Naringin and Naringenin in Liver Health: A Review of Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
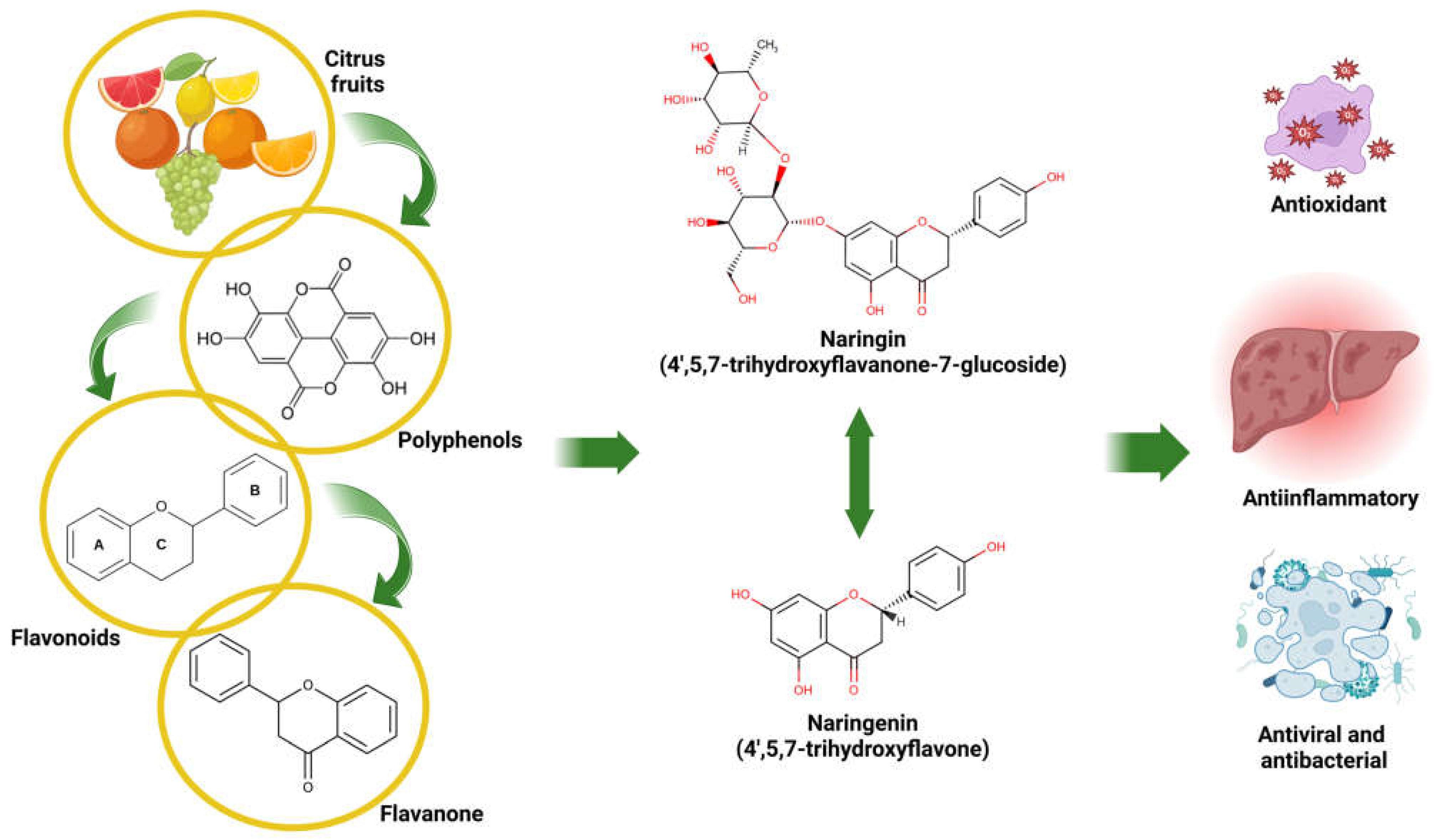
3. NARI and NAR: Two Phytochemicals with Promising Health Benefits
3.1. Physicochemical and Pharmacological Properties of NARI and NAR
3.2. NARI: Biotransformation and Metabolism
3.3. NAR: Biotransformation and Metabolism
3.4. Key Pharmacokinetic Studies in Humans
4. NARI and NAR in Liver Diseases: Efficacy, Safety, and Insights into Gene Regulatory Mechanisms
4.1. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ALD)
4.2. Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease: Viral Hepatitis
4.3. Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease: Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
4.4. Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI)
4.5. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
5. NARI and NAR as Epigenetic Modulators and Their Impact on Treating Liver Diseases
5.1. Epigenetic Targets in Liver Diseases Landscape
5.2. Natural Compounds with Epigenetic Targets and Their Use in Liver Diseases
5.3. Epigenetic Regulation Modulated by NARI and NAR, an Opportunity Area for the Therapeutic Positioning of These Flavonoids: Basic and Clinical Evidence
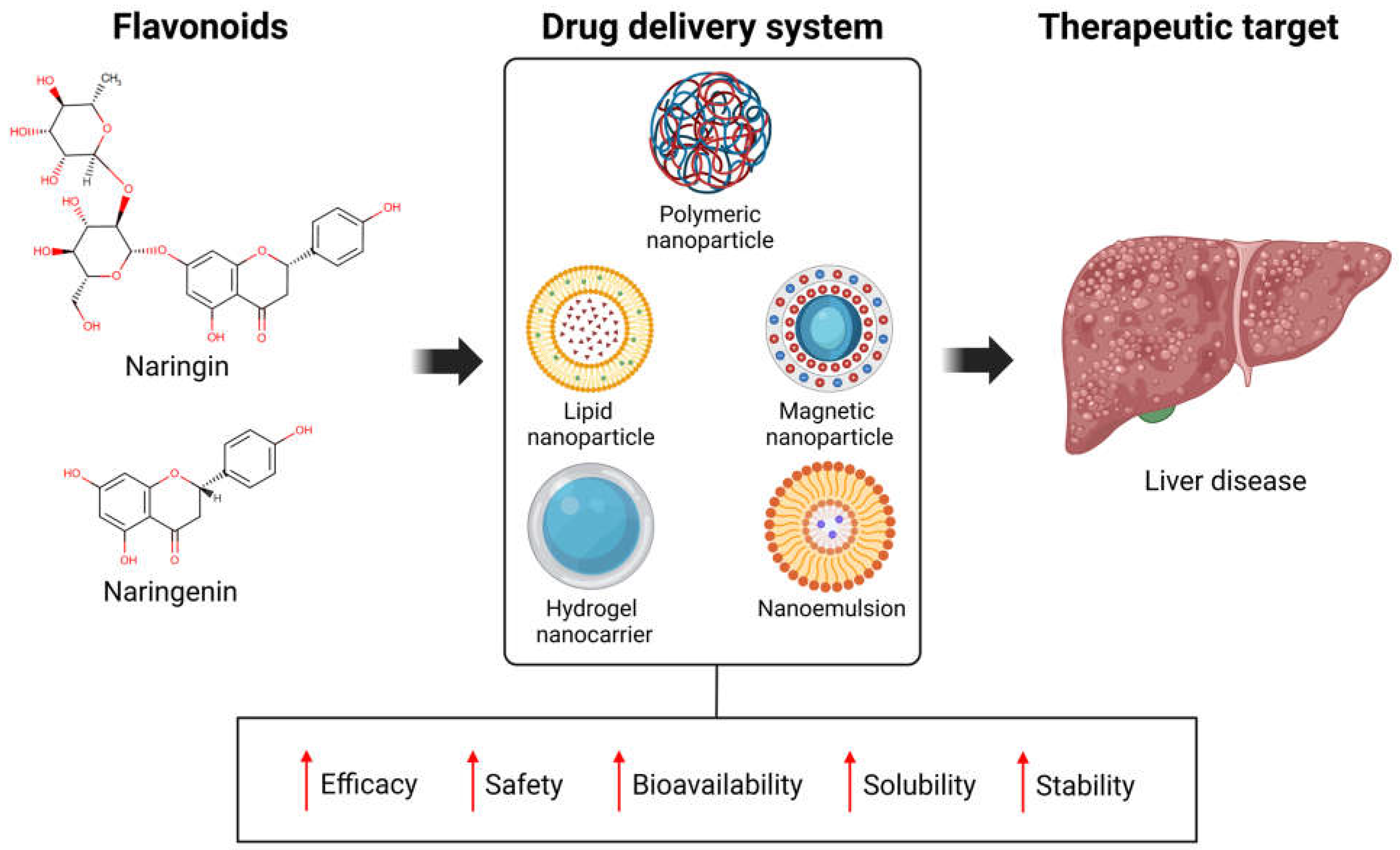
6. Nanoformulations and Emerging Strategies to Optimize the Delivery of NARI and NAR
6.1. Polymeric Nanoparticles
6.2. Lipid Nanoparticles
6.3. Magnetic Nanoparticles
6.4. Hydrogel Nanocarriers
6.5. Nanoemulsions
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Elshafie, H.S.; Camele, I.; Mohamed, A.A. A Comprehensive Review on the Biological, Agricultural and Pharmaceutical Properties of Secondary Metabolites Based-Plant Origin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomford, N.E.; Senthebane, D.A.; Rowe, A.; Munro, D.; Seele, P.; Maroyi, A.; Dzobo, K. Natural Products for Drug Discovery in the 21st Century: Innovations for Novel Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safer, A.M.; Afzal, M.; Hanafy, N.; Mousa, S. Green tea extract therapy diminishes hepatic fibrosis mediated by dual exposure to carbon tetrachloride and ethanol: A histopathological study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Zucca, P.; Pezzani, R.; Martins, N.; Sharifi-Rad, J. The Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin: A Review of Clinical Trials. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Wen, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.; Lan, D.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Dai, X.; Song, T.; Wang, X.; et al. Naringenin: A flavanone with anti-inflammatory and anti-infective properties. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Y.; Su, W.; Li, P. Epigenetic regulation by naringenin and naringin: A literature review focused on the mechanisms underlying its pharmacological effects. Fitoterapia 2024, 181, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, H.; Gao, J.; Kong, X.; Che, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Dong, E.; Xiao, J. Liver diseases: Epidemiology, causes, trends and predictions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devarbhavi, H.; Asrani, S.K.; Arab, J.P.; Nartey, Y.; Pose, E.; Kamath, P.S. Global burden of liver disease: 2023 update. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 516–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Effenberger, M. From NAFLD to MAFLD: When pathophysiology succeeds. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabini, J.H.; Timotius, K.H. Hepatoprotective and Fat-Accumulation-Reductive Effects of Curcumin on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Subhan, N.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, S.J.; Reza, H.M.; Sarker, S.D. Effect of citrus flavonoids, naringin and naringenin, on metabolic syndrome and their mechanisms of action. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, S. Natural Polyphenols in Metabolic Syndrome: Protective Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębińska, A.; Sozańska, B. Dietary Polyphenols-Natural Bioactive Compounds with Potential for Preventing and Treating Some Allergic Conditions. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasmi, A.; Mujawdiya, P.K.; Noor, S.; Lysiuk, R.; Darmohray, R.; Piscopo, S.; Lenchyk, L.; Antonyak, H.; Dehtiarova, K.; Shanaida, M.; et al. Polyphenols in Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2022, 27, 6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, N.; Sun, X.; Zhan, H.; Tian, J.; Fei, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y. Controllable biotransformation of naringin to prunin by naringinase immobilized on functionalized silica. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpa, V.S.; Shams, R.; Dash, K.K.; Pandey, V.K.; Dar, A.H.; Ayaz Mukarram, S.; Harsányi, E.; Kovács, B. Phytochemical Properties, Extraction, and Pharmacological Benefits of Naringin: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 442428, Naringin. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/aurantiin (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 439246, Naringenin. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Naringenin (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Felgines, C.; Texier, O.; Morand, C.; Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Régerat, F.; Rémésy, C. Bioavailability of the flavanone naringenin and its glycosides in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 279, G1148–G1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, R.; Kulkarni, Y.A.; Wairkar, S. Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic and formulations aspects of Naringenin: An update. Life Sci. 2018, 215, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semalty, A.; Semalty, M.; Singh, D.; Rawat, M.S.M. Preparation and characterization of phospholipid complexes of naringenin for effective drug delivery. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2010, 67, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W.; Su, W. Toxicological evaluation of naringin: Acute, subchronic, and chronic toxicity in Beagle dogs. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 111, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, S.; Guan, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Peng, W.; Su, W.; Zhang, K. Acute and 13 weeks subchronic toxicological evaluation of naringin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, S.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Hu, C.; Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; Su, W. Six months chronic toxicological evaluation of naringin in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Andrade, R.R.; Sánchez-Salgado, J.C.; Navarrete-Vázquez, G.; Webster, S.P.; Binnie, M.; García-Jiménez, S.; León-Rivera, I.; Cigarroa-Vázquez, P.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Estrada-Soto, S. Antidiabetic and toxicological evaluations of naringenin in normoglycaemic and NIDDM rat models and its implications on extra-pancreatic glucose regulation. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2008, 10, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, U.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, H.O.; Park, E.J.; Kim, H.K.; Jeong, T.S.; Choi, M.S. Naringin supplementation lowers plasma lipids and enhances erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Q.; Dong, S.; Su, Z.H.; Zhang, H.W.; Peng, J.B.; Yu, C.Y.; Zou, Z.M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of naringin in rat after oral administration of chaihu-shu-gan-san aqueous extract and naringin alone. Metabolites 2013, 3, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cao, X.; Fang, X.; Guo, A.; Li, E. Involvement of phase II enzymes and efflux transporters in the metabolism and absorption of naringin, hesperidin and their aglycones in rats. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Andrade, R.; Araujo-León, J.A.; Sánchez-Recillas, A.; Navarrete-Vazquez, G.; González-Sánchez, A.A.; Hidalgo-Figueroa, S.; Alonso-Castro, Á.J.; Aranda-González, I.; Hernández-Núñez, E.; Coral-Martínez, T.I.; et al. Toxicological Screening of Four Bioactive Citroflavonoids: In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Silico Approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Bharti, S.; Krishnamurthy, B.; Bhatia, J.; Sharma, C.; Kamal, M.A.; Ojha, S.; Arya, D.S. Pharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin: A Citrus Flavonoid of Pharmaceutical Promise. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4341–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaze, F.I.; Bounartzi, M.I.; Georgarakis, M.; Niopas, I. Pharmacokinetics of the citrus flavanone aglycones hesperetin and naringenin after single oral administration in human subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, C.J.; Beyl, R.A.; Lertora, J.J.L.; Greenway, F.L.; Ravussin, E.; Ribnicky, D.M.; Poulev, A.; Kennedy, B.J.; Castro, H.F.; Campagna, S.R.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of naringenin: A randomized, controlled, single-ascending-dose clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuera-de-la-Tijera, F.; Lira-Vera, J.E.; Morales-Gutiérrez, O.; Martínez-Castillo, M.; Medina-Ávila, Z.; Servín-Caamaño, A.; Pérez-Hernández, J.L.; Gutiérrez-Reyes, G. Alcoholic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2022, 19, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Hu, W.; Tu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Han, S. Pathogenic mechanisms and regulatory factors involved in alcoholic liver disease. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, M.; Yang, X.; Deng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. PeerJ 2023, 11, e16398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Lv, F.; Quan, T.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Flavonoids in natural products for the therapy of liver diseases: Progress and future opportunities. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1485065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Lai, Y.; Huang, P.; Xie, L.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Z.; Mo, C.; Deng, G.; Yan, W.; Gao, Z.; et al. Naringin attenuates alcoholic liver injury by reducing lipid accumulation and oxidative stress. Life Sci. 2019, 216, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, J.; Namasivayam, N. Naringenin modulates circulatory lipid peroxidation, anti-oxidant status and hepatic alcohol metabolizing enzymes in rats with ethanol induced liver injury. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 25, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, D.; Yang, M.; Guo, X.; He, J.; Wu, W.; Ji, B.; Cheng, Q.; Zhou, F. Protective Effects of Five Structurally Diverse Flavonoid Subgroups against Chronic Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Damage in a Mouse Model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, N.A.; Abdel Ghafar, M.T.; AbuoHashish, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Eid, A.M.; El-Gohary, R.M.; Abo El Gheit, R.E.; Elshamy, A.M. The Possible Role of Naringenin in the Prevention of Alcohol-Induced Neurochemical and Neurobehavioral Deficits. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Jiao, Q.; Zhou, L.; Peng, S.; Lin, S.; McClements, D.J.; Liu, W. Improving hepatoprotective effect of naringin against alcohol-induced liver injury by encapsulation in microalgae-derived extracellular vesicles. Food Biosci. 2025, 64, 105985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.B.; Giadans, C.G.; Flichman, D.M.; Ré, V.E.; Preciado, M.V.; Valva, P. Viral hepatitis update: Progress and perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4018–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanini, S.; Ustianowski, A.; Pisapia, R.; Zumla, A.; Ippolito, G. Viral hepatitis. Infect. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2019, 33, 1045–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, D.; Gonzalez, A.J.; Alomari, M.; Tandon, K.; Zervos, X.B. From hepatitis A to E: A critical review of viral hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1691–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, H. Global Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North. Am. 2020, 49, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, D.; Kaneoka, Y.; Ono, R.; Kato, M.; Sugawara, Y.; Shimizu, R.; Inami, T.; Nakajima, E.; Tsuge, S.; Sakurai, R.; et al. Current perspectives of viral hepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2402–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for South-East Asia. Governing bodies: Key issues and challenges arising out of the sixty-third World Health Assembly and the 126th and 127th sessions of the WHO Executive Board. In Proceedings of the High-Level Preparatory (HLP) Meeting for the 63rd Session of WHO/SEA Regional Committee WHO/SEARO, New Delhi, India, 28 June–1 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Badshah, S.L.; Faisal, S.; Muhammad, A.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Antiviral activities of flavonoids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizaldi, G.; Hafid, A.F.; Wahyuni, T.S. Promising alkaloids and flavonoids compounds as anti-hepatitis c virus agents: A review. J. Public. Health Afr. 2023, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.J.; Ku, K.L.; Lin, I.H.; Yeh, C.C. Naringenin attenuates hepatitis B virus X protein-induced hepatic steatosis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldwasser, J.; Cohen, P.Y.; Lin, W.; Kitsberg, D.; Balaguer, P.; Polyak, S.J.; Chung, R.T.; Yarmush, M.L.; Nahmias, Y. Naringenin inhibits the assembly and long-term production of infectious hepatitis C virus particles through a PPAR-mediated mechanism. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmias, Y.; Goldwasser, J.; Casali, M.; van Poll, D.; Wakita, T.; Chung, R.T.; Yarmush, M.L. Apolipoprotein B-dependent hepatitis C virus secretion is inhibited by the grapefruit flavonoid naringenin. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1437–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. NAFLD Nomenclature consensus group. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lau, H.C.; Yu, J. Pharmacological treatment for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and related disorders: Current and emerging therapeutic options. Pharmacol. Rev. 2025, 77, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, P.; Tacke, F. Key takeaways from the updated multidisciplinary European MASLD guidelines. eGastroenterology 2025, 3, e100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic, B.; Marjanovic-Haljilji, M.; Mijac, D.; Lukic, S.; Kapor, S.; Kapor, S.; Starcevic, A.; Popovic, D.; Djokovic, A. Molecular Aspects of MAFLD-New Insights on Pathogenesis and Treatment. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9132–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpízar Salazar, M.; Olguín Reyes, S.E.; Medina Estévez, A.; Saturno Lobos, J.A.; De Aldecoa Castillo, J.M.; Carrera Aguas, J.C.; Alaniz Monreal, S.; Navarro Rodríguez, J.A.; Alpízar Sánchez, D.M.F. Natural History of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Metabolic Syndrome to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Medicina 2025, 61, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibullah, M.; Jemmieh, K.; Ouda, A.; Haider, M.Z.; Malki, M.I.; Elzouki, A.N. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A selective review of pathogenesis, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1291501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Astbury, N.M.; Tudor, K.E.; Morris, E.; Henry, J.A.; Noreik, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Aveyard, P. Association of weight loss interventions with changes in biomarkers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2019, 179, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Z.; Bian, Y. Naringenin prevents NAFLD in the diet-induced C57BL/6J obesity model by regulating the intestinal barrier function and microbiota. J. Funct. Foods. 2023, 105, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, R.; Zeng, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, R.; Tang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Shen, T.; et al. Naringin Attenuates High Fat Diet Induced Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Gut Bacterial Dysbiosis in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 585066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Hu, G.; Wen, C.; Yue, S.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, H.; Xiao, H.; et al. Naringenin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulating the NLRP3/NF-κB pathway in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zou, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, M.X.; Huang, W.; Yu, D.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, X.D. Naringenin attenuates Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease by enhancing energy expenditure and regulating autophagy via AMPK. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 687095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namkhah, Z.; Naeini, F.; Rezayat, S.M.; Yaseri, N.M.; Mansouri, S.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.J. Does naringenin supplementation improve lipid profile, severity of hepatic steatosis and probability of liver fibrosis in overweight/obese patients with NAFLD? A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, R.J.; Chalasani, N.; Björnsson, E.S.; Suzuki, A.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Watkins, P.B.; Devarbhavi, H.; Merz, M.; Lucena, M.I.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Drug-induced liver injury. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.; Schaffner, F. (Eds.) Chapter 31—The problem of chronicity in liver disease. In Progress in Liver Diseases, 1st ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: New York, USA, 1965; Volume 2, pp. 519–538. [Google Scholar]
- Björnsson, H.; Björnsson, E. Drug-induced liver injury: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, and practical management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 97, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Geng, Q.; Lin, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, C.; Liu, B.; Yan, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, L.; Lu, P.; et al. Insights gained into the injury mechanism of drug and herb induced liver injury in the hepatic microenvironment. Toxicology 2024, 507, 153900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, V.J.; Khan, I.; Björnsson, E.; Seeff, L.B.; Serrano, J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Liver injury from herbal and dietary supplements. Hepatology 2016, 65, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, J.H.; Björnsson, E.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury—Types and phenotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, J.; Dhull, S.B.; Rose, P.K.; Kidwai, M.K. Drug-induced liver injury and anti-hepatotoxic effect of herbal compounds: A metabolic mechanism perspective. Phytomedicine 2024, 122, 155142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.J.; Liou, I.; Reuben, A.; Suzuki, A.; Fiel, M.I.; Lee, W.; Navarro, V. AASLD practice guidance on drug, herbal, and dietary supplement–induced liver injury. Hepatology 2022, 77, 1036–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floreani, A.; Bizzaro, D.; Shalaby, S.; Taliani, G.; Burra, P. Sex disparity and drug-induced liver injury. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 55, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tang, J.; Mao, Y. Incidence and risk factors of drug-induced liver injury. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia-Correa, B.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, C.; Uribe, M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Herbal medicine in Mexico: A cause of hepatotoxicity. A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Lu, C.; Shen, R.; Lu, T.; Ma, B.; Hua, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Scientometric Investigation (2010–2019). Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xie, L.; Rong, F.; Zhu, X.Y.; Xie, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, T. Progress in the treatment of drug-induced liver injury with natural products. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaled, S.S.; Soliman, H.A.; Abdel-Gabbar, M.; Ahmed, N.A.; El-Nahass, E.S.; Ahmed, O.M. Naringin and naringenin counteract taxol-induced liver injury in Wistar rats via suppression of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 90892–90905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.Z.; Alhazzani, K.; Alrewily, S.Q.; Aljerian, K.; Algahtani, M.M.; Alqahtani, Q.H.; Haspula, D.; Alhamed, A.S.; Alqinyah, M.; Raish, M. The Potential Protective Role of Naringenin against Dasatinib-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, S.; Sini, T.K.; Anandan, R.; Mathew, P.T. Hepatoprotective activity of chitosan against isoniazid and rifampicin-induced toxicity in experimental rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 572, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fan, R.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Nie, H.; Li, K. Naringenin protects against isoniazid- and rifampicin-induced apoptosis in hepatic injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9775–9783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wali, A.F.; Rashid, S.; Rashid, S.M.; Ansari, M.A.; Khan, M.R.; Haq, N.; Alhareth, D.Y.; Ahmad, A.; Rehman, M.U. Naringenin Regulates Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Dysfunction: Impact on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Plants 2020, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Meyer, T.; Sapisochin, G.; Salem, R.; Saborowski, A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2022, 400, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P.; Madke, T.; Chand, P. Global Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Sahu, M.K.; Tripathy, A.; Uthansingh, K.; Behera, M. Hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Hurdles, advances and prospects. Hepat Oncol. 2018, 5, HEP08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Guerra, V.; Carr, B.I.; D’Alessandro, R. Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjerdpongchai, R.; Wudtiwai, B.; Khawon, P. Induction of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cell Apoptosis by Naringin. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3289–3294. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, D.; Yuan, P.; Wang, D.; Jin, H.; Chen, H. Effects of naringin on the expression of miR-19b and cell apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Kang, Q.; Wang, Z. Protective role of naringin loaded solid nanoparticles against aflatoxin B1 induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 351, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.E.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Elesawy, B.H.; Al Askary, A.; Hassaballa, A.; El-Shahawy, A.A.G. Protective Effects of Naringin-Dextrin Nanoformula against Chemically Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Wistar Rats: Roles of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Cell Apoptosis, and Proliferation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, A.G.; Mohamed, T.M.; Beltagy, D.M.; El Gamal, D.M. The therapeutic role of naringenin nanoparticles on hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2025, 26, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Iglesias, O.; Naidoo, V.; Carrera, I.; Corzo, L.; Cacabelos, R. Natural Bioproducts with Epigenetic Properties for Treating Cardiovascular Disorders. Genes. 2025, 16, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cheng, X.; Naumovski, N.; Hu, L.; Wang, K. Epigenetic regulation by quercetin: A comprehensive review focused on its biological mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.A. Epigenetics in liver disease. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1418–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arechederra, M.; Recalde, M.; Gárate-Rascón, M.; Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Ávila, M.A.; Berasain, C. Epigenetic Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Liver Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, T.; Kitamoto, A.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Teranishi, H.; Mizusawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Chayama, K.; et al. Genome-wide scan revealed that polymorphisms in the PNPLA3, SAMM50, and PARVB genes are associated with development and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Japan. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trépo, E.; Nahon, P.; Bontempi, G.; Valenti, L.; Falleti, E.; Nischalke, H.D.; Hamza, S.; Corradini, S.G.; Burza, M.A.; Guyot, E.; et al. Association between the PNPLA3 (rs738409 C>G) variant and hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Hepatology 2014, 59, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, M.C.; Yao, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, A.Q.; Yu, J.; Hui, C.K.; Lau, G.K.; He, M.L.; Sung, J.; et al. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth through down-regulation of stathmin. Hepatology 2007, 46, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Jia, J.; Zhang, Y. Curcumin-induced histone hypoacetylation: The role of reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ai, N.; Hou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lu, H.; Welsh, W.; Yang, C.S. Tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baur, J.A.; Pearson, K.J.; Price, N.L.; Jamieson, H.A.; Lerin, C.; Kalra, A.; Prabhu, V.V.; Allard, J.S.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Lewis, K.; et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 2006, 444, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokumacioglu, E.; Iskender, H.; Aktas, M.S.; Hanedan, B.; Dokumacioglu, A.; Sen, T.M.; Musmul, A. The effect of sulforaphane on oxidative stress and inflammation in rats with toxic hepatitis induced by acetaminophene. Bratisl. Lek. Listy. 2017, 118, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Madureira, M.B.; Concato, V.M.; Cruz, E.M.S.; Bitencourt de Morais, J.M.; Inoue, F.S.R.; Concimo Santos, N.; Gonçalves, M.D.; Cremer de Souza, M.; Basso Scandolara, T.; Fontana Mezoni, M.; et al. Naringenin and Hesperidin as Promising Alternatives for Prevention and Co-Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.W.; Sheng, H.; Bai, Y.F.; Weng, Y.Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Zheng, F.; Fu, J.Q.; Zhang, F. Inhibition of histone acetyltransferase by naringenin and hesperetin suppresses Txnip expression and protects pancreatic β cells in diabetic mice. Phytomedicine 2021, 88, 153454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Li, J.; Fan, Q. Naringin promotes differentiation of bone marrow stem cells into osteoblasts by upregulating the expression levels of microRNA-20a and downregulating the expression levels of PPARγ. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4759–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Peng, W.; Hu, S.; Deng, J. miR-126/VCAM-1 regulation by naringin suppresses cell growth of human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4754–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Shi, R.; Guan, M.; Chen, P.; Wu, H.; Su, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. The Effects of Naringenin on miRNA-mRNA Profiles in HepaRG Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Herrera, S.J.; Luna-Bárcenas, G.; Guevara-González, R.G.; Campos-Vega, R.; Solís-Sáinz, J.C.; Hernández-Puga, A.G.; Vergara-Castañeda, H.A. Fermentation Extract of Naringenin Increases the Expression of Estrogenic Receptor β and Modulates Genes Related to the p53 Signalling Pathway, miR-200c and miR-141 in Human Colon Cancer Cells Exposed to BPA. Molecules 2022, 27, 6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.; Mann, D.A. Epigenetics in liver disease: From biology to therapeutics. Gut 2016, 65, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppusamy, C.; Venkatesan, P. Role of Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery System: A Comprehensive review. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 9, 318. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.C.Q.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Vilela, C.; Freire, C.S.R. Natural Polymers-Based Materials: A Contribution to a Greener Future. Molecules 2021, 27, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, B.; Janssen, P.H.; Frings, J. Degradación microbiana de polímeros naturales y sintéticos nuevos. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1992, 9, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S. Natural biodegradable polymers based nano-formulations for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 244–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Corrigan, N.; Wong, E.H.H.; Boyer, C. Bioactive Synthetic Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydz, J.; Sikorska, W.; Kyulavska, M.; Christova, D. Polyester-based (bio)degradable polymers as environmentally friendly materials for sustainable development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 564–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, T.P.; Völker, C.; Kramm, J.; Landfester, K.; Wurm, F.R. Plastics of the Future? The Impact of Biodegradable Polymers on the Environment and on Society. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gan, L.; Xu, J.; Zhou, G. Recent Advances in Biodegradable and Biocompatible Synthetic Polymers Used in Skin Wound Healing. Materials 2023, 16, 5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Shen, X.; Chai, X.; Li, J.; Pi, J.; Huang, X.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Z. Oral colon-targeted pH-responsive polymeric nanoparticles loading naringin for enhanced ulcerative colitis therapy. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, B.; Wang, Z. Naringenin in Si-Ni-San formula inhibits chronic psychological stress-induced breast cancer growth and metastasis by modulating estrogen metabolism through FXR/EST pathway. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 47, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, D.; Yang, B.; Hong, S.; Pan, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Shi, Y.; et al. Developing liver-targeted naringenin nanoparticles for breast cancer endocrine therapy by promoting estrogen metabolism. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnawasany, S.; Haggag, Y.A.; Shalaby, S.M.; Soliman, N.A.; El Saadany, A.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Badria, F. Anti-cancer effect of nano-encapsulated boswellic acids, curcumin and naringenin against HepG-2 cell line. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsairat, H.; Khater, D.; Sayed, U.; Odeh, F.; Al Bawab, A.; Alshaer, W. Liposomes: Structure, composition, types, and clinical applications. Heliyon. 2022, 8, e09394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Kothari, R.; Pareek, A.; Ratan, Y.; Kashania, P.; Jain, V.; Jeandet, P.; Kumar, P.; Khan, A.A.; Alanazi, A.M.; et al. Development of a new inhaled swellable microsphere system for the dual delivery of naringenin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles and doxofylline for the treatment of asthma. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 193, 106642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, W.; Torbett-Dougherty, M.; Islam, A.; Soleimani, S.; Bruce-Tagoe, T.A.; Johnson, J.A. Magnetic Nanoparticles and Drug Delivery Systems for Anti-Cancer Applications: A Review. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askar, M.A.; El Shawi, O.E.; Abou Zaid, O.A.R.; Mansour, N.A.; Hanafy, A.M. Breast cancer suppression by curcumin-naringenin-magnetic-nano-particles: In vitro and in vivo studies. Tumour Biol. 2021, 43, 225–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, Y. Advances in hydrogel for diagnosis and treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1552586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhoury, K.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, L.; Lavrador, P.; Almeida, R.; Gaspar, V.; Kahn, C.; Cleymand, F.; Arab-Tehrany, E.; Mano, J.F. Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Nanocomposite Hydrogels Embedding Bioactive Naringin Liposomes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Pilehvar, Y.; Kousha, S.; Bi, J. Bioactive Wound Healing 3D Structure Based on Chitosan Hydrogel Loaded with Naringin/Cyclodextrin Inclusion Nanocomplex. ACS Omega. 2024, 9, 10566–10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, H.A.; Abo Dena, A.S.; Sobhy, M.H.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Integrating 3D-printed hydrogels and polymeric nanofibers in a double-layered transdermal patch for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 40187–40197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tan, L.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, M.; He, S.; Luo, Z.; Cai, K.; Hu, Y. Multifunctional layered microneedle patches enable transdermal angiogenesis and immunomodulation for scarless healing of thermal burn injuries. Mater. Today Bio. 2024, 29, 101359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, N.; Waqar, M.A.; Khan, A.M.; Asif, Z.; Alvi, A.S.; Virk, A.A.; Amir, S. A comprehensive insight of innovations and recent advancements in nanocarriers for nose-to-brain drug targeting. Des. Monomers Polym. 2025, 28, 7–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Fan, S.; Luo, R.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Pi, J.; Huang, G. Intratracheal Administration of Stem Cell Membrane-Cloaked Naringin-Loaded Biomimetic Nanoparticles Promotes Resolution of Acute Lung Injury. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| NARI | NAR | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | 4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavanone-7-glucoside | 4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone | [18,19] |
| Molecular Formula | C27H32O14 | C15H12O5 | |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 580.4 | 272.3 | |
| Melting Point | 83 °C | 251 °C | |
| Oral Bioavailability | 5 to 9% | 15% | [20,21] |
| Solubility (µg/mL) | No data | 43.83 | [22] |
| LD50 (g/kg of BW) | >5 (in BD) >16 (in SDR) | >5 (in BD) | [23,24,25,26] |
| NOAEL (mg/kg of BW/per day) | 500 (in BD) >1250 (in SDR) | No data | [23,24] |
| Name of Flavonoid | Mechanism/Outcome | References |
|---|---|---|
| NARI | Promotes the metabolism of fatty acids and cholesterol by decreasing the enzymatic activity of FASN and G6PD in the liver, thereby limiting the availability of long-chain fatty acids required for triglyceride synthesis. | [39] |
| Anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering effects, with decreased ALT, AST, TG, and TC levels. NARI also reduced the expression of Srebp1, Fas, Acc, Scd1, TNF-α, and IL-6. | [65,82,93] | |
| Antioxidant activity, with increased SOD and GPx enzyme activity and reduced ROS levels. | [82,93] | |
| Proapoptotic effect through activation of CASP-8 and CASP-9, induction of Bid proteolysis, and miR-19b expression. | [91,92] | |
| Anticancer effect, reducing hepatic expression of Bcl-2, IQGAP1, IQGAP3, Ras signaling, Ki-67, and miR-126, while counteracting the decrease in VCAM-1. It also increased the expression of IQGAP2, Bax, p53, ATG5, LC3, PDCD5, and miR-126. | [92,94,95,110,111] | |
| Osteogenic effect, increasing miR-20a levels and reducing PPARγ expression. | [109] | |
| NAR | Antioxidant activity, with increased ADH, ALDH, SOD, CAT, and GPx enzyme activity, inhibition of p300/CBP acetyltransferase, and reduced Txnip expression. | [40,81,82,85,86,108] |
| Antifibrotic effect, reducing TGF-β, COL-I, and fibronectin expression, along with signs of fibrosis in the liver. | [41] | |
| Neuroprotective and antioxidant activity, with increased Nrf2, GSH, and NQO1 expression, and reduced RIPK3 expression. | [42,43] | |
| Modulates hepatic apolipoprotein and lipid synthesis, reducing ALT, AST, CHOL, and TG levels, and decreasing mRNA expression of PPARγ and LXRα. | [52] | |
| Antiviral effect through PPARα activation, reducing VLDL production and inhibiting ApoB secretion by decreasing MTP and ACAT activity and expression. | [53,54] | |
| Anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering activity, with decreased TG and TC levels, and negative regulation of NLRP3, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18, p65, MCP-1, COX-2, NF-κB, F4/80, and MPO activity, via AMPK pathway activation. | [64,66,67,68,81,82,83,86] | |
| Anticancer effect, increasing miR-200c and miR-141 expression. | [112] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Peña, R.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Caloca-Camarena, F.; Arceo-Orozco, S.; Salto-Sevilla, J.A.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Naringin and Naringenin in Liver Health: A Review of Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080979
Flores-Peña R, Monroy-Ramirez HC, Caloca-Camarena F, Arceo-Orozco S, Salto-Sevilla JA, Galicia-Moreno M, Armendariz-Borunda J. Naringin and Naringenin in Liver Health: A Review of Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(8):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080979
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Peña, Roberto, Hugo Christian Monroy-Ramirez, Fernando Caloca-Camarena, Scarlet Arceo-Orozco, Jorge Alejandro Salto-Sevilla, Marina Galicia-Moreno, and Juan Armendariz-Borunda. 2025. "Naringin and Naringenin in Liver Health: A Review of Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies" Antioxidants 14, no. 8: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080979
APA StyleFlores-Peña, R., Monroy-Ramirez, H. C., Caloca-Camarena, F., Arceo-Orozco, S., Salto-Sevilla, J. A., Galicia-Moreno, M., & Armendariz-Borunda, J. (2025). Naringin and Naringenin in Liver Health: A Review of Molecular and Epigenetic Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Antioxidants, 14(8), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080979







