.; Mancini-Bourgine, M. Therapeutic vaccines and immune-based therapies for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Perspectives and challenges. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, M.L.; Bourgine, M.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. Therapeutic vaccines in treating chronic hepatitis B: The end of the beginning or the beginning of the end? Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Bauer, T.; Protzer, U. Therapeutic vaccination for chronic hepatitis B. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 23, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, A.J.; Protzer, U. Targeting Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to Cure Chronic HBV Infection. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Pallett, L.J. Defective T-cell immunity in hepatitis B virus infection: Why therapeutic vaccination needs a helping hand. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargill, T.; Barnes, E. Therapeutic vaccination for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulendran, B.; Arunachalam, P.S.; O’Hagan, D.T. Emerging concepts in the science of vaccine adjuvants. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 454–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangare, L.; Manhart, L.; Zehrung, D.; Wang, C.C. Intradermal hepatitis B vaccination: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vaccine 2009, 27, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Pan, C.Q.; Han, S.H.; Trinh, H.N.; Fessel, W.J.; Rodell, T.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.; Sanchez, A.L.; Jerez, E.; Anillo, L.E.; Freyre, F.; Aguiar, J.A.; Leon, Y.; Cinza, Z.; Diaz, P.A.; Figueroa, N.; et al. Five-year Follow-up of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Immunized by Nasal Route with the Therapeutic Vaccine HeberNasvac. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2018, 8, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepapeliere, P.; Lau, G.K.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Horsmans, Y.; Gane, E.; Tawandee, T.; Merican, M.I.; Win, K.M.; Trepo, C.; Cooksley, G.; et al. Therapeutic vaccination of chronic hepatitis B patients with virus suppression by antiviral therapy: A randomized, controlled study of co-administration of HBsAg/AS02 candidate vaccine and lamivudine. Vaccine 2007, 25, 8585–8597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, P.; Dembek, C.; Kuklick, L.; Jager, C.; Tedjokusumo, R.; von Freyend, M.J.; Drebber, U.; Janowicz, Z.; Melber, K.; Protzer, U. A novel therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine induces cellular and humoral immune responses and breaks tolerance in hepatitis B virus (HBV) transgenic mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, E.; Yang, D.; Lu, M. Contribution of Toll-like receptors to the control of hepatitis B virus infection by initiating antiviral innate responses and promoting specific adaptive immune responses. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Champion, C.R. Heplisav-B: A Hepatitis B Vaccine With a Novel Adjuvant. Ann. Pharm. 2021, 55, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Barry, V.; Daffis, S.; Niu, C.; Huntzicker, E.; French, D.M.; Mikaelian, I.; Lanford, R.E.; Delaney, W.E., IV; Fletcher, S.P. Anti-HBV response to toll-like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 is associated with intrahepatic aggregates of T cells and B cells. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackman, R.L.; Mish, M.; Chin, G.; Perry, J.K.; Appleby, T.; Aktoudianakis, V.; Metobo, S.; Pyun, P.; Niu, C.; Daffis, S.; et al. Discovery of GS-9688 (Selgantolimod) as a Potent and Selective Oral Toll-Like Receptor 8 Agonist for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis B. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10188–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, G.; Poeck, H.; Lucifora, J.; Baschuk, N.; Esser, K.; Esposito, I.; Hartmann, G.; Protzer, U. 5′ Triphosphorylated small interfering RNAs control replication of hepatitis B virus and induce an interferon response in human liver cells and mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 696–706, 706.e1-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Goyal, A.; Perelson, A.S.; Ishida, Y.; Saito, T.; Gale, M., Jr. Suppression of hepatitis B virus through therapeutic activation of RIG-I and IRF3 signaling in hepatocytes. Iscience 2021, 24, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horng, J.H.; Lin, W.H.; Wu, C.R.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wu, L.L.; Chen, D.S.; Chen, P.J. HBV X protein-based therapeutic vaccine accelerates viral antigen clearance by mobilizing monocyte infiltration into the liver in HBV carrier mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utzschneider, D.T.; Alfei, F.; Roelli, P.; Barras, D.; Chennupati, V.; Darbre, S.; Delorenzi, M.; Pinschewer, D.D.; Zehn, D. High antigen levels induce an exhausted phenotype in a chronic infection without impairing T cell expansion and survival. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Zhang, E.; Johrden, L.; Liu, J.; Seiz, P.L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Kemper, T.; Fiedler, M.; Glebe, D.; et al. Combination of DNA prime--adenovirus boost immunization with entecavir elicits sustained control of chronic hepatitis B in the woodchuck model. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chuai, X.; Deng, Y.; Wen, B.; Wang, W.; Xiong, S.; Ruan, L.; Tan, W. Optimisation of prime-boost immunization in mice using novel protein-based and recombinant vaccinia (Tiantan)-based HBV vaccine. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, S.; Jager, C.; Dembek, C.J.; Kosinska, A.D.; Bauer, T.; Stephan, A.S.; Dislers, A.; Mutwiri, G.; Busch, D.H.; Babiuk, L.A.; et al. Protein-prime/modified vaccinia virus Ankara vector-boost vaccination overcomes tolerance in high-antigenemic HBV-transgenic mice. Vaccine 2016, 34, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudewijns, R.; Ma, J.; Neyts, J.; Dallmeier, K. A novel therapeutic HBV vaccine candidate induces strong polyfunctional cytotoxic T cell responses in mice. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Festag, J.; Muck-Hausl, M.; Festag, M.M.; Asen, T.; Protzer, U. Immunogenicity and Antiviral Response of Therapeutic Hepatitis B Vaccination in a Mouse Model of HBeAg-Negative, Persistent HBV Infection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, M.; Abdullah, Z.; Chemnitz, J.M.; Maisel, D.; Sander, J.; Lehmann, C.; Thabet, Y.; Shinde, P.V.; Schmidleithner, L.; Kohne, M.; et al. Tumor-necrosis factor impairs CD4(+) T cell-mediated immunological control in chronic viral infection. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Martins, J.; Hammerschmidt, S.I.; Cossmann, A.; Odak, I.; Stankov, M.V.; Ramos, G.M.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Heidemann, A.; Ritter, C.; Friedrichsen, M.; et al. Immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 variants after heterologous and homologous ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/BNT162b2 vaccination. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1525–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenbusch, M.; Schumacher, S.; Vogel, E.; Priller, A.; Held, J.; Steininger, P.; Beileke, S.; Irrgang, P.; Brockhoff, R.; Salmanton-García, J.; et al. Heterologous prime-boost vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2 mRNA. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1212–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispe, I.N. Immune tolerance in liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 2109–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, D.L.; Wherry, E.J.; Masopust, D.; Zhu, B.; Allison, J.P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J.; Ahmed, R. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 2006, 439, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisicaro, P.; Valdatta, C.; Massari, M.; Loggi, E.; Biasini, E.; Sacchelli, L.; Cavallo, M.C.; Silini, E.M.; Andreone, P.; Missale, G.; et al. Antiviral intrahepatic T-cell responses can be restored by blocking programmed death-1 pathway in chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 682–693.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benechet, A.P.; De Simone, G.; Di Lucia, P.; Cilenti, F.; Barbiera, G.; Le Bert, N.; Fumagalli, V.; Lusito, E.; Moalli, F.; Bianchessi, V.; et al. Dynamics and genomic landscape of CD8(+) T cells undergoing hepatic priming. Nature 2019, 574, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, E.; Ma, Z.; Wu, W.; Kosinska, A.; Zhang, X.; Moller, I.; Seiz, P.; Glebe, D.; Wang, B.; et al. Enhancing virus-specific immunity in vivo by combining therapeutic vaccination and PD-L1 blockade in chronic hepadnaviral infection. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gane, E.; Verdon, D.J.; Brooks, A.E.; Gaggar, A.; Nguyen, A.H.; Subramanian, G.M.; Schwabe, C.; Dunbar, P.R. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: A pilot study. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Kang, Y.K.; Hou, M.M.; Numata, K.; Yeo, W.; Chopra, A.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Sorafenib-experienced Asian cohort analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, H.; Isogawa, M.; Freeman, G.J.; Chisari, F.V. PD-1:PD-L1 interactions contribute to the functional suppression of virus-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes in the liver. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2714–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Liu, L.; Yang, D.; Fu, S.; Bian, Y.; Sun, Z.; He, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, H.; et al. Clearing Persistent Extracellular Antigen of Hepatitis B Virus: An Immunomodulatory Strategy To Reverse Tolerance for an Effective Therapeutic Vaccination. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3079–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudi, I.; Kawashima, K.; Isogawa, M. HBV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Tolerance in the Liver. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 721975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannacone, M.; Guidotti, L.G. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenkel, O.; Tacke, F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, F.; Peusquens, J.; Ludwig-Portugall, I.; Kohlhepp, M.; Ergen, C.; Niemietz, P.; Martin, C.; van Rooijen, N.; Ochando, J.C.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Liver inflammation abrogates immunological tolerance induced by Kupffer cells. Hepatology 2015, 62, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; Andreata, F.; Bleriot, C.; Fumagalli, V.; Laura, C.; Garcia-Manteiga, J.M.; Di Lucia, P.; Gilotto, S.; Ficht, X.; De Ponti, F.F.; et al. Identification of a Kupffer cell subset capable of reverting the T cell dysfunction induced by hepatocellular priming. Immunity 2021, 54, 2089–2100.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.R.; Wohlleber, D.; Reisinger, F.; Jenne, C.N.; Cheng, R.L.; Abdullah, Z.; Schildberg, F.A.; Odenthal, M.; Dienes, H.P.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. Intrahepatic myeloid-cell aggregates enable local proliferation of CD8(+) T cells and successful immunotherapy against chronic viral liver infection. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebula, M.; Riehn, M.; Hillebrand, U.; Kratzer, R.F.; Kreppel, F.; Koutsoumpli, G.; Daemen, T.; Hauser, H.; Wirth, D. TLR9-Mediated Conditioning of Liver Environment Is Essential for Successful Intrahepatic Immunotherapy and Effective Memory Recall. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2017, 25, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosinska, A.D.; Moeed, A.; Kallin, N.; Festag, J.; Su, J.; Steiger, K.; Michel, M.L.; Protzer, U.; Knolle, P.A. Synergy of therapeutic heterologous prime-boost hepatitis B vaccination with CpG-application to improve immune control of persistent HBV infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).