Immunodominant Linear B-Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Identified by Sera from K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with the WT or Variant Viruses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Strains
2.2. Serum Samples
2.2.1. Humans
2.2.2. Mice
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assaay (ELISA)
2.4. Epitope Mapping
2.5. Results Analysis
2.6. Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT)
3. Results
3.1. General Design of the Study and Antibodies Used for Epitope Mapping
3.2. Determination of the Epitope Landscape of the Spike Protein by Epitope Array Screening
3.3. Cross-Variant Neutralization by Plaque-Reduction Neutralization Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noh, J.Y.; Jeong, H.W.; Shin, E.C. SARS-CoV-2 mutations, vaccines, and immunity: Implication of variants of concern. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 183, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Li, C.; Huang, A.; Xia, S.; Lu, S.; Shi, Z.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Potent binding of 2019 novel coronavirus spike protein by a SARS coronavirus-specific human monoclonal antibody. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaimes, J.A.; Millet, J.K.; Whittaker, G.R. Proteolytic Cleavage of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and the Role of the Novel S1/S2 Site. iScience 2020, 23, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.S.; Jones, F.K.; Nodoushani, A.; Kelly, M.; Becker, M.; Slater, D.; Mills, R.; Teng, E.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; et al. Persistence and decay of human antibody responses to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe0367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, L.; Segovia-Chumbez, B.; Jadi, R.; Martinez, D.R.; Raut, R.; Markmann, A.; Cornaby, C.; Bartelt, L.; Weiss, S.; Park, Y.; et al. The receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein is an immunodominant and highly specific target of antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrock, E.; Fujimura, E.; Kula, T.; Timms, R.T.; Lee, I.H.; Leng, Y.; Robinson, M.L.; Sie, B.M.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Viral epitope profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals cross-reactivity and correlates of severity. Science 2020, 370, eabd4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, X.; Liang, T.; Wang, D.; Teng, F.; Dai, J.; Duan, H.; Guo, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Proteome Microarray for Mapping COVID-19 Antibody Interactions at Amino Acid Resolution. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2238–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poh, C.M.; Carissimo, G.; Wang, B.; Amrun, S.N.; Lee, C.Y.; Chee, R.S.; Fong, S.W.; Yeo, N.K.; Lee, W.H.; Torres-Ruesta, A.; et al. Two linear epitopes on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that elicit neutralising antibodies in COVID-19 patients. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, M.; De Marco, A.; Lempp, F.A.; Tortorici, M.A.; Pinto, D.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Chen, A.; Liu, Z.; Zatta, F.; et al. N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2. Cell 2021, 184, 2332–2347.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadevara, N.; Shrihari, S.; Gilchuk, P.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Binshtein, E.; Zost, S.J.; Nargi, R.S.; Sutton, R.E.; Winkler, E.S.; Chen, E.C.; et al. Neutralizing and protective human monoclonal antibodies recognizing the N-terminal domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Cell 2021, 184, 2316–2331.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makdasi, E.; Zvi, A.; Alcalay, R.; Noy-Porat, T.; Peretz, E.; Mechaly, A.; Levy, Y.; Epstein, E.; Chitlaru, T.; Tennenhouse, A.; et al. The neutralization potency of anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutic human monoclonal antibodies is retained against viral variants. Cell Rep 2021, 36, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Casner, R.G.; Nair, M.S.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Cerutti, G.; Liu, L.; Kwong, P.D.; Huang, Y.; Shapiro, L.; et al. Increased resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variant P.1 to antibody neutralization. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 747–751.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.I.; Ghany, S.; Gilkes, T.; Umakanthan, S. Review of COVID-19 vaccine subtypes, efficacy and geographical distributions. Postgrad Med. J. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, V.; Bose, S. Immunoinformatics-aided identification of T cell and B cell epitopes in the surface glycoprotein of 2019-nCoV. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Quadeer, A.A.; McKay, M.R. Preliminary Identification of Potential Vaccine Targets for the COVID-19 Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Based on SARS-CoV Immunological Studies. Viruses 2020, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grifoni, A.; Sidney, J.; Zhang, Y.; Scheuermann, R.H.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. A Sequence Homology and Bioinformatic Approach Can Predict Candidate Targets for Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 671–680.e672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, M.; von Bulow, S.; Blanc FE, C.; Gecht, M.; Covino, R.; Hummer, G. Computational epitope map of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Ahmad, S.; Azam, S.S. Immunoinformatics characterization of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein for prioritization of epitope based multivalent peptide vaccine. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 314, 113612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lai, D.Y.; Zhang, H.N.; Jiang, H.W.; Tian, X.; Ma, M.L.; Qi, H.; Meng, Q.F.; Guo, S.J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Linear epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein elicit neutralizing antibodies in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Chu, H.; Han, S.; Shuai, H.; Deng, J.; Hu, Y.F.; Gong, H.R.; Lee, A.C.; Zou, Z.; Yau, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects human neural progenitor cells and brain organoids. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping Neutralizing and Immunodominant Sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain by Structure-Guided High-Resolution Serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042.e1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrera-Soler, L.; Daguer, J.P.; Barluenga, S.; Vadas, O.; Cohen, P.; Pagano, S.; Yerly, S.; Kaiser, L.; Vuilleumier, N.; Winssinger, N. Identification of immunodominant linear epitopes from SARS-CoV-2 patient plasma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noy-Porat, T.; Mechaly, A.; Levy, Y.; Makdasi, E.; Alcalay, R.; Gur, D.; Aftalion, M.; Falach, R.; Leviatan Ben-Arye, S.; Lazar, S.; et al. Therapeutic antibodies, targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike N-terminal domain, protect lethally infected K18-hACE2 mice. iScience 2021, 24, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, R.; Noy-Porat, T.; Mechaly, A.; Makdasi, E.; Levy, Y.; Alcalay, R.; Falach, R.; Aftalion, M.; Epstein, E.; Gur, D.; et al. Post-exposure protection of SARS-CoV-2 lethal infected K18-hACE2 transgenic mice by neutralizing human monoclonal antibody. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noy-Porat, T.; Makdasi, E.; Alcalay, R.; Mechaly, A.; Levy, Y.; Bercovich-Kinori, A.; Zauberman, A.; Tamir, H.; Yahalom-Ronen, Y.; Israeli, M.; et al. A panel of human neutralizing mAbs targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike at multiple epitopes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babicki, S.; Arndt, D.; Marcu, A.; Liang, Y.; Grant, J.R.; Maciejewski, A.; Wishart, D.S. Heatmapper: Web-enabled heat mapping for all. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W147–W153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Plante, K.S.; Plante, J.A.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Ku, Z.; An, Z.; Scharton, D.; Schindewolf, C.; et al. the N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 transmission. bioRxiv Update in: Nature 2021. 2021, 2021.03.08.434499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, S.M.; Janowska, K.; McDowell, S.; Mansouri, K.; Parks, R.; Stalls, V.; Kopp, M.F.; Manne, K.; Li, D.; Wiehe, K.; et al. Effect of natural mutations of SARS-CoV-2 on spike structure, conformation, and antigenicity. Science 2021, 373, eabi6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, M.L.; Lei, Q.; Wang, F.; Hong, W.; Lai, D.Y.; Hou, H.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H.; et al. (X) Linear epitope landscape of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein constructed from 1051 COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Z.; Hu, Y.F.; Chen, L.L.; Yau, T.; Tong, Y.G.; Hu, J.C.; Cai, J.P.; Chan, K.H.; Dou, Y.; Deng, J.; et al. Mining of epitopes on spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 from COVID-19 patients. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Huang, X.; Joshi, S.; Guo, C.; Ng, J.; Thakkar, R.; Wu, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Pinapati, R.S.; et al. Immunoreactive peptide maps of SARS-CoV-2. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, T.; Heiss, K.; Mahendran, Y.; Casilag, F.; Kurth, F.; Sander, L.E.; Wendtner, C.M.; Hoechstetter, M.A.; Muller, M.A.; Sekul, R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Proteome-Wide Analysis Revealed Significant Epitope Signatures in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 629185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinda, C.K.; Port, J.R.; Bushmaker, T.; Offei Owusu, I.; Purushotham, J.N.; Avanzato, V.A.; Fischer, R.J.; Schulz, J.E.; Holbrook, M.G.; Hebner, M.J.; et al. K18-hACE2 mice develop respiratory disease resembling severe COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.W.; Cline, C.R.; Zeng, X.; Garrison, A.R.; Carey, B.D.; Mucker, E.M.; White, L.E.; Shamblin, J.D.; Brocato, R.L.; Liu, J.; et al. Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop severe and fatal respiratory disease. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladunni, F.S.; Park, J.G.; Pino, P.A.; Gonzalez, O.; Akhter, A.; Allue-Guardia, A.; Olmo-Fontanez, A.; Gautam, S.; Garcia-Vilanova, A.; Ye, C.; et al. Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection in K18 human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caceres, C.J.; Cardenas-Garcia, S.; Carnaccini, S.; Seibert, B.; Rajao, D.S.; Wang, J.; Perez, D.R. Efficacy of GC-376 against SARS-CoV-2 virus infection in the K18 hACE2 transgenic mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, P.B., Jr.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casadevall, A.; Henderson, J.P.; Joyner, M.J.; Pirofski, L.A. SARS-CoV-2 variants and convalescent plasma: Reality, fallacies, and opportunities. J. Clin. Invest. 2021, 131, e148832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.; et al. Increased Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7 to Antibody Neutralization. Res. Sq. 2021, rs.3.rs-155394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Lee, Y.; Ravichandran, S.; Grubbs, G.; Huang, C.; Stauft, C.B.; Wang, T.; Golding, B.; Golding, H.; Khurana, S. Epitope diversity of SARS-CoV-2 hyperimmune intravenous human immunoglobulins and neutralization of variants of concern. iScience 2021, 24, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
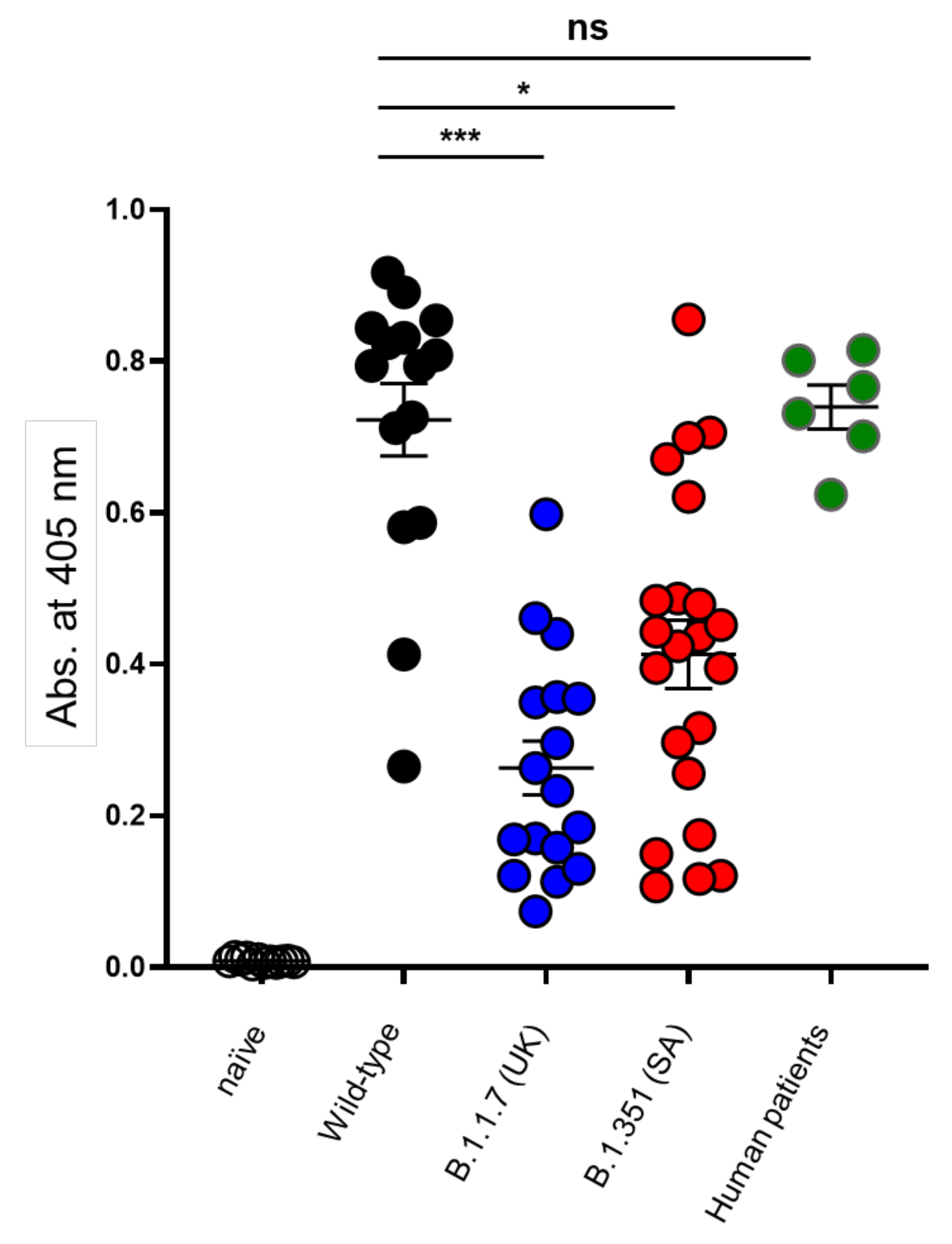
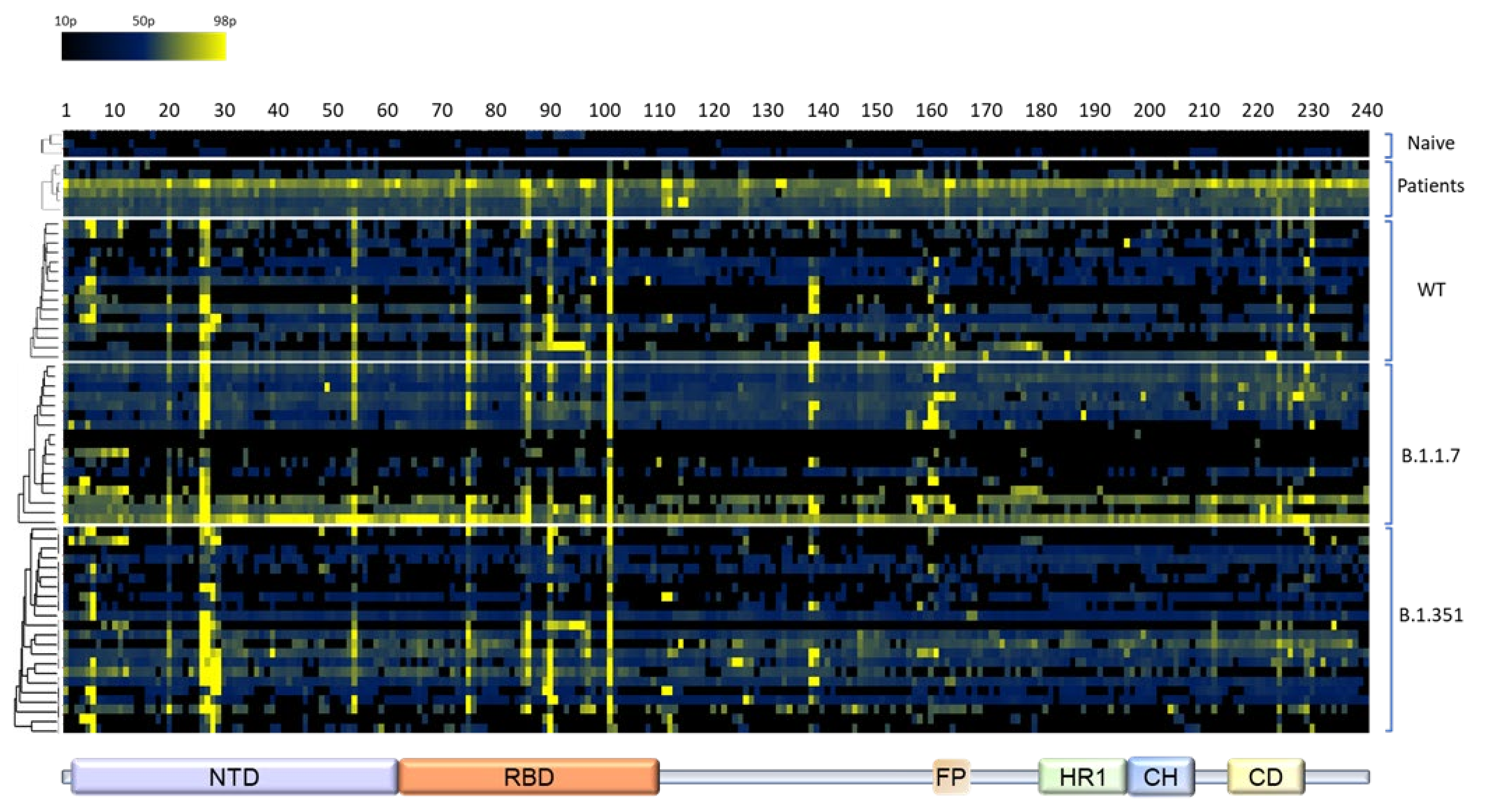
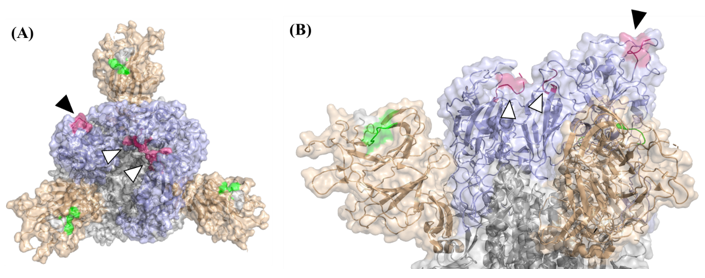

| Peptide No. | Spike aa Position | Spike Domain | Peptide aa Sequence | Fraction of Positive * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT (n = 15) | B.1.1.7 (n = 17) | B.1.351 (n = 22) | Patients (n = 6) | ||||
| 26 | 126–140 | NTD | VVIKVCEFQFCNDPF | 7/15 | 13/17 | 10/22 | 1/6 |
| 27 | 131–145 | NTD | CEFQFCNDPFLGVYY | 5/15 | 8/17 | 11/22 | 1/6 |
| 75 | 371–385 | RBD | SASFSTFKCYGVSPT | 4/15 | 7/17 | 5/22 | 1/6 |
| 86 | 426–440 | RBD | PDDFTGCVIAWNSNN | 3/15 | 6/17 | 5/22 | 2/6 |
| 101 | 501–515 | RBD | NGVGYQPYRVVVLSF | 13/15 | 15/17 | 11/22 | 4/6 |
| 138 | 686–700 | S2 | SVASQSIIAYTMSLG | 5/15 | 7/17 | 5/22 | 0/6 |
| Peptide Type | Spike aa Position | Peptide aa Sequence * | WT | B.1.1.7 | B.1.351 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 131–145 | CEFQFCNDPFLGVY-H | 1/15 | 1/17 | 4/22 | |
| Δ144 | 136–150 | CNDPFLGVY-HKNNKS | 0 | 0 | 2/22 |
| 141–155 | LGVY-HKNNKSWMESE | 0 | 0 | 2/22 | |
| 131–145 | CEFQFCNDPFLGVYY | 10/15 | 13/17 | 10/22 | |
| WT | 136–150 | CNDPFLGVYYHKNNK | 0 | 0 | 13/22 |
| 141–155 | LGVYYHKNNKSWMES | 0 | 0 | 7/22 | |
| 491–505 | PLQSYGFQPTYGVGY | 0 | 0 | 2/22 | |
| N501Y | 496–510 | GFQPTYGVGYQPYRV | 0 | 0 | 2/22 |
| 501–515 | YGVGYQPYRVVVLSF | 10/15 | 15/17 | 10/22 | |
| 491–505 | PLQSYGFQPTNGVGY | 0 | 0 | 2/22 | |
| WT | 496–510 | GFQPTNGVGYQPYRV | 0 | 0 | 2/22 |
| 501–515 | NGVGYQPYRVVVLSF | 8/15 | 13/17 | 8/22 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levy, Y.; Alcalay, R.; Zvi, A.; Makdasi, E.; Peretz, E.; Noy-Porat, T.; Chitlaru, T.; Mandelboim, M.; Mazor, O.; Rosenfeld, R. Immunodominant Linear B-Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Identified by Sera from K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with the WT or Variant Viruses. Vaccines 2022, 10, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020251
Levy Y, Alcalay R, Zvi A, Makdasi E, Peretz E, Noy-Porat T, Chitlaru T, Mandelboim M, Mazor O, Rosenfeld R. Immunodominant Linear B-Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Identified by Sera from K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with the WT or Variant Viruses. Vaccines. 2022; 10(2):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020251
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevy, Yinon, Ron Alcalay, Anat Zvi, Efi Makdasi, Eldar Peretz, Tal Noy-Porat, Theodor Chitlaru, Michal Mandelboim, Ohad Mazor, and Ronit Rosenfeld. 2022. "Immunodominant Linear B-Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Identified by Sera from K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with the WT or Variant Viruses" Vaccines 10, no. 2: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020251
APA StyleLevy, Y., Alcalay, R., Zvi, A., Makdasi, E., Peretz, E., Noy-Porat, T., Chitlaru, T., Mandelboim, M., Mazor, O., & Rosenfeld, R. (2022). Immunodominant Linear B-Cell Epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Identified by Sera from K18-hACE2 Mice Infected with the WT or Variant Viruses. Vaccines, 10(2), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10020251






