Immunogenic Responses Elicited by a Pool of Recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 Strains Surface-Displaying Diverse African Swine Fever Antigens Administered via Different Immunization Routes in a Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Viruses, and Plasmids
2.2. Construction of the Recombinant Plasmids Surface-Expressing the ASFV Antigens
2.3. Construction of the Recombinant NC8 (rNC8) Strains
2.4. Immunofluorescence Identification of Recombinant Proteins on the Surface of rNC8 Strains
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis of Recombinant Proteins Expressed on the Surface of rNC8 Strains
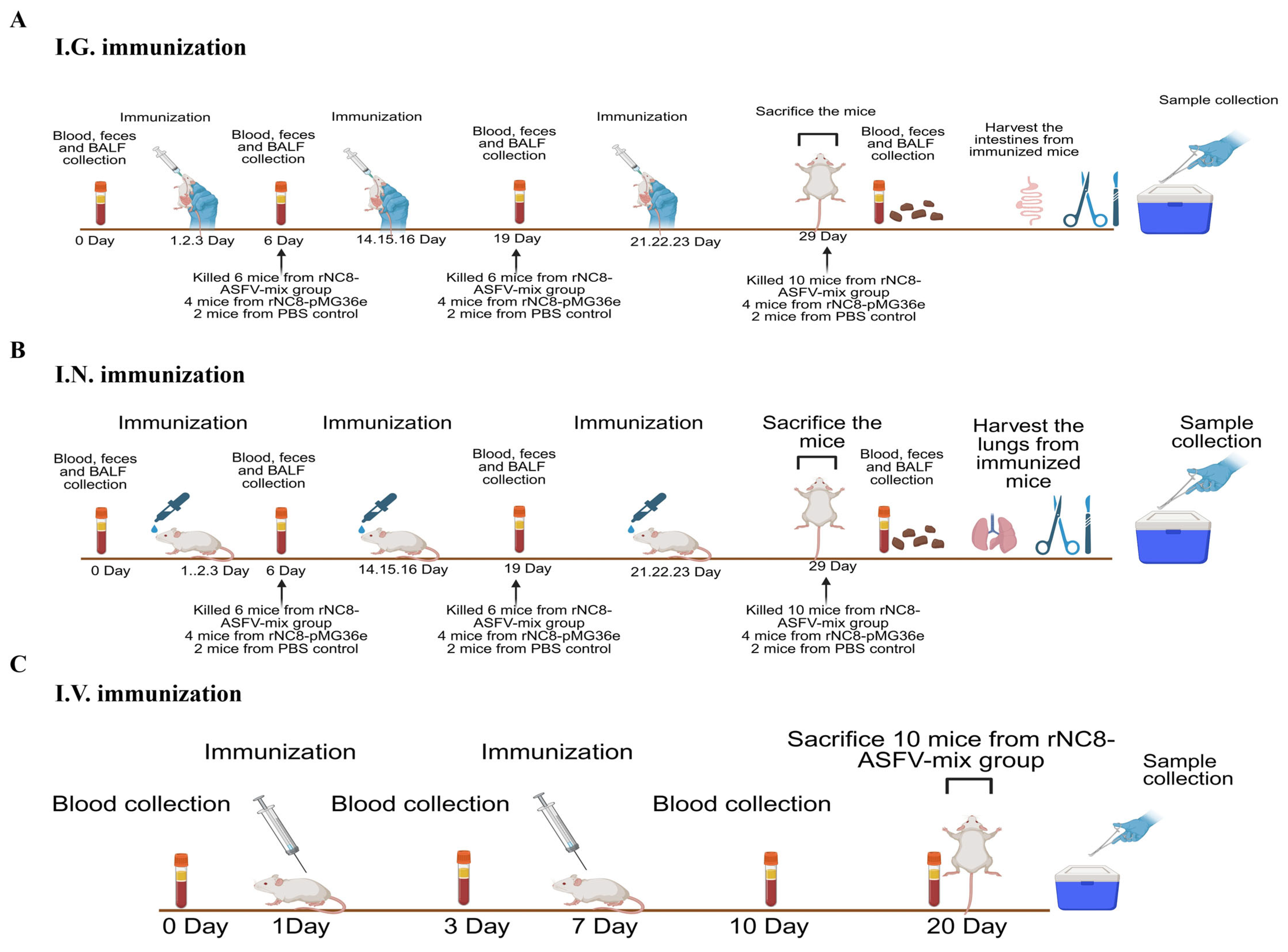
2.6. Immunization of Mice
2.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.8. Isolation of T Lymphocytes from the Spleens of the Immunized Mice
2.9. Proliferation Assay of Splenic T Lymphocytes
2.10. Flow Cytometry Analysis of T-Cell Surface Markers
2.11. Ethics Statements
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surface-Expression Analysis for LP3065 Fused with the ASFV Antigens
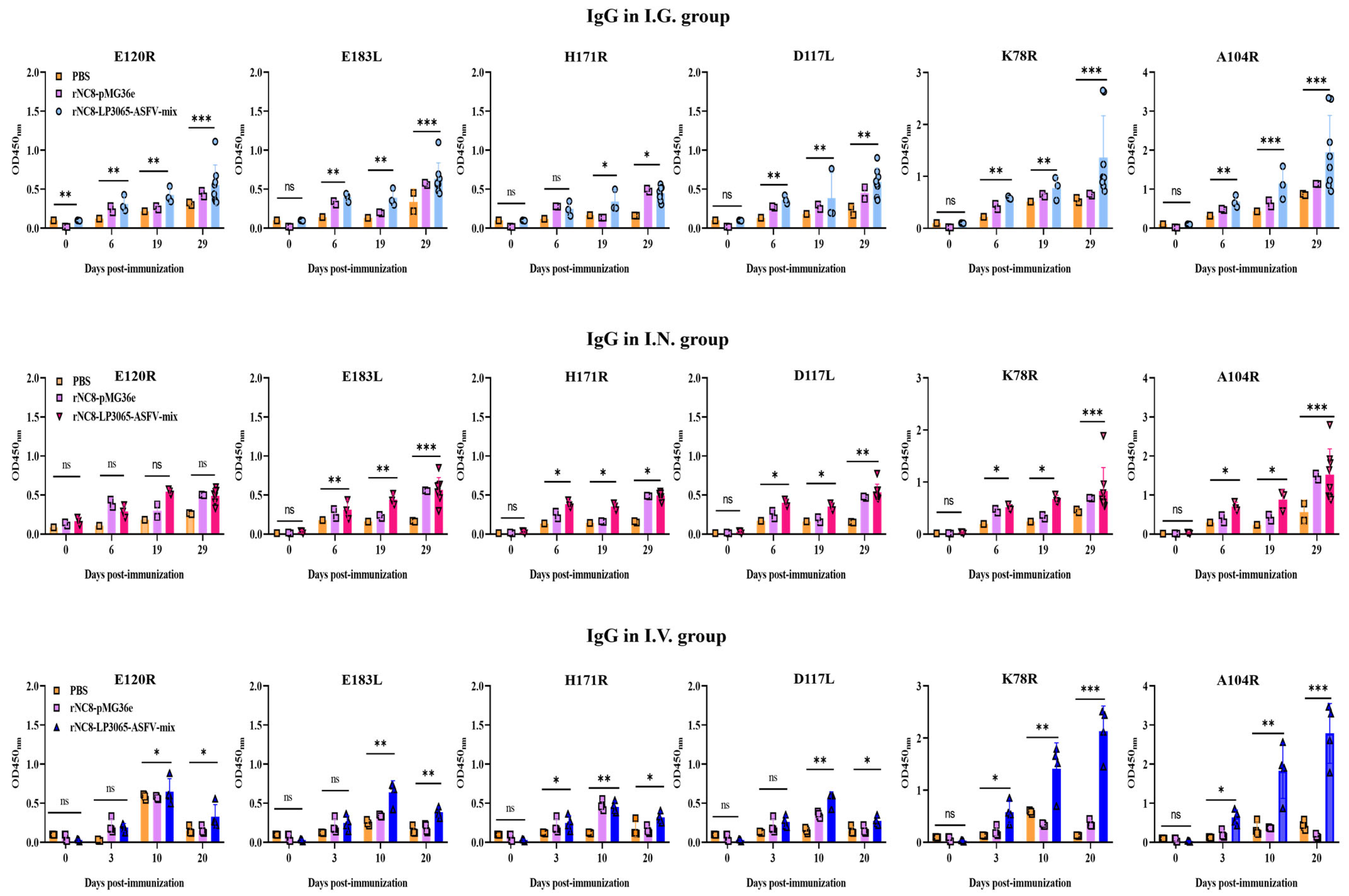
3.2. Analysis of IgG Antibodies Production by rNC8-LP3065-ASFV-mix in Mice
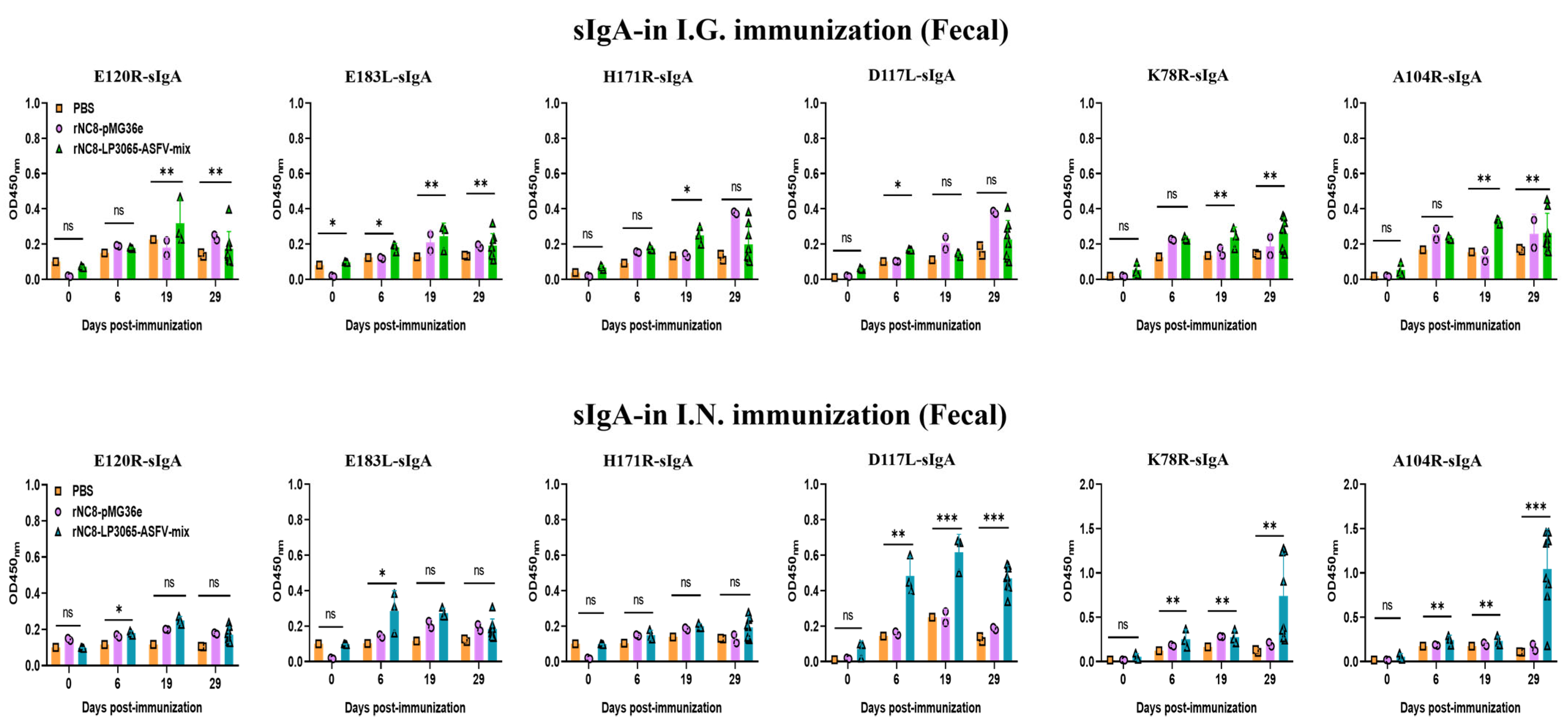
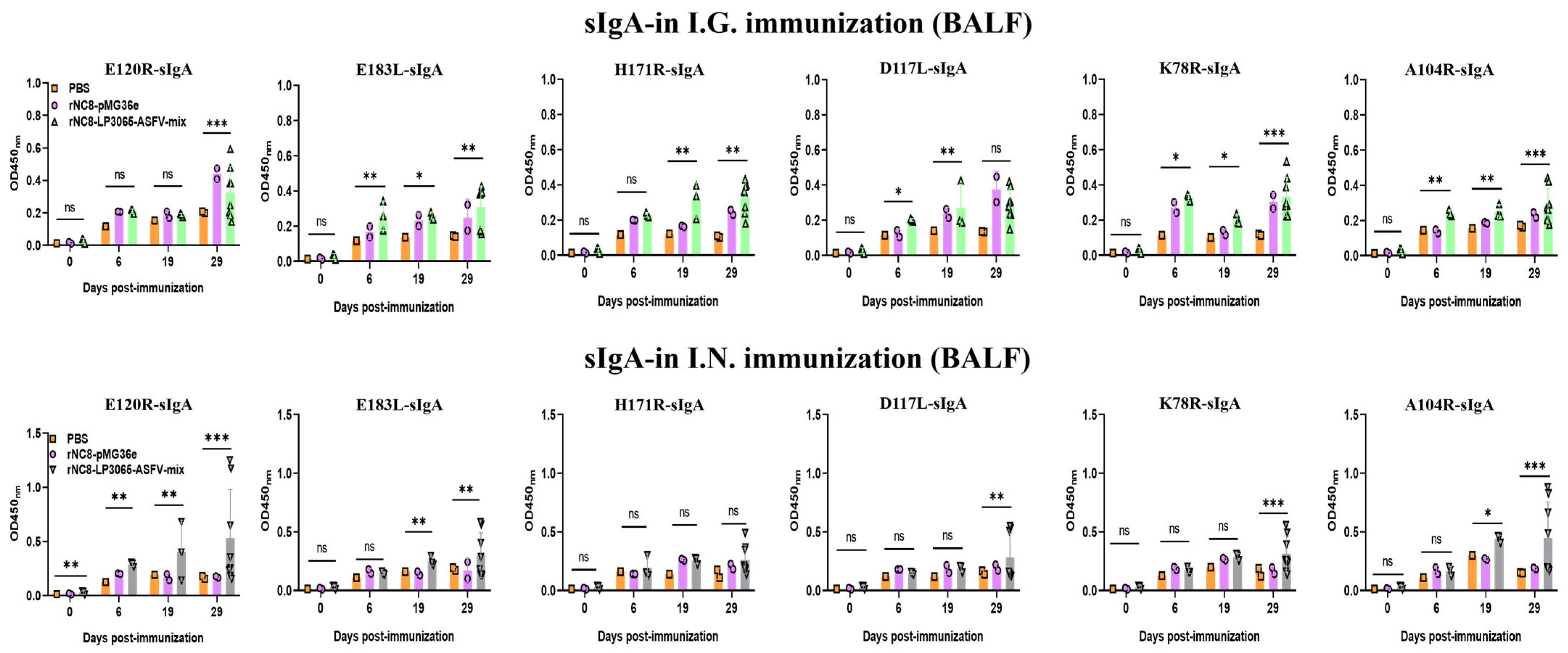
3.3. rNC8-LP3065-ASFV-mix Induced High-Level Secretory IgA Antibodies in Mice
3.4. rNC8-LP3065-ASFV-mix Induces T Cell Proliferation in Mice
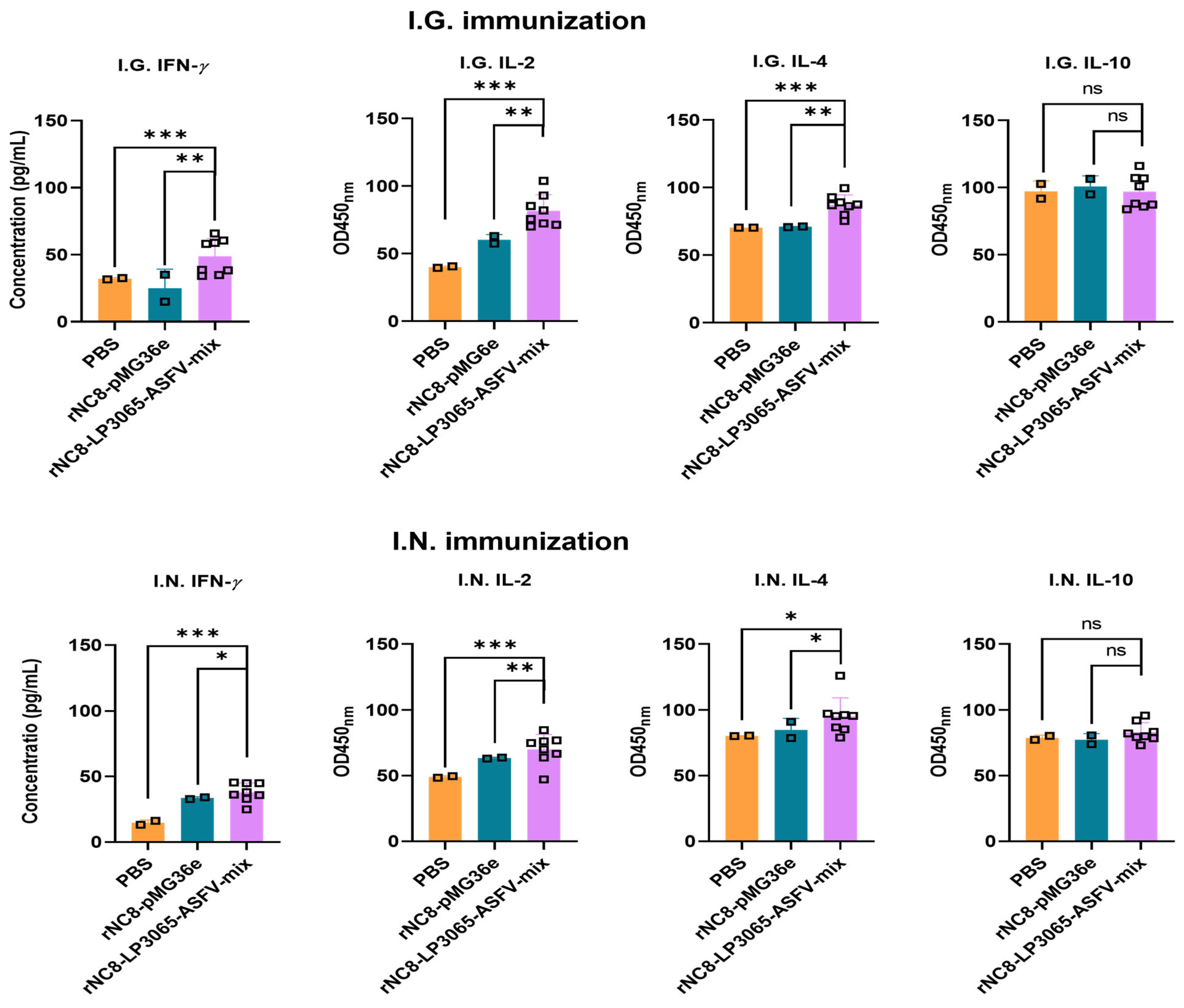
3.5. I.G. and I.N. Immunization of rNC8-LP3065-ASFV-mix Increased Th1 Cytokine Levels and Partially Enhanced Th2 Cytokine Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ASF | African swine fever |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| NC8 | Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 |
| ASFV | African swine fever virus |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| WOAH | World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH) |
| ORFs | Open reading frames |
| dpi | Days post-immunization |
References
- Blome, S.; Franzke, K.; Beer, M. African Swine Fever-A Review of Current Knowledge. Virus Res. 2020, 287, 198099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penrith, M.L.; Kivaria, F.M. One Hundred Years of African Swine Fever in Africa: Where have We been, Where are We Now, Where are We Going? Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1179–e1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Sun, E.; Huang, L.; Ding, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shen, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T. Highly Lethal Genotype I and II Recombinant African Swine Fever Viruses Detected in Pigs. Nat. Comm. 2023, 14, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus: A Review. Viruses 2017, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ai, Q.; Huang, S.; Ou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tong, T.; Fan, H. Immune Escape Mechanism and Vaccine Research Progress of African Swine Fever Virus. Vaccines 2022, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, A.; Marques, M.I.; Costa, J.V. Two Dimensional Analysis of African Swine Fever Virus Proteins and Proteins Induced in Infected Cells. Virology 1986, 152, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shan, H.; Cai, X. Orally Administered Recombinant Lactobacillus Expressing African Swine Fever Virus Antigens that Induced Immunity Responses. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Lv, T.; Yang, C.; Chen, S.; Feng, L.; Lai, L.; Duan, Z.; Chen, X. A New Vaccination Regimen Using Adenovirus Vectored Vaccine Confers Effective Protection Against African Swine Fever Virus in Swine. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, 2233643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Puertas, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Oviedo, J.M.; Brun, A.; Alonso, C.; Escribano, J.M. The African Swine Fever Virus Proteins p54 and p30 are Involved in Two Distinct Steps of Virus Attachment and Both Contribute to the Antibody Mediated Protective Immune Response. Virology 1998, 243, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borca, M.V.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Vuono, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Holinka, L.G.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D.P. Development of A Highly Effective African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine by Deletion of the I177L Gene Results in Sterile Immunity Against the Current Epidemic Eurasia Strain. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e02017-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, A.; Matamoros, T.; Guerra, M.; Andrés, G. A Proteomic Atlas of the African Swine Fever Virus Particle. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01293-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Bi, Y.; Sun, J.; Peng, R.; Song, H.; Zhu, D.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the African Swine Fever Virus. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 836–843.e833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, N.; Qu, H.; Xu, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S. Summary of the Current Status of African Swine Fever Vaccine Development in China. Vaccines 2023, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Ai, C.; Hu, M.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M. Modulation of Peanut Induced Allergic Immune Responses by Oral Lactic Acid Bacteria Based Vaccines in Mice. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 6353–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, M.P.; Elmastour, F.; Sane, F.; Drider, D.; Fiocco, D.; Spano, G.; Hober, D. Inhibition of Coxsackievirus B4 by Lactobacillus plantarum. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 210, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Yu, Q.; Xie, L.; Ran, L.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Gan, L.; Song, Z. Inhibitory Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Metabolites on Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 139, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Wang, J.H.; Zhao, W.; Shi, C.W.; Yang, K.D.; Niu, T.M.; Yang, G.L.; Cao, X.; Jiang, Y.L.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum Surface Displayed ASFV (p54) with Porcine IL-21 Generally Stimulates Protective Immune Responses in Mice. AMB Express 2021, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, A.; Huang, J.; Song, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, H.; Qiu, H. Immune Responses Induced by a recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Surface-Displaying the gD Protein of Pseudorabies Virus. Viruses 2024, 16, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teklue, T.; Sun, Y.; Abid, M.; Luo, Y.; Qiu, H.J. Current Status and Evolving Approaches to African Swine Fever Vaccine Development. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas-Fernandez, E.; Sanchez-Vizcaino, J.M.; Kosowska, A.; Rivera, B.; Mayoral-Alegre, F.; Rodriguez-Bertos, A.; Yao, J.; Bray, J.; Lokhandwala, S.; Mwangi, W. Adenovirus Vectored African Swine Fever Virus Antigens Cocktail is not Protective Against Virulent Arm07 Isolate in Eurasian Wild Boar. Pathogens 2020, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Sun, X.; Hui, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, H.; Qi, Y.; Li, S.; Ke, J. Newcastle Disease Virus-Vectored African Swine Fever Virus Antigen Cocktail Delays the Onset of ASFV-SY18 but Is Not Protective. Microorganism 2024, 12, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jung, D.I.; Yang, I.Y.; Jang, S.H.; Kim, J.; Truong, T.T.; Pham, T.V.; Truong, N.U.; Lee, K.Y.; Jang, Y.S. Application of an M-cell-Targeting Ligand for Oral Vaccination Induces Efficient Systemic and Mucosal Immune Responses Against a Viral Antigen. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, N.; Du, G.; Zhong, X.; Sun, X. Recombinant Lactic Acid Bacteria as Promising Vectors for Mucosal Vaccination. Exploration 2021, 1, 20210026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Jin, Y.B.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.L.; Wang, P.B.; Jiang, Y.L.; Shi, C.W.; Huang, H.B.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Construction and Immunogenicity Analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum Expressing a Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus S Gene Fused to a DC-targeting Peptide. Virus Res. 2018, 247, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carasi, P.; Racedo, S.M.; Jacquot, C.; Romanin, D.E.; Serradell, M.; Urdaci, M. Impact of Kefir Derived Lactobacillus kefiri on the Mucosal Immune Response and Gut Microbiota. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 361604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilander, A.C.; Dean, G.A. Adjuvant Strategies for Lactic Acid Bacterial Mucosal Vaccines. Vaccines 2019, 7, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Nguyen, M.T.; Das, A.; Ton-That, H. Anchoring Surface Proteins to the Bacterial Cell Wall by Sortase Enzymes: How it Started and What We Know now. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 60, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischetti, V.; Pancholi, V.; Schneewind, O. Conservation of a Hexapeptide Sequence in the Anchor Region of Surface Proteins from Gram Positive cocci. Mol. Microbiol. 1990, 4, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ton-That, H.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Faull, K.F.; Schneewind, O. Anchoring of Surface Proteins to the Cell Wall of Staphylococcus aureus: Sortase Catalyzed in vitro Transpeptidation Reaction using LPxTG Peptide and NH2-Gly3substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9876–9881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, L.E.; Temprana, C.F.; Argüelles, M.; Glikmann, G.; Castello, A.A. Antigenicity and Immunogenicity of Rotavirus VP6 Protein Expressed on the Surface of Lactococcus lactis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 298598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raya-Tonetti, F.; Müller, M.; Sacur, J.; Kitazawa, H.; Villena, J.; Vizoso-Pinto, M.G. Novel LysM Motifs for Antigen Display on lactobacilli for Mucosal Immunization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 4, 21691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Perez, N.G.; Lefèvre, F.; Corthier, G.; Adel-Patient, K.; Langella, P.; Bermúdez-Humarán, L.G. Influence of the Route of Immunization and the Nature of the Bacterial Vector on Immunogenicity of Mucosal Vaccines Based on Lactic Acid Bacteria. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6581–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazmanian, S.K.; Liu, G.; Ton-That, H.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus Sortase, an Enzyme that Anchors Surface Proteins to the Cell Wall. Science 1999, 285, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xie, M.; Wu, W.; Chen, Z. Structures and Functional Diversities of ASFV Proteins. Viruses 2021, 13, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodrow, K.A.; Bennett, K.M.; Lo, D.D. Mucosal Vaccine Design and Delivery. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, L. Lactic Acid Bacteria as Mucosal Delivery Vehicles: A Realistic Therapeutic Option. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5691–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangette, C.; Muller-Alouf, H.; Goudercourt, D.; Geoffroy, M.-C.; Turneer, M.; Mercenier, A. Mucosal Immune Responses and Protection Against Tetanus Toxin after Intranasal Immunization with Recombinant Lactobacillus plantarum. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J. Mucosal Vaccination and Therapy with Genetically Modified Lactic Acid Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 423–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primers | Sequence a (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| E120R-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGGCTGATTTTAATTCACCAATTC |
| E120R-R | CGGGATCCGCCGCCTTTAGATTTATGAGATG |
| E183L-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGGATTCAGAATTTTTCCAACCA |
| E183L-R | CGGGATCCGCCGCCAAGAGAATTTTCTAAATC |
| D117L-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGGATACAGAAACTTCACCTCTTCTT |
| D117L-R | CGGGATCCGCCGCCTGAATGTGCAAGTTCAG |
| H171R-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGGTTGTTTATGATCTTCTTGTTTCA |
| H171R-R | CGGGATCCGCCGCCATTTTTAATAGAAAACA |
| K78R-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGCCTACAAAAGCTGGCACAAAAAGTACCGC |
| K78R-R | CGGGATCCTTTTGACCGTTTAATTTTTTT |
| A104R-F | ACCGCTCGAGATGTCGACAAAAAAAAAGCCCACAATTACCAAGCAAGA |
| A104R-R | CGGGATCCGTTTAACATATCATGGACAGGT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, A.; Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Li, L.-F.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Gao, T.; et al. Immunogenic Responses Elicited by a Pool of Recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 Strains Surface-Displaying Diverse African Swine Fever Antigens Administered via Different Immunization Routes in a Mouse Model. Vaccines 2025, 13, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090897
Moon A, Wu H, Wang T, Li L-F, Li Y, Xu Z, Li J, Wang Y, Huang J, Gao T, et al. Immunogenic Responses Elicited by a Pool of Recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 Strains Surface-Displaying Diverse African Swine Fever Antigens Administered via Different Immunization Routes in a Mouse Model. Vaccines. 2025; 13(9):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090897
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Assad, Hongxia Wu, Tao Wang, Lian-Feng Li, Yongfeng Li, Zhiqiang Xu, Jia Li, Yanjin Wang, Jingshan Huang, Tianqi Gao, and et al. 2025. "Immunogenic Responses Elicited by a Pool of Recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 Strains Surface-Displaying Diverse African Swine Fever Antigens Administered via Different Immunization Routes in a Mouse Model" Vaccines 13, no. 9: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090897
APA StyleMoon, A., Wu, H., Wang, T., Li, L.-F., Li, Y., Xu, Z., Li, J., Wang, Y., Huang, J., Gao, T., Sun, Y., & Qiu, H.-J. (2025). Immunogenic Responses Elicited by a Pool of Recombinant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NC8 Strains Surface-Displaying Diverse African Swine Fever Antigens Administered via Different Immunization Routes in a Mouse Model. Vaccines, 13(9), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13090897







