Using MicroRNA Arrays as a Tool to Evaluate COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy
Abstract
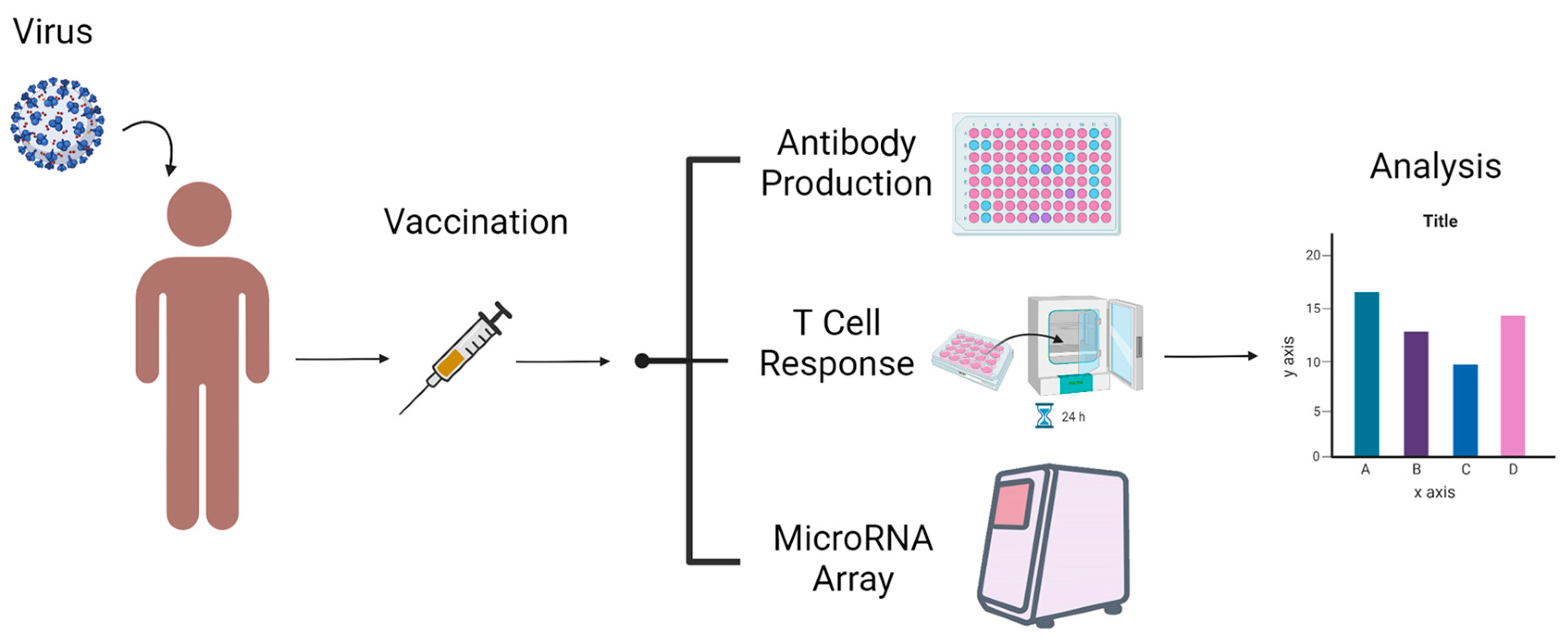
:1. Introduction
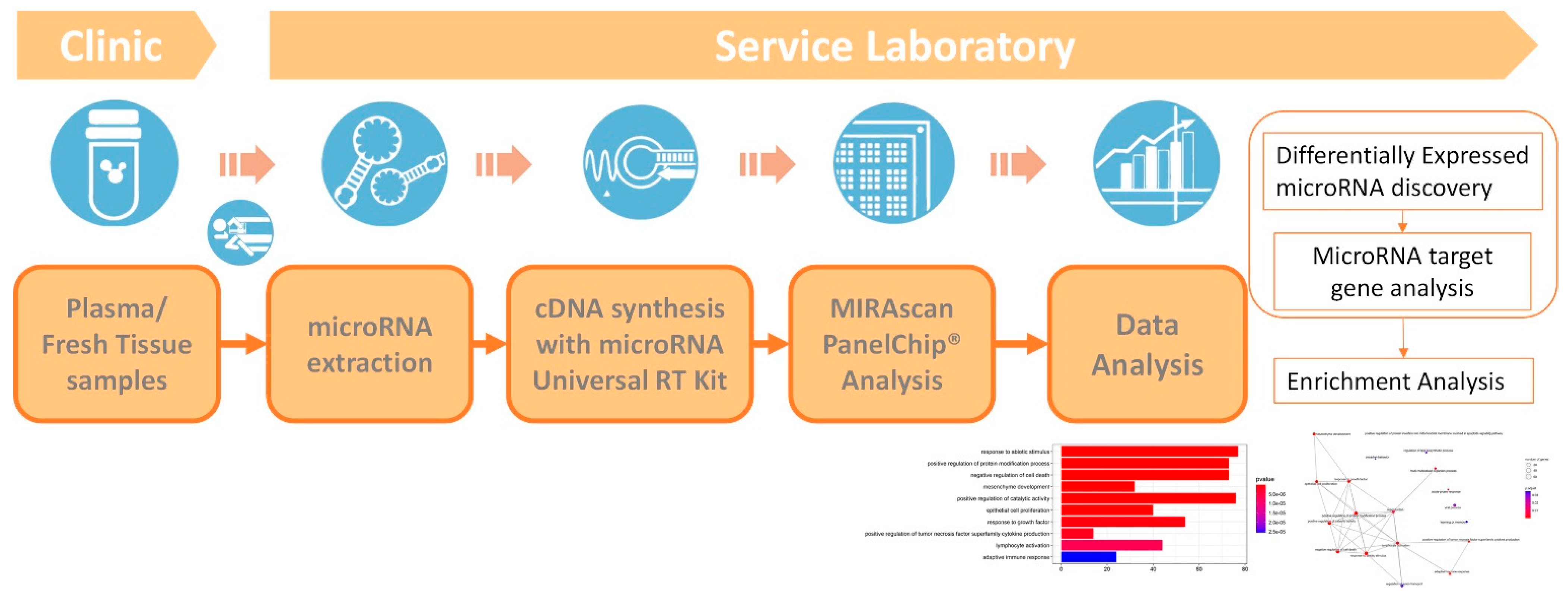
2. Methods
3. Results—Clinical Samples from Two Pregnant Women
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hui, D.S.; Azhar, E.I.; Madani, T.A.; Ntoumi, F.; Kock, R.; Dar, O.; Ippolito, G.; Mchugh, T.D.; Memish, Z.A.; Drosten, C.; et al. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 264–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlake, T.; Thess, A.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Kallen, K.-J. Developing mRNA-vaccine technologies. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iavarone, C.; O’hagan, D.T.; Yu, D.; Delahaye, N.F.; Ulmer, J.B. Mechanism of action of mRNA-based vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2017, 16, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, L.J.; Jorquera, P.A.; Bakre, A.A.; Tripp, R.A. Determining Immune and miRNA Biomarkers Related to Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Vaccine Types. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiumi, H. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles Carry Immune Regulatory miRNAs and Regulate Vaccine Efficacy and Local Inflammatory Response After Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 685344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas-Padilla, M.; Mata-Haro, V. Regulation of TLR signaling pathways by microRNAs: Implications in inflammatory diseases. Cent.-Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 43, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvi, V.; Gianello, V.; Tiberio, L.; Sozzani, S.; Bosisio, D. Cytokine Targeting by miRNAs in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.; Liang, M.; Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.; Jinyu, J.; Feng, Z.; Mei, Z. The role of microRNA-16 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgueta, R.; De Vries, V.C.; Noelle, R.J. The immortality of humoral immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraley, E.; LeMaster, C.; Geanes, E.; Banerjee, D.; Khanal, S.; Grundberg, E.; Selvarangan, R.; Bradley, T. Humoral immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine administration in seropositive and seronegative individuals. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxford Immunotec. T-SPOT.COVID Package Insert. Available online: https://www.tspotcovid.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/5/2021/03/PI-T-SPOT.COVID-IVD-UK-v3.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Arend, S.M.; Geluk, A.; van Meijgaarden, K.E.; van Dissel, J.T.; Theisen, M.; Andersen, P.; Ottenhoff, T.H. Antigenic equivalence of human T-cell responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific RD1-encoded protein antigens ESAT-6 and culture filtrate protein 10 and to mixtures of synthetic peptides. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaganathan, S.; Stieber, F.; Rao, S.N.; Nikolayevskyy, V.; Manissero, D.; Allen, N.; Boyle, J.; Howard, J. Preliminary Evaluation of QuantiFERON SARS-CoV-2 and QIAreach Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Total Test in Recently Vaccinated Individuals. Infect. Dis. 2021, 10, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, E.; Locci, M. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines: Immunological Mechanism and Beyond. Vaccines 2021, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Lagniton, P.N.P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, R.H. mRNA vaccines for COVID-19: What, why and how. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzman, A. Molecular biology of the cell (4th ed.): Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., Roberts, K., and Walter, P. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2003, 31, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T. Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teijaro, J.R.; Farber, D.L. COVID-19 Vaccines: Modes of Immune Activation and Future Challenges. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.F.; Yen, C.L.; Fu, Y.C.; Cheng, C.M.; Shen, T.C.; Chang, P.D.; Cheng, K.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, P.L.; et al. Innate Immune Responses of Vaccinees Determine Early Neutralizing Antibody Production after ChAdOx1nCoV-19 Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 807454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyashita, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Takagi, Y.; Tsukamoto, H.; Takashima, K.; Kouwaki, T.; Makino, K.; Fukushima, S.; Nakamura, K.; Oshiumi, H. Circulating extracellular vesicle microRNAs associated with adverse reactions, proinflammatory cytokine, and antibody production after COVID-19 vaccination. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Légaré, C.; Clément, A.A.; Desgagné, V.; Thibeault, K.; White, F.; Guay, S.P.; Arsenault, B.J.; Scott, M.S.; Jacques, P.É.; Perron, P.; et al. Human plasma pregnancy-associated miRNAs and their temporal variation within the first trimester of pregnancy. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 doses (M1) | No dose (M2) | ||
| Parity | 2 | 3 | |
| Age (year) | 36 | 40 | |
| BMI | 21.797 | 28.377 | |
| Weeks of gestation at delivery | 40 | 39 | |
| Kind of COVID-19 vaccine for first/ second/ third dose | Moderna/Moderna/Moderna | -/-/- | |
| Normalized Cq value | |||
| 3 doses (M1) | No dose (M2) | ΔCq (M1-M2) | |
| hsa-miR-1972 | 7.8294 | 11.0089 | −3.1795 |
| hsa-miR-191-5p | 9.2544 | 11.2722 | −2.0178 |
| hsa-miR-423-5p | 10.7744 | 12.7122 | −1.9378 |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | 8.3869 | 6.1593 | 2.2276 |
| hsa-miR-486-5p | 9.8724 | 7.5511 | 2.3213 |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | 9.1844 | 7.6378 | 1.5466 |
| hsa-miR-451a | 8.0427 | 5.0866 | 2.9561 |
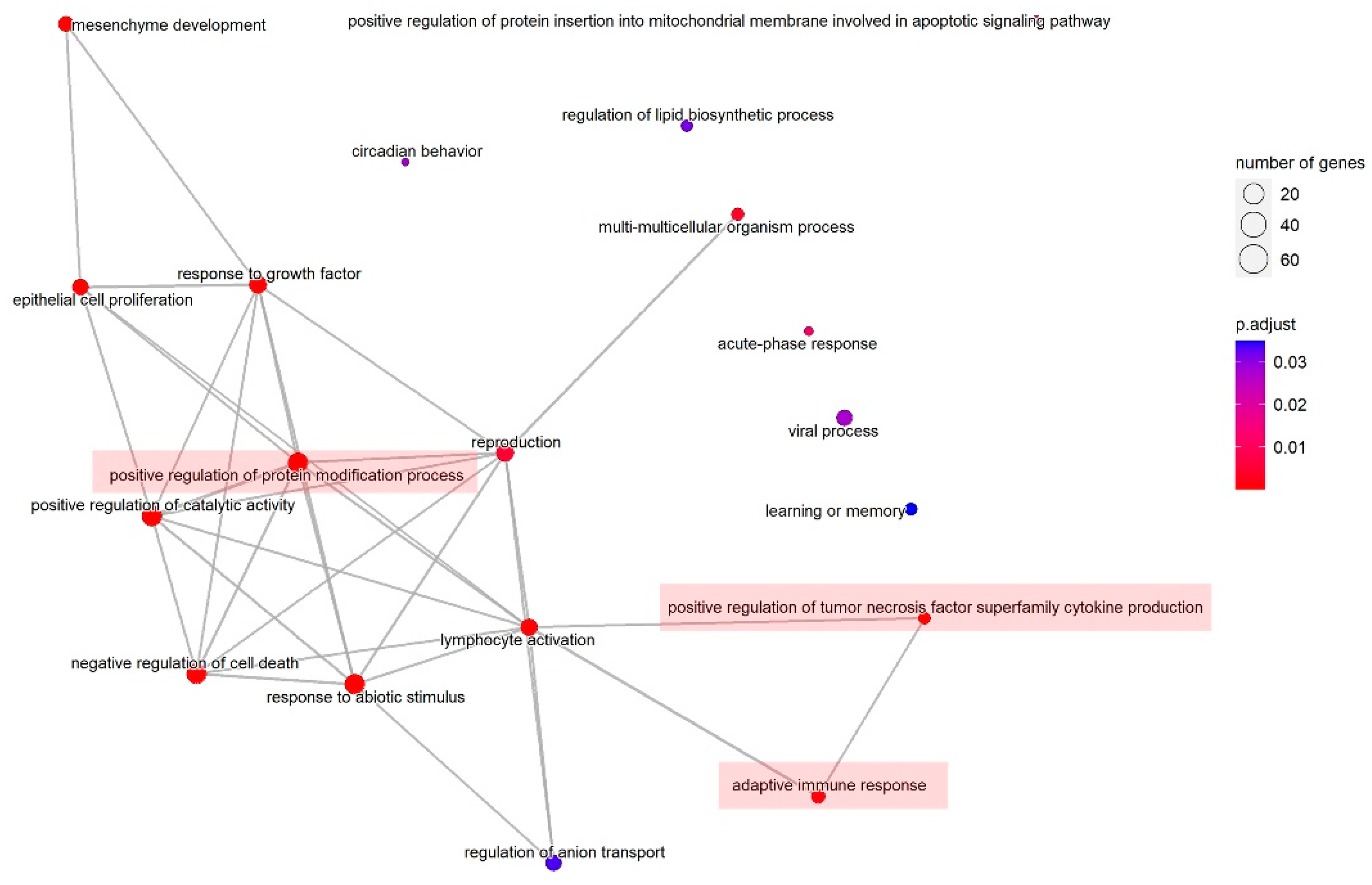
| ID | Description | GeneRatio | BgRatio | p Value (Adjust) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0009628 | response to abiotic stimulus | 77/232 | 441/2689 | 1.06 × 10−7 |
| GO:0031401 | positive regulation of protein modification process | 73/232 | 433/2689 | 1.28 × 10−6 |
| GO:0060548 | negative regulation of cell death | 73/232 | 439/2689 | 1.67 × 10−6 |
| GO:0060485 | mesenchyme development | 32/232 | 130/2689 | 9.37 × 10−6 |
| GO:0043085 | positive regulation of catalytic activity | 76/232 | 494/2689 | 1.07 × 10−5 |
| GO:0050673 | epithelial cell proliferation | 40/232 | 205/2689 | 4.97 × 10−5 |
| GO:0070848 | response to growth factor | 54/232 | 333/2689 | 0.00014 |
| GO:1903557 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | 14/232 | 39/2689 | 0.00022 |
| GO:0046649 | lymphocyte activation | 44/232 | 265/2689 | 0.00050 |
| GO:0002250 | adaptive immune response | 24/232 | 115/2689 | 0.00109 |
| ID | Pathway Description | ** Gene ID | * Differentially Expressed microRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| GO:1903557 | positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine production | APP/CLU/HMGB1/IFNG/IL1A/ IL6/IL12B/MIF/MYD88/PIK3R1/ STAT3/TLR3/BCL10/RASGRP1 | hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-21-5p hsa-miR-191-5p hsa-miR-451a hsa-miR-486-5p |
| GO:0002250 | adaptive immune response | JAG1/BCL6/CLU/MTOR/MSH6/ HMGB1/ICAM1/IFNG/IL1B/IL6/ IL6R/IL12A/IL12B/SMAD7/MEF2C/ MSH2/MYD88/STAT3/TAP1/TSC1/ UNG/BCL10/DUSP10/ICOSLG | hsa-miR-16-5p hsa-miR-21-5p hsa-miR-451a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-P.; Hsieh, Y.-S.; Cheng, M.-H.; Shen, C.-F.; Shen, C.-J.; Cheng, C.-M. Using MicroRNA Arrays as a Tool to Evaluate COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101681
Lin Y-P, Hsieh Y-S, Cheng M-H, Shen C-F, Shen C-J, Cheng C-M. Using MicroRNA Arrays as a Tool to Evaluate COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101681
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yen-Pin, Yi-Shan Hsieh, Mei-Hsiu Cheng, Ching-Fen Shen, Ching-Ju Shen, and Chao-Min Cheng. 2022. "Using MicroRNA Arrays as a Tool to Evaluate COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101681
APA StyleLin, Y.-P., Hsieh, Y.-S., Cheng, M.-H., Shen, C.-F., Shen, C.-J., & Cheng, C.-M. (2022). Using MicroRNA Arrays as a Tool to Evaluate COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy. Vaccines, 10(10), 1681. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101681







