A Rabies Virus Nucleocapsid-Like Nanostructure Vaccine Based on Dual-Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Viruses
2.3. Animals
2.4. Construction of the Recombinant Template Plasmid
2.5. In Vitro Transcription (IVT)
2.6. Transfection of 293T Cells
2.7. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) Staining
2.8. Western Blotting (WB)
2.9. Recombinant Expression of RABV-N
2.10. LNP Formulation and Encapsulation
2.11. RiboGreen Fluorescence Assay
2.12. Quality Control of LNP Vaccine
2.13. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.14. Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT)
2.15. Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay (ELISPOT)
2.16. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.17. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
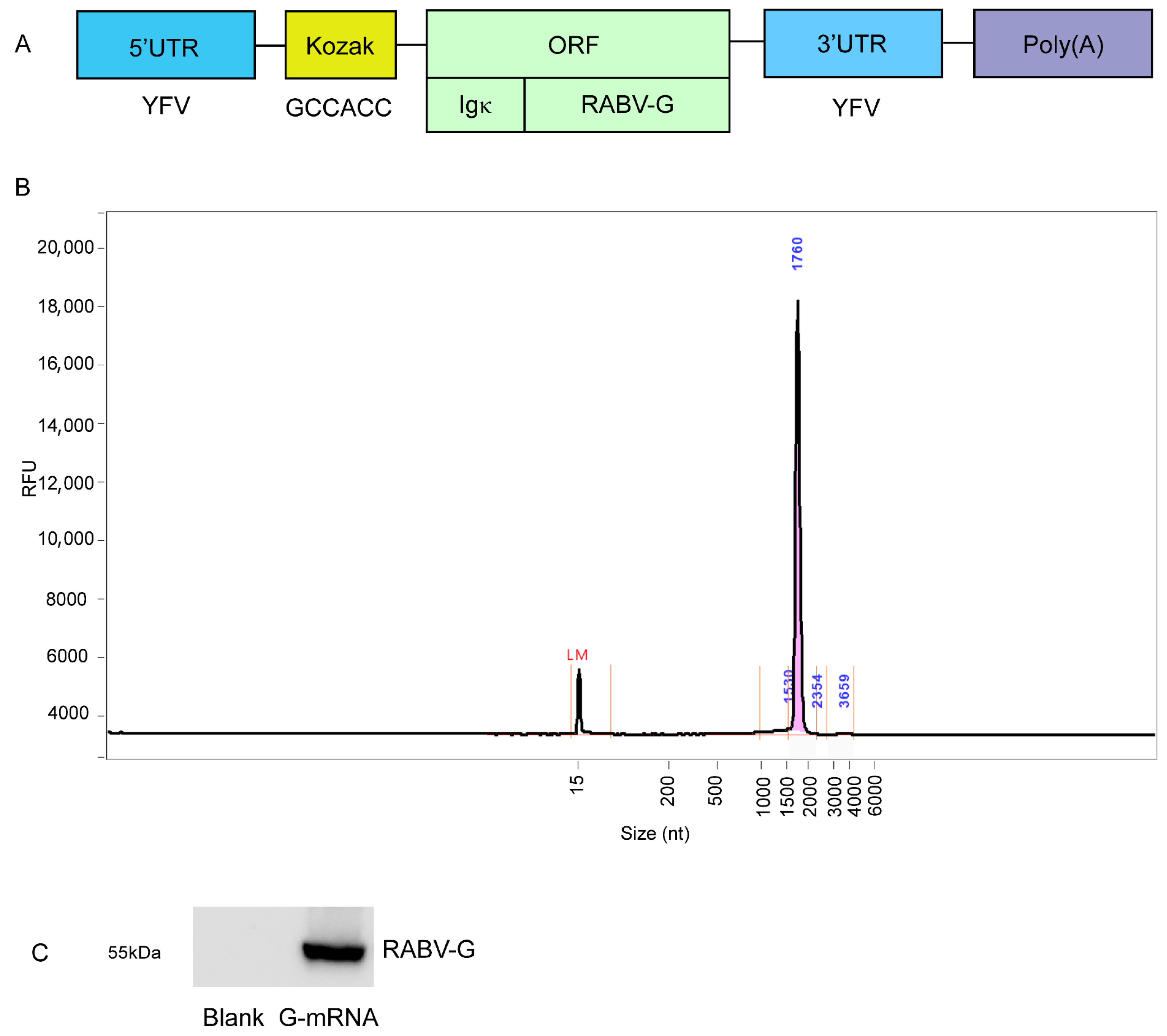
3.1. Preparation of G-mRNA of RABV
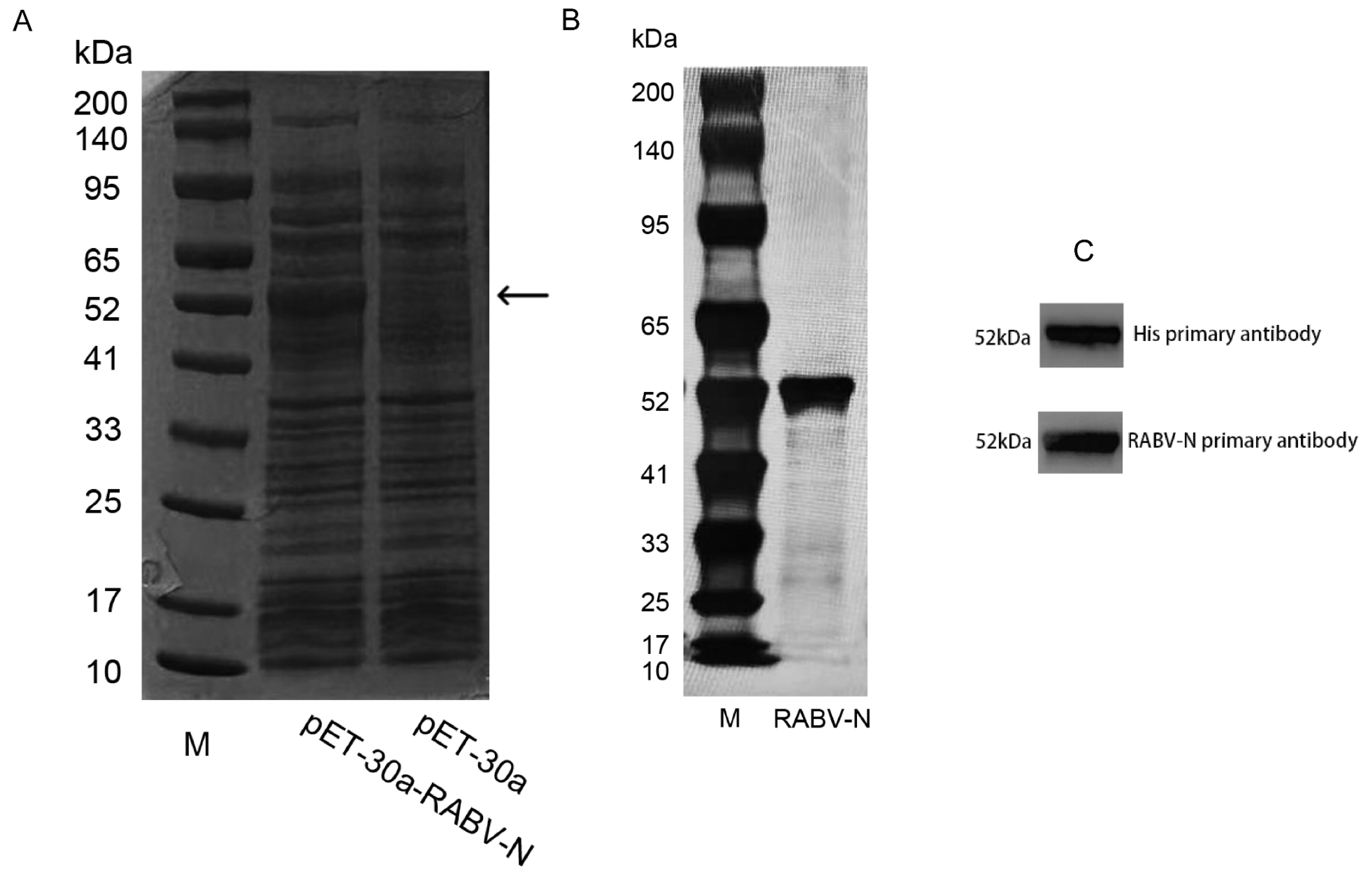
3.2. Expression and Purification of RABV-N in E. coli
3.3. Quality Control of the LNP-Encapsulated RABV G-mRNA and NLS Vaccines
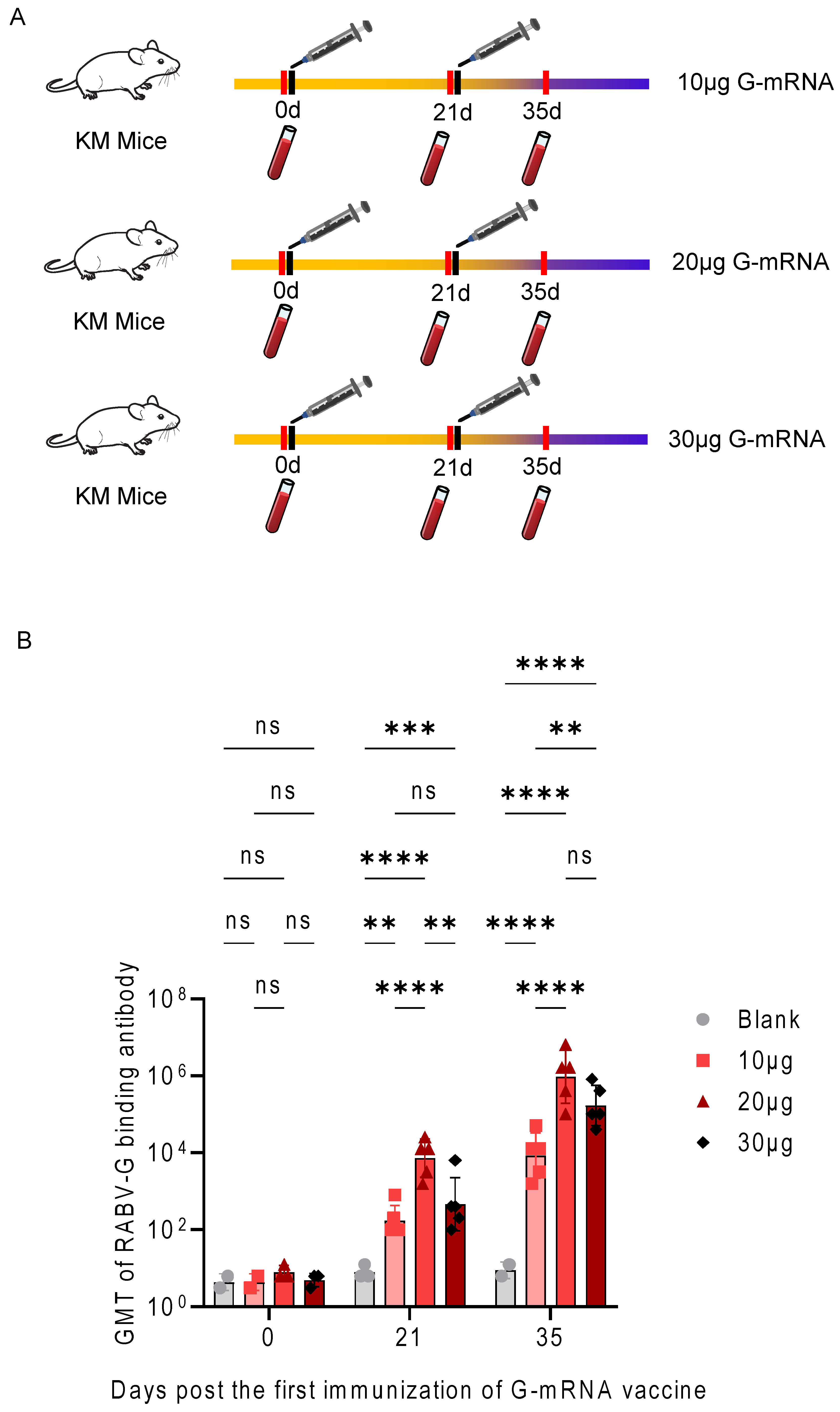
3.4. Determination of the Immunization Dose for the RABV G-mRNA Vaccine
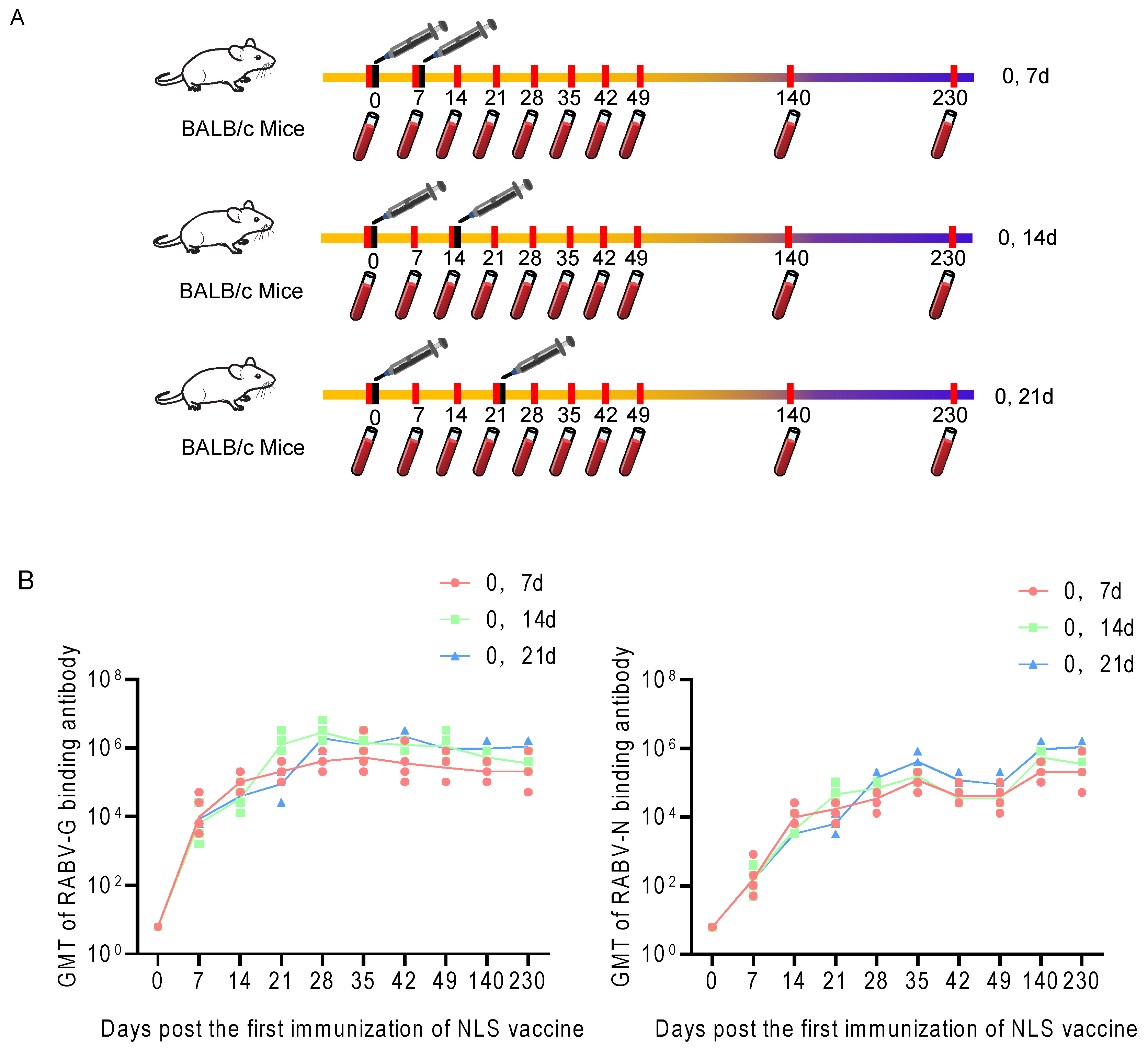
3.5. Dynamics of the Humoral Immune Response to RABV-G and RABV-N Induced by Different Immunization Schedules of the RABV NLS Vaccine
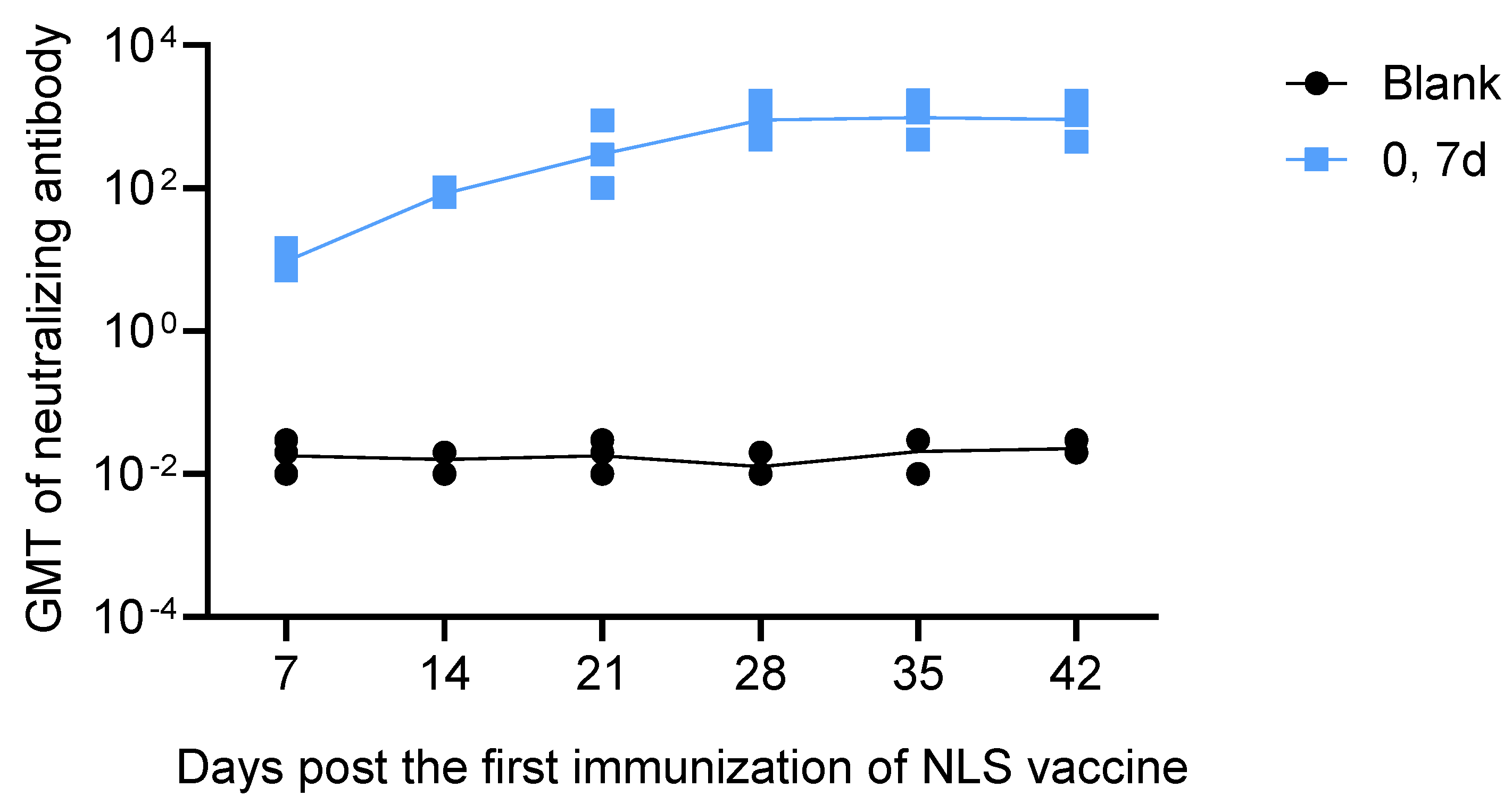
3.6. Neutralizing Antibody Response to the RABV NLS Vaccine Measured by RFFIT
3.7. Specific CTL Response Profiling Elicited by the RABV NLS Vaccine, G-mRNA Vaccine and INV
3.8. Challenge Protection Assay with RABV CVS-24 Strain
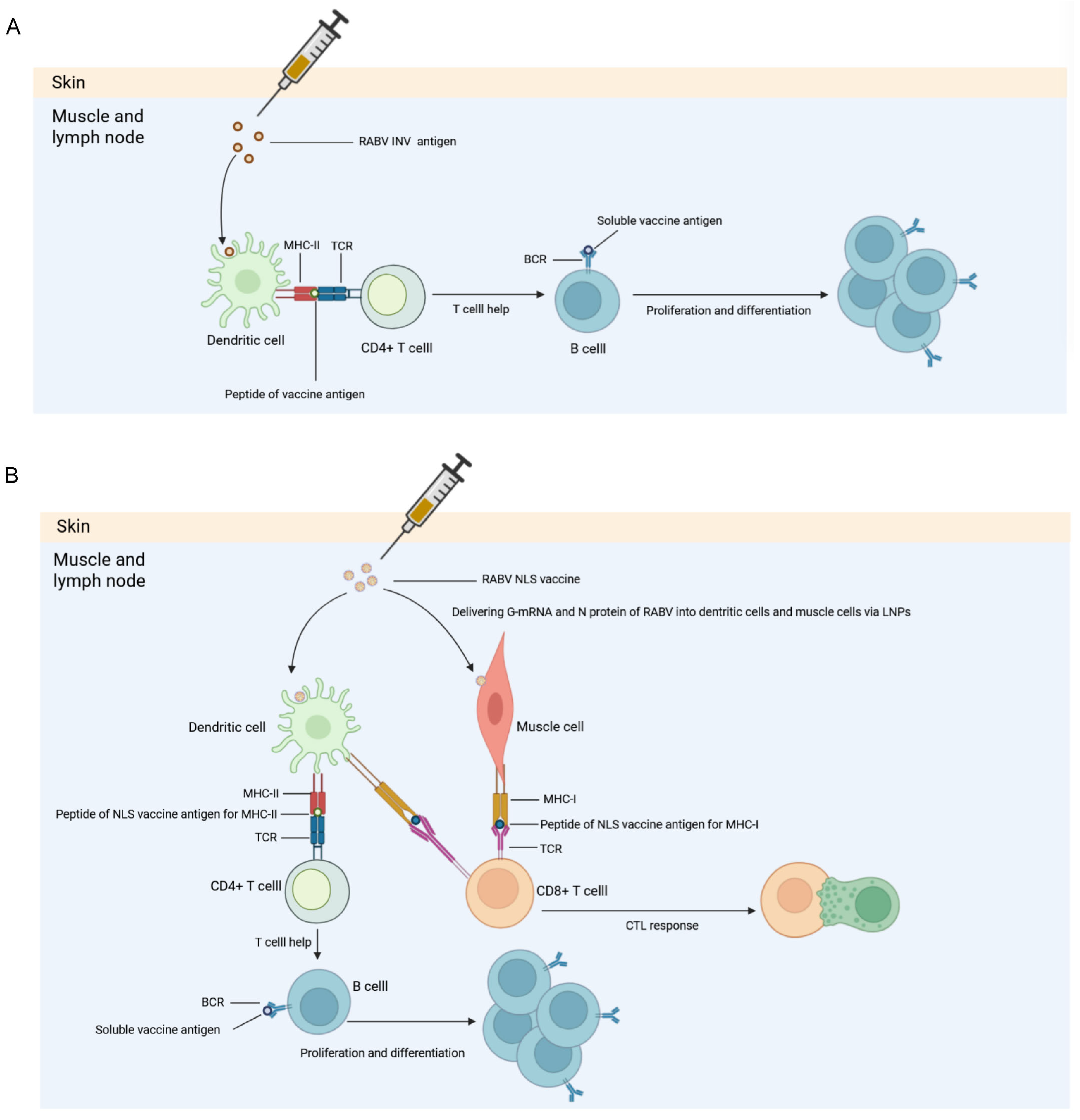
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RABV | Rabies virus |
| G | glycoprotein |
| M | matrix protein |
| P | phosphoprotein |
| L | RNA polymerase |
| N | nucleoprotein |
| INV | inactivated vaccine |
| RABV-G | G protein of rabies virus |
| VLP | virus-like particle |
| LNP | lipid nanoparticle |
| nAb | neutralizing antibody |
| Th | helper T cell |
| CTL | cytotoxic T cell |
| G-mRNA | mRNA encoding the G protein |
| RABV-N | N protein of rabies virus |
| ADCC | antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity |
| NK | natural killer |
| NLS | nucleocapsid-like nanostructure |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| CVS | challenge virus standard |
| SPF | specific-pathogen-free |
| KM | Kunming |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate—polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| CBB | Coomassie brilliant blue |
| WB | Western blotting |
| IPTG | isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| ORF | open reading frame |
| IVT | in vitro transcription |
| ECL | enhanced chemiluminescence |
| FRR | flow-rate ratio |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| PDI | polydispersity index |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GMT | geometric mean titers |
| RFFIT | rapid fluorescent focus inhibition test |
| ELISPOT | enzyme-linked immunospot assay |
| SFU | spot-forming units |
| qPCR | quantitative real-time PCR |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| DC | dendritic cell |
Appendix A
| Sequence Name | Sequence Length (bp/AA) | Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 5′-UTR from flavivirus | 118 | agtaaatcctgtgtgctaattgaggtgcattggtctgcaaatcgagttgctagg caataaacacatttggattaattttaatcgttcgttgagcgattagcagagaact gaccagaac |
| Kozak sequence | 6 | gccacc |
| Igκ secretory signal | 21 | METDTLLLWVLLLWVPGSTGD |
| RABV-G ORF | 439 | KFPIYTIPDKLGPWSPIDIHHLSCPNNLVVEDEGCTN LSGFSYMELKVGYISAIKVNGFTCTGVVTEAETYTNF VGYVTTTFKRKHFRPTPDACRSAYNWKMAGDPRYE ESLHNPYPDYHWLRTVKTTKESVVIISPSVADLDPYD KSLHSRVFPRGKCSGITVSSAYCSTNHDYTIWMPENP RLGTSCDIFTNSRGKRASKGSKTCGFVDERGLYKSLK GACKLKLCGVLGLRLMDGTWVAIQTSNETKWCPP DQLVNLHDFHSDEIEHLVVEELVKKREECLDALESI MTTKSVSFRRLSHLRKLVPGFGKAYTIFNKTLMEAD AHYKSVRTWNEIIPSKGCLRVGGRCHPHVNGVFFN GIILGPDGHVLIPEMQSSLLQQHMELLESSVIPLMHP LADPSTVFKDGDEVEDFVEVHLPDVHKQVSGVDLG LPNWGK |
| 3′-UTR from flavivirus | 123 | gacactgttccaagcaacaaccaagaactagaccttgtacataggacaaaact gaaaccgggataaaaaccacggatggagaaccggactccacacatcaaaca gaagaggatgtcagcccag |
| Poly(A) tail | 138 | aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaagcatatgact aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaccgcgtgctgaa aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa |
| Sequence Name | Sequence Length (AA) | Amino Acid Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| 6× His Tag | 6 | HHHHHH |
| N-protein | 449 | DADKIVFKVNNQVVSLKPEIIVDQYEYKYPAI KDLKKPCITLGKAPDLNKAYKSVLSGMNAA KLDPDDVCSYLAAAMQFFEGTCPEDWTSYG ILIARKGDRITPNSLVEIKRTDVEGNWALTGG MELTRDPTVSEHASLVGLLLSLYRLSKISGQN TGNYKTNIADRIEQIFETAPFVKIVEHHTLMT THKMCANWSTIPNFRFLAGTYDMFFSRIEHL YSAIRVGTVVTAYEDCSGLVSFTGFIKQINLT AREAILYFFHKNFEEEIRRMFEPGQETAVPHS YFIHFRSLGLSGKSPYSSNAVGHVFNLIHFVG CYMGQVRSLNATVIAACAPHEMSVLGGYLG EEFFGKGTFERRFFRDEKELQEYEAAELTKSD VALADDGTVNSDDEDYFSGETRSPEAVYTRI MMNGGRLKRSHIRRYVSVSSNHQARPNSFA EFLNKTYSNDS |
References
- Fooks, A.R.; Cliquet, F.; Finke, S.; Freuling, C.; Hemachudha, T.; Mani, R.S.; Müller, T.; Nadin-Davis, S.; Picard-Meyer, E.; Wilde, H.; et al. Rabies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Chikwamba, R. Rabies and Related Lyssaviruses. In Prospects of Plant-Based Vaccines in Veterinary Medicine; MacDonald, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 45–87. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Cai, M.; Jiang, J.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H. Real-time Imaging of Rabies Virus Entry into Living Vero cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.H.; Xing, L. The roles of rabies virus structural proteins in immune evasion and implications for vaccine development. Can. J. Microbiol. 2024, 70, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xu, B.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Huang, S.; Guo, X. Autophagy and Apoptosis in Rabies Virus Replication. Cells 2024, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhou, K.; Alvarez-Cabrera, A.L.; Si, Z.; Wang, H.; He, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z.H. Structural Heterogeneity of the Rabies Virus Virion. Viruses 2024, 16, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-J.; Rai, C.-I.; Wang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Infection and Prevention of Rabies Viruses. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanton, J.; Gold, S.; Donnelly, C.A.; Nouvellet, P.; Woodroffe, R. Rabies virus-neutralising antibodies in healthy, unvaccinated individuals: What do they mean for rabies epidemiology? PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhatt, S.; Kumar, A.; Rana, T. Canine rabies: An epidemiological significance, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and public health issues. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 97, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Expert Consultation on Rabies Third Report; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Rabies vaccines: WHO position paper—Recommendations. Vaccine 2010, 28, 7140–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, M.A.; Santos, A.S.; Astray, R.M.; Pereira, C.A.; Jorge, S.A. Rabies virus glycoprotein expression in Drosophila S2 cells. I: Design of expression/selection vectors, subpopulations selection and influence of sodium butyrate and culture medium on protein expression. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 143, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Yang, X. Rabies virus-like particles comprised of G and M proteins protect BALB_c mice from lethal dose challenging. J. Appl. Virol. 2015, 4, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fooks, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Ertl, H.C.J. New human rabies vaccines in the pipeline. Vaccine 2019, 37 (Suppl. S1), A140–A145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldrich, C.; Leroux–Roels, I.; Huang, K.B.; Bica, M.A.; Loeliger, E.; Schoenborn-Kellenberger, O.; Walz, L.; Leroux-Roels, G.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Oostvogels, L. Proof-of-concept of a low-dose unmodified mRNA-based rabies vaccine formulated with lipid nanoparticles in human volunteers: A phase 1 trial. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z.; Luo, L.; Peng, S.; et al. An mRNA-based rabies vaccine induces strong protective immune responses in mice and dogs. Virol. J. 2022, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Min, M. Immunogenicity of rabies virus G mRNA formulated with lipid nanoparticles and nucleic acid immunostimulators in mice. Vaccine 2023, 41, 7129–7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yu, P.; Zhu, W. Development of mRNA rabies vaccines. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2024, 20, 2382499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczkó, D.; Hogan, M.J.; Toulmin, S.A.; Hicks, P.; Lederer, K.; Gaudette, B.T.; Castaño, D.; Amanat, F.; Muramatsu, H.; Oguin, T.H.; et al. A Single Immunization with Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Vaccines Elicits Strong Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice. Immunity 2020, 53, 724–732.e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masatani, T.; Ito, N.; Shimizu, K.; Ito, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Sawaki, Y.; Koyama, H.; Sugiyama, M. Rabies Virus Nucleoprotein Functions To Evade Activation of the RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Response. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombari, W.; Khamessi, O.; Othman, H.; Kallala, O.; Mahjoub, R.; Ghedira, K.; Trabelsi, A. A novel mRNA-based multi-epitope vaccine for rabies virus computationally designed via reverse vaccinology and immunoinformatics. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 30355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zeng, F.; Mu, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Peng, X.; He, L.; Su, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Virus-like structures for combination antigen protein mRNA vaccination. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Ma, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Mu, C.; Peng, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, C.; He, L.; et al. Lipid Ddlivery System and VirusI-like Structure (VLS) Vaccine Constructed Therefrom. U.S. Patent 11911460, 27 February 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rupprecht, C.E.; Fooks, A.R.; Abela-Ridder, B. WHO Laboratory Techniques in Rabies, 5th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, K.; Hooper, D.C.; Carbaugh, H.; Fu, Z.F.; Koprowski, H.; Dietzschold, B. Rabies virus quasispecies: Implications for pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3152–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevers, Q.; Scrima, N.; Glon, D.; Le Bars, R.; Decombe, A.; Garnier, N.; Ouldali, M.; Lagaudriere-Gesbert, C.c.; Blondel, D.; Albertini, A.l.; et al. Properties of rabies virus phosphoprotein and nucleoprotein biocondensates formed in vitro and in cellulo. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1011022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Jia, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Cao, Y.; Huang, X.; Cao, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Exposed nucleoprotein inside rabies virus particle as an ideal target for real-time quantitative evaluation of rabies virus particle integrity in vaccine quality control. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0013077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Terrell, J.R.; McManus, S.A. Nucleocapsid Structure of Negative Strand RNA Virus. Viruses 2020, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofland, T.; Danelli, L.; Cornish, G.; Donnarumma, T.; Hunt, D.M.; de Carvalho, L.P.S.; Kassiotis, G. CD4+ T cell memory is impaired by species-specific cytotoxic differentiation, but not by TCF-1 loss. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1168125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osum, K.C.; Jenkins, M.K. Toward a general model of CD4+ T cell subset specification and memory cell formation. Immunity 2023, 56, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Kawagoe, T.; Mizuki, N.; Okuda, K.; Shimada, M. Current Vaccine Platforms in Enhancing T-Cell Response. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina-Campos, M.; Scharping, N.E.; Goldrath, A.W. CD8+ T cell metabolism in infection and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 718–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knörck, A.; Schäfer, G.; Alansary, D.; Richter, J.; Thurner, L.; Hoth, M.; Schwarz, E.C. Cytotoxic Efficiency of Human CD8+ T Cell Memory Subtypes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 838484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.K.; Kagari, T.; Clingan, J.M.; Matloubian, M. Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR3 on T cells affects the balance between effector and memory CD8 T-cell generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E118–E127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabău, G.; Badii, M.; Mirea, A.M.; Gaal, O.I.; van Emst, L.; Popp, R.A.; Crișan, T.O.; Joosten, L.A.B. Long-Lasting Enhanced Cytokine Responses Following SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination. Vaccines 2024, 12, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Ewijk, C.E.; Suárez Hernández, S.; Jacobi, R.H.J.; Knol, M.J.; Hahné, S.J.M.; Wijmenga-Monsuur, A.J.; Boer, M.C.; van de Garde, M.D.B. Innate immune response after BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccination associates with reactogenicity. Vaccine X 2025, 22, 100593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, A.J.; Jiang, A.Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D.G. The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joura, E.A.; Giuliano, A.R.; Iversen, O.-E.; Bouchard, C.; Mao, C.; Mehlsen, J.; Moreira, E.D.; Ngan, Y.; Petersen, L.K.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; et al. A 9-Valent HPV Vaccine against Infection and Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Ende, C.; Marano, C.; Van Ahee, A.; Bunge, E.M.; De Moerlooze, L. The immunogenicity and safety of GSK’s recombinant hepatitis B vaccine in adults: A systematic review of 30 years of experience. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 811–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group Name | Group Size (n) | Immunogen | Immunization Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-mRNA | n = 8, 5 for ELISpot, 3 for qPCR | 20 μg G-mRNA | 0, 21 |
| NLS | n = 8, 5 for ELISpot, 3 for qPCR | 20 μg G-mRNA and 5 μg RABV-N | 0, 21 |
| INV | n = 8, 5 for ELISpot, 3 for qPCR | INV | 0, 7, 21 |
| Blank | n = 8, 5 for ELISpot, 3 for qPCR | Empty LNPs | 0, 21 |
| Group Name | Group Size (n) | Immunogen | Immunization Schedule |
|---|---|---|---|
| G-mRNA | n = 22, 10 for the challenge protection test, 12 for the viral load kinetics assay | 20 μg G-mRNA | 0, 21 |
| NLS | n = 22, 10 for the challenge protection test, 12 for the viral load kinetics assay | 20 μg G-mRNA and 5 μg RABV-N | 0, 21 |
| INV | n = 22, 10 for the challenge protection test, 12 for the viral load kinetics assay | INV | 0, 7, 21 |
| Blank | n = 22, 10 for the challenge protection test, 12 for the viral load kinetics assay | Empty LNPs | 0, 21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mu, C.; Ma, K.; Gao, D.; Liu, C.; Feng, L.; Peng, X.; Si, J.; Li, H.; et al. A Rabies Virus Nucleocapsid-Like Nanostructure Vaccine Based on Dual-Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13121196
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Mu C, Ma K, Gao D, Liu C, Feng L, Peng X, Si J, Li H, et al. A Rabies Virus Nucleocapsid-Like Nanostructure Vaccine Based on Dual-Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles. Vaccines. 2025; 13(12):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13121196
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhixiao, Jingjing Zhang, Changyong Mu, Kaili Ma, Dongxiu Gao, Chang’e Liu, Lin Feng, Xiaowu Peng, Junbo Si, Hongbing Li, and et al. 2025. "A Rabies Virus Nucleocapsid-Like Nanostructure Vaccine Based on Dual-Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles" Vaccines 13, no. 12: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13121196
APA StyleZhang, Z., Zhang, J., Mu, C., Ma, K., Gao, D., Liu, C., Feng, L., Peng, X., Si, J., Li, H., Su, Y., Zeng, F., He, L., Wang, A., Zhou, C., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Li, Q., Li, J., ... Li, Q. (2025). A Rabies Virus Nucleocapsid-Like Nanostructure Vaccine Based on Dual-Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles. Vaccines, 13(12), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13121196






