Proinflammatory Risk Factors in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Hypertension, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.2. Dyslipidemia, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.3. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.4. Chronic Alcohol Consumption, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.5. Smoking, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.6. Obesity, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.7. Atrial Fibrillation, Ischemic Stroke and Neuroinflammation
4.8. History of TIA and Ischemic Stroke
4.8.1. Completeness and Applicability of Evidence
4.8.2. Dominance of Research Locations
4.8.3. Participant Representativeness
4.8.4. Participant Variation
4.8.5. Quality of the Evidence
4.8.6. Potential Biases in the Review Process
4.8.7. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Clinical Translation Box
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADH | Alcohol Dehydrogenase |
| AF | Atrial fibrillation |
| ALC | Chronic alcohol consumption |
| ALDH2 | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| DL | Dyslipidemia |
| DM2 | Diabetes mellitus type 2 |
| eNOS | Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| GRADE | Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation |
| HT | Hypertension |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MeSH | Medical Subject Headings |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (reduced form) |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| NOX | NADPH Oxidase |
| OB | Obesity |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| ox-LDL | Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| RAAS | Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System |
| REML | Restricted maximum-likelihood estimator |
| RNS | Reactive Nitrogen Species |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SM | Smoking |
| smLDL | Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| TCA | Tricarboxylic Acid (cycle) |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
| TLR | Toll-Like Receptor |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| VLDL | Very Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| WOS | Web of Science |
References
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Hou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, G. Global, regional, and national epidemiology of ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021. Eur. J. Neurol. 2024, 31, E16481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Romania: WHO Statistical Profile; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Available online: https://data.who.int/countries/642 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Ekker, M.S.; Boot, E.M.; Singhal, A.B.; Tan, K.S.; Debette, S.; Tuladhar, A.M.; de Leeuw, F.-E. Epidemiology, aetiology, and management of ischaemic stroke in young adults. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strilciuc, S.; Grad, D.A.; Mixich, V.; Stan, A.; Buzoianu, A.D.; Vladescu, C.; Vintan, M.A. Societal Cost of Ischemic Stroke in Romania: Results from a Retrospective County-Level Study. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, A.; Strilciuc, S.; Gherghel, N.; Cozma, A.; Alexander, C.; Ilut, S.; Blesneag, A.; Vacaras, V.; Stanca, D.; Stan, H.; et al. Aphasia after Acute Ischemic Stroke in Romania: Epidemiology and Impact on Tertiary Care Resources. Preprints 2021, 2021090043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke: Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. Stroke 1993, 24, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, V.; Moreno, P.R.; Fayad, Z.A.; Corti, R.; Badimon, J.J. Atherothrombosis and high-risk plaque: Part I: Evolving concepts. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature 2002, 420, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Maida, C.; Pinto, A. Inflammation and Inflammatory Cell Recruitment in Acute Cerebrovascular Diseases. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 11, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietz, A.; Gorey, S.; Kelly, P.J.; Katan, M.; McCabe, J.J. Targeting inflammation to reduce recurrent stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2024, 19, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghi, S.; Raz, E.; Yang, D.; Cutting, S.; Mac Grory, B.; Elkind, M.S.; de Havenon, A. Lacunar stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoor, A.J.; Pothineni, N.V.K.; Palagiri, D.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2017, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, A.J.; Machin, D.R.; Lesniewski, L.A. Mechanisms of dysfunction in the aging vasculature and role in age-related disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, A.J.; Eskurza, I.; Silver, A.E.; Levy, A.S.; Pierce, G.L.; Gates, P.E.; Seals, D.R. Direct evidence of endothelial oxidative stress with aging in humans: Relation to impaired endothelium-dependent dilation and upregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.; Tarantini, S.; Donato, A.J.; Galvan, V.; Csiszar, A. Mechanisms of vascular aging. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 849–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, C.; Gehwolf, R.; Tempfer, H.; Krizbai, I.; Hennig, B.; Bauer, H.C.; Bauer, H. Oxidative stress and blood-brain barrier dysfunction under particular consideration of matrix metalloproteinases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1305–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; De Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, M.T.; Casciaro, M.; Gangemi, S.; Buquicchio, R. Immunosenescence in aging: Between immune cells depletion and cytokines up-regulation. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2017, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, M.A.; Ekker, M.S.; Allach, Y.; Cai, M.; Aarnio, K.; Arauz, A.; Arnold, M.; Bae, H.-J.; Bandeo, L.; Barboza, M.A.; et al. Global Differences in Risk Factors, Etiology, and Outcome of Ischemic Stroke in Young Adults—A Worldwide Meta-analysis: The GOAL Initiative. Neurology 2022, 98, e573–e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, M.; Swarnkar, P.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A.; Misra, S.; Kumar, P. Association of modifiable risk factors with ischaemic stroke subtypes in Asian versus Caucasian populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 52, e13849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.F.; Anderson, N.; Thomas, B.; Sudlow, C.L. Risk factors for ischemic stroke and its subtypes in Chinese vs. Caucasians: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Geng, N.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.; Cao, L. Prevalence, causes and risk factors of hospital readmissions after acute stroke and transient ischemic attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yao, B. Impact of risk factors for recurrence after the first ischemic stroke in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 60, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorthuis, M.H.; Algra, A.M.; Algra, A.; Kappelle, L.J.; Klijn, C.J. Female- and Male-Specific Risk Factors for Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Blanco, C.; Rodríguez-Almagro, J.; Onieva-Zafra, M.D.; Parra-Fernández, M.L.; Prado-Laguna, M.D.C.; Hernández-Martínez, A. Physical Activity and Sedentary Lifestyle in University Students: Changes during Confinement Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadar-Shoval, D.; Alon-Tirosh, M.; Asraf, K.; Tannous-Haddad, L.; Tzischinsky, O. Lifestyle Changes, Emotional Eating, Gender, and Stress during COVID-19 Lockdown. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.F.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Anderson, N.; Jeng, J.S. Variations of risk factors for ischemic stroke and its subtypes in Chinese patients in Taiwan. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, I.F.; Borné, Y.; Zaigham, S.; Söderholm, M.; Johnson, L.; Persson, M.; Melander, O.; Engström, G. Comparison of risk factors for ischemic stroke and coronary events in a population-based cohort. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Luo, L.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y. Patient Readmission for Ischemic Stroke: Risk Factors and Impact on Mortality. Inq. J. Health Care Organ. Provis. Financ. 2024, 61, 469580241241271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langanay, L.; Gonzalez Sanchez, R.; Hamroun, A.; Dauchet, L.; Amouyel, P.; Dallongeville, J.; Meirhaeghe, A.; Gauthier, V. Ischemic stroke subtypes: Risk factors, treatments, and 1-month prognosis—The Lille, France Stroke Registry. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 33, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, N.; Li, J.; Pang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Risk Factors and Clinical Characteristics of First-ever Ischemic Stroke Caused by ICAS with Leukoaraiosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wu, K.; Wu, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Lan, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y. Relationship between the cumulative exposure to atherogenic index of plasma and ischemic stroke: A retrospective cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, A.; Drake, I.; Engström, G.; Acosta, S. Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic Ischemic Stroke among Subjects in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, W.; Lu, Q. Risk factors affecting the 1-year outcomes of minor ischemic stroke: Results from Xi’an stroke registry study of China. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, A.; Liao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; et al. The relationship between systemic inflammation index, systemic immune-inflammatory index, and inflammatory prognostic index and 90-day outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, W.; Qi, J.; Yang, B.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H. The incidence and risk factors of perioperative recurrent stroke in elderly patients with previous ischemic stroke receiving hip fracture surgery. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2024, 25, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Tang, J.; Li, P.; Liao, B.; Qin, C. Distribution of cerebral artery stenosis and risk factors in ethnic Zhuang and Han patients with ischemic stroke in Guangxi province. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittrich, T.D.; Schneider, T.; Katan, M.; Luft, A.R.; Mono, M.L.; Bolognese, M.; Nedeltchev, K.; Kahles, T.; Arnold, M.; Heldner, M.; et al. Swiss Stroke Registry Investigators. Risk Factors, Treatments, and Outcomes of Adults Aged <55 Years with Acute Ischemic Stroke with Undetermined Versus Determined Pathogenesis: A Nationwide Swiss Cohort Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2024, 13, e036761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, N.A.; Patel, P.N.; Kamanu, F.K.; Nordio, F.; Melloni, G.M.; Roselli, C.; Gurmu, Y.; Weng, L.-C.; Bonaca, M.P.; Giugliano, R.P.; et al. Clinical Application of a Novel Genetic Risk Score for Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Cardiometabolic Disease. Circulation 2021, 143, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupore, N.; Strat, D.; Mackey, T.; Brown, K.; Snell, A.; Nathaniel, T.I. Cholesterol reducer and thrombolytic therapy in acute ischemic stroke patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Dong, S.; Feng, F.; Kan, W.; Shi, T.; Ding, H.; Dong, R. Identification of specific risk factors and predictive analytics for cardio-cerebral arterial stenosis: A comparative study utilizing Framingham risk stratification insights. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsalam, F.I.; Somsri, P.; Papitak, P.; Tussanabunyong, K.; Chaveepojnkamjorn, W.; Phoosuwan, N. Factors associated with quality of life among newly diagnosed acute ischemic stroke patients: A community-based case-control study. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Yu, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Stroke History is an Independent Risk Factor for Poor Prognosis in Ischemic Stroke Patients: Results from a Large Nationwide Stroke Registry. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2020, 17, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Lee, B.N.; Kim, Y.S.; Shin, B.S.; Kang, H.G. Sex differences and risk factors in recurrent ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1028431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joundi, R.A.; Patten, S.B.; Williams, J.V.; Smith, E.E. Vascular risk factors and stroke risk across the life span: A population-representative study of half a million people. Int. J. Stroke 2022, 17, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzuner, N.; Uzuner, G.T. Risk factors for multiple recurrent ischemic strokes. Brain Circ. 2023, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Luo, H.; Zhou, J.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Tan, L.; Wei, W.; Li, J. Prevalence of stroke and stroke related risk factors: A population-based cross-sectional survey in southwestern China. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuthpongtorn, C.; Jereerat, T.; Suwanwela, N.C. Stroke risk factors, subtypes and outcome in elderly Thai patients. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namaganda, P.; Nakibuuka, J.; Kaddumukasa, M.; Katabira, E. Stroke in young adults, stroke types and risk factors: A case-control study. BMC Neurol. 2022, 22, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.J.S.; Werring, D.J. New Insights Into Cerebrovascular Pathophysiology and Hypertension. Stroke 2022, 53, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohgi, H.; Tajima, T.; Konno, T.; Towada, S.; Kamata, A.; Yamazaki, M. The risk of cerebral infarction in non-valvular atrial fibrillation: Effects of age, hypertension and antihypertensive treatment. Eur. Neurol. 1991, 31, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Ovbiagele, B.; Hong, K.S.; Kwon, S.U. Association of Systolic Blood Pressure with Progression of Symptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, J.; Feng, M.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L. White matter changes, duration of hypertension, and age are associated with cerebral microbleeds in patients with different stages of hypertension. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, M.; Zhang, N.; Guo, L. Cerebral microbleeds are associated with blood pressure levels in individuals with hypertension. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2020, 42, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Howard, S.C.; Dolan, E.; O’Brien, E.; Dobson, J.E.; Dahlof, B.; Sever, P.S.; Poulter, N.R. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010, 375, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amponsah-Offeh, M.; Diaba-Nuhoho, P.; Speier, S.; Morawietz, H. Oxidative stress, antioxidants and hypertension. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.; Wilcox, C.S. Oxidative stress in hypertension: Role of the kidney. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 74–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.-L.; Schultz, H.D.; Liu, D.; Cornish, K.G.; Zucker, I.H. Sympathoexcitation by central ANG II: Roles for AT1 receptor upregulation and NAD(P)H oxidase in RVLM. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H2271–H2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboukhater, D.; Morad, B.; Nasrallah, N.; Nasser, S.A.; Sahebkar, A.; Kobeissy, F.; Boudaka, A.; Eid, A.H. Inflammation and hypertension: Underlying mechanisms and emerging understandings. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloubani, A.; Nimer, R.; Samara, R. Relationship between Hyperlipidemia, Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke: A Systematic Review. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2021, 17, E051121189015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekic, J.; Stromsnes, K.; Mazzalai, S.; Zeljkovic, A.; Rizzo, M.; Gambini, J. Oxidative stress, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular risk. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmysłowski, A.; Szterk, A. Current knowledge on the mechanism of atherosclerosis and pro-atherosclerotic properties of oxysterols. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, E.; Sarapultsev, A. Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Insights from the Theory of General Pathological Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, C.; Moon, Y.P.; Paik, M.C.; Rundek, T.; Mora-McLaughlin, C.; Vieira, J.R.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S. Duration of diabetes and risk of ischemic stroke: The northern Manhattan study. Stroke 2012, 43, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissela, B.M.; Khoury, J.; Kleindorfer, D.; Woo, D.; Schneider, A.; Alwell, K.; Miller, R.; Ewing, I.; Moomaw, C.J.; Szaflarski, J.P.; et al. Epidemiology of ischemic stroke in patients with diabetes: The greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky stroke study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Paul, S.K.; Bethel, M.A.; Matthews, D.R.; Neil, H.A. 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1577–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.; Shakya, A.K.; Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Dave, K.R. Cerebral ischemic damage in diabetes: An inflammatory perspective. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Kalra, S.; Punyani, H.; Deshmukh, S.; Taur, S. “Oxidative stress”—A new target in the management of diabetes mellitus. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2023, 12, 2552–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, P.A.; Rutter, G.A. The role of oxidative stress and hypoxia in pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 26, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Shaper, A.G. Patterns of alcohol intake and risk of stroke in middle-aged British men. Stroke 1996, 27, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantakomi, S.H.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Sivenius, J.; Kauhanen, J.; Kurl, S. Alcohol consumption and the risk of stroke among hypertensive and overweight men. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieber, C.S. Metabolism of alcohol. Clin. Liver Dis. 2005, 9, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, R.K.; Beal, M.F. Mitochondrial diseases of the brain. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 63, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter-Lopez, L.; Khan, M.A.S.; Wang, X.; Song, B.-J. Roles of oxidative stress and autophagy in alcohol-mediated brain damage. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, P.P.; Morel, C.; Ambade, A.; Iracheta-Vellve, A.; Kwiatkowski, E.; Satishchandran, A.; Furi, I.; Cho, Y.; Gyongyosi, B.; Catalano, D.; et al. Chronic alcohol-induced neuroinflammation involves CCR2/5-dependent peripheral macrophage infiltration and microglia alterations. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.M.; Cole, J.W.; Sorkin, J.D.; Wozniak, M.A.; Malarcher, A.M.; Giles, W.H.; Stern, B.J.; Kittner, S.J. Dose-response relationship between cigarette smoking and risk of ischemic stroke in young women. Stroke 2008, 39, 2439–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thun, M.J.; Apicella, L.F.; Henley, S.J. Smoking vs other risk factors as the cause of smoking-attributable deaths: Confounding in the courtroom. JAMA 2000, 284, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griendling, K.K.; Sorescu, D.; Ushio-Fukai, M. NAD(P)H oxidase: Role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ. Res. 2000, 86, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, A.; Pawliczak, R. Cigarette smoking and oxidative stress. Alergol. Pol. 2022, 9, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Guo, M.; Mehra, M.; Royal, W. 3rd. Inflammation and oxidative stress induced by cigarette smoke in Lewis rat brains. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 254, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strazzullo, P.; D’Elia, L.; Kandala, N.B.; Cappuccio, F.P. Salt intake, stroke, and cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2009, 339, b4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ogden, L.G.; Vupputuri, S.; Bazzano, L.A.; Loria, C.; Whelton, P.K. Dietary sodium intake and subsequent risk of cardiovascular disease in overweight adults. JAMA 1999, 282, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, S.H.; Sacco, R.L.; Boden-Albala, B.; Cheun, J.F.; Pittman, J.G.; Elkind, M.S.; Paik, M.C. Abdominal obesity and risk of ischemic stroke: The northern Manhattan stroke study. Stroke 2003, 34, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chin, S.L.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Rangarajan, S.; Islam, S.; Pais, P.; McQueen, M.J.; et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): A case-control study. Lancet 2010, 376, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren-Morag, N.; Goldbourt, U.; Tanne, D. Relation between the metabolic syndrome and ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack: A prospective cohort study in patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Stroke 2005, 36, 1366–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, G.A.; Amitay, E.L.; Chatterjee, S.; Steubl, D. The Bidirectional Association of Chronic Kidney Disease, Type 2 Diabetes, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, and Heart Failure: The Cardio-Renal-Metabolic Syndrome. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2023, 21, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, M.; Yu, G.Z.; Mian, A.; Cramer, A.; Meysami, S.; Merrill, D.A.; Samara, A.; Eisenstein, S.A.; Hershey, T.; Babulal, G.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation: A Modifiable Pathway Linking Obesity, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 31, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Castrejón-Téllez, V.; Soto, M.E.; Rubio-Ruiz, M.E.; Manzano-Pech, L.; Guarner-Lans, V. Oxidative stress, plant natural antioxidants, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnink, E.; Zabern, M.; Boersma, L.; Glikson, M. Mechanisms and Prediction of Ischemic Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychala, M.S.; Honarpisheh, P.; McCullough, L.D. Sex differences in neuroinflammation and neuroprotection in ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2017, 95, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
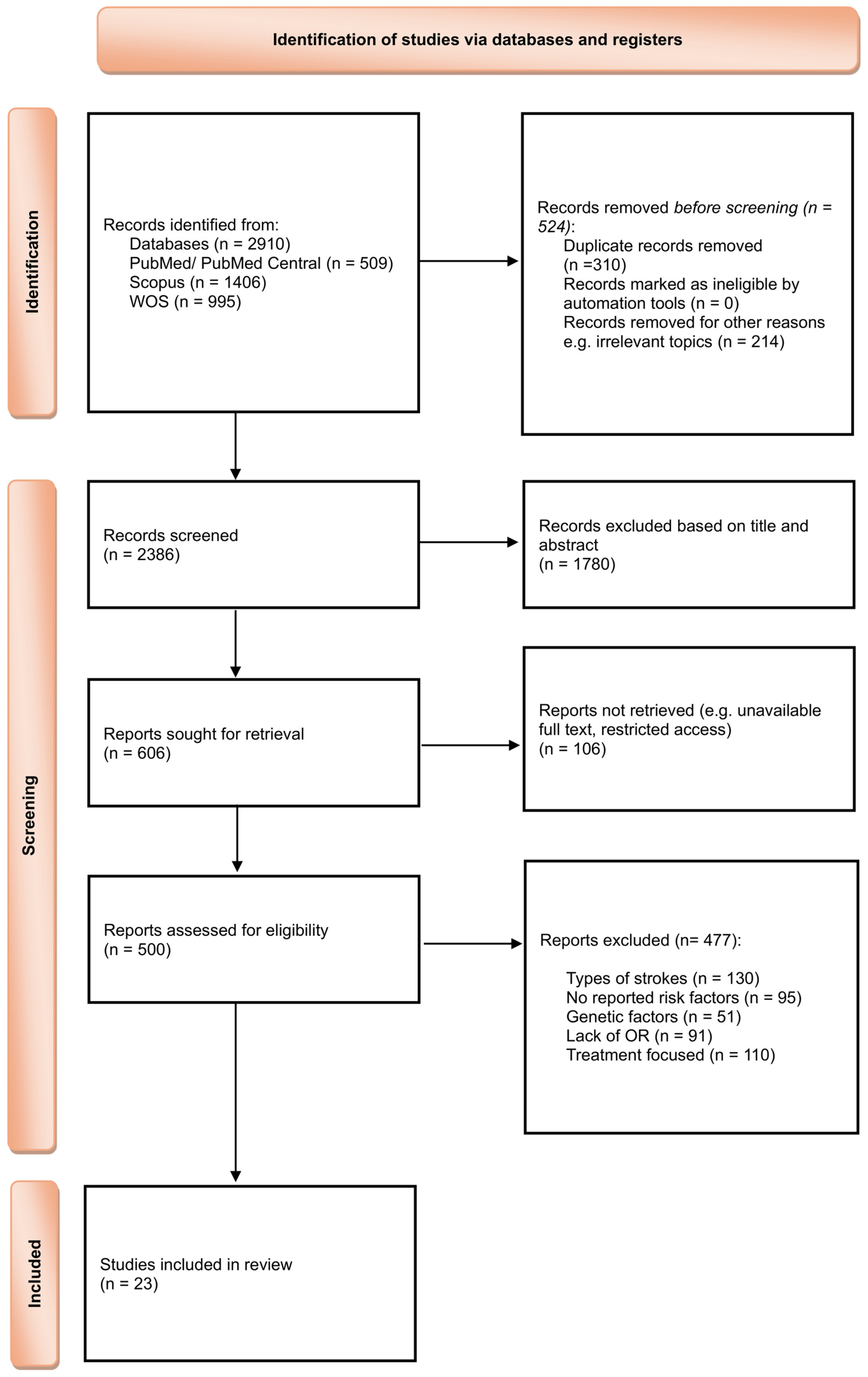
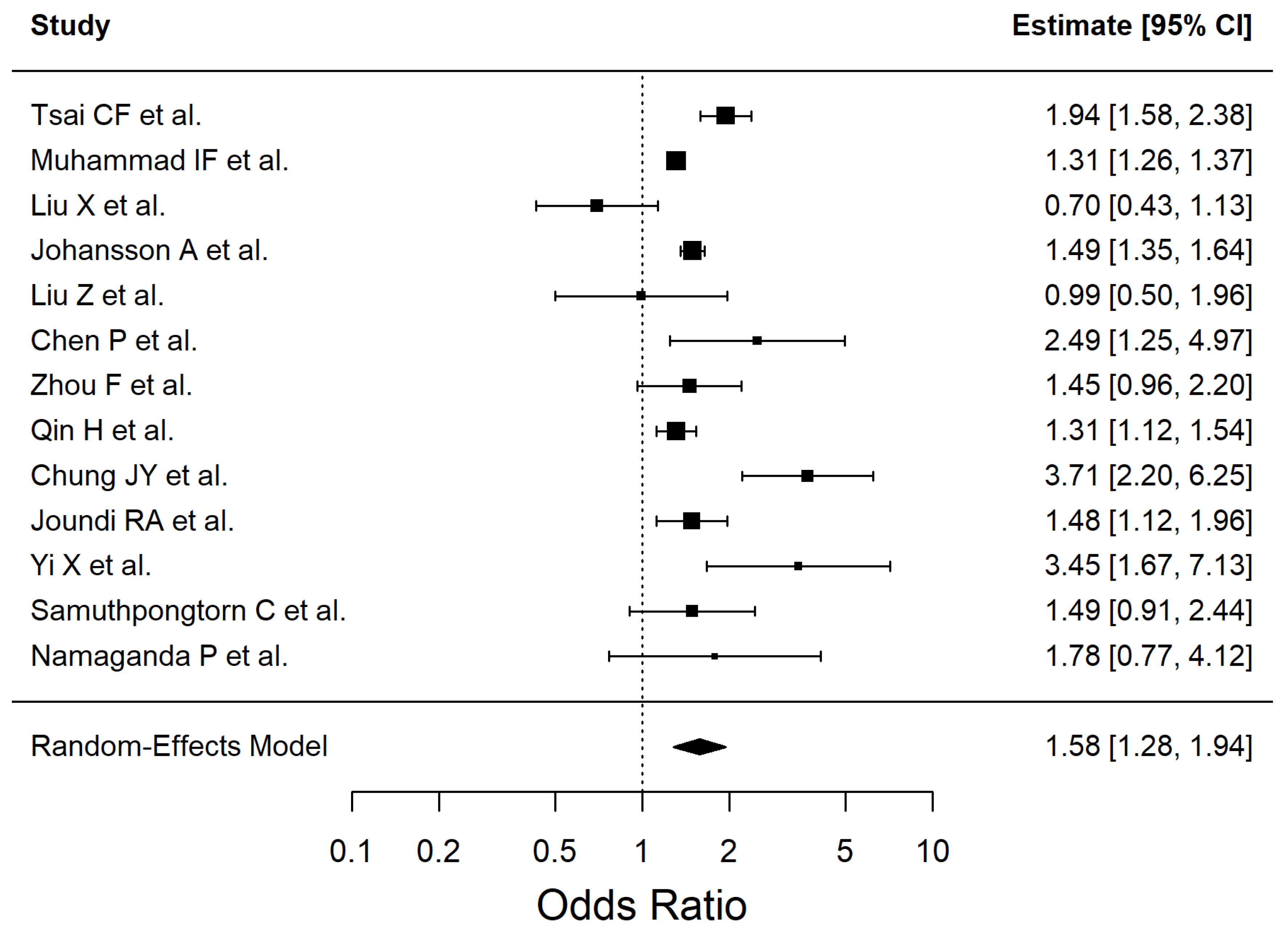
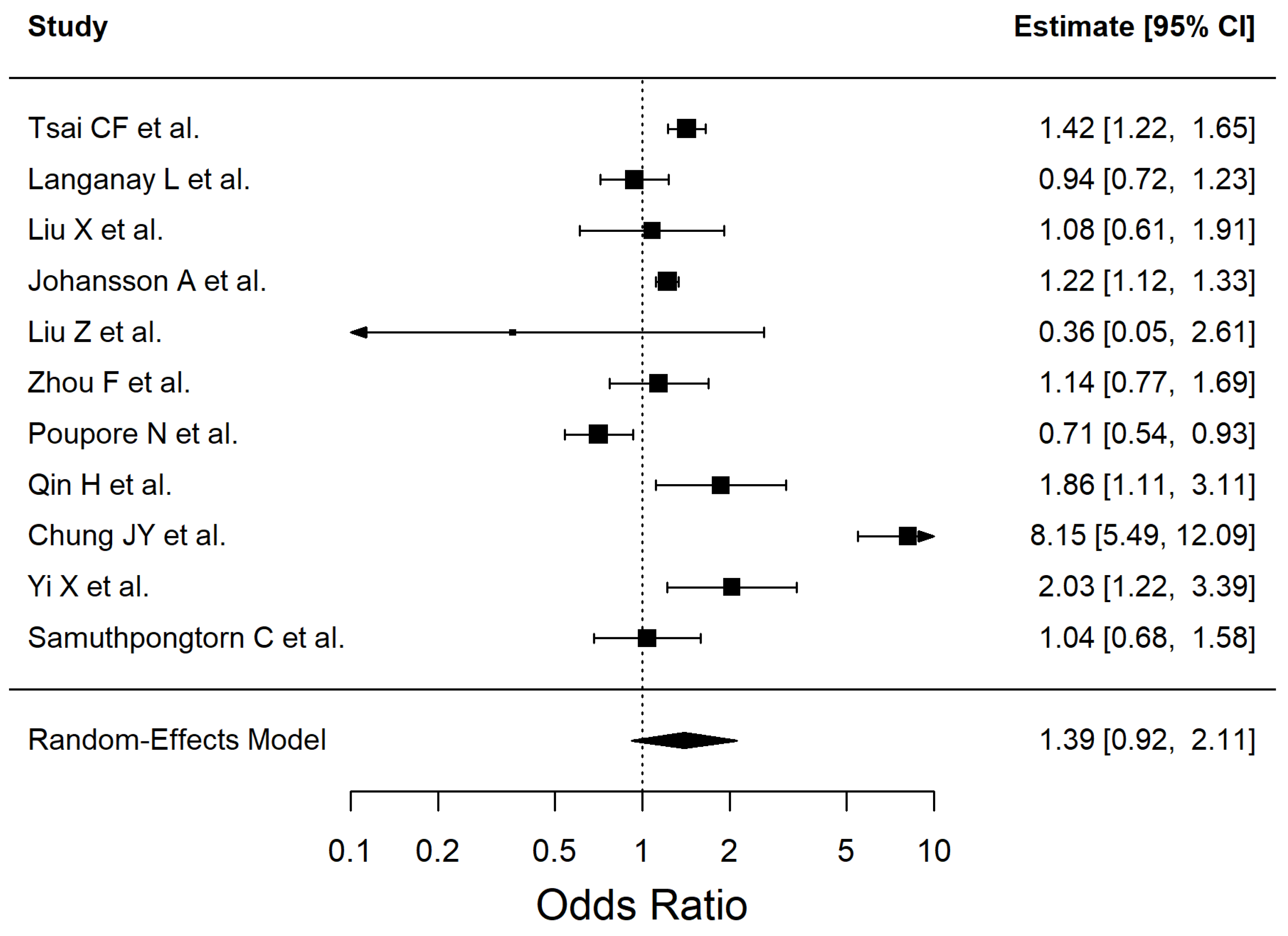
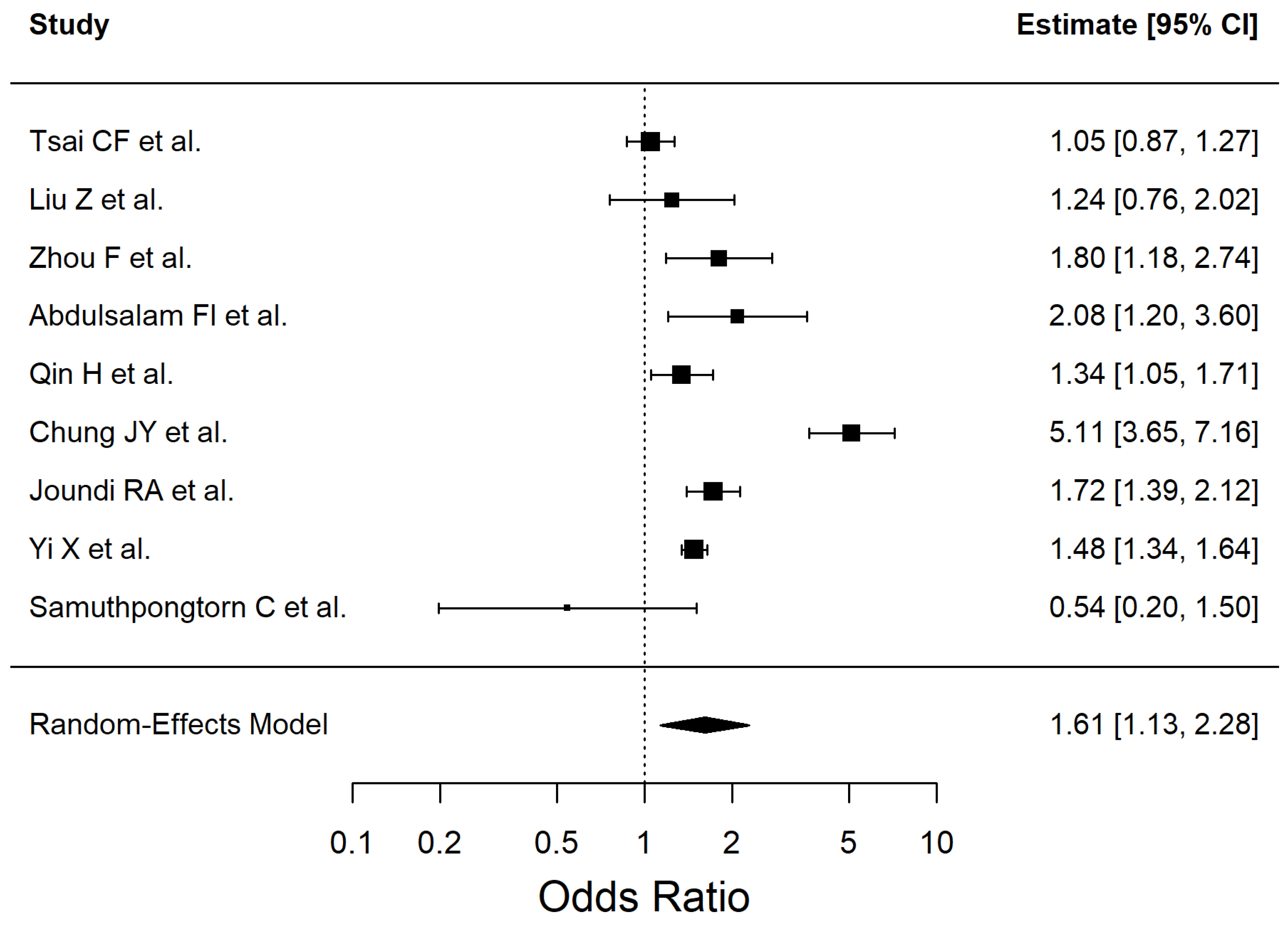

| Nr. Crt. | Study | Country | Study Design | Sample Size | Primary Outcome | Key Risk Factors * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tsai CF et al., 2021 [34] | Taiwan | Cohort | 4953 | Incident stroke | HT, DL, SM, DM2, ALC, TIA |
| 2. | Muhammad IF et al., 2021 [35] | Sweden | Cohort | 1838 | Incident stroke | HT, SM, DM 2 |
| 3. | Liu C et al., 2024 [36] | China | Retrospective | 24,355 | Post-stroke outcome | DM 2 |
| 4. | Langanay L et al., 2024 [37] | France | Cohort | 1912 | Post-stroke outcome | DL, AF |
| 5. | Liu X et al., 2024 [38] | China | Cross-sectional | 504 | Incident stroke | HT, DL, DM2, OB, ALC |
| 6. | Zheng H et al., 2023 [39] | China | Cohort | 54,123 | Incident stroke | HT, SM, DM2, ALC |
| 7. | Johansson A et al., 2021 [40] | Sweden | Cohort | 26,549 | Incident stroke | HT, DL, DM2, OB, ALC, |
| 8. | Liu Z et al., 2020 [41] | China | Cohort | 1121 | Post-stroke outcome | HT, DL, SM, DM2, ALC, AF |
| 9. | Ma F et al., 2023 [42] | China | Retrospective | 190 | Post-stroke outcome | HT, DM2 |
| 10. | Chen P et al., 2024 [43] | USA | Retrospective | 51 | Recurrent stroke | HT |
| 11. | Zhou F et al., 2020 [44] | China | Cross-sectional | 1101 | Incident stroke | HT, DL, SM, DM2, ALC |
| 12. | Dittrich TD et al., 2024 [45] | Switzerland | Cohort | 3995 | Post-stroke outcome | HT, DL, DM2 |
| 13. | Marston NA et al., 2022 [46] | International | Cohort | 51,288 | Incident stroke | Polygenic risk score (GRS); descriptive only, not pooled. |
| 14. | Poupore N et al., 2020 [47] | USA | Retrospective | 5469 | Post-stroke outcome | DL, OB, ALC, AF, TIA |
| 15. | Zhang G et al., 2025 [48] | China | Cross-sectional | 5816 | Other (stenosis phenotype) | HT, DL, DM2 |
| 16. | Abdulsalam FI et al., 2024 [49] | Thailand | Cross-sectional | 708 | Post-stroke outcome | SM, OB, ALC |
| 17. | Qin H et al., 2020 [50] | China | Cohort | 12,415 | Post-stroke outcome | HT, DL, SM, DM 2, OB, ALC |
| 18. | Chung JY et al., 2023 [51] | USA | Retrospective | 787 | Recurrent stroke | HT, DL, SM, DM2, ALC |
| 19. | Joundi RA et al., 2022 [52] | Canada | Cross-sectional | 492,400 | Incident stroke | HT, SM, DM2, OB, ALC |
| 20. | Uzuner N et al., 2023 [53] | Turkey | Retrospective | 927 | Recurrent stroke | DM 2 |
| 21. | Yi X et al., 2020 [54] | China | Cross-sectional | 429 | Incident stroke | HT, SM, DM2, OB, AF |
| 22. | Samuthpongtorn C et al., 2021 [55] | Thailand | Cross-sectional | 542 | Post-stroke outcome | HT, DL, SM, DM2, AF, TIA |
| 23. | Namaganda P et al., 2022 [56] | Uganda | Case–control | 51 | Incident stroke | HT |
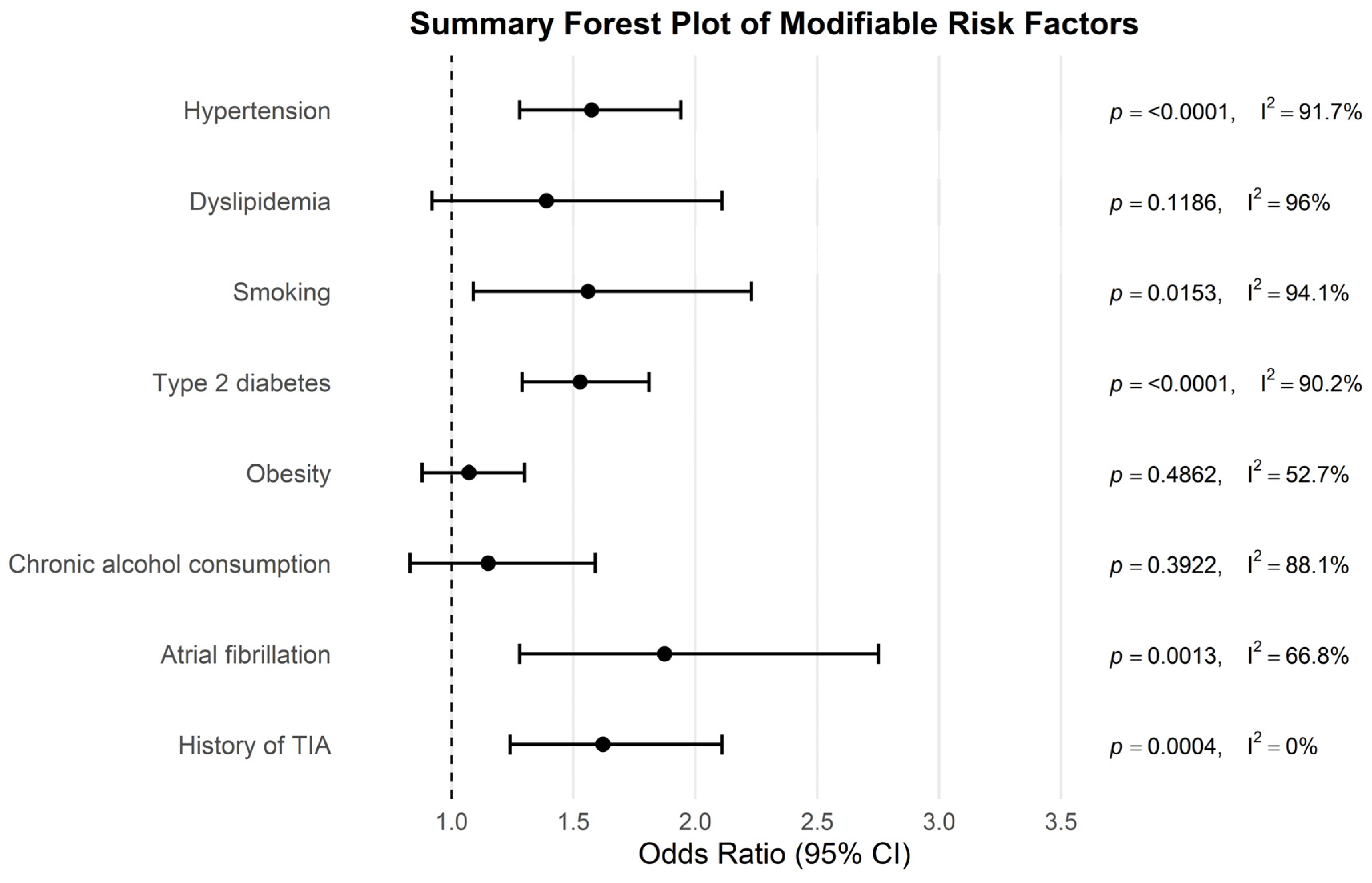
| Risk Factor | Pooled OR | 95% CI | p-Value | I2% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | 1.575 | 1.28–1.94 | <0.0001 | 91.72 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.39 | 0.92–2.11 | 0.1186 | 96.03 |
| Smoking | 1.56 | 1.09–2.23 | 0.0153 | 94.07 |
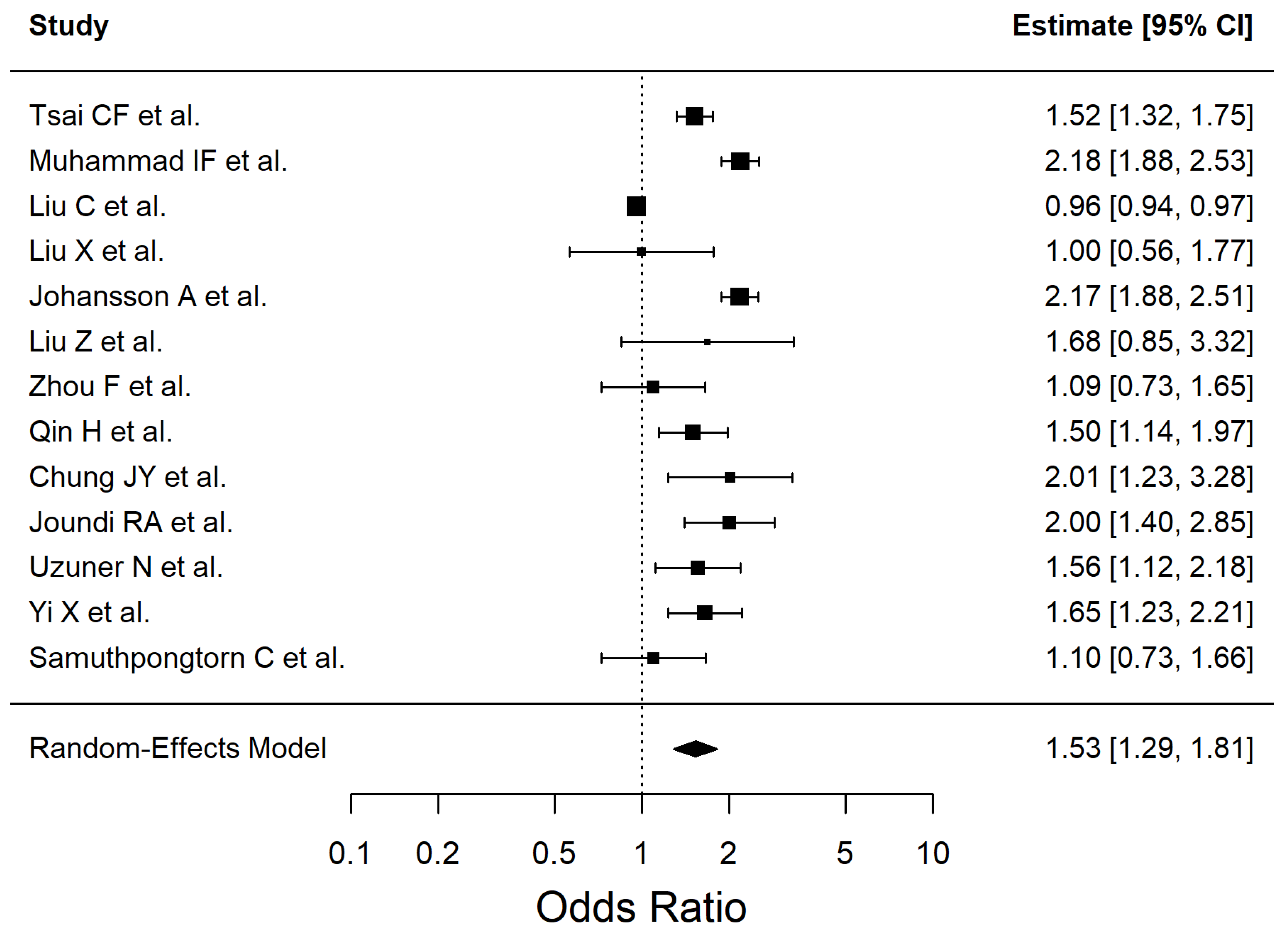
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 1.528 | 1.29–1.81 | <0.0001 | 90.22 |
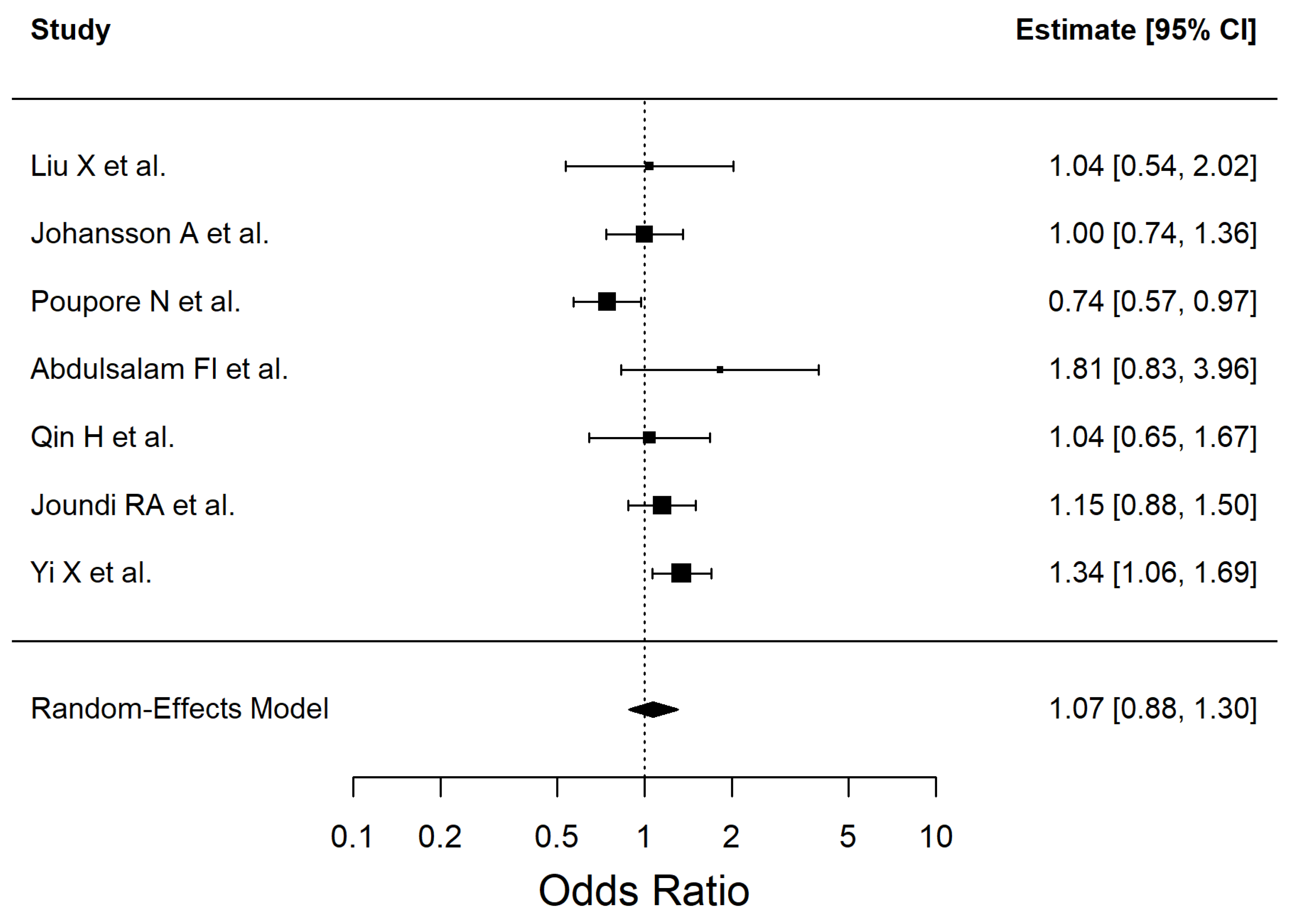
| Obesity | 1.072 | 0.88–1.30 | 0.4862 | 52.74 |
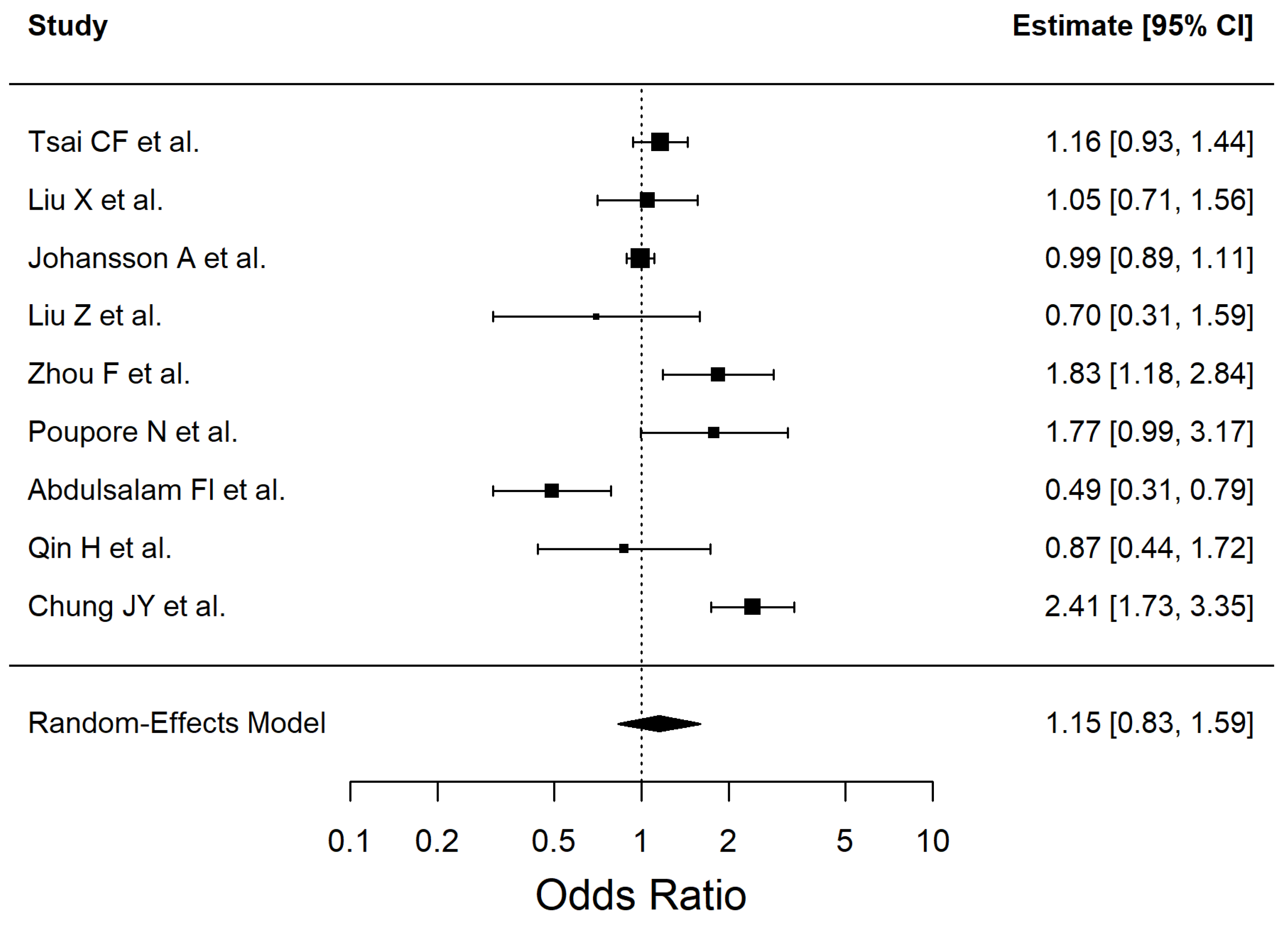
| Chronic alcohol consumption | 1.15 | 0.83–1.59 | 0.3922 | 88.13 |
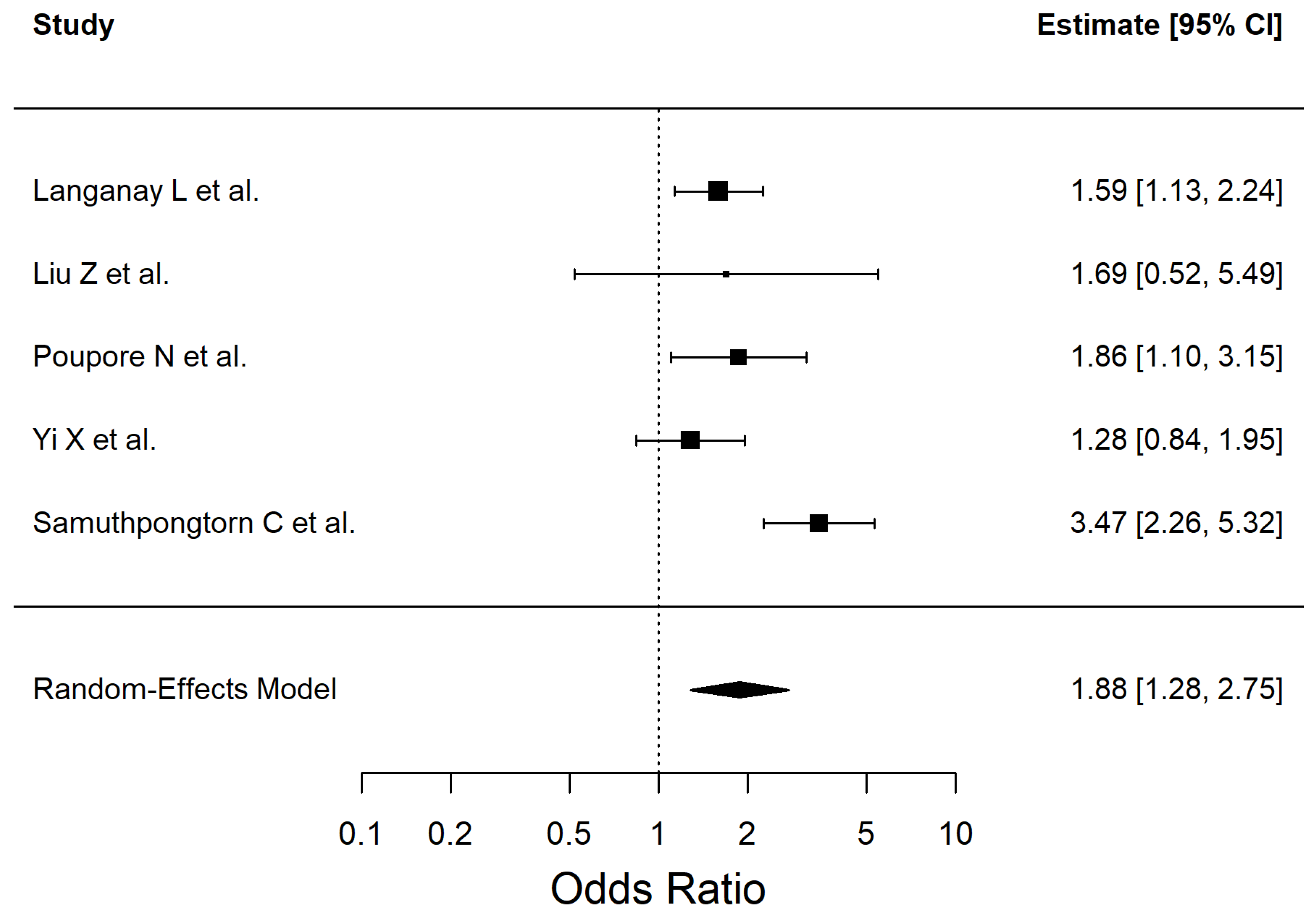
| Atrial fibrillation | 1.874 | 1.28–2.75 | 0.0013 | 66.75 |
| History of TIA | 1.621 | 1.24–2.11 | 0.0004 | 0 |
| Risk Factor | Effect Estimate (OR, 95% CI) | No. of Studies | No. of Participants | Certainty of Evidence (GRADE) | Reasons for Downgrade (If Any) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | 1.58 (1.28–1.94) | 13 | 542,741 | Very low | Serious inconsistency (I2 = 91.7%), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Diabetes mellitus type 2 | 1.53 (1.29–1.81) | 13 | 567,921 | Low | Inconsistency (I2 = 90%), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.39 (0.92–2.11) | 11 | 55,782 | Very low | Inconsistency (I2 = 96%), Imprecision (95% CI crosses null effect), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Smoking | 1.56 (1.09–2.23) | 9 | 514,456 | Low | Inconsistency (I2 = 94%), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Obesity | 1.07 (0.88–1.30) | 6 | 526,059 | Very low | Imprecision (95% CI crosses null effect), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Chronic alcohol consumption | 1.15 (0.83–1.59) | 9 | 53,607 | Very low | Inconsistency (I2 = 88.13%), Imprecision (CI include 1), Study design (observational evidence) |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 1.87 (1.28–2.75) | 5 | 9473 | Low | Inconsistency (I2 = 66.75%), Study design (observational evidence) |
| History of TIA | 1.62 (1.24–2.11) | 3 | 10,964 | Low | Study design (observational evidence) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gerdanovics, A.; Stănescu, I.C.; Mîrza, C.M.; Dogaru, G.B.; Nicula, C.A.; Boarescu, P.-M.; Gerdanovics, C.-A.; Bulboacă, A.E. Proinflammatory Risk Factors in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101229
Gerdanovics A, Stănescu IC, Mîrza CM, Dogaru GB, Nicula CA, Boarescu P-M, Gerdanovics C-A, Bulboacă AE. Proinflammatory Risk Factors in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(10):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101229
Chicago/Turabian StyleGerdanovics, Alexandru, Ioana Cristina Stănescu, Camelia Manuela Mîrza, Gabriela Bombonica Dogaru, Cristina Ariadna Nicula, Paul-Mihai Boarescu, Cezara-Andreea Gerdanovics, and Adriana Elena Bulboacă. 2025. "Proinflammatory Risk Factors in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Antioxidants 14, no. 10: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101229
APA StyleGerdanovics, A., Stănescu, I. C., Mîrza, C. M., Dogaru, G. B., Nicula, C. A., Boarescu, P.-M., Gerdanovics, C.-A., & Bulboacă, A. E. (2025). Proinflammatory Risk Factors in Patients with Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants, 14(10), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101229








