Cross-Species Insights into In Vitro Maturation Defects of the Oocyte and Identification of Crucial Regulators for Sheep Oocyte Maturation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oocyte In Vitro Maturation, Fertilization, and Embryo In Vitro Culture
2.2. Collection of Oocytes, Cumulus Cells, and Mural Granulosa Ccells Under Different Maturation Conditions
2.3. Assessment of the Nuclear Maturation and Blastocyst Cell Number
2.4. Measurement of Intracellular ROS and GSH Levels
2.5. Measurement of Lipid Droplet and Fatty Acid
2.6. Protein Aggregation Assay and Proteasome Activity Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Smart-Seq2 and Data Preparation
2.11. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.12. Data Collection and Workflow of RNA-Seq Data Processing
2.13. Differential Expression and Functional Enrichment
2.14. Cell–Cell Communication Analysis
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
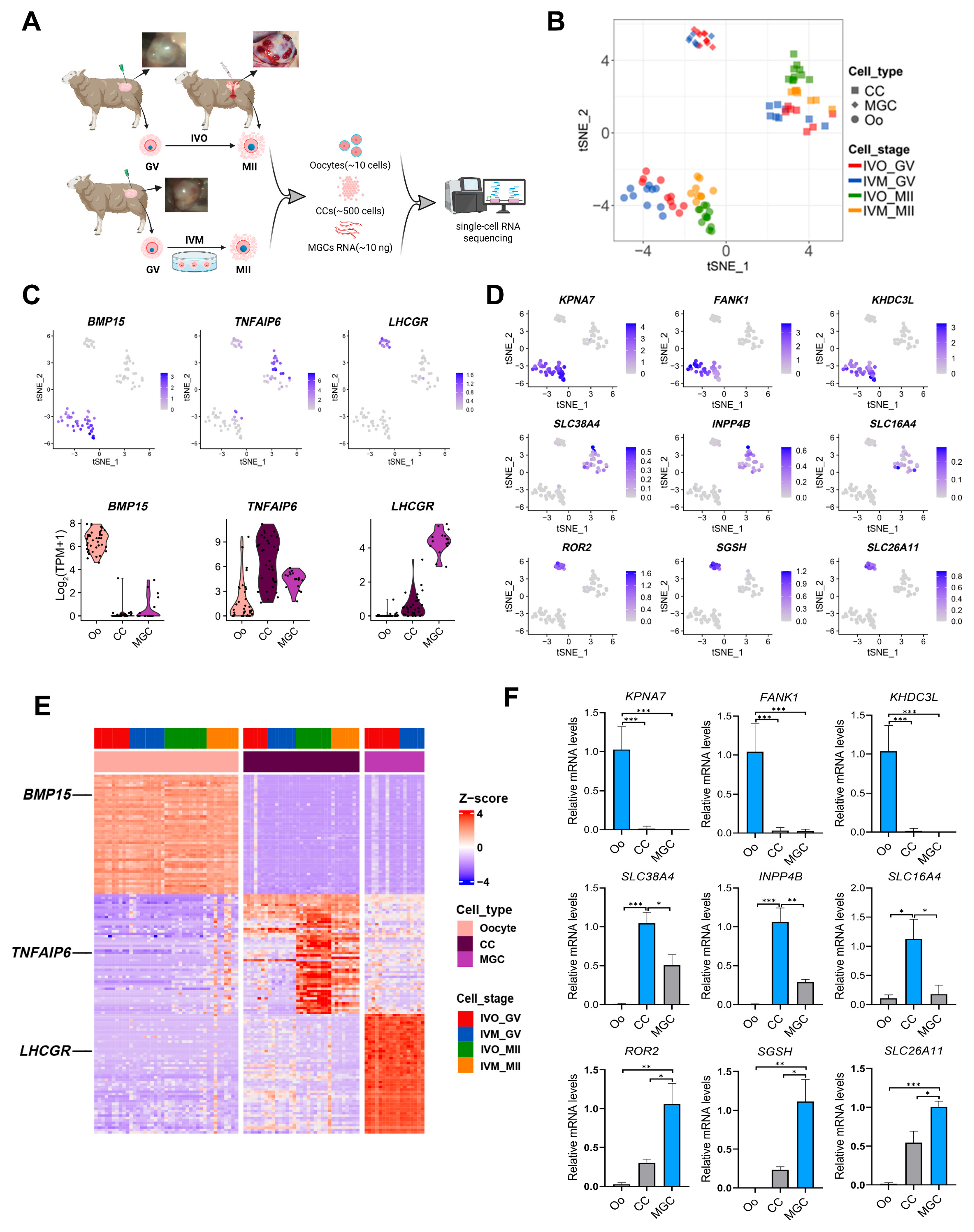
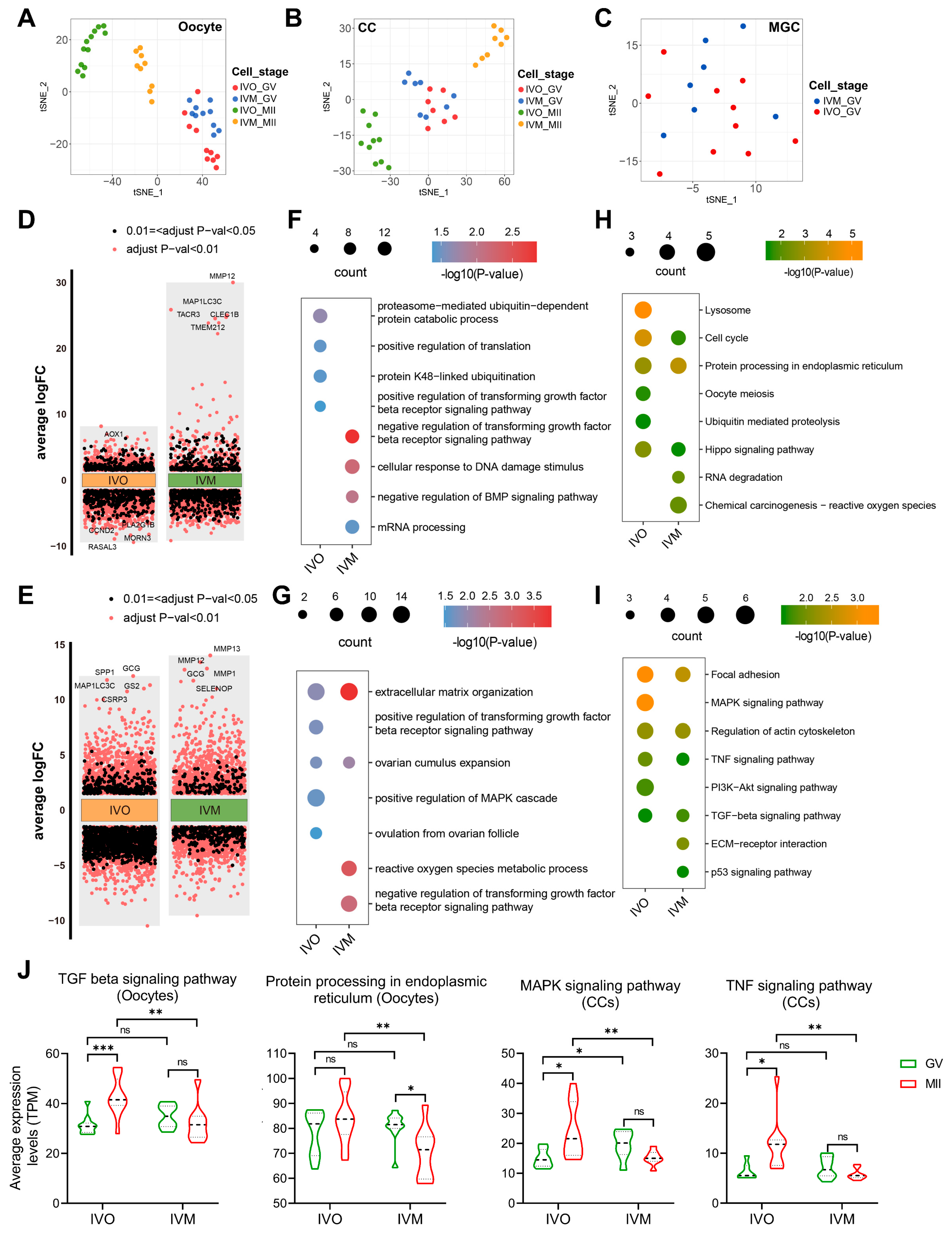
3.1. Global Transcriptomic Landscape of Sheep Oocytes and Granulosa Cells Matured In Vivo and In Vitro
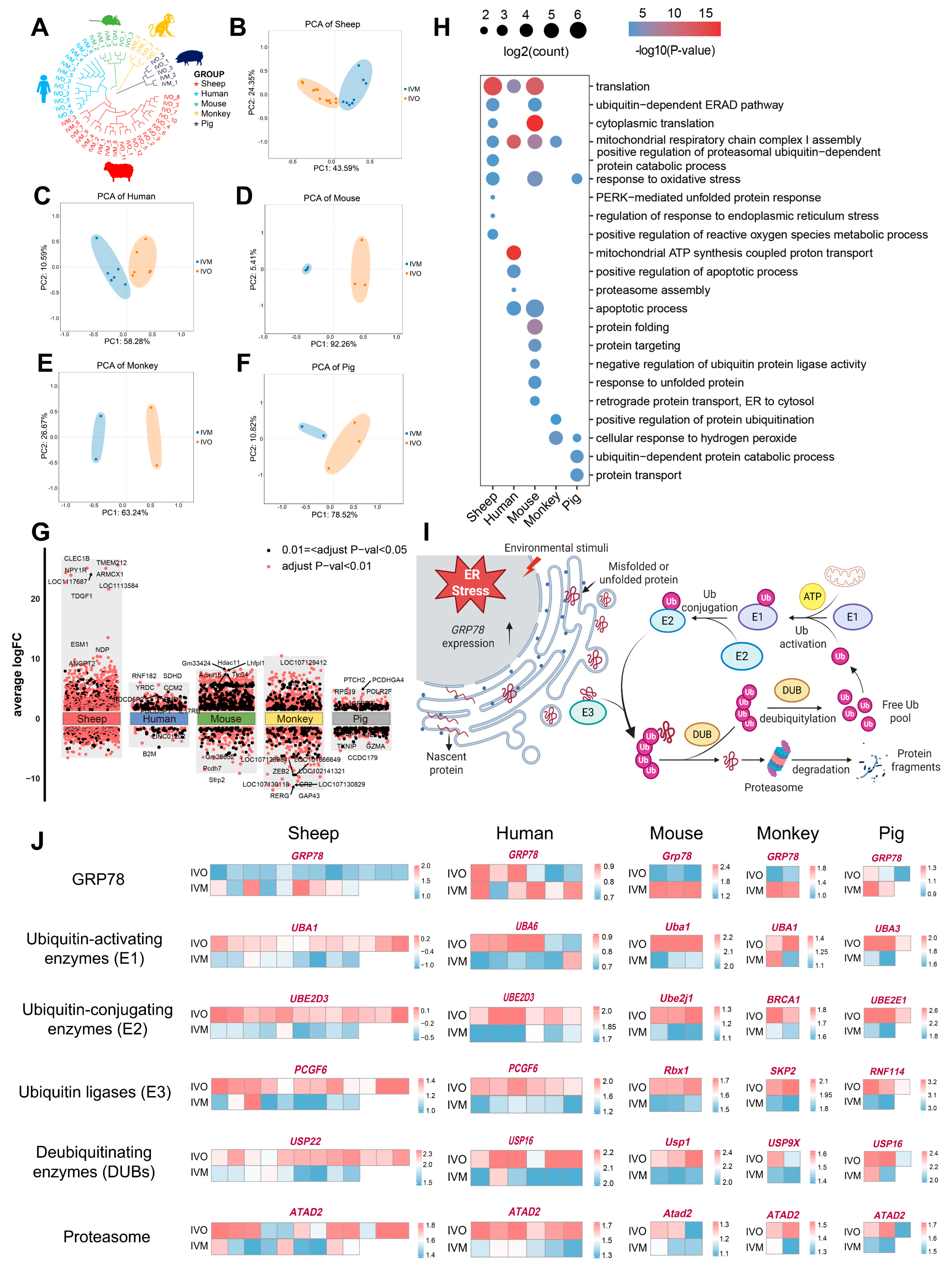
3.2. Conserved Determinants of Oocyte Maturation: A Cross-Species Comparison Between In Vivo and In Vitro Environments
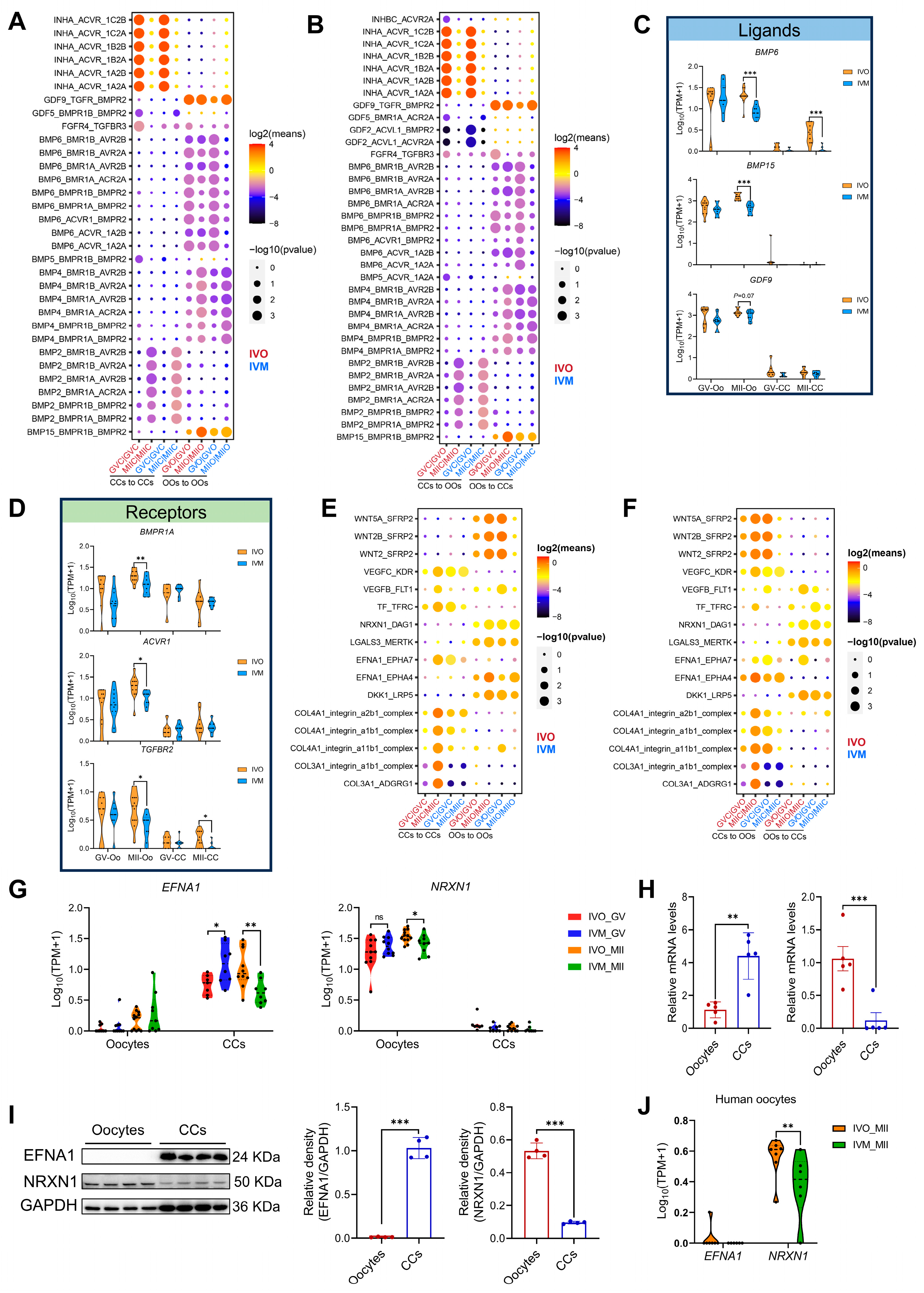
3.3. Ligand–Receptor Interactions Between Oocytes and Cumulus Cells in In Vivo and In Vitro Maturation Environments
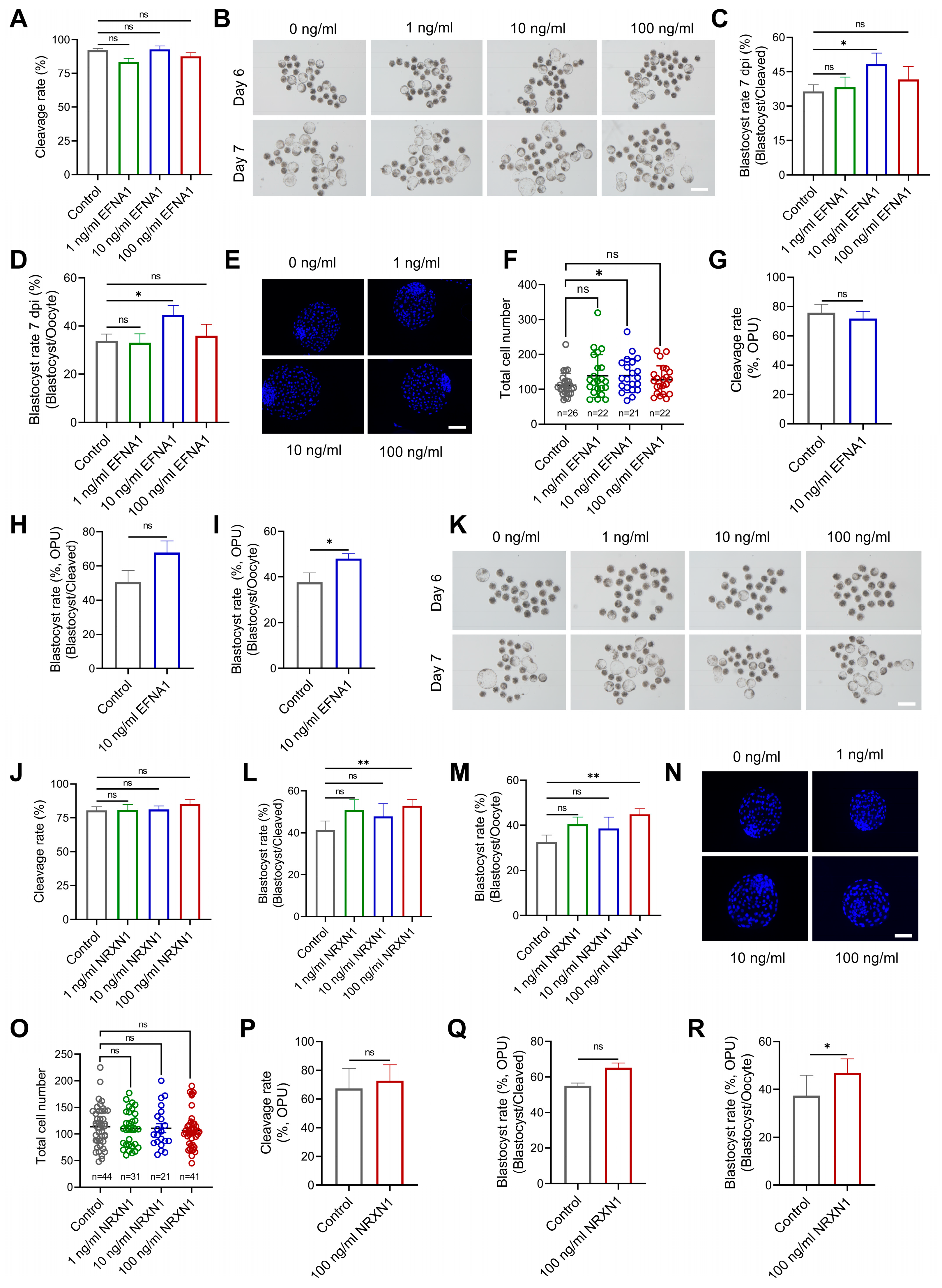
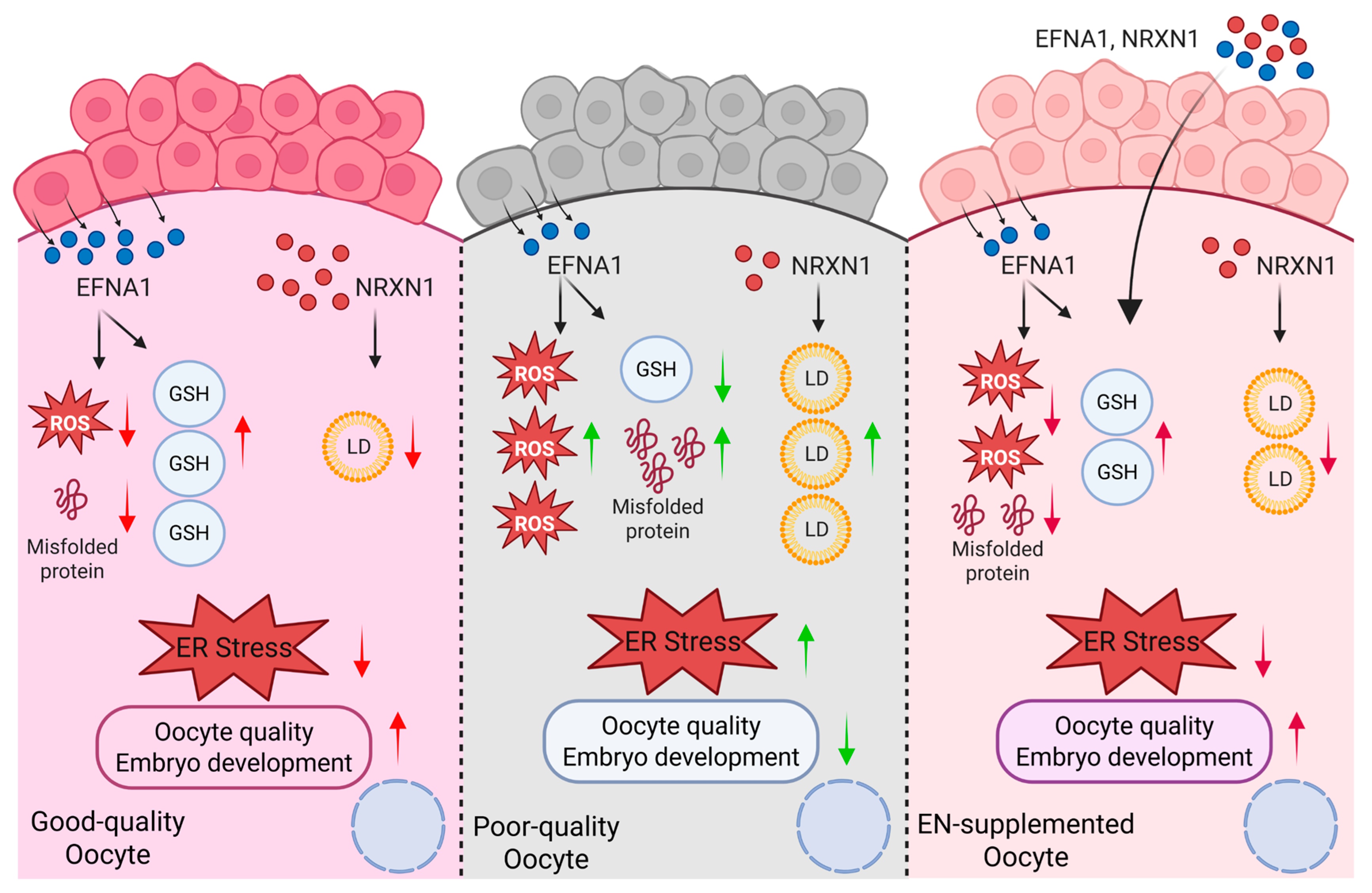
3.4. EFNA1 and NRXN1 Enhance Oocyte Developmental Competence
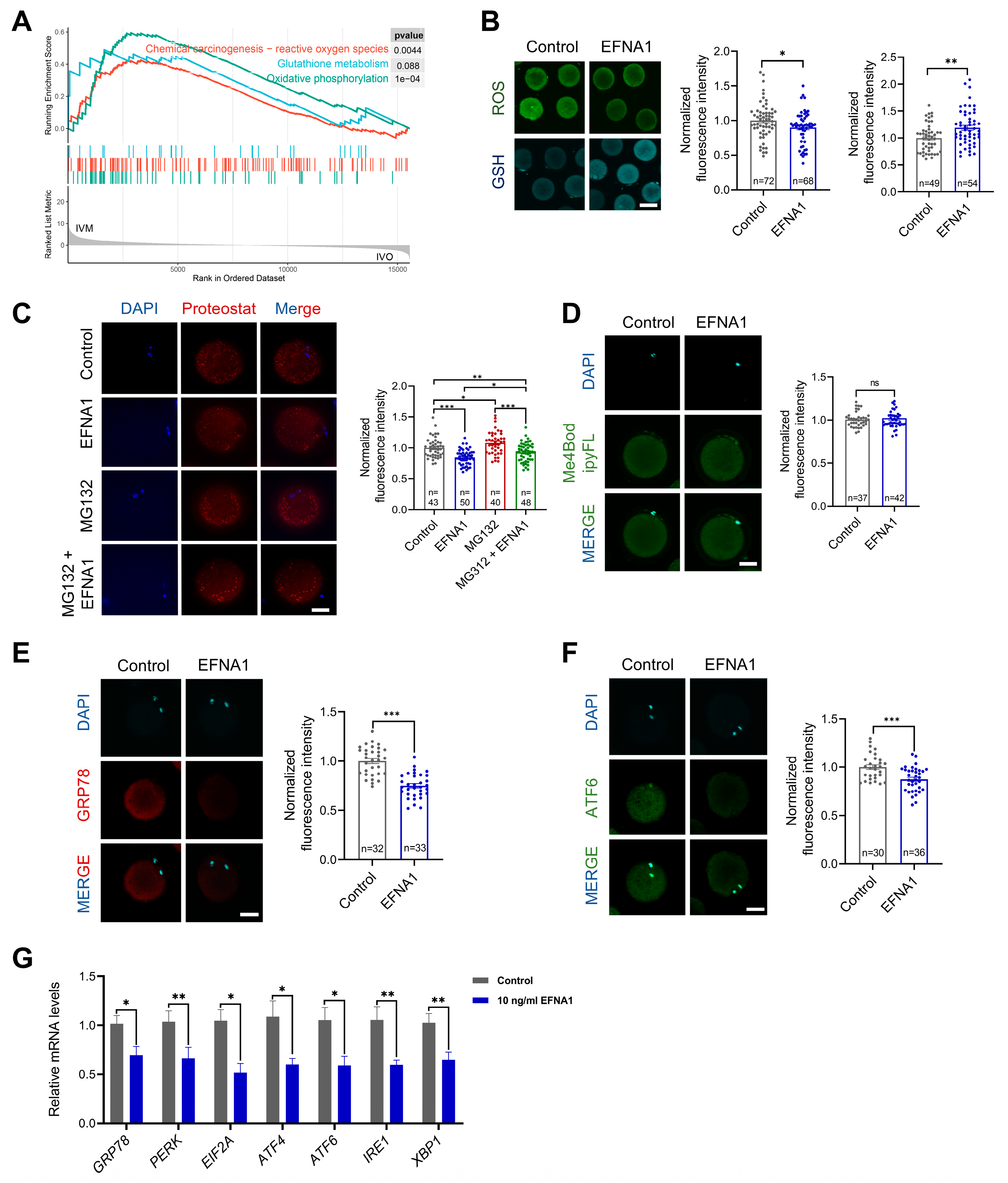
3.5. EFNA1 Alleviates Excessive Misfolded Protein Accumulation in Oocytes During IVM
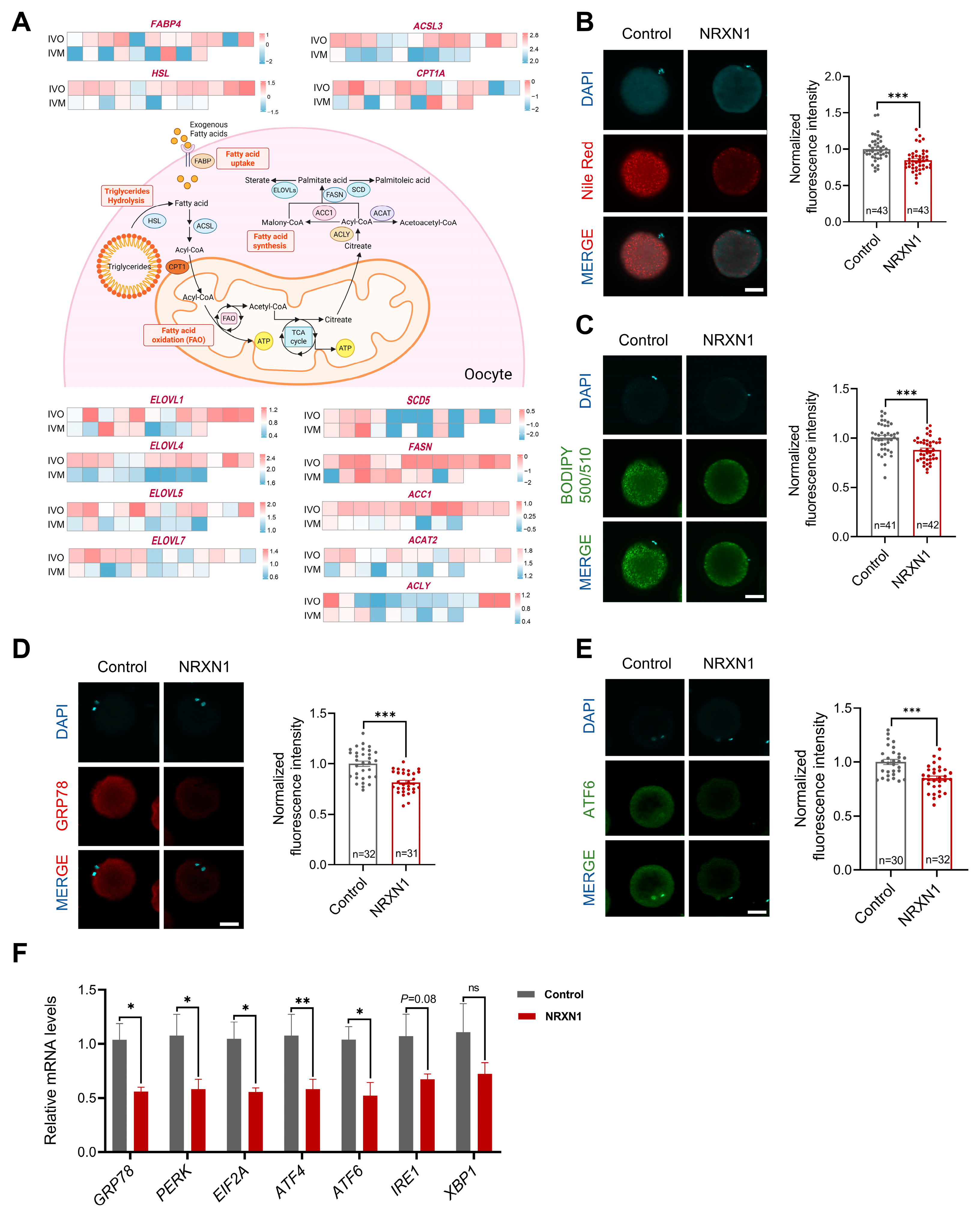
3.6. NRXN1 Mitigates Aberrant Lipid Deposition and ER Stress in Oocytes During IVM
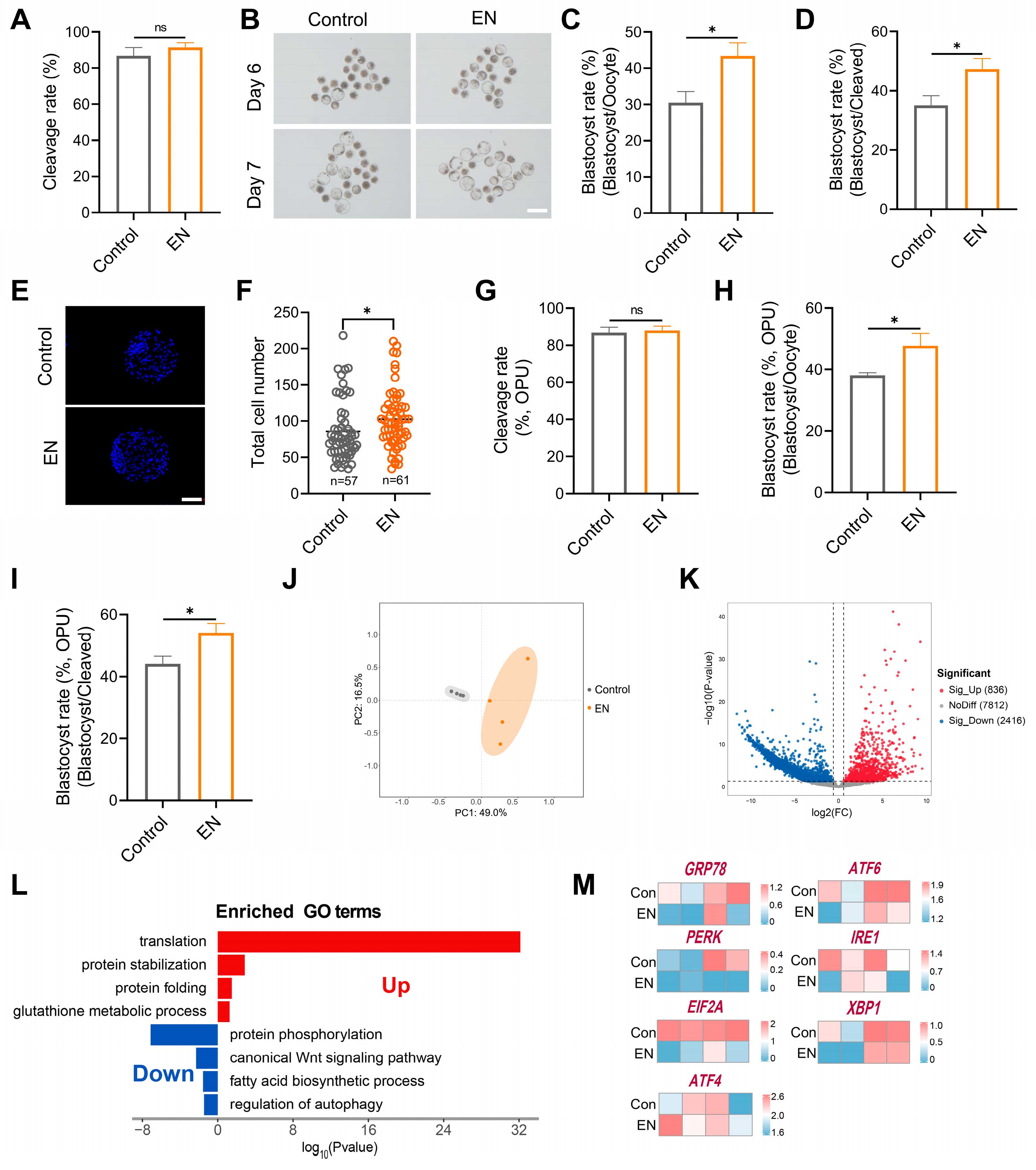
3.7. Synergistic EFNA1-NRXN1 Supplementation in IVM Medium Improves Oocyte Developmental Competence and Blastocyst Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hardy, K.; Wright, C.S.; Franks, S.; Winston, R.M. In vitro maturation of oocytes. Br. Med. Bull. 2000, 56, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chian, R.C.; Li, J.H.; Lim, J.H.; Yoshida, H. IVM of human immature oocytes for infertility treatment and fertility preservation. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2023, 22, e12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Moawad, A.R.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, H.F.; Ren, J.Y.; Dai, Y.F. Advances in in vitro production of sheep embryos. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Med. 2018, 6, S15–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humaidan, P.; Nelson, S.M.; Devroey, P.; Coddington, C.C.; Schwartz, L.B.; Gordon, K.; Frattarelli, J.L.; Tarlatzis, B.C.; Fatemi, H.M.; Lutjen, P.; et al. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: Review and new classification criteria for reporting in clinical trials. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coticchio, G.; Dal-Canto, M.; Guglielmo, M.C.; Mignini-Renzini, M.; Fadini, R. Human oocyte maturation in vitro. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Jamal, M.A.; Su, Y.; Wei, H.J.; Qing, Y.; Cheng, W. Towards Improving the Outcomes of Multiple Ovulation and Embryo Transfer in Sheep, with Particular Focus on Donor Superovulation. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte maturation: Emerging concepts and technologies to improve developmental potential in vitro. Theriogenology 2007, 67, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banwell, K.M.; Thompson, J.G. In vitro maturation of Mammalian oocytes: Outcomes and consequences. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2008, 26, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillova, A.; Smitz, J.E.J.; Sukhikh, G.T.; Mazunin, I. The Role of Mitochondria in Oocyte Maturation. Cells 2021, 10, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppig, J.J.; O’Brien, M.J.; Wigglesworth, K.; Nicholson, A.; Zhang, W.; King, B.A. Effect of in vitro maturation of mouse oocytes on the health and lifespan of adult offspring. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Albertini, D.F. The road to maturation: Somatic cell interaction and self-organization of the mammalian oocyte. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Heras, S.; Paramio, M.T. Impact of oxidative stress on oocyte competence for in vitro embryo production programs. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Collado, M.; da Silveira, J.C.; Oliveira, M.L.F.; Alves, B.; Simas, R.C.; Godoy, A.T.; Coelho, M.B.; Marques, L.A.; Carriero, M.M.; Nogueira, M.F.G.; et al. In vitro maturation impacts cumulus-oocyte complex metabolism and stress in cattle. Reproduction 2017, 154, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combelles, C.M.; Gupta, S.; Agarwal, A. Could oxidative stress influence the in-vitro maturation of oocytes? Reprod. Biomed. Online 2009, 18, 864–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimura, S.; Matoba, S.; Hashiyada, Y.; Aikawa, Y.; Ohtake, M.; Matsuda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Konishi, K.; Imai, K. Oxidative phosphorylation-linked respiration in individual bovine oocytes. J. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 58, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Collado, M.; Saraiva, N.Z.; Lopes, F.L.; Gaspar, R.C.; Padilha, L.C.; Costa, R.R.; Rossi, G.F.; Vantini, R.; Garcia, J.M. Influence of bovine serum albumin and fetal bovine serum supplementation during in vitro maturation on lipid and mitochondrial behaviour in oocytes and lipid accumulation in bovine embryos. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2015, 28, 1721–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Bertolini, M.; Bertolini, L.; Silva, C.; Rondina, D. Lipotoxicity: Impact on oocyte quality and reproductive efficiency in mammals. Anim. Reprod. 2015, 12, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Lane, M.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte-secreted factors: Regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum. Reprod. Update 2008, 14, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashourzadeh, S.; Khalili, m.a.; Omidi, M.; Nottola, S.; Faramarzi, A.; Cas Press, C. Supplementation of IVM culture media with GDF-9 can potentially enhance oocyte quality, fertilization and embryo development in ICSI procedure. Cent. Asian J. Med. Pharm. Sci. Innov. 2021, 1, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.C.; Hamilton, T.; Mendes, C.M.; Siqueira, A.F.P.; Goissis, M.D.; Buratini, J.; Assumpção, M. Bone morphogenetic protein 15 supplementation enhances cumulus expansion, nuclear maturation and progesterone production of in vitro-matured bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, H.; Sangalli, J.R.; Alves, L.; da Silveira, J.C.; Meirelles, F.V.; Perecin, F. NPPC and AREG supplementation in IVM systems alter mRNA translation and decay programs-related gene expression in bovine COC. Anim. Reprod. 2024, 21, e20230101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richani, D.; Sutton-McDowall, M.L.; Frank, L.A.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Thompson, J.G. Effect of epidermal growth factor-like peptides on the metabolism of in vitro- matured mouse oocytes and cumulus cells. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatroudi, M.H.; Khalili, M.A.; Ashourzadeh, S.; Anbari, F.; Shahedi, A.; Safari, S. Growth differentiation factor 9 and cumulus cell supplementation in in vitro maturation culture media enhances the viability of human blastocysts. Clin. Exp. Reprod. Med. 2019, 46, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Roda, M.; Paramio, M.-T.; Vila-Beltrán, J.; Izquierdo, D. Effect of BMP15 and GDF9 in the IVM medium on subsequent oocyte competence and embryo development of prepubertal goats. Theriogenology 2025, 234, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Shim, H. Treatment of Exogenous GDF9 and BMP15 during In vitro Maturation of Oocytes increases the Cell Number of Blastocysts in Pigs. J. Embryo Transf. 2016, 31, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machlin, J.H.; Shikanov, A. Single-cell RNA-sequencing of retrieved human oocytes and eggs in clinical practice and for human ovarian cell atlasing. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2022, 89, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armingol, E.; Officer, A.; Harismendy, O.; Lewis, N.E. Deciphering cell-cell interactions and communication from gene expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Türei, D.; Garrido-Rodriguez, M.; Burmedi, P.L.; Nagai, J.S.; Boys, C.; Ramirez Flores, R.O.; Kim, H.; Szalai, B.; Costa, I.G.; et al. Comparison of methods and resources for cell-cell communication inference from single-cell RNA-Seq data. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremova, M.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Teichmann, S.A.; Vento-Tormo, R. CellPhoneDB: Inferring cell-cell communication from combined expression of multi-subunit ligand-receptor complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1484–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Liao, J.; Li, C.; Lu, X.; Cheng, J.; Fan, X. CellTalkDB: A manually curated database of ligand-receptor interactions in humans and mice. Brief Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbaa269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Zou, B.; Tan, P.; Cui, T.; Dou, Y.; Ning, L.; et al. CellCall: Integrating paired ligand-receptor and transcription factor activities for cell-cell communication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 8520–8534. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yue, Y.; Chen, D.; Chou, C.; An, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J. Field outcomes of laparoscopic ovum pick-up combined with in vitro embryo production in sheep: Effects of long-acting recombinant ovine FSH pre-stimulation, collection frequency, and donor breed. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2024, 87, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Lee, E.; Bonilla, L.; Francis, J.; Koh, J.; Block, J.; Chen, S.; Hansen, P.J. Treatment with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 during the end of oocyte maturation improves oocyte competence for development after fertilization in cattle. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qin, Q.; Nisenblat, V.; Chang, H.M.; Yu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lu, C.; Yang, M.; Yang, S.; et al. Transcriptome Landscape of Human Folliculogenesis Reveals Oocyte and Granulosa Cell Interactions. Mol. Cell. 2018, 72, 1021–1034.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vértesy, Á.; Arindrarto, W.; Roost, M.S.; Reinius, B.; Torrens-Juaneda, V.; Bialecka, M.; Moustakas, I.; Ariyurek, Y.; Kuijk, E.; Mei, H.; et al. Parental haplotype-specific single-cell transcriptomics reveal incomplete epigenetic reprogramming in human female germ cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Viualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, E.R.; Pitman, J.L. Intrafollicular growth differentiation factor 9: Bone morphogenetic 15 ratio determines litter size in mammals. Biol Reprod. 2019, 100, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Di, R.; Wang, F.; Yu, P.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Mwacharo, J.M.; Pan, L.; Chu, M. Detection of Novel Variations Related to Litter Size in BMP15 Gene of Luzhong Mutton Sheep (Ovis aries). Animals 2021, 11, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assidi, M.; Dufort, I.; Ali, A.; Hamel, M.; Algriany, O.; Dielemann, S.; Sirard, M.A. Identification of potential markers of oocyte competence expressed in bovine cumulus cells matured with follicle-stimulating hormone and/or phorbol myristate acetate in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 79, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophir, L.; Yung, Y.; Yerushalmi, G.M.; Baum, M.; Machtinger, R.; Maman, E.; Hourvitz, A. An optimized model for hCG stimulation of human mural granulosa cell culture. Reprod. Biol. 2019, 19, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, H. Ubiquitination-Proteasome System (UPS) and Autophagy Two Main Protein Degradation Machineries in Response to Cell Stress. Cells 2022, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Bo, S.; Qiao, J.; Xia, G.; Su, Y.; Zhang, M. Transforming growth factor-β is involved in maintaining oocyte meiotic arrest by promoting natriuretic peptide type C expression in mouse granulosa cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottershead, D.G.; Sugimura, S.; Al-Musawi, S.L.; Li, J.J.; Richani, D.; White, M.A.; Martin, G.A.; Trotta, A.P.; Ritter, L.J.; Shi, J.; et al. Cumulin, an Oocyte-secreted Heterodimer of the Transforming Growth Factor-β Family, Is a Potent Activator of Granulosa Cells and Improves Oocyte Quality. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24007–24020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.T.; Ng, J.K.W.; Liao, J.; Luk, A.C.; Suen, A.H.C.; Chan, T.T.H.; Cheung, M.Y.; Chu, H.T.; Tang, N.L.S.; Zhao, M.P.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies molecular targets associated with poor in vitro maturation performance of oocytes collected from ovarian stimulation. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 36, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Xu, Y.; Ju, J.Q.; Pan, Z.N.; Liu, J.C.; Sun, S.C. Increased Environment-Related Metabolism and Genetic Expression in the In vitro Matured Mouse Oocytes by Transcriptome Analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 642010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Bian, X.; Sun, Q. Nuclear transfer improves the developmental potential of embryos derived from cytoplasmic deficient oocytes. iScience 2023, 26, 107299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spate, L.D.; Brown, A.N.; Redel, B.K.; Whitworth, K.M.; Murphy, C.N.; Prather, R.S. Dickkopf-related protein 1 inhibits the WNT signaling pathway and improves pig oocyte maturation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, J.W.; Shin, H.Y.; Lee, J.B.; Jin, D.I. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress and Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) in Mammalian Oocyte Maturation and Preimplantation Embryo Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, Q.; Wigglesworth, K.; Rangarajan, A.; Kattamuri, C.; Peterson, R.T.; Eppig, J.J.; Thompson, T.B.; Matzuk, M.M. Growth differentiation factor 9:bone morphogenetic protein 15 heterodimers are potent regulators of ovarian functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E776–E785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persani, L.; Rossetti, R.; Di Pasquale, E.; Cacciatore, C.; Fabre, S. The fundamental role of bone morphogenetic protein 15 in ovarian function and its involvement in female fertility disorders. Hum. Reprod. Update 2014, 20, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, H.; Bu, G.; Liu, Z.; Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.L. Maternal Cytokines CXCL12, VEGFA, and WNT5A Promote Porcine Oocyte Maturation via MAPK Activation and Canonical WNT Inhibition. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonai, S.; Nakanishi, T.; Yamaoka, M.; Okamoto, A.; Shimada, M.; Yamashita, Y. Pre-culture with transferrin-Fe(3+) before in vitro maturation improves the developmental competence of porcine oocytes matured in vitro. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2023, 22, e12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jiang, H.; Lv, P.; Cui, K.; Liu, Q.; Yin, S.; Liu, H.; Li, Z. Transcriptome analyses reveal transcriptional profiles of horse oocytes before and after in vitro maturation. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2023, 58, 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, X.; Yin, S.; Yan, J.; Lv, P.; Shan, H.; Cui, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Revealed the Gene Expression Pattern during the In vitro Maturation of Donkey Oocytes. Genes 2021, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.C.; Shastri, M.D.; Eri, R. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Oxidative Stress: A Vicious Nexus Implicated in Bowel Disease Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Zhu, Z.; Du, Y.; Long, L.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, F. EFNA4-enhanced deubiquitination of SLC7A11 inhibits ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Apoptosis 2025, 30, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basseri, S.; Austin, R.C. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipid metabolism: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 841362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, K.A.; Weisz, E.D.; Jongens, T.A. Loss of neurexin-1 in Drosophila melanogaster results in altered energy metabolism and increased seizure susceptibility. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 3422–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozdemir, N.; Cakir, C.; Cinar, O.; Cinar, F.U. Antioxidant-supplemented media modulates ROS by regulating complex I during mouse oocyte maturation. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Collado, M.; da Silveira, J.C.; Sangalli, J.R.; Andrade, G.M.; Sousa, L.; Silva, L.A.; Meirelles, F.V.; Perecin, F. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 And Transzonal Projections Are Involved In Lipid Accumulation During In vitro Maturation of Bovine Oocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratini, J.; Caixeta, E. Paracrine and autocrine factors in the differentiation of the cumulus-oocyte complex. Anim. Reprod. 2012, 9, 414–419. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cui, Z.; Bao, C. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 Is Involved in Oocyte Maturation Through an Autocrine/Paracrine Pathway in Scylla paramamosain. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 748928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pioltine, E.M.; Costa, C.B.; Barbosa Latorraca, L.; Franchi, F.F.; Dos Santos, P.H.; Mingoti, G.Z.; de Paula-Lopes, F.F.; Nogueira, M.F.G. Treatment of in vitro-Matured Bovine Oocytes with Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Modulates the Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 623852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, N.; Gutierrez, K.; Currin, L.; de Macedo, M.P.; Glanzner, W.G.; Mondadori, R.G.; Michalak, M.; Agellon, L.B.; Bordignon, V. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid/TGR5 signaling promotes survival and early development of glucose-stressed porcine embryos. Biol. Reprod. 2021, 105, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malamitsi-Puchner, A.; Sarandakou, A.; Baka, S.; Hasiakos, D.; Kouskouni, E.; Creatsas, G. In vitro fertilization: Angiogenic, proliferative, and apoptotic factors in the follicular fluid. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 997, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arici, A.; Oral, E.; Bahtiyar, O.; Engin, O.; Seli, E.; Jones, E.E. Leukaemia inhibitory factor expression in human follicular fluid and ovarian cells. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, E.E.; Skinner, M.K. Kit ligand and basic fibroblast growth factor interactions in the induction of ovarian primordial to primary follicle transition. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2004, 214, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Spate, L.D.; Redel, B.K.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Prather, R.S.; Roberts, R.M. Quadrupling efficiency in production of genetically modified pigs through improved oocyte maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5796–E5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Yang, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Feng, X.; Hao, H.; Du, W.; Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Yu, W.; et al. Combination of CNP, MT and FLI during IVM Significantly Improved the Quality and Development Abilities of Bovine Oocytes and IVF-Derived Embryos. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Ebara, F.; Kawasaki, K.; Konno, T.; Tatemoto, H.; Yamanaka, K.I. Attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress improves invitro growth and subsequent maturation of bovine oocytes. Theriogenology 2024, 228, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sun, M.; Cui, Y.; Guo, D.; Yang, F.; Sun, Q.; Ding, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Ou, G.; et al. Ephrin A1 functions as a ligand of EGFR to promote EMT and metastasis in gastric cancer. EMBO J. 2025, 44, 1464–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, I.; Liu, Z.; Mullany, L.K.; Mihara, T.; Richards, J.S.; Shimada, M. EGF-like factors induce expansion of the cumulus cell-oocyte complexes by activating calpain-mediated cell movement. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parri, M.; Buricchi, F.; Giannoni, E.; Grimaldi, G.; Mello, T.; Raugei, G.; Ramponi, G.; Chiarugi, P. EphrinA1 activates a Src/focal adhesion kinase-mediated motility response leading to rho-dependent actino/myosin contractility. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19619–19628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitasaka, H.; Kawai, T.; Hoque, S.A.M.; Umehara, T.; Fujita, Y.; Shimada, M. Inductions of granulosa cell luteinization and cumulus expansion are dependent on the fibronectin-integrin pathway during ovulation process in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjørlund, M.D.; Nielsen, J.; Pankratova, S.; Li, S.; Korshunova, I.; Bock, E.; Berezin, V. Neuroligin-1 induces neurite outgrowth through interaction with neurexin-1β and activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4174–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Lu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Liang, G.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. FGF21-FGFR1 Coordinates Phospholipid Homeostasis, Lipid Droplet Function, and ER Stress in Obesity. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4754–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liang, Y.; Bao, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dun, X.; Xu, Z.; Ji, A.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Real-ambient particulate matter exposure-induced FGFR1 methylation contributes to cardiac dysfunction via lipid metabolism disruption. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 161903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, J.; Zhao, X.; Hao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Rong, J.; Qiu, C.; Chen, D.; et al. Cross-Species Insights into In Vitro Maturation Defects of the Oocyte and Identification of Crucial Regulators for Sheep Oocyte Maturation. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121499
Cui J, Zhao X, Hao J, Liu X, Wang W, He L, Wang Y, Rong J, Qiu C, Chen D, et al. Cross-Species Insights into In Vitro Maturation Defects of the Oocyte and Identification of Crucial Regulators for Sheep Oocyte Maturation. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(12):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121499
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Jian, Xiurong Zhao, Jia Hao, Xingyuan Liu, Wenjing Wang, Lixia He, Yubing Wang, Jinfu Rong, Chunjuan Qiu, Dayong Chen, and et al. 2025. "Cross-Species Insights into In Vitro Maturation Defects of the Oocyte and Identification of Crucial Regulators for Sheep Oocyte Maturation" Antioxidants 14, no. 12: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121499
APA StyleCui, J., Zhao, X., Hao, J., Liu, X., Wang, W., He, L., Wang, Y., Rong, J., Qiu, C., Chen, D., Cheng, L., Tian, J., Zhang, J., & Xi, G. (2025). Cross-Species Insights into In Vitro Maturation Defects of the Oocyte and Identification of Crucial Regulators for Sheep Oocyte Maturation. Antioxidants, 14(12), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14121499




