Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from Vitis vinifera for Anticancer Activity on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Stilbenes from Vitis vinifera
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
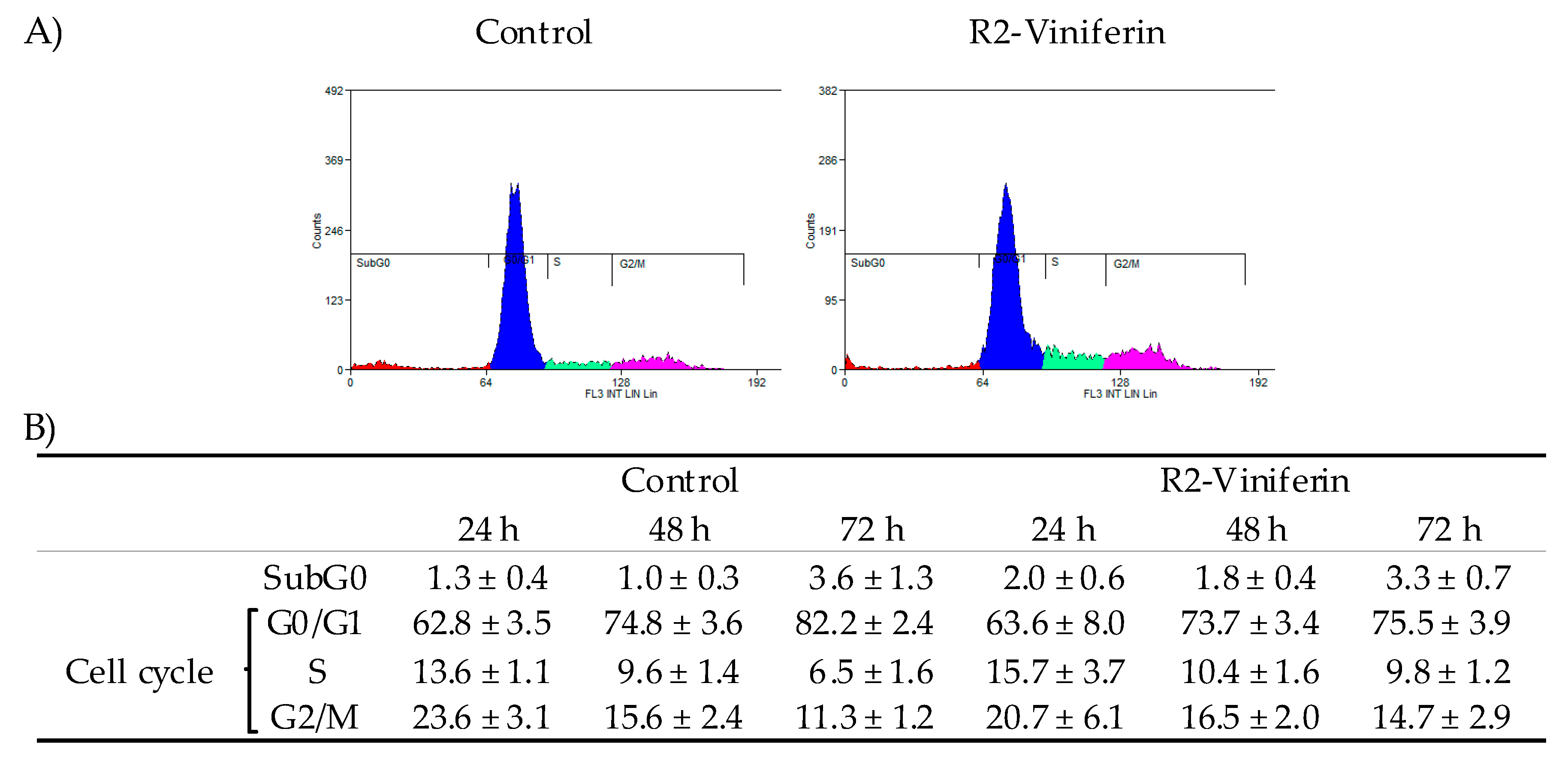
2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.5. Intracellular ROS and Mitochondrial O2− Measurement
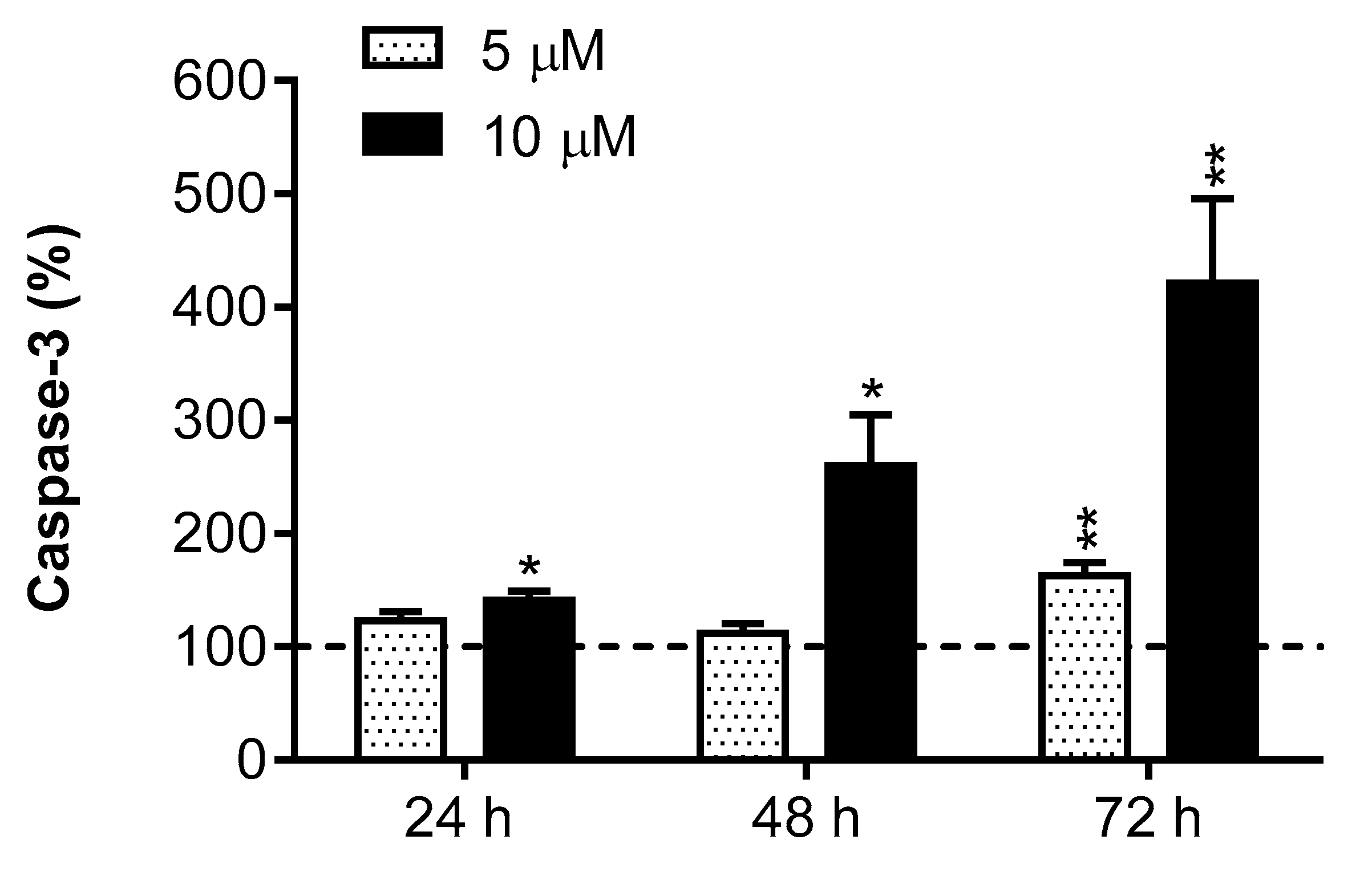
2.6. Caspase-3 Activity
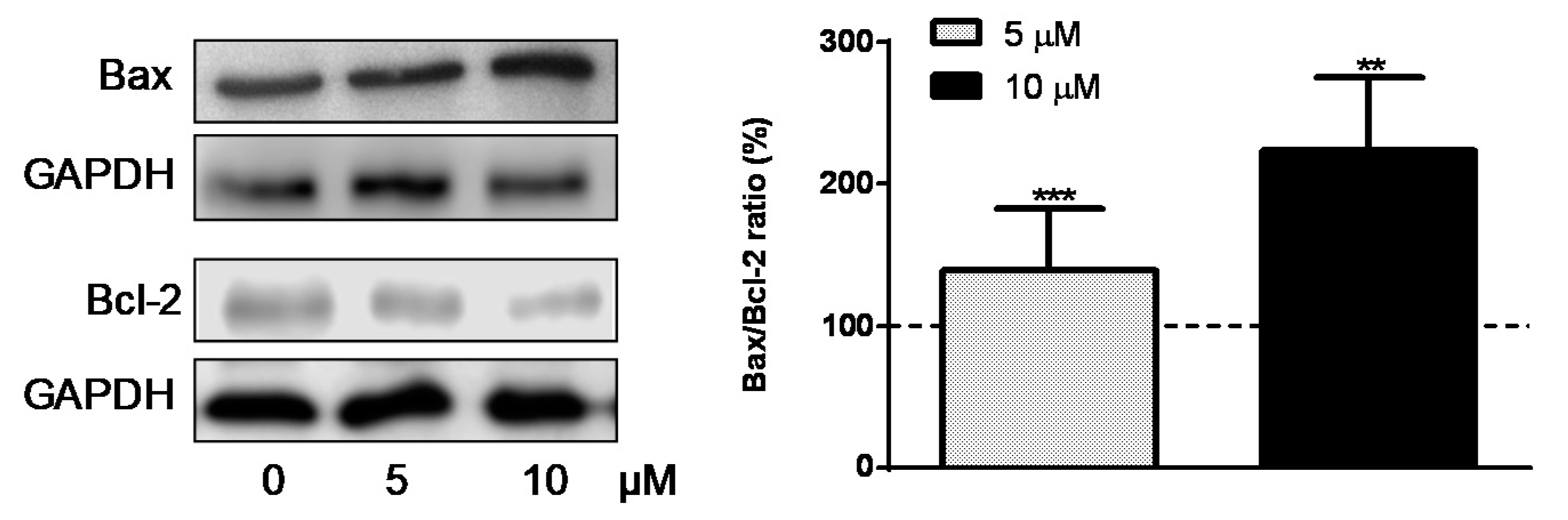
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CDKs | Cyclin-dependent kinases |
| DCF | 2´,7´-Dichlorofluorescein |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| EGTA | Ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid |
| ERK | Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| H2DCF-DA | 2′,7′ Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HEPES | 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| O2− | Superoxide anion |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Mittal, S.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: Consider the population. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 47, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C. Molecular epidemiology of human cancer: Contribution of mutation spectra studies of tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4023–4037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Link, T.; Iwakuma, T. Roles of p53 in extrinsic factor-induced liver carcinogenesis. Hepatoma Res. 2017, 3, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.P.; Schwank, J.; Staib, F.; Wang, X.W.; Harris, C.C. TP53 mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights into the etiology and pathogenesis of liver cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunst, C.; Haderer, M.; Heckel, S.; Schlosser, S.; Müller, M. The p53 family in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, L.; Zalko, D.; Audebert, M. Evaluation of four human cell lines with distinct biotransformation properties for genotoxic screening. Mutagenesis 2016, 31, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant Polyphenols as Dietary Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khawand, T.; Courtois, A.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. A review of dietary stilbenes: Sources and bioavailability. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iveta Pugajeva, I.; Perkonsa, I.; Górnaś, P. Identification and determination of stilbenes by Q-TOF in grape skins, seeds, juice and stems. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2018, 74, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loupit, G.; Prigent, S.; Franc, C.; De Revel, G.; Richard, T.; Cookson, S.Y.; Valls, J. Polyphenol profiles of just pruned grapevine canes from wild Vitis accessions and Vitis vinifera cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero, R.F.; Valls-Fonayet, J.; Richard, T.; Cantos-Villar, E. A rapid quantification of stilbene content in wine by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography – Mass spectrometry. Food Control 2020, 108, 06821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, C.; Qiu, S.; Yuan, X.; Li, L. Effects of Resveratrol on Glucose Control and Insulin Sensitivity in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vervandier-Fasseur, D.; Latruffe, N. The Potential Use of Resveratrol for Cancer Prevention. Molecules 2019, 24, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.K.; Luo, J.Y.; Lau, C.W.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tian, X.Y.; Huang, Y. Pharmacological basis and new insights of resveratrol action in the cardiovascular system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 2019, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.Y.; Wang, Q.; Simonyi, A.; Sun, G.Y. Resveratrol as a therapeutic agent for neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 41, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaston, J.; El Khawand, T.; Waffo-Teguo, P.; Decendit, A.; Richard, T.; Mérillon, J.M.; Pavela, R. Stilbenes from grapevine root: A promising natural insecticide against Leptinotarsa decemlineata. J. Pest. Sci. 2018, 91, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepiana, J.; Meijide, S.; Navarro, R.; Hernandez, M.L.; Ruiz-Sanz, J.I.; Ruiz-Larrea, M.B. Influence of oxygen partial pressure on the characteristics of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willenberg, I.; Brauer, W.; Empl, M.T.; Schebb, N.H. Development of a rapid LC-UV method for the investigation of chemical and metabolic stability of resveratrol oligomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7844–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Inaoka, P.T. Gnetin-C and other resveratrol oligomers with cancer chemopreventive potential. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1403, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baechler, S.A.; Schroeter, A.; Dicker, M.; Steinberg, P.; Marko, D. Topoisomerase II-targeting properties of a grapevine-shoot extract and resveratrol oligomers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, D.; Lancon, A.; Delmas, D.; Lizard, G.; Abrossinow, J.; Kahn, E.; Jannin, B.; Latruffe, N. Antiproliferative activities of resveratrol and related compounds in human hepatocyte derived HepG2 cells are associated with biochemical cell disturbance revealed by fluorescence analyses. Biochimie 2008, 90, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, D.; Zhelev, Z.; Semkova, S.; Aoki, I.; Bakalova, R. Resveratrol Modulates the Redox-status and Cytotoxicity of Anticancer Drugs by Sensitizing Leukemic Lymphocytes and Protecting Normal Lymphocytes. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 3745–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.M.; Tsai, C.W.; Chang, W.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Hung, Y.W.; Lee, H.T.; Shen, C.C.; Sheu, M.L.; Wang, J.Y.; Gong, C.L.; et al. Novel Combination of Arsenic Trioxide (As2O3) Plus Resveratrol in Inducing Programmed Cell Death of Human Neuroblastoma SK-N-SH Cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2018, 15, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Blanco, S.; Fernández, J.; Gutiérrez-Del-Río, I.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. New Insights toward Colorectal Cancer Chemotherapy Using Natural Bioactive Compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisruangsin, A.; Hikita, K.; Seto, N.; Niwa, M.; Takaya, Y.; Kaneda, N. Structural analysis of the inhibitory effects of polyphenols, (+)-hopeaphenol and (−)-isohopeaphenol, on human SIRT1. Biofactors 2018, 45, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asenstrfer, R.E.; Markides, A.J.; Iland, P.G.; Jones, G.P. Formation of R2-viniferin during red wine fermentation and maturation. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2003, 9, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kwon, H.Y.; Sohn, E.J.; Nam, M.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.C.; Ryu, S.Y.; Park, B.; Kim, S.H. Upregulation of death receptor 5 and production of reactive oxygen species mediate sensitization of PC-3 prostate cancer cells to TRAIL induced apoptosis by R2-viniferin. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, M.J.; Davaatseren, M.; Kim, W.; Park, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Hur, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kwon, D.Y. Vitisin A suppresses LPS-induced NO production by inhibiting ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, X.; Yin, Y.; Cai, D.; Li, M.; Zhu, R. JIB-04 induces cell apoptosis via activation of the p53/Bcl-2/caspase pathway in MHCC97H and HepG2 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 3812–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Ding, G. Sepia ink oligopeptide induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines via caspase-3 activation and elevation of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2153–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, D.; Jannin, B.; Cherkaoui, M.; Latruffe, N. Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on the proliferation of human and rat hepatic derived cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2000, 7, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.; Persson, J.L. Cancer therapy: Targeting cell cycle regulators. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongmei Luo, H.; Yang, A.; Schulte, B.A.; Wargovich, M.J.; Wang, G.Y. Resveratrol Induces Premature Senescence in Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated DNA Damage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.A.; Chen, H.; Wan, X.; Tania, M.; Xu, A.; Chen, F.; Zhanget, D. Regulatory effects of resveratrol on antioxidant enzymes: A mechanism of growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in cancer cells. Mol. Cells 2013, 35, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1215, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, S.A.; Gollner, A.; Chiriac, M.I. Regioselective reactions for programmable resveratrol oligomer synthesis. Nature 2011, 474, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, B.S.; Keylor, M.H.; Li, B.; Lin, Y.; Allison, S.; Pratt, D.A.; Stephenson, C.R. A scalable biomimetic synthesis of resveratrol dimers and systematic evaluation of their antioxidant activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 3754–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keylor, M.H.; Matsuura, B.S.; Griesser, M.; Chauvin, J.R.; Harding, R.A.; Kirillova, M.S.; Zhu, X.; Fischer, O.J.; Pratt, D.A.; Stephenson, C.R. Synthesis of resveratrol tetramers via a stereoconvergent radical equilibrium. Science 2016, 354, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Min, J.S.; Kim, D.; Zheng, Y.F.; Mailar, K.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, C.; Bae, S.K. A simple and sensitive liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for trans-ε-viniferin quantification in mouse plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, A.; Atgié, C.; Marchal, A.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Lapèze, C.; Faure, C.; Richard, T.; Krisa, S. Tissular distribution and metabolism of trans-ε-viniferin after intraperitoneal injection in rat. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Hu, M. Bioavailability challenges associated with development of anti-cancer phenolics. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 550–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtois, A.; Garcia, M.; Krisa, S.; Atgié, C.; Sauvant, P.; Richard, T.; Faure, C. Encapsulation of ε-viniferin in onion-type multi-lamellar liposomes increases its solubility and its photo-stability and decreases its cytotoxicity on Caco-2 intestinal cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
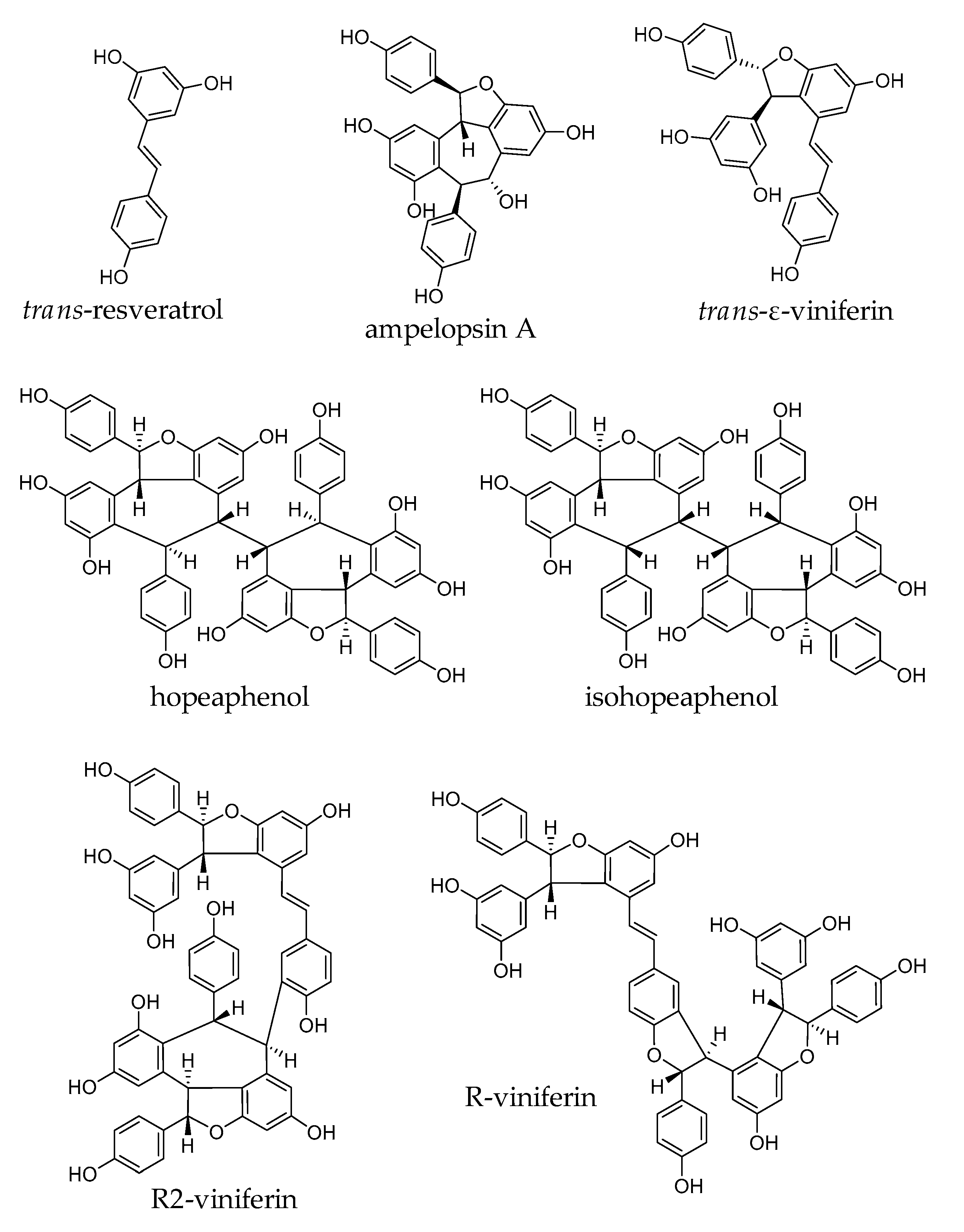
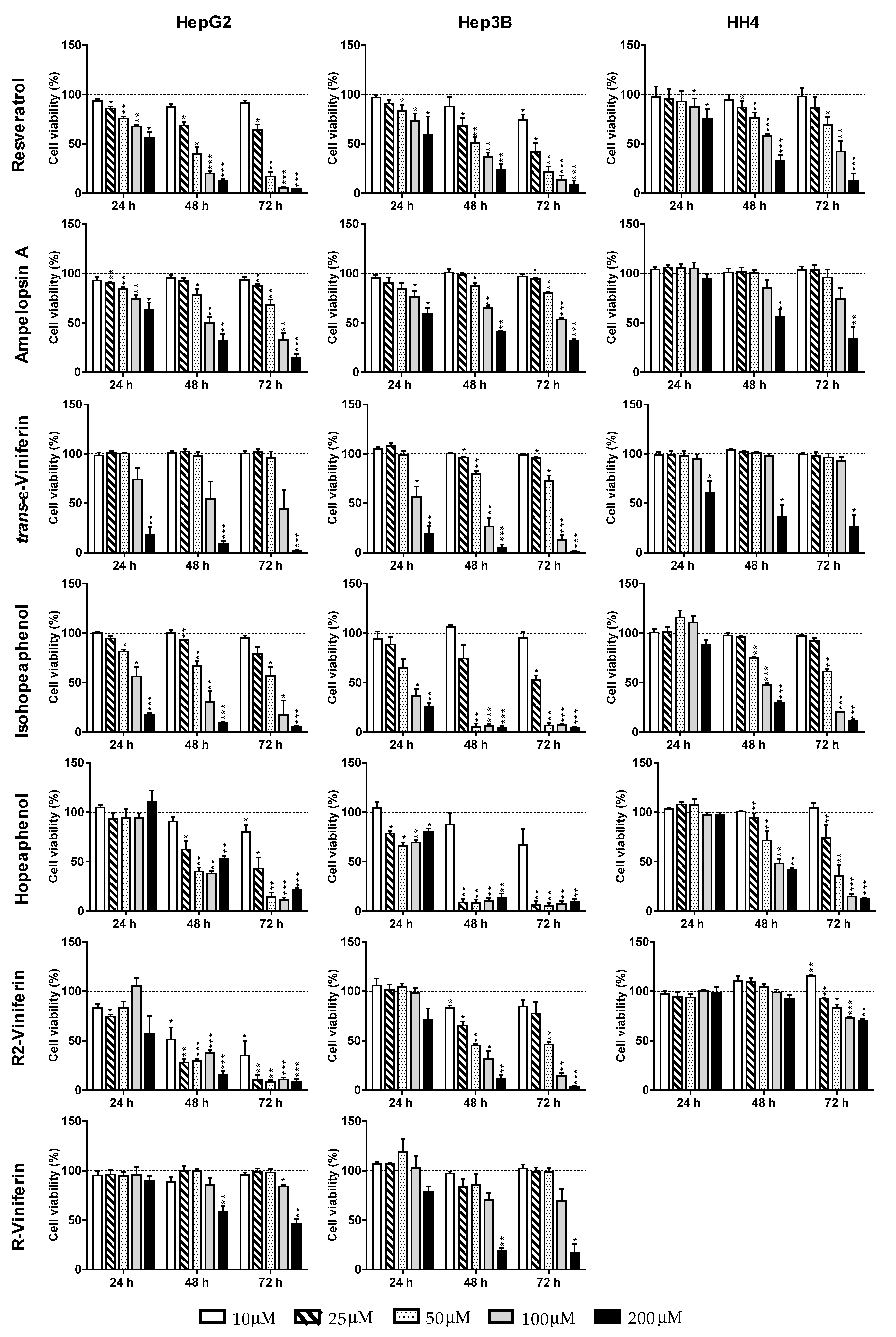
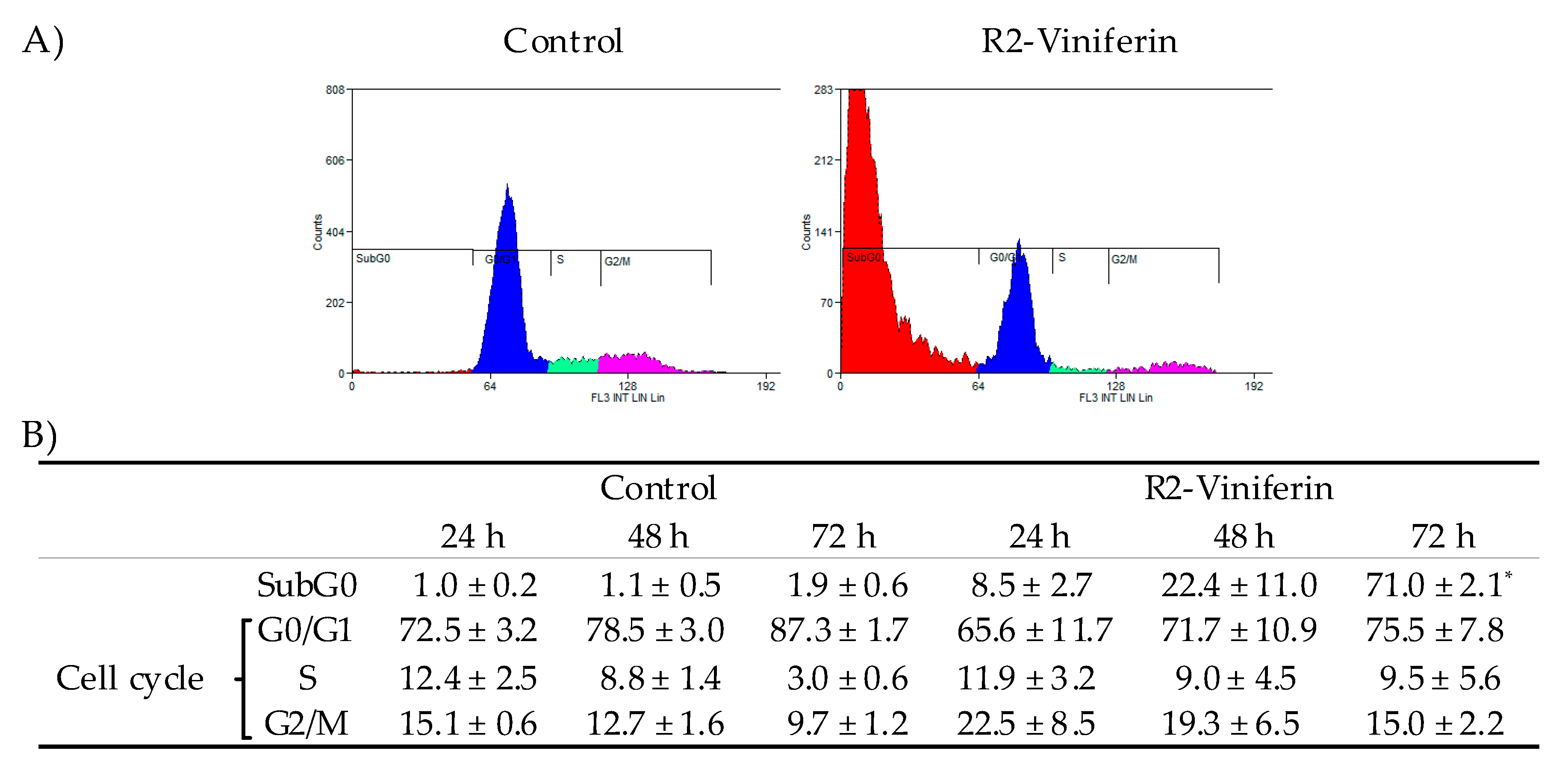

| Compound | Time (h) | HepG2 | Hep3B | HH4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monomer | ||||
| trans-Resveratrol | 24 h | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 48 h | 40.3 ± 9.3 | 42.0 ± 11.6 | 135.0 ± 9.0 | |
| 72 h | 30.3 ± 4.4 | 21.0 ± 16.8 | 93.0 ± 16.1 | |
| Dimer | ||||
| Ampelopsin A | 24 h | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 48 h | 98.6 ± 24.9 | 147.8 ± 14.4 | 178.3 ± 67.8 | |
| 72 h | 75.5 ± 21.5 | 109.1 ± 7.3 | 133.8 ± 34.7 | |
| trans-ε-Viniferin | 24 h | 140.0 ± 39.7 | 108.1 ± 31.8 | >200 |
| 48 h | 103.7 ± 19.2 | 73.9 ± 17.3 | 192.7 ± 21.1 | |
| 72 h | 94.8 ± 28.3 | 63.1 ± 10.8 | 177.9 ± 20.5 | |
| Tetramer | ||||
| Hopeaphenol | 24 h | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 48 h | 27.0 ± 3.3 | 16.8 ± 2.3 | 92.0 ± 38.0 | |
| 72 h | 24.4 ± 2.0 | 13.1 ± 4.1 | 37.6 ± 13.0 | |
| Isohopeaphenol | 24 h | 113.0 ± 33.0 | 86.6 ± 11.7 | >200 |
| 48 h | 68.8 ± 31.0 | 37.0 ± 4.5 | 96.0 ± 5.5 | |
| 72 h | 54.1 ± 34.0 | 26.0 ± 3.0 | 63.7 ± 3.7 | |
| R2-Viniferin | 24 h | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 48 h | 10.2 ± 8.2 | 43.9 ± 3.6 | >200 | |
| 72 h | 9.7 ± 0.4 | 47.8 ± 2.8 | >200 | |
| R-Viniferin | 24 h | >200 | >200 | n.d b |
| 48 h | >200 | 137.2 ± 19.8 | n.d b | |
| 72 h | 192.0 ± 27.1 | 134.9 ± 35.7 | n.d b | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aja, I.; Ruiz-Larrea, M.B.; Courtois, A.; Krisa, S.; Richard, T.; Ruiz-Sanz, J.-I. Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from Vitis vinifera for Anticancer Activity on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060469
Aja I, Ruiz-Larrea MB, Courtois A, Krisa S, Richard T, Ruiz-Sanz J-I. Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from Vitis vinifera for Anticancer Activity on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants. 2020; 9(6):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060469
Chicago/Turabian StyleAja, Iris, M. Begoña Ruiz-Larrea, Arnaud Courtois, Stéphanie Krisa, Tristan Richard, and José-Ignacio Ruiz-Sanz. 2020. "Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from Vitis vinifera for Anticancer Activity on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells" Antioxidants 9, no. 6: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060469
APA StyleAja, I., Ruiz-Larrea, M. B., Courtois, A., Krisa, S., Richard, T., & Ruiz-Sanz, J.-I. (2020). Screening of Natural Stilbene Oligomers from Vitis vinifera for Anticancer Activity on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Antioxidants, 9(6), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060469