Quantification of Antiviral Cytokines in Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Croatia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Serology
2.2.2. Cytokine Quantification
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
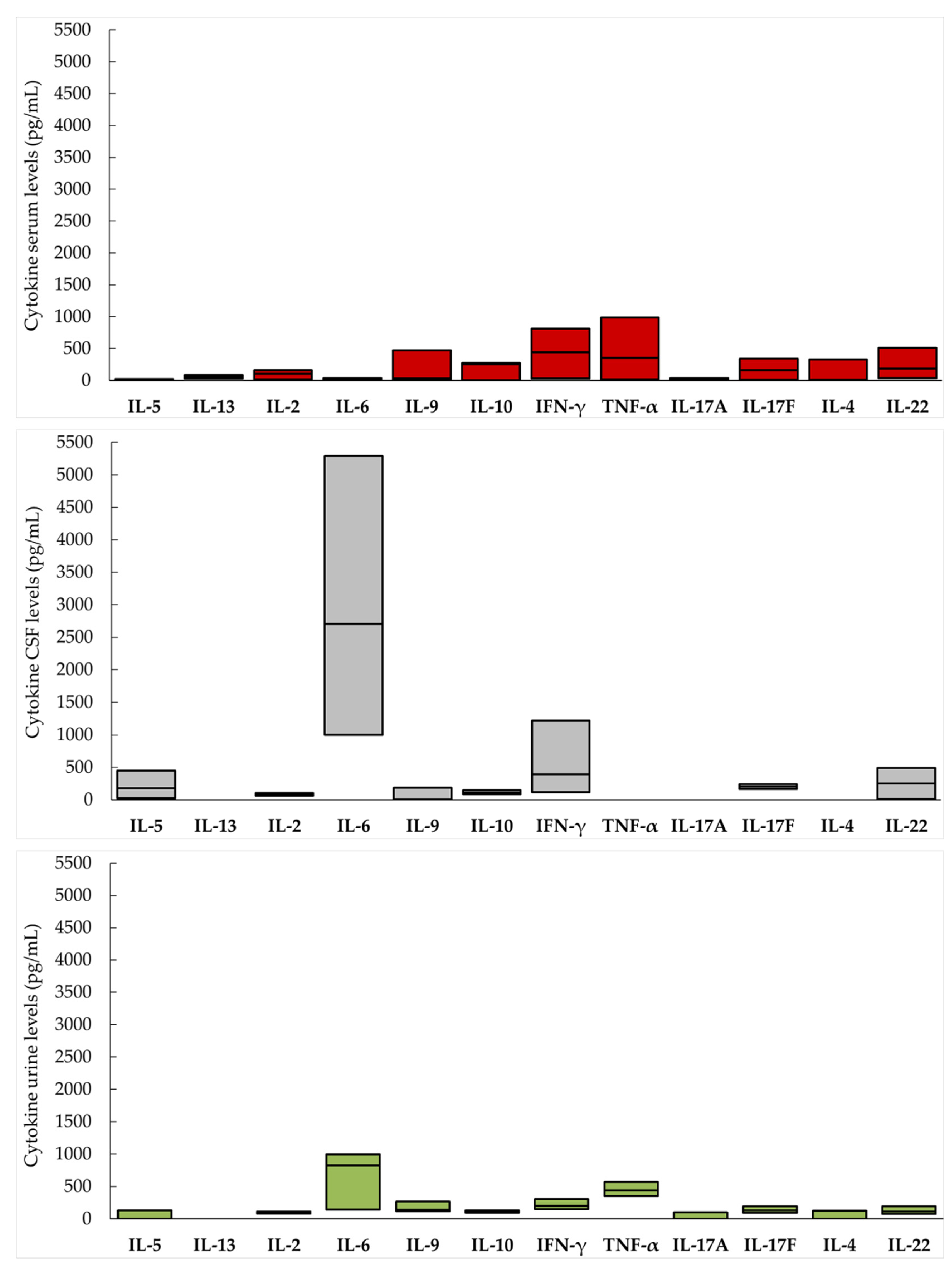
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruzek, D.; Avšič Županc, T.; Borde, J.; Chrdle, A.; Eyer, L.; Karganova, G.; Kholodilov, I.; Knap, N.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Matveev, A.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and Russia: Review of pathogenesis, clinical features, therapy, and vaccines. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 23–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojkiewicz, E.; Toczyłowski, K.; Sulik, A. Tick-borne encephalitis—A review of current epidemiology, clinical symptoms, management and prevention. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2020, 74, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondim, M.A.; Czupryna, P.; Pancewicz, S.; Kruszewska, E.; Groth, M.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A. Epidemiological Trends of Trans-Boundary Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Europe, 2000–2019. Pathogens 2022, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, M.; Barbic, L.; Bogdanic, M.; Tabain, I.; Savic, V.; Kosanovic Licina, M.L.; Kaic, B.; Jungic, A.; Vucelja, M.; Angelov, V.; et al. Tick-borne encephalitis outbreak following raw goat milk consumption in a new micro-location, Croatia, June 2019. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Barbic, L.; Mrzljak, A.; Brnic, D.; Klobucar, A.; Ilic, M.; Janev-Holcer, N.; Bogdanic, M.; Jemersic, L.; Stevanovic, V.; et al. Emerging and Neglected Viruses of Zoonotic Importance in Croatia. Pathogens 2021, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erber, W.; Vuković-Janković, T. TBE in Croatia. In The TBE Book, 3rd ed.; Dobler, G., Erber, W., Bröker, M., Schmitt, H.J., Eds.; Global Health Press: Singapore, 2020; pp. 191–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bogovic, P.; Strle, F. Tick-borne encephalitis: A review of epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovič, P.; Kastrin, A.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Ogrinc, K.; Županc, T.A.; Korva, M.; Knap, N.; Strle, F. Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics and Outcome of Illness Caused by Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus without Central Nervous System Involvement. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmann, H. Diagnosis of tick-borne encephalitis. Vaccine 2003, 21 (Suppl. 1), S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Barbic, L.; Stevanovic, V.; Petrovic, G.; Mlinaric-Galinovic, G. IgG Avidity: An Important Serologic Marker for the Diagnosis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Czupryna, P.; Sulik, A.; Toczyłowski, K.; Siemieniako-Werszko, A.; Żebrowska, A.; Pancewicz, S.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A. The Detectability of the Viral RNA in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepej, S.Z.; Misić-Majerus, L.; Jeren, T.; Rode, O.D.; Remenar, A.; Sporec, V.; Vince, A. Chemokines CXCL10 and CXCL11 in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tick-borne encephalitis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 115, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczylowski, K.; Grygorczuk, S.; Osada, J.; Wojtkowska, M.; Bojkiewicz, E.; Wozinska-Klepadlo, M.; Potocka, P.; Sulik, A. Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid CXCL13 concentrations and lymphocyte subsets in tick-borne encephalitis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 93, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, J.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Pancewicz, S.A.; Muszyńska-Mazur, A.; Kondrusik, M.; Grygorczuk, S.; Swierzbińska-Pijanowska, R.; Dunaj, J.; Czupryna, P. Evaluation of CXCL10, CXCL11, CXCL12 and CXCL13 chemokines in serum and cerebrospinal fluid in patients with tick borne encephalitis (TBE). Adv. Med. Sci. 2011, 56, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Parczewski, M.; Świerzbińska, R.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko, A.; Dunaj, J.; Kondrusik, M.; Pancewicz, S. The increased concentration of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with tick-borne encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Świerzbińska, R.; Kondrusik, M.; Dunaj, J.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko, A.; Siemieniako, A.; Pancewicz, S. The intrathecal expression and pathogenetic role of Th17 cytokines and CXCR2-binding chemokines in tick-borne encephalitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Osada, J.; Toczyłowski, K.; Sulik, A.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Kondrusik, M.; Świerzbińska, R.; Dunaj, J.; Pancewicz, S.; et al. The lymphocyte populations and their migration into the central nervous system in tick-borne encephalitis. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grygorczuk, S.; Czupryna, P.; Pancewicz, S.; Świerzbińska, R.; Dunaj, J.; Siemieniako, A.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A. The increased intrathecal expression of the monocyte-attracting chemokines CCL7 and CXCL12 in tick-borne encephalitis. J. Neurovirol. 2021, 27, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrasheuskaya, A.V.; Fredeking, T.M.; Ignatyev, G.M. Changes in immune parameters and their correction in human cases of tick-borne encephalitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palus, M.; Formanová, P.; Salát, J.; Žampachová, E.; Elsterová, J.; Růžek, D. Analysis of serum levels of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and monoamine neurotransmitters in patients with tick-borne encephalitis: Identification of novel inflammatory markers with implications for pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogovič, P.; Kastrin, A.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Ogrinc, K.; Avšič Županc, T.; Korva, M.; Knap, N.; Resman Rus, K.; Strle, K.; Strle, F. Comparison of laboratory and immune characteristics of the initial and second phase of tick-borne encephalitis. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, Å.; Ygberg, S.; Bogdanovic, G.; Wickström, R. Biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid of children with tick-borne encephalitis: Association with long-term outcome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2016, 35, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, G.; Haglund, M.; Lindquist, L.; Forsgren, M.; Andersson, J.; Andersson, B.; Sköldenberg, B. Tick-borne encephalitis is associated with low levels of interleukin-10 in cerebrospinal fluid. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2011, 1, 6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogovič, P.; Lusa, L.; Korva, M.; Pavletič, M.; Rus, K.R.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Strle, K.; Strle, F. Inflammatory Immune Responses in the Pathogenesis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogovič, P.; Lusa, L.; Korva, M.; Lotrič-Furlan, S.; Resman-Rus, K.; Pavletič, M.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Strle, K.; Strle, F. Inflammatory Immune Responses in Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis: Dynamics and Association with the Outcome of the Disease. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. EU Case Definitions. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/all-topics/eu-case-definitions (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Stupica, D.; Strle, F.; Avšič-Županc, T.; Logar, M.; Pečavar, B.; Bajrović, F.F. Tick borne encephalitis without cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis. BioMed Cent. Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.S.; Rughwani, P.; Kolenovic, M.; Ji, S.; Sun, B. LEGENDplex: Bead-assisted multiplex cytokine profiling by flow cytometry. Methods Enzymol. 2019, 629, 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- LEGENDPlex Multi-analyte Flow Assay Kit, Human Th Cytokine Panel. Available online: https://www.biolegend.com/en-us/products/legendplex-hu-th-cytokine-panel-12-plex-wfp-v02-19471 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Rothaug, M.; Becker-Pauly, C.; Rose-John, S. The role of interleukin-6 signaling in nervous tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863 Pt A, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Barbic, L.; Ilic, M.; Savic, V.; Tabain, I.; Ferenc, T.; Grgic, I.; Gorenec, L.; Bogdanic, M.; et al. Antiviral Cytokine Response in Neuroinvasive and Non-Neuroinvasive West Nile Virus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.; Haberle, S.; Židovec-Lepej, S.; Savić, V.; Kusulja, M.; Papić, N.; Višković, K.; Župetić, I.; Savini, G.; Barbić, L.; et al. Severe West Nile Virus Neuroinvasive Disease: Clinical Characteristics, Short- and Long-Term Outcomes. Pathogens 2022, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Ledina, D.; Knezevic, S.; Savic, V.; Tabain, I.; Ivic, I.; Slavuljica, I.; Bogdanic, M.; Grgic, I.; et al. Clinical, Virological, and Immunological Findings in Patients with Toscana Neuroinvasive Disease in Croatia: Report of Three Cases. Trop Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Hirahara, K.; Onodera, A.; Endo, Y.; Hosokawa, H.; Shinoda, K.; Tumes, D.J.; Okamoto, Y. Th2 Cells in Health and Disease. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 53–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do-Thi, V.A.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S. Crosstalk between the Producers and Immune Targets of IL-9. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Cao, F.; Cui, L.; Ciric, B.; Zhang, G.X.; Rostami, A. IL-9 signaling affects central nervous system resident cells during inflammatory stimuli. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, S.; Thome, R.; Konno, S.; Mari, E.R.; Rasouli, J.; Hwang, D.; Boehm, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.X.; Ciric, B.; et al. IL-9 Controls Central Nervous System Autoimmunity by Suppressing GM-CSF Production. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Navashenaq, J.G.; Shabgah, O.G.; Mohammadi, H.; Sahebkar, A. Interleukin-22 in human inflammatory diseases and viral infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eken, A.; Erdem, S.; Haliloglu, Y.; Zehra Okus, F.; Cakir, M.; Fatih Yetkin, M.; Akcakoyunlu, M.; Karayigit, M.O.; Azizoglu, Z.B.; Bicer, A.; et al. Temporal overexpression of IL-22 and Reg3γ differentially impacts the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunology 2021, 164, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bai, F.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Dai, J.; Gate, D.; Cheng, G.; Yang, L.; Qian, F.; Yuan, X.; Montgomery, R.R.; et al. IL-22 signaling contributes to West Nile encephalitis pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H.; Saijo, S.; Nakae, S. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 2011, 34, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietikäinen, A.; Maksimow, M.; Kauko, T.; Hurme, S.; Salmi, M.; Hytönen, J. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in Lyme neuroborreliosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, D.; Wang, P.; Paul, A.M.; Dai, J.; Gate, D.; Lowery, J.E.; Stokic, D.S.; Leis, A.A.; Flavell, R.A.; Town, T.; et al. Interleukin-17A Promotes CD8+ T Cell Cytotoxicity to Facilitate West Nile Virus Clearance. J. Virol. 2016, 91, e01529-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, D.M.; Vega, R.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Niño, Á.; Rodríguez, R.; Ortiz, Á.; DeLaura, I.; Bosch, I.; Narváez, C.F. Clinical, laboratory and immune aspects of Zika virus-associated encephalitis in children. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 90, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Characteristic | N Tested (%) | Median, YRS (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with TBE | Gender | ||
| Male | 34 (72.2) | 47.8 (36–61) | |
| Female | 13 (27.8) | 50.8 (35.5–67.5) | |
| Clinical presentation | |||
| Meningitis | 25 (50.0) | 48.5 (36–63.5) | |
| Meningoencephalitis | 15 (31.3) | 49.0 (36.0–58.0) | |
| ‘Febrile headache’ | 9 (18.7) | 51.0 (26.0–62.0) | |
| Control group | Gender | ||
| male | 8 (47.1) | 65.2 (57.5–75.5) | |
| Female | 9 (52.9) | 71 (63.5–70) | |
| Clinical presentation | |||
| ‘Febrile headache’ | 6 (35.3) | 43.6 (32–56) | |
| ‘Febrile headache’, impaired consciousness | 11 (64.7) | 67 (61–76) |
| Group | Parameter | Median | IQR | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with TBE | Leukocyte count (cells/μL) | 186 | 105–323 | 0–5 |
| Proteins (g/L) | 0.756 | 0.624–0.800 | 0.170–0.370 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 3.05 | 2.93–3.30 | 2.45–3.33 | |
| Neutrophils (%) | 36 | 18–72 | ||
| Lymphocytes (%) | 56 | 31–79 | 100 | |
| Control group | Leukocyte count | 1.7 | 1–2.5 | 0–5 |
| Proteins (g/L) | 0.464 | 0.333–0.591 | 0.170–0.370 | |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 3.70 | 3.36–4.35 | 2.45–3.33 |
| TBEV Patients (N = 28) | Controls (N = 17) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cytokine (CSF) | N (%) Positive | 95% CI | N (%) Positive | 95% CI | cOR (95% CI) | p | aOR (95% CI) | p |
| IL-5 | 4 (14.3) | 4.0–32.7 | 1 (5.9) | 0.1–28.7 | 2.7 (0.2–139.4) | 0.38 | 1.2 (0.1–15.3) | 0.89 |
| IL-13 | 0 (0) | 0–12.3 * | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-2 | 3 (10.7) | 2.2–28.2 | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-6 | 24 (85.7) | 67.3–95.8 | 10 (58.8) | 32.9–81.5 | 4.2 (0.8–23.5) | 0.04 | 3.0 (0.6–16.0) | 0.19 |
| IL-9 | 19 (67.9) | 47.6–84.1 | 15 (88.2) | 63.5–98.5 | 0.3 (0.03–1.7) | 0.1 | 0.2 (0.02–1.2) | 0.08 |
| IL-10 | 10 (35.7) | 18.6–55.9 | 6 (35.3) | 14.2–61.7 | 1.02 (0.2–4.4) | 0.97 | 0.6 (0.1–2.6) | 0.48 |
| IFN-Ƴ | 24 (85.7) | 67.3–95.8 | 8 (47.1) | 22.9–72.2 | 6.7 (1.3–37.1) | 0.006 | 4.5 (0.97–20.9) | 0.05 |
| TNF-α | 1 (3.6) | 0.1–18.3 | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-17A | 0 (0) | 0–12.3 * | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-17F | 2 (7.1) | 0.1–23.5 | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-4 | 1 (3.6) | 0.1–18.3 | 0 (0) | 0–19.5 * | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-22 | 20 (71.4) | 51.3–86.8 | 16 (94.1) | 71.1–98.8 | 0.2 (0.00–1.4) | 0.06 | 0.2 (0.02–2.0) | 0.16 |
| Cytokine | TBEV Patients | Controls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (pg/mL) | IQR | Median (pg/mL) | IQR | p * | |
| IL-5 | 181.1 | 25.4–450.3 | 122.3 | NA | NA |
| IL-13 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-2 | 81.5 | 61.7–106.0 | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-6 | 2705.7 | 1000.4–5293.6 | 3224.8 | 1247.8–6032.2 | 0.64 |
| IL-9 | 7.4 | 3.9–186.9 | 242.9 | 171.4–352.9 | 0.0001 |
| IL-10 | 113.1 | 86.6–150.9 | 121.0 | 91.4–128.5 | 0.81 |
| IFN-γ | 394.3 | 120.4–1221.5 | 206.5 | 180.5–337.1 | 0.36 |
| TNF-α | 1246.2 | 1246.2–1246.2 | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-17A | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-17F | 203.8 | 166.8–240.8 | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-4 | 241.0 | 241.0–241.0 | NA | NA | NA |
| IL-22 | 254.5 | 11.8–491.7 | 172.7 | 110.3–201.7 | 0.31 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zidovec-Lepej, S.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Ilic, M.; Gorenec, L.; Grgic, I.; Bogdanic, M.; Radmanic, L.; Ferenc, T.; Sabadi, D.; Savic, V.; et al. Quantification of Antiviral Cytokines in Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Croatia. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111825
Zidovec-Lepej S, Vilibic-Cavlek T, Ilic M, Gorenec L, Grgic I, Bogdanic M, Radmanic L, Ferenc T, Sabadi D, Savic V, et al. Quantification of Antiviral Cytokines in Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Croatia. Vaccines. 2022; 10(11):1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111825
Chicago/Turabian StyleZidovec-Lepej, Snjezana, Tatjana Vilibic-Cavlek, Maja Ilic, Lana Gorenec, Ivana Grgic, Maja Bogdanic, Leona Radmanic, Thomas Ferenc, Dario Sabadi, Vladimir Savic, and et al. 2022. "Quantification of Antiviral Cytokines in Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Croatia" Vaccines 10, no. 11: 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111825
APA StyleZidovec-Lepej, S., Vilibic-Cavlek, T., Ilic, M., Gorenec, L., Grgic, I., Bogdanic, M., Radmanic, L., Ferenc, T., Sabadi, D., Savic, V., Hruskar, Z., Svitek, L., Stevanovic, V., Peric, L., Lisnjic, D., Lakoseljac, D., Roncevic, D., & Barbic, L. (2022). Quantification of Antiviral Cytokines in Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid and Urine of Patients with Tick-Borne Encephalitis in Croatia. Vaccines, 10(11), 1825. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10111825











