The Dark Triad of Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Coronary Artery Disease: What About the Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Strategy
3. Particulate Matter
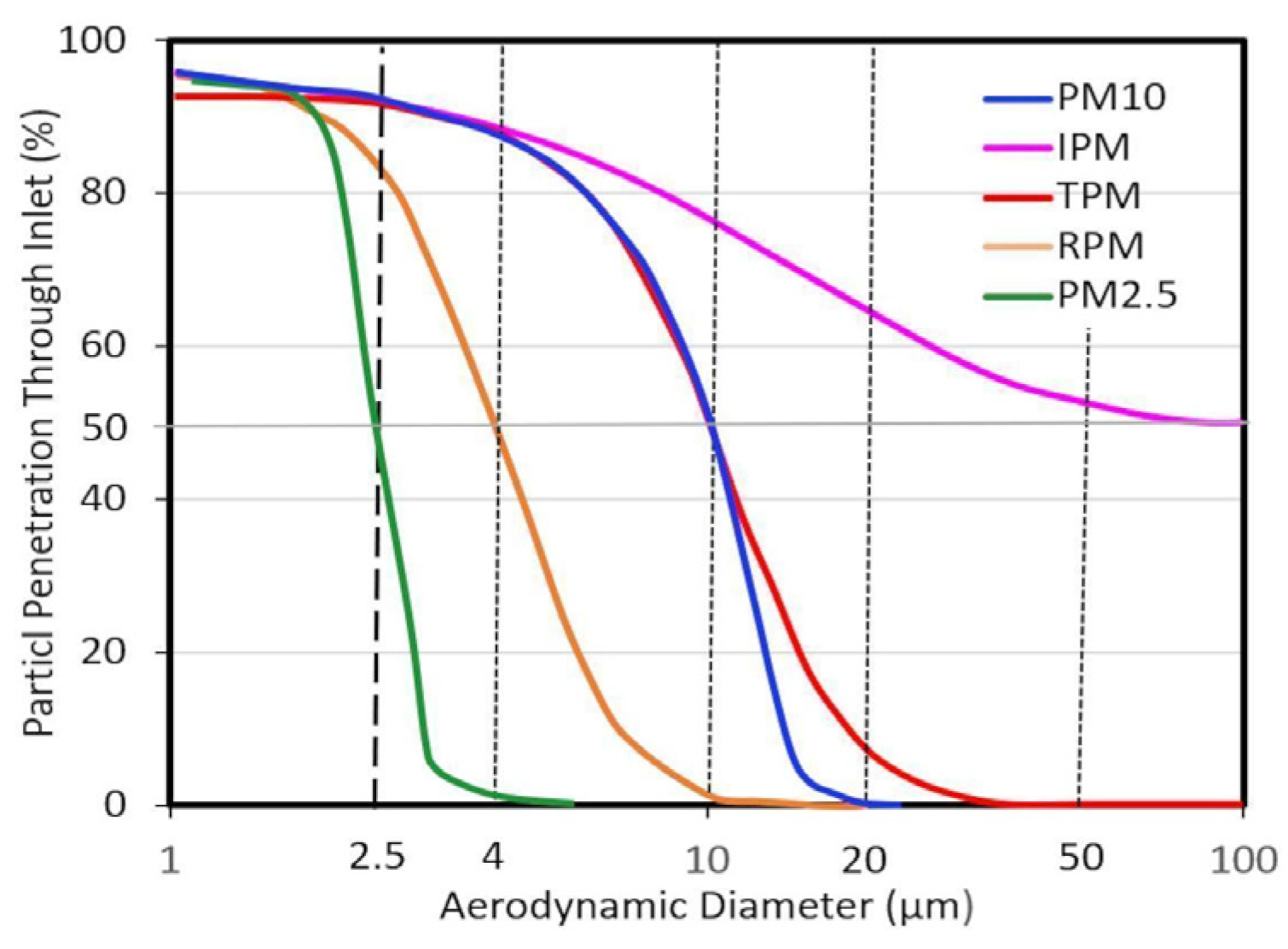
3.1. Particle Size Fractions
3.1.1. Modal Classification
3.1.2. Sampler Cut Point Classification
3.1.3. Dosimetry Classification
3.2. Main Sources and Composition of Particulate Matter
3.2.1. Traffic
3.2.2. Industrial Activities
3.2.3. Biomass Burning
3.2.4. Mineral Desert Dust
3.2.5. Sea Spray
3.2.6. Biogenic Emissions
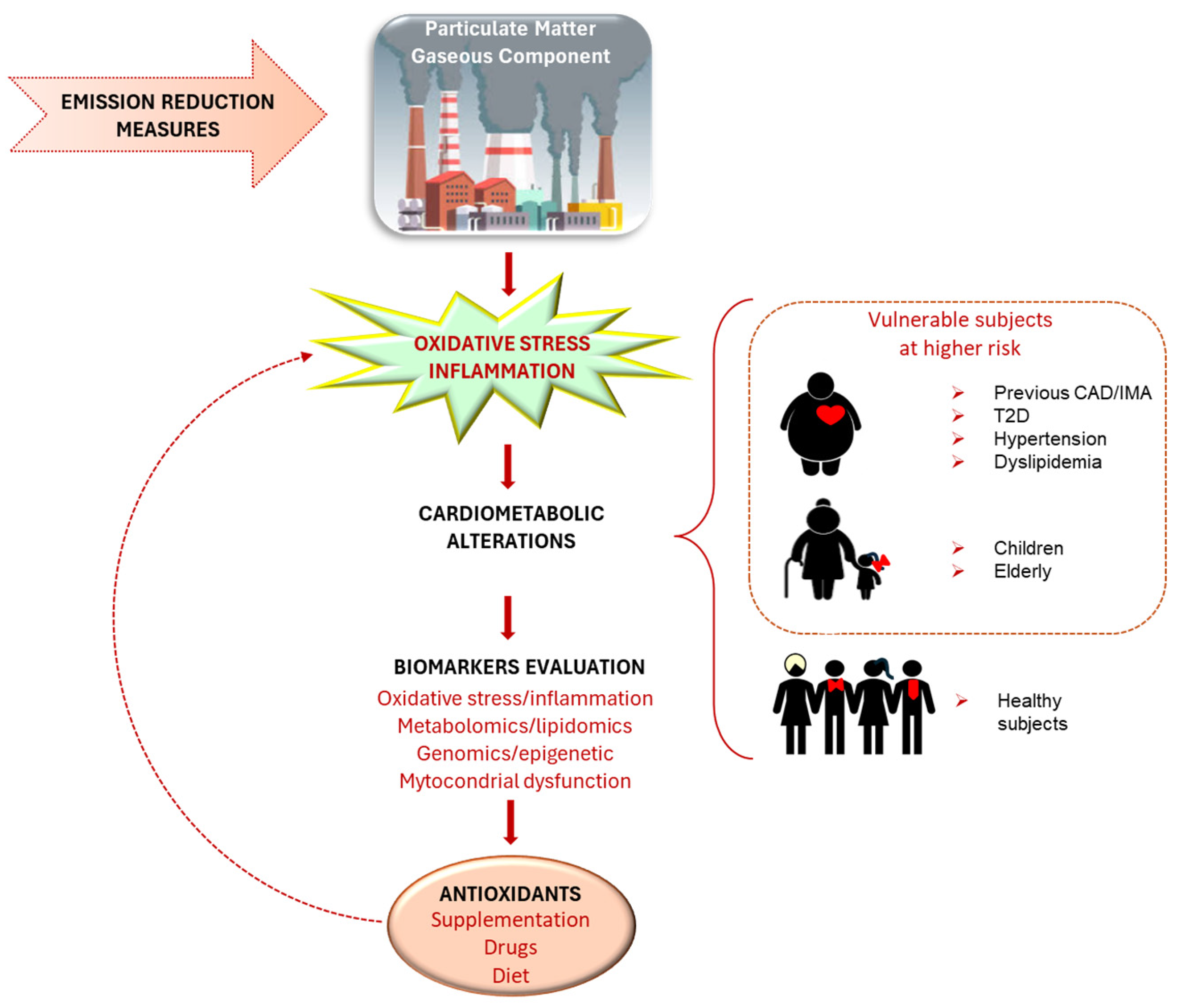
4. Particulate Matter and Cardiovascular Diseases
5. Oxidative Stress and Other Mechanisms Mediating Particulate Matter Effects on the Cardiovascular System
- (1)
- Primary initiating responses in the lung—these occur following pollutant inhalation and include (a) either exogenous (pollutant-induced) or endogenous OS, (b) pulmonary inflammation and (c) ion channel/receptor activation;
- (2)
- Transmission pathways—these facilitate the systemic impact of initial pulmonary responses and include (a) generation of biologic intermediates (e.g., oxidized lipids, cytokines, activated immune cells, microparticles, microRNA, vasoconstrictors) (b) autonomic imbalance/afferent neurological circuits leading to the central nervous system (sympathetic or hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis activation);
- (3)
- End-organ effector mechanisms—the previous pathways, in turn, lead to end-organ effector mechanisms responsible for atherosclerotic events [116].
6. Metabolomics and Lipidomics Study
7. Particulate Matter, Genomic Instability, Epigenetic Changes and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
8. General Prevention Strategies
9. Antioxidant Strategies
9.1. Antioxidant Nutrients and Healthy Dietary Habits
9.2. Probiotics
9.3. Cardiovascular Drugs
9.3.1. Beta-Blockers
9.3.2. Statins
9.3.3. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
10. Final Remarks: Points to Solve and Future Directions
10.1. Individual Issues and Biomarkers
10.2. Exposure Misclassification
10.3. Sampling Methodology and Variability in Particulate Matter Measurement
10.4. Antioxidant-Related Strategies
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| ARB | Angiotensin receptor blocker |
| AS | Atherosclerosis |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CAC | Coronary artery calcium |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| Da | aerodynamic diameter |
| DE | Diesel exhaust |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GPx-1 | Glutathione peroxidase 1 |
| GST | Glutathione-S transferase |
| GSTM1 | Glutathione-S transferase M1 |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HF | Heart failure |
| HRV | Heart rate variability |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IMT | Intima media thickness |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| eNOS | Endothelial NO synthase |
| iNOS | Inducible NO synthase |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MD | Mediterranean diet |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NF-κb | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cell |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NO2 | Nitrogen dioxide |
| OC | Organic compound |
| Omega-3 PUFA | Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| OS | Oxidative stress |
| Ox-LDL | Oxidized low-density lipoprotein |
| O3 | Ozone |
| PAH | Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon |
| PI3K-AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Protein Kinase B |
| PM | Particulate matter |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter with a diameter less than 2.5 µm |
| PM10 | Particulate matter with a diameter less than 10 µm |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| TL | Telomere length |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor α |
| UFP | Ultrafine particle |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Yang, M.; Wu, K.; Wu, Q.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z.; Ho, H.C.; Tao, J.; Zheng, H.; Hossain, M.Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Air Pollution and Angina Pectoris Attacks: Identification of Hazardous Pollutant, Short-Term Effect, and Vulnerable Population. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 32246–32254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J.J. Trends in Ambient Air Pollution Levels and PM2.5 Chemical Compositions in Four Chinese Cities from 1995 to 2017. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 6396–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Davaakhuu, N.; Escamilla Nuñez, M.C.; Hadley, M.; Kass, D.; Miller, M.; Prabhakaran, D.; Sliwa, K.; Su, T.-C.; Vaartjes, I.C.H.; et al. Clean Air, Smart Cities, Healthy Hearts: Action on Air Pollution for Cardiovascular Health. Glob. Heart 2021, 16, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dockery, D.W.; Schwartz, J.; Spengler, J.D. Air Pollution and Daily Mortality: Associations with Particulates and Acid Aerosols. Environ. Res. 1992, 59, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global Burden of 87 Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Burden of Disease from Ambient Air Pollution for 2016 Description of Method. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/air-quality-database/aqd-2018/aap_bod_methods_apr2018_final.pdf?sfvrsn=30ac0d62_3 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-92-4-003422-8. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Kumar, V.; S, H.; Huligowda, L.K.D.; Umesh, M.; Chakraborty, P.; Thazeem, B.; Singh, A.P. Environmental Pollutants as Emerging Concerns for Cardiac Diseases: A Review on Their Impacts on Cardiac Health. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J. The Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Morbidity: Mechanistic Evidence; Committee on the Medical Effects of Air Pollutants (COMEAP): London, UK, 2018; p. 96. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/air-pollution-and-cardiovascular-disease-mechanistic-evidence (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Newby, D.E.; Mannucci, P.M.; Tell, G.S.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Brook, R.D.; Donaldson, K.; Forastiere, F.; Franchini, M.; Franco, O.H.; Graham, I.; et al. Expert Position Paper on Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 83–93b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Franklin, B.; Cascio, W.; Hong, Y.; Howard, G.; Lipsett, M.; Luepker, R.; Mittleman, M.; Samet, J.; Smith, S.C.; et al. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the Expert Panel on Population and Prevention Science of the American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 109, 2655–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A.; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: An Update to the Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics—From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-471-72018-8. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Air Quality Criteria for Particulate Matter; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; ISBN EPA/600/P-99/002aF.
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Tignor, M.M.; Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Alegría, A.; Craig, M.; Langsdorf, S.; Löschke, S.; Möller, V.; et al. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J. Particulate Matter in the Atmosphere: Which Particle Properties Are Important for Its Effects on Health? Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Wang, Y.; Rosenfeld, D.; Liu, X. Review of Aerosol–Cloud Interactions: Mechanisms, Significance, and Challenges. J. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 73, 4221–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, H. The Role of Initial Cloud Condensation Nuclei Concentration in Hail Using the WRF NSSL 2-Moment Microphysics Scheme. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2017, 34, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginoux, P.; Prospero, J.M.; Gill, T.E.; Hsu, N.C.; Zhao, M. Global-Scale Attribution of Anthropogenic and Natural Dust Sources and Their Emission Rates Based on MODIS Deep Blue Aerosol Products. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.S.; De Carvalho, J.A.; Costa, M.A.M.; Pinheiro, C. An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1327–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, A.I.; Alves, C.; Castro, A.; Pont, V.; Vicente, A.M.; Fraile, R. Research on Aerosol Sources and Chemical Composition: Past, Current and Emerging Issues. Atmos. Res. 2013, 120–121, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.E.; Chow, J.C.; Claiborn, C.; Fusheng, W.; Engelbrecht, J.; Watson, J.G. Monitoring of Particulate Matter Outdoors. Chemosphere 2002, 49, 1009–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.E.; Suh, H.H. Fine Particles and Coarse Particles: Concentration Relationships Relevant to Epidemiologic Studies. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeke, K.; Whitby, K.T. Atmospheric Aerosols: Size Distribution Interpretation. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1975, 25, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Revisions to the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter. Fed. Regist. 1987, 52, 24634–24669. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. National Ambient Air Quality Standards for Particulate Matter. Fed. Regist. 1997, 62, 38652–38752. [Google Scholar]
- Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2008/50/oj (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH). Appendix D: Particle Size-Selective Sampling Criteria for Airborne Particulate Matter. In 1994–1995 Threshold Limit Values for Chemical Substances and Physical Agents and Biological Exposure Indices; ACGIH: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1994; pp. 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Marr, L.C.; Dunlea, E.J.; Herndon, S.C.; Jayne, J.T.; Kolb, C.E.; Knighton, W.B.; Rogers, T.M.; Zavala, M.; Molina, L.T.; et al. Vehicle Fleet Emissions of Black Carbon, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons, and Other Pollutants Measured by a Mobile Laboratory in Mexico City. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3377–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.B.; Sloan, J.J. A High-Resolution NOx Emission Factor Model for North American Motor Vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5214–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A.; Harrison, R.M. Sources and Properties of Non-Exhaust Particulate Matter from Road Traffic: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 270–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortenkrans, D.S.T.; Bergbäck, B.G.; Häggerud, A.V. Metal Emissions from Brake Linings and Tires: Case Studies of Stockholm, Sweden 1995/1998 and 2005. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5224–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirico, R.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Heringa, M.F.; Tritscher, T.; Richter, R.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Dommen, J.; Weingartner, E.; Wehrle, G.; Gysel, M.; et al. Impact of Aftertreatment Devices on Primary Emissions and Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation Potential from In-Use Diesel Vehicles: Results from Smog Chamber Experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11545–11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; de Vlieger, I.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of Maritime Transport Emissions on Coastal Air Quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Maritime Organization (IMO). Amendments to the Annex of the Protocol of 1997 to Amend the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships, 1973, as Modified by the Protocol of 1978 Relating Thereto (Inclusion of Regulations on Energy Efficiency for Ships in MARPOL Annex VI). Resolution MEPC.203(62); IMO: London, UK, 2011; Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.203%2862%29.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Miracolo, M.A.; Hennigan, C.J.; Ranjan, M.; Nguyen, N.T.; Gordon, T.D.; Lipsky, E.M.; Presto, A.A.; Donahue, N.M.; Robinson, A.L. Secondary Aerosol Formation from Photochemical Aging of Aircraft Exhaust in a Smog Chamber. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starik, A.M. Gaseous and Particulate Emissions with Jet Engine Exhaust and Atmospheric Pollution. In Advances on Propulsion Technology for High-Speed Aircraft; Educational Notes RTO-EN-AVT-150, Paper 15; Research and Technology Organization (RTO), NATO: Neuilly-sur-Seine, France, 2008; pp. 15-1–15-22. Available online: https://www.sto.nato.int/publications/STO%20Educational%20Notes/RTO-EN-AVT-150/EN-AVT-150-15.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Shindell, D.; Faluvegi, G. The Net Climate Impact of Coal-Fired Power Plant Emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3247–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Harrison, R.M.; Hopke, P.K.; Winiwarter, W.; Vallius, M.; Szidat, S.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; et al. Source Apportionment of Particulate Matter in Europe: A Review of Methods and Results. J. Aerosol Sci. 2008, 39, 827–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; de la Rosa, J.D.; González-Castanedo, Y.; Fernández-Camacho, R.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X.; Pio, C. High Concentrations of Heavy Metals in PM from Ceramic Factories of Southern Spain. Atmos. Res. 2010, 96, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Gil, J.I.; Menéndez, M. Identification of PM Sources by Principal Component Analysis (PCA) Coupled with Wind Direction Data. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, A.I.; Castro, A.; Pont, V.; Cuetos, M.J.; Sánchez, M.E.; Fraile, R. Aerosol Size Distribution and Gaseous Products from the Oven-Controlled Combustion of Straw Materials. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Jin, Y.; van Leeuwen, T.T. Global Fire Emissions and the Contribution of Deforestation, Savanna, Forest, Agricultural, and Peat Fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11707–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz de Zárate, I.; Ezcurra, A.; Lacaux, J.P.; Van Dinh, P.; de Argandoña, J.D. Pollution by Cereal Waste Burning in Spain. Atmos. Res. 2005, 73, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, C.; Tofful, L.; Torre, S.D.; Sargolini, T.; Canepari, S. Biomass Burning Contribution to PM10 Concentration in Rome (Italy): Seasonal, Daily and Two-Hourly Variations. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Karanasiou, A.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Severi, M.; Becagli, S.; Gianelle, V.L.; Colombi, C.; et al. AIRUSE-LIFE+: A Harmonized PM Speciation and Source Apportionment in Five Southern European Cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3289–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserini, S.; Livio, S.; Giugliano, M.; Grosso, M.; Rigamonti, L. LCA of Domestic and Centralized Biomass Combustion: The Case of Lombardy (Italy). Biomass Bioenergy 2010, 34, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, J.; Zielinska, B.; Fujita, E.M.; Sagebiel, J.C.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Fine Particle and Gaseous Emission Rates from Residential Wood Combustion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2080–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA. EU Emission Inventory Report 1990–2011 Under the UNECE Convention on LRTAP; EEA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Perrino, C.; Catrambone, M.; Dalla Torre, S.; Rantica, E.; Sargolini, T.; Canepari, S. Seasonal Variations in the Chemical Composition of Particulate Matter: A Case Study in the Po Valley. Part I: Macro-Components and Mass Closure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 3999–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Giannoni, M.; Giardi, F.; Becagli, S.; Severi, M.; Traversi, R.; Lucarelli, F. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Florence (Italy) by PMF Analysis of Aerosol Composition Records. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardi, F.; Nava, S.; Calzolai, G.; Pazzi, G.; Chiari, M.; Faggi, A.; Andreini, B.P.; Collaveri, C.; Franchi, E.; Nincheri, G.; et al. PM10 Variation, Composition, and Source Analysis in Tuscany (Italy) Following the COVID-19 Lockdown Restrictions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 9987–10005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Lucarelli, F.; Amato, F.; Becagli, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Giannoni, M.; Traversi, R.; Udisti, R. Biomass Burning Contributions Estimated by Synergistic Coupling of Daily and Hourly Aerosol Composition Records. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannoni, M.; Martellini, T.; Del Bubba, M.; Gambaro, A.; Zangrando, R.; Chiari, M.; Lepri, L.; Cincinelli, A. The Use of Levoglucosan for Tracing Biomass Burning in PM2.5 Samples in Tuscany (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2012, 167, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Bergström, R.; Fountoukis, C.; Johansson, C.; Pandis, S.N.; Simpson, D.; Visschedijk, A.J.H. Particulate Emissions from Residential Wood Combustion in Europe—Revised Estimates and an Evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 6503–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.S.; Koppmann, R.; Eck, T.F.; Eleuterio, D.P. A Review of Biomass Burning Emissions Part II: Intensive Physical Properties of Biomass Burning Particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.; Cameron, S.; Morrell, C.; Lowenstein, C.; Ling, F.; Zareba, W.; Hopke, P.; Utell, M.; Thurston, S.; Thevenet-Morrison, K.; et al. Associations between Ambient Wood Smoke and Other Particulate Pollutants and Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation, Coagulation and Thrombosis in Cardiac Patients. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Kulka, R.; Lavigne, E.; van Rijswijk, D.; Brauer, M.; Villeneuve, P.J.; Stieb, D.; Joseph, L.; Burnett, R.T. Biomass Burning as a Source of Ambient Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Acute Myocardial Infarction. Epidemiology 2017, 28, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Yang, K.; Darmenov, A.; Wu, C.; Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; et al. Understanding Processes That Control Dust Spatial Distributions with Global Climate Models and Satellite Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 13835–13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; Schulz, M.; Textor, C.; Guibert, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.E.; Berntsen, T.; Berglen, T.F.; Boucher, O.; Chin, M.; et al. An AeroCom Initial Assessment—Optical Properties in Aerosol Component Modules of Global Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahowald, N.M.; Li, L.; Albani, S.; Hamilton, D.S.; Kok, J.F. Opinion: The Importance of Historical and Paleoclimate Aerosol Radiative Effects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 533–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, R.B.; Aldrin, M.; Berntsen, T.K.; Holden, M.; Huseby, R.B.; Myhre, G.; Storelvmo, T. The Aerosol Pathway Is Crucial for Observationally Constraining Climate Sensitivity and Anthropogenic Forcing. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2024, 15, 1435–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szopa, S.; Naik, V.; Adhikary, B.; Artaxo, P.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.; Fuzzi, S.; Gallardo, L.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; Klimont, Z.; et al. Short-Lived Climate Forcers. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 817–922. ISBN 978-1-00-915788-9. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, A.; Báez-Ferrer, N.; Abreu-González, P.; Rodríguez, S.; Díaz, R.; Avanzas, P.; Hernández-Vaquero, D. Impact of Desert Dust Events on the Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsyfakis, M.; Zarogiannis, S.G.; Patelarou, E. The Health Impact of Saharan Dust Exposure. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2019, 32, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Zauli-Sajani, S.; Pey, J.; Samoli, E.; Alessandrini, E.; Basagaña, X.; Cernigliaro, A.; Chiusolo, M.; Demaria, M.; Díaz, J.; et al. Desert Dust Outbreaks in Southern Europe: Contribution to Daily PM10 Concentrations and Short-Term Associations with Mortality and Hospital Admissions. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasiou, A.; Moreno, N.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; de Leeuw, F.; Querol, X. Health Effects from Sahara Dust Episodes in Europe: Literature Review and Research Gaps. Environ. Int. 2012, 47, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrouzou, M.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Gkikas, A.; Korras-Carraca, M.-B.; Mihalopoulos, N. A Global Climatology of Dust Aerosols Based on Satellite Data: Spatial, Seasonal and Inter-Annual Patterns over the Period 2005–2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M.; Ginoux, P.; Torres, O.; Nicholson, S.E.; Gill, T.E. Environmental Characterization of Global Sources of Atmospheric Soil Dust Identified with the Nimbus 7 Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer (Toms) Absorbing Aerosol Product. Rev. Geophys. 2002, 40, 2-1–2-31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaver, A.; Formenti, P.; Caquineau, S.; Chevaillier, S.; Ausset, P.; Calzolai, G.; Osborne, S.; Johnson, B.; Harrison, M.; Dubovik, O. Physico-Chemical and Optical Properties of Sahelian and Saharan Mineral Dust: In Situ Measurements during the GERBILS Campaign. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 1193–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.; Calzolai, G.; Chiari, M.; Nava, S.; García, M.I.; López-Solano, J.; Marrero, C.; López-Darias, J.; Cuevas, E.; Alonso-Pérez, S.; et al. Rapid Changes of Dust Geochemistry in the Saharan Air Layer Linked to Sources and Meteorology. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnaba, F.; Bolignano, A.; Di Liberto, L.; Morelli, M.; Lucarelli, F.; Nava, S.; Perrino, C.; Canepari, S.; Basart, S.; Costabile, F.; et al. Desert Dust Contribution to PM10 Loads in Italy: Methods and Recommendations Addressing the Relevant European Commission Guidelines in Support to the Air Quality Directive 2008/50. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 161, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Agulló, E.; Barriopedro, D.; García, R.D.; Alonso-Pérez, S.; González-Alemán, J.J.; Werner, E.; Suárez, D.; Bustos, J.J.; García-Castrillo, G.; García, O.; et al. Sharp Increase in Saharan Dust Intrusions over the Western Euro-Mediterranean in February–March 2020–2022 and Associated Atmospheric Circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 4083–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Pey, J.; Pérez, N.; Querol, X.; Artíñano, B. Increasing Atmospheric Dust Transport towards the Western Mediterranean over 1948–2020. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.H. Chemical Markers for Sea Salt in IMPROVE Aerosol Data. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pósfai, M.; Molnár, Á. Atmospheric Aerosol Particles: A Mineralogical Introduction. In Environmental Mineralogy II; Vaughan, D.J., Wogelius, R.A., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of Great Britain and Ireland: Middlesex, UK, 2012; Volume 13, pp. 1–38. ISBN 978-0-903056-32-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.-P.; Zhang, H.-H.; Zhou, L.-M.; Yang, J. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Dimethylsulfide (DMS) and Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiwarter, W.; Bauer, H.; Caseiro, A.; Puxbaum, H. Quantifying Emissions of Primary Biological Aerosol Particle Mass in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of Global Terrestrial Isoprene Emissions Using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, D.K.; Seinfeld, J.H. Global Secondary Organic Aerosol from Isoprene Oxidation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L09812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Xu, X.; Chu, M.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J. Air Particulate Matter and Cardiovascular Disease: The Epidemiological, Biomedical and Clinical Evidence. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, E8–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Pei, Y.-H.; Gu, Y.-Y.; Zhu, J.-F.; Yu, P.; Chen, X.-H. Association between Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Heart Failure: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of More than 7 Million Participants. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 948765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadi, Z.; Abulghasem Gorgi, H.; Shabaninejad, H.; Aghajani Delavar, M.; Torani, S. Association between PM2.5 and Risk of Hospitalization for Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, D.Q.; Peters, A.; Schneider, A.; Zareba, W.; Breitner, S.; Oakes, D.; Wiltshire, J.; Kane, C.; Frampton, M.W.; Hampel, R.; et al. Ambient and Controlled Particle Exposures as Triggers for Acute ECG Changes. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2016, 186, 5–75. [Google Scholar]
- Tonne, C.; Yanosky, J.D.; Beevers, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Kelly, F.J. PM Mass Concentration and PM Oxidative Potential in Relation to Carotid Intima-Media Thickness. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provost, E.B.; Madhloum, N.; Int Panis, L.; De Boever, P.; Nawrot, T.S. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness, a Marker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis, and Particulate Air Pollution Exposure: The Meta-Analytical Evidence. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, M.H.; Simon-Friedt, B.; Yahya, T.; Khan, A.Y.; Hassan, S.Z.; Kash, B.; Blankstein, R.; Blaha, M.J.; Virani, S.S.; Rajagopalan, S.; et al. Associations between Particulate Matter Air Pollution, Presence and Progression of Subclinical Coronary and Carotid Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review. Atherosclerosis 2020, 306, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hou, Z.-H.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Budoff, M.J.; Szpiro, A.A.; Kaufman, J.D.; Vedal, S.; Lu, B. Association of Estimated Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Traffic Proximity with a Marker for Coronary Atherosclerosis in a Nationwide Study in China. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e196553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennig, F.; Geisel, M.H.; Kälsch, H.; Lucht, S.; Mahabadi, A.A.; Moebus, S.; Erbel, R.; Lehmann, N.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Scherag, A.; et al. Air Pollution and Progression of Atherosclerosis in Different Vessel Beds-Results from a Prospective Cohort Study in the Ruhr Area, Germany. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 107003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbo Edlund, K.; Sallsten, G.; Molnár, P.; Andersson, E.M.; Ögren, M.; Segersson, D.; Fagman, E.; Fagerberg, B.; Barregard, L.; Bergström, G.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution, Coronary Artery Calcification, and Carotid Artery Plaques in the Population-Based Swedish SCAPIS Gothenburg Cohort. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, F.; Sabatino, L.; Gaggini, M.; Chatzianagnostou, K.; Vassalle, C. Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in the Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes and Air Pollution. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Mao, H.; Zeng, H.; Lv, F.; Wang, J. Causal Relationship Between Air Pollutants and Blood Pressure Phenotypes: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Glob. Heart 2025, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossoli, A.; Cetti, F.; Gomaraschi, M. Air Pollution: Another Threat to HDL Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasslöf, H.; Molnár, P.; Andersson, E.M.; Spanne, M.; Gustafsson, S.; Stroh, E.; Engström, G.; Stockfelt, L. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Atherosclerosis in the Carotid Arteries in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Lin, Z.; He, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Huang, K.; Cao, J.; et al. Effect of Air Pollution on Heart Failure: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 76001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, W.; Cheng, C.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Qin, P.; Chen, C.; Luo, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-H.; Jørgensen, J.T.; So, R.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Mehta, A.J.; Amini, H.; Bräuner, E.V.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; Liu, S.; Mortensen, L.H.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution, Road Traffic Noise, and Heart Failure Incidence: The Danish Nurse Cohort. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Tian, A.; Peng, K.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Association between Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Clinical Outcomes among Patients with Heart Failure: Findings from the China PEACE Prospective Heart Failure Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Danesh Yazdi, M.; Moyer, J.; Weaver, A.M.; Cascio, W.E.; Di, Q.; Schwartz, J.D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Long-Term Exposure to Particulate Air Pollution Is Associated with 30-Day Readmissions and Hospital Visits Among Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, P.; Kasdagli, M.-I.; Pérez Velasco, R.; Samoli, E. Long-Term Exposure to Particulate Matter and Mortality: An Update of the WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Public Health 2024, 69, 1607683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, J.; Hu, P.; Deng, C.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, W.; Zhu, G.; Zheng, G.; et al. Key Factors in Epidemiological Exposure and Insights for Environmental Management: Evidence from Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinn, L.A.; Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Neas, L.M.; Schneider, A.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Cascio, W.E.; Kraus, W.E.; Hauser, E.; Dowdy, E.; Haynes, C.; et al. Association between Satellite-Based Estimates of Long-Term PM2.5 Exposure and Coronary Artery Disease. Environ. Res. 2016, 145, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Zong, Q.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, H.; Yan, S.; Mao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, S.; Lv, C. Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Myocardial Infarction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 616355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Muhlestein, J.B.; May, H.T.; Renlund, D.G.; Anderson, J.L.; Horne, B.D. Ischemic Heart Disease Events Triggered by Short-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Air Pollution. Circulation 2006, 114, 2443–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-C.; Chen, P.-L. Effect of Short-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter and Particulate Matter Pollutants on Triggering Acute Myocardial Infarction and Acute Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 175, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancini, G.; Farina, F.; Battaglia, C.; Cifola, I.; Mangano, E.; Mantecca, P.; Camatini, M.; Palestini, P. Health Risk Assessment for Air Pollutants: Alterations in Lung and Cardiac Gene Expression in Mice Exposed to Milano Winter Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredeck, G.; Busch, M.; Rossi, A.; Stahlmecke, B.; Fomba, K.W.; Herrmann, H.; Schins, R.P.F. Inhalable Saharan dust induces oxidative stress, NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and inflammatory cytokine release. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.; Katra, I.; Schaeur, J.J.; Rudich, Y. Mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress induced by desert dust in rat alveolar macrophages. Geohealth 2017, 6, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Chan, C.C.; Wang, P.Y.; Cheng, T.J. Effects of concentrated ambient particles on heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac contractility in spontaneously hypertensive rats during a dust storm event. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Seki, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Kaikita, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Tsujita, K.; Masuda, I.; Kawakami, K. Association of short term exposure to Asian dust with increased blood pressure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 19, 17630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Mu, M.; Fang, K.; Qian, Y.; Xue, S.; Hu, W.; Ye, M. Occupational exposure to silica and risk of heart disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 7, e029653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, R.; Michikawa, T.; Ueda, K.; Nitta, H.; Kawasaki, T.; Tashiro, H.; Mohri, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Desert dust is a risk factor for the incidence of acute myocardial infarction in Western Japan. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2014, 7, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, M.; Seki, T.; Kaikita, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Nakai, M.; Sumita, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Yasuda, S.; et al. Short-term exposure to desert dust and the risk of acute myocardial infarction in Japan: A time-stratified case-crossover study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevan, G.H.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D.; Münzel, T.; Rajagopalan, S. Ambient Air Pollution and Atherosclerosis: Insights into Dose, Time, and Mechanisms. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfino, R.J.; Staimer, N.; Tjoa, T.; Gillen, D.L.; Polidori, A.; Arhami, M.; Kleinman, M.T.; Vaziri, N.D.; Longhurst, J.; Sioutas, C. Air pollution exposures and circulating biomarkers of effect in a susceptible population: Clues to potential causal component mixtures and mechanisms. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Neas, L.; Herbst, M.C.; Case, M.; Williams, R.W.; Cascio, W.; Hinderliter, A.; Holguin, F.; Buse, J.B.; Dungan, K.; et al. Endothelial dysfunction: Associations with exposure to ambient fine particles in diabetic individuals. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigano, J.; Baccarelli, A.; Wright, R.O.; Suh, H.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Air Pollution, Obesity, Genes and Cellular Adhesion Molecules. Occup. Environ. Med. 2010, 67, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilbo Edlund, K.; Xu, Y.; Andersson, E.M.; Christensson, A.; Dehlin, M.; Forsblad-d’Elia, H.; Harari, F.; Ljunggren, S.; Molnár, P.; Oudin, A.; et al. Long-term ambient air pollution exposure and renal function and biomarkers of renal disease. Environ. Health 2024, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.X.; Bloom, M.S.; Qian, Z.M.; Liu, E.; Jansson, D.R.; Vaughn, M.G.; Lin, H.L.; Xiao, L.W.; Duan, C.W.; Yang, L.; et al. Association between ambient air pollution and hyperuricemia in traffic police officers in China: A cohort study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2021, 31, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.K.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, K.; Chen, N.; Ma, L.L.; Yan, Y.X. Associations between long-term exposure to ambient fine particulate pollution with the decline of kidney function and hyperuricemia: A longitudinal cohort study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 40507–40518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassalle, C.; Mazzone, A.; Sabatino, L.; Carpeggiani, C. Uric Acid for Cardiovascular Risk: Dr. Jekyll or Mr. Hide? Diseases 2016, 26, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.H.; Zeeshan, M.; Huang, G.F.; Chen, D.H.; Xie, M.; Liu, J.; Dong, G.H. Influence of Air Pollution Exposures on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Review. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2023, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, S.; Jin, S.; Liu, H.; Xia, W.; Liang, G.; Xu, S.; Fang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; et al. Fine particulate matter exposure and perturbation of serum metabolome: A longitudinal study in Baoding, China. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Feng, A.; Tang, Z. Association between total bilirubin and gender-specific incidence of fundus arteriosclerosis in a Chinese population: A retrospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 11, 11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmanesh, E.; Dianat, M.; Badavi, M.; Goudarzi, G.; Mard, S.A.; Radan, M. Protective effect of crocin on hemodynamic parameters, electrocardiogram parameters, and oxidative stress in isolated hearts of rats exposed to PM10. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2022, 25, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepu, R.S.; Dostal, D.E.; Garcia, C.; Kennedy, R.H.; Sethi, R. Cardiac dysfunction subsequent to chronic ozone exposure in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 360, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Antioxidant enzyme induction: A new protective approach against the adverse effects of diesel exhaust particles. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. Inhaled glutathione for the prevention of air pollution-related health effects: A brief review. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2008, 14, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.Y.; Roh, H.T. Impact of Particulate Matter Exposure and Aerobic Exercise on Circulating Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Status, and Inflammation in Young and Aged Mice. Life 2023, 13, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.V.; Langrish, J.P.; Nair, H.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Global Association of Air Pollution and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet 2013, 382, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, D.; Franco, F.; Bravo Baptista, S.; Cabral, S.; Cachulo, M.d.C.; Dores, H.; Peixeiro, A.; Rodrigues, R.; Santos, M.; Timóteo, A.T.; et al. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Position Paper. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2022, 41, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter; Final Report; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Rajagopalan, S.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Brook, R.D. Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2054–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yang, D.; Wei, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Shima, M.; Deng, F.; Guo, X. Association of Chemical Constituents and Pollution Sources of Ambient Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress Associated with Atherosclerosis: A Panel Study among Young Adults in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, T.; Kipen, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Rich, D.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, S.-E.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; et al. Cardiorespiratory Biomarker Responses in Healthy Young Adults to Drastic Air Quality Changes Surrounding the 2008 Beijing Olympics. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2013, 5, 174. [Google Scholar]
- Münzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Sørensen, M.; Lelieveld, J.; Duerr, G.D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Daiber, A. Environmental Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Diseases: A Comprehensive Expert Review. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2880–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Role of Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes Following Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itabe, H. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein as a Biomarker of in Vivo Oxidative Stress: From Atherosclerosis to Periodontitis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2012, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Witztum, J.L. Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein and Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuda, O.; Jenkins, C.M.; Skinner, J.R.; Moon, S.H.; Su, X.; Gross, R.W.; Abumrad, N.A. CD36 Protein Is Involved in Store-Operated Calcium Flux, Phospholipase A2 Activation, and Production of Prostaglandin E2. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17785–17795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, L.; Emmerechts, J.; Mathieu, C.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Fierens, F.; Hoet, P.H.; Nemery, B.; Nawrot, T.S. Air Pollution Related Prothrombotic Changes in Persons with Diabetes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelishadi, R.; Mirghaffari, N.; Poursafa, P.; Gidding, S.S. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors Associated with Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance in Children. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ning, Z.; Cui, J.; Khalsa, B.; Ai, L.; Takabe, W.; Beebe, T.; Majumdar, R.; Sioutas, C.; Hsiai, T. Ultrafine Particles from Diesel Engines Induce Vascular Oxidative Stress via JNK Activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagryantseva, Y.; Novotna, B.; Rossner, P.; Chvatalova, I.; Milcova, A.; Svecova, V.; Lnenickova, Z.; Solansky, I.; Sram, R.J. Oxidative Damage to Biological Macromolecules in Prague Bus Drivers and Garagemen: Impact of Air Pollution and Genetic Polymorphisms. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossner, P.; Svecova, V.; Milcova, A.; Lnenickova, Z.; Solansky, I.; Santella, R.M.; Sram, R.J. Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress Markers in Bus Drivers. Mutat. Res. 2007, 617, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brucker, N.; Moro, A.M.; Charão, M.F.; Durgante, J.; Freitas, F.; Baierle, M.; Nascimento, S.; Gauer, B.; Bulcão, R.P.; Bubols, G.B.; et al. Biomarkers of Occupational Exposure to Air Pollution, Inflammation and Oxidative Damage in Taxi Drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-H.; Huang, H.-B.; Chang, Y.-C.; Su, T.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, G.-C.; Chen, J.-E.; Tang, C.-S.; Wu, T.-N.; Liou, S.-H. Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter Causes Oxidative and Methylated DNA Damage in Young Adults: A Longitudinal Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Bo, L.; Gong, C.; Du, X.; Kan, H.; Xie, Y.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. Traffic-Related Air Pollution Is Associated with Cardio-Metabolic Biomarkers in General Residents. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2016, 89, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, N.; Mao, S.; Ma, R.; He, H.; Niu, Z.; Chen, X.; Xiang, H. The Short- and Long-Term Associations of Particulate Matter with Inflammation and Blood Coagulation Markers: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Lavigne, E.; Evans, G.; Pollitt, K.; Burnett, R.T. Ambient PM2.5 and Risk of Emergency Room Visits for Myocardial Infarction: Impact of Regional PM2.5 Oxidative Potential: A Case-Crossover Study. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Rodriguez, A.; Rodríguez, S.; Abreu-Gonzalez, P.; Avanzas, P.; Juarez-Prera, R.A. Black Carbon Exposure, Oxidative Stress Markers and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 188, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodosthenous, R.S.; Coull, B.A.; Lu, Q.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J.D.; Baccarelli, A.A. Ambient Particulate Matter and microRNAs in Extracellular Vesicles: A Pilot Study of Older Individuals. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aztatzi-Aguilar, O.G.; Uribe-Ramírez, M.; Arias-Montaño, J.A.; Barbier, O.; De Vizcaya-Ruiz, A. Acute and Subchronic Exposure to Air Particulate Matter Induces Expression of Angiotensin and Bradykinin-Related Genes in the Lungs and Heart: Angiotensin-II Type-I Receptor as a Molecular Target of Particulate Matter Exposure. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Kido, T.; Suzuki, H.; Yang, G.; Kavanagh, T.J.; Kaufman, J.D.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; van Breemen, C.; Eeden, S.F. van Changes in Atherosclerotic Plaques Induced by Inhalation of Diesel Exhaust. Atherosclerosis 2011, 216, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Lawal, A.; Ricks, J.; Fox, J.R.; Larson, T.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Rosenfeld, M.E.; Araujo, J.A. Diesel Exhaust Induces Systemic Lipid Peroxidation and Development of Dysfunctional Pro-Oxidant and pro-Inflammatory High-Density Lipoprotein. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; McLean, S.G.; Duffin, R.; Lawal, A.O.; Araujo, J.A.; Shaw, C.A.; Mills, N.L.; Donaldson, K.; Newby, D.E.; Hadoke, P.W.F. Diesel Exhaust Particulate Increases the Size and Complexity of Lesions in Atherosclerotic Mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodavanti, U.P.; Thomas, R.; Ledbetter, A.D.; Schladweiler, M.C.; Shannahan, J.H.; Wallenborn, J.G.; Lund, A.K.; Campen, M.J.; Butler, E.O.; Gottipolu, R.R.; et al. Vascular and Cardiac Impairments in Rats Inhaling Ozone and Diesel Exhaust Particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.K.; Lucero, J.; Harman, M.; Madden, M.C.; McDonald, J.D.; Seagrave, J.C.; Campen, M.J. The Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Mediates Vascular Effects of Inhaled Vehicle Emissions. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorr, M.W.; Youtz, D.J.; Eichenseer, C.M.; Smith, K.E.; Nelin, T.D.; Cormet-Boyaka, E.; Wold, L.E. In Vitro Particulate Matter Exposure Causes Direct and Lung-Mediated Indirect Effects on Cardiomyocyte Function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H53-62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, L.E.; Ying, Z.; Hutchinson, K.R.; Velten, M.; Gorr, M.W.; Velten, C.; Youtz, D.J.; Wang, A.; Lucchesi, P.A.; Sun, Q.; et al. Cardiovascular Remodeling in Response to Long-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter Air Pollution. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Navab, M.; Pakbin, P.; Ning, Z.; Navab, K.; Hough, G.; Morgan, T.E.; Finch, C.E.; Araujo, J.A.; Fogelman, A.M.; et al. Ambient Ultrafine Particles Alter Lipid Metabolism and HDL Anti-Oxidant Capacity in LDLR-Null Mice. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.A.; Barajas, B.; Kleinman, M.; Wang, X.; Bennett, B.J.; Gong, K.W.; Navab, M.; Harkema, J.; Sioutas, C.; Lusis, A.J.; et al. Ambient Particulate Pollutants in the Ultrafine Range Promote Early Atherosclerosis and Systemic Oxidative Stress. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liao, R.; Cao, W.; Huang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Li, Y. Subacute PM2.5 Exposure Induces Hepatic Insulin Resistance Through Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; André, L.; Tanguy, S.; Boissiere, J.; Farah, C.; Lopez-Lauri, F.; Gayrard, S.; Richard, S.; Boucher, F.; Cazorla, O.; et al. Simulated Urban Carbon Monoxide Air Pollution Exacerbates Rat Heart Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 298, H1445-1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, G.; André, L.; Kleindienst, A.; Singh, F.; Tanguy, S.; Richard, S.; Obert, P.; Boucher, F.; Jover, B.; Cazorla, O.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Increases Inducible NOS Expression That Mediates CO-Induced Myocardial Damage during Ischemia-Reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 308, H759–H767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perepu, R.S.P.; Garcia, C.; Dostal, D.; Sethi, R. Enhanced Death Signaling in Ozone-Exposed Ischemic-Reperfused Hearts. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 336, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.G.; Davey, M.P.; Viant, M.R. Environmental Metabolomics: A Critical Review and Future Perspectives. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tang, Z.; Diver, W.R.; Sarnat, J.A.; Chow, S.S.; Cheng, H.; Deubler, E.L.; Tan, Y.; Eick, S.M.; Jerrett, M.; et al. Metabolomics Signatures of Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution: A Large-Scale Metabolome-Wide Association Study in the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassan, F.L.; Kelly, R.S.; Kosheleva, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Vokonas, P.S.; Lasky-Su, J.A.; Schwartz, J.D. Metabolomic Signatures of the Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Temperature. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, T.; et al. Lipidomics Identified Novel Cholesterol-Independent Predictors for Risk of Incident Coronary Heart Disease: Mediation of Risk from Diabetes and Aggravation of Risk by Ambient Air Pollution. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 65, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, F.; Qian, Z.M.; Wei, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Arnold, L.D.; McMillin, S.E.; et al. Association of Metabolic Signatures of Air Pollution with MASLD: Observational and Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Pérez, R.D.; Taborda, N.A.; Gómez, D.M.; Narvaez, J.F.; Porras, J.; Hernandez, J.C. Inflammatory Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 42390–42404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, E.H. Structure and Function of Telomeres. Nature 1991, 350, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, J.M.J.; Moonen, H.J.J.; van Schooten, F.J.; Hageman, G.J. Telomere Length Assessment: Biomarker of Chronic Oxidative Stress? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.Y.Y.; De Vivo, I.; Lin, X.; Christiani, D.C. Cumulative PM(2.5) Exposure and Telomere Length in Workers Exposed to Welding Fumes. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2014, 77, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Wang, S.; Dou, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Avula, U.; Hoxha, M.; Díaz, A.; McCracken, J.; et al. Air Pollution Exposure and Telomere Length in Highly Exposed Subjects in Beijing, China: A Repeated-Measure Study. Environ. Int. 2012, 48, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhen, S.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Liao, J.; Zhu, B.; Duan, J.; Yang, X.; et al. Outdoor Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Telomere Length in Humans: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 275, 116206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Mehta, A.; Mordukhovich, I.; Just, A.C.; Shen, J.; Hou, L.; Koutrakis, P.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. Differential DNA Methylation and PM2.5 Species in a 450K Epigenome-Wide Association Study. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellavia, A.; Urch, B.; Speck, M.; Brook, R.D.; Scott, J.A.; Albetti, B.; Behbod, B.; North, M.; Valeri, L.; Bertazzi, P.A.; et al. DNA Hypomethylation, Ambient Particulate Matter, and Increased Blood Pressure: Findings from Controlled Human Exposure Experiments. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2013, 2, e000212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigano, J.; Baccarelli, A.; Mittleman, M.A.; Wright, R.O.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Tarantini, L.; Schwartz, J. Prolonged Exposure to Particulate Pollution, Genes Associated with Glutathione Pathways, and DNA Methylation in a Cohort of Older Men. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, L.; Bonzini, M.; Apostoli, P.; Pegoraro, V.; Bollati, V.; Marinelli, B.; Cantone, L.; Rizzo, G.; Hou, L.; Schwartz, J.; et al. Effects of Particulate Matter on Genomic DNA Methylation Content and iNOS Promoter Methylation. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marketou, M.E.; Kontaraki, J.E.; Zacharis, E.A.; Kochiadakis, G.E.; Giaouzaki, A.; Chlouverakis, G.; Vardas, P.E. TLR2 and TLR4 Gene Expression in Peripheral Monocytes in Nondiabetic Hypertensive Patients: The Effect of Intensive Blood Pressure-Lowering. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2012, 14, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boovarahan, S.R.; Kurian, G.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Key Player in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Diseases Linked to Air Pollution. Rev. Environ. Health 2018, 33, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annesley, S.J.; Fisher, P.R. Mitochondria in Health and Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotty, J.; Kluza, J.; De Sousa, C.; Tardivel, M.; Anthérieu, S.; Alleman, L.-Y.; Canivet, L.; Perdrix, E.; Loyens, A.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Mitochondrial Alterations Triggered by Repeated Exposure to Fine (PM2.5–0.18) and Quasi-Ultrafine (PM0.18) Fractions of Ambient Particulate Matter. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Wu, T.; Tang, M. Urban Particulate Matter Disturbs the Equilibrium of Mitochondrial Dynamics and Biogenesis in Human Vascular Endothelial Cells. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloquet, H.; Ferchaud-Roucher, V.; Duengler, F.; Zair, Y.; Maugere, P.; Krempf, M. Insulin Effects on Acetate Metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E561–E565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Su, H.; Ahmed, R.Z.; Zheng, Y.; Jin, X. Critical Biomarkers for Myocardial Damage by Fine Particulate Matter: Focused on PPARα-Regulated Energy Metabolism. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Popp, A.; Schneider, A.; Breitner, S.; Hampel, R.; Rathmann, W.; Herder, C.; Roden, M.; Koenig, W.; Meisinger, C.; et al. Association Between Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Biomarkers Related to Insulin Resistance, Subclinical Inflammation, and Adipokines. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3314–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, M.; Zhang, J.; Duan, J.; Hu, D.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Jia, X.; Deng, F.; Sun, Z. Urine Metabolites Associated with Cardiovascular Effects from Exposure of Size-Fractioned Particulate Matter in a Subway Environment: A Randomized Crossover Study. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Elmariah, S.; Gerszten, R.E.; Dyck, J.R.B. The Emerging Role of Metabolomics in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2850–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate-Gonzalez, G.; Brown, P.; Cisneros, R. Assessing Public Support for Air Pollution Mitigation and Control Policies: Health, Socioeconomic, and Ideological Predictors in an Overburdened and Vulnerable Region of the U.S. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Lu, S.-E.; Kipen, H.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M.; Lin, W.; Rich, D.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Diehl, S.R.; et al. Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Responses of Healthy Young Adults to Changes in Air Quality during the Beijing Olympics. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, D.Q.; Kipen, H.M.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ohman-Strickland, P.; Hu, M.; Philipp, C.; Diehl, S.R.; et al. Association between Changes in Air Pollution Levels during the Beijing Olympics and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Thrombosis in Healthy Young Adults. JAMA 2012, 307, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Air Pollution. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/air-pollution#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- Barthelemy, J.; Sanchez, K.; Miller, M.R.; Khreis, H. New Opportunities to Mitigate the Burden of Disease Caused by Traffic Related Air Pollution: Antioxidant-Rich Diets and Supplements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péter, S.; Holguin, F.; Wood, L.G.; Clougherty, J.E.; Raederstorff, D.; Antal, M.; Weber, P.; Eggersdorfer, M. Nutritional Solutions to Reduce Risks of Negative Health Impacts of Air Pollution. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10398–10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresti, A.L. Association between Micronutrients and Heart Rate Variability: A Review of Human Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Jiang, S.; Xie, Y.; Kan, H.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. Effect of Vitamin E and Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Protecting Ambient PM2.5-Induced Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress in Vascular Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jiang, S.; Bo, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Xie, Y.; He, Q.; Ye, X.; Song, W.; Zhao, J. Combined Effects of Vitamin E and Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Protecting Ambient PM2.5-Induced Cardiovascular Injury in Rats. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuckles, T.L.; Jaskot, R.; Richards, J.H.; Miller, C.A.; Ledbetter, A.; McGee, J.; Linak, W.P.; Dreher, K.L. Biokinetically-Based in Vitro Cardiotoxicity of Residual Oil Fly Ash: Hazard Identification and Mechanisms of Injury. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2013, 13, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-B.; Kim, C.; Choi, E.; Park, S.; Park, H.; Pak, H.-N.; Lee, M.-H.; Shin, D.C.; Hwang, K.-C.; Joung, B. Particulate Air Pollution Induces Arrhythmia via Oxidative Stress and Calcium Calmodulin Kinase II Activation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 259, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bao, X.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Amelioration of Metabolic Disorders in H9C2 Cardiomyocytes Induced by PM2.5 Treated with Vitamin C. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 47, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Karlsson, O.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Lin, X.; Zemplenyi, M.; Sanchez-Guerra, M.; Trevisi, L.; Urch, B.; et al. B Vitamins Attenuate the Epigenetic Effects of Ambient Fine Particles in a Pilot Human Intervention Trial. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3503–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Huang, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H. Vitamin B Ameliorates PM2.5-Induced Kidney Damage by Reducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress in Pregnant Mice and HK-2. Toxicology 2023, 494, 153568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Ge, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Cardiovascular Benefits of Fish-Oil Supplementation Against Fine Particulate Air Pollution in China. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Rappold, A.G.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Steck, S.E.; Berntsen, J.; Cascio, W.E.; Devlin, R.B.; Samet, J.M. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation Appears to Attenuate Particulate Air Pollution-Induced Cardiac Effects and Lipid Changes in Healthy Middle-Aged Adults. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Guo, W.; An, Z.; Zeng, X.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Wu, W. Amelioration of PM2.5-Induced Lung Toxicity in Rats by Nutritional Supplementation with Fish Oil and Vitamin E. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S.; Shen, W.; Salazar, C.; Schneider, A.; Wyatt, L.H.; Rappold, A.G.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Devlin, R.B.; Samet, J.M.; et al. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Attenuate Cardiovascular Effects of Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, M.; Radmanesh, E.; Badavi, M.; Mard, S.A.; Goudarzi, G. Disturbance Effects of PM10 on iNOS and eNOS mRNA Expression Levels and Antioxidant Activity Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Isolated Rat Heart: Protective Role of Vanillic Acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 5154–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Kim, H.J. High Air Pollution Exposure, Vitamin D Deficiency and Ever Smokers Were Associated with Higher Prevalence of Hypercholesterolemia: A Cross-Sectional Study from the 2008–2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Res. 2025, 134, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhan, Z.; Li, D.; Chen, H.; Li, A.; Hu, J.; Huang, Z.; Yi, B. Protective Role of Vitamin D Receptor against Mitochondrial Calcium Overload from PM2.5-Induced Injury in Renal Tubular Cells. Redox Biol. 2025, 80, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J.; Shao, Y.; Silverman, D.T.; Jones, R.R.; Thurston, G.D. Mediterranean Diet and the Association Between Air Pollution and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Risk. Circulation 2019, 139, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Maugeri, A.; Quattrocchi, A.; Barone, G.; Mazzoleni, P.; Catalfo, A.; De Guidi, G.; Iemmolo, M.G.; Crimi, N.; Agodi, A. Mediterranean Diet and Particulate Matter Exposure Are Associated with LINE-1 Methylation: Results From a Cross-Sectional Study in Women. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandayataray, P.; Murthy, M.K. Dietary Interventions in Mitigating the Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Alzheimer’s Disease—A Review. Neuroscience 2024, 563, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Velasco, O.A.; Morales-Suárez-Varela, M.; Llopis-González, A. Dietary Flavonoids: Mitigating Air Pollution’s Cardiovascular Risks. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, K.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Wen, D. Hydroxytyrosol Prevents PM2.5-Induced Adiposity and Insulin Resistance by Restraining Oxidative Stress Related NF-κB Pathway and Modulation of Gut Microbiota in a Murine Model. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 141, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Tsai, H.-T.; Weng, C.-Y.; Yet, S.-F.; Lin, P. Ambient Particulate Matter Induces Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Changes via NOX1/ROS/NF-κB Dependent and Independent Pathways: Protective Effects of Polyphenols. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.-C.; Nicol, C.J.B.; Yang, Y.-P.; Chiang, T.; Yen, C. Protective Effects of Resveratrol against PM2.5-Induced Damage in hNSCs and Its Mitigation of PM2.5-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in a 3D Scaffold System. Neuroscience 2025, 569, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.-W.; Lee, H.-S.; Na, J.-I.; Huh, C.-H.; Park, K.-C.; Choi, H.-R. Resveratrol Inhibits Particulate Matter-Induced Inflammatory Responses in Human Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qian, W.; Wang, D.; Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, C.; Zhong, C.; Fu, S. Resveratrol Relieves Particulate Matter (Mean Diameter < 2.5 Μm)-Induced Oxidative Injury of Lung Cells through Attenuation of Autophagy Deregulation. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Abd El-Gawaad, N.S.; Osman Abdallah, S.A.; Al-Dossari, M. Possible Modulating Functions of Probiotic Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum in Particulate Matter-Associated Pulmonary Inflammation. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1290914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Pei, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Shi, S.; Shen, Z.; Li, S.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Probiotics Ameliorates Pulmonary Inflammation via Modulating Gut Microbiota and Rectifying Th17/Treg Imbalance in a Rat Model of PM2.5 Induced Lung Injury. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 244, 114060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, L.; Xia, Y. The Interaction between Genetic Predicted Gut Microbiome Abundance and Particulate Matter on the Risk of Incident Asthma in Adults. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 291, 117848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Z.; Du, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prophylactic Supplementation with Lactobacillus Reuteri or Its Metabolite GABA Protects Against Acute Ischemic Cardiac Injury. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2307233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borshchev, Y.Y.; Sonin, D.L.; Burovenko, I.Y.; Borshchev, V.Y.; Cheburkin, Y.V.; Borshcheva, O.V.; Galagudza, M.M. The Effect of Probiotic Strains on Myocardial Infarction Size, Biochemical and Immunological Parameters in Rats with Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome and Polymorbidity. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 58, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghzadeh, J.; Vakili, A.; Sameni, H.R.; Shadnoush, M.; Bandegi, A.-R.; Zahedi Khorasani, M. The Effect of Oral Consumption of Probiotics in Prevention of Heart Injury in a Rat Myocardial Infarction Model: A Histopathological, Hemodynamic and Biochemical Evaluation. Iran. Biomed. J. 2017, 21, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Gao, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X. Remodeling of the Gut Microbiome by Lactobacillus Johnsonii Alleviates the Development of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1140498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.T.; Ettinger, G.; Huang, C.X.; Burton, J.P.; Haist, J.V.; Rajapurohitam, V.; Sidaway, J.E.; Martin, G.; Gloor, G.B.; Swann, J.R.; et al. Probiotic Administration Attenuates Myocardial Hypertrophy and Heart Failure after Myocardial Infarction in the Rat. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, V.; Su, J.; Koprowski, S.; Hsu, A.; Tweddell, J.S.; Rafiee, P.; Gross, G.J.; Salzman, N.H.; Baker, J.E. Intestinal Microbiota Determine Severity of Myocardial Infarction in Rats. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekkanen, J.; Peters, A.; Hoek, G.; Tiittanen, P.; Brunekreef, B.; de Hartog, J.; Heinrich, J.; Ibald-Mulli, A.; Kreyling, W.G.; Lanki, T.; et al. Particulate Air Pollution and Risk of ST-Segment Depression during Repeated Submaximal Exercise Tests among Subjects with Coronary Heart Disease: The Exposure and Risk Assessment for Fine and Ultrafine Particles in Ambient Air (ULTRA) Study. Circulation 2002, 106, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoden, C.R.; Wellenius, G.A.; Ghelfi, E.; Lawrence, J.; González-Flecha, B. PM-Induced Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Dysfunction Are Mediated by Autonomic Stimulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1725, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.; Thomson, A.L.; Carter, R.; Stott, H.R.; Shaw, C.A.; Hadoke, P.W.F.; Newby, D.E.; Miller, M.R.; Gray, G.A. Pulmonary Diesel Particulate Increases Susceptibility to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Activation of Sensory TRPV1 and Β1 Adrenoreceptors. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarella, S.E.; Soberanes, S.; Urich, D.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Nigdelioglu, R.; Green, D.; Young, J.B.; Gonzalez, A.; Rosario, C.; Misharin, A.V.; et al. Β2-Adrenergic Agonists Augment Air Pollution-Induced IL-6 Release and Thrombosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Kwong, J.C.; Kaufman, J.S.; Benmarhnia, T.; Chen, C.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Kim, J.; Lu, H.; Burnett, R.T.; et al. Effect Modification by Statin Use Status on the Association between Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and Cardiovascular Mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 53, dyae084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.; Park, S.K.; O’Neill, M.S.; Vokonas, P.S.; Sparrow, D.; Weiss, S.; Kelsey, K. Glutathione-S-Transferase M1, Obesity, Statins, and Autonomic Effects of Particles: Gene-by-Drug-by-Environment Interaction. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Ren, Y. Atorvastatin Ameliorated PM2.5-Induced Atherosclerosis in Rats. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2023, 78, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Lv, J. Statin Attenuated Myocardial Inflammation Induced by PM2.5 in Rats. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2017, 33, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostro, B.; Malig, B.; Broadwin, R.; Basu, R.; Gold, E.B.; Bromberger, J.T.; Derby, C.; Feinstein, S.; Greendale, G.A.; Jackson, E.A.; et al. Chronic PM2.5 Exposure and Inflammation: Determining Sensitive Subgroups in Mid-Life Women. Environ. Res. 2014, 132, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexeeff, S.E.; Coull, B.A.; Gryparis, A.; Suh, H.; Sparrow, D.; Vokonas, P.S.; Schwartz, J. Medium-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution and Markers of Inflammation and Endothelial Function. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartiala, J.; Breton, C.V.; Tang, W.H.W.; Lurmann, F.; Hazen, S.L.; Gilliland, F.D.; Allayee, H. Ambient Air Pollution Is Associated with the Severity of Coronary Atherosclerosis and Incident Myocardial Infarction in Patients Undergoing Elective Cardiac Evaluation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Jeong, S.; Choi, S.; Chang, J.; Choi, D.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.R.; Park, S.M. Cardiovascular Benefit of Statin Use Against Air Pollutant Exposure in Older Adults. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 32, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghelfi, E.; Wellenius, G.A.; Lawrence, J.; Millet, E.; Gonzalez-Flecha, B. Cardiac Oxidative Stress and Dysfunction by Fine Concentrated Ambient Particles (CAPs) Are Mediated by Angiotensin-II. Inhal. Toxicol. 2010, 22, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Lee, H.-H.; Gong, D.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Yi, E.; Schini-Kerth, V.; Oak, M.-H. Fine Air Pollution Particles Induce Endothelial Senescence via Redox-Sensitive Activation of Local Angiotensin System. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, G.L.; Romieu, I.; Sienra-Monge, J.J.; Collins, W.J.; Ramirez-Aguilar, M.; del Rio-Navarro, B.E.; Reyes-Ruiz, N.I.; Morris, R.W.; Marzec, J.M.; London, S.J. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) reduced:quinone oxidoreductase and glutathione S-transferase M1 polymorphisms and childhood asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.J.; Collier, A.C.; Bowen, L.D.; Pritsos, K.L.; Goodrich, G.G.; Arger, K.; Cutter, G.; Pritsos, C.A. Polymorphisms in the NQO1, GSTT and GSTM genes are associated with coronary heart disease and biomarkers of oxidative stress. Mutat. Res. 2009, 674, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Aggarwal, S.G. On the techniques and standards of particulate matter sampling. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2022, 72, 791–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Hsu, N.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Levy, R.C.; Lyapustin, A.; Sayer, A.M.; Winker, D.M. Global Estimates of Fine Particulate Matter Using a Combined Geophysical-Statistical Method with Information from Satellites, Models, and Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PM-Related Factors | ||
| PM characteristics | different chemical and physical properties | -mass, -number -size, shape -surface area -reactivity -acidity -solubility -internal or surface positioning of chemicals on the particles |
| heterogeneity in composition | -metals -salts -organic chemicals -biological materials | |
| varying mechanisms of formation | -nucleation process -condensation process -coagulation process -mechanical process | |
| anthropogenic and natural emission sources | -traffic, industrial activities, biomass burning, mineral desert dust, sea spray, biogenic emissions | |
| -geographical area asset | ||
| PM transport and deposition processes | diffusion, dilution and deposition patterns over time and space | -meteorological variables, as air temperature, humidity, wind and other parameters |
| Interaction with other pollutants | gaseous pollutants | NO2, SO2, O3 |
| no interaction vs. potential additivity, synergism or antagonism | ||
| Sampling methodology | differences between fixed monitoring points and mobile or individual monitoring assessment | -wearable device -sensors mounted on vehicles -geospatial assessment -fixed monitoring stations |
| different monitoring instrumentation | different spatial and temporal resolution | |
| Individual Characteristics | ||
| Individual factors | anthropometric, genetic and social characteristics | -age -sex -genetic profile -socioeconomic status |
| comorbidities and pre-existing diseases | -cardiovascular disease -respiratory diseases -presence of diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension | |
| behaviors | -diet -outdoor activity -occupation -exercise -smoking -mobility | |
| Modifying or Mitigating Factors | ||
| Antioxidant intake | choice of antioxidant | single compound vs. combination/cocktail |
| mechanism of action | direct vs. indirect | |
| administration | -timing -appropriate dosage -duration of use | |
| use in the general population vs. targeted application in vulnerable groups | -children, -elderly, -smokers, -individuals with chronic conditions | |
| Individual protectors | wearable or stationary technological devices | -face masks, -indoor air purifiers and filtration systems -air quality warning systems |
| general measures | -air exchange | |
| health interventions | -regular medical screening in subjects at high-risk -lifestyle changes | |
| Community interventions | environmental and policy strategies | -reducing source of pollution: policies to limit emissions -improvement of air quality assessment -urban planning -public health campaigns and education -improvement of public transports |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grifoni, D.; Bustaffa, E.; Sabatino, L.; Calastrini, F.; Minichilli, F.; Gaggini, M.; Berti, S.; Vassalle, C. The Dark Triad of Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Coronary Artery Disease: What About the Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050572
Grifoni D, Bustaffa E, Sabatino L, Calastrini F, Minichilli F, Gaggini M, Berti S, Vassalle C. The Dark Triad of Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Coronary Artery Disease: What About the Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(5):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050572
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrifoni, Daniele, Elisa Bustaffa, Laura Sabatino, Francesca Calastrini, Fabrizio Minichilli, Melania Gaggini, Sergio Berti, and Cristina Vassalle. 2025. "The Dark Triad of Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Coronary Artery Disease: What About the Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential" Antioxidants 14, no. 5: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050572
APA StyleGrifoni, D., Bustaffa, E., Sabatino, L., Calastrini, F., Minichilli, F., Gaggini, M., Berti, S., & Vassalle, C. (2025). The Dark Triad of Particulate Matter, Oxidative Stress and Coronary Artery Disease: What About the Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential. Antioxidants, 14(5), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14050572









