The Functions of the Mammalian Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase System and Related Diseases
Abstract
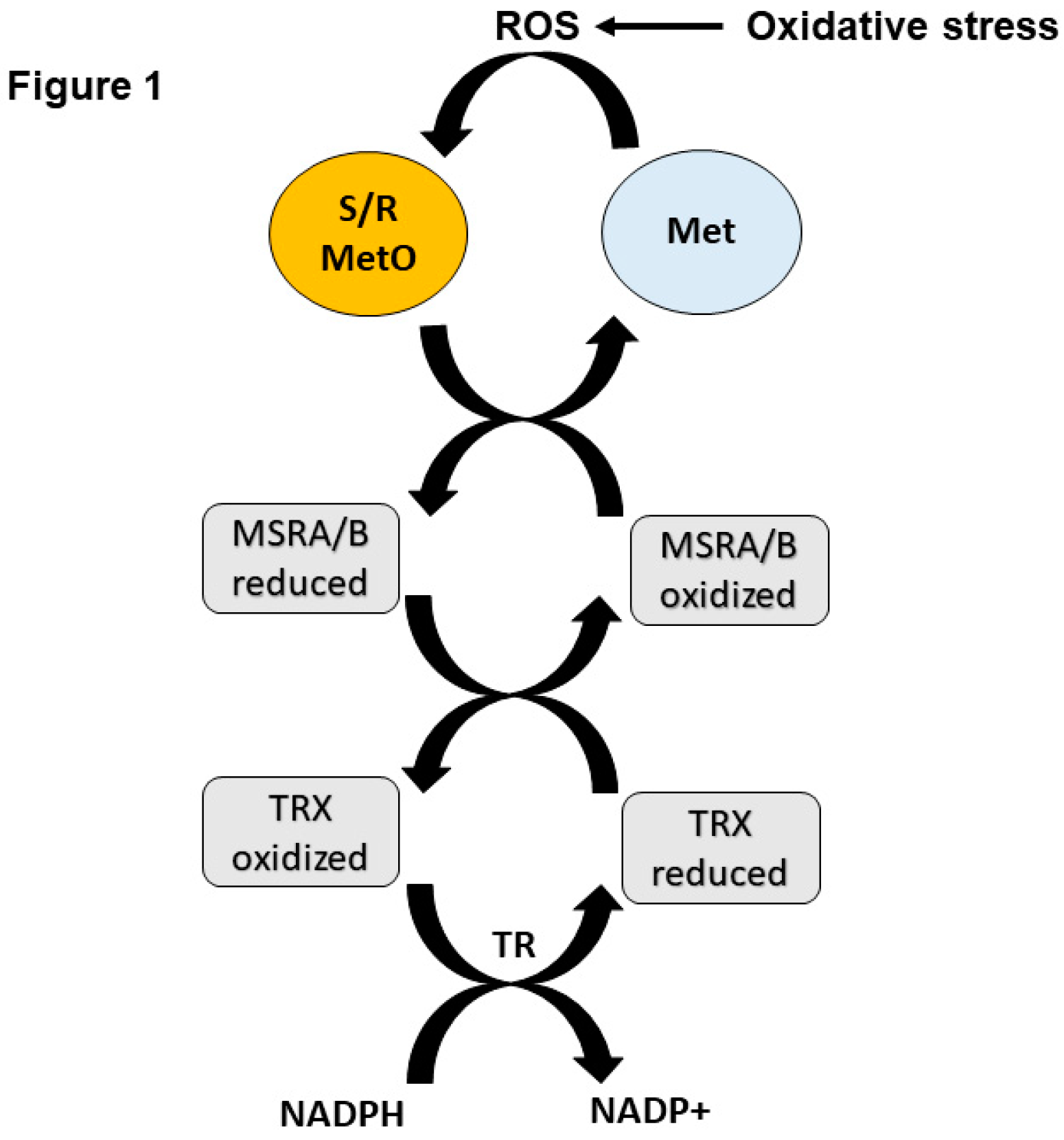
1. Introduction
2. MSRA and Protection Against Oxidative Stress in Mammals
3. MSRA and Neurodegenerative Diseases
3.1. MetO and MSRA and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD)
3.2. MetO and MSRA and Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
3.3. MetO and MSRA and Dopamine-Related Neurological Abnormalities
3.4. MSRA and Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
3.5. MSRA and Liver and Kidney Toxicity
3.6. Role of MSRA and MSRB in Cancer
3.7. Role of MSRA and MSRB in Hearing Loss
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oien, D.B.; Moskovitz, J. Substrates of the methionine sulfoxide reductase system and their physiological relevance. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2008, 80, 134–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ejiri, S.I.; Weissbach, H.; Brot, N. Reduction of methionine sulfoxide to methionine by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 139, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Johnson, L.C.; Weissbach, H.; Brot, N.; Lively, M.O.; Lowther, W.T. Free methionine-(R)-sulfoxide reductase from Escherichia coli reveals a new GAF domain function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9597–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oien, D.B.; Moskovitz, J. Selenium and the methionine sulfoxide reductase system. Molecules 2009, 14, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Cole, N.B.; Lim, J.C.; Zhao, H.; Levine, R.L. Dual sites of protein initiation control the localization and myristoylation of methionine sulfoxide reductase A. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18085–18094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Gilbert, D.J.; Copeland, N.G.; Jursky, F.; Weissbach, H.; Brot, N. Chromosomal localization of the mammalian peptide-methionine sulfoxide reductase gene and its differential expression in various tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 3205–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Stadtman, E.R. Selenium-deficient diet enhances protein oxidation and affects methionine sulfoxide reductase (MSRB) protein level in certain mouse tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7486–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fomenko, D.E.; Novoselov, S.V.; Natarajan, S.K.; Lee, B.C.; Koc, A.; Carlson, B.A.; Lee, T.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Hatfield, D.L.; Gladyshev, V.N. MSRB1 (methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase 1) knock-out mice: Roles of MSRB1 in redox regulation and identification of a novel selenoprotein form. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5986–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J. Methionine sulfoxide reductases: Ubiquitous enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, protein regulation, and prevention of aging-associated diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1703, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Oien, D.B.; Ersen, F.Y.; Moskovitz, J. Elevated levels of brain-pathologies associated with neurodegenerative diseases in the methionine sulfoxide reductase A knockout mouse. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 180, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Du, F.; Bowman, C.F.; Yan, S.S. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A affects β-amyloid solubility and mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E388–E393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oien, D.B.; Osterhaus, G.L.; Latif, S.A.; Pinkston, J.W.; Fulks, J.; Johnson, M.; Fowler, S.C.; Moskovitz, J. MSRA knockout mouse exhibits abnormal behavior and brain dopamine levels. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Walss-Bass, C.; Cruz, D.A.; Thompson, P.M.; Bortolato, M. Methionine sulfoxide reductase regulates brain catechol-O-methyl transferase activity. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1707–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Walss-Bass, C.; Cruz, D.A.; Thompson, P.M.; Hairston, J.; Bortolato, M. The enzymatic activities of brain catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and methionine sulphoxide reductase are correlated in a COMT Val/Met allele-dependent fashion. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2015, 41, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, J.R.; Joiner, M.L.; Guan, X.; Kutschke, W.; Yang, J.; Oddis, C.V.; Bartlett, R.K.; Lowe, J.S.; O’Donnell, S.E.; Aykin-Burns, N.; et al. A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation. Cell 2008, 133, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.P.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, H.Y. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A deficiency exacerbates acute liver injury induced by acetaminophen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 484, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Sanna, F.; Sallese, M.; Ruggiero, C.; Grossi, M.; Sacchetta, P.; Rossi, C.; De Laurenzi, V.; Di Ilio, C.; Favaloro, B. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A down-regulation in human breast cancer cells results in a more aggressive phenotype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18628–18633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.F.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhu, X.Q.; Lu, P.C.; Sun, B.S.; Jia, H.L.; Ren, N.; Ye, Q.H.; Sun, H.C.; Wang, L.; et al. Identification of MSRA gene on chromosome 8p as a candidate metastasis suppressor for human hepatitis B virus-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.B.; Doshi, V.K.; Blackman, S.M.; Naughton, K.M.; Pace, R.G.; Moskovitz, J.; Knowles, M.R.; Durie, P.R.; Drumm, M.L.; Cutting, G.R. Variation in MSRA modifies risk of neonatal intestinal obstruction in cystic fibrosis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, 1002580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman, E.R.; Moskovitz, J.; Berlett, B.S.; Levine, R.L. Cyclic oxidation and reduction of protein methionine residues is an important antioxidant mechanism. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2002, 234–235, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskovitz, J.; Berlett, B.S.; Poston, J.M.; Stadtman, E.R. The yeast peptide-methionine sulfoxide reductase functions as an antioxidant in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 9585–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Bar-Noy, S.; Williams, W.M.; Requena, J.; Berlett, B.S.; Stadtman, E.R. Methionine sulfoxide reductase (MSRA) is a regulator of antioxidant defense and lifespan in mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12920–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, A.B.; Pérez, V.I.; Bokov, A.; Jernigan, A.; Kim, G.; Zhao, H.; Levine, R.L.; Richardson, A. Lack of methionine sulfoxide reductase A in mice increases sensitivity to oxidative stress but does not diminish life span. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3601–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Flescher, E.; Berlett, B.S.; Azare, J.; Poston, J.M.; Stadtman, E.R. Overexpression of peptide-methionine sulfoxide reductase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human T cells provides them with high resistance to oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14071–14075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Tang, X.D.; Chen, M.L.; Joiner, M.L.; Sun, G.; Brot, N.; Weissbach, H.; Heinemann, S.H.; Iverson, L.; Wu, C.F.; et al. High-quality life extension by the enzyme peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2748–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minniti, A.N.; Cataldo, R.; Trigo, C.; Vasquez, L.; Mujica, P.; Leighton, F.; Inestrosa, N.C.; Aldunate, R. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A expression is regulated by the DAF-16/FOXO pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 2009, 8, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskovitz, J.; Maiti, P.; Lopes, D.H.; Oien, D.B.; Attar, A.; Liu, T.; Mittal, S.; Hayes, J.; Bitan, G. Induction of methionine-sulfoxide reductases protects neurons from amyloid β-protein insults in vitro and in vivo. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 10687–10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, J.M.; Carrasco, G.A.; Moskovitz, J. Induction of methionine sulfoxide reductase activity by pergolide, pergolide sulfoxide, and S-adenosyl-methionine in neuronal cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 533, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Pappolla, M.A.; Wade, R.; Hirai, K.; Chiba, S.; Smith, M.A. RNA oxidation is a prominent feature of vulnerable neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 741–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, K.; Aliev, G.; Nunomura, A.; Fujioka, H.; Russell, R.L.; Atwood, C.S.; Johnson, A.B.; Kress, Y.; Vinters, H.V.; Tabaton, M.; et al. Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 3017–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praticò, D. Evidence of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease brain and antioxidant therapy: Lights and shadows. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1147, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitan, G.; Tarus, B.; Vollers, S.S.; Lashuel, H.A.; Condron, M.M.; Straub, J.E.; Teplow, D.B. A molecular switch in amyloid assembly: Met35 and amyloid beta-protein oligomerization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 25, 15359–15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, J.; Schierhorn, A.; Hellman, U.; Lannfeltm, L.; Roses, A.D.; Tjernberg, L.O.; Silberring, J.; Gandy, S.E.; Winblad, B.; Greengard, P. Relative abundance of Alzheimer A beta amyloid peptide variants in Alzheimer disease and normal aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 8378–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.M.; Kokjohn, T.A.; Beach, T.G.; Sue, L.I.; Brune, D.; Lopez, J.C.; Kalback, W.M.; Abramowski, D.; Sturchler-Pierrat, C.; Staufenbiel, M.; et al. Comparative analysis of amyloid-beta chemical structure and amyloid plaque morphology of transgenic mouse and Alzheimer’s disease brains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12991–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Atwood, C.S.; Anderson, V.E.; Siedlak, S.L.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G.; Carey, P.R. Metal binding and oxidation of amyloid-beta within isolated senile plaque cores: Raman microscopic evidence. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 2768–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutte, A.M.; Woltjer, R.L.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Stamer, S.L.; Montine, K.S.; Manno, M.V.; Cimino, P.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Montine, T.J. Selectively increased oxidative modifications mapped to detergent-insoluble forms of Abeta and beta-III tubulin in Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Boyd-Kimball, D. The critical role of methionine 35 in Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1703, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triguero, L.; Singh, R.; Prabhakar, R. Comparative molecular dynamics studies of wild-type and oxidized forms of full-length Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptides Abeta (1-40) and Abeta (1-42). J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 7123–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oien, D.B.; Shinogle, H.E.; Moore, D.S.; Moskovitz, J. Clearance and phosphorylation of alpha-synuclein are inhibited in methionine sulfoxide reductase a null yeast cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2009, 39, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassef, R.; Haenold, R.; Hansel, A.; Brot, N.; Heinemann, S.H.; Hoshi, T. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A and a dietary supplement S-methyl-l-cysteine prevent Parkinson’s-like symptoms. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12808–12816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Hindupur, J.; Nguyen, J.L.; Ruf, K.J.; Zhu, J.; Schieler, J.L.; Bonham, C.C.; Wood, K.V.; Davisson, V.J.; Rochet, J.C. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A protects dopaminergic cells from Parkinson’s disease-related insults. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooley, C.M.; Sher, R.B.; Kale, A.; Frankel, W.N.; Cox, G.A.; Seburn, K.L. Gait analysis detects early changes in transgenic SOD1(G93A) mice. Muscle Nerve 2005, 32, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oien, D.B.; Ortiz, A.N.; Rittel, A.G.; Dobrowsky, R.T.; Johnson, M.A.; Levant, B.; Fowler, S.C.; Moskovitz, J. Dopamine D(2) receptor function is compromised in the brain of the methionine sulfoxide reductase A knockout mouse. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.P.; Kwak, G.H.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, H.Y. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A protects hepatocytes against acetaminophen-induced toxicity via regulation of thioredoxin reductase 1 expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, M.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, K.M. Methionine sulfoxide Reductase A deficiency exacerbates cisplatin-Induced nephrotoxicity via increased mitochondrial damage and renal cell death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Li, H.; Meng, F.; Sun, X.; Feng, X.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase B1 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Invasion via the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 5287971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, G.H.; Kim, H.Y. MSRB3 deficiency induces cancer cell apoptosis through p53-independent and ER stress-dependent pathways. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 621, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, A.P.; Ginestier, C.; Pommier, R.M.; Cabaud, O.; Ruiz, E.; Wicinski, J.; Devouassoux-Shisheboran, M.; Combaret, V.; Finetti, P.; Chassot, C.; et al. A stemness-related ZEB1-MSRB3 axis governs cellular pliancy and breast cancer genome. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.M.; Yousaf, R.; Lee, B.C.; Khan, S.N.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Husnain, T.; Rehman, A.U.; Bonneux, S.; Ansar, M.; et al. Functional null mutations of MSRB3 encoding methionine sulfoxide reductase are associated with human deafness DFNB74. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, T.J.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, U.K.; Lee, E.; Oh, S.K.; Bok, J.; Bae, Y.C.; Yi, J.K.; Lee, J.W.; Ryoo, Z.Y.; et al. Methionine sulfoxide reductase B3 deficiency causes hearing loss due to stereocilia degeneration and apoptotic cell death in cochlear hair cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqudah, S.; Chertoff, M.; Durham, D.; Moskovitz, J.; Staecker, H.; Peppi, M. Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A Knockout Mice Show Progressive Hearing Loss and Sensitivity to Acoustic Trauma. Audiol. Neurootol. 2018, 23, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Adams, Z.; Liu, R.; Hepowit, N.L.; Wu, Y.; Bowmann, C.F.; Moskovitz, J.; Maupin-Furlow, J.A. Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase A (MSRA) and Its Function in Ubiquitin-Like Protein Modification in Archaea. mBio 2017, 8, e01169-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Rankin, C.L.; Toyo-Oka, K.; Richter, M.L.; Maupin-Furlow, J.A.; Moskovitz, J. Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) mediates the ubiquitination of 14-3-3 protein isotypes in brain. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, B.; Moskovitz, J. The Functions of the Mammalian Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase System and Related Diseases. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7090122
Jiang B, Moskovitz J. The Functions of the Mammalian Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase System and Related Diseases. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(9):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7090122
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Beichen, and Jackob Moskovitz. 2018. "The Functions of the Mammalian Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase System and Related Diseases" Antioxidants 7, no. 9: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7090122
APA StyleJiang, B., & Moskovitz, J. (2018). The Functions of the Mammalian Methionine Sulfoxide Reductase System and Related Diseases. Antioxidants, 7(9), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7090122





