Peripheral IFN-ɣ Production after Blood Stimulation with Different Mycobacterial Antigens in Goats Vaccinated against Paratuberculosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Ethical Approval
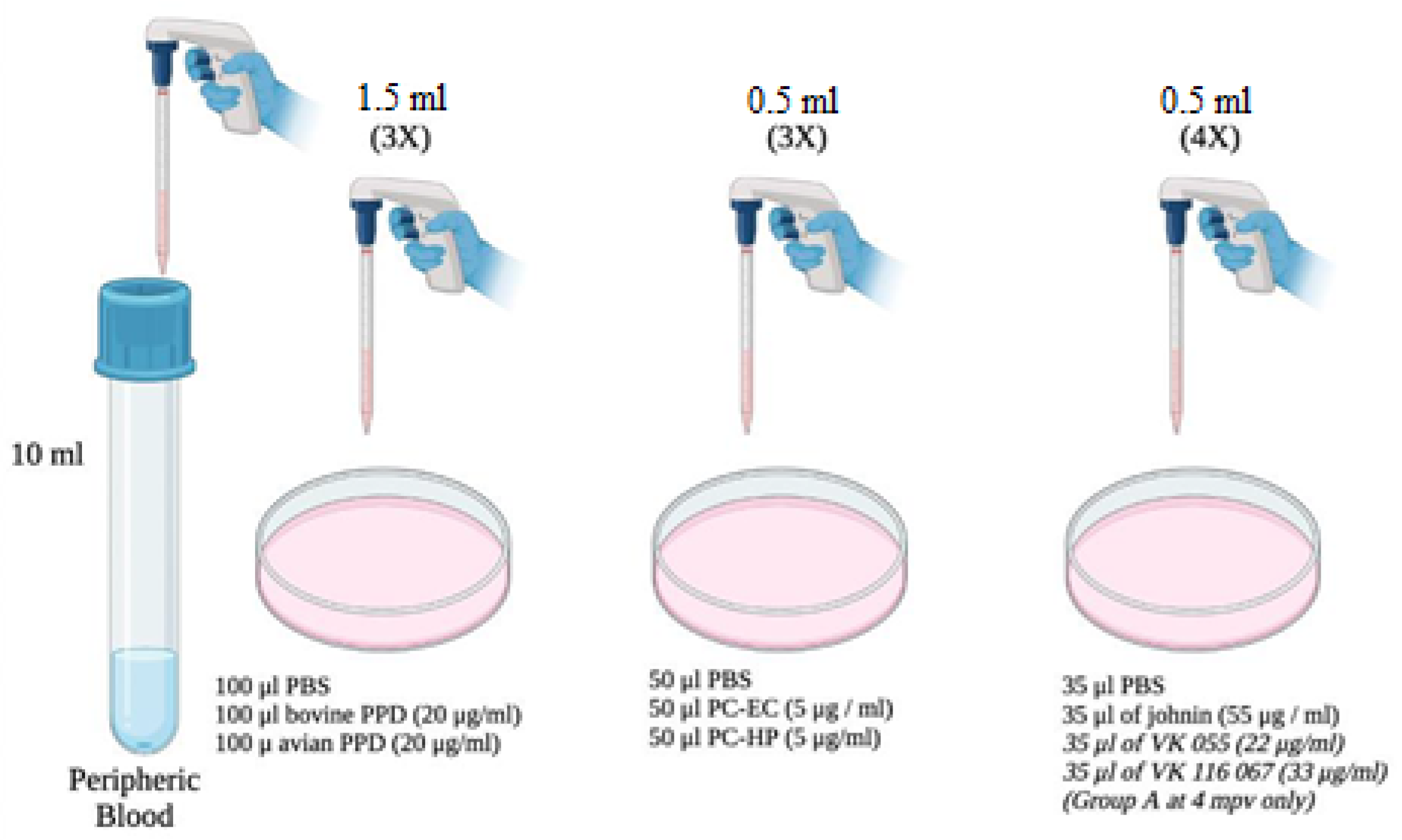
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Antigens
- (a)
- purified protein derivatives obtained from heat-treated Maa or M. bovis cultures, known as avian and bovine PPD, respectively (CZ Veterinaria, Porriño, Pontevedra).
- (b)
- Johnin (Neiker-Tecnalia, Derio, Vizcaya, Spain): purified protein derivative obtained from a heat-treated Map culture.
- (c)
- PC-EC and PC-HP peptide cocktails (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), which are combinations of different proteins of M. bovis: the PC-EC cocktail has two proteins in its formulation: ESAT-6 and CFP-10, while the PC-HP has these same proteins, plus Rv-3615c. These peptide cocktails have previously been used in the diagnosis of bovine and caprine tuberculosis with satisfactory results [6,8,18].
- (d)
- VK 055 and VK 067 antigens (Vacunek®, Derio, Vizcaya, Spain) purified from Map. The latter, due to availability, were used only in samples from Group A, at 4 months post vaccination (mpv) (120 dpv or 90 dpi).
2.3. Determination of IFN-γ Production in Peripheral Blood
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, P.; Barkema, H.W.; Mason, S.; Beaulieu, E.; Hall, D.C. Economic losses due to Johne’s disease (paratuberculosis) in dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 3123–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Juste, R. Paratuberculosis control: A review with a focus on vaccination. J. Immune Based Ther. Vaccines 2011, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, J.; Fernández, M.; Royo, M.; Grau, A.; Collazos, J.A.; Benavides, J.; Ferreras, M.C.; Mínguez, O.; Pérez, V. Influence of vaccination against paratuberculosis on the diagnosis of caprine tuberculosis during official eradication programmes in Castilla y León (Spain). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Agricultura Pesca y Alimentación (MAPA). Programa Nacional de Erradicación de la Tuberculosis Bovina 2021. Available online: https://www.mapa.gob.es/es/ganaderia/temas/sanidad-animal-higiene-ganadera/programatb2021versionabril_tcm30-561045.pdf (accessed on 26 August 2022).
- Nedrow, A.; Gavalchin, J.; Smith, M.; Stehman, S.; Maul, J.; McDonough, S.; Thonney, M. Antibody and skin-test responses of sheep vaccinated against Johne ’s disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 116, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez de Val, B.; Nofrarías, M.; López-Soria, S.; Garrido, J.; Vordermeier, H.; Villarreal-Ramos, B.; Martín, M.; Puentes, E.; Juste, R.; Domingo, M. Effects of vaccination against paratuberculosis on tuberculosis in goats: Diagnostic interferences and cross-protection. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garrido, J.; Vazquez, P.; Molina, E.; Plazaola, J.; Sevilla, I.; Geijo, M.; Alonso-Hearn, M.; Juste, R. Paratuberculosis vaccination causes only limited cross-reactivity in the skin test for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.; Elguezabal, N.; Sevilla, I.A.; Geijo, M.V.; Molina, E.; Arrazuria, R.; Urkitza, A.; Gareth, J.; Vordermeier, M.; Garrido, J.M.; et al. Tuberculosis detection in paratuberculosis vaccinated calves: New alternatives against interference. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Good, M.; Duignan, A. Perspectives on the history of bovine TB and the role of tuberculin in bovine TB eradication. Vet. Med. Int. 2011, 2011, 410470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogall, T.; Wolters, J.; Flohr, T.; Böttger, E.C. Towards a phylogeny and definition of species at the molecular level within the genus Mycobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1990, 40, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitulle, C.; Dorsch, M.; Kazda, J.; Wolters, W.; Stackebrandt, E. Phylogeny of rapidly growing members of the genus Mycobacterium. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1992, 42, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordermeier, H.M.; Whelan, A.; Cockle, P.J.; Farrant, L.; Palmer, N.; Hewinson, R.G. Use of synthetic peptides derived from the antigens ESAT-6 and CFP-10 for differential diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis in cattle. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Middleton, S.; Steinbach, S.; Coad, M.; McGill, K.; Brady, C.; Duignan, A.; Wiseman, J.; Gormley, E.; Jones, G.J.; Vordermeier, M. A molecularly defined skin test reagent for the diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis compatible with vaccination against Johne’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roupie, V.; Alonso-Velasco, E.; Van Der Heyden, S.; Holbert, S.; Duytschaever, L.; Berthon, P.; Van Dosselaer, I.; Van Campe, W.; Mostin, L.; Biet, F.; et al. Evaluation of mycobacteria-specific gamma interferon and antibody responses before and after a single intradermal skin test in cattle naturally exposed to M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis and experimentally infected with M. bovis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2018, 196, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, H.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.; Hughes, V.; Stevenson, K.; Bakker, D.; Willemsen, P.; Bay, S.; Ganneau, C.; Biet, F.; Vordermeier, M. Interferon-γ Response of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis Infected Goats to Recombinant and Synthetic Mycobacterial Antigens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 645251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, V.; Denham, S.; Bannantine, J.P.; Chianini, F.; Kerr, K.; May, L.; McLuckie, J.; Nath, M.; Stevenson, K. Interferon gamma responses to proteome-determined specific recombinant proteins: Potential as diagnostic markers for ovine Johne’s disease. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 155, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, V.; McNair, J.; Strain, S.; Barry, C.; McLuckie, J.; Nath, M.; Caldow, G.; Stevenson, K. Gamma interferon responses to proteome-determined specific recombinant proteins in cattle experimentally- and naturally-infected with paratuberculosis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2017, 114, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casal, C.; Bezos, J.; Díez-Guerrier, A.; Álvarez, J.; Romero, B.; de Juan, L.; Rodríguez-Campos, S.; Vordermeier, M.; Whelan, A.; Hewinson, R.G.; et al. Evaluation of two cocktails containing ESAT-6, CFP-10 and Rv-3615c in the intradermal test and the interferon-γ assay for diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 105, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Benavides, J.; Sevilla, I.; Fuertes, M.; Castaño, P.; Delgado, L.; García-Marín, J.; Garrido, J.; Ferreras, M.; Pérez, V. Experimental infection of lambs with C and S-type strains of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis: Immunological and pathological findings. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez, J.; de Juan, L.; Bezos, J.; Romero, B.; Sáez, J.L.; Reviriego-Gordejo, F.J.; Briones, V.; Moreno, M.A.; Mateos, A.; Domínguez, L.; et al. Interference of paratuberculosis with the diagnosis of tuberculosis in a goat flock with a natural mixed infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 128, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daniel, R.; Evans, H.; Rolfe, S.; de la Rua-Domenech, R.; Crawshaw, T.; Higgins, R.J.; Schock, A.; Clifton-Hadley, R. Outbreak of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium bovis in golden Guernsey goats in Great Britain. Vet. Rec. 2009, 165, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napp, S.; Allepuz, A.; Mercader, I.; Nofrarías, M.; López-Soria, S.; Domingo, M.; Romero, B.; Bezos, J.; Pérez de Val, B. Evidence of goats acting as domestic reservoirs of bovine tuberculosis. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koets, A.; Eda, S.; Sreevatsan, S. The within host dynamics of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis infection in cattle: Where time and place matter. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, M.; Fuertes, M.; Elguezabal, N.; Castaño, P.; Royo, M.; Ferreras, M.C.; Benavides, J.; Pérez, V. Immunohisto-chemical expression of interferon-γ in different types of granulomatous lesions associated with bovine paratuberculosis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corpa, J.; Pérez, V.; García-Marín, J. Differences in the immune responses in lambs and kids vaccinated against paratuberculosis, according to the age of vaccination. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 77, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Hovingh, E.; Linscott, R.; Martel, E.; Lawrence, J.; Wolfgang, D.; Griswold, D. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis antibody response, fecal shedding, and antibody cross-reactivity to Mycobacterium bovis in M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis-infected cattle herds vaccinated against Johne’s disease. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 21, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, P.; Shippy, D.; Talaat, A. Superior protection elicited by live-attenuated vaccines in the murine model of paratuberculosis. Vaccine 2015, 33, 7262–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arrazuria, R.; Molina, E.; Garrido, J.; Pérez, V.; Juste, R.; Elguezabal, N. Vaccination sequence effects on immunological response and tissue bacterial burden in paratuberculosis infection in a rabbit model. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juste, R.A.; Geijo, M.V.; Elguezabal, N.; Sevilla, I.A.; Alonso-Hearn, M.; Garrido, J.M. Paratuberculosis vaccination specific and non-specific effects on cattle lifespan. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwozdz, J.; Thompson, K.; Manktelow, B.; Murray, A.; West, D. Vaccination against paratuberculosis of lambs already infected experimentally with Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Aust. Vet. J. 2000, 78, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, L.; García-Marín, J.; Muñoz, M.; Benavides, J.; Juste, R.; García-Pariente, C.; Fuertes, M.; González, J.; Ferreras, M.; Pérez, V. Pathological findings in young and adult sheep following experimental infection with 2 different doses of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, H.; Gyra, H.; Zimmer, K.; Dräger, K.; Burkert, B.; Lemser, B.; Hausleithner, D.; Cubler, K.; Klawonn, W.; Hess, R. Immune reactions in cattle after immunization with a Mycobacterium paratuberculosis vaccine and implications for the diagnosis of M. paratuberculosis and M. bovis infections. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2001, 48, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskens, J.; Van Zijderveld, F.; Eger, A.; Bakker, D. Evaluation of the long-term immune response in cattle after vaccination against paratuberculosis in two Dutch dairy herds. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 86, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindi, L.; Garzelli, C. Genetic diversity and phylogeny of Mycobacterium avium. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.L.; Doherety, M.L.; Collins, J.D.; Kazda, J.F.; Quinn, P.J. The tuberculin test. Vet. Microbiol. 1994, 40, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gormley, E.; Doyle, M.B.; Fitzsimons, S.; McGill, K.; Collins, J.D. Diagnosis of Mycobacterium bovis infection in cattle by use of the gamma-interferon (Bovigam) assay. Vet. Microbiol. 2006, 112, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, P.; Brémaud, I.; Gautier, M.P. Vaccination of kids under one month of age with a killed vaccine and reduction in the frequency of faecal shedding of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis. Small Rumin. Res. 2014, 121, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartier, C.; Mercier, P.; Pellet, M.; Vialard, J. Effect of an inactivated paratuberculosis vaccine on the intradermal testing of goats for tuberculosis. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, C.; Govaerts, M.; Meikle, V.; Gutiérrez-Pabello, J.A.; McNair, J.; Andersen, P.; Suárez-Güemes, F.; Pollock, J.; Espitia, C.; Cataldi, A. Detection of bovine tuberculosis in herds with different disease prevalence and influence of paratuberculosis infection on PPDB and ESAT-6/CFP10 specificity. Prev. Vet. Med. 2010, 96, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risalde, M.Á.; Thomas, J.; Sevilla, I.; Serrano, M.; Ortíz, J.A.; Garrido, J.; Domínguez, M.; Domínguez, L.; Gortázar, C.; Ruíz-Fons, J.F. Development and evaluation of an interferon gamma assay for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in red deer experimentally infected with Mycobacterium bovis. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, P.; Doherty, T. The success and failure of BCG—Implications for a novel tuberculosis vaccine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnaggar, M.M.; El-Naggar, M.M.; Abdellrazeq, G.S.; Sester, M.; Khaliel, S.A.; Singh, M.; Torky, H.A.; Davis, W.C. Development of an improved ESAT-6 and CFP-10 peptide-based cytokine flow cytometric assay for bovine tuberculosis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidders, B.; Pirson, C.; Hogarth, P.J.; Hewinson, R.G.; Stoker, N.G.; Vordermeier, H.M.; Ewer, K. Screening of highly expressed mycobacterial genes identifies Rv3615c as a useful differential diagnostic antigen for the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikkelsen, H.; Aagaard, C.; Nielsen, S.S.; Jungersen, G. Novel antigens for detection of cell mediated immune responses to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis infection in cattle. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2011, 143, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holbert, S.; Branger, M.; Souriau, A.; Lamoureux, B.; Ganneau, C.; Richard, G.; Cochard, T.; Tholoniat, C.; Bay, S.; Winter, N.; et al. Interferon gamma response to Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis specific lipopentapeptide antigen L5P in cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 102, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jungersen, G.; Huda, A.; Hansen, J.J.; Lind, P. Interpretation of the gamma interferon test for diagnosis of subclinical paratuberculosis in cattle. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2002, 9, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández, M.; Royo, M.; Arteche-Villasol, N.; Ferreras, M.C.; Benavides, J.; Pérez, V. Peripheral IFN-ɣ Production after Blood Stimulation with Different Mycobacterial Antigens in Goats Vaccinated against Paratuberculosis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101709
Fernández M, Royo M, Arteche-Villasol N, Ferreras MC, Benavides J, Pérez V. Peripheral IFN-ɣ Production after Blood Stimulation with Different Mycobacterial Antigens in Goats Vaccinated against Paratuberculosis. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101709
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández, Miguel, Marcos Royo, Noive Arteche-Villasol, M. Carmen Ferreras, Julio Benavides, and Valentín Pérez. 2022. "Peripheral IFN-ɣ Production after Blood Stimulation with Different Mycobacterial Antigens in Goats Vaccinated against Paratuberculosis" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101709
APA StyleFernández, M., Royo, M., Arteche-Villasol, N., Ferreras, M. C., Benavides, J., & Pérez, V. (2022). Peripheral IFN-ɣ Production after Blood Stimulation with Different Mycobacterial Antigens in Goats Vaccinated against Paratuberculosis. Vaccines, 10(10), 1709. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101709





