High Prevalence of Anti-PF4 Antibodies Following ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) Vaccination Even in the Absence of Thrombotic Events
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Laboratory Methodology
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
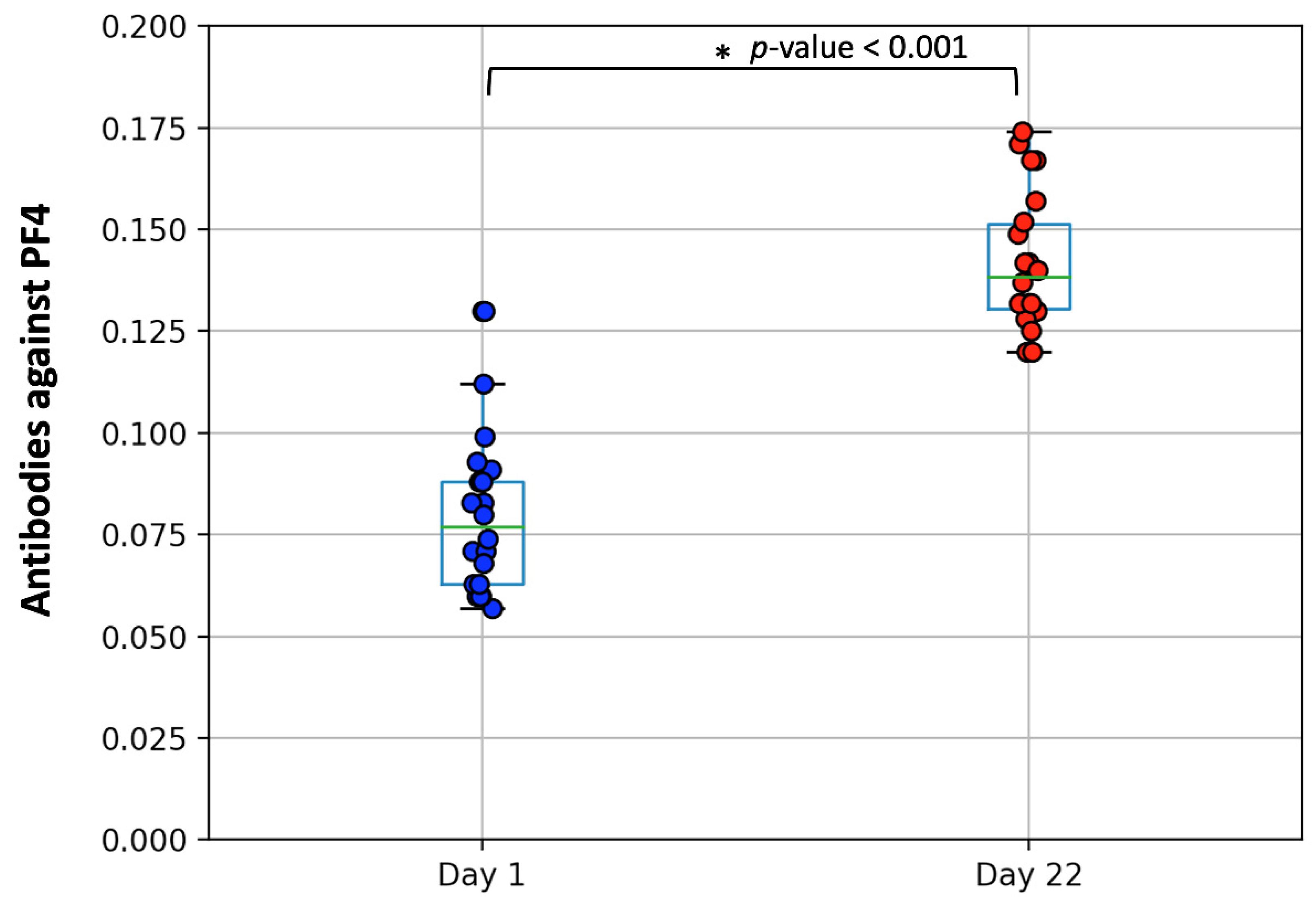
3.2. Measurement of PF4/Heparin IgG Antibodies
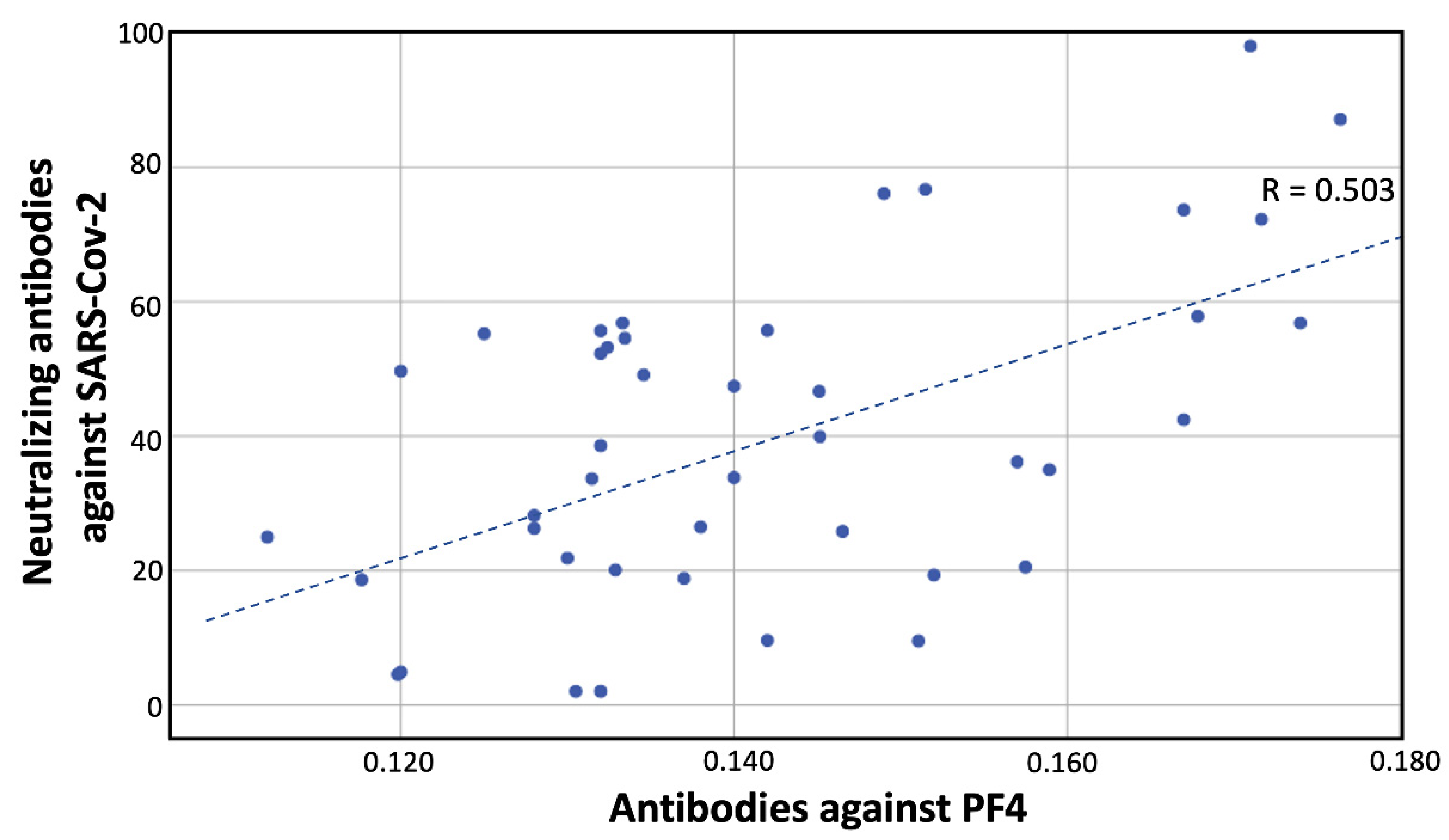
3.3. Correlations with Antibody Response and Clinical Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Organ-specific manifestations of COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trougakos, I.P.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Terpos, E.; Tsitsilonis, O.E.; Aivalioti, E.; Paraskevis, D.; Kastritis, E.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Insights to SARS-CoV-2 life cycle, pathophysiology, and rationalized treatments that target COVID-19 clinical complications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Migkou, M.; Tzanninis, I.G.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Emerging treatment strategies for COVID-19 infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korompoki, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Hicklen, R.S.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Kastritis, E.; Fotiou, D.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Terpos, E.; Kotanidou, A.; Hagberg, C.A.; et al. Epidemiology and organ specific sequelae of post-acute COVID19: A Narrative Review. J. Infect. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Perez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, M.N.; Minassian, A.M.; Ewer, K.J.; Flaxman, A.L.; Folegatti, P.M.; Owens, D.R.; Voysey, M.; Aley, P.K.; Angus, B.; Babbage, G.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine administered in a prime-boost regimen in young and old adults (COV002): A single-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2021, 396, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Thiele, T.; Warkentin, T.E.; Weisser, K.; Kyrle, P.A.; Eichinger, S. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCov-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, N.H.; Sorvoll, I.H.; Michelsen, A.E.; Munthe, L.A.; Lund-Johansen, F.; Ahlen, M.T.; Wiedmann, M.; Aamodt, A.H.; Skattor, T.H.; Tjonnfjord, G.E.; et al. Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Liumbruno, G.M.; Pezzo, M. COVID-19 Vaccine-associated Immune Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia (VITT): Diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations for a new syndrome. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinacher, A.; Selleng, K.; Warkentin, T.E. Autoimmune heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warkentin, T.E. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: A review. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2019, 12, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Hundelshausen, P.; Lorenz, R.; Siess, W.; Weber, C. Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT): Targeting pathomechanisms with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, M.; Singh, D.; Lown, R.; Poles, A.; Solomon, T.; Levi, M.; Goldblatt, D.; Kotoucek, P.; Thomas, W.; Lester, W. Pathologic Antibodies to Platelet Factor 4 after ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 Vaccination. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazy, I.; Jevtic, S.D.; Moore, J.C.; Huynh, A.; Smith, J.W.; Kelton, J.G.; Arnold, D.M. Platelet-activating immune complexes identified in critically ill COVID-19 patients suspected of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodard, J.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Fontana, P.; Studt, J.D.; Gruel, Y.; Greinacher, A. COVID-19 patients often show high-titer non-platelet-activating anti-PF4/heparin IgG antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadkhoda, K. Post-adenoviral-based COVID-19 vaccines thrombosis: A proposed mechanism. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elalamy, I.; Gerotziafas, G.; Alamowitch, S.; Laroche, J.P.; van Dreden, P.; Ageno, W.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Cohen, A.T.; Jimenez, D.; Brenner, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine and thrombosis: Expert opinions. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentolouris, A.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Vlachakis, P.K.; Tsilimigras, D.I.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Dimopoulos, M.A. COVID-19: Time to flatten the infodemic curve. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 21, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoryan, L.; Pulendran, B. The immunology of SARS-CoV-2 infections and vaccines. Semin. Immunol. 2020, 50, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Pade, C.; Gibbons, J.M.; Butler, D.K.; Otter, A.D.; Menacho, K.; Fontana, M.; Smit, A.; Sackville-West, J.E.; Cutino-Moguel, T.; et al. Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection rescues B and T cell responses to variants after first vaccine dose. Science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, N.; Eddy, D.; Huntley, C.; van Schalkwyk, M.C.I.; Shrotri, M.; Leeman, D.; Rigby, S.; Williams, S.V.; Bermingham, W.H.; Kellam, P.; et al. Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel-Kopp, M.C.; Mullier, F.; Gkalea, V.; Bakchoul, T.; Minet, V.; Elalamy, I.; Ward, C.M. Subcommittee on Platelet Immunology; Heparin-induced multi-electrode aggregometry method for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia testing: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 2548–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Papassotiriou, I.; Sklirou, A.D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Fotiou, D.; Kastritis, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Low Neutralizing Antibody Responses Against SARS-CoV-2 in Elderly Myeloma Patients After the First BNT162b2 Vaccine Dose. Blood 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Apostolakou, F.; Charitaki, I.; Sklirou, A.D.; Mavrianou, N.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Liacos, C.I.; Gumeni, S.; Rentziou, G.; et al. Age-dependent and gender-dependent antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in health workers and octogenarians after vaccination with the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine. Am. J. Hematol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based Covid-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, T.; Ulm, L.; Holtfreter, S.; Schonborn, L.; Kuhn, S.O.; Scheer, C.; Warkentin, T.E.; Broker, B.; Becker, K.; Aurich, K.; et al. Frequency of positive anti-PF4/polyanion antibody tests after COVID-19 vaccination with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 and BNT162b2. Blood 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorvoll, I.H.; Horvei, K.D.; Ernstsen, S.L.; Laegreid, I.J.; Lund, S.; Gronli, R.H.; Olsen, M.K.; Jacobsen, H.K.; Eriksson, A.; Halstensen, A.M.; et al. An observational study to identify the prevalence of thrombocytopenia and anti-PF4/polyanion antibodies in Norwegian health care workers after COVID-19 vaccination. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platton, S.; Bartlett, A.; MacCallum, P.; Makris, M.; McDonald, V.; Singh, D.; Scully, M.; Pavord, S. Evaluation of laboratory assays for anti-Platelet Factor 4 antibodies after ChAdOx1 nCOV-19 vaccination. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E.; Makris, M.; Jay, R.M.; Kelton, J.G. A spontaneous prothrombotic disorder resembling heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am. J. Med. 2008, 121, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merad, M.; Martin, J.C. Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonagle, D.; O’Donnell, J.S.; Sharif, K.; Emery, P.; Bridgewood, C. Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e437–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yuan, X.; Chen, H.; Chaturvedi, S.; Braunstein, E.M.; Brodsky, R.A. Direct activation of the alternative complement pathway by SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins is blocked by factor D inhibition. Blood 2020, 136, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, A.; Jones, C.G.; Pechauer, S.M.; Curtis, B.R.; Bougie, D.W.; Irani, M.S.; Bryant, B.J.; Alperin, J.B.; Deloughery, T.G.; Mulvey, K.P.; et al. IVIg for Treatment of Severe Refractory Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Chest 2017, 152, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greinacher, A.; Juhl, D.; Strobel, U.; Wessel, A.; Lubenow, N.; Selleng, K.; Eichler, P.; Warkentin, T.E. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: A prospective study on the incidence, platelet-activating capacity and clinical significance of antiplatelet factor 4/heparin antibodies of the IgG, IgM, and IgA classes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhl, D.; Eichler, P.; Lubenow, N.; Strobel, U.; Wessel, A.; Greinacher, A. Incidence and clinical significance of anti-PF4/heparin antibodies of the IgG, IgM, and IgA class in 755 consecutive patient samples referred for diagnostic testing for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2006, 76, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warkentin, T.E. Laboratory diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2019, 41 (Suppl. S1), 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hursting, M.J.; Pai, P.J.; McCracken, J.E.; Hwang, F.; Suvarna, S.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Bandarenko, N.; Arepally, G.M. Platelet factor 4/heparin antibodies in blood bank donors. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 134, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruthi, R.K.; Daniels, P.R.; Nambudiri, G.S.; Warkentin, T.E. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) during postoperative warfarin thromboprophylaxis: A second example of postorthopedic surgery ‘spontaneous’ HIT. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay, R.M.; Warkentin, T.E. Fatal heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) during warfarin thromboprophylaxis following orthopedic surgery: Another example of ‘spontaneous’ HIT? J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 1598–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauel, K.; Potschke, C.; Weber, C.; Kessler, W.; Furll, B.; Ittermann, T.; Maier, S.; Hammerschmidt, S.; Broker, B.M.; Greinacher, A. Platelet factor 4 binds to bacteria, [corrected] inducing antibodies cross-reacting with the major antigen in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2011, 117, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of participants | 43 |
| Age (median, range) (years) | 62 (60–64) |
| Gender (n, %) | |
| Women | 21 (48.8%) |
| Men | 22 (51.2%) |
| BMI (n, %) | |
| Normal weight | 12 (27.9%) |
| Overweight | 18 (41.8%) |
| Obese | 13 (30.2%) |
| Co-morbidities of all participants (n, %) | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 14 (32.5%) |
| Hypertension | 12 (28%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 11 (25.5%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 4 (9.3%) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 2 (4.6%) |
| Hematologic malignancy Current treatment | 12 (28%) 6/12 (50%) |
| Co-morbidities of women (n, %) | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 6 (13.9%) |
| Hypertension | 2 (4.65%) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 7 (16.3%) |
| Hypothyroidism | 3 (7.0%) |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 1 (2.3%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terpos, E.; Politou, M.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Karalis, V.; Merkouri, E.; Fotiou, D.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Malandrakis, P.; Kastritis, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; et al. High Prevalence of Anti-PF4 Antibodies Following ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) Vaccination Even in the Absence of Thrombotic Events. Vaccines 2021, 9, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070712
Terpos E, Politou M, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Karalis V, Merkouri E, Fotiou D, Gavriatopoulou M, Malandrakis P, Kastritis E, Trougakos IP, et al. High Prevalence of Anti-PF4 Antibodies Following ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) Vaccination Even in the Absence of Thrombotic Events. Vaccines. 2021; 9(7):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070712
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerpos, Evangelos, Marianna Politou, Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Vangelis Karalis, Efrosyni Merkouri, Despina Fotiou, Maria Gavriatopoulou, Panagiotis Malandrakis, Efstathios Kastritis, Ioannis P. Trougakos, and et al. 2021. "High Prevalence of Anti-PF4 Antibodies Following ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) Vaccination Even in the Absence of Thrombotic Events" Vaccines 9, no. 7: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070712
APA StyleTerpos, E., Politou, M., Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I., Karalis, V., Merkouri, E., Fotiou, D., Gavriatopoulou, M., Malandrakis, P., Kastritis, E., Trougakos, I. P., & Dimopoulos, M. A. (2021). High Prevalence of Anti-PF4 Antibodies Following ChAdOx1 nCov-19 (AZD1222) Vaccination Even in the Absence of Thrombotic Events. Vaccines, 9(7), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9070712











