Rapid Communication: Plasma Interleukin-35 in Children with Autism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Blood Collection and Cytokine Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
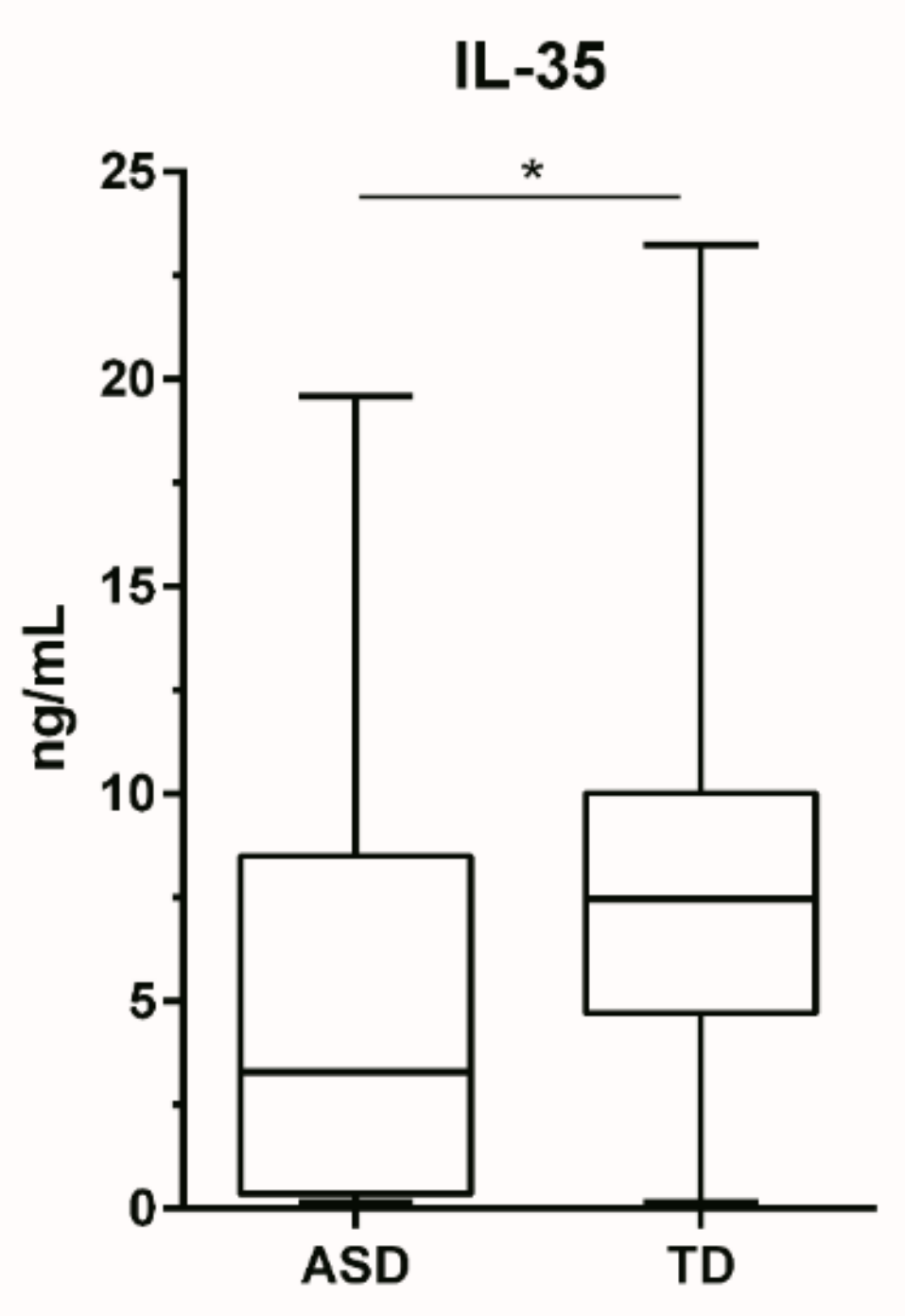
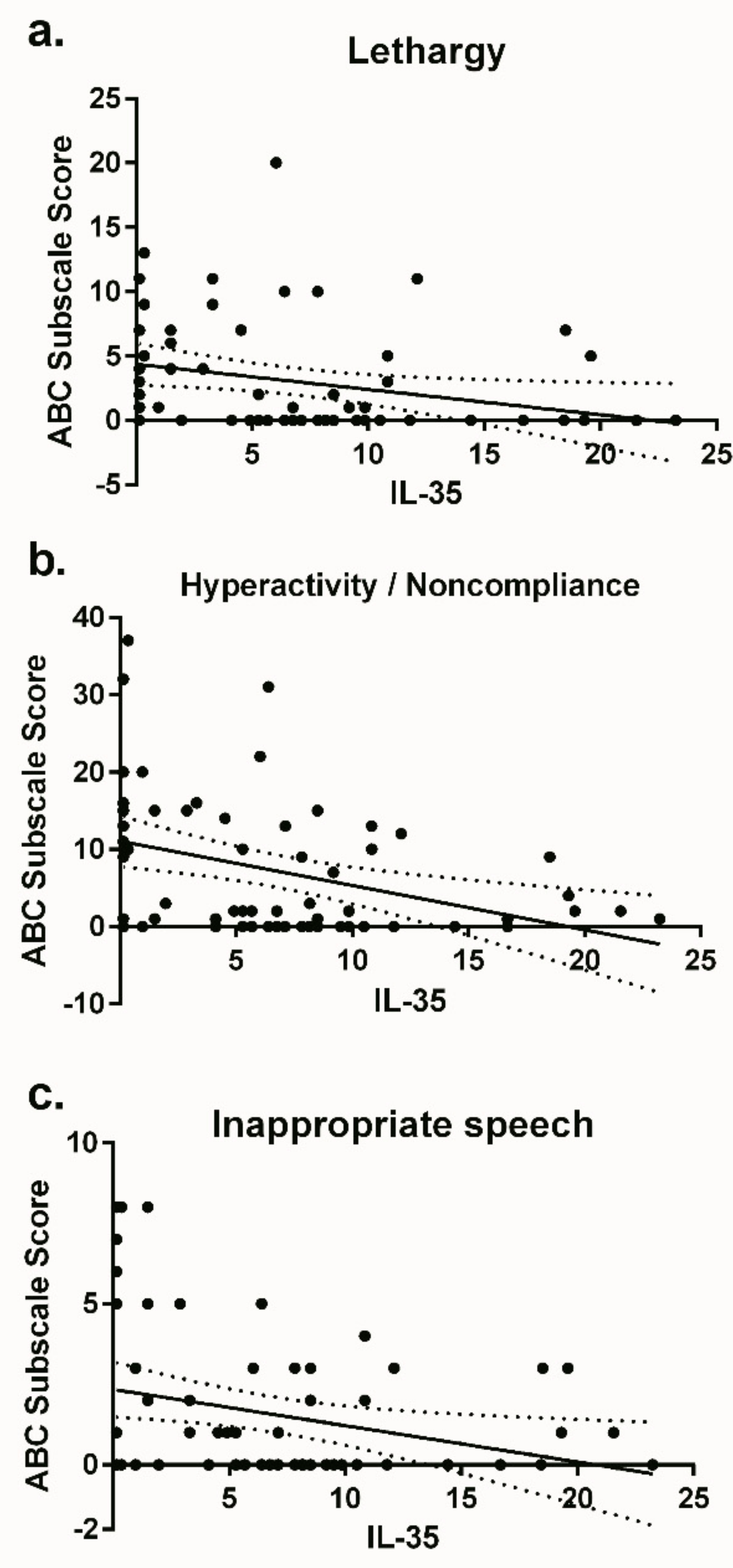
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baio, J.; Wiggins, L.; Christensen, D.L.; Maenner, M.J.; Daniels, J.; Warren, Z.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; Zahorodny, W.; Robinson Rosenberg, C.; White, T.; et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years—Autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 67, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, H.K.; Ko, E.M.; Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. Immune dysfunction and autoimmunity as pathological mechanisms in autism spectrum disorders. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onore, C.; Careaga, M.; Ashwood, P. The role of immune dysfunction in the pathophysiology of autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, J.; Ashwood, P. Evidence supporting an altered immune response in ASD. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 163, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goines, P.E.; Croen, L.A.; Braunschweig, D.; Yoshida, C.K.; Grether, J.; Hansen, R.; Kharrazi, M.; Ashwood, P.; van de Water, J. Increased midgestational IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-5 in women bearing a child with autism: A case-control study. Mol. Autism 2011, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.L.; Croen, L.A.; Yoshida, C.K.; Heuer, L.; Hansen, R.; Zerbo, O.; DeLorenze, G.N.; Kharrazi, M.; Yolken, R.; Ashwood, P.; et al. Autism with intellectual disability is associated with increased levels of maternal cytokines and chemokines during gestation. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowiak, P.; Goines, P.E.; Tancredi, D.J.; Ashwood, P.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; van de Water, J. Neonatal cytokine profiles associated with autism spectrum disorder. Biolog. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.R.; Careaga, M.; Van De Water, J.; McAllister, K.; Bauman, M.D.; Ashwood, P. Long-term altered immune responses following fetal priming in a non-human primate model of maternal immune activation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 63, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.R.; Yang, H.; Serena, G.; Sturgeon, C.; Ma, B.; Careaga, M.; Hughes, H.K.; Angkustsiri, K.; Rose, M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; et al. Differential immune responses and microbiota profiles in children with autism spectrum disorders and co-morbid gastrointestinal symptoms. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 70, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente, F.; Anthony, A.; Heuschkel, R.B.; A Thomson, M.; Ashwood, P.; Murch, F.S.H.; Murch, S.H. Focal-enhanced gastritis in regressive autism with features distinct from crohn’s and helicobacter pylori gastritis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente, F.; Ashwood, P.; Day, R.; Machado, N.; I Furlano, R.; Anthony, A.; E Davies, S.; Wakefield, A.J.; A Thomson, M.; A Walker-Smith, J.; et al. Small intestinal enteropathy with epithelial IgG and complement deposition in children with regressive autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyall, K.; Ashwood, P.; Van de Water, J.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Maternal immune-mediated conditions, autism spectrum disorders, and developmental delay. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croen, L.A.; Grether, J.K.; Yoshida, C.K.; Odouli, R.; van de Water, J. Maternal autoimmune diseases, asthma and allergies, and childhood autism spectrum disorders: A case-control study. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2005, 159, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, R.; Lenti, C.; Saccani, M.; Curatolo, P.; Manzi, B.; Bravaccio, C.; Persico, A.M. Cluster analysis of autistic patients based on principal pathogenetic components. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wills, S.; Cabanlit, M.; Bennett, J.; Ashwood, P.; Amaral, D.G.; van de Water, J. Detection of autoantibodies to neural cells of the cerebellum in the plasma of subjects with autism spectrum disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2009, 23, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabanlit, M.; Wills, S.; Goines, P.; Ashwood, P.; van de Water, J. Brain-specific autoantibodies in the plasma of subjects with autistic spectrum disorder. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1107, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Careaga, M.; Rogers, S.; Hansen, R.L.; Amaral, D.G.; van de Water, J.; Ashwood, P. Immune endophenotypes in children with autism spectrum disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 81, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Enstrom, A.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.L.; Croen, L.A.; Ozonoff, S.; Pessah, I.N.; DeWater, J.; van de Water, J. Decreased transforming growth factor beta1 in autism: a potential link between immune dysregulation and impairment in clinical behavioral outcomes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 204, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.; Van de Water, J. Elevated plasma cytokines in autism spectrum disorders provide evidence of immune dysfunction and are associated with impaired behavioral outcome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Geng, L.; Davidow, A.L. Cytokine profiles by peripheral blood monocytes are associated with changes in behavioral symptoms following immune insults in a subset of ASD subjects: An inflammatory subtype? J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Sun, S.; Le, H. Proinflammatory and regulatory cytokine production associated with innate and adaptive immune responses in children with autism spectrum disorders and developmental regression. J. Neuroimmunol. 2001, 120, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Iwata, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Tsujii, M.; Tsuchiya, K.J.; Sekine, Y.; Suda, S.; Suzuki, K.; Sugihara, G.-I.; et al. Decreased serum levels of transforming growth factor-β1 in patients with autism. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Boil. Psychiatr. 2007, 31, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.W.; Larsen, N.; Mortensen, E.L.; Atladóttir, H. Ó.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Grove, J.; Hougaard, D.M. Neonatal levels of cytokines and risk of autism spectrum disorders: An exploratory register-based historic birth cohort study utilizing the Danish Newborn Screening Biobank. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 252, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwood, P.; Anthony, A.; Torrente, F.; Wakefield, A.J. Spontaneous mucosal lymphocyte cytokine profiles in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms: mucosal immune activation and reduced counter regulatory interleukin-10. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ayadhi, L.; Alhowikan, A.M.; Halepoto, D.M. Impact of auditory integrative training on transforming growth factor-β1 and its effect on behavioral and social emotions in children with autism spectrum disorder. Med Princ. Pr. 2018, 27, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Krakowiak, P.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Hansen, R.; Pessah, I.N.; Van de Water, J. Altered T cell responses in children with autism. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, G.A.; Al Shehab, A.; Fouad, N.R. Frequency of CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of Egyptian children with autism. J. Child Neurol. 2010, 25, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkas, L.I.; Mavropoulos, A.; Perricone, C.; Bogdanos, D.P. IL-35: A new immunomodulator in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teymouri, M.; Pirro, M.; Fallarino, F.; Gargaro, M.; Sahebkar, A. IL-35, a hallmark of immune-regulation in cancer progression, chronic infections and inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2105–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Croen, L.A.; Hansen, R.; Jones, C.R.; Van De Water, J.; Pessah, I.N. The CHARGE Study: An epidemiologic investigation of genetic and environmentalfactors contributing to autism. Environ. Heal. Perspect. 2006, 114, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. Potential cytokine biomarkers in autism spectrum disorders. Biomarkers Med. 2014, 8, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, A.; Quintana, D.S.; Glozier, N.; Lloyd, A.R.; Hickie, I.B.; Guastella, A.J. Cytokine aberrations in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, M.W.; Mortensen, E.L.; Greaves-Lord, K.; Larsen, N.; Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C.; Norgaard-Pedersen, B.; Hougaard, D.M.; Grove, J. Neonatal levels of neurotrophic factors and risk of autism spectrum disorders. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 2013, 128, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, M.M.; Anitha, A.; Thanseem, I.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, T.; Wakuda, T.; Iwata, K.; Tsujii, M.; Sugiyama, T.; et al. Serum microRNA profiles in children with autism. Mol. Autism 2014, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ander, B.P.; Barger, N.; Stamova, B.; Sharp, F.R.; Schumann, C.M. Atypical miRNA expression in temporal cortex associated with dysregulation of immune, cell cycle, and other pathways in autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Autism 2015, 6, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Long, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Qiu, R.; Zhuang, W.; Tang, B.; Xia, K.; Jiang, H. Investigation of gene regulatory networks associated with autism spectrum disorder based on mirna expression in china. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwood, P.; Wakefield, A.J. Immune activation of peripheral blood and mucosal CD3+ lymphocyte cytokine profiles in children with autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 173, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyonouchi, H.; Geng, L.; Ruby, A.; Zimmerman-Bier, B. Dysregulated innate immune responses in young children with autism spectrum disorders: their relationship to gastrointestinal symptoms and dietary intervention. Neuropsychobiology 2005, 51, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, R.P.; Yonk, L.J.; Burger, R.A.; Cole, P.; Odell, J.D.; Warren, W.L.; White, E.; Singh, V.K. Deficiency of suppressor-inducer (CD4+CD45RA+) T cells in autism. Immunol. Invest. 1990, 19, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denney, D.R.; Frei, B.W.; Gaffney, G.R. Lymphocyte subsets and interleukin-2 receptors in autistic children. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1996, 26, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougle, C.J.; Landino, S.M.; Vahabzadeh, A.; O’Rourke, J.; Zürcher, N.R.; Finger, B.C.; Palumbo, M.L.; Helt, J.; Mullett, J.E.; Hooker, J.M.; et al. Toward an immune-mediated subtype of autism spectrum disorder. Brain Res. 2015, 1617, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Qiuwaxi, J.-N.-T.; Ashwood, P.; Cho, S.C.; Huan, Y.; Ge, R.-C.; Chen, X.-W.; Wang, Z.-J.; et al. Transplantation of human cord blood mononuclear cells and umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in autism. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, G.; Sun, J.M.; Davlantis, K.S.; Murias, M.; Franz, L.; Troy, J.; Simmons, R.; Durham, R.; Kurtzberg, J.; Sabatos-DeVito, M.; et al. Autologous cord blood infusions are safe and feasible in young children with autism spectrum disorder: Results of a single-center phase I open-label trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rose, D.; Ashwood, P. Rapid Communication: Plasma Interleukin-35 in Children with Autism. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9070152
Rose D, Ashwood P. Rapid Communication: Plasma Interleukin-35 in Children with Autism. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(7):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9070152
Chicago/Turabian StyleRose, Destanie, and Paul Ashwood. 2019. "Rapid Communication: Plasma Interleukin-35 in Children with Autism" Brain Sciences 9, no. 7: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9070152
APA StyleRose, D., & Ashwood, P. (2019). Rapid Communication: Plasma Interleukin-35 in Children with Autism. Brain Sciences, 9(7), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9070152



