Immunoproteomic Screening of Candidate Antigens for the Preliminary Development of a Novel Multi-Component and Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Streptococcus suis Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Cell Wall Protein Extraction
2.3. Immunogenic Proteins Identified by 2D-Western Blot
2.4. MALDI-TOF-MS and Database Retrieval
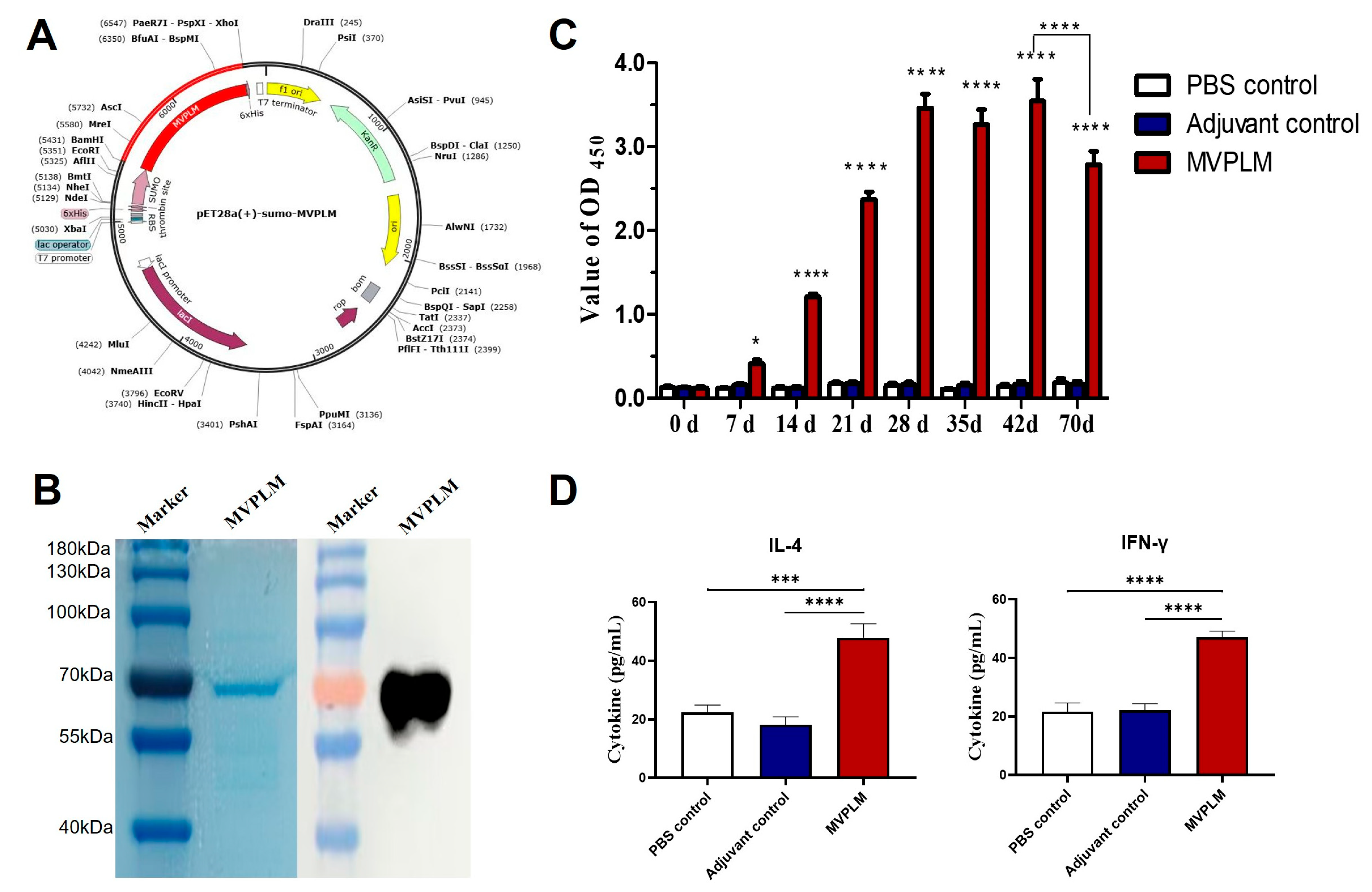
2.5. Cloning, Expression, and Purification of the Recombinant Proteins
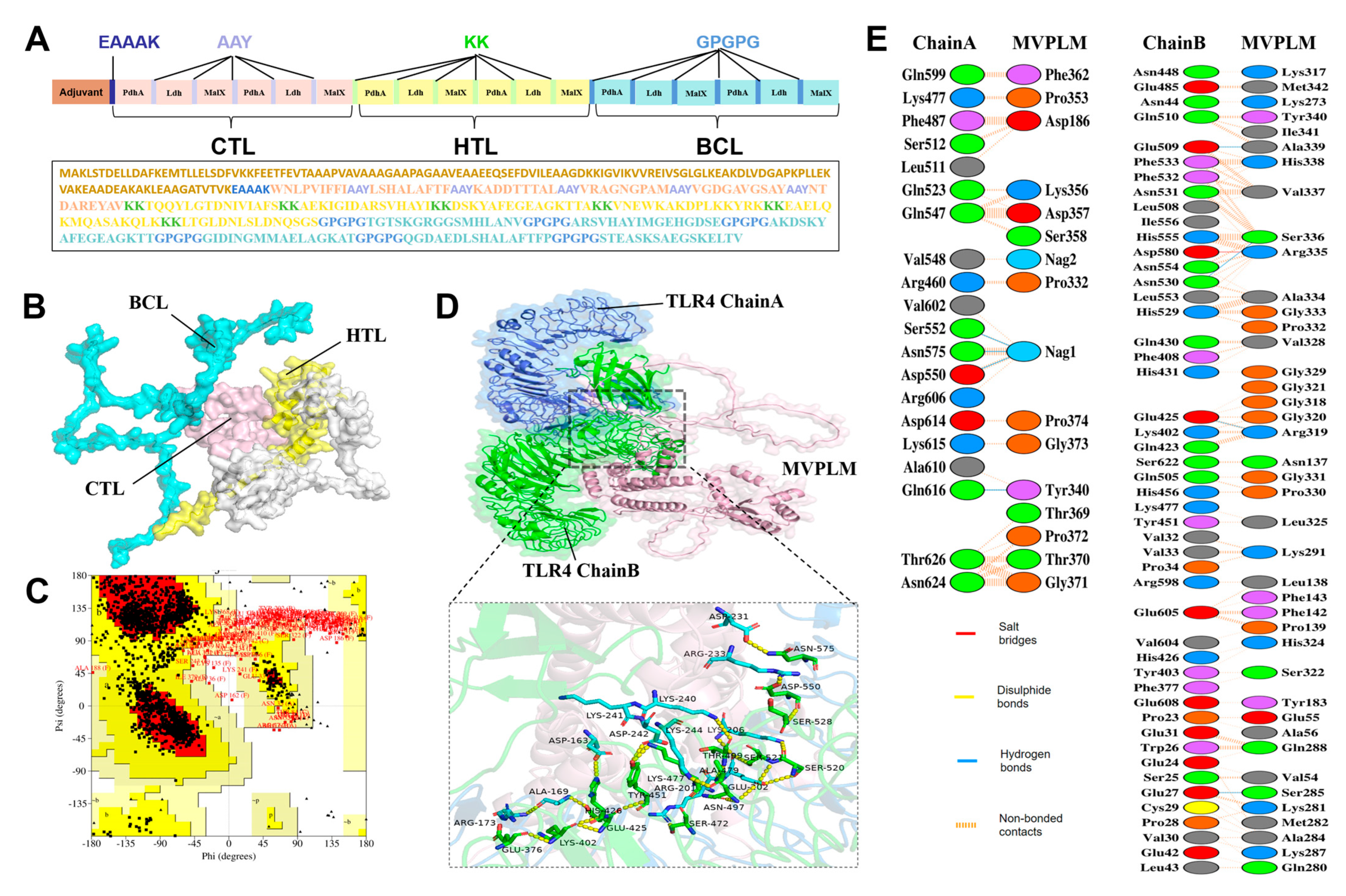
2.6. Multi-Epitope Vaccine Designing and Processing
2.7. Immunization and Challenge Studies
2.8. Histopathological Analysis
2.9. Antibody Determination
2.10. Adherence Inhibition Assays
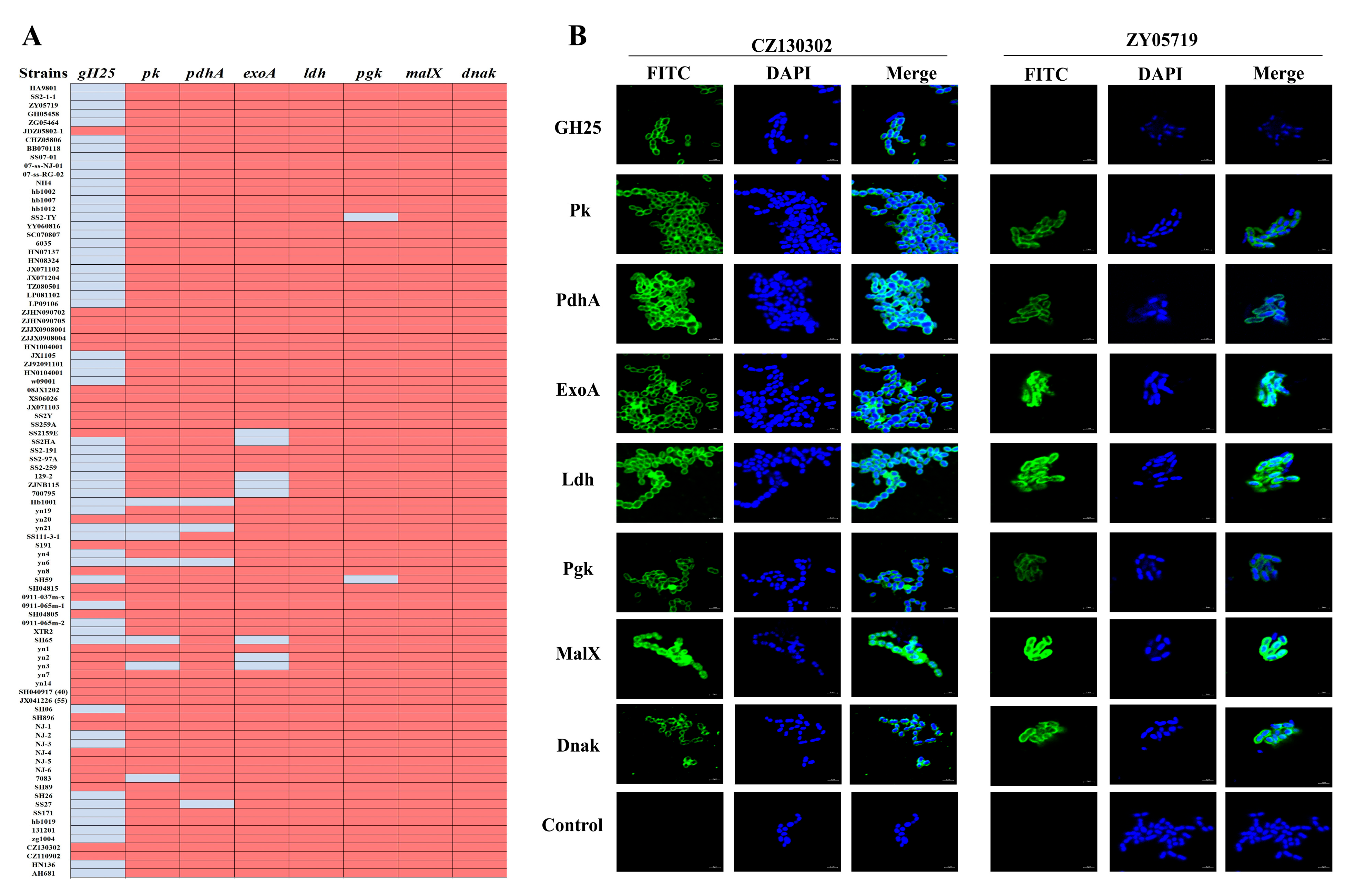
2.11. Distribution Analysis
2.12. Indirect Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.13. Antimicrobial Assay In Vitro
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
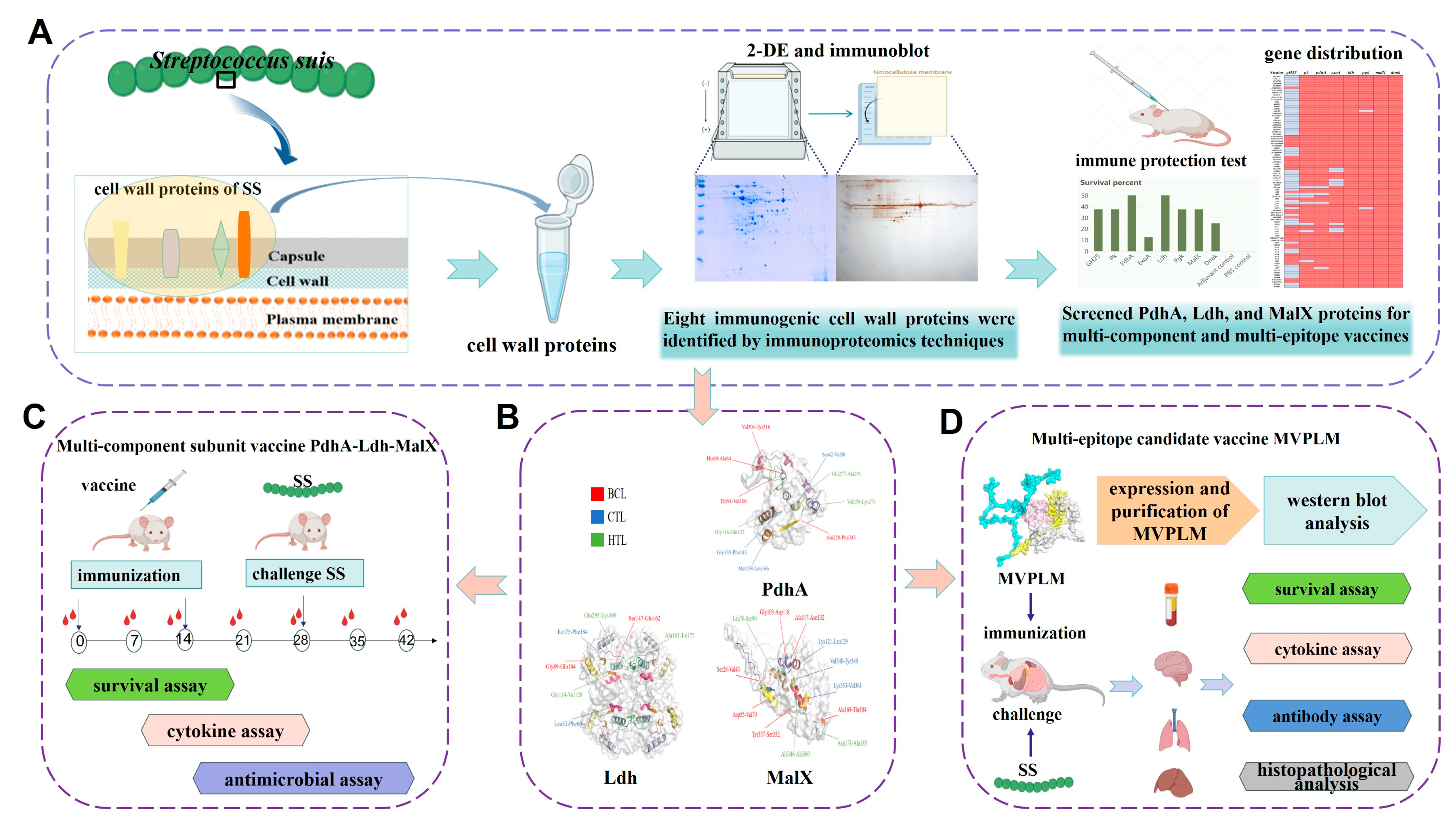
3.1. Eight Candidate Immunogens Identified by Proteomics and 2D Western Blot Assays
3.2. The Protective Efficacy of Eight Vaccine Candidates In Vivo
3.3. Alignment and Distribution of the Eight Vaccine Candidates
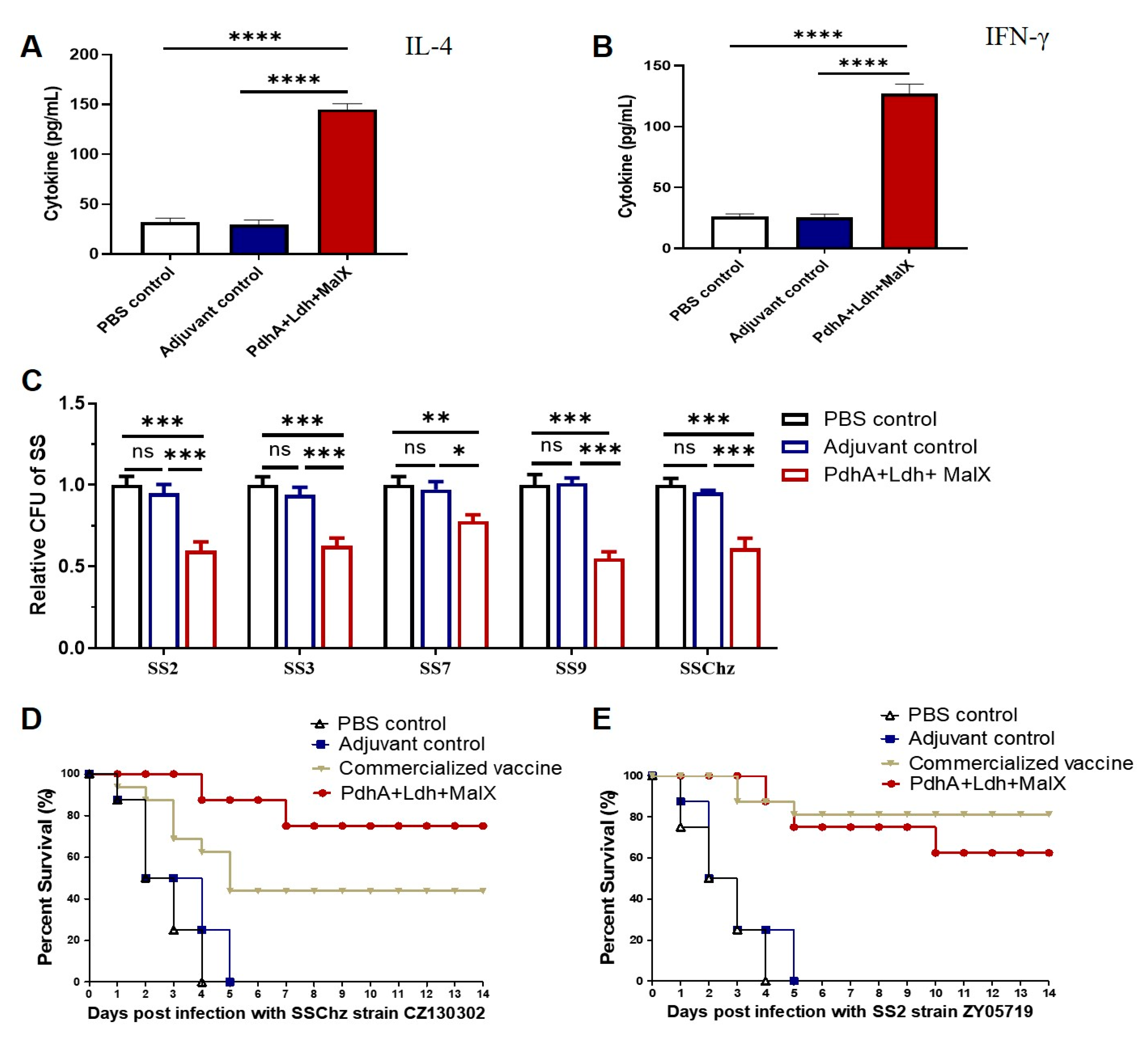
3.4. Improved Immune Protection of the Multi-Component Subunit Vaccine Composed of PdhA, Ldh, and MalX Proteins
3.5. Development of a Multi-Epitope Candidate Vaccine (MVPLM) Using Immunoinformatics
3.6. Evaluation of the Immunization Effect of the Multi-Epitope MVPLM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, F.; Zhang, S.; Erdeljan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis: Epidemiology and resistance evolution of an emerging zoonotic bacteria. One Health 2025, 21, 101098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; He, P.; Bai, Q.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Yao, H.; Pan, Z. Insight into the role of Streptococcus suis zinc metalloprotease C from the new serotype causing meningitis in piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meekhanon, N.; Kaewmongkol, S.; Phimpraphai, W.; Okura, M.; Osaki, M.; Sekizaki, T.; Takamatsu, D. Potentially hazardous Streptococcus suis strains latent in asymptomatic pigs in a major swine production area of Thailand. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralova, N.; Fittipaldi, N.; Zouharova, M.; Nedbalcova, K.; Matiaskova, K.; Gebauer, J.; Kulich, P.; Simek, B.; Matiasovic, J. Streptococcus suis strains with novel and previously undescribed capsular loci circulate in Europe. Vet. Microbiol. 2024, 298, 110265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechene-Tempier, M.; de Boisseson, C.; Lucas, P.; Bougeard, S.; Libante, V.; Marois-Crehan, C.; Payot, S. Virulence genes, resistome and mobilome of Streptococcus suis strains isolated in France. Microb. Genom. 2024, 10, 001224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Schwarz, S.; Li, X.S.; Shang, Y.H.; Du, X.D. Emergence of a tet(M) Variant Conferring Resistance to Tigecycline in Streptococcus suis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 709327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Bai, Q.; Dong, W.; Pan, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Yao, H. CrfP, a fratricide protein, contributes to natural transformation in Streptococcus suis. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarska, A.; Janas, K.; Pejsak, Z.; Otulak-Koziel, K.; Garbaczewska, G.; Hryniewicz, W.; Sadowy, E. Diversity of serotypes and new cps loci variants among Streptococcus suis isolates from pigs in Poland and Belarus. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.; Xu, J.; Tan, C.; Wang, X.; Bei, W.; Li, J. A Streptococcus suis Live Vaccine Suppresses Streptococcal Toxic Shock-Like Syndrome and Provides Sequence Type-Independent Protection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutkiewicz, J.; Zajac, V.; Sroka, J.; Wasinski, B.; Cisak, E.; Sawczyn, A.; Kloc, A.; Wojcik-Fatla, A. Streptococcus suis: A re-emerging pathogen associated with occupational exposure to pigs or pork products. Part II Pathogenesis. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2018, 25, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.D.; Clifton-Hadley, F.; Tai, J. Streptococcal infection in young pigs. V. An immunogenic polysaccharide from Streptococcus suis type 2 with particular reference to vaccination against streptococcal meningitis in pigs. J. Hyg. 1980, 85, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Calzas, C.; Shiao, T.C.; Neubauer, A.; Kempker, J.; Roy, R.; Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. Protection against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2 Infection Using a Capsular Polysaccharide Glycoconjugate Vaccine. Infect. Immun. 2016, 84, 2059–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzas, C.; Lemire, P.; Auray, G.; Gerdts, V.; Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. Antibody response specific to the capsular polysaccharide is impaired in Streptococcus suis serotype 2-infected animals. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenenbaum, T.; Asmat, T.M.; Seitz, M.; Schroten, H.; Schwerk, C. Biological activities of suilysin: Role in Streptococcus suis pathogenesis. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiße, C.; Dittmar, D.; Jakóbczak, B.; Florian, V.; Schütze, N.; Alber, G.; Klose, K.; Michalik, S.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Völker, U.; et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Streptococcus suis vaccine composed of six conserved immunogens. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Kong, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J. TLR4 Agonist Combined with Trivalent Protein JointS of Streptococcus suis Provides Immunological Protection in Animals. Vaccines 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yao, H. Multilocus sequence typing and virulence genotyping of Streptococcus suis serotype 9 isolates revealed high genetic and virulence diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, fnx192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. Virulence genotyping and population analysis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 isolates from China. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 36, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Esgleas, M.; Lacouture, S.; Dubreuil, J.D.; Willson, P.; Harel, J. Immunization with recombinant Sao protein confers protection against Streptococcus suis infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, K.J.; Cheng, L.T.; Lee, J.W.; Chung, Y.C.; Chung, W.B.; Chu, C.Y. Immunization with Streptococcus suis bacterin plus recombinant Sao protein in sows conveys passive immunity to their piglets. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seele, J.; Beineke, A.; Hillermann, L.M.; Jaschok-Kentner, B.; von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Valentin-Weigand, P.; Baums, C.G. The immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, IdeSsuis, is involved in complement evasion. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieckmann, K.; Seydel, A.; Klose, K.; Alber, G.; Baums, C.G.; Schutze, N. Vaccination with the immunoglobulin M-degrading enzyme of Streptococcus suis, Ide (Ssuis), leads to protection against a highly virulent serotype 9 strain. Vaccine X 2019, 3, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Sun, L.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Wen, W.Y.; Li, X.K.; Mei, J.J.; Ding, K.; Wu, T.C.; Grenier, D. Identification and characterization of a Streptococcus suis immunogenic ornithine carbamoytransferase involved in bacterial adherence. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yao, X.; Pan, R.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Dong, N.; Wei, J.; Liu, K.; Qiu, Y.; Sealey, K.; et al. Subunit Vaccine Targeting Phosphate ABC Transporter ATP-Binding Protein, PstB, Provides Cross-Protection against Streptococcus suis Serotype 2, 7, and 9 in Mice. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Liao, X.; Luo, J.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Peptidyl isomerase PrsA is surface-associated on Streptococcus suis and offers cross-protection against serotype 9 strain. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.A.; Sun, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; Shi, H. Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis vector delivering a dual-antigen expression cassette provides mouse cross-protection against Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 7, 9, and 1/2. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, S.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, H.; Liu, G. Combined Immunoinformatics to Design and Evaluate a Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines 2024, 12, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludolf, F.; Ramos, F.F.; Coelho, E.A.F. Immunoproteomics and phage display in the context of leishmaniasis complexity. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1112894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Ding, C.; Tu, J.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; Duan, Y.; Yu, S. Immunoproteomics analysis of whole cell bacterial proteins of Riemerella anatipestifer. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 157, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.R.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Pires, S.D.F.; Andrade, H.M.; Lage, A.P. Immunoproteomics of Brucella abortus reveals potential of recombinant antigens for discriminating vaccinated from naturally infected cattle. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 147, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Du, D.; Yu, Y.; Ma, C.; Jiao, F.; Yao, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W. Identification of Novel Laminin- and Fibronectin-binding Proteins by Far-Western Blot: Capturing the Adhesins of Streptococcus suis Type 2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, T.U.; Hussain, Z.; Asghar, F.; Nawaz, W. Reverse vaccinology-based identification and in silico characterization of immunogenic membrane proteins of Salmonella Typhimurium as novel vaccine targets against multidrug-resistant infections. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sidney, J.; Kim, Y.; Sette, A.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M.; Peters, B. Peptide binding predictions for HLA DR, DP and DQ molecules. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreatta, M.; Nielsen, M. Gapped sequence alignment using artificial neural networks: Application to the MHC class I system. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein-protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Pu, W.; Pan, X.; Li, P.; Bai, Q.; Liang, S.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. A multi-epitope subunit vaccine providing broad cross-protection against diverse serotypes of Streptococcus suis. NPJ Vaccines 2024, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Z.; He, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Shao, J.; Wang, K.; Wu, Z.; Yao, H.; et al. SssP1, a Fimbria-like component of Streptococcus suis, binds to the vimentin of host cells and contributes to bacterial meningitis. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briles, D.E.; Paton, J.C.; Mukerji, R.; Swiatlo, E.; Crain, M.J. Pneumococcal Vaccines. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, J.; Soldaini, E.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Rittenhouse, S.; Bagnoli, F.; Phogat, S. Staphylococcus aureus Vaccine Research and Development: The Past, Present and Future, Including Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiwan, N.; Calland, J.K.; Mourkas, E.; Hitchings, M.D.; Murray, S.; Tadee, P.; Tadee, P.; Duangsonk, K.; Meric, G.; Sheppard, S.K.; et al. Genetic diversity and variation in antimicrobial-resistance determinants of non-serotype 2 Streptococcus suis isolates from healthy pigs. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, mgen000882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Du, X.; Gao, Y.; Shan, X.; Hu, Z.; Hu, Q. PaR1 secreted by the type IX secretion system is a protective antigen of Riemerella anatipestifer. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1082712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Chaperonin GroEL: A novel phylogenetically conserved protein with strong immunoreactivity of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from duck identified by immunoproteomics. Vaccine 2013, 31, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontijo, M.T.P.; Teles, M.P.; Vidigal, P.M.P.; Brocchi, M. Expanding the Database of Signal-Anchor-Release Domain Endolysins Through Metagenomics. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Luo, M.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Min, X.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, W.; Li, D.; et al. Structural basis of the novel S. pneumoniae virulence factor, GHIP, a glycosyl hydrolase 25 participating in host-cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquart, M.E. Pathogenicity and virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae: Cutting to the chase on proteases. Virulence 2021, 12, 766–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Klerk, N.; de Vogel, C.; Fahal, A.; van Belkum, A.; van de Sande, W.W. Fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and pyruvate kinase, two novel immunogens in Madurella mycetomatis. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairn, B.L.; Lee, G.T.; Chumber, A.K.; Steck, P.R.; Mire, M.O.; Lima, B.P.; Herzberg, M.C. Uncovering Roles of Streptococcus gordonii SrtA-Processed Proteins in the Biofilm Lifestyle. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 203, e00544-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Immunoproteomic assay of surface proteins of Streptococcus suis serotype 9. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korithoski, B.; Levesque, C.M.; Cvitkovitch, D.G. The involvement of the pyruvate dehydrogenase E1alpha subunit, in Streptococcus mutans acid tolerance. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 289, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bezerra, D.S.; Stipp, R.N.; Neves, B.G.; Guedes, S.F.; Nascimento, M.M.; Rodrigues, L.K. Insights into the Virulence Traits of Streptococcus mutans in Dentine Carious Lesions of Children with Early Childhood Caries. Caries Res. 2016, 50, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.R.; Libby, S.J.; Fang, F.C. A nitric oxide-inducible lactate dehydrogenase enables Staphylococcus aureus to resist innate immunity. Science 2008, 319, 1672–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Zheng, C.; Yuan, F.; Chen, H.; Bei, W.; Li, J. Evaluation of the protective efficacy of four novel identified membrane associated proteins of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vaccine 2015, 33, 2254–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsen, C.; Espelid, S.; Willassen, N.P.; Paulsen, S.M. Identification and cloning of immunogenic Aliivibrio salmonicida Pal-like protein present in profiled outer membrane and secreted subproteome. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Huang, H.Y.; Tsai, M.A.; Wang, P.C.; Jiang, B.H.; Chen, S.C. Phosphoglycerate kinase enhanced immunity of the whole cell of Streptococcus agalactiae in tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 41, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Research Advances on Tilapia Streptococcosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelburne, S.A., 3rd; Keith, D.; Horstmann, N.; Sumby, P.; Davenport, M.T.; Graviss, E.A.; Brennan, R.G.; Musser, J.M. A direct link between carbohydrate utilization and virulence in the major human pathogen group A Streptococcus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, K.L.; Gierahn, T.M.; Lu, Y.J.; Gouveia, P.; Alderson, M.; Flechtner, J.B.; Higgins, D.E.; Malley, R. T(H)17-based vaccine design for prevention of Streptococcus pneumoniae colonization. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narciso, A.R.; Iovino, F.; Thorsdottir, S.; Mellroth, P.; Codemo, M.; Spoerry, C.; Righetti, F.; Muschiol, S.; Normark, S.; Nannapaneni, P.; et al. Membrane particles evoke a serotype-independent cross-protection against pneumococcal infection that is dependent on the conserved lipoproteins MalX and PrsA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122386119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, L.; Wu, Z.; Shao, J.; Liu, G.; Fan, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Comparative proteomic analysis of Streptococcus suis biofilms and planktonic cells that identified biofilm infection-related immunogenic proteins. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; Fan, H. Screening for phagocytosis resistance-related genes via a transposon mutant library of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Virulence 2020, 11, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Dang, W.; Deng, T.; Sun, L. Edwardsiella tarda DnaK: Expression, activity, and the basis for the construction of a bivalent live vaccine against E. tarda and Streptococcus iniae. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, E.; Cohan, R.A.; Sotoodehnejadnematalahi, F.; Mousavi, S.F. In-silico design and evaluation of an epitope-based serotype-independent promising vaccine candidate for highly cross-reactive regions of pneumococcal surface protein A. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir Ul Qamar, M.; Ahmad, S.; Fatima, I.; Ahmad, F.; Shahid, F.; Naz, A.; Abbasi, S.W.; Khan, A.; Mirza, M.U.; Ashfaq, U.A.; et al. Designing multi-epitope vaccine against Staphylococcus aureus by employing subtractive proteomics, reverse vaccinology and immuno-informatics approaches. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xiong, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Development of a Universal Multi-Epitope Vaccine Candidate against Streptococcus suis Infections Using Immunoinformatics Approaches. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
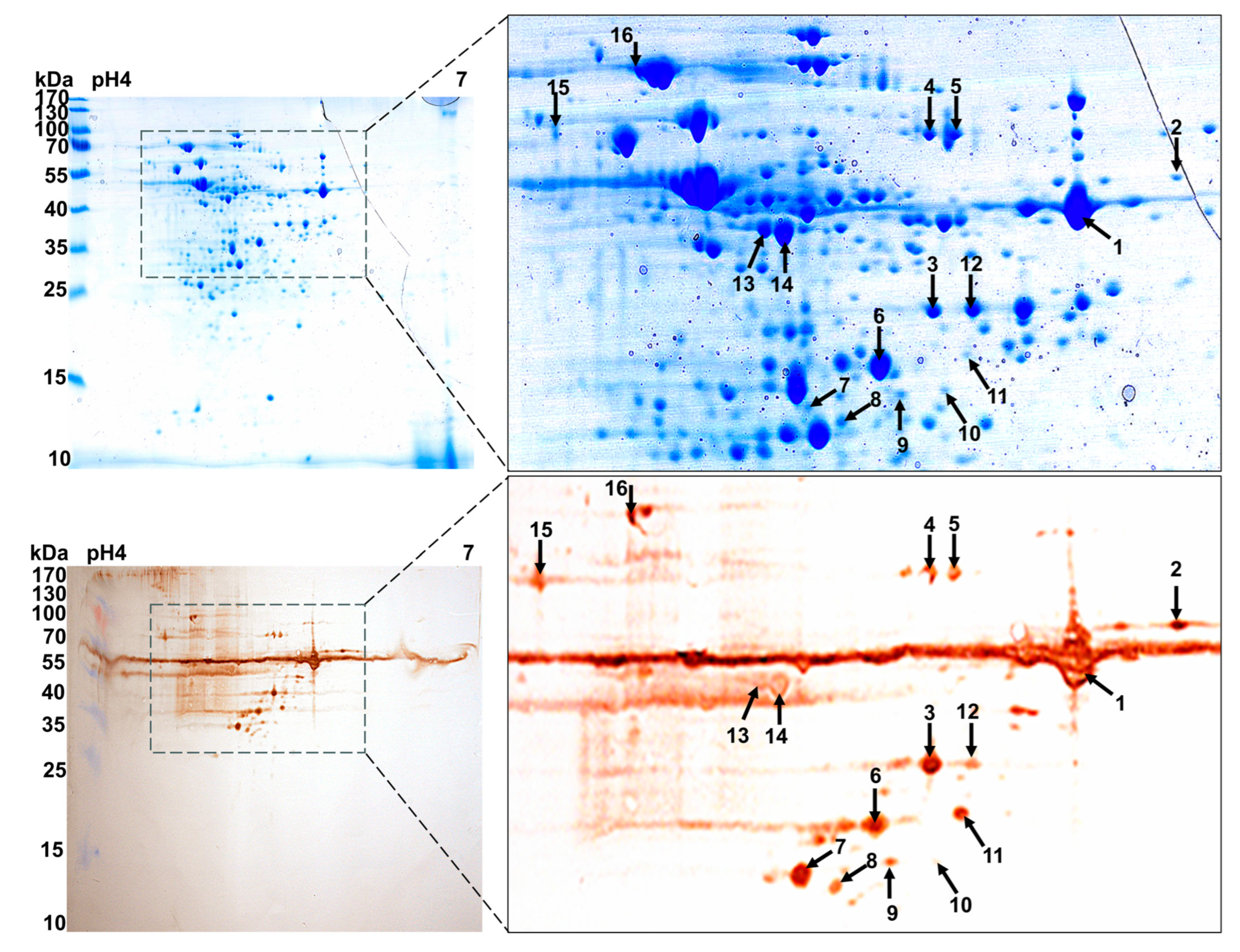



| Spot Munber | Identified Protein | Peptides Matched | Protein Score | Score C.I.% | Intensity Matched | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mascot Results | Annotation | MW(Da)/pI | |||||
| 1 | gi|353533998 | Family 25 glycosyl hydrolase (GH25) | 39,164.4/5.52 | 15 | 347 | 100 | 68.239 |
| 2 | gi|353533998 | Family 25 glycosyl hydrolase (GH25) | 39,164.4/5.52 | 12 | 207 | 100 | 43.623 |
| 3 | gi|353533998 | Family 25 glycosyl hydrolase (GH25) | 39,164.4/5.52 | 14 | 73 | 99.539 | 16.845 |
| 4 | gi|353533539 | Pyruvate kinase (Pk) | 56,311.1/5.19 | 28 | 226 | 100 | 58.357 |
| 5 | gi|353533539 | Pyruvate kinase (Pk) | 56,311.1/5.19 | 20 | 209 | 99.832 | 57.876 |
| 6 | gi|353737021 | Acetoin dehydrogena-se E1 component alpha subunit (PdhA) | 35,447.7/4.91 | 9 | 59 | 95.325 | 54.352 |
| 9 | gi|166223157 | L-lactate dehydrogenase (Ldh) | 35,400.3/5.05 | 8 | 56 | 97.957 | 46.845 |
| 10 | gi|556049758 | Exodeoxyribonuclease (ExoA) | 31,017.7/5.52 | 11 | 63 | 95.705 | 18.344 |
| 13 | gi|353737491 | Phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk) | 42,016.1/4.86 | 25 | 746 | 99.786 | 79.568 |
| 14 | gi|353737491 | Phosphoglycerate kinase (Pgk) | 42,016.1/4.86 | 23 | 346 | 99.786 | 79.568 |
| 15 | gi|353532515 | ABC transporter subs-trate binding protein maltose (MalX) | 44,358.8/4.53 | 17 | 196 | 100 | 20.541 |
| 16 | gi|661304267 | Molecular chaperone DnaK (Dnak) | 64,746.3/4.62 | 28 | 835 | 100 | 85.457 |
| Group | No. of Surviving/Total Infected Mice | Survival Percent |
|---|---|---|
| GH25 | 6/16 | 37.5% |
| Pk | 6/16 | 37.5% |
| PdhA | 8/16 | 50% |
| ExoA | 2/16 | 12.5% |
| Ldh | 8/16 | 50% |
| Pgk | 6/16 | 37.5% |
| MalX | 6/16 | 37.5% |
| Dnak | 4/16 | 25% |
| Adjuvant control | 0/16 | 0% |
| PBS control | 0/16 | 0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Gu, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Zu, S. Immunoproteomic Screening of Candidate Antigens for the Preliminary Development of a Novel Multi-Component and Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101020
Zhang Y, Li C, Feng Y, Gu Q, Hu J, Li Y, Xia L, Zu S. Immunoproteomic Screening of Candidate Antigens for the Preliminary Development of a Novel Multi-Component and Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines. 2025; 13(10):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101020
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yue, Caiying Li, Yutong Feng, Qibing Gu, Jinwang Hu, Yuhang Li, Lu Xia, and Shaopo Zu. 2025. "Immunoproteomic Screening of Candidate Antigens for the Preliminary Development of a Novel Multi-Component and Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Streptococcus suis Infection" Vaccines 13, no. 10: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101020
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, C., Feng, Y., Gu, Q., Hu, J., Li, Y., Xia, L., & Zu, S. (2025). Immunoproteomic Screening of Candidate Antigens for the Preliminary Development of a Novel Multi-Component and Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Streptococcus suis Infection. Vaccines, 13(10), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13101020





