How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods of in Ovo Vaccination
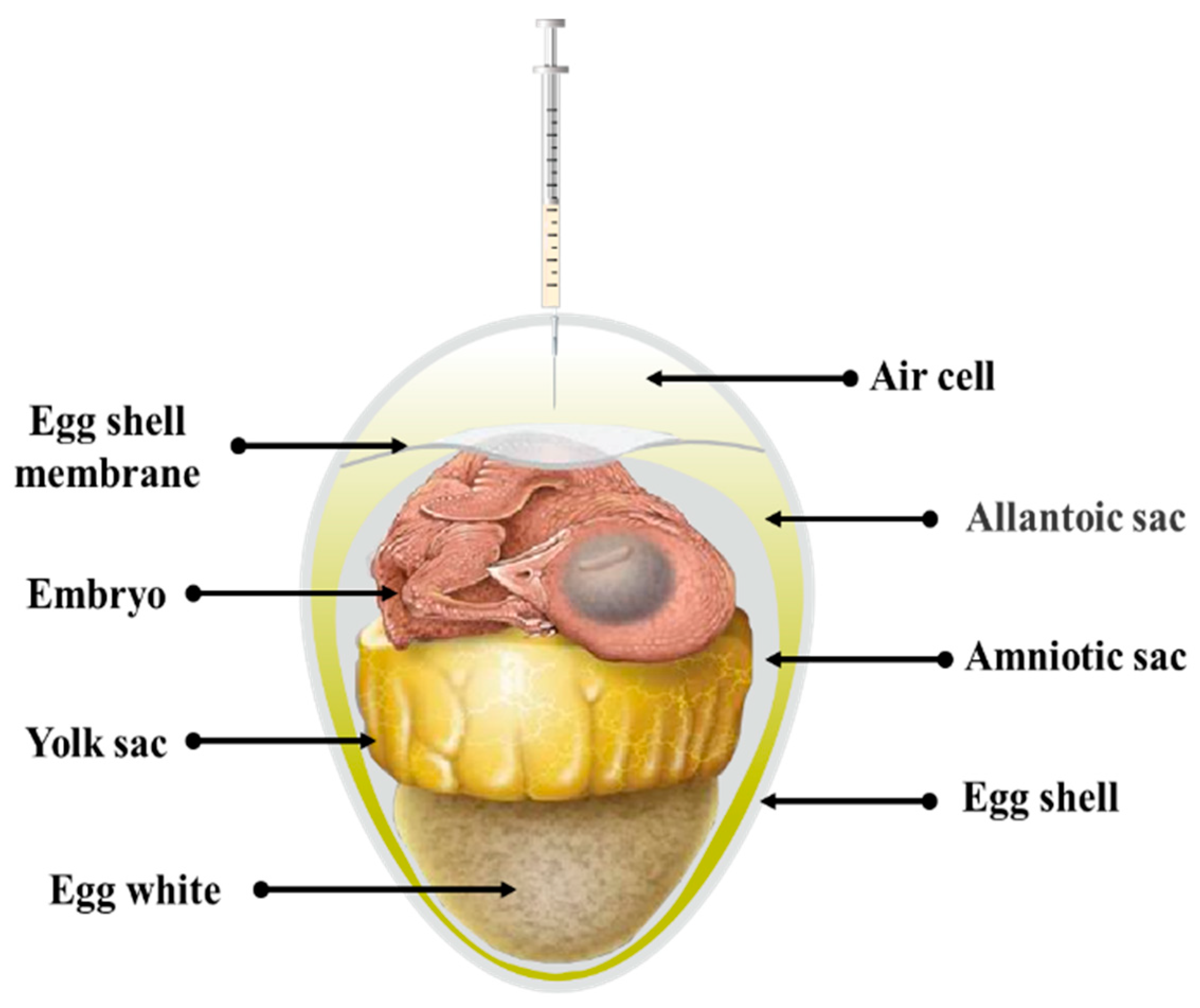
2.1. Physiological Basis for in Ovo Vaccination
2.2. Principles and Methods of in Ovo Vaccination
3. Development and Applications of in Ovo Vaccination Technology
3.1. Applications of in Ovo Vaccination Technology
3.2. Research Progress of in Ovo Vaccination Technology
4. Bottlenecks in the Development of in Ovo Vaccination
5. How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination
5.1. Understanding the Initiation Mechanism of Chicken Embryo Adaptive Immune Response
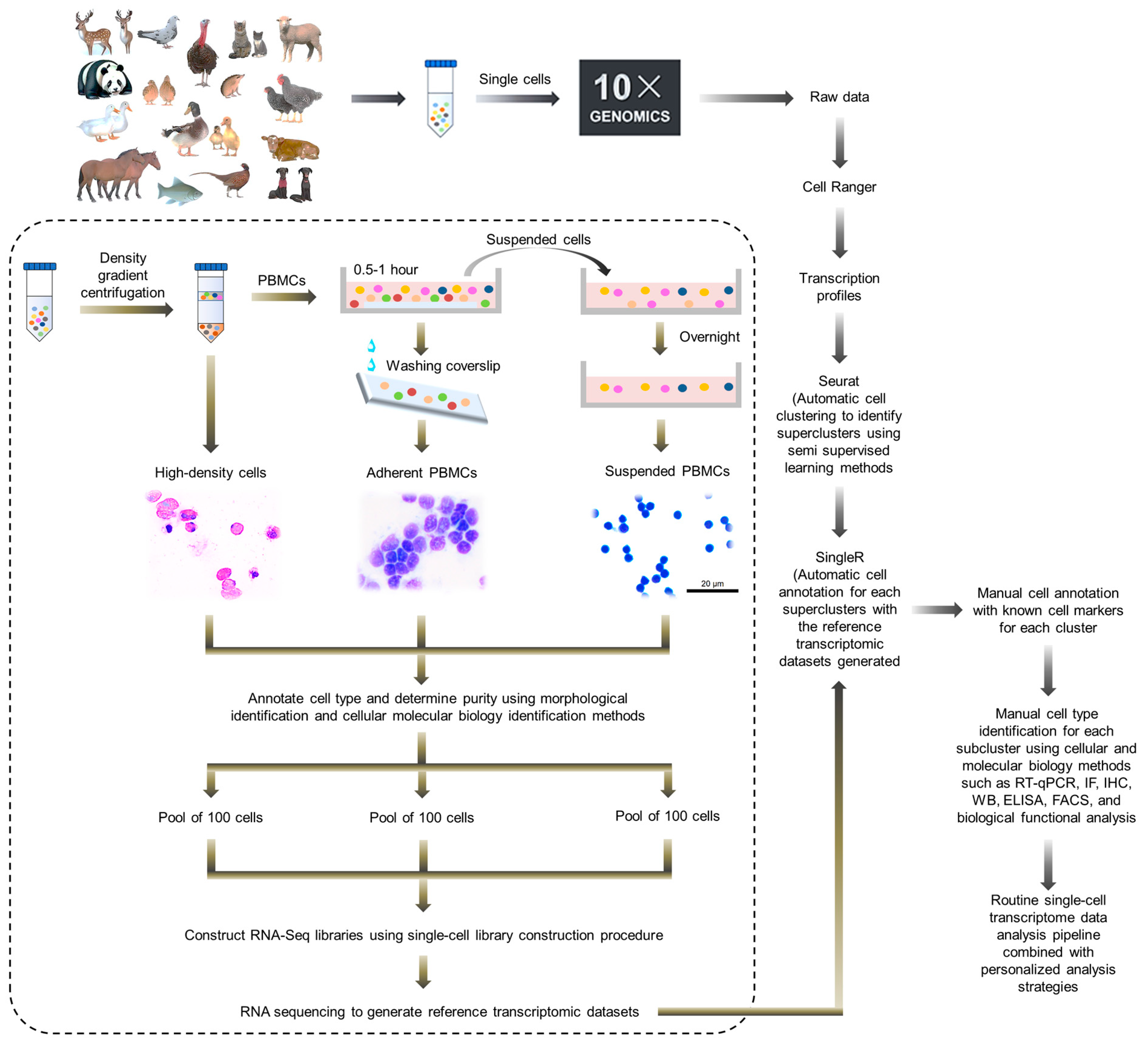
5.2. Utilizing New Detection Technologies and Developing Suitable Analysis Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J. Research on China’s Poultry Trade under the Background of “The Belt and Road”-Based on the Perspective of Trade Facilitation; Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zang, L.; Su, Y. Prospects for China’s agricultural modernization in 2035. Res. Agric. Mod. 2020, 41, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z. China’s poultry eggs outlook for 2014–2023. Agric. Outlook 2014, 10, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Jagdev, M.S.; Cathering, A.R.; Zhou, X. Prospects of chicken embryo inoculation technology. China Poult. 2003, 25, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Peebles, E.D. In ovo applications in poultry: A review. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2322–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J. Comparative revelation of the development process of the egg chicken industry in China and the United States. Guide Chin. Poult. 2015, 32, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Janković, B.D.; Isaković, K.; Lukić, M.L.; Vujanović, N.L.; Petrović, S.; Marković, B.M. Immunological capacity of the chicken embryo. I. Relationship between the maturation of lymphoid tissues and the occurrence of cell-mediated immunity in the developing chicken embryo. Immunology 1975, 29, 497–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Komi, D.E.A. The morphological basis of the development of the chick embryo immune system. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 381, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, L.; Luo, Q.; Ren, Z.; Wang, H.; Tang, G.; Luo, L.; Zhang, T.; Shang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Research progress and prospect of in-ovo vaccine for chickens. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2018, 57, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.M.; Burmester, B.R. Resistance to Marek’s disease at hatching in chickens vaccinated as embryos with the turkey herpesvirus. Avian Dis. 1982, 26, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricks, C.A.; Ava kian, A.; Bryan, T.; Gildersleeve, R.; Haddad, E.; Ilich, R.; King, S.; Murray, L.; Phelps, P.; Poston, R.; et al. In ovo vaccination technology. Adv. Vet. Med. 1999, 41, 495–515. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, J.M. Effect of infectious bursal disease virus on protection against Marek’s disease by turkey herpesvirus vaccine. Avian Dis. 1984, 28, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embrex Inovoject and Embrex Inovoject m Comparison Table. Available online: https://www.thepoultrysite.com/focus/zoetis/zoetis-global-poultry-embrex-inovoject-m-invovoject-inovoject-m (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Launch Ultimate In-Ovo Egg Injection System. Available online: https://www.innovatec.com/news-events/innovatec-launches-ultimate-in-ovo-egg-injection (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Egginject® in Ovo System: Designed for Safety. Available online: https://poultry.ceva.com/data-and-equipment/hatchery-vaccination/egginject/ (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Chicken Meat Production Worldwide in 2022 and 2023, by Country. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/237597/leading-10-countries-worldwide-in-poultry-meat-production-in-2007/ (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- In Ovo Vaccination. Introducing a New Approach to in Ovo Vaccination for Modern Hatcheries. Available online: http://www.positiveaction.info/digital/Supplements/In_Ovo_Vaccination/pdf/In-Ovo_Supplement.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Avisite. Pintos de Corte Sofreram Expressivo Refluxo em Novembro/14. Available online: http://www.avisite.com.br/economia/index.php?acao=producaopintos (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Romanutti, C.; Keller, L.; Zanetti, F.A. Current status of virus-vectored vaccines against pathogens that affect poultry. Vaccine 2020, 38, 6990–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wang, X.; Tian, M.; Wen, Z.; Feng, Q.; Qi, X.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Bu, Z. Novel in-ovo chimeric recombinant Newcastle disease vaccine protects against both Newcastle disease and infectious bursal disease. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, T.; Luo, Z.; Yang, M.; Lin, L.; Jiang, X. Effect of in ovo vaccination with live HVT-IBDV carrier vaccine on the immunological efficacy and performance of broilers in large-scale white-feathered broiler farms. China Poult. 2019, 41, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, R.; Koopman, R.; Garcia, M.; Armour, N.; Dunn, J.R.; Barbosa, T.; Martinez, A. Review of poultry recombinant vector vaccines. Avian Dis. 2021, 65, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehoj, H.S.; Jang, S.I.; Panebra, A.; Lillehoj, E.P.; Dupuis, L.; Ben Arous, J.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, S.T. In ovo vaccination using Eimeria profilin and Clostridium perfringens NetB proteins in Montanide IMS adjuvant increases protective immunity against experimentally-induced necrotic enteritis. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, A.; Duan, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Jin, L. Immunological effect of Lactic acid bacteria adjuvant on in ovo injection of Newcastle disease vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 280, 109710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaghan, C.; Browning, M.; Fares, A.M.; Abdul-Careem, M.F.; Gimeno, I.M.; Kulkarni, R.R. In Ovo Vaccination with Recombinant Herpes Virus of the Turkey-Laryngotracheitis Vaccine Adjuvanted with CpG-Oligonucleotide Provides Protection against a Viral Challenge in Broiler Chickens. Viruses 2023, 15, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauw, F.; Gardin, Y.; Palya, V.; Anbari, S.; Lemaire, S.; Boschmans, M.; van den Berg, T.; Lambrecht, B. Improved vaccination against Newcastle disease by an in ovo recombinant HVT-ND combined with an adjuvanted live vaccine at day-old. Vaccine 2010, 28, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Sharma, J.M. Protection against hemorrhagic enteritis and Newcastle disease in turkeys by embryo vaccination with monovalent and bivalent vaccines. Avian Dis. 1993, 37, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebatsion, T.; Verstegen, S.; De Vaan, L.T.; Römer-Oberdörfer, A.; Schrier, C.C. A recombinant newcastle disease virus with low-level V protein expression is immunogenic and lacks pathogenicity for chicken embryos. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokale, A.O.; Williams, C.J.; Cummings, T.S.; Gerard, P.D.; Bello, A.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of in ovo injection of different doses of coccidiosis vaccine and turn-out times on broiler performance. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokale, A.O.; Williams, C.J.; Hoerr, F.J.; Collins, K.E.C.; Peebles, E.D. Effects of administration of an in ovo coccidiosis vaccine at different embryonic ages on vaccine cycling and performance of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, H.; Mitchell, B.; Brugh, M. In ovo vaccination of chicken embryos with experimental Newcastle disease and avian influenza oil-emulsion vaccines. Avian Dis. 1997, 41, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, P.; Wang, Y.; Viallet, J.; Macek Jilkova, Z. The chicken embryo model: A novel and relevant model for immune-based studies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 791081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundeková, B.; Máčajová, M.; Meta, M.; Čavarga, I.; Bilčík, B. Chorioallantoic membrane models of various avian species: Differences and applications. Biology 2021, 10, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.H.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, G.; Gu, M.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, B.C.; Park, T.S.; Han, S.H.; Yun, C.H. Changes in bursal B cells in chicken during embryonic development and early life after hatching. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janse, E.M.; Jeurissen, S.H. Ontogeny and function of two non-lymphoid cell populations in the chicken embryo. Immunobiology 1991, 182, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masteller, E.L.; Thompson, C.B. B cell development in the chicken. Poult. Sci. 1994, 73, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernd, K.; Karel, A.S.; Thomas, W.G. (Eds.) Avian Immunology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vainio, O.; Imhof, B.A. The immunology and developmental biology of the chicken. Immunol. Today 1995, 16, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunon, D.; Allioli, N.; Vainio, O.; Ody, C.; Imhof, B.A. Quantification of T-cell progenitors during ontogeny: Thymus colonization depends on blood delivery of progenitors. Blood 1999, 93, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenthal, J.W.; Connick, T.E.; McWaters, P.G.; York, J.J. Development of T cell immune responsiveness in the chicken. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1994, 72, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollum, F.J. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase as a hematopoietic cell marker. Blood 1979, 54, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penit, C.; Jotereau, F.; Gelabert, M.J. Relationships between terminal transferase expression, stem cell colonization, and thymic maturation in the avian embryo: Studies in thymic chimeras resulting from homospecific and heterospecific grafts. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltey, M.; Jotereau, F.V.; Le Douarin, N.M. Evidence for a cyclic renewal of lymphocyte precursor cells in the embryonic chick thymus. Cell Differ. 1987, 22, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coltey, M.; Bucy, R.P.; Chen, C.H.; Cihak, J.; Lösch, U.; Char, D.; Le Douarin, N.M.; Cooper, M.D. Analysis of the first two waves of thymus homing stem cells and their T cell progeny in chick-quail chimeras. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, K.M.; Pietryk, H.C.; Ciminera, J.L. Acquired immunological tolerance to a protein antigen in chickens. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1958, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sharma, J.M. Immunological tolerance in chickens hatching from eggs injected with cell-associated herpesvirus of Turkey (HVT). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2003, 27, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, I.; Glick, B.; Törö, I. Bursal development in normal and testosterone-treated chick embryos. Poult. Sci. 1986, 65, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, M.J. Antibodies, immunoglobulin genes and the bursa of Fabricius in chicken B cell development. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, N.; Busalt, F.; Halasy, V.; Kohn, M.; Schmieder, S.; Fejszak, N.; Kaspers, B.; Härtle, S. In and out of the bursa-the role of CXCR4 in chicken B cell development. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, C.A.; Bertocci, B.; Dahan, A.; Weill, J.C. Formation of the chicken B-cell repertoire: Ontogenesis, regulation of Ig gene rearrangement, and diversification by gene conversion. Adv. Immunol. 1994, 57, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.M.; Coulson, B.D.; Young, E. Effect of in vitro adaptation of Marek’s disease virus on pock induction on the chorioallantoic membrane of embryonated chicken eggs. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.M.; Lee, L.F.; Wakenell, P.S. Comparative viral, immunologic, and pathologic responses of chickens inoculated with herpesvirus of turkeys as embryos or at hatch. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1984, 45, 1619–1623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Islam, Z.; Khalil, M.; Islam, R. Effects of age in the structure of the bursa of Fabricius of deshi chicken of Bangladesh. Mymensingh. Med. J. 2002, 11, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khalil, M.; Khan, Z.I.; Khalil, M.; Islam, R. A prospective study of prenatal and postnatal development of thymus of Deshi chicken. Mymensingh. Med. J. 2003, 12, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.A.; Browning, G.F.; Washington, E.A.; Crabb, B.S.; Kaiser, P. Embryonic age influences the capacity for cytokine induction in chicken thymocytes. Immunology 2003, 110, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crivellato, E.; Nico, B.; Battistig, M.; Beltrami, C.A.; Ribatti, D. The thymus is a site of mast cell development in chicken embryos. Anat. Embryol. 2005, 209, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, J.; Fröhlich, T.; Kohn, M.; Kaspers, B.; Arnold, G.J.; Härtle, S. 2D DIGE analysis of the bursa of Fabricius reveals characteristic proteome profiles for different stages of chicken B-cell development. Proteomics 2013, 13, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuthalapati, N.K.; Evans, J.D.; Taylor, R.L.; Branton, S.L.; Nanduri, B.; Pharr, G.T. Transcriptomic analysis of early B-cell development in the chicken embryo. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5342–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, I.M.; Faiz, N.M.; Cortes, A.L.; Barbosa, T.; Villalobos, T.; Pandiri, A.R. In ovo vaccination with Turkey herpesvirus hastens maturation of chicken embryo immune responses in specific-pathogen-free chickens. Avian Dis. 2015, 59, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, C.; Li, P.; Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, Q.; Ma, F.; Shi, W.; Shi, M.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the transcriptomic characteristics of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in hepatitis B vaccine non-responders. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1091237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Xu, C.; Chen, W.; Liao, M. Progress on chicken T cell immunity to viruses. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Shang, S. The evaluation of cellular immunity to avian viral diseases: Methods, applications, and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 794514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Cui, L.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Li, H. Single-cell analysis of the in vivo dynamics of host circulating immune cells highlights the importance of myeloid cells in avian flaviviral infection. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 2878–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Sun, H.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Q.; You, B.; Xu, F.; Liao, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y.; et al. Duck CD8+ T cell response to H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza virus infection in vivo and in vitro. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Zhu, S.; An, Z.; You, B.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V.; Liao, M. Dissection of key factors correlating with H5N1 avian influenza virus driven inflammatory lung injury of chicken identified by single-cell analysis. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Li, S.H.; Yu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Qu, L.; Sun, Y.; Bi, Y.; Tang, F.; et al. Transcriptome profiling in swine macrophages infected with African swine fever virus at single-cell resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201288119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, M.; Peng, Q.; Li, J.; Chang, X.; Shi, D.; Yin, J.; et al. Identification of cell types and transcriptome landscapes of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus-infected porcine small intestine using single-cell RNA sequencing. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Liu, X.; Cui, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming. Vaccines 2024, 12, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010048
Li X, Liu X, Cui L, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Li H. How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming. Vaccines. 2024; 12(1):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xuefeng, Xiaoxiao Liu, Lu Cui, Zheyi Liu, Yu Zhang, and Hai Li. 2024. "How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming" Vaccines 12, no. 1: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010048
APA StyleLi, X., Liu, X., Cui, L., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., & Li, H. (2024). How to Break through the Bottlenecks of in Ovo Vaccination in Poultry Farming. Vaccines, 12(1), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010048




