Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Expressing gB Gene from Predominantly Epidemic Infectious Larygnotracheitis Virus Strain Demonstrates Better Immune Protection in SPF Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statements
2.2. Plasmid, Viruses, Cells, gB Protein, and Experimental Animals
2.3. Sequence Analysis of I6E1 and WG Strain
2.4. Construction of rFPV-gB
2.5. Characterization of rFPV-gB
2.6. Immunization and Challenge Study
2.6.1. Challenge Efficacy of ILTVs
Amplification and Determination of EID50 of ILTVs
Challenge Efficacy of ILTVs in SPF Chickens
2.6.2. Protective Efficacy of rFPV-gB against ILTVs in SPF Chickens
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Analysis of I6E1 and WG Strain
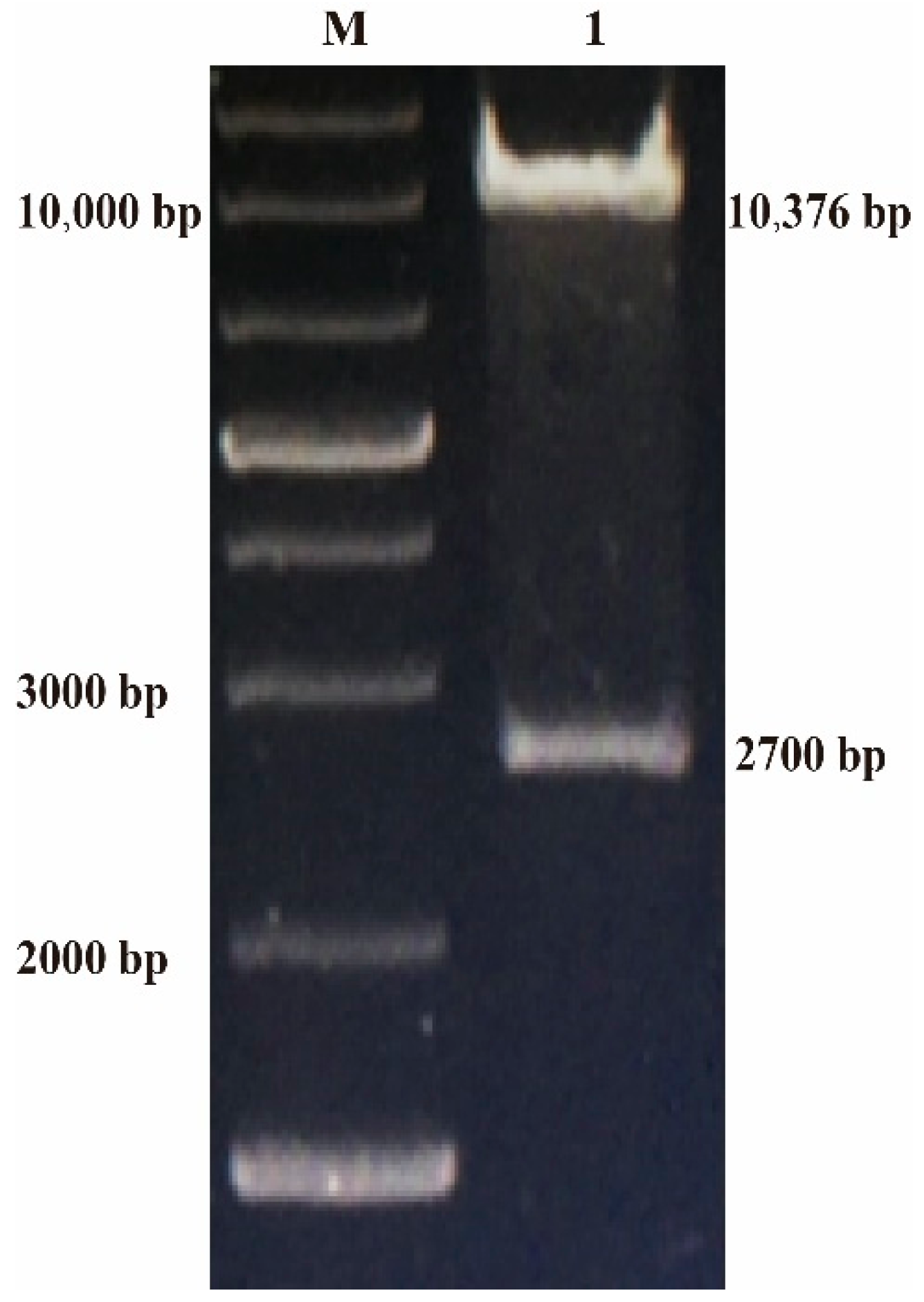
3.2. Construction of rFPV of ILTV gB Gene
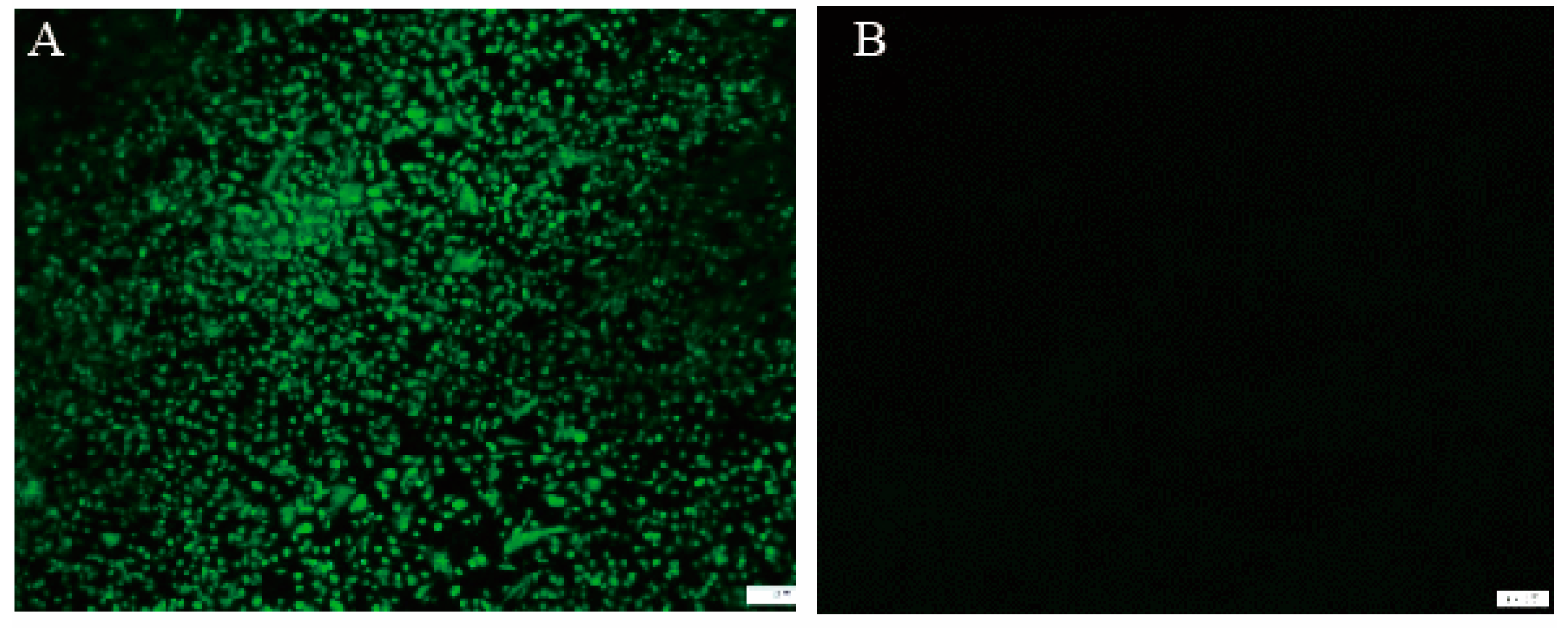
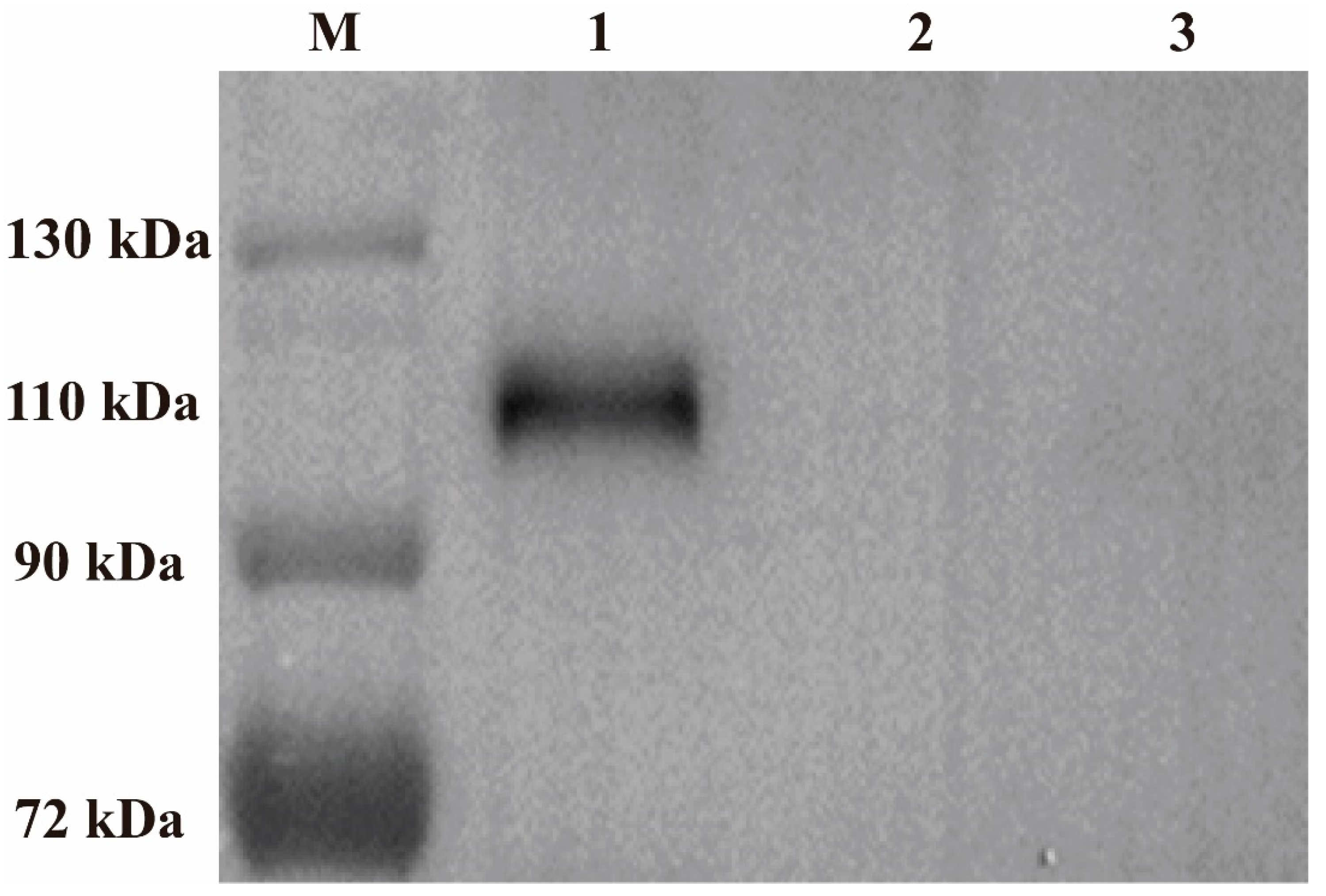
3.3. Characterization and Expression of ILTV gB Gene in rFPV
3.4. Virus Growth Curve
3.5. Challenge Study of ILTVs in SPF Chickens
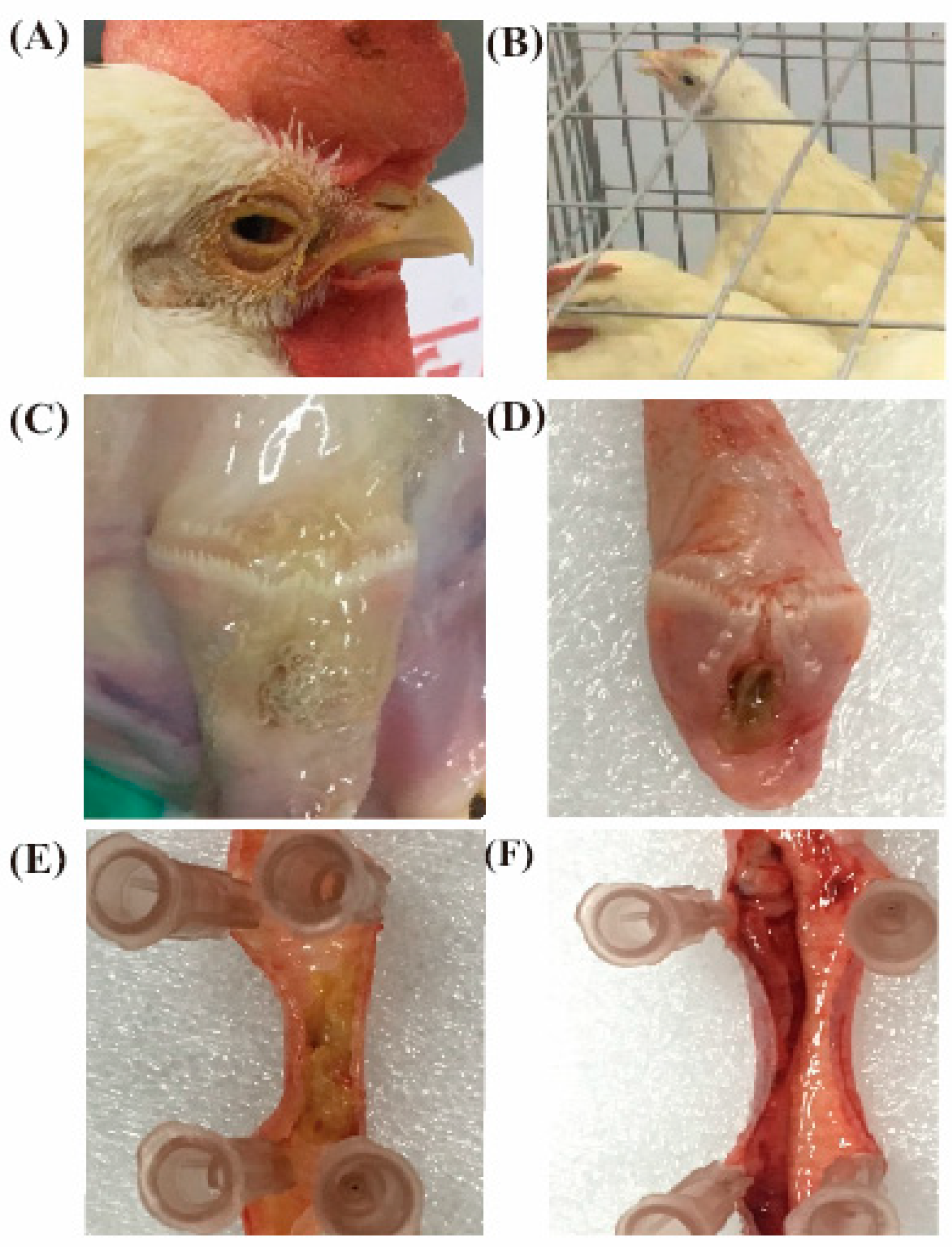
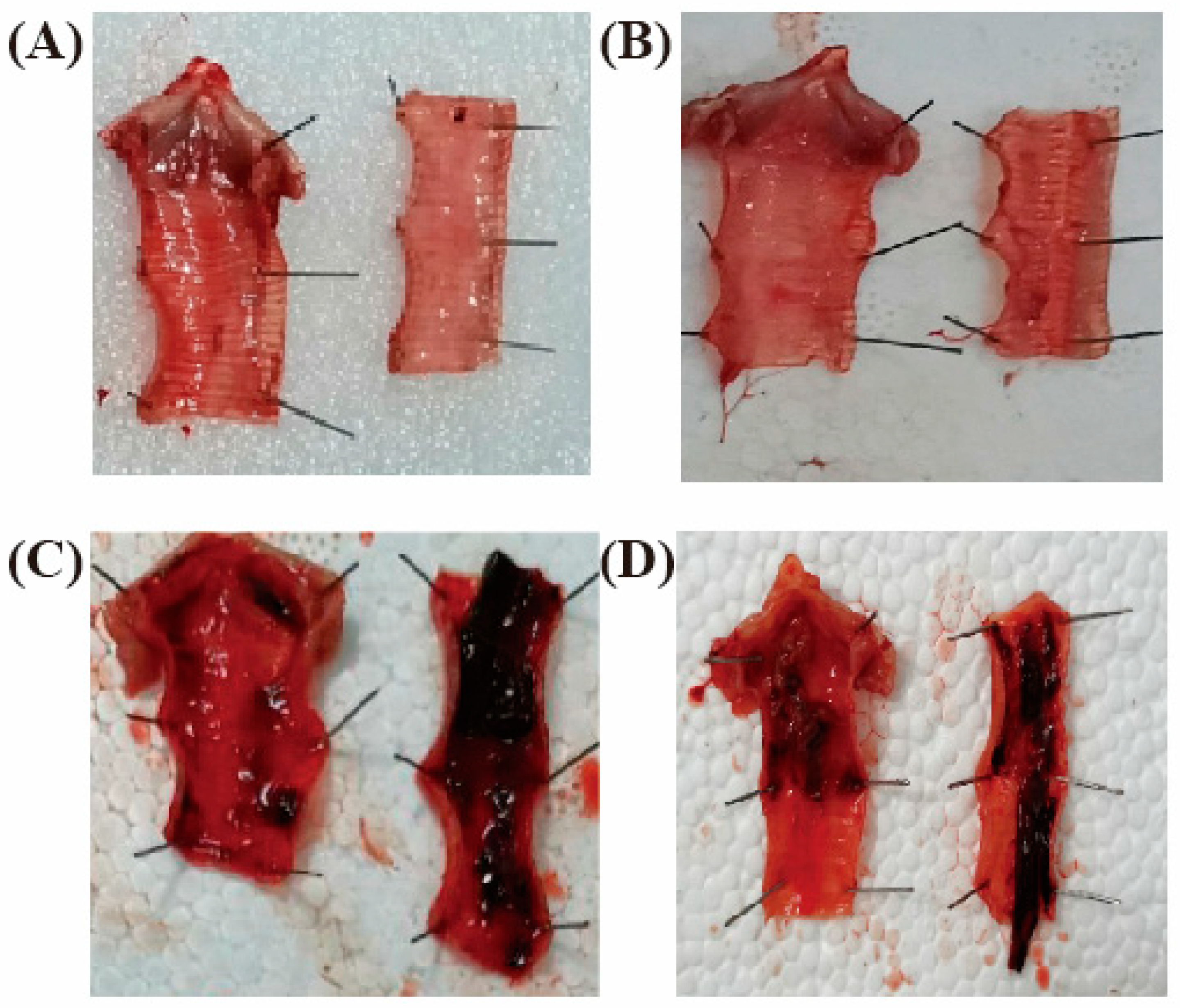
3.5.1. Clinical Signs and Throat Tracheal Lesions of Chickens after Challenge
3.5.2. The Clinical Index, Morbidity, and Mortality of I1E1, I6E1, WG, and I19
3.6. Protection Induced by Immunization with rFPV-gB
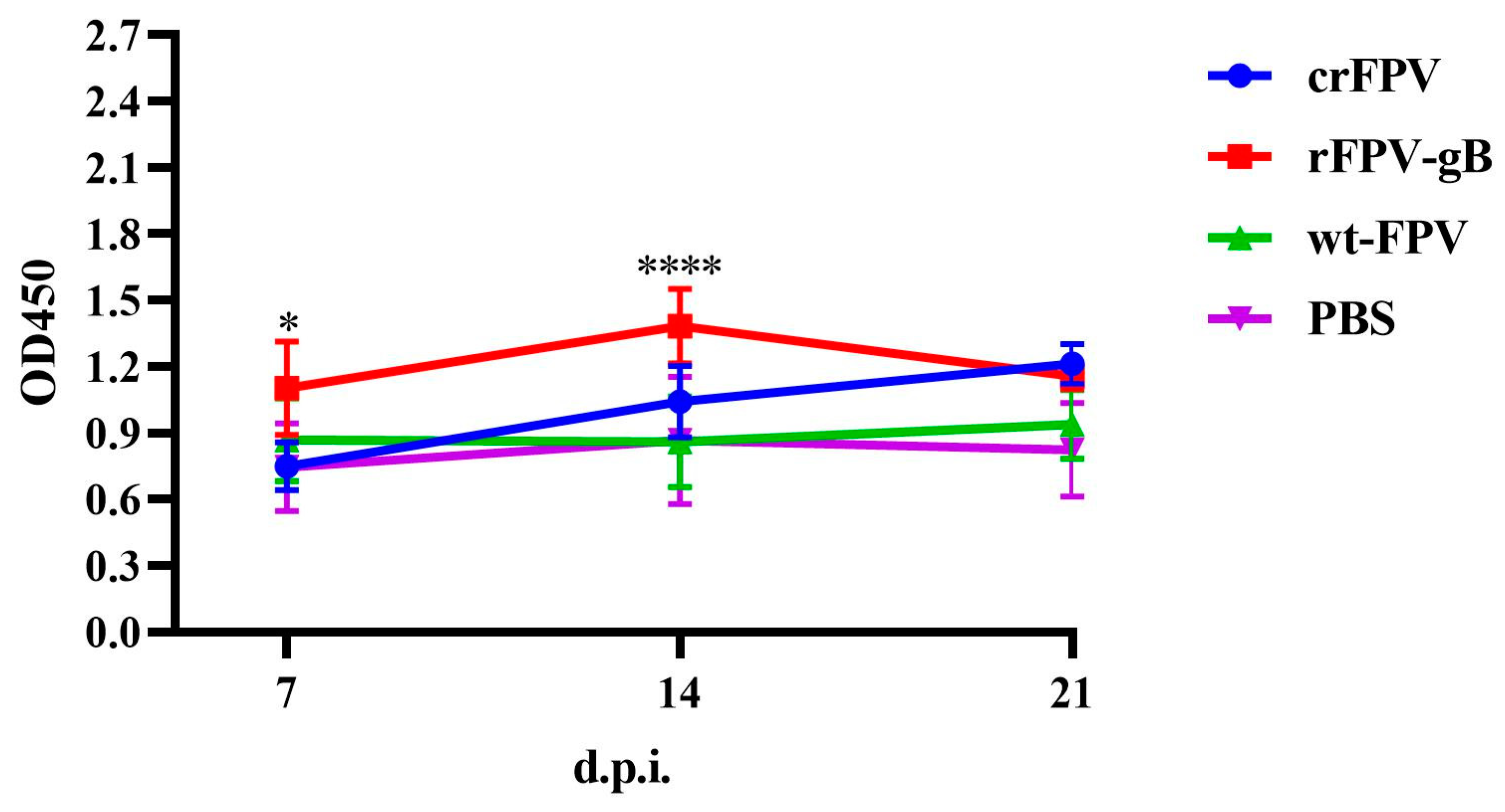
3.6.1. Antibody Responses to ILTV after Vaccination
3.6.2. Clinical Signs and Laryngotracheal Lesions of Chickens after Immunization with rFPV-gB against ILTV Strain I19
3.6.3. The Clinical Index, Morbidity, and Mortality of Chickens after Immunization with rFPV-gB against ILTV Strain I19
3.6.4. Protection Percentage of SPF Chickens by Immunization with rFPV-gB
3.6.5. Virus Shedding
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.G.; Ma, J.; Xue, C.Y.; Wang, W.; Guo, C.; Chen, F.; Qin, J.P.; Huang, N.H.; Bi, Y.Z.; Cao, Y.C. Dynamic distribution and tissue tropism of infectious laryngotracheitis virus in experimentally infected chickens. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagust, T.J.; Jones, R.C.; Guy, J.S. Avian infectious laryngotracheitis. Rev. Sci Tech. 2000, 19, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufour-Zavala, L. Epizootiology of infectious laryngotracheitis and presentation of an industry control program. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, H.; Xue, M.; Wang, Y. Complete genome sequence of the first Chinese virulent infectious laryngotracheitis virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kong, C.; Cui, X.; Cui, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, S.; Hao, L.; Wang, Y. Detection of infectious laryngotracheitis virus by real-time PCR in naturally and experimentally infected chickens. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.; Volkening, J.; Riblet, S.; Spatz, S. Genomic sequence analysis of the United States infectious laryngotracheitis vaccine strains chicken embryo origin (CEO) and tissue culture origin (TCO). Virology 2013, 440, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenczei, E.F.; Marty, E.W. Strain Stability and Immunologic Characteristics of a Tissue-Culture-Modified Infectious Laryngotracheitis Virus. Avian Dis. 1965, 9, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samberg, Y.; Cuperstein, E.; Bendheim, U.; Aronovici, I. The development of a vaccine against avian infectious laryngotracheitis. IV. Immunization of chickens with a modified laryngotracheitis vaccine in the drinking water. Avian Dis. 1971, 15, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathne, D.S.; Noormohammadi, A.H.; Browning, G.F.; Quinteros, J.A.; Underwood, G.J.; Hartley, C.A.; Coppo, M.J.; Devlin, J.M.; Diaz-Mendez, A. Pathogenesis and tissue tropism of natural field recombinants of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew-Crumpton, R.; Vaz, P.K.; Devlin, J.M.; O’Rourke, D.; Blacker-Smith, H.P.; Konsak-Ilievski, B.; Hartley, C.A.; Noormohammadi, A.H. Spread of the newly emerging infectious laryngotracheitis viruses in Australia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 43, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.M.; Levings, R.L.; Davis, A.J.; Sturtz, D.R. Recombination of pseudorabies virus vaccine strains in swine. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1991, 52, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brun, A.; Albina, E.; Barret, T.; Chapman, D.A.; Czub, M.; Dixon, L.K.; Keil, G.M.; Klonjkowski, B.; Le Potier, M.F.; Libeau, G.; et al. Antigen delivery systems for veterinary vaccine development. Viral-vector based delivery systems. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6508–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.A.; Laidlaw, S.M.; Eldaghayes, I.; Kaiser, P.; Cottingham, M.G. Fowlpox virus as a recombinant vaccine vector for use in mammals and poultry. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2005, 4, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagnozzi, A.; Zavala, G.; Riblet, S.M.; Mundt, A.; Garcia, M. Protection induced by commercially available live-attenuated and recombinant viral vector vaccines against infectious laryngotracheitis virus in broiler chickens. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, A.R.; Schat, K.A.; Lee, L.F.; Hunt, H.D. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response in chickens immunized with a recombinant fowlpox virus expressing Marek’s disease herpesvirus glycoprotein B. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 62, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.; Christensen, L.; Gettig, R.; Goebel, J.; Bouquet, J.F.; Mickle, T.R.; Paoletti, E. Efficacy of a recombinant fowl pox-based Newcastle disease virus vaccine candidate against velogenic and respiratory challenge. Avian Dis. 1996, 40, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursnell, M.E.; Green, P.F.; Samson, A.C.; Campbell, J.I.; Deuter, A.; Peters, R.W.; Millar, N.S.; Emmerson, P.T.; Binns, M.M. A recombinant fowlpox virus expressing the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase gene of Newcastle disease virus (NDV) protects chickens against challenge by NDV. Virology 1990, 178, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swayne, D.E.; Beck, J.R.; Kinney, N. Failure of a recombinant fowl poxvirus vaccine containing an avian influenza hemagglutinin gene to provide consistent protection against influenza in chickens preimmunized with a fowl pox vaccine. Avian Dis. 2000, 44, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.I.; Vagnozzi, A.; Dorea, F.; Riblet, S.M.; Mundt, A.; Zavala, G.; Garcia, M. Protection against infectious laryngotracheitis by in ovo vaccination with commercially available viral vector recombinant vaccines. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, S.; Gingerich, E.N.; Casavant, S.; Eckroade, R.J. Evaluation of the efficacy of a live fowlpox-vectored infectious laryngotracheitis/avian encephalomyelitis vaccine against ILT viral challenge. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, G.Z.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, L.; Qiu, H.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, M. Protection of chickens from infectious laryngotracheitis with a recombinant fowlpox virus expressing glycoprotein B of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Avian Pathol. 2001, 30, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, W.J.; Chen, S.J.; Shi, H.Y.; Liu, X.F. Influence of nonessential region on protective efficacy of recombinant fowlpox viruses. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2005, 45, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, H.X.; Han, Z.X.; Kong, X.G.; Liu, S.W. Pathogenicity study of infectious laryngotracheitis virus LJS09. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2015, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Yadav, K.; Kumar, R.; Chaudhary, N.; Kumar, S. Glycoprotein D peptide-based diagnostic approach for the detection of avian infectious laryngotracheitis antibodies. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; La, T.M.; Choi, I.S.; Song, C.S.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, S.W. Genotyping of infectious laryngotracheitis virus using allelic variations from multiple genomic regions. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spatz, S.J.; Garcia, M.; Riblet, S.; Ross, T.A.; Volkening, J.D.; Taylor, T.L.; Kim, T.; Afonso, C.L. MinION sequencing to genotype US strains of infectious laryngotracheitis virus. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, L.; Moss, B. Oligonucleotide sequence signaling transcriptional termination of vaccinia virus early genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6417–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earl, P.L.; Hugin, A.W.; Moss, B. Removal of cryptic poxvirus transcription termination signals from the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope gene enhances expression and immunogenicity of a recombinant vaccinia virus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 2448–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, D.; Wang, M.; Tan, P.; Li, X.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Construction and characterization of novel fowlpox virus shuttle vectors. Virus Res. 2015, 197, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, X.R.; Chen, S.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Peng, D.X.; Liu, X.F. Construction of recombinant fowlpox virus coexpressing HA gene from H5N1 avian influenza virus and chicken interleukin-2 gene and assessment of its protective efficacy. Chin. J. Virol. 2009, 25, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.J.; Sun, L.; Liu, W.J.; Sun, X.H.; Liu, X.F. Recombinant fowlpox virus coexpressing HA and NA gene from subtype H5N1 of avian influenza virus and its protective efficacy. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2006, 46, 111–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bagust, T.J.; Calnek, B.W.; Fahey, K.J. Gallid-1 herpesvirus infection in the chicken. 3. Reinvestigation of the pathogenesis of infectious laryngotracheitis in acute and early post-acute respiratory disease. Avian Dis. 1986, 30, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Jenkins, K.A.; Hilton, L.S.; Kimpton, W.G.; Bean, A.G.; Lowenthal, J.W. Cytokines as adjuvants for avian vaccines. Immunol.Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Chen, S.; Ding, P.; Chai, M.; Xu, C.; Gan, J.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. The immune response of a recombinant fowlpox virus coexpressing the HA gene of the H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus and chicken interleukin 6 gene in ducks. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6279–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, K.; Sharma, J.M.; Winslow, B.J.; Junker, D.E.; Reddy, S.; Cochran, M.; McMillen, J. Recombinant fowlpox viruses coexpressing chicken type I IFN and Newcastle disease virus HN and F genes: Influence of IFN on protective efficacy and humoral responses of chickens following in ovo or post-hatch administration of recombinant viruses. Vaccine 1998, 16, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Cui, B.A.; Cui, P.; Sheng, M.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.J.; Geng, J.W. Construction and immunogenicity of a recombinant fowlpox vaccine coexpressing S1 glycoprotein of infectious bronchitis virus and chicken IL-18. Vaccine 2010, 28, 8112–8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Jin, N.; Shen, G.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H.J.; Zheng, M.; Lu, H.; Huo, X.; Jin, M.; Yin, G.; et al. Immune responses of swine inoculated with a recombinant fowlpox virus co-expressing P12A and 3C of FMDV and swine IL-18. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 121, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Sun, Y.K.; Tian, Z.C.; Shi, X.M.; Tong, G.Z.; Liu, S.W.; Zhi, H.D.; Kong, X.G.; Wang, M. Protection of chickens against infectious bronchitis by a recombinant fowlpox virus co-expressing IBV-S1 and chicken IFNgamma. Vaccine 2009, 27, 7046–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiley, K.L.; McNeal, M.M.; Basu, M.; Choi, A.H.; Clements, J.D.; Ward, R.L. Association of gamma interferon and interleukin-17 production in intestinal CD4+ T cells with protection against rotavirus shedding in mice intranasally immunized with VP6 and the adjuvant LT(R192G). J. Virol. 2007, 81, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, W.; Ziemann, K.; Teifke, J.P.; Werner, O.; Mettenleiter, T.C. The non-essential UL50 gene of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus encodes a functional dUTPase which is not a virulence factor. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Class | TK (%) | ICP4 | ORFB-TK | gB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WG | I6E1 | WG | I6E1 | WG | I6E1 | WG | I6E1 | |
| 1 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| 2 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| 3 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| 4 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.7 | 100 | 100 |
| 5 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| 6 | 99.5 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.8 |
| 7 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.9 | 99.8 | 99.7 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| 8 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99.7 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 9 | 100 | 100 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.9 | 99.7 | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| 10 | 100 | 100 | 99.6 | 99.6 | 99.7 | 99.5 | 99.7 | 99.6 |
| Group a | Dose | Challenge Route | Clinical Index (Total Score/Total Chickens) b | Morbidity (Number of Cases/Total Chickens) c | Mortality (Number of Deaths/Total Chickens) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1E1 | 105 EID50/per | intraocular-nasal route | 0.75 (3/4) | 75% (3/4) | 0 (0/4) |
| I6E1 | 105 EID50/per | intraocular-nasal route | 0.75 (3/4) | 75% (3/4) | 0 (0/4) |
| WG | 105 EID50/per | intraocular-nasal route | 1.5 (6/4) | 100% (4/4) | 0 (0/4) |
| 106 EID50/per | oropharyngeal route | 3 (12/4) | 100% (4/4) | 100% (4/4) | |
| I19 | 105 EID50/per | intraocular-nasal route | 1.5 (6/4) | 100% (4/4) | 0 (0/4) |
| 106 EID50/per | oropharyngeal route | 2.5 (10/4) | 100% (4/4) | 50% (2/4) |
| Immunization Group a. | Clinical Index (Total Score/Total Chickens) b | Morbidity (Number of Cases/Total Chickens) c | Mortality (Number of Deaths/Total Chickens) c |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial rFPV vaccine | 0.6 (6/10) | 40% (4/10) a | 10% (1/10) |
| rFPV-gB | 0.3 (3/10) | 30% (3/10) a | 0 (0/10) |
| wt-FPV | 2.5 (25/10) | 100% (10/10) b | 60% (6/10) |
| PBS | 2.4 (24/10) | 100% (10/10) | 60% (6/10) |
| Immunization Group | Immunization Dose | Mortality (Number of Deaths/Total Chickens) | Protection Index (PI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial rFPV vaccine | 105 PFU c/0.2 mL | 1/10 (10%) b | 83.3 |
| rFPV-gB | 105 PFU/0.2 mL | 0/10 (0) a | 100 |
| wt-FPV | 105 PFU/0.2 mL | 6/10 (60%) b | 0 |
| PBS | 0.2 mL | 6/10 (60%) | 0 |
| Immunization Group | I19 Virus Isolation Rate (Positive Number/Total Number) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d.p.i. a | 5 d.p.i. | 7 d.p.i. | |
| Commercial rFPV vaccine | 90% b (9/10) c | 100% (9/9) | 100% (9/9) |
| rFPV282E4-gB | 70% (7/10) | 100% (10/10) | 100% (10/10) |
| wt-FPV282E4 | 100% (10/10) | 100% (4/4) | 100% (4/4) |
| PBS | 100% (10/10) | 100% (7/7) | 100% (4/4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Xu, N.; Ta, L.; Li, S.; Su, X.; Xue, J.; Du, Y.; Qin, T.; Peng, D. Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Expressing gB Gene from Predominantly Epidemic Infectious Larygnotracheitis Virus Strain Demonstrates Better Immune Protection in SPF Chickens. Vaccines 2020, 8, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040623
Chen S, Xu N, Ta L, Li S, Su X, Xue J, Du Y, Qin T, Peng D. Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Expressing gB Gene from Predominantly Epidemic Infectious Larygnotracheitis Virus Strain Demonstrates Better Immune Protection in SPF Chickens. Vaccines. 2020; 8(4):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040623
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Sujuan, Nuo Xu, Lei Ta, Shi Li, Xiang Su, Jing Xue, Yinping Du, Tao Qin, and Daxin Peng. 2020. "Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Expressing gB Gene from Predominantly Epidemic Infectious Larygnotracheitis Virus Strain Demonstrates Better Immune Protection in SPF Chickens" Vaccines 8, no. 4: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040623
APA StyleChen, S., Xu, N., Ta, L., Li, S., Su, X., Xue, J., Du, Y., Qin, T., & Peng, D. (2020). Recombinant Fowlpox Virus Expressing gB Gene from Predominantly Epidemic Infectious Larygnotracheitis Virus Strain Demonstrates Better Immune Protection in SPF Chickens. Vaccines, 8(4), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8040623





