Inspiring Anti-Tick Vaccine Research, Development and Deployment in Tropical Africa for the Control of Cattle Ticks: Review and Insights
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Origin of Anti-Tick Vaccines and Immunological Control of Tick Infestations
3. The Bm86/95-Based Anti-Tick Vaccines
4. Exploring Tick Biology for Antigen Identification and Vaccine Development
- (a)
- Tick Attachment and Feeding to Repletion
- (b)
- Immunomodulation and regulation of enzyme activity
- (c)
- Osmoregulation (water balance)
- (d)
- Blood digestion (Hemoglobinolysis)
- (e)
- Heme and iron transport and storage
- (f)
- Detoxification (elimination of toxic substances)
- (g)
- Embryogenesis (yolk accumulation and degradation)
- (h)
- Enzymatic disruption and remodeling of host tissues
- (i)
- Tick engorgement and development of reproductive structures
5. Insights into the Future
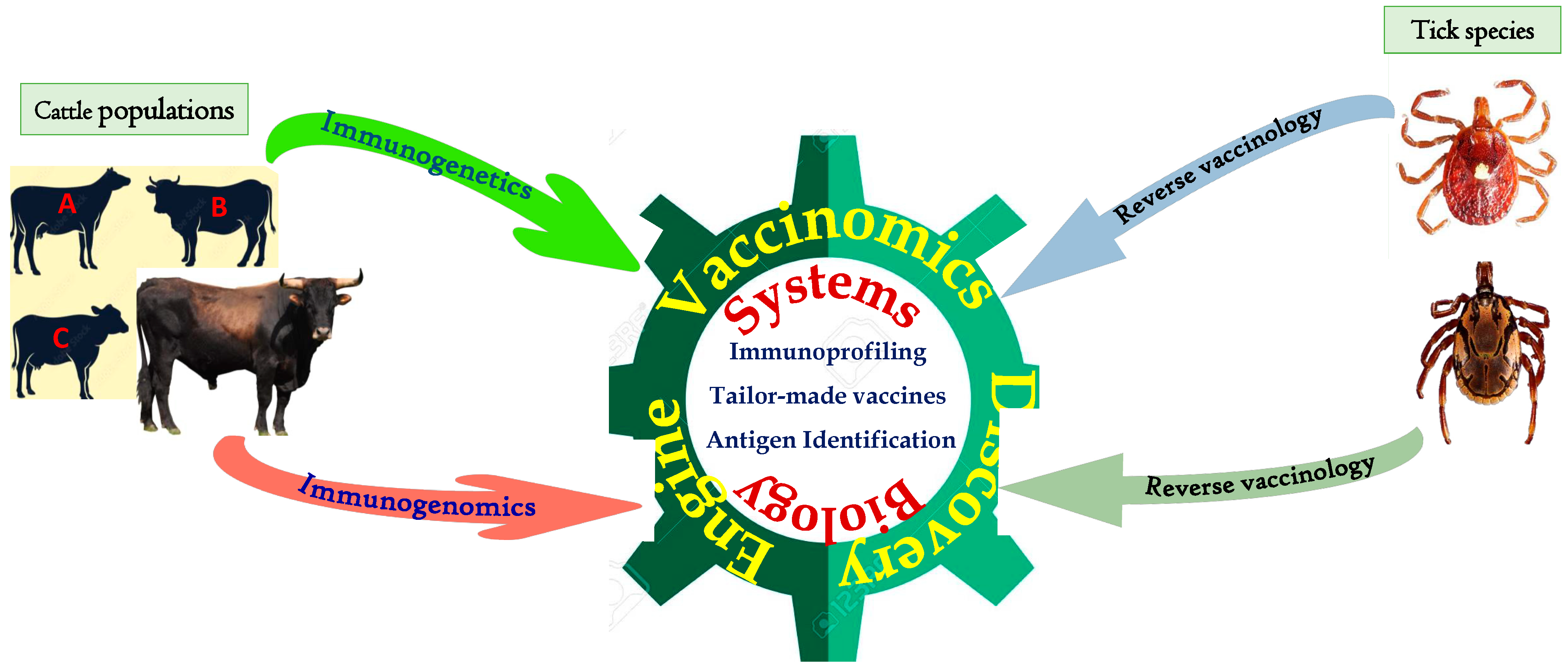
5.1. Reverse Vaccinology
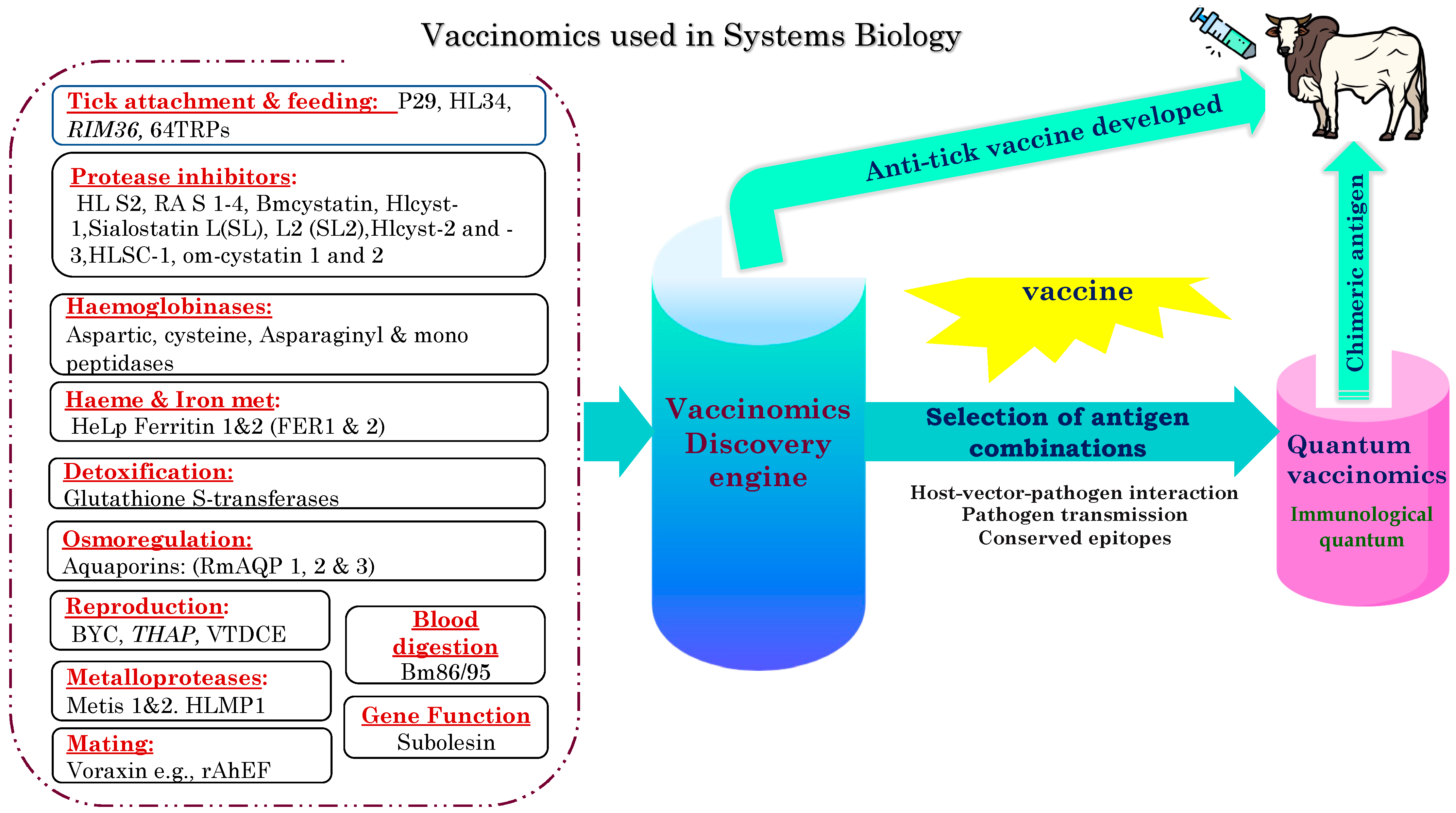
5.2. Vaccinomics and Systems Biology
5.3. Quantum Vaccinomics
6. Anti-Tick Vaccines in Africa
7. Opinion on the Possible Impact of Incorporating Anti-Tick Vaccines into the Integrated Approach for Tick Control: Case of Uganda
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de la Fuente, J.; Contreras, M. Tick vaccines: Current status and future directions. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, O.J.B.; Giraldo-Ríos, C. Economic and health impact of the ticks in production animals. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; Abubakar, M., Perera, P.K., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaka, N.W.; Kanduma, E.G.; Wieland, B.; Darghouth, M.A.; Bishop, R.P. Acaricide resistance in livestock ticks infesting cattle in Africa: Current status and potential mitigation strategies. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector-Borne Dis. 2022, 2, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerario, I.I.; Simuunza, M.; Laisser, E.L.K.; Chenyambuga, S. Exploring knowledge and management practices on ticks and tick-borne diseases among agro-pastoral communities in Southern Highlands, Tanzania. Vet. World 2018, 11, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongejan, F.; Uilenberg, G. The global importance of ticks. Parasitology 2004, 129, S3–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J. Vaccines for vector control: Exciting possibilities for the future. Vet. J. 2012, 194, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kasaija, P.D.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Contreras, M.; Kirunda, H.; de la Fuente, J. Cattle ticks and tick-borne diseases: A review of Uganda’s situation. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.S.; Groocock, C.M.; Kariuki, D.P. Integrated control of ticks and tick-borne diseases of cattle in Africa. Parasitology 1988, 96, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi, L.F.; Pohl, P.C.; Masuda, A.; Junior, I.D.S.V. New approaches toward anti-Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus tick vaccine. Rev. Bras. De Parasitol. Veterinária 2009, 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Azhahianambi, P.; Yadav, M.P. Upcoming and future strategies of tick control: A review. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2007, 44, 79–89. [Google Scholar]
- Klafke, G.M.; Sabatini, G.A.; de Albuquerque, T.A.; Martins, J.R.; Kemp, D.H.; Miller, R.J.; Schumaker, T.T.S. Larval immersion tests with ivermectin in populations of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) from State of Sao Paulo, Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 142, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Montero, C.; Redondo, M.; García-García, J.C.; Méndez, L.; Serrano, E.; Valdés, M.; Enríquez, A.; Canales, M.; et al. Vaccination against ticks (Boophilus spp.): The experience with the Bm86-based vaccine Gavac((TM)). Genet. Anal. Biomol. Eng. 1999, 15, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willadsen, P.; Smith, D.; Cobon, G.; McKenna, R.V. Comparative vaccination of cattle against Boophilus microplus with recombinant antigen Bm86 alone or in combination with recombinant Bm91. Parasite Immunol. 1996, 18, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparin, G.; Miyata, M.; Coutinho, L.L.; Martinez, M.L.; Teodoro, R.L.; Furlong, J.; Machado, M.A.; Silva, M.V.G.B.; Sonstegard, T.S.; Regitano, L.C.A. Mapping of quantitative trait loci controlling tick [Riphicephalus (Boophilus) microplus] resistance on bovine chromosomes 5, 7 and 14. Anim. Genet. 2007, 38, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapholi, N.O.; Marufu, M.C.; Maiwashe, A.; Banga, C.B.; Muchenje, V.; MacNeil, M.D.; Chimonyo, M.; Dzama, K. Towards a genomics approach to tick (Acari: Ixodidae) control in cattle: A review. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhanga, C.; Collins, N.E.; Knobel, D.; Kabasa, W.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Veterinary Parasitology: Regional Studies and Reports Endemic status of tick-borne infections and tick species diversity among transhumant zebu cattle in Karamoja Region, Uganda: Support for control approaches. Veter. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2015, 1–2, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vudriko, P.; Okwee-Acai, J.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Byaruhanga, J.; Kakooza, S.; Wampande, E.; Omara, R.; Muhindo, J.B.; Tweyongyere, R.; Owiny, D.O.; et al. Emergence of multi-acaricide resistant Rhipicephalus ticks and its implication on chemical tick control in Uganda. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenyambuga, S.W.; Waiswa, C.; Saimo, M.; Ngumi, P.; Gwakisa, P.S. Knowledge and perceptions of traditional livestock keepers on tick-borne diseases and sero-prevalence of Theileria parva around Lake Victoria Basin. Livest. Res. Rural Dev. 2010, 22, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Mugisha, A.; McLeod, A.; Percy, R.; Kyewalabye, E. Socio-economic factors influencing control of vector-borne diseases in the pastoralist system of south western Uganda. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayebwa, D.S.; Vudriko, P.; Tuvshintulga, B.; Guswanto, A.; Nugraha, A.B.; Gantuya, S.; Batiha, G.E.S.; Musinguzi, S.P.; Komugisha, M.; Bbira, J.S.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Babesia species, Theileria parva, and Anaplasma marginale infecting cattle and the tick control malpractices in Central and Eastern Uganda. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vudriko, P.; Okwee-Acai, J.; Byaruhanga, J.; Tayebwa, D.S.; Okech, S.G.; Tweyongyere, R.; Wampande, E.M.; Okurut, A.R.A.; Mugabi, K.; Muhindo, J.B.; et al. Chemical tick control practices in southwestern and northwestern Uganda. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.Z.; Zaman, M.A.; Colwell, D.D.; Gilleard, J.; Iqbal, Z. Acaricide resistance in cattle ticks and approaches to its management: The state of play. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Fernando Parizi, L.; Garcia Guizzo, M.; Tirloni, L.; Seixas, A.; Silva Vaz, I.; Termignoni, C. Immunoprotective potential of a Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus metalloprotease. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 207, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdusek, O.; Almazán, C.; Loosova, G.; Villar, M.; Canales, M.; Grubhoffer, L.; Kopacek, P.; de la Fuente, J. Characterization of ferritin 2 for the control of tick infestations. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Kocan, K.M.; Almazán, C.; Blouin, E.F. RNA interference for the study and genetic manipulation of ticks. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, O.; Almazán, C.; Canales, M.; Villar, M.; Moreno-Cid, J.A.; Galindo, R.C.; De la Fuente, J. Targeting the tick protective antigen subolesin reduces vector infestations and pathogen infection by Anaplasma marginale and Babesia bigemina. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8575–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, J.; Almazán, C.; Canales, M.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Kocan, K.M.; Willadsen, P. A ten-year review of commercial vaccine performance for control of tick infestations on cattle. Anim. Health Res. Rev. Conf. Res. Work. Anim. Dis. 2007, 8, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willadsen, P. Antigen cocktails: Valid hypothesis or unsubstantiated hope? Trends Parasitol. 2008, 24, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, J.; Estrada-Peña, A. Why New Vaccines for the Control of Ectoparasite Vectors Have Not Been Registered and Commercialized? Vaccines 2019, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi Luís, F.; Githaka, N.W.; Logullo, C.; Konnai, S.; Masuda, A.; Ohashi, K.; da Silva Vaz, I. The quest for a universal vaccine against ticks: Cross-immunity insights. Vet. J. 2012, 194, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.C.; De León, A.A.P.; Leite, F.P.L.; Pinto, L.D.S.; Júnior, A.G.D.S.; Andreotti, R. Bovine immunoprotection against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus with recombinant Bm86-Campo Grande antigen. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2012, 21, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odongo, D.; Kamau, L.; Skilton, R.; Mwaura, S.; Nitsch, C.; Musoke, A.; Taracha, E.; Daubenberger, C.; Bishop, R. Vaccination of cattle with TickGARD induces cross-reactive antibodies binding to conserved linear peptides of Bm86 homologues in Boophilus decoloratus. Vaccine 2007, 25, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Cid, J.A.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Villar, M.; Jiménez, M.; Pinal, R.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Molina, R.; Lucientes, J.; Gortázar, C.; de la Fuente, J. Control of multiple arthropod vector infestations with subolesin/akirin vaccines. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, C.; Moreno-Cantú, O.; Moreno-Cid, J.A.; Galindo, R.C.; Canales, M.; Villar, M.; de la Fuente, J. Control of tick infestations in cattle vaccinated with bacterial membranes containing surface-exposed tick protective antigens. Vaccine 2012, 30, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torina, A.; A Moreno-Cid, J.; Blanda, V.; de Mera, I.G.F.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Scimeca, S.; Blanda, M.; Scariano, M.E.; Briganò, S.; Disclafani, R.; et al. Control of tick infestations and pathogen prevalence in cattle and sheep farms vaccinated with the recombinant Subolesin-Major Surface Protein 1a chimeric antigen. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, O.; Alberdi, P.; De La Lastra, J.M.P.; De La Fuente, J. Tick vaccines and the control of tick-borne pathogens. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-García, J.C.; Montero, C.; Redondo, M.; Vargas, M.; Canales, M.; Boue, O.; Rodríguez, M.; Joglar, M.; Machado, H.; González, I.L.; et al. Control of ticks resistant to immunization with Bm86 in cattle vaccinated with the recombinant antigen Bm95 isolated from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Vaccine 2000, 18, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.R.; Humphreys, S.J. Immunization of Guinea pigs and cattle against ticks. Nature 1979, 280, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.A. Resistance of Cattle to the Tick Boophilus microplus (Canestrini). I. Development of Ticks on Bos taurus. J. Parasitol. 1968, 54, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.; Lambson, B.; Wells, C.; Pandit, P.; Osaso, J.; Nkonge, C.; Morzaria, S.; Musoke, A.; Nene, V. A cement protein of the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus, located in the secretory e cell granules of the type III salivary gland acini, induces strong antibody responses in cattle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubach, M.; Halliday, J.; Cleaveland, S.; Crump, J.A. Brucellosis in low-income and middle-income countries. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Rodríguez, M.; Redondo, M.; Montero, C.; García-García, J.C.; Méndez, L.; Serrano, E.; Valdés, M.; Enriquez, A.; Canales, M.; et al. Field studies and cost-effectiveness analysis of vaccination with Gavac(TM) against the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Vaccine 1998, 16, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canales, M.; Enríquez, A.; Ramos, E.; Cabrera, D.; Dandie, H.; Soto, A.; Falcón, V.; Rodríguez, M.; De la Fuente, J. Large-scale production in Pichia pastoris of the recombinant vaccine Gavac(TM) against cattle tick. Vaccine 1997, 15, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brake, D.K.; Pérez De León, A.A. Immunoregulation of bovine macrophages by factors in the salivary glands of Rhipicephalus microplus. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Contreras, M.; Kasaija, P.D.; Gortazar, C.; Ruiz-Fons, J.F.; Mateo, R.; Kabi, F. Towards a Multidisciplinary Approach to Improve Cattle Health and Production in Uganda. Vaccines 2019, 7, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvin, C.M.; Kemp, D.H. Generic approaches to obtaining efficacious antigens from vector arthropods. Int. J. Parasitol. 1994, 24, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlíková, S.; Roller, L.; Koči, J.; Trimnell, A.R.; Kazimírová, M.; Klempa, B.; Nuttall, P.A. Functional role of 64P, the candidate transmission-blocking vaccine antigen from the tick, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willadsen, P.; A Riding, G.; McKenna, R.V.; Kemp, D.H.; Tellam, R.L.; Nielsen, J.N.; Lahnstein, J.; Cobon, G.S.; Gough, J.M. Immunologic control of a parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Willadsen, P.; McKenna, R.V.; Riding, G.A. Isolation from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus, of antigenic material capable of eliciting a protective immunological response in the bovine host. Int. J. Parasitol. 1988, 18, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, M.R.; Mèndez, L.; Valdez, M.; Redondo, M.; Espinosa, C.M.; Vargas, M.; Cruz, R.L.; Barrios, H.P.; Seoane, G.; Ramirez, E.S.; et al. Integrated control of Boophilus microplus ticks in Cuba based on vaccination with the anti-tick vaccine GavacTM. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2004, 34, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Fuente, J.; Kocan, K.M. Advances in the identification and characterization of protective antigens for recombinant vaccines against tick infestations. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2003, 2, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vos, S.; Zeinstra, L.; Taoufik, O.; Willadsen, P.; Jongejan, F. Evidence for the utility of the Bm86 antigen from Boophilus microplus in vaccination against other tick species. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2001, 25, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canales, M.; Almazán, C.; Naranjo, V.; Jongejan, F.; de la Fuente, J. Vaccination with recombinant Boophilus annulatus Bm86 ortholog protein, Ba86, protects cattle against B. annulatus and B. microplus infestations. BMC Biotechnol. 2009, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Kopáček, P.; Lew-Tabor, A.; Maritz-Olivier, C. Strategies for new and improved vaccines against ticks and tick-borne diseases. Parasite Immunol. 2016, 38, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.F.; Magnarelli, L.A. Biology of Ticks. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 22, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotál, J.; Langhansová, H.; Lieskovská, J.; Andersen, J.F.; Francischetti, I.M.; Chavakis, T.; Kopecký, J.; Pedra, J.H.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Chmelař, J. Modulation of host immunity by tick saliva. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, J.G.; Belkaid, Y.; Garfield, M.K.; Mendez, S.; Kamhawi, S.; Rowton, E.D.; Sacks, D.L.; Ribeiro, J.M. Toward a defined anti-Leishmania vaccine targeting vector antigens: Characterization of a protective salivary protein. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, B.R.; Baithalu, R.K.; Allaie, I.M.; Mishra, C.; Samal, L. Mechanism of immunity to tick infestation in livestock. Vet. World 2011, 4, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikel, S.K. Tick-host-pathogen systems immunobiology an interactive trio. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimírová, M.; Štibrániová, I. Tick salivary compounds: Their role in modulation of host defences and pathogen transmission. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, M.E.; Thangamani, S. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines at the skin interface during powassan virus transmission. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2280–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermance, M.E.; Thangamani, S. Tick Saliva Enhances Powassan Virus Transmission to the Host, Influencing Its Dissemination and the Course of Disease. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 7852–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulenga, A.; Sugimoto, C.; Sako, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Musoke, A.; Shubash, M.; Onuma, M. Molecular characterization of a Haemaphysalis longicornis tick salivary gland-associated 29-kilodalton protein and its effect as a vaccine against tick infestation in rabbits. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, A.; Mulenga, A.; Sugimoto, C.; Nakajima, M.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. cDNA cloning, characterization and vaccine effect analysis of Haemaphysalis longicornis tick saliva proteins. Vaccine 2001, 19, 4287–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.Z.; Voigt, W.P.; Fujisaki, K. Tick antigens recognized by serum from a guinea pig resistant to infestation with the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus. J. Parasitol. 1986, 72, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimnell, A.R.; Davies, G.M.; Lissina, O.; Hails, R.S.; Nuttall, P.A. A cross-reactive tick cement antigen is a candidate broad-spectrum tick vaccine. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4329–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimnell, A.R.; Hails, R.S.; Nuttall, P.A. Dual action ectoparasite vaccine targeting “exposed” and “concealed” antigens. Vaccine 2002, 20, 3560–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga, O.O. Evidence and mechanisms of immunosuppression in tick infestations. Genet. Anal. Biomol. Eng. 1999, 15, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikel, S.K. Host immunity to ticks. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettins, P.G.W. Serpins: Structure, Function and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, H. Serine protease inhibitors (SERPINS): Where mechanism meets medicine. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 632–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, S.; da Silva Vaz Junior, I.; Sugino, M.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. A serine protease inhibitor (serpin) from Haemaphysalis longicornis as an anti-tick vaccine. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, R.; Gomes, A.; Malavazi-Piza, K.C.; Sasaki, S.D.; Sampaio, C.A.; Tanaka, A.S. BmTI antigens induce a bovine protective immune response against Boophilus microplus tick. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, M.; Imamura, S.; Mulenga, A.; Nakajima, M.; Tsuda, A.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. A serine proteinase inhibitor (serpin) from ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis; cloning and preliminary assessment of its suitability as a candidate for a tick vaccine. Vaccine 2003, 21, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulenga, A.; Tsuda, A.; Onuma, M.; Sugimoto, C. Four serine proteinase inhibitors (serpin) from the brown ear tick, Rhiphicephalus appendiculatus; cDNA cloning and preliminary characterization. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, S.; Namangala, B.; Tajima, T.; Tembo, M.E.; Yasuda, J.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Two serine protease inhibitors (serpins) that induce a bovine protective immune response against Rhipicephalus appendiculatus ticks. Vaccine 2006, 24, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.A.; Sasaki, S.D.; Tanaka, A.S. Bmcystatin, a cysteine proteinase inhibitor characterized from the tick Boophilus microplus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 347, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavašnik-Bergant, T.; Turk, B. Cysteine cathepsins in the immune response. Tissue Antigens 2006, 67, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Karim, S.; Andersen, J.F.; Mather, T.N.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Selective cysteine protease inhibition contributes to blood-feeding success of the tick Ixodes scapularis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29256–29263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Anderson, J.M.; Andersen, J.F.; Calvo, E.; Francischetti, I.M.B.; Mather, T.N.; Valenzuela, J.G.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Cutting Edge: Immunity against a “Silent” Salivary Antigen of the Lyme Vector Ixodes scapularis Impairs Its Ability to Feed. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5209–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, K.; Tsuji, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Islam, M.K.; Hatta, T.; Alim, M.A.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Kushibiki, S.; Fujisaki, K. A salivary cystatin, HlSC-1, from the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis play roles in the blood-feeding processes. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 106, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ueda, M.; Umemiya, R.; Battsetseg, B.; Boldbaatar, D.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. A secreted cystatin from the tick Haemaphysalis longicornis and its distinct expression patterns in relation to innate immunity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 36, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Valdés, J.J.; Kotsyfakis, M. The role of cystatins in tick physiology and blood feeding. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, K.; Tsuji, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Islam, M.K.; Hatta, T.; Alim, M.A.; Anisuzzaman Takenaka, A.; Fujisaki, K. Hemoglobinase activity of a cysteine protease from the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunclová, L.; Horn, M.; Vancová, M.; Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Mareš, M.; Kopáček, P. Two secreted cystatins of the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata: Differential expression pattern and inhibitory specificity. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salát, J.; Paesen, G.C.; Řezáčová, P.; Kotsyfakis, M.; Kovářová, Z.; Šanda, M.; Majtán, J.; Grunclová, L.; Horká, H.; Andersen, J.F.; et al. Crystal structure and functional characterization of an immunomodulatory salivary cystatin from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.S.; Sauer, J.R. Tick salivary glands: Function, physiology and future. Parasitology 2004, 129, S67–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megaw, M.W.J. Studies on the water balance mechanism of the tick, Boophilus microplus canestrini. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Part A: Physiol. 1974, 48, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, J.G. Exploring tick saliva: From biochemistry to “sialomes” and functional genomics. Parasitology 2004, 129, S83–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.M.; Ball, A.; Hoppler, S.; Bowman, A.S. Invertebrate aquaporins: A review. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2008, 178, 935–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, F.D.; Andreotti, R.; Bendele, K.G.; Cunha, R.C.; Miller, R.J.; Yeater, K.; León, A.A.P.D. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus aquaporin as an effective vaccine antigen to protect against cattle tick infestations. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, D.; Franta, Z.; Horn, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Mareš, M.; Kopáček, P. New insights into the machinery of blood digestion by ticks. Trends Parasitol. 2013, 29, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Frantova, H.; Dvorak, J.; Horn, M.; Srba, J.; Talacko, P.; Mares, M.; Schneider, E.; Craik, C.S.; et al. IrCL1—The haemoglobinolytic cathepsin L of the hard tick, Ixodes ricinus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2011, 41, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, N.; Miyoshi, T.; Battsetseg, B.; Matsuo, T.; Xuan, X.; Fujisaki, K. A Cysteine Protease Is Critical for Babesia spp. Transmission in Haemaphysalis Ticks. PLOS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Edwards, M.J.; Grubhoffer, L. Differential expression of Ixodes ricinus tick genes induced by blood feeding or Borrelia burgdorferi infection. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Horn, M.; Nussbaumerová, M.; Šanda, M.; Kovářová, Z.; Srba, J.; Franta, Z.; Sojka, D.; Bogyo, M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Kopáček, P.; et al. Hemoglobin Digestion in Blood-Feeding Ticks: Mapping a Multipeptidase Pathway by Functional Proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, F.A.; Lins, U.; Bechara, G.H.; Oliveira, P.L. Tracing heme in a living cell: Hemoglobin degradation and heme traffic in digest cells of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akov, S. Blood Digestion in Ticks. In Physiology of Ticks; Elsevier Press Ltd.: Pergamon, Turkey, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, G.; Lara, F.A.; de Cardoso, F.C.; Miguens, F.C.; Dansa-Petretski, M.; Termignoni, C.; Masuda, A. Expression and immunolocalization of a Boophilus microplus cathepsin L-like enzyme. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, F.A.; Lins, U.; Paiva-Silva, G.; Almeida, I.C.; Braga, C.M.; Miguens, F.C.; Oliveira, P.L.; Dansa-Petretski, M. A new intracellular pathway of haem detoxification in the midgut of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus: Aggregation inside a specialized organelle, the hemosome. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, T.H.; Frezzatti, W.A., Jr.; Schreier, S. Hemin-Induced Lipid Membrane Disorder and Increased Permeability: A Molecular Model for the Mechanism of Cell Lysis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1993, 307, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz, G.R.C.; Coelho, H.S.L.; Masuda, H.; Oliveira, P.L. A missing metabolic pathway in the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Daffre, S.; Logullo, C.; Lara, F.A.; Alves, E.W.; Capurro, M.L.; Zingali, R.; Almeida, I.C.; Oliveira, P.L. HeLp, a heme lipoprotein from the hemolymph of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36584–36589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Coons, L.B. Purification and partial characterization of vitellin from the eggs of the hard tick, Dermacentor variabilis. Insect Biochem. 1991, 21, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Alves, L.R.; Pinhal, N.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Oliveira, P.L. HeLp, a heme-transporting lipoprotein with an antioxidant role. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopáček, P.; Hajdušek, O.; Burešová, V.; Daffre, S. Chapter 8 R Tick Innate Immunity; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 137–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Lv, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhou, L.; Wang, S.; Luo, J.; Liu, J.; Shang, P. Iron and leukemia: New insights for future treatments. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galay, R.L.; Aung, K.M.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, T.; Kawaguchi, H.; Miyoshi, N.; Suzuki, H.; Xuan, X.; Mochizuki, M.; et al. Multiple ferritins are vital to successful blood feeding and reproduction of the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galay, R.L.; Umemiya-Shirafuji, R.; Bacolod, E.T.; Maeda, H.; Kusakisako, K.; Koyama, J.; Tsuji, N.; Mochizuki, M.; Fujisaki, K.; Tanaka, T. Two kinds of ferritin protect ixodid ticks from iron overload and consequent oxidative stress. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parizi Luís Fernando Utiumi, K.U.; Imamura, S.; Onuma, M.; Ohashi, K.; Masuda, A.; da Silva Vaz, I. Cross immunity with Haemaphysalis longicornis glutathione S-transferase reduces an experimental Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus infestation. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, D. Structure, function and evolution of glutathione transferases: Implications for classification of non-mammalian members of an ancient enzyme superfamily. Biochem. J. 2001, 360, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vontas, J.G.; Enayati, A.A.; Small, G.J.; Hemingway, J. A simple biochemical assay for glutathione S-transferase activity and its possible field application for screening glutathione S-transferase-based insecticide resistance. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 68, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalek, J.C.; Rew, R.S.; Heavner, J. Glutathione-S-transferase, a possible drug-metabolizing enzyme, in Haemonchus contortus: Comparative activity of a cambendazole-resistant and a susceptible strain. Int. J. Parasitol. 1984, 14, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Liu, S.; Perally, S.; Xue, J.; Fujiwara, R.; Brophy, P.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Williamson, A.; et al. Biochemical characterization and vaccine potential of a heme-binding glutathione transferase from the adult hookworm Ancylostoma caninum. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 6903–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Vaz, I.; Torino Lermen, T.; Michelon, A.; Sanchez Ferreira, C.A.; Joaquim De Freitas, D.R.; Termignoni, C.; Masuda, A. Effect of acaricides on the activity of a Boophilus microplus glutathione S-transferase. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 119, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Vaz, I.; Martinez, R.H.M.; Oliveira, A.; Heck, A.; Logullo, C.; Gonzales, J.C.; Dewes, H.; Masuda, A. Functional bovine immunoglobulins in Boophilus microplus hemolymph. Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 62, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raikhel, A.S.; Dhadialla, T.S. Accumulation of yolk proteins in insect oocytes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1992, 37, 217–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, A.; Estrela, A.B.; Ceolato, J.C.; Pontes, E.G.; Lara, F.; Gondim, K.C.; Termignoni, C. Localization and function of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus vitellin-degrading cysteine endopeptidase. Parasitology 2010, 137, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorgine, M.H.F.; Logullo, C.; Zingali, R.B.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Juliano, L.; Oliveira, P.L. A heme-binding aspartic proteinase from the eggs of the hard tick Boophilus microplus. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28659–28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logullo, C.; Da Silva Vaz, I.; Sorgine, M.H.F.; Paiva-Silva, G.O.; Faria, F.S.; Zingali, R.B.; De Lima, M.F.R.; Abreu, L.; Fialho Oliveira, E.; Alves, E.W.; et al. Isolation of an aspartic proteinase precursor from the egg of a hard tick, Boophilus microplus. Parasitology 1998, 116, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento-Silva, M.C.L.; Leal, A.T.; Daffre, S.; Juliano, L.; da Silva Vaz, I.; Paiva-Silva G de, O.; Oliveira, P.L.; Sorgine, M.H.F. BYC, an atypical aspartic endopeptidase from Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus eggs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 149, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo Estrela, A.; Seixas, A.; de Oliveira Nunes Teixeira, V.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Termignoni, C. Vitellin- and hemoglobin-digesting enzymes in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus larvae and females. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 157, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Vaz, I.; Logullo, C.; Sorgine, M.; Velloso, F.F.; Rosa De Lima, M.F.; Gonzales, J.C.; Masuda, H.; Oliveira, P.L.; Masuda, A. Immunization of bovines with an aspartic proteinase precursor isolated from Boophilus microplus eggs. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 66, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logullo, C.; Moraes, J.; Dansa-Petretski, M.; Vaz, I.S.; Masuda, A.; Sorgine, M.H.F.; Braz, G.R.; Masuda, H.; Oliveira, P.L. Binding and storage of heme by vitellin from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 32, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas, A.; Leal, A.T.; Nascimento-Silva, M.C.L.; Masuda, A.; Termignoni, C.; da Silva Vaz, I. Vaccine potential of a tick vitellin-degrading enzyme (VTDCE). Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2008, 124, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seixas, A.; Oliveira, P.; Termignoni, C.; Logullo, C.; Masuda, A.; da Silva Vaz, I.J. Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus embryo proteins as target for tick vaccine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 148, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.; Khrestchatisky, M.; Kaczmarek, L.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Jaworski, D.M. Metzincin proteases and their inhibitors: Foes or friends in nervous system physiology? J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 15337–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiz-Rüth, F.X. Catalytic domain architecture of metzincin metalloproteases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15353–15357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francischetti, I.M.B.; Mather, T.N.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Cloning of a salivary gland metalloprotease and characterization of gelatinase and fibrin(ogen)lytic activities in the saliva of the Lyme disease tick vector Ixodes scapularis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francischetti, I.M.B.; Mather, T.N.; Ribeiro, J.M.C. Tick saliva is a potent inhibitor of endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 94, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrem, Y.; Beaufays, J.; Blasioli, V.; Lahaye, K.; Brossard, M.; Vanhamme, L.; Godfroid, E. A family of putative metalloproteases in the salivary glands of the tick Ixodes ricinus. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decrem, Y.; Mariller, M.; Lahaye, K.; Blasioli, V.; Beaufays, J.; Zouaoui Boudjeltia, K.; Vanhaeverbeek, M.; Cérutti, M.; Brossard, M.; Vanhamme, L.; et al. The impact of gene knock-down and vaccination against salivary metalloproteases on blood feeding and egg laying by Ixodes ricinus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, S.; da Silva Vaz, I.J.; Konnai, S.; Yamada, S.; Nakajima, C.; Onuma, M.; Ohashi, K. Effect of vaccination with a recombinant metalloprotease from Haemaphysalis longicornis. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2009, 48, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.L.; Kaufman, W.R. Two feeding-induced proteins from the male gonad trigger engorgement of the female tick Amblyomma hebraeum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5874–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahli, R.; Germond, J.; Diehl, P. Ornithodoros moubata: Spermateleosis and secretory activity of the sperm. Exp. Parasitol. 1985, 60, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, L.; Skilton, R.A.; Odongo, D.O.; Mwaura, S.; Githaka, N.; Kanduma, E.; Obura, M.; Kabiru, E.; Orago, A.; Musoke, A.; et al. Differential transcription of two highly divergent gut-expressed Bm86 antigen gene homologues in the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus (Acari: Ixodida). Insect Mol. Biol. 2011, 20, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parizi, L.F.; Reck, J.; Oldiges, D.P.; Guizzo, M.G.; Seixas, A.; Logullo, C.; de Oliveira, P.L.; Termignoni, C.; Martins, J.R.; Vaz, I.D.S. Multi-antigenic vaccine against the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus: A field evaluation. Vaccine 2012, 30, 6912–6917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Contreras, M.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Targeting a global health problem: Vaccine design and challenges for the control of tick-borne diseases. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5089–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhanguzi, D. Anti-Tick Vaccines: Current Advances and Future Prospects. In Vaccine Design. Methods in Molecular Biology; Thomas, S., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2411, pp. 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sette, A.; Rappuoli, R. Reverse vaccinology: Developing vaccines in the era of genomics. Immunity 2010, 33, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente, J.; Contreras, M. Vaccinomics: A future avenue for vaccine development against emerging pathogens. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambieva, I.H.; Poland, G.A. Vaccinomics, predictive vaccinology and the future of vaccine development. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1757–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Kennedy, R.B.; Haralambieva, I.H.; Jacobson, R.M. Vaccinomics and a new paradigm for the development of preventive vaccines against viral infections. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2011, 15, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, G.A.; Kennedy, R.B.; McKinney, B.A.; Ovsyannikova, I.G.; Lambert, N.D.; Jacobson, R.M.; Oberg, A.L. Vaccinomics, adversomics, and the immune response network theory: Individualized vaccinology in the 21st century. Semin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D.R. Bioinformatics for Vaccinology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas-Jerónimo, S.; Pastor Comín, J.J.; Villar, M.; Contreras, M.; Alberdi, P.; Viera, I.L.; Soto, L.; Cordero, R.; Valdés, J.J.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; et al. A novel combined scientific and artistic approach for the advanced characterization of interactomes: The akirin/subolesin model. Vaccines 2020, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Maritz-Olivier, C.; Naranjo, V.; Ayoubi, P.; Nijhof, A.M.; Almazán, C.; Canales, M.; de la Lastra, J.M.P.; Galindo, R.C.; Blouin, E.F.; et al. Evidence of the role of tick subolesin in gene expression. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaija, P.D.; Contreras, M.; Kabi, F.; Mugerwa, S.; de la Fuente, J. Vaccination with recombinant subolesin antigens provides cross-tick species protection in bos indicus and crossbred cattle in Uganda. Vaccines 2020, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbulaiteye-Saimo, M.; Odongo, D.; Mwaura, S.; Bishop, R.P.; Vlak, J.M.; Musoke, A.J.; Lubega, G.W.; van Oers, M.M. Recombinant Rhipicephalus appendiculatus gut (Ra86) and salivary gland cement (Trp64) proteins as candidate antigens for inclusion in tick vaccines: Protective effects of Ra86 on infestation with adult R. appendiculatus. Vaccine Dev. Ther. 2011, 1, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kamau, L.M. Isolation, Recombinant Expression and Characterization of Polymorphism of BM86 Vaccine Antigen Homologues from rhipicephalus appendiculatus. Ph.D. Thesis, Kenyatta University, Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Dogo, G.; Kwaga, J.; Umoh, J.; Agbede, R.; Jongejan, F. Molecular Detection and Characterization of Bm86 Gene Homologues from Hyalomma truncatum, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) decoloratus for the Development of an Anti-Tick Vaccine in Nigeria. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2015, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Said, M. Molecular and Phylogenetic Study of Bm86 Gene Ortholog from Hyalomma excavatum Tick from Tunisia: Taxonomic and Immunologic Interest. Hered. Genet. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Republic of Uganda. The presidential technical advisory committee on the tick resistance challenge. In Strategy for Efficient, Effective and Sustainable Management of Ticks, Acaricide Resistance and Tick-Borne Diseases in Uganda; Republic of Uganda: Kampala, Uganda, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lodos Jorge Boue, O.; De, J. A model to simulate the effect of vaccination against Boophilus ticks on cattle. Veter. Parasitol. 1999, 87, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodos, J.; Ochagavia, M.; Rodriguez, M.; La Fuente, J. A simulation study of the effects of acaricides and vaccination on Boophilus cattle–tick populations. Prev. Veter. Med. 1999, 38, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, B.D.; Young, A.S. The past and future roles of epidemiology and economics in the control of tick-borne diseases of livestock in Africa: The case of theileriosis. Prev. Vet. Med. 1995, 25, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvin, A.D.; Mcdermott, J.J.; Perry, B.D. Epidemiology of Ticks and Tick-borne Diseases in Eastern, Central and Southern Africa. In Proceedings of a Workshop Held in Harare; ILRI: Nairobi, Kenia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasaija, P.D.; Contreras, M.; Kirunda, H.; Nanteza, A.; Kabi, F.; Mugerwa, S.; de la Fuente, J. Inspiring Anti-Tick Vaccine Research, Development and Deployment in Tropical Africa for the Control of Cattle Ticks: Review and Insights. Vaccines 2023, 11, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010099
Kasaija PD, Contreras M, Kirunda H, Nanteza A, Kabi F, Mugerwa S, de la Fuente J. Inspiring Anti-Tick Vaccine Research, Development and Deployment in Tropical Africa for the Control of Cattle Ticks: Review and Insights. Vaccines. 2023; 11(1):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasaija, Paul D., Marinela Contreras, Halid Kirunda, Ann Nanteza, Fredrick Kabi, Swidiq Mugerwa, and José de la Fuente. 2023. "Inspiring Anti-Tick Vaccine Research, Development and Deployment in Tropical Africa for the Control of Cattle Ticks: Review and Insights" Vaccines 11, no. 1: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010099
APA StyleKasaija, P. D., Contreras, M., Kirunda, H., Nanteza, A., Kabi, F., Mugerwa, S., & de la Fuente, J. (2023). Inspiring Anti-Tick Vaccine Research, Development and Deployment in Tropical Africa for the Control of Cattle Ticks: Review and Insights. Vaccines, 11(1), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines11010099







