Ultrasound-Induced Changes in Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Antioxidative Properties of Whey-Protein-Concentrate-Encapsulated 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.3. Ultrasound Treatment of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
2.4. Freeze Drying
2.5. Nanoparticles Characterization
2.5.1. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta Potential
2.5.2. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%)
2.6. Rheological Determination
2.7. Color and pH Measurement
2.8. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.10. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.11. Antioxidant Activity
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Particle Size, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta Potential of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
3.2. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
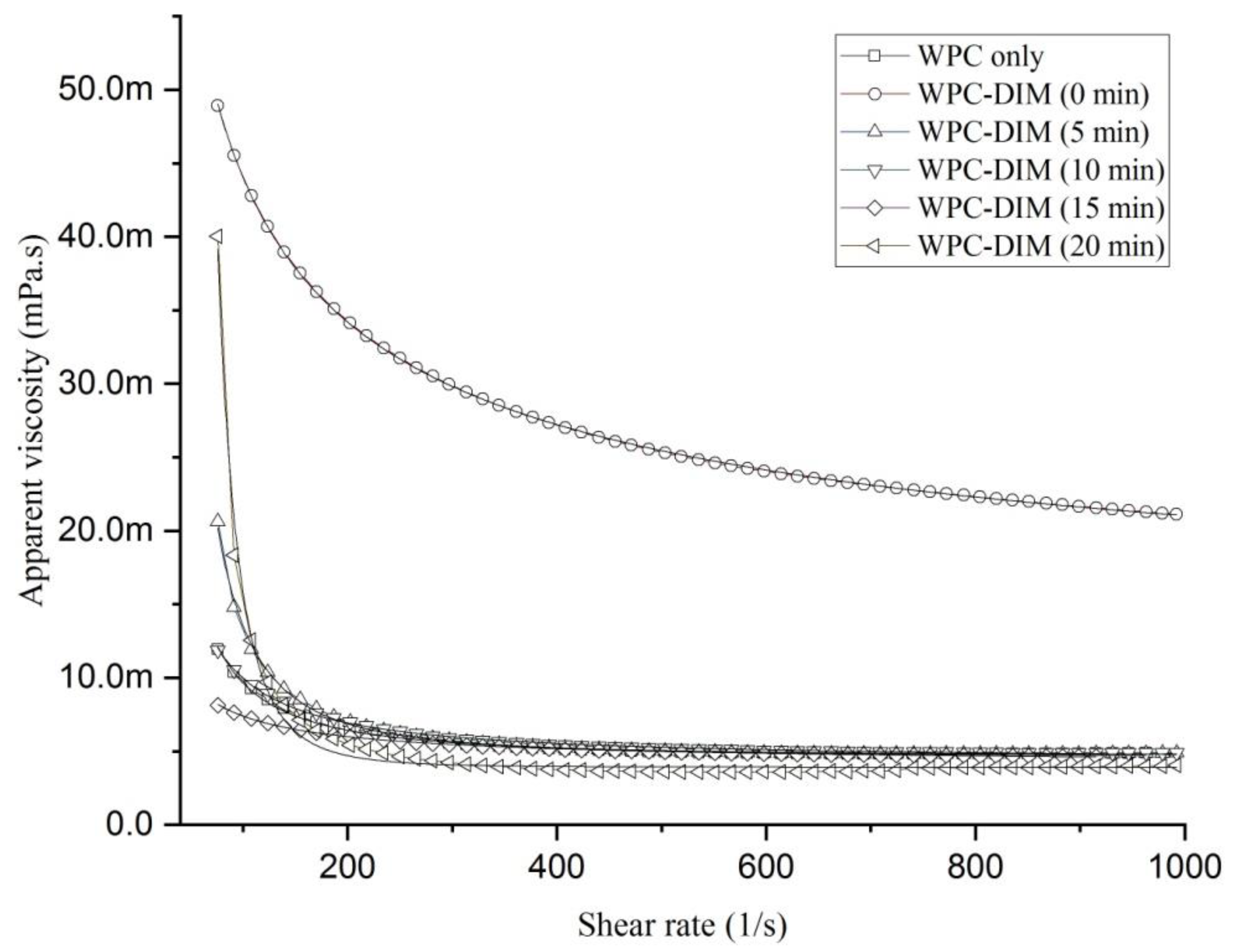
3.3. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Rheological Properties of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
3.4. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Color and pH of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
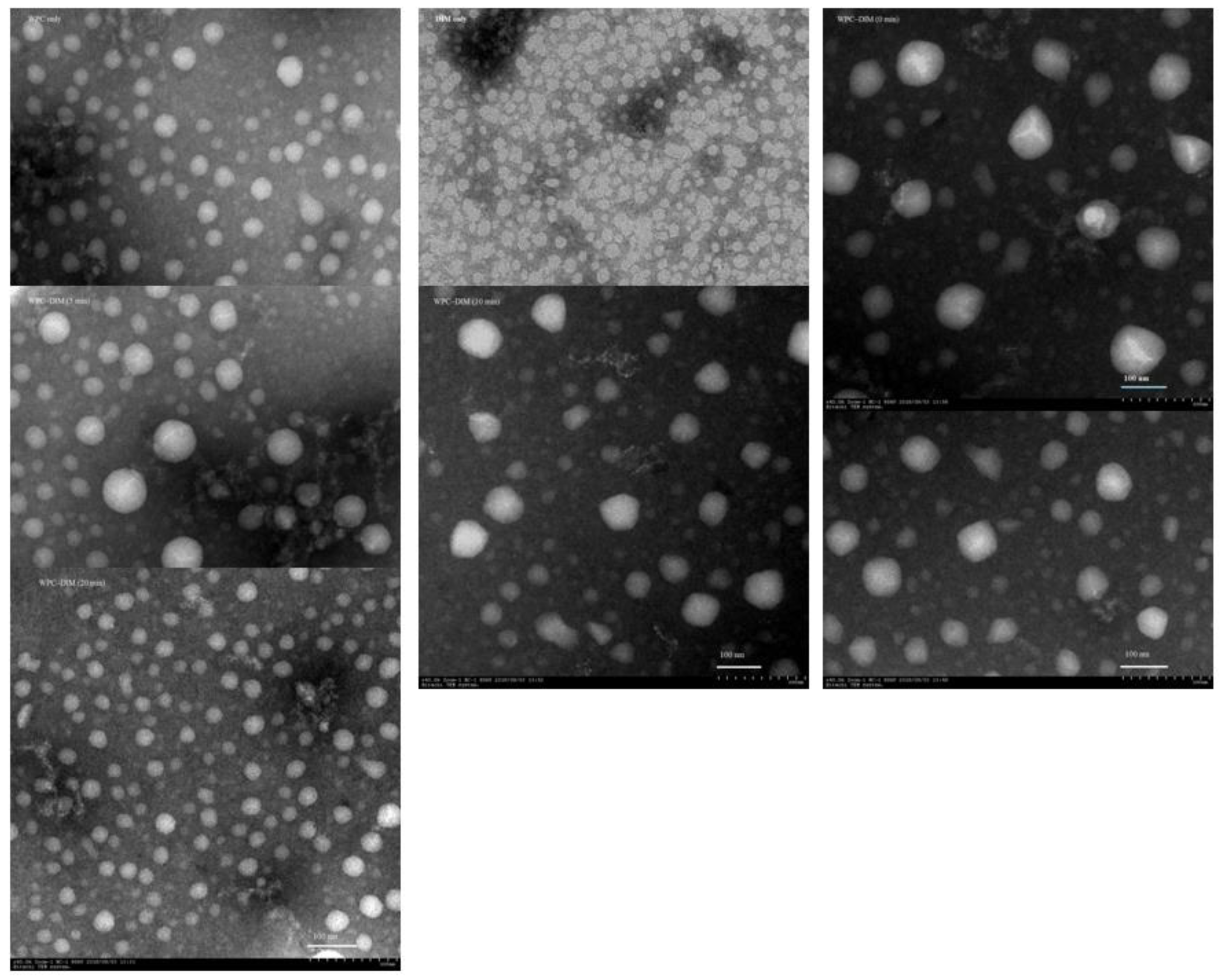
3.5. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Microstructure of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
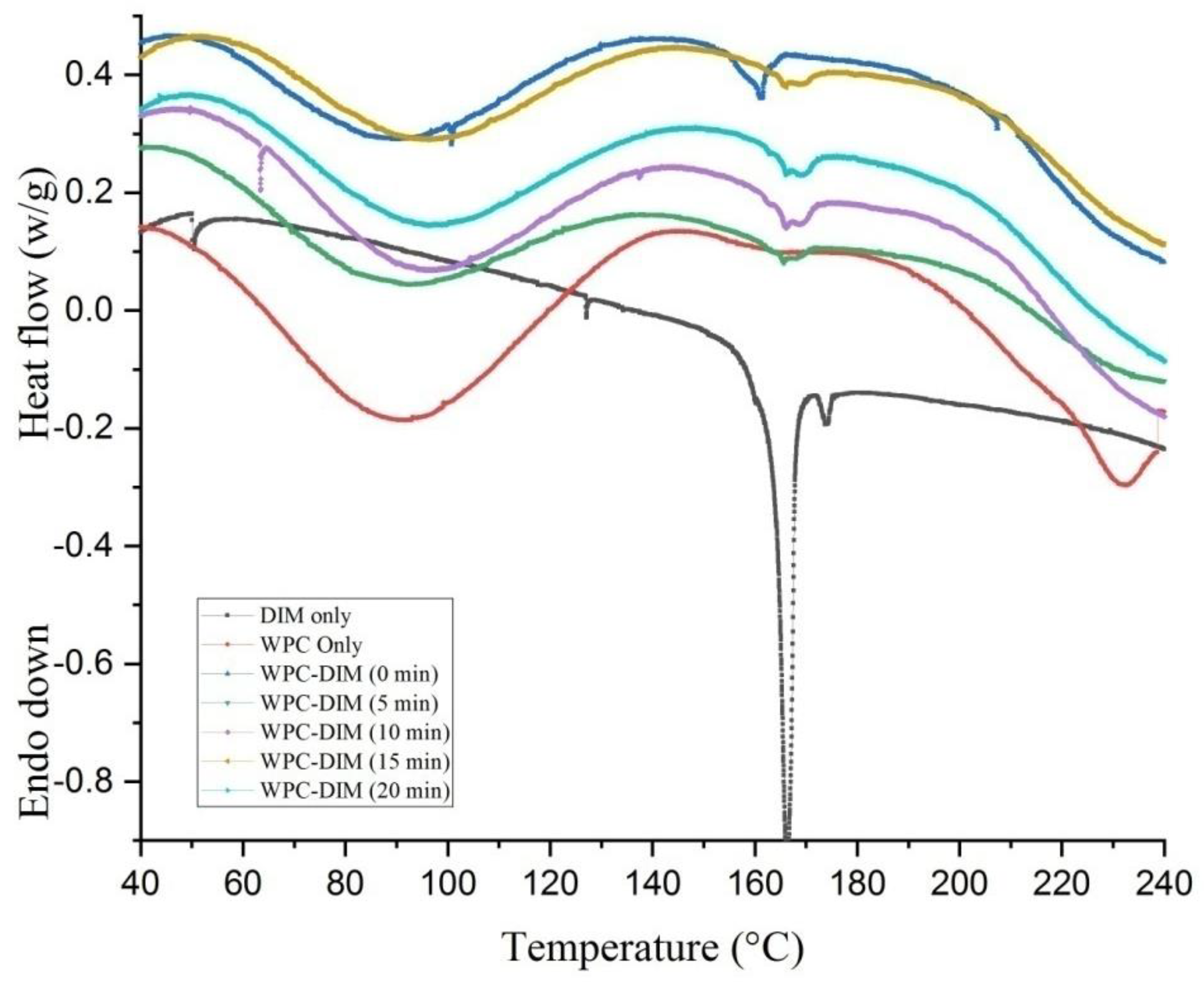
3.6. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
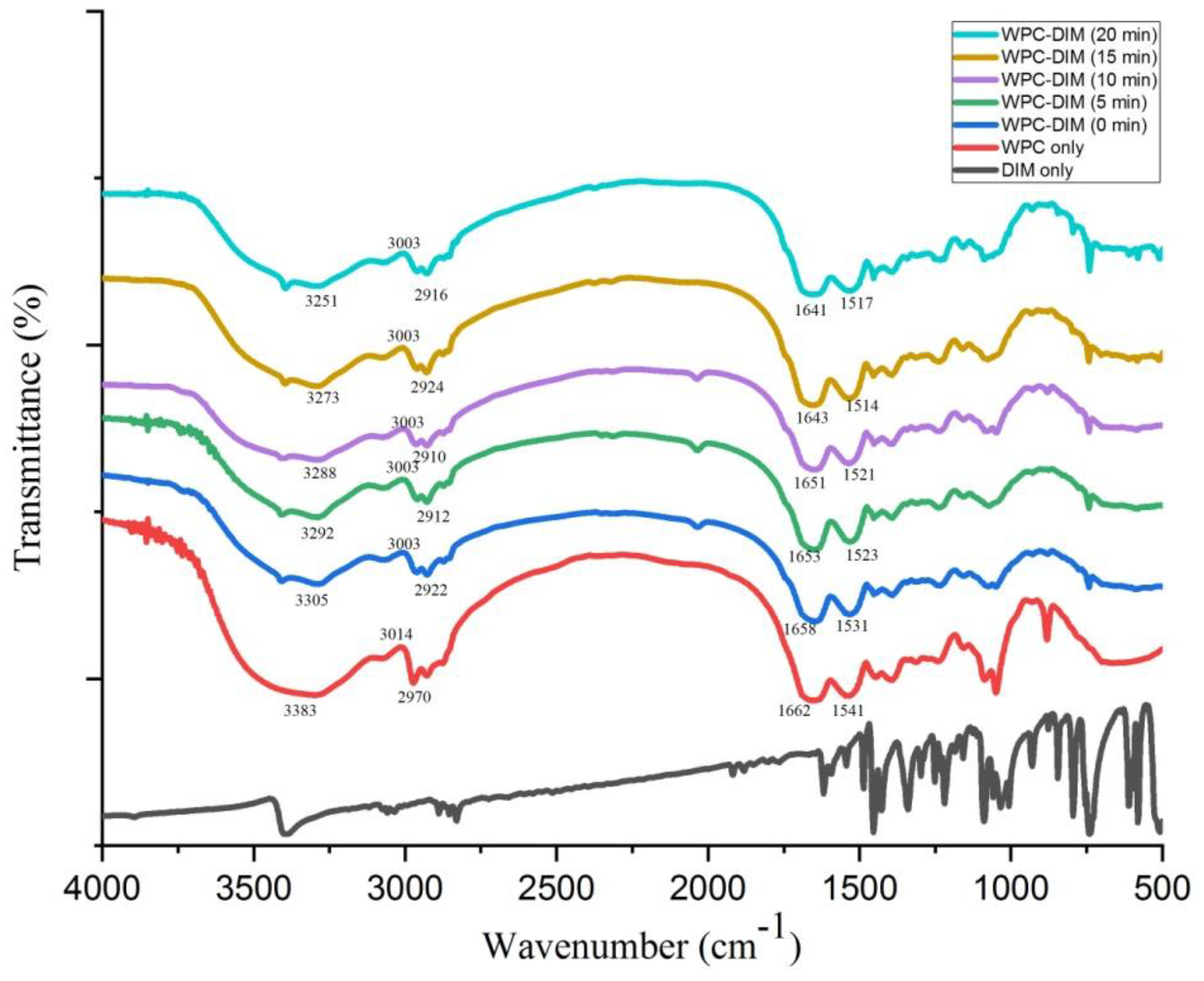
3.7. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectra of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
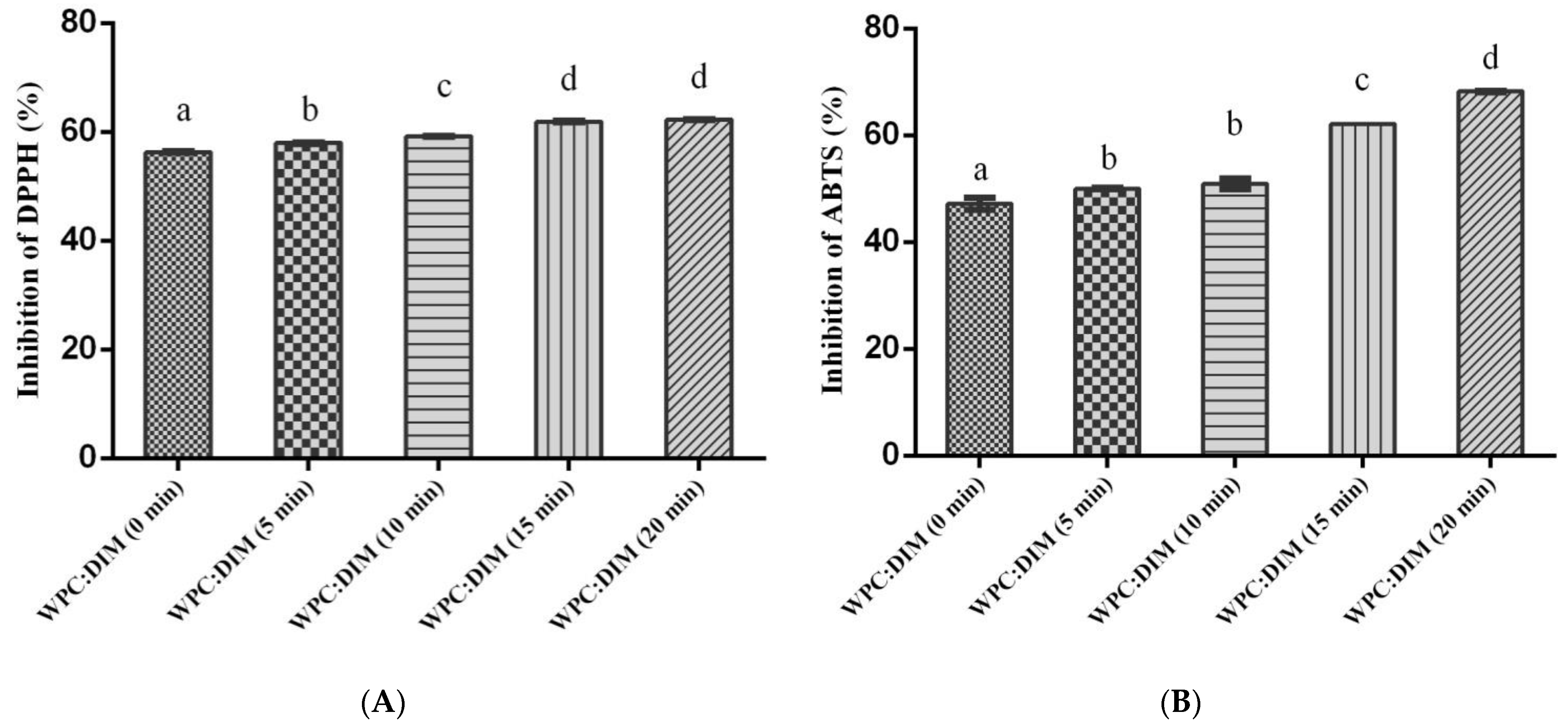
3.8. Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on Antioxidant Activity of WPC–DIM Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fares, F. The Anti-Carcinogenic Effect of Indole-3-Carbinol and 3,3’-Diindolylmethane and their Mechanism of Action. Med. Chem. S 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Ahmad, A.; Bao, B.; Sarkar, F.H. Antioxidant function of isoflavone and 3,3′-diindolylmethane: Are they important for cancer prevention and therapy? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiazzi, J.; Sari, M.H.M.; Brum, T.d.B.; Araújo, P.C.O.; Nadal, J.M.; Farago, P.V.; Nogueira, C.W.; Cruz, L. 3′-Diindolylmethane nanoencapsulation improves its antinociceptive action: Physicochemical and behavioral studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Gajbhiye, R.; Mandal, M.; Pal, C.; Meyyapan, A.; Mukherjee, J.; Jaisankar, P. Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of 3,3′-diindolylmethane derivatives. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, E.I.; Heilbrun, L.K.; Li, J.; Vaishampayan, U.; Harper, F.; Pemberton, P.; Sarkar, F.H. A phase I dose-escalation study of oral BR-DIM (BioResponse 3,3’-diindolylmethane) in castrate-resistant, non-metastatic prostate cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2010, 2, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Seon, M.R.; Lee, Y.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-K.; Kim, S.G.; Park, J.H.Y. 3′-Diindolylmethane Suppresses the Inflammatory Response to Lipopolysaccharide in Murine Macrophages. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.P.; Ngoubilly, N.; Neavyn, M.; Lanza-Jacoby, S. 3′-Diindolylmethane and Paclitaxel Act Synergistically to Promote Apoptosis in HER2/Neu Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 132, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Killpartrick, A.; Guo, M. Physicochemical and microstructural properties of polymerized whey protein encapsulated 3,30-diindolylmethane nanoparticles. Molecules 2019, 24, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Teng, Z.; Chen, P.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q. Encapsulation of indole-3-carbinol,3′-diindolylmethane in zein/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles with controlled release property and improved stability. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; Killpartrick, A.; Guo, M. Preparation and Characterization of Whey Protein Isolate–DIM Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isabella, S.; Mirunalini, S. Protective effect of 3,3’-Diindolylmethane encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles prop up with lipid metabolism and biotransformation enzymes against possible mammary cancer. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Ahmad, T.; Aadil, R.M.; Spotti, M.J.; Bakry, A.M.; Khan, I.M.; Zhao, L.; Riaz, T.; Tong, Q. Pectin polymers as wall materials for the nano-encapsulation of bioactive compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, J.; Estevinho, B.N.; Santos, L. Microencapsulation of natural antioxidants for food application—The specific case of coffee antioxidants—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Thakur, D.; Ghoshal, G.; Katare, O.P.; Shivhare, U.S. Microencapsulation by Complex Coacervation Using Whey Protein Isolates and Gum Acacia: An Approach to Preserve the Functionality and Controlled Release of β-Carotene. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Guo, M. Physicochemical Properties of Whey-Protein-Stabilized Astaxanthin Nanodispersion and Its Transport via a Caco-2 Monolayer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.M.; Wang, C.N.; Guo, M.R. Interactions between whey protein or polymerized whey protein and soybean lecithin in model system. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 9680–9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.D.; Cheng, Z.; Selomulya, C. On enhancing the solubility of curcumin by microencapsulation in whey protein isolate via spray drying. J. Food Eng. 2016, 169, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Rosenberg, M. Microencapsulation of theophylline in whey proteins: Effects of core-to- wall ratio. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 205, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Guo, M. Effects of ultrasound treatment on physiochemical properties and antimicrobial activities of whey protein-totarol nanoparticles. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, F.P.; Singh, R.K.; Kong, F. Physical and storage properties of spray-dried blueberry pomace extract with whey protein isolate as wall material. J. Food Eng. 2014, 137, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wang, C.N.; Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, T.T.; Lv, J.P.; Shen, X.; Guo, M.R. Effects of gamma radiation on microbial, physicochemical, and structural properties of whey protein model system. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Fang, T.; Gao, F.; Guo, M. Effects of ultrasound treatment on physicochemical and emulsifying properties of whey proteins pre- and post-thermal aggregation. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hou, T.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, D.; Xu, B.; Chen, X.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ma, H. Effects of frequency ultrasound on the properties of zein-chitosan complex coacervation for resveratrol encapsulation. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godugu, C.; Doddapaneni, R.; Safe, S.H.; Singh, M. Novel diindolylmethane derivatives based NLC formulations to improve the oral bioavailability and anticancer effects in triple negative breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, Q.; Ren, X.; Zhang, X.; Hou, T.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ma, H.; Xu, B. Effect of ultrasound on the preparation of resveratrol-loaded zein particles. J. Food Eng. 2018, 221, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Puligundla, P.; Wan, X. Encapsulation of epigallocatechin gallate in zein/chitosan nanoparticles for controlled applications in food systems. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Sharifian, P.; Soltanizadeh, N. Application of ultrasound treatment for improving the physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of myofibrillar proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Zheng, X.; Luan, D.; Shao, P.; Sun, P. Preparation and characterization of zein-based phytosterol nanodispersions fabricated by ultrasonic assistant anti-solvent precipitation. LWT 2019, 107, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanović, A.B.; Jovanović, J.R.; Dojčinović, M.B.; Lević, S.M.; Nedović, V.A.; Bugarski, B.M.; Knežević-Jugović, Z.D. Effect of the Controlled High-Intensity Ultrasound on Improving Functionality and Structural Changes of Egg White Proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, O.; Saricaoglu, F.T.; Besir, A.; Atalar, I.; Yazici, F. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the properties of nano-emulsion films obtained from hazelnut meal protein and clove essential oil. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Li, Q.; Miao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L. Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical properties of emulsion stabilized by fish myofibrillar protein and xanthan gum. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, V.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Carrara, C.R. Droplet size distribution, rheological behavior and stability of corn oil emulsions stabilized by a novel hydrocolloid (Brea gum) compared with gum arabic. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez-Santos, L.E.; Martínez-Girón, J.; Arias-Jaramillo, M.E. Effect of ultrasound treatment on visual color, vitamin C, total phenols, and carotenoids content in Cape gooseberry juice. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Lelas, V.; Herceg, Z.; Herceg, I.L. Effect of ultrasound treatment on solubility and foaming properties of whey protein suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Lelas, V.; Mason, T.J.; Krešić, G.; Badanjak, M. Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, K.M.; Nicoletti, V.R. Ultrasound impact on whey protein concentrate-pectin complexes and in the O/W emulsions with low oil soybean content stabilization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Q. Development of zein nanoparticles coated with carboxymethyl chitosan for encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Guo, M. Interactions between β-lactoglobulin, 3,3′-diindolylmethane in model system. Molecules 2019, 24, 2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, X.; Du, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H. Effect of ultrasound assisted heating on structure and antioxidant activity of whey protein peptide grafted with galactose. LWT 2019, 109, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiazzi, J.; Sari, M.H.M.; Lautenchleger, R.; Prá, M.D.; Braganhol, E.; Cruz, L. Incorporation of 3,3′-Diindolylmethane into Nanocapsules Improves Its Photostability, Radical Scavenging Capacity, and Cytotoxicity Against Glioma Cells. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential | EE% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPC only | 230.50 ± 11.66 ac | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | −21.93 ± 0.55 a | |
| WPC-DIM (0 min) | 265.96 ± 14.5 b | 0.49 ± 0.02 b | −27.96 ± 0.64 b | 76.46 ± 0.05 a |
| WPC-DIM (5 min) | 255.86 ± 2.55 ab | 0.48 ± 0.03 bc | −30.26 ± 1.05 c | 77.36 ± 0.23 b |
| WPC-DIM (10 min) | 253.36 ± 12.46 ab | 0.45 ± 0.01 abc | −30.40 ± 1.40 c | 79.03 ± 0.05 c |
| WPC-DIM (15 min) | 250.03 ± 16.87 abc | 0.43 ± 0.0 ac | −30.76 ± 0.49 cd | 81.50 ± 0.10 d |
| WPC-DIM (20 min) | 218.46 ± 9.37 c | 0.43 ± 0.02 ac | −32.83 ± 0.37 d | 88.51 ± 0.02 d |
| Samples | η∞ (mPa∙s) Infinite-Shear-Rate Viscosity | kᴑ Consistency Index | n Flow Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| WPC only | 4.51 ± 0.27 ac | 3.55 ± 0.03 a | −0.41 ± 0.02 |
| WPC-DIM (0 min) | 10.35 ± 0.14 b | 0.33 ± 0.04 b | 0.50 ± 0.03 |
| WPC-DIM (5 min) | 4.7 ± 0.24 ac | 1.01 ± 0.05 c | −1.03 ± 0.02 |
| WPC-DIM (10 min) | 4.36 ± 0.36 acd | 1.02 ± 0.09 c | −0.13 ± 0.02 |
| WPC-DIM (15 min) | 3.99 ± 0.19 cd | 0.11 ± 0.04 d | 0.23 ± 0.09 |
| WPC-DIM (20 min) | 2.34 ± 0.11 e | 0.27 ± 0.09 b | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Samples | Color Coordinates | pH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L* | a* | b* | ||
| WPC only | 49.33 ± 3.63 a | −1.92 ± 0.20 a | 15.36 ± 0.05 a | |
| WPC-DIM (0 min) | 64.80 ± 1.92 b | −0.57 ± 0.07 bc | 19.28 ± 0.35 b | 6.95 ± 0.01 a |
| WPC-DIM (5 min) | 64.75 ± 2.32 b | −0.53 ± 0.05 bc | 18.5 ± 0.60 b | 7.00 ± 0.01 b |
| WPC-DIM (10 min) | 64.99 ± 3.45 b | −0.87 ± 0.09 cd | 19.27 ± 0.30 b | 7.01 ± 0.00 bc |
| WPC-DIM (15 min) | 64.78 ± 2.56 b | −1.32 ± 0.31 d | 18.29 ± 0.22 b | 7.03 ± 0.01 c |
| WPC-DIM (20 min) | 66.87 ± 3.05 b | −0.38 ± 0.11 b | 22.59 ± 0.39 c | 7.08 ± 0.00 d |
| Samples | Ton (°C) | ΔTd (°C) | Td (°C) | ΔHd (mW/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPC-DIM (0 min) | 51 | 51–149 | 90.46 | 179.80 |
| WPC-DIM (5 min) | 54.8 | 54.8–151.58 | 90.57 | 173.70 |
| WPC-DIM (10 min) | 63.31 | 63.31–159.49 | 93.94 | 224.90 |
| WPC-DIM (15 min) | 61.15 | 61.15–158.02 | 94.96 | 165.40 |
| WPC-DIM (20 min) | 63.66 | 63.66–164.76 | 96.04 | 194.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.; Wang, C.; Killpartrick, A.; Guo, M. Ultrasound-Induced Changes in Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Antioxidative Properties of Whey-Protein-Concentrate-Encapsulated 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030273
Khan A, Wang C, Killpartrick A, Guo M. Ultrasound-Induced Changes in Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Antioxidative Properties of Whey-Protein-Concentrate-Encapsulated 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Nanoparticles. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(3):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030273
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Abbas, Cuina Wang, Adam Killpartrick, and Mingruo Guo. 2025. "Ultrasound-Induced Changes in Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Antioxidative Properties of Whey-Protein-Concentrate-Encapsulated 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Nanoparticles" Antioxidants 14, no. 3: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030273
APA StyleKhan, A., Wang, C., Killpartrick, A., & Guo, M. (2025). Ultrasound-Induced Changes in Physicochemical, Microstructural, and Antioxidative Properties of Whey-Protein-Concentrate-Encapsulated 3,3′-Diindolylmethane Nanoparticles. Antioxidants, 14(3), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14030273









