Transcriptome Analysis in the Head Kidney of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Immunized with a Combined Vaccine of Formalin-Inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. Vaccine Preparation
2.3. Vaccination and Sampling
2.4. Q-PCR
2.5. Transcriptome Analysis
2.5.1. RNA Library Construction and Mass Sequencing
2.5.2. Transcriptome Annotation
2.5.3. DEGs’ Analysis
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Vaccine on Adaptive Immune Gene Expression
3.2. Transcriptome Sequencing
3.3. Differential Expression Analysis
3.4. GO Enrichment Analysis
3.5. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
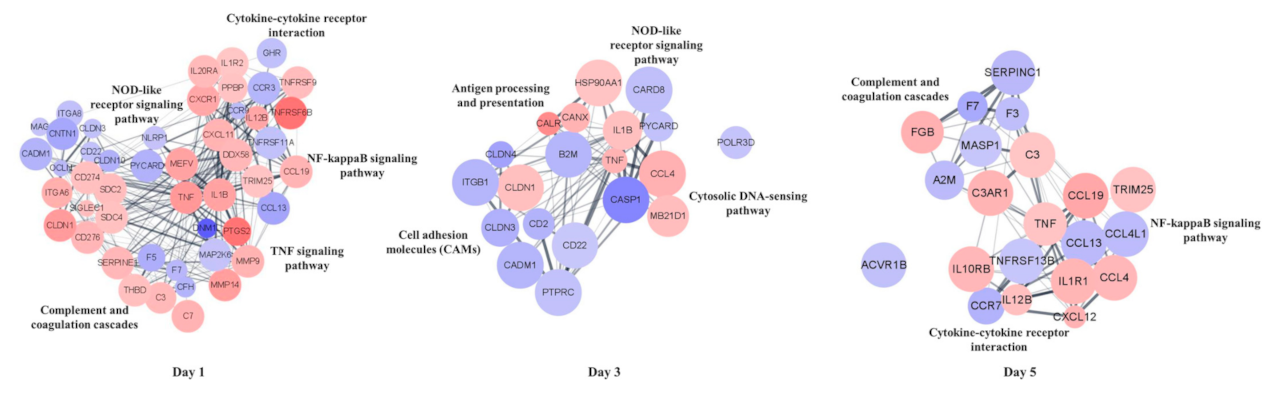
3.6. PPI Analysis of DEGs
3.7. Analysis of DEGs in Immune-Related Pathways
3.8. Validation of RNA-seq Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aksnes, A.; Hope, B.; Jönsson, E.; Bjornsson, B.T.; Albrektsen, S. Size-fractionated fish hydrolysate as feed ingredient for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed high plant protein diets. I: Growth, growth regulation and feed utilization. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Statistical Information Service. Available online: http://kosis.kr/eng/ (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Aeromonas salmonicida: Updates on an old acquaintance. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2016, 120, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frans, I.; Michiels, C.; Bossier, P.; Willems, K.A.; Lievens, B.; Rediers, H. Vibrio anguillarum as a fish pathogen: Virulence factors, diagnosis and prevention. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 643–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallaire-Dufresne, S.; Tanaka, K.H.; Trudel, M.V.; Lafaille, A.; Charette, S.J. Virulence, genomic features, and plasticity of Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida, the causative agent of fish furunculosis. Veter. Microbiol. 2014, 169, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, H.; Kim, W.; Cho, M.; Jeong, S.; Han, H. Characteristics of Vibrio anguillarum Isolated from Seawater Cultured Rainbow Trout Oncorhynchus mykiss in Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 51, 254–261. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Dong, X.; Hu, G. Transcriptome analysis of red sea bream (Pagrus major) head kidney and spleen infected by Vibrio anguillarum. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 21, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals the mechanism of β-glucan in protecting rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) from Aeromonas salmonicida infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 98, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Hou, Z.S.; Zhao, H.K.; Xin, Y.R.; Liu, M.Q.; Yang, X.D.; Li, J.F. Identification and characterization of caspases genes in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and their expression profiles after Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum infec-tion. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 118, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, D.C.B. The oral immunization of trout against Bacterium salmonicida. J. Immunol. 1942, 44, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Kamata, T.; Ozaki, H. Studies on the vibrio disease of rainbow trout. II. Prophylactic vaccination against the vibrio disease. J. Fac. Fish. Pref. Univ. Mie 1964, 6, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Marana, M.H.; Jørgensen, L.V.G.; Skov, J.; Chettri, J.K.; Mattsson, A.H.; Dalsgaard, I.; Kania, P.W.; Buchmann, K. Subunit vaccine candidates against Aeromonas salmonicida in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres-Corral, Y.; Girons, A.; González-Barreiro, O.; Seoane, R.; Riaza, A.; Santos, Y. Effect of Bivalent Vaccines against Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida Subspecie achromogenes on Health and Survival of Turbot. Vaccines 2021, 9, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Xu, H.; Tang, X.; Sheng, X.; Zhan, W.A. DNA vaccine encoding the VAA gene of Vibrio anguillarum induces a pro-tective immune response in flounder. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Mo, Z. The efficacy and side-effects of oil-based adjuvants emulsified Vibrio anguillarum bivalent inactivated vaccine in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) under production mode. Aquaculture 2020, 524, 735259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, P.; Terech-Majewska, E.; Siwicki, A.K.; Kazuń, B.; Demska-Zakęś, K.; Rożyński, M.; Zakęś, Z. Effect of Different Routes of Vaccination against Aeromonas salmonicida on Rearing Indicators and Survival after an Experimental Challenge of Pikeperch (Sander lucioperca) in Controlled Rearing. Vaccines 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marana, M.H.; Sepúlveda, D.; Chen, D.; Al-Jubury, A.; Jaafar, R.M.; Kania, P.W.; Henriksen, N.H.; Krossøy, B.; Dalsgaard, I.; Lorenzen, N.; et al. A pentavalent vaccine for rainbow trout in Danish aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, P.; Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Synergistic effect of a combined live Vibrio anguillarum and Edwardsiella piscicida vaccine in turbot. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.M.; Eissa, A.E.; ElBanna, N.I.; Albutti, A. Efficiency of monovalent and polyvalent Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio Para-haemolyticus vaccines on the immune response and protection in gilthead sea bream, Sparus aurata (L.) against vibriosis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 111, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Blaney, S.; Houlihan, D.; Secombes, C. Transcriptome response following administration of a live bacterial vaccine in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fei, C.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Transcriptome Profiling Reveals Th17-Like Immune Responses Induced in Zebrafish Bath-Vaccinated with a Live Attenuated Vibrio anguillarum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, L.M.; Whyte, S.K.; Brown, A.B.J.; Van Iderstine, C.; Letendre, C.; Groman, D.; Lewis, J.; Purcell, S.L.; Hori, T.; Fast, M.D. Vaccine-Induced Protection Against Furunculosis Involves Pre-emptive Priming of Humoral Immunity in Arctic Charr. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Hong, S. Characterization of Aeromonas salmonicida and A. sobria isolated from cultured salmonid fish in Korea and development of a vaccine against furunculosis. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Park, J.; You, S.G.; Hong, S. Immuno-stimulatory effects of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Codium fragile in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Li, R.; Xu, Q.; Secombes, C.J.; Wang, T. Two types of TNF-α exist in teleost fish: Phylogeny, expression, and bioactivity analysis of type-II TNF-α3 in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. J. Immunol. Res. 2013, 191, 5959–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Cho, M.; Kim, K.I.; Min, E.Y.; Lim, J.; Hong, S. Transcriptome profiling in head kidney of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) after infection with the low-virulent Nagano genotype of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differ-ential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romstad, A.B.; Reitan, L.J.; Midtlyng, P.; Gravningen, K.; Evensen, Ø. Antibody responses correlate with antigen dose and in vivo protection for oil-adjuvanted, experimental furunculosis (Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida) vaccines in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) and can be used for batch potency testing of vaccines. Vaccine 2013, 31, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origgi, F.C.; Benedicenti, O.; Segner, H.; Sattler, U.; Wahli, T.; Frey, J. Aeromonas salmonicida type III secretion sys-tem-effectors-mediated immune suppression in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 60, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Niu, C.; Storset, A.; Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. Comparison of Aeromonas salmonicida resistant and susceptible salmon families: A high immune response is beneficial for the survival against Aeromonas salmonicida challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broere, F.; van Eden, W. T Cell Subsets and T Cell-Mediated Immunity. In Nijkamp and Parnham’s Principles of Immunopharmacology; Parnham, M.J., Nijkamp, F.P., Rossi, A.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 23–35. ISBN 978-3-030-10811-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kanhere, A.; Hertweck, A.; Bhatia, U.; Gökmen, M.R.; Perucha, E.; Jackson, I.; Lord, G.M.; Jenner, R.G. T-bet and GATA3 orchestrate Th1 and Th2 differentiation through lineage-specific targeting of distal regulatory elements. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Holland, J.W.; Martin, S.; Secombes, C.J. Sequence and expression analysis of two T helper master transcription factors, T-bet and GATA3, in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss and analysis of their expression during bacterial and parasitic infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2010, 29, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleto, I.; Morel, E.; Muñoz-Atienza, E.; Díaz-Rosales, P.; Tafalla, C. Aeromonas salmonicida activates rainbow trout IgM+ B cells signalling through Toll like receptors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflamma-tion-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caipang, C.M.; Hynes, N.; Puangkaew, J.; Brinchmann, M.F.; Kiron, V. Intraperitoneal vaccination of Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua with heat-killed Listonella anguillarum enhances serum antibacterial activity and expression of immune response genes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Sepulcre, M.P.; Roca, F.J.; Castellana, B.; Planas, J.; Meseguer, J.; Mulero, V. The type II interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1RII) of the bony fish gilthead seabream Sparus aurata is strongly induced after infection and tightly regulated at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, M.; Candusso, S.; Galeotti, M.; Volpatti, D. Preliminary study on expression of antimicrobial peptides in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) following in vivo infection with Vibrio anguillarum. A time course experiment. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 43, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelsma, M.; Huising, M.O.; van Muiswinkel, W.B.; Flik, G.; Kwang, J.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Kemenade, B.V.-V. Neuroendocrine–immune interactions in fish: A role for interleukin-1. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2002, 87, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétrilli, V.; Dostert, C.; Muruve, D.A.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A danger sensing complex triggering innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmora, N.; Levy, M.; Pevsner-Fishcer, M.; Elinav, E. Inflammasomes and intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Eigenbrod, T.; Muñoz-Planillo, R.; Nuñez, G. The inflammasome: A caspase-1-activation platform that regulates immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Vale, A.D.; Pereira, P.; Azevedo, J.E.; Dos Santos, N.M.S. Caspase-1 and IL-1β Processing in a Teleost Fish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakamaki, K.; Satou, Y. Caspases: Evolutionary aspects of their functions in vertebrates. J. Fish Biol. 2009, 74, 727–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brisse, M.; Ly, H. Comparative Structure and Function Analysis of the RIG-I-Like Receptors: RIG-I and MDA5. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, L.-F.; Lu, X.-B.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.-A. Grass carp cGASL negatively regulates fish IFN response by targeting MITA. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.-Y.; Zhang, Q.-M.; Gui, J.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B. SVCV infection triggers fish IFN response through RLR signaling pathway. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 86, 1058–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.H.; MacMillan, J.B.; Chen, Z.J. RNA polymerase III detects cytosolic DNA and induces type I interferons through the RIG-I pathway. Cell 2009, 138, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallejo, A.N.; Miller, N.W.; Harvey, N.E.; Cuchens, M.A.; Warr, G.W.; Clem, L.W. Cellular Pathway(S) of Antigen Processing and Presentation in Fish APC: Endosomal Involvement and Cell-Free Antigen Presentation. Dev. Immunol. 1992, 3, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinay, D.S.; Kwon, B.S. 4-1BB signaling beyond T cells. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomiyama, H.; Hieshima, K.; Osada, N.; Kato-Unoki, Y.; Otsuka-Ono, K.; Takegawa, S.; Izawa, T.; Yoshizawa, A.; Kikuchi, Y.; Tanase, S.; et al. Extensive expansion and diversification of the chemokine gene family in zebrafish: Identification of a novel chemokine subfamily CX. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alejo, A.; Tafalla, C. Chemokines in teleost fish species. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2011, 35, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobanga, I.D.; Petrosiute, A.; Huang, A.Y. Chemokines as Cancer Vaccine Adjuvants. Vaccines 2013, 1, 444–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoniak, S. The coagulation system in host defense. Res. Pr. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkelberger, J.R.; Song, W.-C. Complement and its role in innate and adaptive immune responses. Cell Res. 2009, 20, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boshra, H.; Li, J.; Sunyer, J. Recent advances on the complement system of teleost fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2006, 20, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Løvoll, M.; Fischer, U.; Mathisen, G.S.; Bøgwald, J.; Ototake, M.; Dalmo, R.A. The C3 subtypes are differentially regulated after immunostimulation in rainbow trout, but head kidney macrophages do not contribute to C3 transcription. Veter. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.-W.; Zhu, C.-K.; Zhang, Q.-Z. Molecular characterization and expression analysis of complement component C3 in southern catfish (Silurus meridionalis) and a whole mount in situ hybridization study on its ontogeny. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 84, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Li, J. Complement component 3 (C3): An important role in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) experimentally exposed to Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Løvoll, M.; Dalmo, R.A.; Bøgwald, J. Extrahepatic synthesis of complement components in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2007, 23, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Matsushita, M.; Endo, Y. The lectin-complement pathway–its role in innate immunity and evolution. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 198, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.S.; Xin, Y.R.; Yang, X.D.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, H.K.; Liu, M.Q.; Zhang, M.Z.; Daniel, J.G.; Li, J.F.; Wen, H.S. Transcriptional profiles of genes related to stress and immune response in Rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) symptomatically or asymp-tomatically infected with Vibrio anguillarum. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 639489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Time (Day) | Category | Pathway ID | Pathway Terms | No. of DEGs | Fold Enrichment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04060 | Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | 16 | 2.35 |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04514 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | 15 | 3.77 | |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04080 | Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | 14 | 1.80 | |
| Cancer: overview | hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 13 | 2.32 | |
| Infectious disease: viral | hsa05164 | Influenza A | 10 | 2.05 | |
| Signal transduction | hsa04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 8 | 3.28 | |
| Digestive system | hsa04974 | Protein digestion and absorption | 8 | 3.24 | |
| Infectious disease: viral | hsa05160 | Hepatitis C | 8 | 2.14 | |
| Infectious disease: parasitic | hsa05144 | Malaria | 7 | 5.09 | |
| Immune system | hsa04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | 7 | 3.62 | |
| Infectious disease: parasitic | hsa05146 | Amoebiasis | 7 | 2.35 | |
| Signal transduction | hsa04668 | TNF signaling pathway | 7 | 2.33 | |
| Infectious disease: parasitic | hsa05140 | Leishmaniasis | 6 | 3.01 | |
| Digestive system | hsa04970 | Salivary secretion | 6 | 2.49 | |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04512 | ECM–receptor interaction | 6 | 2.46 | |
| Endocrine system | hsa04913 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | 5 | 3.64 | |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | hsa00620 | Pyruvate metabolism | 5 | 4.46 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00270 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 5 | 4.69 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00260 | Glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism | 5 | 4.57 | |
| Infectious disease: bacterial | hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 5 | 3.30 | |
| Immune system | hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 5 | 3.18 | |
| Lipid metabolism | hsa00590 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 5 | 2.92 | |
| Infectious disease: parasitic | hsa05143 | African trypanosomiasis | 4 | 4.32 | |
| Day 3 | Cancer: overview | hsa05205 | Proteoglycans in cancer | 9 | 2.13 |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04514 | Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | 8 | 2.67 | |
| Folding, sorting, and degradation | hsa04141 | Protein processing in the endoplasmic reticulum | 8 | 2.25 | |
| Infectious disease: viral | hsa05164 | Influenza A | 8 | 2.18 | |
| Signal transduction | hsa04020 | Calcium signaling pathway | 8 | 2.12 | |
| Infectious disease: bacterial | hsa05133 | Pertussis | 6 | 3.80 | |
| Immune system | hsa04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 6 | 5.08 | |
| Immune system | hsa04623 | Cytosolic DNA sensing pathway | 6 | 4.45 | |
| Nucleotide metabolism | hsa00240 | Pyrimidine metabolism | 6 | 2.82 | |
| Global and overview maps | hsa01200 | Carbon metabolism | 6 | 2.52 | |
| Infectious disease: bacterial | hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 5 | 4.39 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00260 | Glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism | 5 | 6.08 | |
| Immune system | hsa04612 | Antigen processing and presentation | 5 | 3.12 | |
| Day 5 | Global and overview maps | hsa01100 | Metabolic pathways | 50 | 1.43 |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04080 | Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | 14 | 1.76 | |
| Metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides | hsa01130 | Biosynthesis of antibiotics | 13 | 2.14 | |
| Global and overview maps | hsa01200 | Carbon metabolism | 12 | 3.71 | |
| Signaling molecules and interaction | hsa04060 | Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | 12 | 1.72 | |
| Lipid metabolism | hsa00140 | Steroid hormone biosynthesis | 9 | 5.42 | |
| Signal transduction | hsa04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 8 | 3.21 | |
| Immune system | hsa04610 | Complement and coagulation cascades | 8 | 4.05 | |
| Digestive system | hsa04976 | Bile secretion | 8 | 4.05 | |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | hsa00010 | Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis | 8 | 4.17 | |
| Endocrine system | hsa04922 | Glucagon signaling pathway | 7 | 2.47 | |
| Infectious disease: parasitic | hsa05143 | African trypanosomiasis | 6 | 6.35 | |
| Infectious disease: bacterial | hsa05134 | Legionellosis | 6 | 3.88 | |
| Endocrine system | hsa04913 | Ovarian steroidogenesis | 6 | 4.28 | |
| Global and overview maps | hsa01230 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | 6 | 2.91 | |
| Xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism | hsa00980 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | 6 | 2.83 | |
| Metabolism of cofactors and vitamins | hsa00760 | Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 4 | 4.82 | |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | hsa00630 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 4 | 5.17 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00340 | Histidine metabolism | 4 | 6.35 | |
| Carbohydrate metabolism | hsa00040 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 4 | 4.23 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00250 | Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism | 4 | 3.99 | |
| Amino acid metabolism | hsa00260 | Glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism | 4 | 3.58 |
| Category/Gene Name | Description | Fold-Change/p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 5 | |||||
| Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction | |||||||
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 3.87 | 0.0016 | 2.11 | 0.00485 | ||
| TNFRSF11A | TNF receptor superfamily member 11A | −2.18 | 0.00005 | ||||
| TNFRSF13B | TNF receptor superfamily member 13B | −2.04 | 0.00065 | ||||
| TNFRSF6B | TNF receptor superfamily member 6B | 5.39 | 0.00005 | ||||
| TNFRSF9 | TNF receptor superfamily member 9 | 2.43 | 0.00005 | ||||
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 beta | 3.46 | 0.00015 | ||||
| IL10Rβ | Interleukin 10 receptor subunit beta | 2.63 | 0.00005 | ||||
| IL12β | Interleukin 12B | 3.33 | 0.0258 | 2.26 | 0.0314 | ||
| IL1R1 | Interleukin 1 receptor type 1 | 2.73 | 0.00005 | ||||
| IL1R2 | Interleukin 1 receptor type 2 | 2.02 | 0.00005 | ||||
| IL20RA | Interleukin 20 receptor subunit alpha | 2.51 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CCL13 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 13 | −3.4 | 0.00005 | −2.5 | 0.00005 | ||
| CCL19 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 19 | 2.74 | 0.00005 | 3.28 | 0.00005 | ||
| CCL4 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 | 2.64 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CCL4L2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 like 2 | −2.43 | 0.00015 | ||||
| CCR3 | C-C motif chemokine receptor 3 | −2.68 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CCR7 | C-C motif chemokine receptor 7 | −2.85 | 0.0189 | ||||
| CCR9 | C-C motif chemokine receptor 9 | −2.48 | 0.046 | ||||
| CXCL11 | C-X-C motif chemokine 11 | 2.78 | 0.00115 | ||||
| CXCL12 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 | 2.83 | 0.0495 | ||||
| CXCR1 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 | 3.29 | 0.0005 | ||||
| ACVR1B | Activin A receptor type 1B | −2.23 | 0.0009 | ||||
| GHR | Growth hormone receptor | −2.25 | 0.0072 | ||||
| PPBP | Pro-platelet basic protein | 2.16 | 0.00855 | ||||
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | |||||||
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 3.87 | 0.0016 | 2.11 | 0.00485 | ||
| TNFRSF11A (RANK) | TNF receptor superfamily member 11A | −2.18 | 0.00005 | ||||
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 beta | 3.46 | 0.00015 | ||||
| IL1R1 | Interleukin 1 receptor type 1 | 2.73 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CXCL12 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 | 2.83 | 0.0495 | ||||
| CCL4L2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 like 2 | −2.43 | 0.00015 | ||||
| CCL4 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 | 2.64 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CCL19 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 19 | 2.74 | 0.00005 | 3.28 | 0.00005 | ||
| CCL13 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 13 | −3.4 | 0.00005 | −2.5 | 0.00005 | ||
| TRIM25 | Tripartite motif-containing 25 | 2.09 | 0.00005 | 2.15 | 0.00015 | ||
| PTGS2 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 | 5.34 | 0.01175 | ||||
| DDX58 (RIG-I) | DExD/H-Box Helicase 58 | 2.62 | 0.00005 | ||||
| TNF signaling pathway | |||||||
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 3.87 | 0.0016 | ||||
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 beta | 3.46 | 0.00015 | ||||
| PTGS2 | Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 | 5.34 | 0.01175 | ||||
| MMP9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | 2.81 | 0.00005 | ||||
| MMP14 | Matrix metallopeptidase 14 | 3.65 | 0.00005 | ||||
| MAP2K6 (MKK6) | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 6 | −2.15 | 0.00005 | ||||
| DNM1L (Drp1) | Dynamin 1 Like | −6.23 | 0.03775 | ||||
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | |||||||
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 3.87 | 0.0016 | 2.82 | 0.03365 | ||
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 beta | 3.46 | 0.00015 | 2.34 | 0.01225 | ||
| PYCARD (ASC) | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD | −2.89 | 0.00005 | −2.18 | 0.02475 | ||
| NLRP1 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 1 | −2.16 | 0.0259 | ||||
| MEFV (Pyrin) | MEFV innate immunity regulator, pyrin | 3.43 | 0.00005 | ||||
| HSP90AA1 (Hsp90) | Heat shock protein 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 2.06 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CARD8 | Caspase recruitment domain family member 8 | −2.25 | 0.00005 | ||||
| Cytosolic DNA sensing pathway | |||||||
| IL1β | Interleukin 1 beta | 2.34 | 0.01225 | ||||
| CCL4 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 4 | 2.92 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CASP1 | Caspase 1 | −4.55 | 0.00035 | ||||
| PYCARD (ASC) | Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD | −2.18 | 0.02475 | ||||
| POLR3D (RNA pol III) | RNA polymerase III Subunit D | −2.08 | 0.02185 | ||||
| MB21D1(cGAS) | Cyclic GMP–AMP Synthase | 2.35 | 0.0078 | ||||
| Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) | |||||||
| CD2 | Cluster of differentiation 2 | −2.81 | 0.024 | ||||
| CD22 | Cluster of differentiation 22 | −2.18 | 0.03475 | −2.02 | 0.001 | ||
| CD274 | Cluster of differentiation 274 | 2.32 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CD276 | Cluster of differentiation 276 | 2.69 | 0.0001 | ||||
| CLDN1 | Claudin 1 | 3.78 | 0.00005 | 2.25 | 0.0005 | ||
| CLDN10 | Claudin 10 | −2.96 | 0.03065 | ||||
| CLDN3 | Claudin-3 | −2.24 | 0.03815 | −2.87 | 0.0136 | ||
| CLDN4 | Claudin 4 | −3.49 | 0.0321 | ||||
| CNTN1 | Contactin 1 | −3.33 | 0.00125 | ||||
| CADM1 | Cell adhesion molecule 1 | −2.81 | 0.00005 | −2.66 | 0.00005 | ||
| ITGA6 | Integrin subunit alpha 6 | 2.97 | 0.00565 | ||||
| ITGA8 | Integrin subunit alpha 8 | −2.28 | 0.01655 | ||||
| ITGB1 | Integrin beta-1 | −2.73 | 0.00005 | ||||
| MAG | Myelin associated glycoprotein | −2.09 | 0.0414 | ||||
| OCLN | Occludin | −2.57 | 0.0476 | ||||
| PTPRC | Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C | −2.16 | 0.00005 | ||||
| SDC2 | Syndecan 2 | 2.4 | 0.00005 | ||||
| SDC4 | Syndecan 4 | 2.21 | 0.00005 | ||||
| SIGLEC1 | Sialic acid-binding Ig like lectin 1 | 2.41 | 0.04695 | ||||
| Complement and coagulation cascades | |||||||
| C3 | Complement C3 | 2.57 | 0.0036 | 2.06 | 0.00005 | ||
| C3AR1 | Complement C3a receptor 1 | 2.74 | 0.00005 | ||||
| C7 | Complement C7 | 2.85 | 0.00005 | ||||
| CFH (Factor H) | Complement factor H | −2.75 | 0.0349 | ||||
| MASP1 | MBL-associated serine protease 1 | −2.01 | 0.00735 | ||||
| A2M | Alpha-2-macroglobulin | −2.48 | 0.01375 | ||||
| F3 | Coagulation factor III | −2.35 | 0.0262 | ||||
| F5 | Coagulation factor V | −3.05 | 0.0147 | ||||
| F7 | Coagulation factor VII | −2.63 | 0.0329 | −3.2 | 0.03335 | ||
| FGB (Fibrinogen) | Fibrinogen beta chain | 2.91 | 0.0063 | ||||
| SERPINC1 (AT3) | Serpin family C member 1 | −2.56 | 0.0021 | ||||
| SERPINE1 (PAI) | Serine protease inhibitor (serpin) protein | 2.63 | 0.00005 | ||||
| THBD (TM) | Thrombomodulin | 2.25 | 0.00005 | ||||
| Antigen processing and presentation | |||||||
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | 2.82 | 0.03365 | ||||
| B2M | Beta-2-microglobulin | −2.73 | 0.00045 | ||||
| CALR | Calreticulin | 4.36 | 0.037 | ||||
| CANX | Calnexin | 2.75 | 0.0272 | ||||
| HSP90AA1 (Hsp90) | Heat shock protein 90 alpha family class A member 1 | 2.06 | 0.00005 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, J.; Hong, S. Transcriptome Analysis in the Head Kidney of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Immunized with a Combined Vaccine of Formalin-Inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111234
Lim J, Hong S. Transcriptome Analysis in the Head Kidney of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Immunized with a Combined Vaccine of Formalin-Inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum. Vaccines. 2021; 9(11):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111234
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Jongwon, and Suhee Hong. 2021. "Transcriptome Analysis in the Head Kidney of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Immunized with a Combined Vaccine of Formalin-Inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum" Vaccines 9, no. 11: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111234
APA StyleLim, J., & Hong, S. (2021). Transcriptome Analysis in the Head Kidney of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Immunized with a Combined Vaccine of Formalin-Inactivated Aeromonas salmonicida and Vibrio anguillarum. Vaccines, 9(11), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines9111234






