An Advax-Adjuvanted Inactivated Cell-Culture Derived Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Induces Broadly Neutralising Anti-Flavivirus Antibodies, Robust Cellular Immunity and Provides Single Dose Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Cell and Viruses
2.3. Immunisation Schedule
2.4. Antibody Isotypes
2.5. Plaque Reduction Neutralisation Tests
2.6. Antibody-Dependent Infection Enhancement Assay
2.7. Multiplex Immunoassay for Quantification of Secreted Cytokines
2.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunospot (ELISPOT) Assay
2.9. JEV Challenge
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. ccJE+Advax Vaccine Induces Broadly Cross-Neutralising Antibody
3.2. ccJE+Advax Stimulates a Balanced Th1/Th2 Antibody Response
3.3. Antibody-Dependent Infection Enhancement
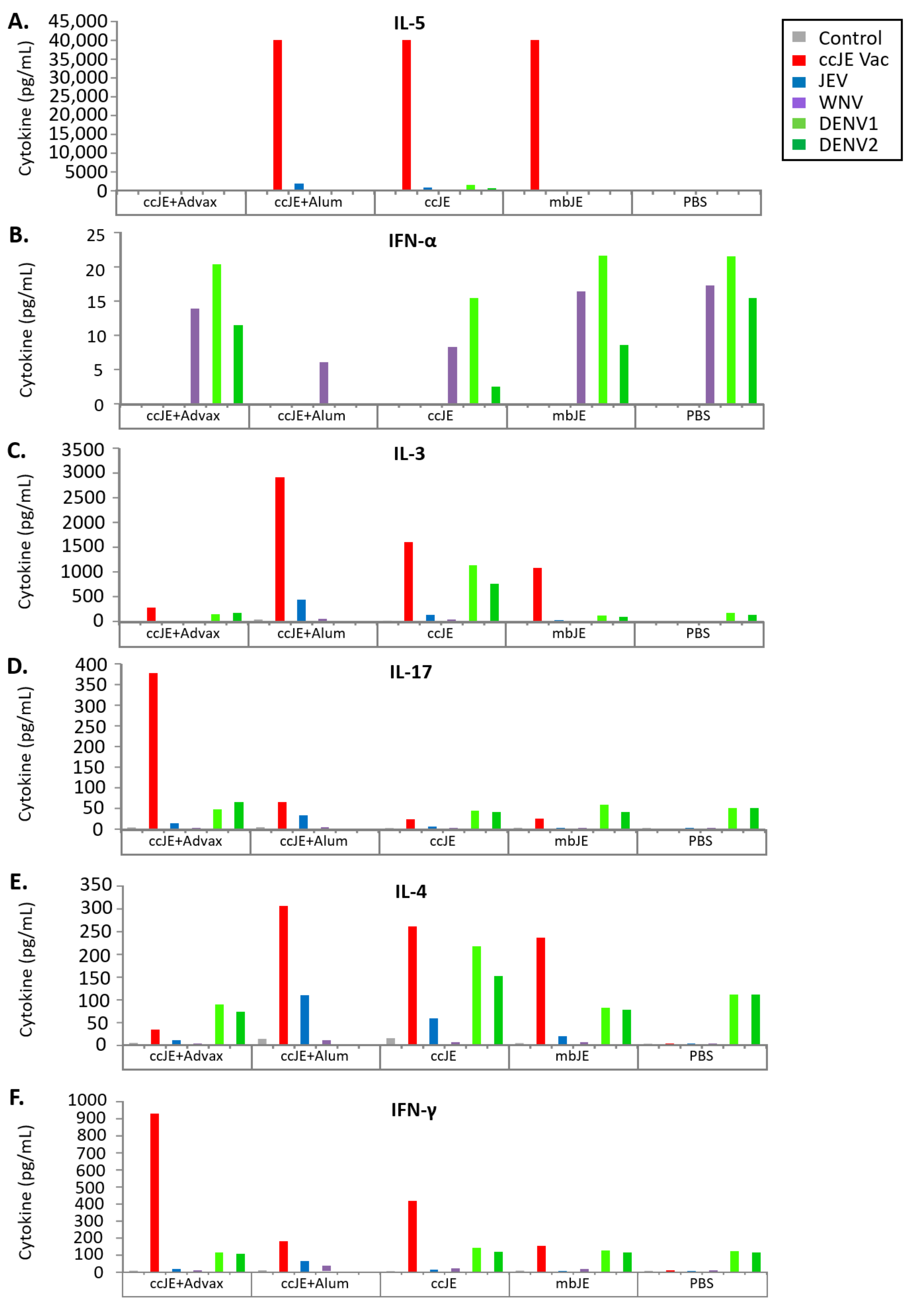
3.4. Cellular Immune Response
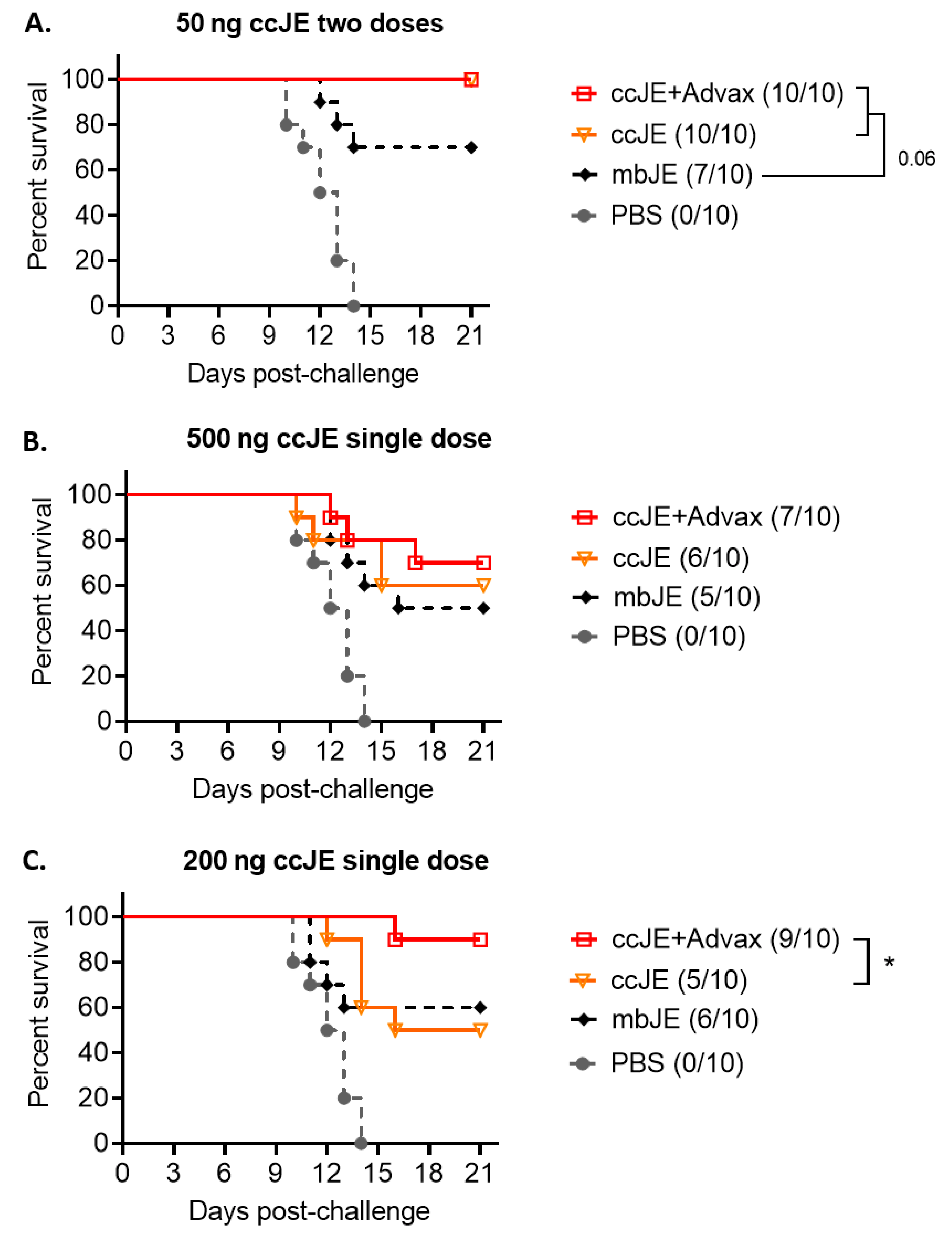
3.5. ccJE-Advax Provides Robust JEV Protection
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erlanger, T.E.; Weiss, S.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J.; Wiedenmayer, K. Past, present, and future of Japanese encephalitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.L.; Hills, S.L.; Fischer, M.; Jacobson, J.A.; Hoke, C.H.; Hombach, J.M.; Marfin, A.A.; Solomon, T.; Tsai, T.F.; Tsu, V.D. Estimated global incidence of Japanese encephalitis: A systematic review. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.; Bunn, W.B. The changing epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis and New data: The implications for New recommendations for Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2017, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoke, C.H.; Nisalak, A.; Sangawhipa, N.; Jatanasen, S.; Laorakapongse, T.; Innis, B.L.; Kotchasenee, S.-O.; Gingrich, J.B.; Latendresse, J.; Fukai, K. Protection against Japanese encephalitis by inactivated vaccines. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 319, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, E.; Dewasthaly, S. Japanese encephalitis vaccines–needs, flaws and achievements. Biol Chem. 2008, 389, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.R.; Gore, M.M. Japanese encephalitis vaccines: Immunogenicity, protective efficacy, effectiveness, and impact on the burden of disease. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Chang, G.J.; Xie, H.; Trent, D.W.; Barrett, A.D. Molecular basis of attenuation of neurovirulence of wild-type Japanese encephalitis virus strain SA14. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76 Pt 2, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromowski, G.D.; Firestone, C.Y.; Bustos-Arriaga, J.; Whitehead, S.S. Genetic and phenotypic properties of vero cell-adapted Japanese encephalitis virus SA14-14-2 vaccine strain variants and a recombinant clone, which demonstrates attenuation and immunogenicity in mice. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nitayaphan, S.; Grant, J.A.; Chang, G.J.; Trent, D.W. Nucleotide sequence of the virulent SA-14 strain of Japanese encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, SA-14-14-2. Virology 1990, 177, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, E.; Kollaritsch, H.; Korinek, M.; Rendi-Wagner, P.; Jilma, B.; Firbas, C.; Schranz, S.; Jong, E.; Klingler, A.; Dewasthaly, S. Safety and immunogenicity of a Vero-cell-derived, inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine: A non-inferiority, phase III, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Flohic, G.; Porphyre, V.; Barbazan, P.; Gonzalez, J.-P. Review of climate, landscape, and viral genetics as drivers of the Japanese encephalitis virus ecology. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, A.P.S.; St John, A.L. Cross-Reactive Immunity Among Flaviviruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, B.E.; Koraka, P.; van Den Doel, P.; van Amerongen, G.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Osterhaus, A.D. Immunization with West Nile virus envelope domain III protects mice against lethal infection with homologous and heterologous virus. Vaccine 2008, 26, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaki, T.; Yabe, S.; Nerome, R.; Ito, M.; Yamada, K.-I.; Kurane, I. Partial protective effect of inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine on lethal West Nile virus infection in mice. Vaccine 2003, 21, 4514–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobigs, M.; Pavy, M.; Hall, R. Cross-protective and infection-enhancing immunity in mice vaccinated against flaviviruses belonging to the Japanese encephalitis virus serocomplex. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1572–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobigs, M.; Larena, M.; Alsharifi, M.; Lee, E.; Pavy, M. Live chimeric and inactivated Japanese encephalitis virus vaccines differ in their cross-protective values against Murray Valley encephalitis virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2436–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.; Smith, D.; Broom, A.; Mackenzie, J.; Hall, R.; Shellam, G.; McMinn, P. Antibody-dependent enhancement of Murray Valley encephalitis virus virulence in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1723–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broom, A.K.; Wallace, M.J.; Mackenzie, J.S.; Smith, D.W.; Hall, R.A. Immunisation with gamma globulin to Murray Valley encephalitis virus and with an inactivated Japanese encephalitis virus vaccine as prophylaxis against Australian encephalitis: Evaluation in a mouse model. J. Med Virol. 2000, 61, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P.; Mishra, G.; Jain, P.; Pandey, N.; Nagar, R.; Gupta, S.; Prakash, S.; Prakash, O.; Khan, D.N.; Shrivastav, S. Co-positivity of anti-dengue virus and anti-Japanese encephalitis virus IgM in endemic area: Co-infection or cross reactivity? Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahala, W.M.; De Silva, A.M. The human antibody response to dengue virus infection. Viruses 2011, 3, 2374–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali-Krishna, K.; Ravi, V.; Manjunath, R. Protection of adult but not newborn mice against lethal intracerebral challenge with Japanese encephalitis virus by adoptively transferred virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes: Requirement for L3T4+ T cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77 Pt 4, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashok, M.S.; Rangarajan, P.N. Immunization with plasmid DNA encoding the envelope glycoprotein of Japanese Encephalitis virus confers significant protection against intracerebral viral challenge without inducing detectable antiviral antibodies. Vaccine 1999, 18, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sulochana, P.; Nirmala, G.; Chandrashekar, R.; Haridattatreya, M.; Satchidanandam, V. Impaired T helper 1 function of nonstructural protein 3-specific T cells in Japanese patients with encephalitis with neurological sequelae. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovsky, N.; Cooper, P.D. Advax™, a novel microcrystalline polysaccharide particle engineered from delta inulin, provides robust adjuvant potency together with tolerability and safety. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5920–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobigs, M.; Pavy, M.; Hall, R.A.; Lobigs, P.; Cooper, P.; Komiya, T.; Toriniwa, H.; Petrovsky, N. An inactivated Vero cell-grown Japanese encephalitis vaccine formulated with Advax, a novel inulin-based adjuvant, induces protective neutralizing antibody against homologous and heterologous flaviviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, D.; Shirai, K.; Aoki, K.; Nagata, N.; Simantini, D.S.; Kitaura, K.; Takamatsu, Y.; Gould, E.; Suzuki, R.; Morita, K. TNF-α acts as an immunoregulator in the mouse brain by reducing the incidence of severe disease following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licon Luna, R.M.; Lee, E.; Müllbacher, A.; Blanden, R.V.; Langman, R.; Lobigs, M. Lack of both Fas ligand and perforin protects from flavivirus-mediated encephalitis in mice. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 3202–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toriniwa, H.; Komiya, T. Long-term stability of Vero cell-derived inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine prepared using serum-free medium. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3680–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, M.L.; Lim, C.-K.; Chua, K.B.; Takasaki, T.; Kurane, I. Dengue virus infection-enhancing activity in serum samples with neutralizing activity as determined by using FcγR-expressing cells. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gessel, Y.; Klade, C.S.; Putnak, R.; Formica, A.; Krasaesub, S.; Spruth, M.; Cena, B.; Tungtaeng, A.; Gettayacamin, M.; Dewasthaly, S. Correlation of protection against Japanese encephalitis virus and JE vaccine (IXIARO(®)) induced neutralizing antibody titers. Vaccine 2011, 29, 5925–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelman, F.; Katona, I.; Mosmann, T.; Coffman, R. IFN-gamma regulates the isotypes of Ig secreted during in vivo humoral immune responses. J. Immunol. 1988, 140, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalton, D.K.; Pitts-Meek, S.; Keshav, S.; Figari, I.S.; Bradley, A.; Stewart, T.A. Multiple defects of immune cell function in mice with disrupted interferon-gamma genes. Science 1993, 259, 1739–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilder-Smith, A.; Ooi, E.E.; Horstick, O.; Wills, B. Dengue. Lancet 2019, 393, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Moi, M.L.; Takeshita, N.; Lim, C.-K.; Shiba, H.; Hosono, K.; Saijo, M.; Kurane, I.; Takasaki, T. Japanese encephalitis vaccine-facilitated dengue virus infection-enhancement antibody in adults. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larena, M.; Regner, M.; Lobigs, M. Cytolytic effector pathways and IFN-γ help protect against J apanese encephalitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Aoshi, T.; Haseda, Y.; Kobiyama, K.; Wijaya, E.; Nakatsu, N.; Igarashi, Y.; Standley, D.M.; Yamada, H.; Honda-Okubo, Y. Advax, a delta inulin microparticle, potentiates in-built adjuvant property of co-administered vaccines. EBioMedicine 2017, 15, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.; Kelley, P.; Heinzel, S.; Cooper, P.; Petrovsky, N. Immunogenicity and safety of Advax™, a novel polysaccharide adjuvant based on delta inulin, when formulated with hepatitis B surface antigen: A randomized controlled Phase 1 study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.L.; Sajkov, D.; Honda-Okubo, Y.; Wilks, S.H.; Aban, M.; Barr, I.G.; Petrovsky, N. Human Phase 1 trial of low-dose inactivated seasonal influenza vaccine formulated with Advax™ delta inulin adjuvant. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3780–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.L.; Sajkov, D.; Woodman, R.J.; Honda-Okubo, Y.; Cox, M.M.; Heinzel, S.; Petrovsky, N. Randomized clinical trial of immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant H1N1/2009 pandemic influenza vaccine containing Advax™ polysaccharide adjuvant. Vaccine 2012, 30, 5407–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.; Richmond, P.C.; Formica, N.T.; Höschler, K.; Skeljo, M.V.; Stoney, T.; McVernon, J.; Hartel, G.; Sawlwin, D.C.; Bennet, J. Safety and immunogenicity of a prototype adjuvanted inactivated split-virus influenza A (H5N1) vaccine in infants and children. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6383–6391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heddle, R.; Smith, A.; Woodman, R.; Hissaria, P.; Petrovsky, N. Randomized controlled trial demonstrating the benefits of delta inulin adjuvanted immunotherapy in patients with bee venom allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovsky, N.; Larena, M.; Siddharthan, V.; Prow, N.A.; Hall, R.A.; Lobigs, M.; Morrey, J. An inactivated cell culture Japanese encephalitis vaccine (JE-ADVAX) formulated with delta inulin adjuvant provides robust heterologous protection against West Nile encephalitis via cross-protective memory B cells and neutralizing antibody. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10324–10333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Fierens, K.; Lambrecht, B.N. Alum adjuvant: Some of the tricks of the oldest adjuvant. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanesa-Thasan, N.; Putnak, J.; Mangiafico, J.; Saluzzo, J.; Ludwig, G. absence of protective neutralizng antibodies to West Nile virus in subjects following vaccination with Japanese encephalitis or dengue vaccines. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Zhang, J.-S.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Q.-M.; Zhang, F.; Wu, X.-M.; Yang, H.; Ly, H.; Cao, W.-C. Failure of Japanese encephalitis vaccine and infection in inducing neutralizing antibodies against West Nile virus, People’s Republic of China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 78, 999–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, J.D.; Bruce Cropp, C.; Craven, R.B.; Monath, T.P. Evaluation of the potency and safety of inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine in US inhabitants. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, S.B.; Jacobson, J.; Dubischar-Kastner, K. Japanese encephalitis vaccines. In Vaccines, 6th ed.; Plotkin, S.A., Orenstein, W.A., Offit, P.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 311–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuhara, S.; Nakamura, H.; Hayashida, K.; Obata, J.; Abe, M.; Sonoda, K.; Nishiyama, K.; Sugawara, K.; Takeda, K.; Honda, T. Non-clinical and phase I clinical trials of a Vero cell-derived inactivated Japanese encephalitis vaccine. Vaccine 2003, 21, 4519–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, T.; Cromer, M.A.; Cramer, J.P.; Mills, D.J.; Lessans, K.; Gherardin, A.W.; Barnett, E.D.; Hagmann, S.H.; Askling, H.H.; Kiermayr, S. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated Vero cell_derived Japanese encephalitis vaccine (IXIARO®, JESPECT®) in a pediatric population in JE non-endemic countries: An uncontrolled, open-label phase 3 study. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.C.; Brault, A.C.; Hunsperger, E. The contribution of rodent models to the pathological assessment of flaviviral infections of the central nervous system. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Sasaki, M.; Okumura, M.; Kim, E.; Sawa, H. Flavivirus encephalitis: Pathological aspects of mouse and other animal models. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Challenge Virus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immunised Mouse Sera | JEV | WNV | MVEV | SLEV | DENV1 | DENV2 |
| (i) ccJE+Advax | 2.67 | 1.20 | 1.87 | 0.37 | 1.21 | 1.91 |
| (ii) ccJE+alum | 2.99 | 0.96 | 1.45 | N.D. | 0.89 | 1.81 |
| (iii) ccJE | 2.89 | 0.87 | 1.45 | N.D. | 1.02 | 1.56 |
| (iv) mbJE | 3.37 | N.D. | 1.19 | N.D. | N.D. | 0.74 |
| Host Mouse | Antigen Specific Antibodies | Immunised Mouse Sera (IgG2b/IgG1 Ratio) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ccJE+Advax | ccJE+Alum | ccJE | mbJE | ||
| (i) Wild Type | JEV | 1.75 | 0.58 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| (ii) Wild Type | WNV | 3.28 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.85 |
| (iii) Wild Type | DENV2 | 3.6 | 0.24 | 9.2 | 11.5 |
| (iv) IFN-γ KO | JEV | 1.87 | 0.36 | 0.53 | 0.22 |
| (v) IFN-γ KO | WNV | 2.46 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.10 |
| Immunised Mouse Sera | DENV2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) Plaque-Reduction Neutralisation Test (PRNT50) | (B) Infection Enhancement | |||
| BHK | BHK-FcγRIIA | BHK | BHK-FcγRIIA | |
| (i) ccJE+Advax | 1.37 | 1.31 | 0.07 | 0.15 |
| (ii) ccJE+alum | 1.13 | N.D. | 0.33 | 3.06 |
| (iii) ccJE | 1.51 | N.D. | 0.20 | 2.21 |
| (iv) mbJE | N.D. | N.D. | 0.66 | 11.31 |
| Immunised Mouse Sera | JEV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Double | ||
| 500 ng | 200 ng | 50 ng | |
| (i) ccJE+Advax | 1.972 | 0.967 | 2.512 |
| (ii) ccJE | 1.182 | 0.786 | 2.098 |
| (iii) mbJE | 0.966 | 1.433 | 1.343 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komiya, T.; Honda-Okubo, Y.; Baldwin, J.; Petrovsky, N. An Advax-Adjuvanted Inactivated Cell-Culture Derived Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Induces Broadly Neutralising Anti-Flavivirus Antibodies, Robust Cellular Immunity and Provides Single Dose Protection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111235
Komiya T, Honda-Okubo Y, Baldwin J, Petrovsky N. An Advax-Adjuvanted Inactivated Cell-Culture Derived Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Induces Broadly Neutralising Anti-Flavivirus Antibodies, Robust Cellular Immunity and Provides Single Dose Protection. Vaccines. 2021; 9(11):1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111235
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomiya, Tomoyoshi, Yoshikazu Honda-Okubo, Jeremy Baldwin, and Nikolai Petrovsky. 2021. "An Advax-Adjuvanted Inactivated Cell-Culture Derived Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Induces Broadly Neutralising Anti-Flavivirus Antibodies, Robust Cellular Immunity and Provides Single Dose Protection" Vaccines 9, no. 11: 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111235
APA StyleKomiya, T., Honda-Okubo, Y., Baldwin, J., & Petrovsky, N. (2021). An Advax-Adjuvanted Inactivated Cell-Culture Derived Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Induces Broadly Neutralising Anti-Flavivirus Antibodies, Robust Cellular Immunity and Provides Single Dose Protection. Vaccines, 9(11), 1235. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111235







