Nonhuman Primates Are Protected against Marburg Virus Disease by Vaccination with a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Prepared under Conditions to Allow Advancement to Human Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Recombinant VSV
2.2. Flow-Virometry
2.3. Genome Integrity Analysis and Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of GP Expression
2.5. VSV∆G-MARV-GP Vaccination
2.6. Analysis of Anti-MARV GP Serum IgG
2.7. MARV Challenge Virus and Vaccine Efficacy
3. Results
3.1. Generation of a rVSVΔG-MARV-GP to Support Human Vaccine Development
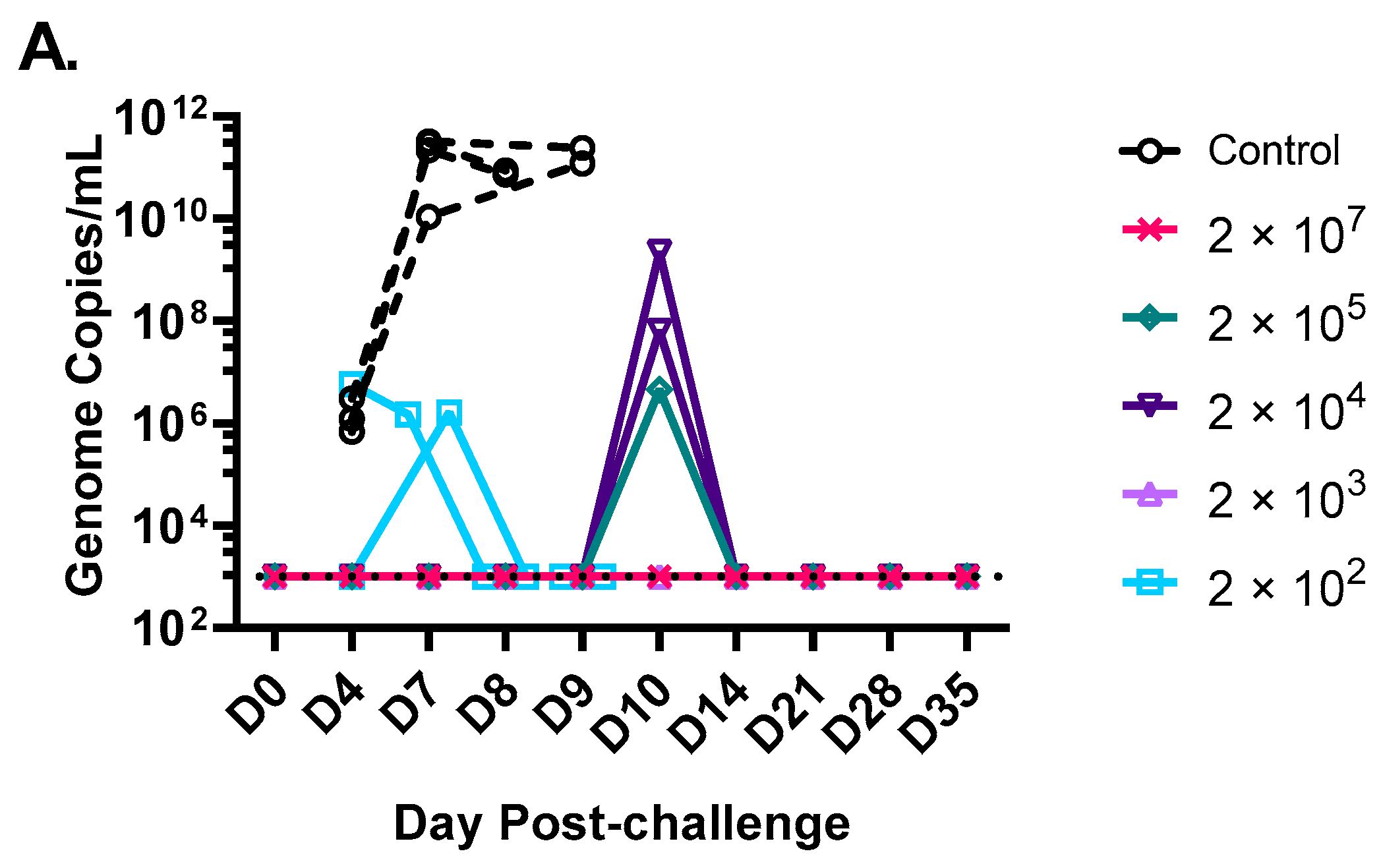
3.2. A Single Vaccination with a Wide Range of rVSVΔG-MARV-GP (Musoke) Doses Protects from MARV Angola Challenge
3.3. Humoral Immune Responses against MARV GP Induced by rVSV∆G-MARV-GP Vaccination
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Sun, J.; Uwishema, O.; Kassem, H.; Abbass, M.; Uweis, L.; Rai, A.; El Saleh, R.; Adanur, I.; Onyeaka, H. Ebola virus outbreak returns to the Democratic Republic of Congo: An urgent rising concern. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 79, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keita, A.K.; Koundouno, F.R.; Faye, M.; Dux, A.; Hinzmann, J.; Diallo, H.; Ayouba, A.; Le Marcis, F.; Soropogui, B.; Ifono, K.; et al. Resurgence of Ebola virus in 2021 in Guinea suggests a new paradigm for outbreaks. Nature 2021, 597, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Ebola Virus Disease—Democratic Republic of the Congo. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2022-DON377 (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Munster, V.J.; Bausch, D.G.; de Wit, E.; Fischer, R.; Kobinger, G.; Munoz-Fontela, C.; Olson, S.H.; Seifert, S.N.; Sprecher, A.; Ntoumi, F.; et al. Outbreaks in a Rapidly Changing Central Africa—Lessons from Ebola. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigott, D.M.; Golding, N.; Mylne, A.; Huang, Z.; Weiss, D.J.; Brady, O.J.; Kraemer, M.U.; Hay, S.I. Mapping the zoonotic niche of Marburg virus disease in Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundouno, F.R.; Kafetzopoulou, L.E.; Faye, M.; Renevey, A.; Soropogui, B.; Ifono, K.; Nelson, E.V.; Kamano, A.A.; Tolno, C.; Annibaldis, G.; et al. Detection of Marburg Virus Disease in Guinea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2528–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Ghana Reports First-Ever Suspected Cases of Marburg Virus Disease. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/countries/ghana/news/ghana-reports-first-ever-suspected-cases-marburg-virus-disease (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Carlson, C.J.; Albery, G.F.; Merow, C.; Trisos, C.H.; Zipfel, C.M.; Eskew, E.A.; Olival, K.J.; Ross, N.; Bansal, S. Climate change increases cross-species viral transmission risk. Nature 2022, 607, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehedi, M.; Groseth, A.; Feldmann, H.; Ebihara, H. Clinical aspects of Marburg hemorrhagic fever. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieslak, T.J.; Kortepeter, M.G.; Wojtyk, R.J.; Jansen, H.J.; Reyes, R.A.; Smith, J.O.; Panel, N.B.M.A. Beyond the Dirty Dozen: A Proposed Methodology for Assessing Future Bioweapon Threats. Mil. Med. 2018, 183, e59–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borio, L.; Inglesby, T.; Peters, C.J.; Schmaljohn, A.L.; Hughes, J.M.; Jahrling, P.B.; Ksiazek, T.; Johnson, K.M.; Meyerhoff, A.; O’Toole, T.; et al. Hemorrhagic fever viruses as biological weapons: Medical and public health management. JAMA 2002, 287, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, J.G.; Coller, B.G.; Dubey, S.A.; Jenal, U.; Lapps, W.; Wang, L.; Wolf, J. Environmental Risk Assessment for rVSVDeltaG-ZEBOV-GP, a Genetically Modified Live Vaccine for Ebola Virus Disease. Vaccines 2020, 8, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, D.N.; Taylor, M.J.; Zarrabian, A.G. Lessons learned from Zaire ebolavirus to help address urgent needs for vaccines against Sudan ebolavirus and Marburg virus. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2020, 16, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.; Jannat, R.; Dubey, S.; Troth, S.; Onorato, M.T.; Coller, B.A.; Hanson, M.E.; Simon, J.K. Development of Pandemic Vaccines: ERVEBO Case Study. Vaccines 2021, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, F.; Donato, A.; Lucchesi, S.; Sorgi, S.; Gerlini, A.; Haks, M.C.; Ottenhoff, T.H.M.; Gonzalez-Dias, P.; VSV-EBOVAC Consortium; VSV-EBOPLUS Consortium; et al. Human Transcriptomic Response to the VSV-Vectored Ebola Vaccine. Vaccines 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinski, A.N.; Messaoudi, I. To B or Not to B: Mechanisms of Protection Conferred by rVSV-EBOV-GP and the Roles of Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longet, S.; Mellors, J.; Carroll, M.W.; Tipton, T. Ebolavirus: Comparison of Survivor Immunology and Animal Models in the Search for a Correlate of Protection. Front. Immunol 2020, 11, 599568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilinykh, P.A.; Bukreyev, A. Antibody responses to filovirus infections in humans: Protective or not? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e348–e355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, H.; Feldmann, F.; Marzi, A. Ebola: Lessons on Vaccine Development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 2018, 72, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grais, R.F.; Kennedy, S.B.; Mahon, B.E.; Dubey, S.A.; Grant-Klein, R.J.; Liu, K.; Hartzel, J.; Coller, B.-A.; Welebob, C.; Hanson, M.E.; et al. Estimation of the correlates of protection of the rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP Zaire ebolavirus vaccine: A post-hoc analysis of data from phase 2/3 clinical trials. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e70–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphire, E.O. A glimpse into immune responses evolving against Ebola virus. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1470–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphire, E.O.; Schendel, S.L.; Gunn, B.M.; Milligan, J.C.; Alter, G. Antibody-mediated protection against Ebola virus. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzi, A.; Menicucci, A.R.; Engelmann, F.; Callison, J.; Horne, E.J.; Feldmann, F.; Jankeel, A.; Feldmann, H.; Messaoudi, I. Protection Against Marburg Virus Using a Recombinant VSV-Vaccine Depends on T and B Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, A.; Jankeel, A.; Menicucci, A.R.; Callison, J.; O’Donnell, K.L.; Feldmann, F.; Pinski, A.N.; Hanley, P.W.; Messaoudi, I. Single Dose of a VSV-Based Vaccine Rapidly Protects Macaques From Marburg Virus Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 774026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolsey, C.; Jankeel, A.; Matassov, D.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Borisevich, V.; Cross, R.W.; Deer, D.J.; Fenton, K.A.; Latham, T.E.; et al. Immune correlates of postexposure vaccine protection against Marburg virus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolsey, C.; Cross, R.W.; Agans, K.N.; Borisevich, V.; Deer, D.J.; Geisbert, J.B.; Gerardi, C.; Latham, T.E.; Fenton, K.A.; Egan, M.A.; et al. A highly attenuated Vesiculovax vaccine rapidly protects nonhuman primates against lethal Marburg virus challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, J.B.; Agans, K.N.; Satterfield, B.A.; Versteeg, K.M.; Fritz, E.A.; Feldmann, H.; Hensley, L.E.; Geisbert, T.W. Durability of a vesicular stomatitis virus-based marburg virus vaccine in nonhuman primates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Product Development under the Animal Rule Guidance for Industry; Office of Communications, Division of Drug Information, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Accelerated Approval Program. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/information-health-care-professionals-drugs/accelerated-approval-program (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Finch, C.L.; Martinez, C.; Leffel, E.; Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Hacker, A.; Mwesigwa, B.; Maiga, D.; Mugisa, I.; Munkwase, G.; Rustomjee, R. Vaccine Licensure in the Absence of Human Efficacy Data. Vaccines 2022, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, H.; Sprecher, A.; Geisbert, T.W. Ebola. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulin, N.; Spanier, A.; Merino, K.; Hutter, J.N.; Waterman, P.E.; Lee, C.; Hamer, M.J. Systematic review of Marburg virus vaccine nonhuman primate studies and human clinical trials. Vaccine 2021, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Feldmann, H. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus-based vaccines against Ebola and Marburg virus infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, S1075–S1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.; Dahlke, C.; Addo, M.M. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vector vaccines for WHO blueprint priority pathogens. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 2269–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. A WHO Strategic Agenda for Filovirus Research and Monitoring (AFIRM)—Roadmap Meeting. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/events/detail/2022/03/30/default-calendar/save-the-date-a-who-strategic-agenda-for-filovirus-research-and-monitoring-(afirm)---roadmap-meeting (accessed on 8 July 2022).
- Dean, N.E.; Longini, I.M. The ring vaccination trial design for the estimation of vaccine efficacy and effectiveness during infectious disease outbreaks. Clin. Trials 2022, 19, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Daddario-Dicaprio, K.M.; Geisbert, J.B.; Reed, D.S.; Feldmann, F.; Grolla, A.; Stroher, U.; Fritz, E.A.; Hensley, L.E.; Jones, S.M.; et al. Vesicular stomatitis virus-based vaccines protect nonhuman primates against aerosol challenge with Ebola and Marburg viruses. Vaccine 2008, 26, 6894–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Geisbert, J.B.; Leung, A.; Daddario-DiCaprio, K.M.; Hensley, L.E.; Grolla, A.; Feldmann, H. Single-injection vaccine protects nonhuman primates against infection with marburg virus and three species of ebola virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7296–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Hensley, L.E.; Geisbert, J.B.; Leung, A.; Johnson, J.C.; Grolla, A.; Feldmann, H. Postexposure treatment of Marburg virus infection. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.M.; Feldmann, H.; Stroher, U.; Geisbert, J.B.; Fernando, L.; Grolla, A.; Klenk, H.D.; Sullivan, N.J.; Volchkov, V.E.; Fritz, E.A.; et al. Live attenuated recombinant vaccine protects nonhuman primates against Ebola and Marburg viruses. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mire, C.E.; Miller, A.D.; Carville, A.; Westmoreland, S.V.; Geisbert, J.B.; Mansfield, K.G.; Feldmann, H.; Hensley, L.E.; Geisbert, T.W. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vaccine vectors expressing filovirus glycoproteins lack neurovirulence in nonhuman primates. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Strong, J.E.; Feldmann, H. Considerations in the Use of Nonhuman Primate Models of Ebola Virus and Marburg Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212 (Suppl. S2), S91–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaze, E.R.; Roy, M.J.; Dalrymple, L.W.; Lanning, L.L. A Comparison of the Pathogenesis of Marburg Virus Disease in Humans and Nonhuman Primates and Evaluation of the Suitability of These Animal Models for Predicting Clinical Efficacy under the ‘Animal Rule’. Comp. Med. 2015, 65, 241–259. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, P.W.; Keshtkar-Jahromi, M.; Psoter, K.J.; Reisler, R.B.; Warren, T.K.; Johnston, S.C.; Goff, A.J.; Downey, L.G.; Bavari, S.; Cardile, A.P. Virulence of Marburg Virus Angola Compared to Mt. Elgon (Musoke) in Macaques: A Pooled Survival Analysis. Viruses 2018, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbutt, M.; Liebscher, R.; Wahl-Jensen, V.; Jones, S.; Moller, P.; Wagner, R.; Volchkov, V.; Klenk, H.D.; Feldmann, H.; Stroher, U. Properties of replication-competent vesicular stomatitis virus vectors expressing glycoproteins of filoviruses and arenaviruses. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5458–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddario-DiCaprio, K.M.; Geisbert, T.W.; Geisbert, J.B.; Stroher, U.; Hensley, L.E.; Grolla, A.; Fritz, E.A.; Feldmann, F.; Feldmann, H.; Jones, S.M. Cross-protection against Marburg virus strains by using a live, attenuated recombinant vaccine. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9659–9666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeseth, A.S.; Yuan, M.; Citron, M.; Reiserova, L.; Morrow, G.; Wilson, A.; Horton, M.; Rukhman, M.; Kinek, K.; Hou, F.; et al. Preclinical immunogenicity and efficacy of a candidate COVID-19 vaccine based on a vesicular stomatitis virus-SARS-CoV-2 chimera. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyombayire, J.; Anzala, O.; Gazzard, B.; Karita, E.; Bergin, P.; Hayes, P.; Kopycinski, J.; Omosa-Manyonyi, G.; Jackson, A.; Bizimana, J.; et al. First-in-Human Evaluation of the Safety and Immunogenicity of an Intranasally Administered Replication-Competent Sendai Virus-Vectored HIV Type 1 Gag Vaccine: Induction of Potent T-Cell or Antibody Responses in Prime-Boost Regimens. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witko, S.E.; Johnson, J.E.; Kalyan, N.K.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Sidhu, M.K.; Hendry, R.M.; Udem, S.A.; Parks, C.L. Refined methods for propagating vesicular stomatitis virus vectors that are defective for G protein expression. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 164, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witko, S.E.; Kotash, C.S.; Nowak, R.M.; Johnson, J.E.; Boutilier, L.A.; Melville, K.J.; Heron, S.G.; Clarke, D.K.; Abramovitz, A.S.; Hendry, R.M.; et al. An efficient helper-virus-free method for rescue of recombinant paramyxoviruses and rhadoviruses from a cell line suitable for vaccine development. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 135, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, S.; Powell, R.L.; Lindsay, R.W.; Yuan, M.; Carpov, A.; Wilson, A.; Lopez, M.; Coleman, J.W.; Wagner, D.; Sharma, P.; et al. A novel, live-attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus vector displaying conformationally intact, functional HIV-1 envelope trimers that elicits potent cellular and humoral responses in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Jones, S.; Fritz, E.A.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Geisbert, J.B.; Liebscher, R.; Grolla, A.; Stroher, U.; Fernando, L.; Daddario, K.M.; et al. Development of a new vaccine for the prevention of Lassa fever. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolsey, C.; Geisbert, J.B.; Matassov, D.; Agans, K.N.; Borisevich, V.; Cross, R.W.; Deer, D.J.; Fenton, K.A.; Eldridge, J.H.; Mire, C.E.; et al. Postexposure Efficacy of Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vectors Against High and Low Doses of Marburg Virus Variant Angola in Nonhuman Primates. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, S582–S587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddario-DiCaprio, K.M.; Geisbert, T.W.; Stroher, U.; Geisbert, J.B.; Grolla, A.; Fritz, E.A.; Fernando, L.; Kagan, E.; Jahrling, P.B.; Hensley, L.E.; et al. Postexposure protection against Marburg haemorrhagic fever with recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vectors in non-human primates: An efficacy assessment. Lancet 2006, 367, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boritz, E.; Gerlach, J.; Johnson, J.E.; Rose, J.K. Replication-competent rhabdoviruses with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 coats and green fluorescent protein: Entry by a pH-independent pathway. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 6937–6945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, M.J.; Buonocore, L.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. The minimal conserved transcription stop-start signal promotes stable expression of a foreign gene in vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, N.D.; Stillman, E.A.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses from DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, G.; Minsker, K.; Kapish, A.; Osborn, J.; Ha, S.; Davide, J.; Califano, J.P.; Sehlin, D.; Rustandi, R.R.; Dick, L.W., Jr.; et al. Flow virometry for process monitoring of live virus vaccines-lessons learned from ERVEBO. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzi, A.; Reynolds, P.; Mercado-Hernandez, R.; Callison, J.; Feldmann, F.; Rosenke, R.; Thomas, T.; Scott, D.P.; Hanley, P.W.; Haddock, E.; et al. Single low-dose VSV-EBOV vaccination protects cynomolgus macaques from lethal Ebola challenge. EBioMedicine 2019, 49, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konduru, K.; Shurtleff, A.C.; Bavari, S.; Kaplan, G. High degree of correlation between Ebola virus BSL-4 neutralization assays and pseudotyped VSV BSL-2 fluorescence reduction neutralization test. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 254, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, D.E.; Page, M.; Mattiuzzo, G.; Hassall, M.; Dougall, T.; Rigsby, P.; Stone, L.; Minor, P. Comparison of platform technologies for assaying antibody to Ebola virus. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemuth, N.A.; Fallacara, D.; Triplett, C.A.; Tamrakar, S.M.; Rajbhandari, A.; Florence, C.; Ward, L.; Griffiths, A.; Carrion, R., Jr.; Goez-Gazi, Y.; et al. Natural history of disease in cynomolgus monkeys exposed to Ebola virus Kikwit strain demonstrates the reliability of this non-human primate model for Ebola virus disease. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolsey, C.; Fears, A.C.; Borisevich, V.; Agans, K.N.; Dobias, N.S.; Prasad, A.N.; Deer, D.J.; Geisbert, J.B.; Fenton, K.A.; Geisbert, T.W.; et al. Natural history of Sudan ebolavirus infection in rhesus and cynomolgus macaques. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttner, A.; Dayer, J.A.; Yerly, S.; Combescure, C.; Auderset, F.; Desmeules, J.; Eickmann, M.; Finckh, A.; Goncalves, A.R.; Hooper, J.W.; et al. The effect of dose on the safety and immunogenicity of the VSV Ebola candidate vaccine: A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 trial. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSherif, M.S.; Brown, C.; MacKinnon-Cameron, D.; Li, L.; Racine, T.; Alimonti, J.; Rudge, T.L.; Sabourin, C.; Silvera, P.; Hooper, J.W.; et al. Assessing the safety and immunogenicity of recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus Ebola vaccine in healthy adults: A randomized clinical trial. CMAJ 2017, 189, E819–E827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heppner, D.G., Jr.; Kemp, T.L.; Martin, B.K.; Ramsey, W.J.; Nichols, R.; Dasen, E.J.; Link, C.J.; Das, R.; Xu, Z.J.; Sheldon, E.A.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of the rVSVG-ZEBOV-GP Ebola virus vaccine candidate in healthy adults: A phase 1b randomised, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnandji, S.T.; Huttner, A.; Zinser, M.E.; Njuguna, P.; Dahlke, C.; Fernandes, J.F.; Yerly, S.; Dayer, J.A.; Kraehling, V.; Kasonta, R.; et al. Phase 1 Trials of rVSV Ebola Vaccine in Africa and Europe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1647–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrhardt, S.A.; Zehner, M.; Krahling, V.; Cohen-Dvashi, H.; Kreer, C.; Elad, N.; Gruell, H.; Ercanoglu, M.S.; Schommers, P.; Gieselmann, L.; et al. Polyclonal and convergent antibody response to Ebola virus vaccine rVSV-ZEBOV. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilinykh, P.A.; Huang, K.; Santos, R.I.; Gilchuk, P.; Gunn, B.M.; Karim, M.M.; Liang, J.; Fouch, M.E.; Davidson, E.; Parekh, D.V.; et al. Non-neutralizing Antibodies from a Marburg Infection Survivor Mediate Protection by Fc-Effector Functions and by Enhancing Efficacy of Other Antibodies. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 976–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mire, C.E.; Geisbert, J.B.; Borisevich, V.; Fenton, K.A.; Agans, K.N.; Flyak, A.I.; Deer, D.J.; Steinkellner, H.; Bohorov, O.; Bohorova, N.; et al. Therapeutic treatment of Marburg and Ravn virus infection in nonhuman primates with a human monoclonal antibody. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brannan, J.M.; He, S.; Howell, K.A.; Prugar, L.I.; Zhu, W.; Vu, H.; Shulenin, S.; Kailasan, S.; Raina, H.; Wong, G.; et al. Post-exposure immunotherapy for two ebolaviruses and Marburg virus in nonhuman primates. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coller, B.G.; Blue, J.; Das, R.; Dubey, S.; Finelli, L.; Gupta, S.; Helmond, F.; Grant-Klein, R.J.; Liu, K.; Simon, J.; et al. Clinical development of a recombinant Ebola vaccine in the midst of an unprecedented epidemic. Vaccine 2017, 35, 4465–4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.B.; Coller, B.A.; Feinberg, M. Unprecedented pace and partnerships: The story of and lessons learned from one Ebola vaccine program. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2018, 17, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cooper, C.L.; Morrow, G.; Yuan, M.; Coleman, J.W.; Hou, F.; Reiserova, L.; Li, S.L.; Wagner, D.; Carpov, A.; Wallace-Selman, O.; et al. Nonhuman Primates Are Protected against Marburg Virus Disease by Vaccination with a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Prepared under Conditions to Allow Advancement to Human Clinical Trials. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101582
Cooper CL, Morrow G, Yuan M, Coleman JW, Hou F, Reiserova L, Li SL, Wagner D, Carpov A, Wallace-Selman O, et al. Nonhuman Primates Are Protected against Marburg Virus Disease by Vaccination with a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Prepared under Conditions to Allow Advancement to Human Clinical Trials. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101582
Chicago/Turabian StyleCooper, Christopher L., Gavin Morrow, Maoli Yuan, John W. Coleman, Fuxiang Hou, Lucia Reiserova, Shui L. Li, Denise Wagner, Alexei Carpov, Olivia Wallace-Selman, and et al. 2022. "Nonhuman Primates Are Protected against Marburg Virus Disease by Vaccination with a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Prepared under Conditions to Allow Advancement to Human Clinical Trials" Vaccines 10, no. 10: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101582
APA StyleCooper, C. L., Morrow, G., Yuan, M., Coleman, J. W., Hou, F., Reiserova, L., Li, S. L., Wagner, D., Carpov, A., Wallace-Selman, O., Valentin, K., Choi, Y., Wilson, A., Kilianski, A., Sayeed, E., Agans, K. N., Borisevich, V., Cross, R. W., Geisbert, T. W., ... Parks, C. L. (2022). Nonhuman Primates Are Protected against Marburg Virus Disease by Vaccination with a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vector-Based Vaccine Prepared under Conditions to Allow Advancement to Human Clinical Trials. Vaccines, 10(10), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101582





