HIV gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Recombinant HIV gp120 Proteins
2.3. Human IgG Anti-IgE
2.4. Human Monoclonal IgM and Human Polyclonal IgG
2.5. Isolation of HLMCs
2.6. Assays of Histamine, LTC4, and PGD2
2.7. VEGF-A and VEGF-C Release
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
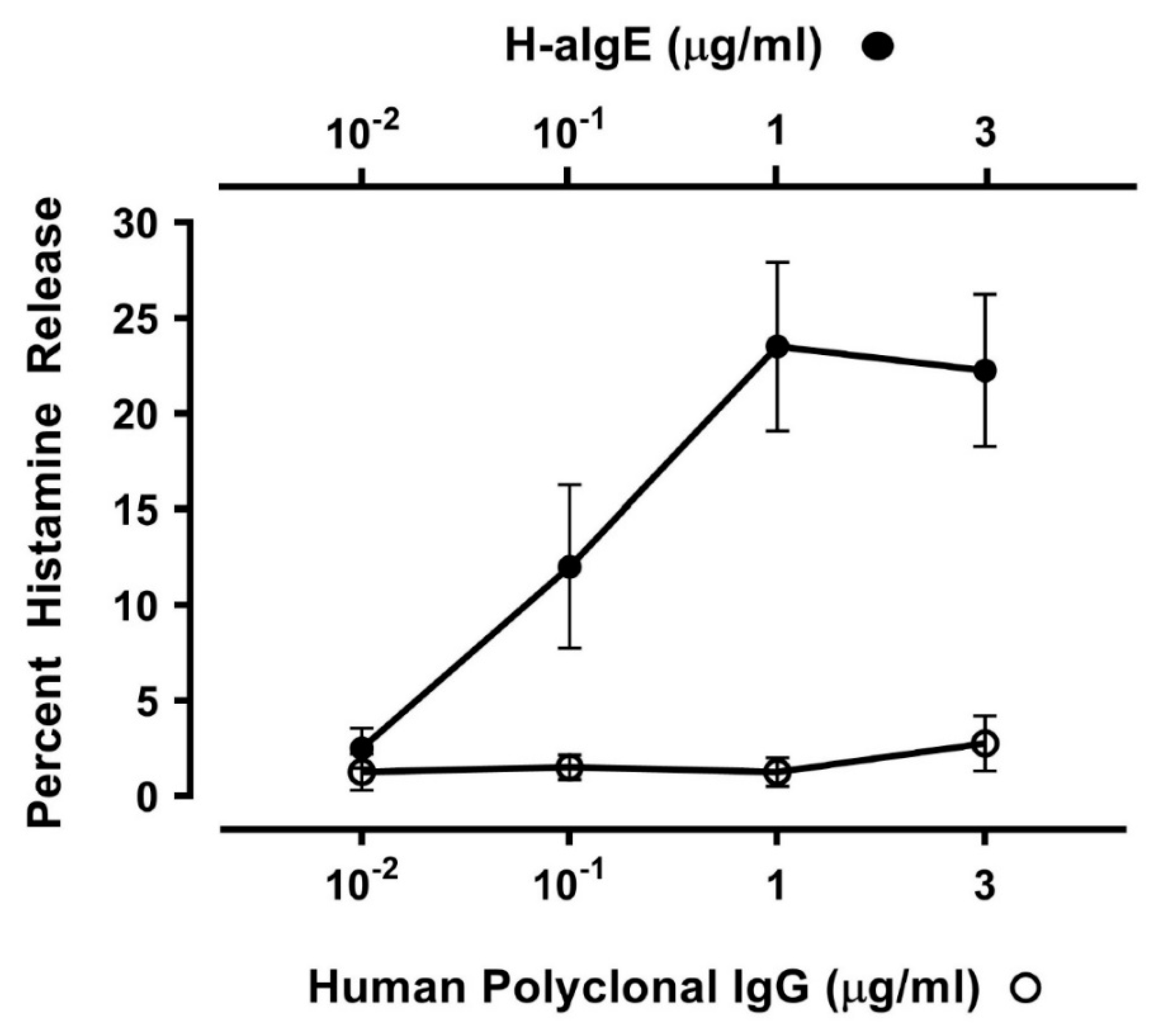
3.1. Effect of Human IgG Anti-IgE on Mediator Release from HLMCs
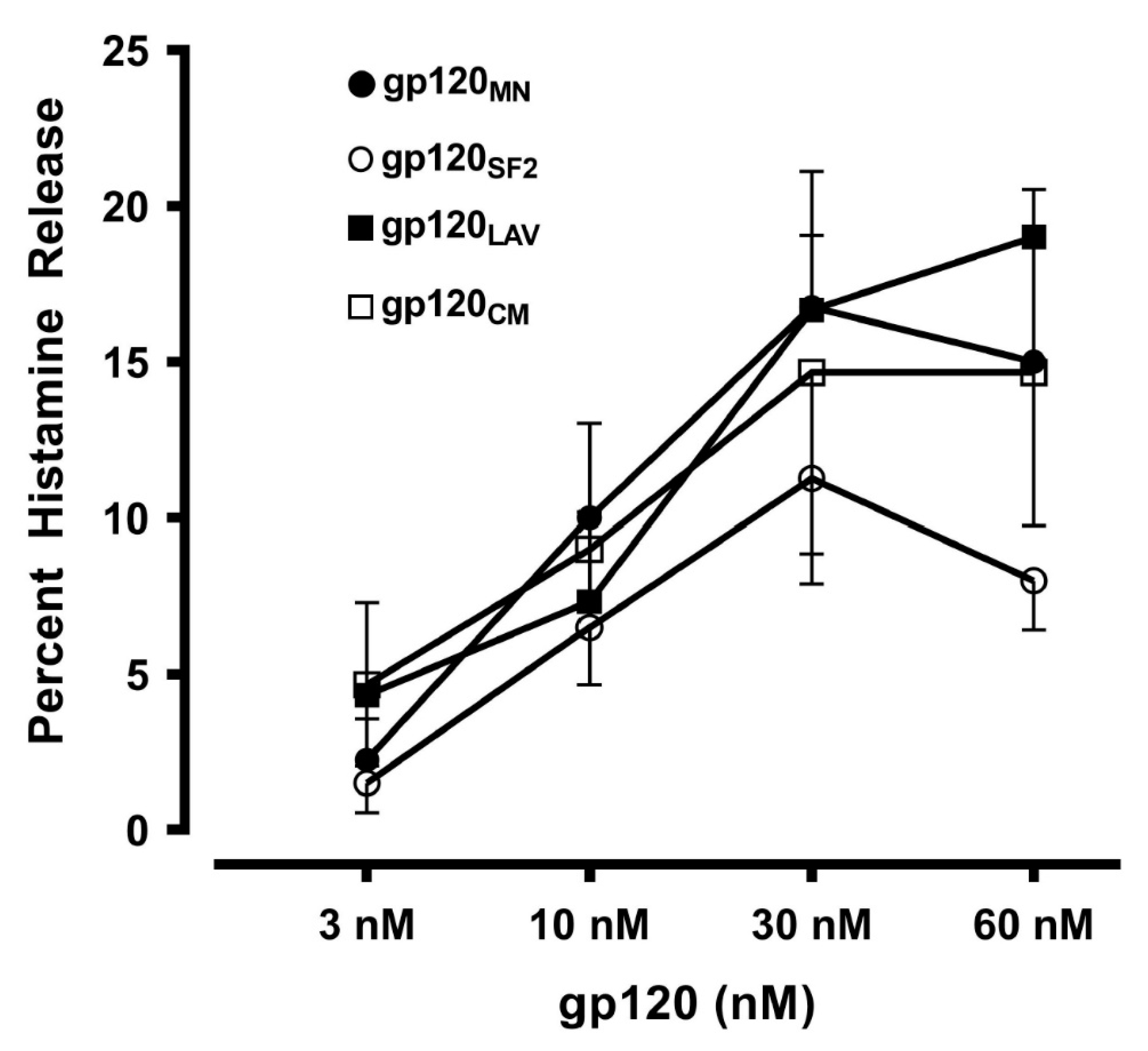
3.2. Effects of gp120 from Divergent HIV Isolates from Different Clades on Mediator Release from HLMCs
3.3. Correlation between Histamine and Tryptase Release Induced by gp120 from HLMCs
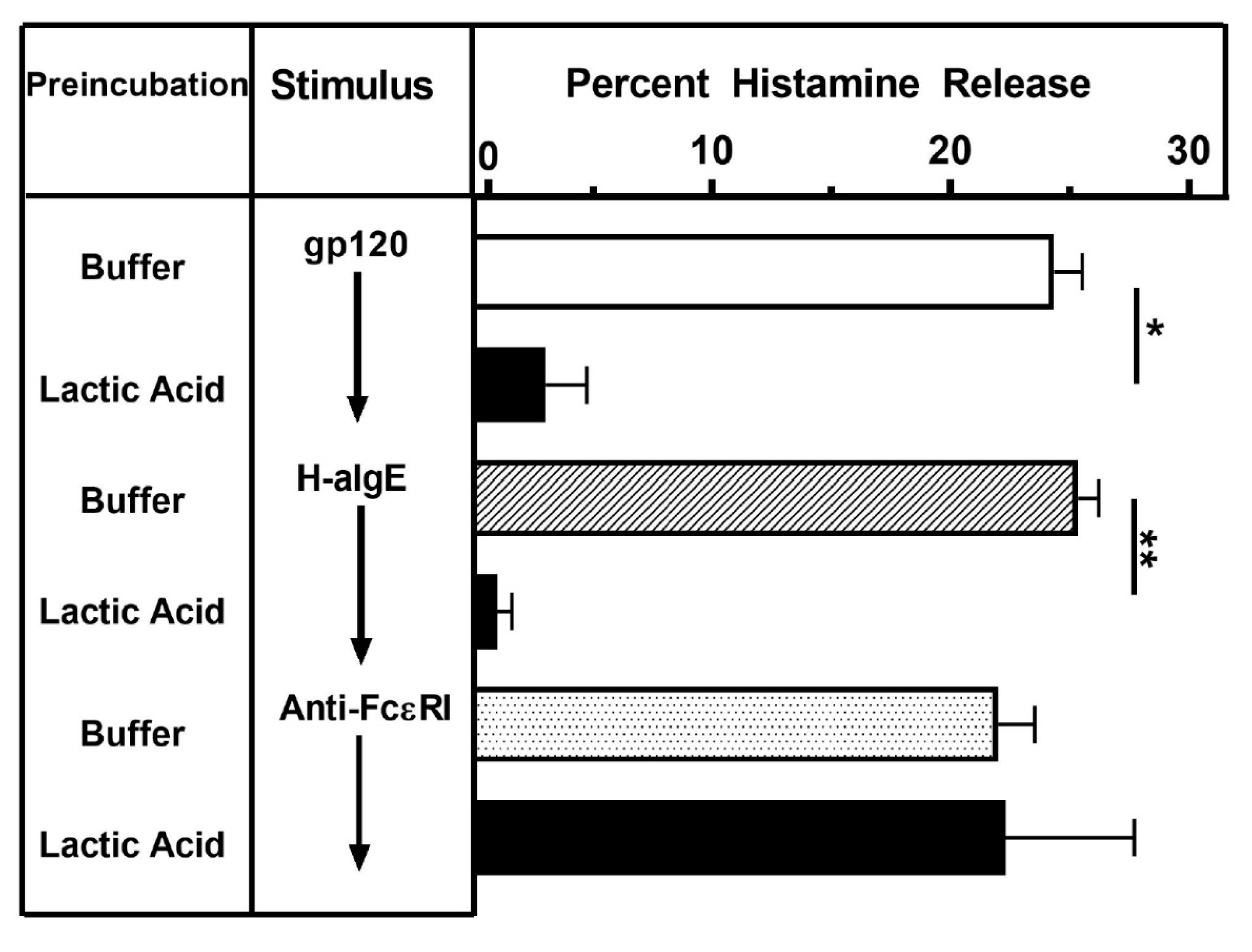
3.4. Effect of Lactic Acid on gp120-Induced Histamine Release from HLMCs
3.5. Effects of Different IgM Myeloma Proteins on gp120-Induced Mediator Release from HLMCs
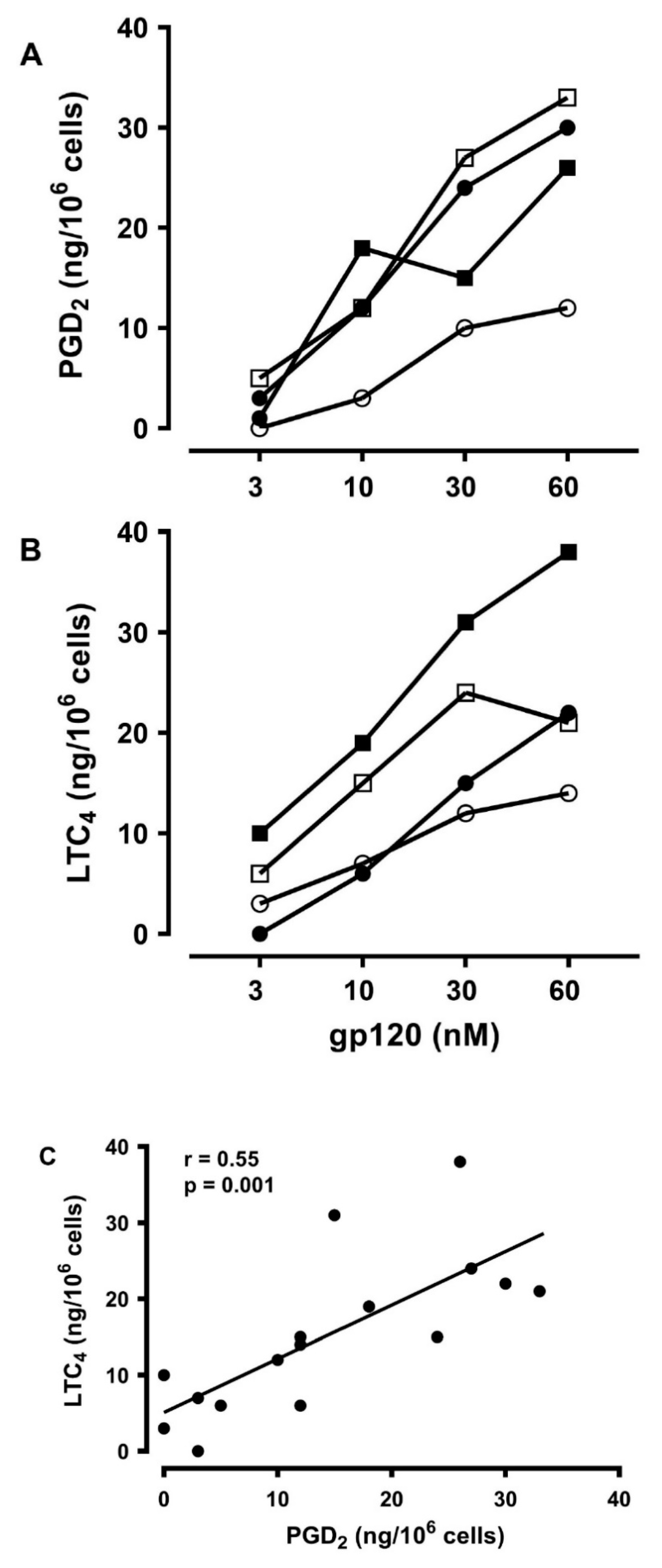
3.6. Effects of gp120 on the De Novo Synthesis of PGD2 and LTC4 from HLMCs
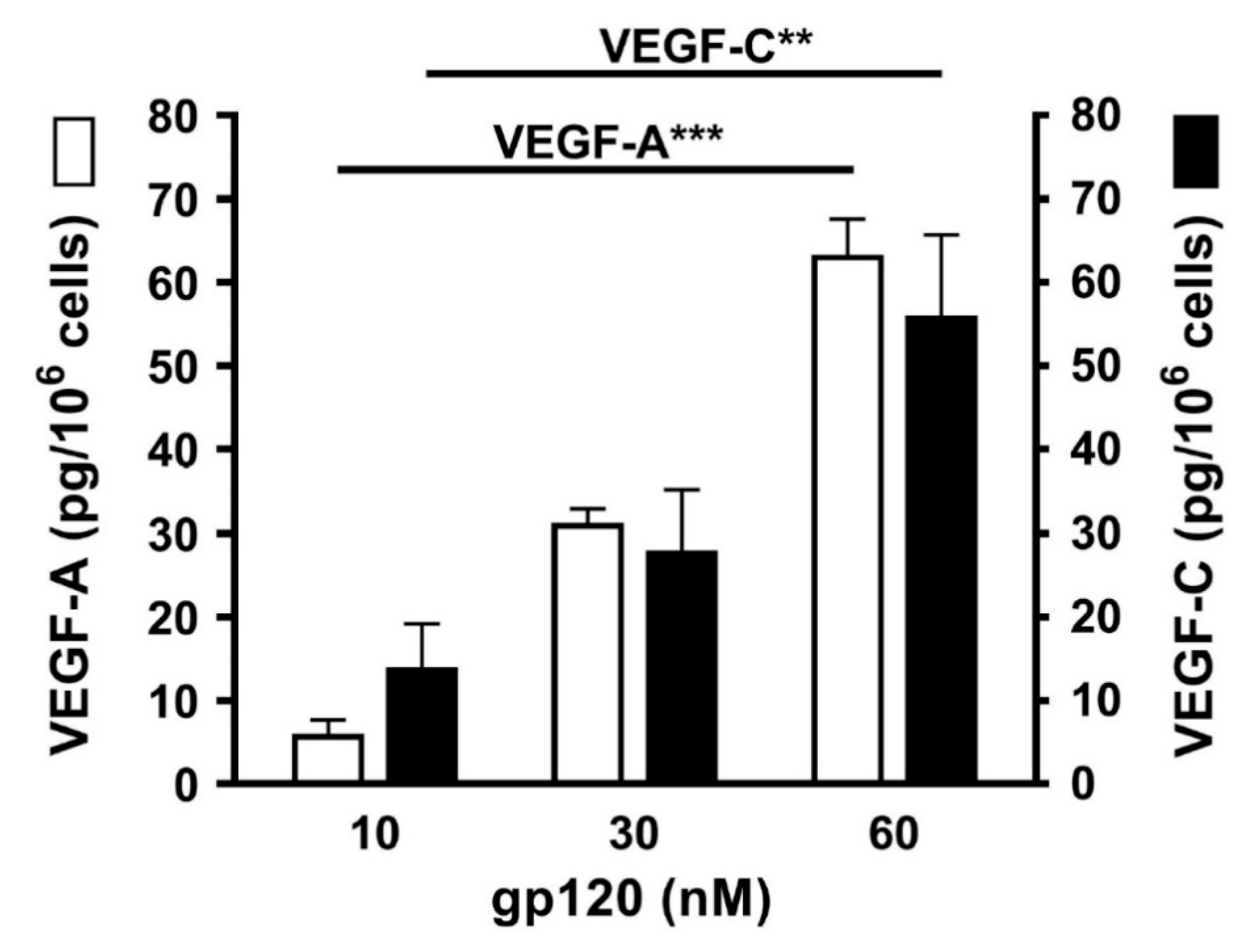
3.7. Effects of gp120 on the Release of Angiogenic and Lymphangiogenic Factors from HLMCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APCs | Antigen-presenting cells |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| FcεRI | High-affinity receptor for IgE |
| FCS | Fetal calf serum |
| gp120 | Glycoprotein 120 |
| H | Heavy |
| H-aIgE | Human IgG anti-IgE |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| HLMCs | Human lung mast cells |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| L | Light |
| LTC4 | Cysteinyl leukotriene C4 |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| PGD2 | Prostaglandin D2 |
| Sag | Superantigen |
| SE | Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| V | Variable |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H. HIV-1 functional cure: Will the dream come true? BMC Med. 2015, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siliciano, J.D.; Kajdas, J.; Finzi, D.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.B.; Kovacs, C.; Gange, S.J.; Siliciano, R.F. Long-term follow-up studies confirm the stability of the latent reservoir for HIV-1 in resting CD4+ T cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiras, M.; Lopez-Huertas, M.R.; Perez-Olmeda, M.; Alcami, J. Understanding HIV-1 latency provides clues for the eradication of long-term reservoirs. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzon, M.J.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Shaw, A.; Seiss, K.; Ouyang, Z.; Martin-Gayo, E.; Leng, J.; Henrich, T.J.; Li, J.Z.; et al. HIV-1 persistence in CD4+ T cells with stem cell-like properties. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Moron, S.; Berenguer, J.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.; Jimenez-Sousa, M.A.; Canorea, I.; Guardiola, J.M.; Crespo, M.; Quereda, C.; Sanz, J.; Carrero, A.; et al. Prevalence of hepatitis E infection in HIV/HCV-coinfected patients in Spain (2012–2014). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Huertas, M.R.; Palladino, C.; Garrido-Arquero, M.; Esteban-Cartelle, B.; Sanchez-Carrillo, M.; Martinez-Roman, P.; Martin-Carbonero, L.; Ryan, P.; Dominguez-Dominguez, L.; Santos, I.L.; et al. HCV-coinfection is related to an increased HIV-1 reservoir size in cART-treated HIV patients: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Kunisaki, K.M.; Morris, A. Pulmonary disease in HIV-infected adults in the era of antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 2018, 32, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githinji, L.N.; Gray, D.M.; Zar, H.J. Lung function in HIV-infected children and adolescents. Pneumonia (Nathan) 2018, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigna, J.J.; Kenne, A.M.; Asangbeh, S.L.; Sibetcheu, A.T. Prevalence of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the global population with HIV: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, e193–e202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiderlen, T.R.; Siehl, J.; Hentrich, M. HIV-Associated Lung Cancer. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2017, 40, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, D.; Bon, J.; Morris, A. Obstructive Lung Disease in HIV-Phenotypes and Pathogenesis. Curr. HIV/Aids Rep. 2019, 16, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel-Diez, J.; Lopez-de-Andres, A.; Jimenez-Garcia, R.; Puente-Maestu, L.; Jimenez-Trujillo, I.; Hernandez-Barrera, V.; Resino, S.; Alvaro-Meca, A. Trends in Epidemiology of COPD in HIV-Infected Patients in Spain (1997-2012). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basyal, B.; Jarrett, H.; Barnett, C.F. Pulmonary Hypertension in HIV. Can. J. Cardiol. 2019, 35, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodewald, H.R.; Feyerabend, T.B. Widespread immunological functions of mast cells: Fact or fiction? Immunity 2012, 37, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reber, L.L.; Marichal, T.; Galli, S.J. New models for analyzing mast cell functions in vivo. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Yi, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.; et al. Adult Connective Tissue-Resident Mast Cells Originate from Late Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Immunity 2018, 49, 640–653e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Galdiero, M.R.; Granata, F.; Criscuolo, G.; Spadaro, G.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G. Physiological Roles of Mast Cells: Collegium Internationale Allergologicum Update 2019. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 179, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, F.; Granata, F.; Varricchi, G.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. Immunopharmacological modulation of mast cells. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2014, 17, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casolaro, V.; Galeone, D.; Giacummo, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Melillo, G.; Marone, G. Human basophil/mast cell releasability. V. Functional comparisons of cells obtained from peripheral blood, lung parenchyma, and bronchoalveolar lavage in asthmatics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989, 139, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilionis, R.; Engblom, C.; Pfirschke, C.; Savova, V.; Zemmour, D.; Saatcioglu, H.D.; Krishnan, I.; Maroni, G.; Meyerovitz, C.V.; Kerwin, C.M.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics of Human and Mouse Lung Cancers Reveals Conserved Myeloid Populations across Individuals and Species. Immunity 2019, 50, 1317–1334.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, A.; Beaven, M.A.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mast cells signal their importance in health and disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piliponsky, A.M.; Romani, L. The contribution of mast cells to bacterial and fungal infection immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Raap, U.; Rivellese, F.; Marone, G.; Gibbs, B.F. Human mast cells and basophils-How are they similar how are they different? Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J. The Mast Cell-IgE Paradox: From Homeostasis to Anaphylaxis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradding, P.; Arthur, G. Mast cells in asthma--state of the art. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 194–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Rivellese, F.; de Paulis, A. Are Basophils and Mast Cells Masters in HIV Infection? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 171, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurmond, J.; Rivellese, F.; Dorjee, A.L.; Bakker, A.M.; Rombouts, Y.J.; Rispens, T.; Wolbink, G.; Zaldumbide, A.; Hoeben, R.C.; Huizinga, T.W.; et al. Toll-like receptor triggering augments activation of human mast cells by anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.S.; Portales-Cervantes, L.; Leong, E. Mast Cell Responses to Viruses and Pathogen Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piliponsky, A.M.; Acharya, M.; Shubin, N.J. Mast Cells in Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal Infection Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voehringer, D. Protective and pathological roles of mast cells and basophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortaz, E.; Folkerts, G.; Redegeld, F. Mast cells and COPD. Pulm. Pharm. 2011, 24, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detoraki, A.; Staiano, R.I.; Granata, F.; Giannattasio, G.; Prevete, N.; de Paulis, A.; Ribatti, D.; Genovese, A.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. Vascular endothelial growth factors synthesized by human lung mast cells exert angiogenic effects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Galdiero, M.R.; Marone, G.; Cristinziano, L.; Granata, F. Innate effector cells in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Granata, F. Mast cells and basophils in inflammatory and tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Eur. J. Pharm. 2016, 778, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Majid, R.M.; Marshall, J.S. Prostaglandin E2 induces degranulation-independent production of vascular endothelial growth factor by human mast cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Zhang, B.; Kempuraj, D.; Tagen, M.; Vasiadi, M.; Angelidou, A.; Alysandratos, K.D.; Kalogeromitros, D.; Asadi, S.; Stavrianeas, N.; et al. IL-33 augments substance P-induced VEGF secretion from human mast cells and is increased in psoriatic skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4448–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detoraki, A.; Granata, F.; Staibano, S.; Rossi, F.W.; Marone, G.; Genovese, A. Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in bronchial asthma. Allergy 2010, 65, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Granata, F.; Loffredo, S.; Genovese, A.; Marone, G. Angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in inflammatory skin disorders. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2015, 73, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Suurmond, J.; Habets, K.; Dorjee, A.L.; Ramamoorthi, N.; Townsend, M.J.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Huizinga, T.W.; Pitzalis, C.; et al. Ability of Interleukin-33- and Immune Complex-Triggered Activation of Human Mast Cells to Down-Regulate Monocyte-Mediated Immune Responses. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Rossi, F.W.; Marone, G.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; de Paulis, A.; Pitzalis, C. Mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis: Friends or foes? Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivellese, F.; Mauro, D.; Nerviani, A.; Pagani, S.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Messemaker, T.; Kurreeman, F.A.S.; Toes, R.E.M.; Ramming, A.; Rauber, S.; et al. Mast cells in early rheumatoid arthritis associate with disease severity and support B cell autoantibody production. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visciano, C.; Liotti, F.; Prevete, N.; Cali, G.; Franco, R.; Collina, F.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Santoro, M.; Melillo, R.M. Mast cells induce epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell features in human thyroid cancer cells through an IL-8-Akt-Slug pathway. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5175–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Marone, G. The immune network in thyroid cancer. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1168556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Marone, G.; Iannone, R.; Granata, F. Are Mast Cells MASTers in Cancer? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Marone, G.; Granata, F.; Borriello, F. Controversial role of mast cells in skin cancers. Exp. Derm. 2017, 26, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.P.; Jiang, J.F.; Wei, J.F.; Guo, M.G.; Qin, Y.; Guo, Q.Q.; Ma, L.; Liu, B.C.; Wang, X.; Veazey, R.S.; et al. Human Mucosal Mast Cells Capture HIV-1 and Mediate Viral trans-Infection of CD4+ T Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 90, 2928–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannert, N.; Farzan, M.; Friend, D.S.; Ochi, H.; Price, K.S.; Sodroski, J.; Boyce, J.A. Human Mast cell progenitors can be infected by macrophagetropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and retain virus with maturation in vitro. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 10808–10814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.C.; Stevens, R.L.; Wadley, R.; Collins, A.; Cooley, M.; Naif, H.M.; Nasr, N.; Cunningham, A.; Katsoulotos, G.; Wanigasek, Y.; et al. IL-16 regulation of human mast cells/basophils and their susceptibility to HIV-1. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 4127–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taub, D.D.; Mikovits, J.A.; Nilsson, G.; Schaffer, E.M.; Key, M.L.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Ruscetti, F.W. Alterations in mast cell function and survival following in vitro infection with human immunodeficiency viruses-1 through CXCR4. Cell Immunol. 2004, 230, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrom, J.B.; Little, D.M.; Villinger, F.; Ellis, J.E.; Ansari, A.A. Signaling through Toll-like receptors triggers HIV-1 replication in latently infected mast cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4391–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundstrom, J.B.; Hair, G.A.; Ansari, A.A.; Secor, W.E.; Gilfillan, A.M.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Kirshenbaum, A.S. IgE-FcepsilonRI interactions determine HIV coreceptor usage and susceptibility to infection during ontogeny of mast cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6401–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundstrom, J.B.; Ellis, J.E.; Hair, G.A.; Kirshenbaum, A.S.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Yi, H.; Cardona, A.C.; Lindsay, M.K.; Ansari, A.A. Human tissue mast cells are an inducible reservoir of persistent HIV infection. Blood 2007, 109, 5293–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, F.; Frattini, A.; Loffredo, S.; Staiano, R.I.; Petraroli, A.; Ribatti, D.; Oslund, R.; Gelb, M.H.; Lambeau, G.; Marone, G.; et al. Production of vascular endothelial growth factors from human lung macrophages induced by group IIA and group X secreted phospholipases A2. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5232–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiano, R.I.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannotti, F.A.; Piscitelli, F.; Orlando, P.; Secondo, A.; Granata, F.; Lepore, M.T.; Fiorelli, A.; et al. Human lung-resident macrophages express CB1 and CB2 receptors whose activation inhibits the release of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic factors. J. Leukoc Biol. 2016, 99, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paulis, A.; Prevete, N.; Fiorentino, I.; Rossi, F.W.; Staibano, S.; Montuori, N.; Ragno, P.; Longobardi, A.; Liccardo, B.; Genovese, A.; et al. Expression and functions of the vascular endothelial growth factors and their receptors in human basophils. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7322–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Iannone, R.; Ferrara, A.L.; Galdiero, M.R.; Gigantino, V.; Esposito, P.; Varricchi, G.; Lambeau, G.; Cassatella, M.A.; et al. Group V Secreted Phospholipase A2 Induces the Release of Proangiogenic and Antiangiogenic Factors by Human Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyon, R.C.; Lowman, M.A.; Church, M.K. Human skin mast cells: Their dispersion, purification, and secretory characterization. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 861–867. [Google Scholar]
- De Paulis, A.; Marino, I.; Ciccarelli, A.; de Crescenzo, G.; Concardi, M.; Verga, L.; Arbustini, E.; Marone, G. Human synovial mast cells. I. Ultrastructural in situ and in vitro immunologic characterization. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.; Herman, A.; Pullen, A.M.; Kubo, R.; Kappler, J.W.; Marrack, P. The V beta-specific superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B: Stimulation of mature T cells and clonal deletion in neonatal mice. Cell 1989, 56, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzin, B.L.; Leung, D.Y.; Kappler, J.; Marrack, P. Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv. Immunol. 1993, 54, 99–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Detoraki, A.; Granata, F.; Genovese, A.; Spadaro, G. Role of superallergens in allergic disorders. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science 1990, 248, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouvet, J.P.; Pires, R.; Lunel-Fabiani, F.; Crescenzo-Chaigne, B.; Maillard, P.; Valla, D.; Opolon, P.; Pillot, J.; Protein, F. A novel F(ab)-binding factor, present in normal liver, and largely released in the digestive tract during hepatitis. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.A.; Ober, B.; Malchiodi, E.L.; Lebedeva, M.I.; Braden, B.C.; Ysern, X.; Kim, J.K.; Shao, X.; Ward, E.S.; Mariuzza, R.A. Crystal structure of the V alpha domain of a T cell antigen receptor. Science 1995, 270, 1821–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Llera, A.; Tsuchiya, D.; Leder, L.; Ysern, X.; Schlievert, P.M.; Karjalainen, K.; Mariuzza, R.A. Three-dimensional structure of the complex between a T cell receptor beta chain and the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Immunity 1998, 9, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchiodi, E.L.; Eisenstein, E.; Fields, B.A.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Schlievert, P.M.; Karjalainen, K.; Mariuzza, R.A. Superantigen binding to a T cell receptor beta chain of known three-dimensional structure. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundberg, E.J.; Li, H.; Llera, A.S.; McCormick, J.K.; Tormo, J.; Schlievert, P.M.; Karjalainen, K.; Mariuzza, R.A. Structures of two streptococcal superantigens bound to TCR beta chains reveal diversity in the architecture of T cell signaling complexes. Structure 2002, 10, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, V.; Capra, J.D. B-cell superantigens? Curr. Biol. 1991, 1, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, G.J.; Goodyear, C.S. A model B-cell superantigen and the immunobiology of B lymphocytes. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 102, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouali, M. B-cell superantigens: Implications for selection of the human antibody repertoire. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, G.; Petraroli, A.; Patella, V.; Triggiani, M.; Marone, G. The immunoglobulin superantigen-binding site of HIV-1 gp120 activates human basophils. AIDS 2000, 14, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patella, V.; Florio, G.; Petraroli, A.; Marone, G. HIV-1 gp120 induces IL-4 and IL-13 release from human Fc epsilon RI+ cells through interaction with the VH3 region of IgE. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karray, S.; Zouali, M. Identification of the B cell superantigen-binding site of HIV-1 gp120. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, G.J. B-cell superantigens. Immunol. Today 1997, 18, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouali, M. B cell superantigens subvert innate functions of B cells. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 93, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, L.; Goodglick, L.; Kipps, T.J.; Braun, J. Immunoglobulin VH3 gene products: Natural ligands for HIV gp120. Science 1993, 261, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Pecoraro, A.; Pucino, V.; Criscuolo, G.; Triassi, M.; Varricchi, G. Prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonists in allergic disorders: Safety, efficacy, and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.A.; Hoffman, A.D.; Kramer, S.M.; Landis, J.A.; Shimabukuro, J.M.; Oshiro, L.S. Isolation of lymphocytopathic retroviruses from San Francisco patients with AIDS. Science 1984, 225, 840–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Pescador, R.; Power, M.D.; Barr, P.J.; Steimer, K.S.; Stempien, M.M.; Brown-Shimer, S.L.; Gee, W.W.; Renard, A.; Randolph, A.; Levy, J.A.; et al. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science 1985, 227, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marone, G.; Casolaro, V.; Paganelli, R.; Quinti, I. IgG anti-IgE from atopic dermatitis induces mediator release from basophils and mast cells. J. Investig. Derm. 1989, 93, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, G.; Spadaro, G.; Palumbo, C.; Condorelli, G. The anti-IgE/anti-FcepsilonRIalpha autoantibody network in allergic and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1999, 29, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patella, V.; Marino, I.; Arbustini, E.; Lamparter-Schummert, B.; Verga, L.; Adt, M.; Marone, G. Stem cell factor in mast cells and increased mast cell density in idiopathic and ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 1998, 97, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patella, V.; Giuliano, A.; Bouvet, J.P.; Marone, G. Endogenous superallergen protein Fv induces IL-4 secretion from human Fc epsilon RI+ cells through interaction with the VH3 region of IgE. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 5647–5655. [Google Scholar]
- Marone, G.; Tamburini, M.; Giudizi, M.G.; Biagiotti, R.; Almerigogna, F.; Romagnani, S. Mechanism of activation of human basophils by Staphylococcus aureus Cowan 1. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, V.; de Crescenzo, G.; Marino, I.; Genovese, A.; Adt, M.; Gleich, G.J.; Marone, G. Eosinophil granule proteins activate human heart mast cells. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Patella, V.; Casolaro, V.; Bjorck, L.; Marone, G. Protein L. A bacterial Ig-binding protein that activates human basophils and mast cells. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3054–3061. [Google Scholar]
- Siraganian, R.P. An automated continuous-flow system for the extraction and fluorometric analysis of histamine. Anal. Biochem. 1974, 57, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paulis, A.; Cirillo, R.; Ciccarelli, A.; de Crescenzo, G.; Oriente, A.; Marone, G. Characterization of the anti-inflammatory effect of FK-506 on human mast cells. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 4278–4285. [Google Scholar]
- Loffredo, S.; Ferrara, A.L.; Bova, M.; Borriello, F.; Suffritti, C.; Veszeli, N.; Petraroli, A.; Galdiero, M.R.; Varricchi, G.; Granata, F.; et al. Secreted Phospholipases A2 in Hereditary Angioedema With C1-Inhibitor Deficiency. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Loffredo, S.; Borriello, F.; Pecoraro, A.; Rivellese, F.; Genovese, A.; Spadaro, G.; Marone, G. Superantigenic Activation of Human Cardiac Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, A.A.; Schechter, N.M.; Craig, S.S.; DeBlois, G.; Schwartz, L.B. Two types of human mast cells that have distinct neutral protease compositions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4464–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejler, G. The emerging role of mast cell proteases in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, L.B.; Irani, A.M.; Roller, K.; Castells, M.C.; Schechter, N.M. Quantitation of histamine, tryptase, and chymase in dispersed human T and TC mast cells. J. Immunol. 1987, 138, 2611–2615. [Google Scholar]
- Patella, V.; Bouvet, J.P.; Marone, G. Protein Fv produced during vital hepatitis is a novel activator of human basophils and mast cells. J. Immunol. 1993, 151, 5685–5698. [Google Scholar]
- Patella, V.; de Crescenzo, G.; Ciccarelli, A.; Marino, I.; Adt, M.; Marone, G. Human heart mast cells: A definitive case of mast cell heterogeneity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1995, 106, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, Y.; Maekawa, A.; Penrose, J.F.; Austen, K.F.; Lam, B.K. Attenuated zymosan-induced peritoneal vascular permeability and IgE-dependent passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice lacking leukotriene C4 synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22608–22613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Kanaoka, Y.; Barrett, N.A.; Feng, C.; Garofalo, D.; Lai, J.; Buchheit, K.; Bhattacharya, N.; Laidlaw, T.M.; Katz, H.R.; et al. Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease Involves a Cysteinyl Leukotriene-Driven IL-33-Mediated Mast Cell Activation Pathway. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigorito, C.; Giordano, A.; Cirillo, R.; Genovese, A.; Rengo, F.; Marone, G. Metabolic and hemodynamic effects of peptide leukotriene C4 and D4 in man. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 1997, 27, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaoka, Y.; Austen, K.F. Roles of cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors in immune cell-related functions. Adv. Immunol. 2019, 142, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; de Paulis, A.; Marone, G.; Galli, S.J. Future Needs in Mast Cell Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Aspelund, A.; Alitalo, K. Lymphangiogenic factors, mechanisms, and applications. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taimeh, Z.; Loughran, J.; Birks, E.J.; Bolli, R. Vascular endothelial growth factor in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2013, 10, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albini, A.; Bruno, A.; Noonan, D.M.; Mortara, L. Contribution to Tumor Angiogenesis From Innate Immune Cells Within the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchi, G.; Harker, J.; Borriello, F.; Marone, G.; Durham, S.R.; Shamji, M.H. T follicular helper (Tfh ) cells in normal immune responses and in allergic disorders. Allergy 2016, 71, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, D.R.; Zajac, R.A.; Melcher, G.P.; Butzin, C.A.; Boswell, R.N. Serum IgE levels in 622 persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection: IgE elevation with marked depletion of CD4+ T-cells. Aids Res. Hum. Retrovir. 1990, 6, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, R.; Scala, E.; Mezzaroma, I.; Pinter, E.; D’Offizi, G.; Fanales-Belasio, E.; Rosso, R.M.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Pandolfi, F.; Aiuti, F. Immunologic aspects of hyperimmunoglobulinemia E-like syndrome in patients with AIDS. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rancinan, C.; Morlat, P.; Chene, G.; Guez, S.; Baquey, A.; Beylot, J.; Salamon, R. IgE serum level: A prognostic marker for AIDS in HIV-infected adults? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998, 102, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secord, E.A.; Kleiner, G.I.; Auci, D.L.; Smith-Norowitz, T.; Chice, S.; Finkielstein, A.; Nowakowski, M.; Fikrig, S.; Durkin, H.G. IgE against HIV proteins in clinically healthy children with HIV disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor-Posner, G.; Miguez-Burbano, M.J.; Lu, Y.; Feaster, D.; Fletcher, M.; Sauberlich, H.; Baum, M.K. Elevated IgE level in relationship to nutritional status and immune parameters in early human immunodeficiency virus-1 disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, A.; Principi, N.; Crupi, L.; Onorato, J.; Vincenzo, Z.G.; Salvaggio, A. Elevation of IgE in HIV-infected children and its correlation with the progression of disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1995, 95, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maun, H.R.; Jackman, J.K.; Choy, D.F.; Loyet, K.M.; Staton, T.L.; Jia, G.; Dressen, A.; Hackney, J.A.; Bremer, M.; Walters, B.T.; et al. An Allosteric Anti-tryptase Antibody for the Treatment of Mast Cell-Mediated Severe Asthma. Cell 2019, 179, 417–431.e419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernersson, S.; Pejler, G. Mast cell secretory granules: Armed for battle. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komi, D.E.A.; Redegeld, F.A. Role of Mast Cells in Shaping the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, P.; Mekori, Y.A.; Shefler, I. Lung cancer-derived extracellular vesicles: A possible mediator of mast cell activation in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, T.J.; Green, R.H.; Richardson, D.; Waller, D.A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Bradding, P. Macrophage and mast-cell invasion of tumor cell islets confers a marked survival advantage in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8959–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, R.M.; Flores, S.C.; Palmer, B.E.; Atkinson, J.J.; Lesko, C.R.; Lau, B.; Fontenot, A.P.; Roman, J.; McDyer, J.F.; Twigg, H.L., 3rd. Mechanisms Underlying HIV-Associated Noninfectious Lung Disease. Chest 2017, 152, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, M.J.; Lau, B.; Achenbach, C.J.; Jing, Y.; Althoff, K.N.; D’Souza, G.; Engels, E.A.; Hessol, N.A.; Brooks, J.T.; Burchell, A.N.; et al. Cumulative Incidence of Cancer Among Persons With HIV in North America: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingo, M.R.; Wenzel, S.E.; Steele, C.; Kessinger, C.J.; Lucht, L.; Lawther, T.; Busch, M.; Hillenbrand, M.E.; Weinman, R.; Slivka, W.A.; et al. Asthma diagnosis and airway bronchodilator response in HIV-infected patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 708–714.e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauci, A.S.; Pantaleo, G.; Stanley, S.; Weissman, D. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, K. Histamine release from rat mast cells induced by Sendai virus. Nature 1977, 270, 614–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St John, A.L.; Rathore, A.P.; Yap, H.; Ng, M.L.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Abraham, S.N. Immune surveillance by mast cells during dengue infection promotes natural killer (NK) and NKT-cell recruitment and viral clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9190–9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.G.; McAlpine, S.M.; Huang, Y.Y.; Haidl, I.D.; Al-Afif, A.; Marshall, J.S.; Anderson, R. RNA sensors enable human mast cell anti-viral chemokine production and IFN-mediated protection in response to antibody-enhanced dengue virus infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, R.; Kawamura, T.; Goshima, F.; Ogawa, Y.; Nakae, S.; Nakao, A.; Moriishi, K.; Nishiyama, Y.; Shimada, S. Mast cells play a key role in host defense against herpes simplex virus infection through TNF-alpha and IL-6 production. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, A.C.; Temple, R.M.; Obar, J.J. Mast cells and influenza a virus: Association with allergic responses and beyond. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhl, S.; Franke, R.; Schielke, A.; Johne, R.; Kruger, D.H.; Babina, M.; Rang, A. Infection of in vivo differentiated human mast cells with hantaviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Becker, M.; Lemmermann, N.A.; Buttner, J.K.; Michel, A.; Taube, C.; Podlech, J.; Bohm, V.; Freitag, K.; Thomas, D.; et al. Mast cells expedite control of pulmonary murine cytomegalovirus infection by enhancing the recruitment of protective CD8 T cells to the lungs. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Lemmermann, N.A.; Ebert, S.; Baars, P.; Renzaho, A.; Podlech, J.; Stassen, M.; Reddehase, M.J. Mast cells as rapid innate sensors of cytomegalovirus by TLR3/TRIF signaling-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marone, G.; Granata, F. Angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and clinical implications. Preface. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 99, XI–XII. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatari, N.; Movassagh, H.; Shan, L.; Koussih, L.; Gounni, A.S. Semaphorin 3E Inhibits House Dust Mite-Induced Angiogenesis in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Heukamp, L.C.; Siobal, M.; Schottle, J.; Wieczorek, C.; Peifer, M.; Frasca, D.; Koker, M.; Konig, K.; Meder, L.; et al. Tumor VEGF:VEGFR2 autocrine feed-forward loop triggers angiogenesis in lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosisio, D.; Ronca, R.; Salvi, V.; Presta, M.; Sozzani, S. Dendritic cells in inflammatory angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 53, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, V.; Tamma, R.; Brunetti, O.; Pisconti, S.; Argentiero, A.; Silvestris, N.; Ribatti, D. Mast cells and angiogenesis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Shao, Z.; Grenier, V.; Mawambo, G.; Daudelin, J.F.; Dejda, A.; Pilon, F.; Popovic, N.; Boulet, S.; Parinot, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 expression in adipose tissue macrophages protects against obesity and metabolic syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stump, B.; Cui, Y.; Kidambi, P.; Lamattina, A.M.; El-Chemaly, S. Lymphatic Changes in Respiratory Diseases: More than Just Remodeling of the Lung? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P.; Yao, L.C.; Feng, J.; Romano, T.; Jung, S.S.; Schreiter, J.L.; Yan, L.; Shealy, D.J.; McDonald, D.M. TNF-alpha drives remodeling of blood vessels and lymphatics in sustained airway inflammation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2954–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.C.; Baluk, P.; Feng, J.; McDonald, D.M. Steroid-resistant lymphatic remodeling in chronically inflamed mouse airways. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1525–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardavella, G.; Tzortzaki, E.G.; Siozopoulou, V.; Galanis, P.; Vlachaki, E.; Avgousti, M.; Stefanou, D.; Siafakas, N.M. Lymphangiogenesis in COPD: Another link in the pathogenesis of the disease. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Andersson, C.K.; Graham, G.J.; Lofdahl, C.G.; Erjefalt, J.S. Increased number and altered phenotype of lymphatic vessels in peripheral lung compartments of patients with COPD. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspelund, A.; Robciuc, M.R.; Karaman, S.; Makinen, T.; Alitalo, K. Lymphatic System in Cardiovascular Medicine. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakenhielm, E.; Alitalo, K. Cardiac lymphatics in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Kataru, R.P.; Koh, G.Y. Inflammation-associated lymphangiogenesis: A double-edged sword? J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, H.R.; Hausmann, E.H.; Ozel, M.; Pauli, G.; Koch, M.A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology 1987, 156, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.; Weiss, J.W.; Leitch, A.G.; McFadden, E.R., Jr.; Corey, E.J.; Austen, K.F.; Drazen, J.M. Effects of leukotriene D on the airways in asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 308, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, S.E.; Bjork, J.; Hedqvist, P.; Arfors, K.E.; Hammarstrom, S.; Lindgren, J.A.; Samuelsson, B. Leukotrienes promote plasma leakage and leukocyte adhesion in postcapillary venules: In vivo effects with relevance to the acute inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3887–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita-Santos, F.P.; Vieira-de-Abreu, A.; Calheiros, A.S.; Figueiredo, I.H.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Weller, P.F.; Bozza, P.T.; Diaz, B.L.; Bandeira-Melo, C. Cutting edge: Prostaglandin D2 enhances leukotriene C4 synthesis by eosinophils during allergic inflammation: Synergistic in vivo role of endogenous eotaxin. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, R.W.; Dixon, C.M.; Dollery, C.T.; Barnes, P.J. Prostaglandin D2 potentiates airway responsiveness to histamine and methacholine. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 133, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, C.C.; Bradding, P.; Robinson, C.; Holgate, S.T. Bronchoconstrictor and antibronchoconstrictor properties of inhaled prostacyclin in asthma. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1988, 64, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.P.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Effect of prostaglandin D2 in modulating histamine release from human basophils. J. Pharm. Exp. 1984, 228, 400–406. [Google Scholar]
- Triggiani, M.; Gentile, M.; Secondo, A.; Granata, F.; Oriente, A.; Taglialatela, M.; Annunziato, L.; Marone, G. Histamine induces exocytosis and IL-6 production from human lung macrophages through interaction with H1 receptors. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 4083–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtin, C.; Blanche, S.; Galoppin, L.; Merval, R.; Griscelli, C.; Scheinmann, P. Blood histamine levels in HIV-1-infected infants and children. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 1990, 91, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Recombinant Envelope Protein | gp120 Isolate | Clade | Geographic Origin | Expression System |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| gp120MN | MN | B | USA | Insect Cells |
| gp120SF2 | SF2 | B | USA | CHO Cells |
| gp120LAV | LAV | B | France | Insect Cells |
| gp120CM | CM | E | Thailand | Insect Cells |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marone, G.; Rossi, F.W.; Pecoraro, A.; Pucino, V.; Criscuolo, G.; de Paulis, A.; Spadaro, G.; Marone, G.; Varricchi, G. HIV gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells. Vaccines 2020, 8, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020208
Marone G, Rossi FW, Pecoraro A, Pucino V, Criscuolo G, de Paulis A, Spadaro G, Marone G, Varricchi G. HIV gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells. Vaccines. 2020; 8(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarone, Giancarlo, Francesca Wanda Rossi, Antonio Pecoraro, Valentina Pucino, Gjada Criscuolo, Amato de Paulis, Giuseppe Spadaro, Gianni Marone, and Gilda Varricchi. 2020. "HIV gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells" Vaccines 8, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020208
APA StyleMarone, G., Rossi, F. W., Pecoraro, A., Pucino, V., Criscuolo, G., de Paulis, A., Spadaro, G., Marone, G., & Varricchi, G. (2020). HIV gp120 Induces the Release of Proinflammatory, Angiogenic, and Lymphangiogenic Factors from Human Lung Mast Cells. Vaccines, 8(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8020208







