Spatial Memory Dysfunction Induced by Vitamin C Deficiency Is Associated with Changes in Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters and Aberrant Synapse Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters
2.3. Protein Extraction
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Statistics
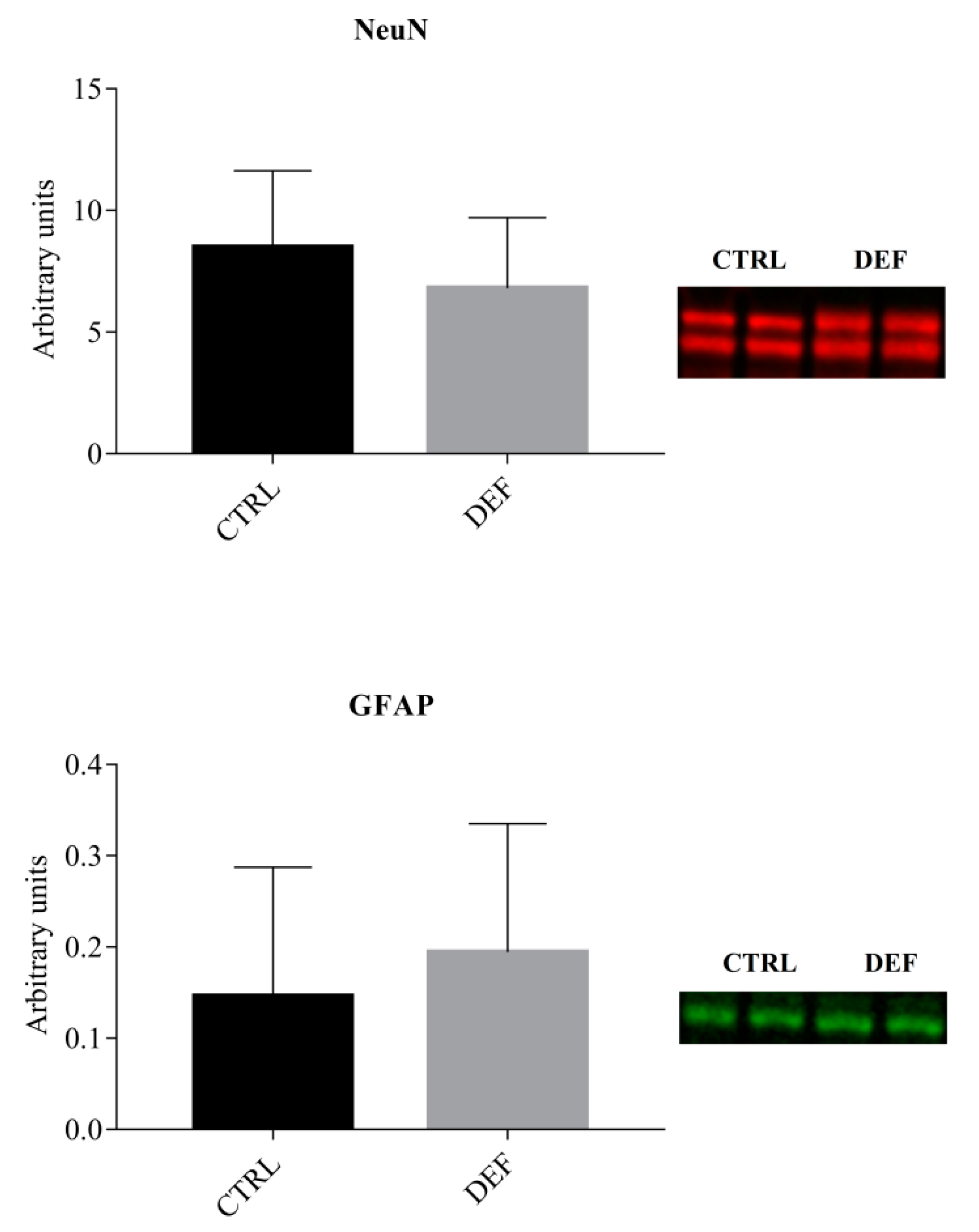
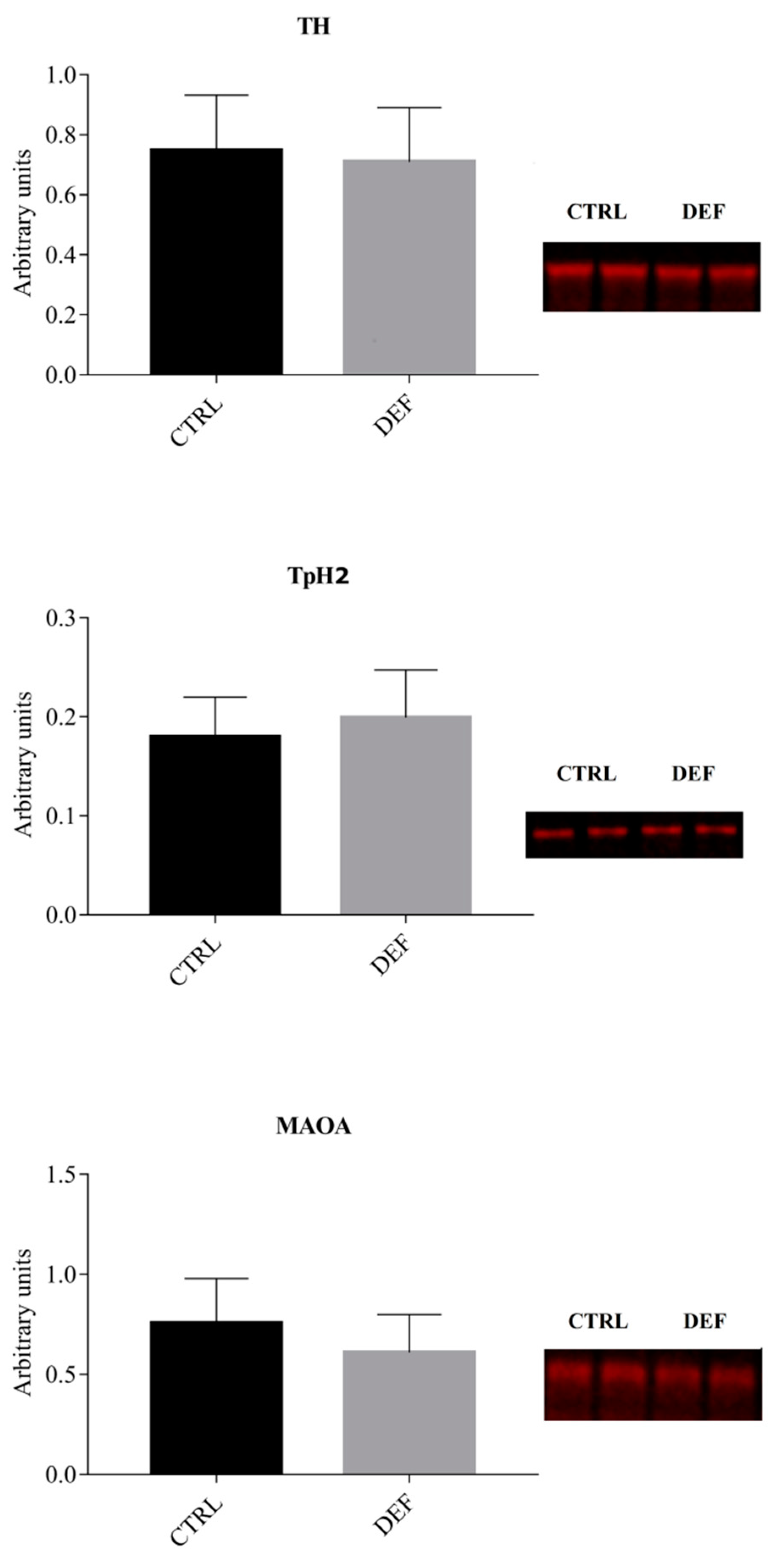
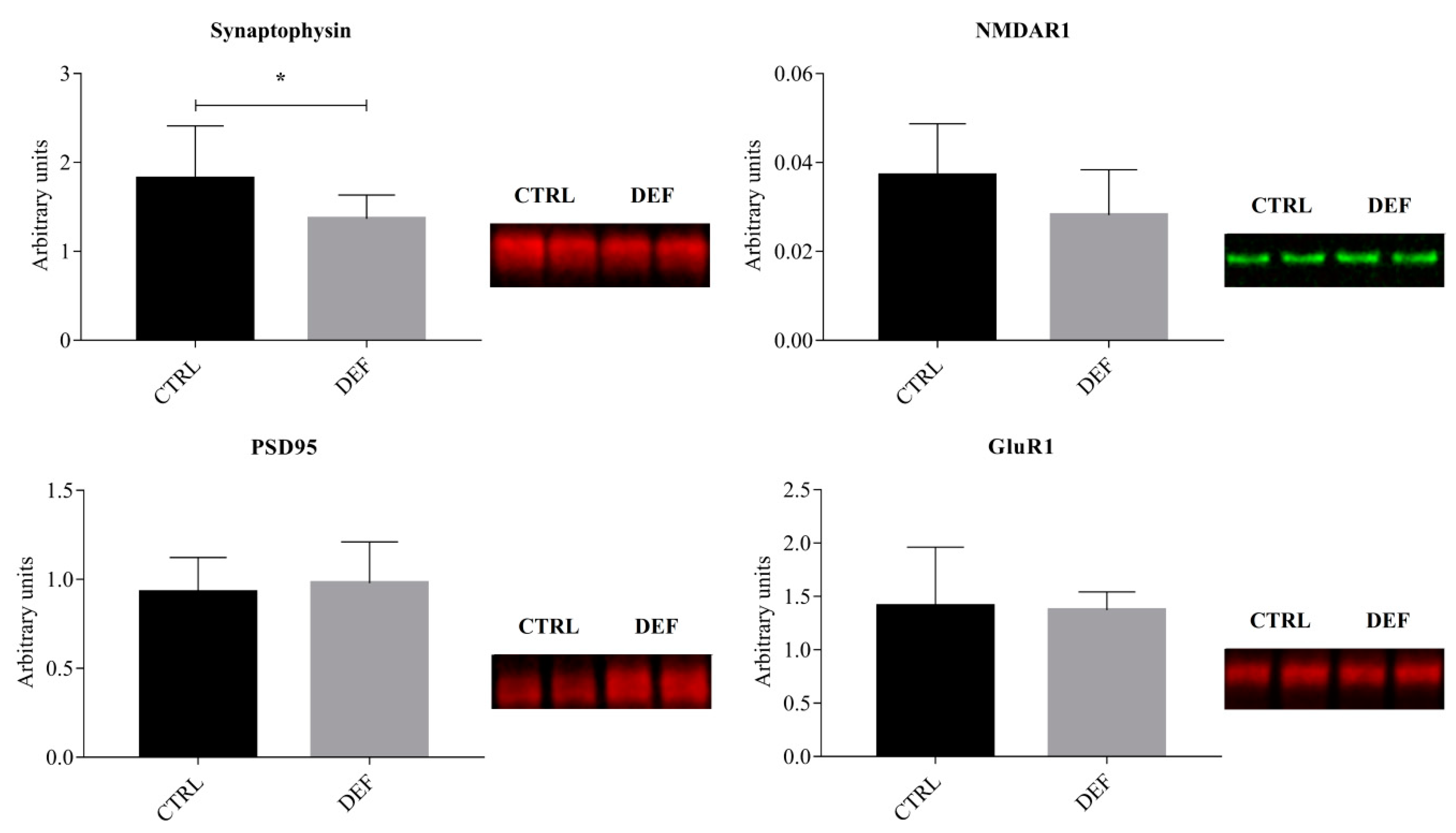
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Langlois, K.; Cooper, M.; Colapinto, C.K. Vitamin C status of Canadian adults: Findings from the 2012/2013 Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Rep. 2016, 27, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hampl, J.S.; Taylor, C.A.; Johnston, C.S. Vitamin C deficiency and depletion in the United States: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988 to 1994. Am. J. Public Health 2004, 94, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüpbach, R.; Wegmüller, R.; Berguerand, C.; Bui, M.; Herter-Aeberli, I. Micronutrient status and intake in omnivores, vegetarians and vegans in Switzerland. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, R.M.; Lopez-Sobaler, A.M.; Quintas, M.E.; Martinez, R.M.; Andres, P. The influence of smoking on vitamin C status during the third trimester of pregnancy and on vitamin C levels in maternal milk. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1998, 17, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, A.M.; Rondó, P.H.C.; Mastroeni, S.S.; Oliveira, J.M. Plasma concentrations of ascorbic acid in parturients from a hospital in Southeast Brazil. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbing, J. Later growth of the brain and its vulnerability. Pediatrics 1974, 53, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikonomidou, C.; Kaindl, A.M. Neuronal death and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 14, 1535–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.E.; Hurley, R.J.; Jones, P.R. Retention of ascorbic acid by guinea pig tissues. Br. J. Nutr. 1971, 26, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasselholt, S.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Distribution of vitamin C is tissue specific with early saturation of the brain and adrenal glands following differential oral dose regimens in guinea pigs. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Johansen, L.K.; Raida, Z.; Villumsen, C.K.; Larsen, J.O.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Vitamin C deficiency in early postnatal life impairs spatial memory and reduces the number of hippocampal neurons in guinea pigs. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Vogt, L.; Schjoldager, J.G.; Jeannet, N.; Hasselholt, S.; Paidi, M.D.; Christen, S.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Maternal vitamin C deficiency during pregnancy persistently impairs hippocampal neurogenesis in offspring of guinea pigs. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishikimi, M.; Kawai, T.; Yagi, K. Guinea pigs possess a highly mutated gene for l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the key ezyme for l-ascorbic-acid biosynthesis missing in this species. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 21967–21972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikimi, M.; Fukuyama, R.; Minoshima, S.; Shimizu, N.; Yagi, K. Cloning and chromosomal mapping of the human nonfunctional gene for l-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase, the ezyme for l-ascorbic-acid biosynthesis missing in man. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 13685–13688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, S.; Li, L.; Weeber, E.J.; May, J.M. Ascorbate transport by primary cultured neurons and its role in neuronal function and protection against excitotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandstrom, M.I.; Rebec, G.V. Extracellular ascorbate modulates glutamate dynamics: Role of behavioral activation. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebec, G.V.; Pierce, R.C. A vitamin as a neuromodulator—Ascorbate release into the extracellular fluid of the brain regulates dopaminergic and glutaminergic transmission. Prog. Neurobiol. 1994, 43, 537–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.S.; Lamb, J.; May, J.M.; Harrison, F.E. Behavioral and monoamine changes following severe vitamin C deficiency. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith, M.E.; May, J.M. Regulation of embryonic neurotransmitter and tyrosine hydroxylase protein levels by ascorbic acid. Brain Res. 2013, 1539, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diliberto, E.J.; Allen, P.L. Semidehydroascorbate as a product of the enzymic conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine—Coupling of semidehydroascorbate reductase to dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Mol. Pharmacol. 1980, 17, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beutler, L.R.; Eldred, K.C.; Quintana, A.; Keene, C.D.; Rose, S.E.; Postupna, N.; Montine, T.J.; Palmiter, R.D. Severely impaired learning and altered neuronal morphology in mice lacking NMDA receptors in medium spiny neurons. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.E.; Greenberg, M.E. Neuronal activity-regulated gene transcription in synapse development and cognitive function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, T.; Gal-Ben-Ari, S.; Dieterich, D.C.; Kreutz, M.R.; Ziv, N.E.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Rosenblum, K. The roles of protein expression in synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copf, T. Impairments in dendrite morphogenesis as etiology for neurodevelopmental disorders and implications for therapeutic treatments. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 68, 946–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schou-Pedersen, A.M.V.; Hansen, S.N.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J. Simultaneous quantification of monoamine neurotransmitters and their biogenic metabolites intracellularly and extracellularly in primary neuronal cell cultures and in sub-regions of guinea pig brain. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1028, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Søgaard, D.; Lindblad, M.M.; Paidi, M.D.; Hasselholt, S.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. In vivo vitamin C deficiency in guinea pigs increases ascorbate transporters in liver but not kidney and brain. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, P.F. Tetrahydropterin-dependent amino acid hydroxylases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutknecht, L.; Kriegebaum, C.; Waider, J.; Schmitt, A.; Lesch, K.P. Spatio-temporal expression of tryptophan hydroxylase isoforms in murine and human brain: Convergent data from Tph2 knockout mice. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 19, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zill, P.; Büttner, A.; Eisenmenger, W.; Möller, H.-J.; Ackenheil, M.; Bondy, B. Analysis of tryptophan hydroxylase I and II mRNA expression in the human brain: A post-mortem study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.Y.; Halaris, A.E. Hippocampal innervation by serotonin neurons of the midbrain raphe in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1975, 164, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabeg, M.M.; Grauthoff, S.; Kollert, S.Y.; Weidner, M.; Heiming, R.S.; Jansen, F.; Popp, S.; Kaiser, S.; Lesch, K.-P.; Sachser, N.; et al. 5-HTT deficiency affects neuroplasticity and increases stress sensitivity resulting in altered spatial learning performance in the Morris Water Maze but not in the Barnes Maze. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saroja, S.R.; Kim, E.-J.; Shanmugasundaram, B.; Höger, H.; Lubec, G. Hippocampal monoamine receptor complex levels linked to spatial memory decline in the aging C57BL/6J. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 264, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The serotonergic 5-HT4 receptor: A unique modulator of hippocampal synaptic information processing and cognition. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2017, 138, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alder, J.; Kanki, H.; Valtorta, F.; Greengard, P.; Poo, M.M. Overexpression of synaptophysin enhances neurotransmitter secretion at Xenopus neuromuscular synapses. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.E.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptophysin regulates the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis in central neurons. Neuron 2011, 70, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarsa, L.; Goda, Y. Synaptophysin regulates activity-dependent synapse formation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, U.; Tanimoto, N.; Seeliger, M.; Schaeffel, F.; Leube, R.E. Detection of behavioral alterations and learning deficits in mice lacking synaptophysin. Neuroscience 2009, 162, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Yue, C.; Tang, Y. Neonatal exposure to BDE 209 impaired learning and memory, decreased expression of hippocampal core SNAREs and synaptophysin in adult rats. Neurotoxicology 2017, 59, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, C.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, L. Long-term neurocognitive dysfunction in offspring via NGF/ ERK/CREB signaling pathway caused by ketamine exposure during the second trimester of pregnancy in rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30956–30970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-J.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-R.; Tseng, G.-F. Hydrocephalus compacted cortex and hippocampus and altered their output neurons in association with spatial learning and memory deficits in rats. Brain Pathol. 2017, 27, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, G.J.O.; Cousin, M.A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of synaptophysin in synaptic vesicle recycling. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullany, P.M.; Lynch, M.A. Evidence for a role for synaptophysin in expression of long-term potentiation in rat dentate gyrus. NeuroReport 1998, 9, 2489–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, J.Z.; Huerta, P.T.; Tonegawa, S. The essential role of hippocampal CA1 NMDA receptor–dependent synaptic plasticity in spatial memory. Cell 1996, 87, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, B.E.; Nicoll, R.A. Long-term potentiation: From CaMKII to AMPA receptor trafficking. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Collingridge, G.L. A synaptic model of memory—Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 1993, 361, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, P.; Bellone, C.; Zhou, Q. NMDA receptor subunit diversity: Impact on receptor properties, synaptic plasticity and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-K.; Takamiya, K.; Han, J.-S.; Man, H.; Kim, C.-H.; Rumbaugh, G.; Yu, S.; Ding, L.; He, C.; Petralia, R.S.; et al. Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit is required for synaptic plasticity and retention of spatial memory. Cell 2003, 112, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Taverna, F.A.; McDonald, R.J.; Muller, R.U.; Roder, J.C. Place-cell impairment in glutamate receptor 2 mutant mice. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, Rc204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group/Neurotransmitter | CTRL (n = 15) | DEF (n = 12) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MHPG | 0.32 ± 0.09 | 0.35 ± 0.10 | NS |
| Norepinephrine | 2.81 ± 1.07 | 2.32 ± 0.75 | NS |
| MHPG/Norepinephrine * | 0.12 (0.10; 0.14) | 0.15 (0.12; 0.19) | NS |
| 5-HIAA | 0.83 ± 0.16 | 0.99 ± 0.27 | NS |
| 5-HT * | 2.07 (1.79; 2.40) | 2.2 (1.75; 2.93) | NS |
| 5-HIAA/5-HT | 0.47 ± 0.12 | 0.36 ± 0.08 | p = 0.0093 |
| HVA | ND | ND | ND |
| DOPAC | ND | ND | ND |
| Dopamine | ND | ND | ND |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansen, S.N.; Schou-Pedersen, A.M.V.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Spatial Memory Dysfunction Induced by Vitamin C Deficiency Is Associated with Changes in Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters and Aberrant Synapse Formation. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070082
Hansen SN, Schou-Pedersen AMV, Lykkesfeldt J, Tveden-Nyborg P. Spatial Memory Dysfunction Induced by Vitamin C Deficiency Is Associated with Changes in Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters and Aberrant Synapse Formation. Antioxidants. 2018; 7(7):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070082
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansen, Stine Normann, Anne Marie V. Schou-Pedersen, Jens Lykkesfeldt, and Pernille Tveden-Nyborg. 2018. "Spatial Memory Dysfunction Induced by Vitamin C Deficiency Is Associated with Changes in Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters and Aberrant Synapse Formation" Antioxidants 7, no. 7: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070082
APA StyleHansen, S. N., Schou-Pedersen, A. M. V., Lykkesfeldt, J., & Tveden-Nyborg, P. (2018). Spatial Memory Dysfunction Induced by Vitamin C Deficiency Is Associated with Changes in Monoaminergic Neurotransmitters and Aberrant Synapse Formation. Antioxidants, 7(7), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox7070082






