Bakuchiol, a Natural Antioxidant, Synergizes with Colistin Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting Iron Homeostasis and Membrane Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Chemicals
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.3. Bacterial Growth Curves and Time–Kill Curves
2.4. Checkerboard Assays
2.5. Lipid Competitive Assays
2.6. Osmotic Stress Testing
2.7. ROS Accumulation and Lipid Peroxidation Assay
2.8. ATP Quantification
2.9. PMF Measurement
2.10. EB Assay
2.11. Membrane Permeability
2.12. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
2.13. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
2.14. Intracellular Fe2+ Quantification
2.15. Hemolysis Assay
2.16. In Vivo Therapeutic Evaluation
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synergistic Antibacterial Effects of BAK-COL Combination
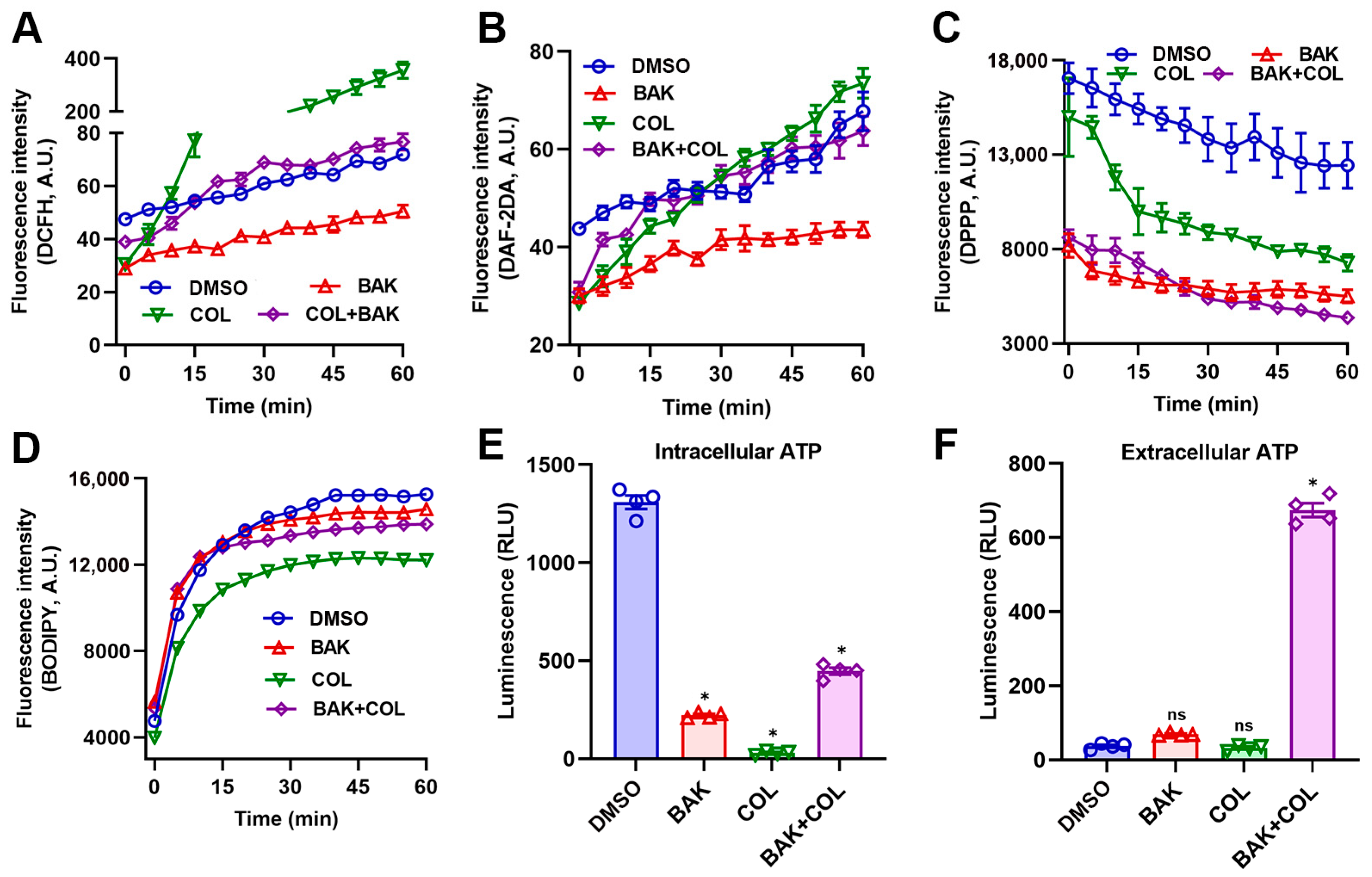
3.2. BAK Induces Redox Imbalance and Metabolic Dysregulation
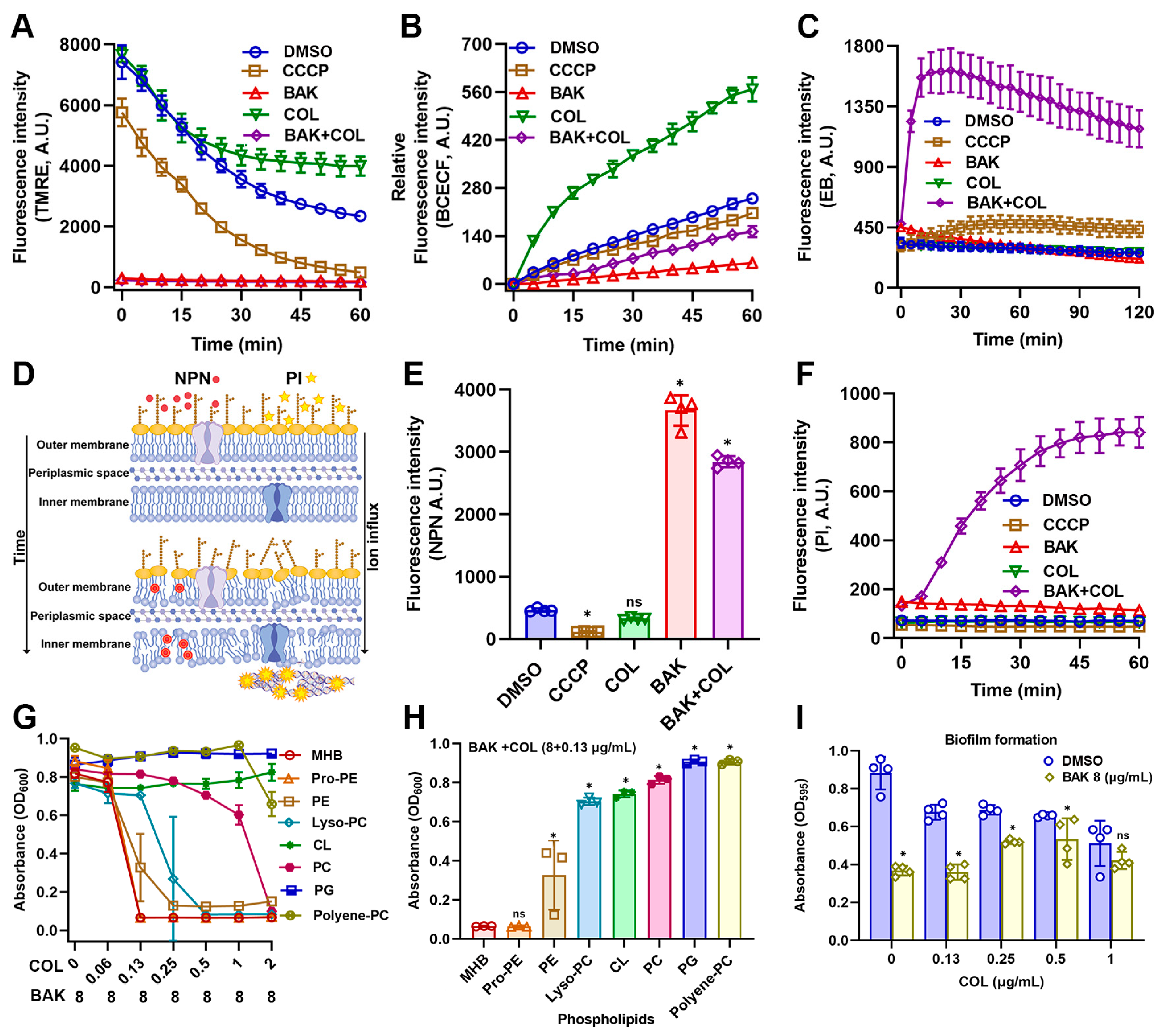
3.3. BAK Disrupts Membrane Integrity and Function
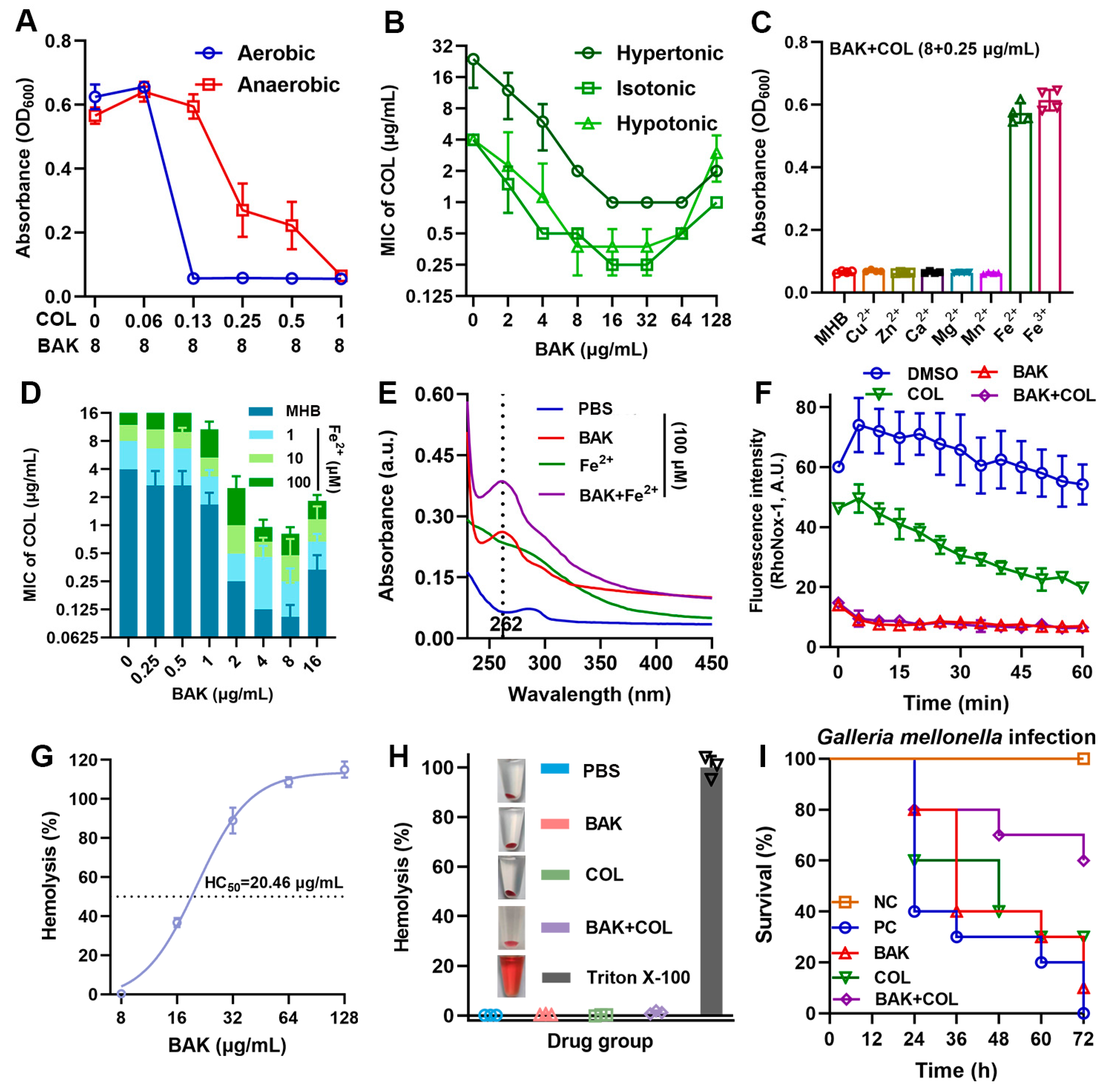
3.4. BAK Disrupts Iron Homeostasis
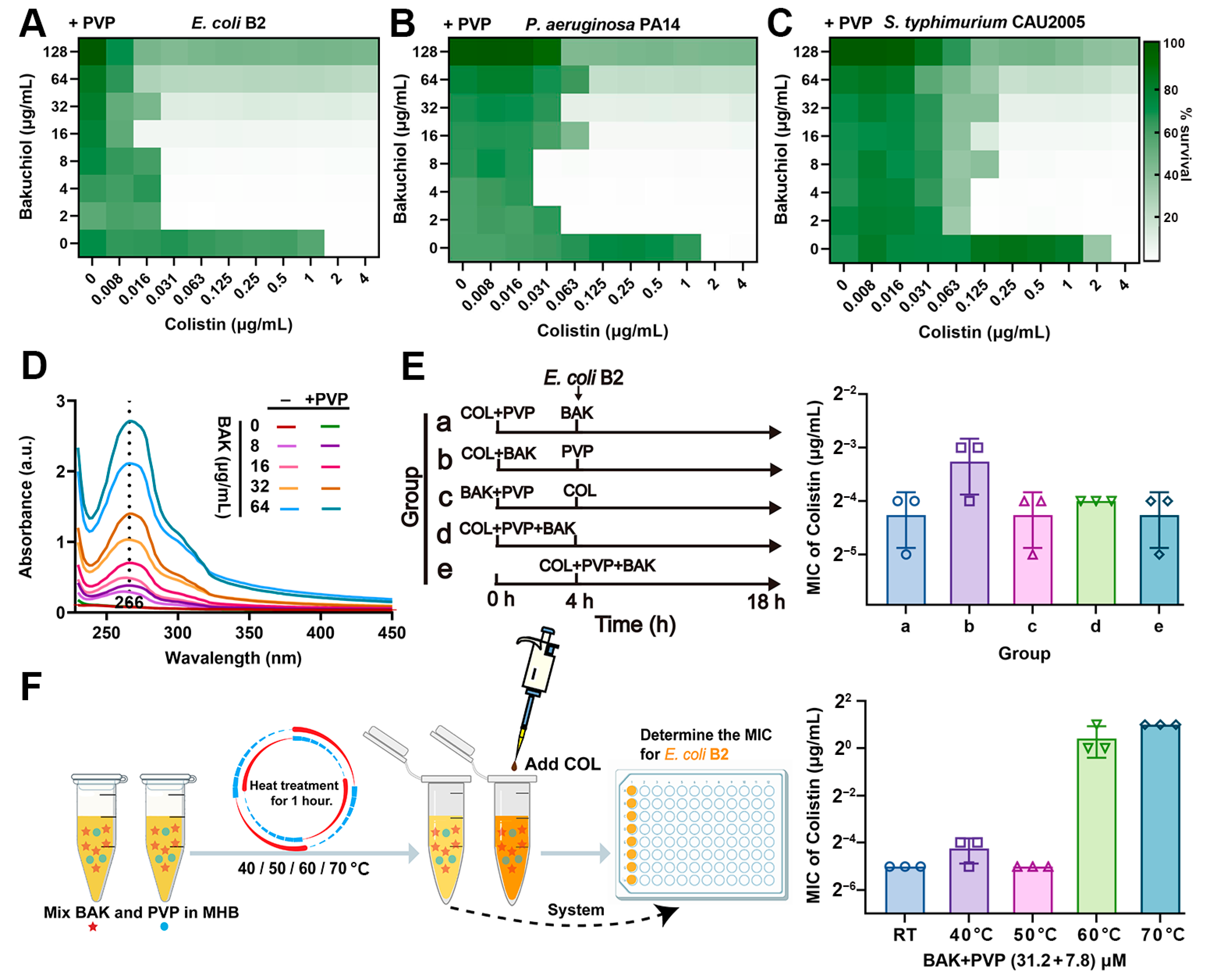
3.5. PVP Promotes the Synergistic Activity of BAK-COL Combination
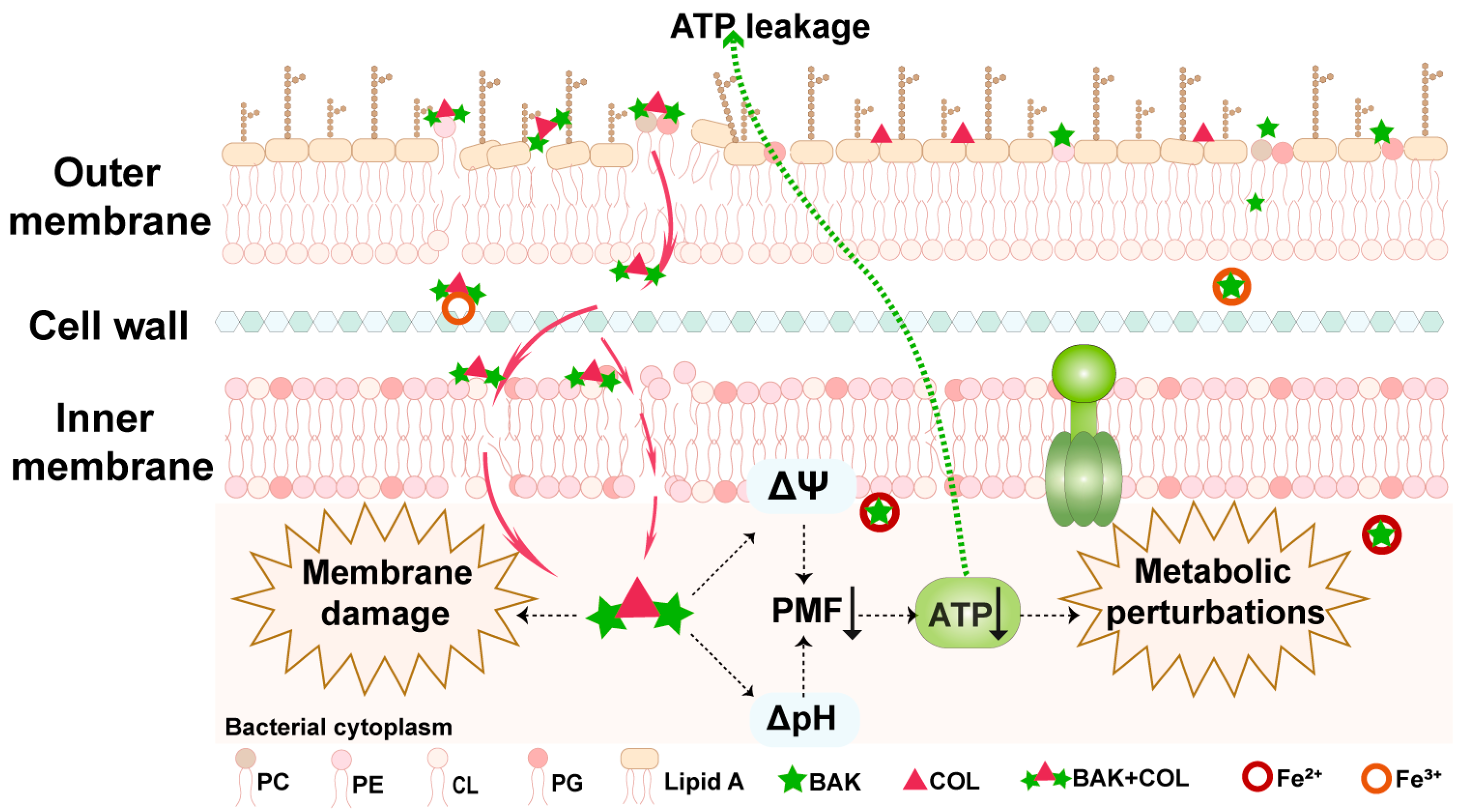
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dai, C.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice involves the mitochondrial, death receptor, and endoplasmic reticulum pathways. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4075–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Nation, R.L.; Turnidge, J.D.; Milne, R.W.; Coulthard, K.; Rayner, C.R.; Paterson, D.L. Colistin: The re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nang, S.C.; Azad, M.A.K.; Velkov, T.; Zhou, Q.T.; Li, J. Rescuing the Last-Line Polymyxins: Achievements and Challenges. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 679–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Shen, Y.B.; Yang, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance genes: Mcr. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yang, K.; Tong, Z.; Shi, J.; Li, R.; Xiao, X.; Ren, W.; Hardeland, R.; Reiter, R.J.; et al. Melatonin overcomes MCR-mediated colistin resistance in Gram-negative pathogens. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10697–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Koohi-Moghadam, M.; Wang, H.; Ho, P.L.; Li, H.; Sun, H. Re-sensitization of mcr carrying multidrug resistant bacteria to colistin by silver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2119417119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Shi, J.; Chen, C.; He, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Structural-Activity Relationship-Inspired the Discovery of Saturated Fatty Acids as Novel Colistin Enhancers. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.; Lee, R.E.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Hiller, S.; Rodnina, M.V.; Schneider, T.; Weingarth, M.; Wohlgemuth, I. Sophisticated natural products as antibiotics. Nature 2024, 632, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Kang, J.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. Rational Design of Natural Xanthones Against Gram-negative Bacteria. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2411923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschner, F.; Mostert, D.; Daniel, J.M.; Voltz, A.; Schneider, D.C.; Khangholi, N.; Bartel, J.; Pessanha de Carvalho, L.; Brauer, M.; Gorelik, T.E.; et al. Natural products chlorotonils exert a complex antibacterial mechanism and address multiple targets. Cell Chem. Biol. 2025, 32, 586–602.e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Peng, H.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Dong, Y.; An, K.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Glabridin restore the sensitivity of colistin against mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli by polypharmacology mechanism. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 293, 128070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Hao, Z.; Ding, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J. Plant Natural Flavonoids Against Multidrug Resistant Pathogens. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cai, Y.; Wu, S.; Mei, C.; Wang, H.; Qu, S. Synergistic antimicrobial efficacy of glabrol and colistin through micelle-based co-delivery against multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens. Phytomedicine 2025, 137, 156371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.X.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Long, T.F.; He, Q.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, Y.F.; Yu, Y.; et al. Natural flavonoids disrupt bacterial iron homeostasis to potentiate colistin efficacy. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Sun, P.; Liu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, J. Psoralea corylifolia L.: A comprehensive review of its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology, quality control and pharmacokinetics. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Ha, T.Y.; Ahn, J.; Kim, S. Estrogenic activities of Psoralea corylifolia L. seed extracts and main constituents. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariola, A.; El Chami, M.; Granatieri, J.; Valgimigli, L. Anti-tyrosinase and antioxidant activity of meroterpene bakuchiol from Psoralea corylifolia (L.). Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Luo, M.; Shen, J.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Luo, J.; Zeng, Z.; Deng, D.; Xiao, J. Bakuchiol from Psoralea corylifolia L. Ameliorates acute kidney injury and improves survival in experimental polymicrobial sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Jeong, S.J. Bakuchiol Suppresses Inflammatory Responses Via the Downregulation of the p38 MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsura, H.; Tsukiyama, R.I.; Suzuki, A.; Kobayashi, M. In vitro antimicrobial activities of bakuchiol against oral microorganisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 3009–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, K.; Lee, Y.; Baek, S.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.; Yang, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, W.; Seo, E.K.; Kim, W. Bakuchiol kills Staphylococcus aureus persisters and potentiates colistin activity against Acinetobacter baumannii persisters. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1592183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. A broad-spectrum antibiotic adjuvant reverses multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, M100, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Kato, S.; Long, J.; Mattingly, H.H.; He, C.; Vural, D.C.; Zucker, S.W.; Emonet, T. Spatial self-organization resolves conflicts between individuality and collective migration. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Yun, S.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Z. Zn(II) enhances the antimicrobial effect of chloroxine and structural analogues against drug-resistant ESKAPE pathogens in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 229, 116482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viveiros, M.; Martins, A.; Paixão, L.; Rodrigues, L.; Martins, M.; Couto, I.; Fähnrich, E.; Kern, W.V.; Amaral, L. Demonstration of intrinsic efflux activity of Escherichia coli K-12 AG100 by an automated ethidium bromide method. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 31, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Z. The antibacterial efficacy of nitroxoline against multidrug resistant Escherichia coli associated with copper binding. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 996, 177576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Tao, H.; Banerjee, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Nemeth, E.; Czaja, M.J.; He, P. Integrated regulation of stress responses, autophagy and survival by altered intracellular iron stores. Redox Biol. 2022, 55, 102407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Aduru, S.V.; Smith, R.P.; Zhao, Z.; Lopatkin, A.J. The role of bacterial metabolism in antimicrobial resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 23, 439–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Acker, H.; Coenye, T. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in Antibiotic-Mediated Killing of Bacteria. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tong, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Bacterial proton motive force as an unprecedented target to control antimicrobial resistance. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 1068–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Zeng, P.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. Otilonium bromide boosts antimicrobial activities of colistin against Gram-negative pathogens and their persisters. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, M.; Karakulska, J.; Sobolewski, P.; Kowalska, U.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Böttcher, D.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Drozd, R. Glycoside hydrolase (PelA(h)) immobilization prevents Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation on cellulose-based wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullin, J.; Bradley, J.M.; Moore, G.R.; Le Brun, N.E.; Wilson, M.T.; Svistunenko, D.A. Electron Transfer from Haem to the Di-Iron Ferroxidase Centre in Bacterioferritin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 8376–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, X.; Fan, B.; Huang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Lou, Z.; Ding, H.; Lyu, J.; Tan, G. Zinc Toxicity and Iron-Sulfur Cluster Biogenesis in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01967-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadar, K.; de Dios, R.; Kadeřábková, N.; Prescott, T.A.K.; Mavridou, D.A.I.; McCarthy, R.R. Disrupting iron homeostasis can potentiate colistin activity and overcome colistin resistance mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Wei, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, C.; de Jong, A.; Chen, J.H.K.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, M.J.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Diez-Echave, P.; Gálvez, J.; et al. Bismuth-based drugs sensitize Pseudomonas aeruginosa to multiple antibiotics by disrupting iron homeostasis. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 2600–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yang, L.; Qu, A.; Li, D.; Yu, M.; Zheng, S.; Ruan, X.; Wang, Q. A design of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum’s flavonoid loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles for improving its bioavailability and biological activities. Food Chem. 2025, 473, 143099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezraty, B.; Vergnes, A.; Banzhaf, M.; Duverger, Y.; Huguenot, A.; Brochado, A.R.; Su, S.Y.; Espinosa, L.; Loiseau, L.; Py, B.; et al. Fe-S cluster biosynthesis controls uptake of aminoglycosides in a ROS-less death pathway. Science 2013, 340, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampaloni, C.; Mattei, P.; Bleicher, K.; Winther, L.; Thäte, C.; Bucher, C.; Adam, J.-M.; Alanine, A.; Amrein, K.E.; Baidin, V.; et al. A novel antibiotic class targeting the lipopolysaccharide transporter. Nature 2024, 625, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewińska, A.; Domżał-Kędzia, M.; Maciejczyk, E.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Bazylińska, U. Design and Engineering of “Green” Nanoemulsions for Enhanced Topical Delivery of Bakuchiol Achieved in a Sustainable Manner: A Novel Eco-Friendly Approach to Bioretinol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Kant, S.; Chaudary, T.K.; Mehra, A.; Singh, A.; Attri, S.; Gasso, S.; Mahajan, A.; Bedi, N. Bakuchiol nanoemulsion loaded electrospun nanofibers for the treatment of burn wounds. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 6075–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Yun, S.; Ren, X.; Wu, S.; Cheng, J.; Huang, X. Bakuchiol, a Natural Antioxidant, Synergizes with Colistin Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting Iron Homeostasis and Membrane Integrity. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101178
Li Q, Yun S, Ren X, Wu S, Cheng J, Huang X. Bakuchiol, a Natural Antioxidant, Synergizes with Colistin Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting Iron Homeostasis and Membrane Integrity. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(10):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qianqian, Shaobo Yun, Xiaomin Ren, Sijie Wu, Jia Cheng, and Xiaoyong Huang. 2025. "Bakuchiol, a Natural Antioxidant, Synergizes with Colistin Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting Iron Homeostasis and Membrane Integrity" Antioxidants 14, no. 10: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101178
APA StyleLi, Q., Yun, S., Ren, X., Wu, S., Cheng, J., & Huang, X. (2025). Bakuchiol, a Natural Antioxidant, Synergizes with Colistin Against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria by Disrupting Iron Homeostasis and Membrane Integrity. Antioxidants, 14(10), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14101178





