Long-Term Consequences of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Brain Structure and Function: Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction: Protective Effect of Exercise on the Human Brain
2. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders, Adolescent Drinking and Modeling of Developmental Alcohol Effects in Experimental Animals
2.1. Impact of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Society
2.2. Modeling Developmental Alcohol Exposure in Animals
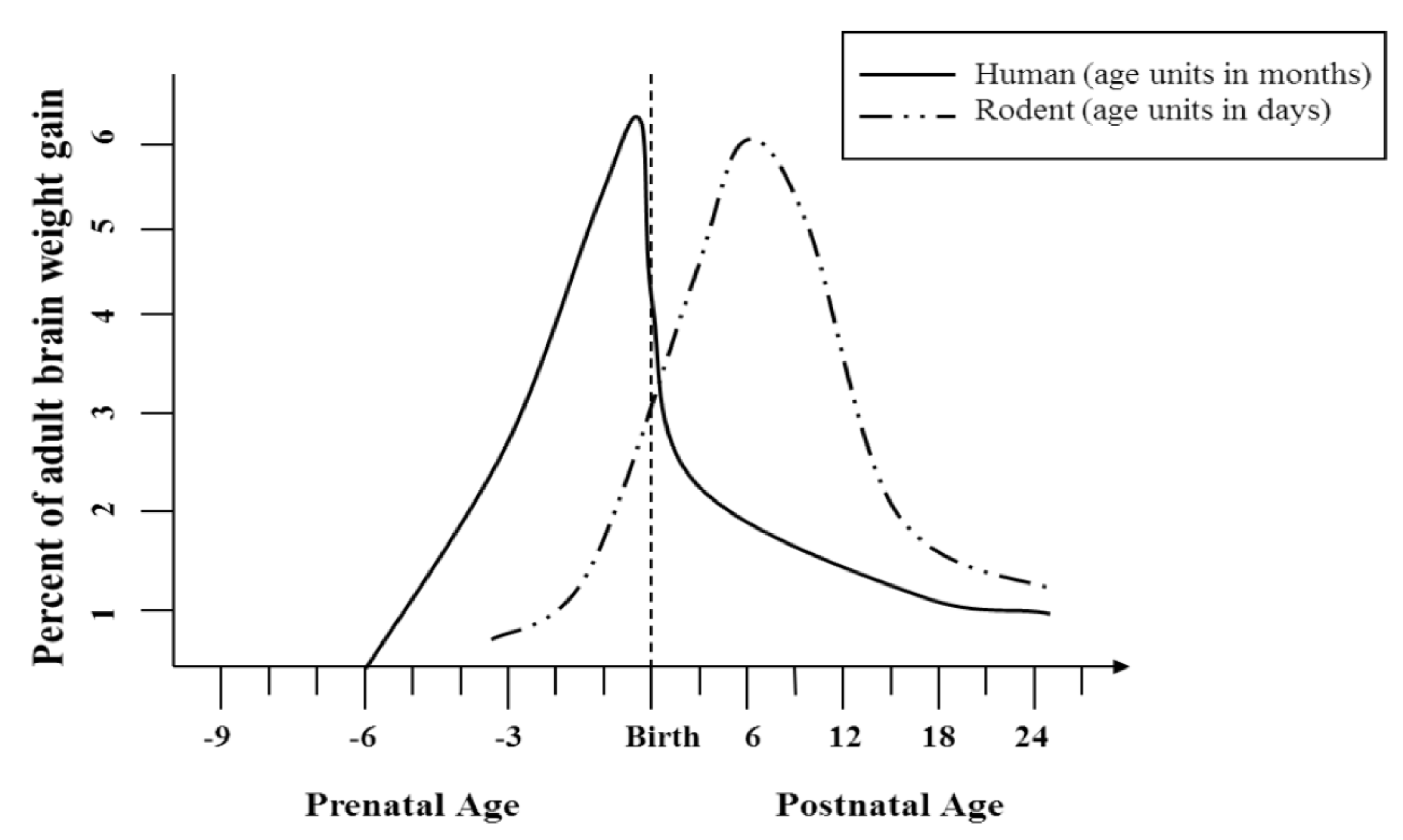
2.3. Use of Animal Models in Determining Long-Term Behavioral and Anatomical Effects of Developmental Alcohol Exposure
2.3.1. Behavioral and Anatomical Effects in Prenatal and Postnatal Models of Developmental Alcohol Exposure
| Behavioral Measures | Alcohol | Exercise | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Exercise | |||
| Executive functioning | ↓ | ↑ | P: [55,56,57]; A: [58] | [59,60,61] |
| Anxiety-like behaviors | ↑ | ↓ | P: [62]; A: [63,64,65] | [62] |
| Depression-like behaviors | ↑ | ↓ | P: [62,66] | P: [62,66] |
| Alcohol Preference as Adult | ↑ | - | A: [67,68] | |
| Balance/Fine motor skills | ↓ | ↑ | A: [36,69,70] | [71,72] |
| Spatial memory | ↓ | ↑ | P: [40,41]; A: [64,65,73,74] | [75,76,77,78,79] |
| Fear conditioning | ↓ | ↓/↑ | P: [42,43,44,45] | [44,80] |
| Eyeblink conditioning | ↓ | ↑ | P: [46,47,48,49] | [81,82] |
| Normative social behavior | ↓ | - | P: [21,33]; A: [83] | |
| Long-term potentiation (LTP) | ↓ | ↑ | P: [51,84] | [85] |
| Molecular Measures | Alcohol | Exercise | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Exercise | |||
| BDNF levels | ↓/↑ | ↑ | P: [52,66,86,87,88,89,90,91,92] A: [90] | [75,77,79,93,94,95,96,97] |
| VEGF levels | ↑ | ↑ | P: [86] | [98,99] |
| Oxidative stress markers | ↑ | ↓ | P: [62,100,101] | P: [62,100,101] |
| Apoptotic markers | ↑ | ↓ | P: [39,102,103,104,105,106] | P: [39,102,103,104,105,106] |
| Gene methylation | ↑ | ↓ | P: [107] | [108] |
| Neuroanatomical Measures | Alcohol | Exercise | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Exercise | |||
| Regional volume | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 18,19,30,31,70] | [ 70,76,109] |
| Cerebellar cell number | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 39] | P: [ 39] |
| Hippocampal cell number | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 43] | [ 110] |
| Dendritic complexity | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 111,112] | [113,114] |
| Spine density | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 115] | [ 113] |
| Synapse number | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 36] | P: [ 36] |
| Adult neurogenesis | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 53,54,116,117]; A: [118] | [ 77,98,117,119] |
| Microvasculature density | ↓ | ↑ | P: [ 120,121,122,123] | [78,99,124,125,126] |
2.3.2. Behavioral and Anatomical Effects in Adolescent Models of Developmental Alcohol Exposure
3. Mechanisms Underlying Alcohol and Exercise Effects on the Developing Brain
3.1. Alcohol and Exercise Effects on Neurotransmitters, Neuromodulators and Hormones
3.2. Neurotrophic Factors
3.3. Microvasculature
3.4. Oxidative Stress
3.5. Cytotoxicity/Apoptosis
4. Exercise as a Therapeutic Intervention to Restore Brain Structure and Function after Developmental Insult
4.1. Therapeutic Role of Exercise Following Developmental Alcohol Exposure
4.2. Exercise Effects in FASD Models
4.3. Exercise Effects in Models of Adolescent Alcohol Exposure
5. Exercise in Other Interventions
6. Conclusions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Cotman, C.W.; Berchtold, N.C. Exercise: A behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivar, C.; Potter, M.C.; Praag, H. All about running: Synaptic plasticity, growth factors and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.L.; Okely, A.D.; Chey, T.; Bauman, A.E.; Macaskill, P. Epidemiology of physical activity participation among new south wales school students. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2002, 26, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, C.H.; Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F. Be smart, exercise your heart: Exercise effects on brain and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hillman, C.H.; Snook, E.M.; Jerome, G.J. Acute cardiovascular exercise and executive control function. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2003, 48, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, S.J.E.; Ainslie, P.N.; Murrell, C.J.; Thomas, K.N.; Franz, E.A.; Cotter, J.D. Effect of age on exercise-induced alterations in cognitive executive function: Relationship to cerebral perfusion. Exp. Gerontol. 2012, 47, 541–551. [Google Scholar]
- McAuley, E.; Blissmer, B.; Marquez, D.X.; Jerome, G.J.; Kramer, A.F.; Katula, J. Social relations, physical activity, and well-being in older adults. Prev. Med. 2000, 31, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.; Paffenbarger, R., Jr. Workshop on epidemiologic and public health aspects of physical activity and exercise: A summary. Public Health Rep. 1985, 100, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Van Praag, H. Exercise and the brain: Something to chew on. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, B.; Breitenstein, C.; Mooren, F.C.; Voelker, K.; Fobker, M.; Lechtermann, A.; Krueger, K.; Fromme, A.; Korsukewitz, C.; Floel, A.; et al. High impact running improves learning. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 87, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angevaren, M.; Aufdemkampe, G.; Verhaar, H.; Aleman, A.; Vanhees, L. Physical activity and enhanced fitness to improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, H.H.; Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Fried, L.P.; Guralnik, J.M.; Williamson, J.D. Predictors of combined cognitive and physical decline. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlskog, J. Does vigorous exercise have a neuroprotective effect in Parkinson disease? Neurology 2011, 77, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.A.; Gossage, J.P.; Kalberg, W.O.; Robinson, L.K.; Buckley, D.; Manning, M.; Hoyme, H.E. Prevalence and epidemiologic characteristics of FASD from various research methods with an emphasis on recent in-school studies. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2009, 15, 176–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendah, D.D.; Grosse, S.D.; Bertrand, J. Medical expenditures of children in the united states with fetal alcohol syndrome. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Alcohol and Public Health. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/fact-sheets/underage-drinking.htm (accessed on 6 October 2012).
- Lupton, C.; Burd, L.; Harwood, R. Cost of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2004, 127C, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, S.; Schoenfeld, A.; Riley, E.P. Teratogenic effects of alcohol on brain and behavior. Alcohol Res. Health 2001, 25, 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P.; Sowell, E.R.; Jernigan, T.L.; Sobel, D.F.; Jones, K.L. A decrease in the size of the basal ganglia in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Roussotte, F.; Kan, E.; Sulik, K.K.; Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P.; Jones, K.L.; Adnams, C.M.; May, P.A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Abnormal cortical thickness alterations in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders and their relationships with facial dysmorphology. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.; Majors, D.; Rovet, J.; Koren, G.; Fantus, E.; Nulman, I.; Desrocher, M. Social problem solving in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 19, e99–e110. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, L.; Deitz, J.; Jirikowic, T.; Astley, S. Children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Problem behaviors and sensory processing. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2008, 62, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.M.; Afifi, R.A.; Bearinger, L.H.; Blakemore, S.-J.; Dick, B.; Ezeh, A.C.; Patton, G.C. Adolescence: A foundation for future health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Underage drinking Costs. Available online: http://www.udetc.org/UnderageDrinkingCosts.asp (accessed on 6 October 2012).
- United States Department of Health and Human Services; Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration; Office of Applied Studies. National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2007 (ICPSR 23782); Inter-University Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPSR): Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski, R.J.; Hammond, P.; O’Leary-Moore, S.K.; Ament, J.J.; Pecevich, S.J.; Jiang, Y.; Budin, F.; Parnell, S.E.; Suttie, M.; Godin, E.A.; et al. Ethanol-induced face-brain dysmorphology patterns are correlative and exposure-stage dependent. PLoS One 2012, 7, e43067. [Google Scholar]
- Sulik, K.K. Genesis of alcohol-induced craniofacial dysmorphism. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing, J.; Sands, J. Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum. Dev. 1979, 3, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, B.; Getz, S.; Galvan, A. The adolescent brain. Dev. Rev. 2008, 28, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, S.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Gamst, A.; Riley, E.; Mattson, S.; Jernigan, T. Brain dysmorphology in individuals with severe prenatal alcohol exposure. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2001, 43, 148–154. [Google Scholar]
- Sowell, E.; Jernigan, T.; Mattson, S.; Riley, E.; Sobel, D.; Jones, K. Abnormal development of the cerebellar vermis in children prenatally exposed to alcohol: Size reduction in lobules I–V. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Willford, J.; Day, R.; Aizenstein, H.; Day, N. Caudate asymmetry: A neurobiological marker of moderate prenatal alcohol exposure in young adults. Neurotoxicol.Teratol. 2010, 32, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irner, T.B.; Teasdale, T.W.; Olofsson, M. Cognitive and social development in preschool children born to women using substances. J. Addict. Dis. 2011, 31, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Clarren, S.; Alvord, E.J.; Sumi, S.; Streissguth, A.; Smith, D. Brain malformations related to prenatal exposure to ethanol. J. Pediatr. 1978, 92, 457–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, K.; Dambska, M.; Sher, J.; Qazi, Q. A clinical neuropathological study of the fetal alcohol syndrome. Neuropediatrics 1983, 14, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintsova, A.Y.; Cowell, R.M.; Swain, R.A.; Napper, R.M.A.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T. Therapeutic effects of complex motor training on motor performance deficits induced by neonatal binge-like alcohol exposure in rats: I. Behavioral results. Brain Res. 1998, 800, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.R.; Hayar, A.; Williams, D.K.; Light, K.E. Developmental alterations in olivary climbing fiber distribution following postnatal ethanol exposure in the rat. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, D.R.; Williams, D.K.; Light, K.E. Purkinje cell vulnerability to developmental ethanol exposure in the rat cerebellum. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Idrus, N.M.; Napper, R.M.A. Acute and long-term purkinje cell loss following a single ethanol binge during the early third trimester equivalent in the rat. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, B.R.; Swann, S.E.; Fox, C.J.; Froc, D.; Lieblich, S.E.; Redila, V.; Webber, A. Voluntary exercise rescues deficits in spatial memory and long-term potentiation in prenatal ethanol-exposed male rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.; Sather, T.; Whinery, L. Voluntary exercise influences behavioral development in rats exposed to alcohol during the neonatal brain growth spurt. Behav. Neurosci. 2008, 122, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.S.; Jacobson, S.E.; Torok, E.J. Deficits in trace fear conditioning in a rat model of fetal alcohol exposure: Dose-response and timing effects. Alcohol 2009, 43, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, N.J.; Klintsova, A.Y.; Stanton, M.E. Neonatal alcohol exposure and the hippocampus in developing male rats: Effects on behaviorally induced ca1 c-fos expression, ca1 pyramidal cell number, and contextual fear conditioning. Neuroscience 2012, 206, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, W.B.; Hunt, P.S. Deficits in trace fear conditioning induced by neonatal alcohol persist into adulthood in female rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, W.B.; St. Cyr, S.A.; Jablonski, S.A.; Hunt, P.S.; Klintsova, A.Y.; Stanton, M.E. Effects of exercise and environmental complexity on deficits in trace and contextual fear conditioning produced by neonatal alcohol exposure in rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.L.; Calizo, L.H.; Stanton, M.E. Dose-dependent deficits in dual interstimulus interval classical eyeblink conditioning tasks following neonatal binge alcohol exposure in rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Stanton, M.E.; Dodge, N.C.; Pienaar, M.; Fuller, D.S.; Molteno, C.D.; Meintjes, E.M.; Hoyme, H.E.; Robinson, L.K.; Khaole, N.; et al. Impaired delay and trace eyeblink conditioning in school-age children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Stanton, M.E.; Molteno, C.D.; Burden, M.J.; Fuller, D.S.; Hoyme, H.E.; Robinson, L.K.; Khaole, N.; Jacobson, J.L. Impaired eyeblink conditioning in children with fetal alcohol syndrome. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 365–372. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.D.; Tran, T.D. Choline supplementation mitigates trace, but not delay, eyeblink conditioning deficits in rats exposed to alcohol during development. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, M.P.; Valenzuela, C.F. Repeated third trimester-equivalent ethanol exposure inhibits long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region of neonatal rats. Alcohol 2010, 44, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterness, A.K.; Christie, B.R. Prenatal ethanol exposure enhances NMDAR-dependent long-term potentiation in the adolescent female dentate gyrus. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehme, F.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Cox, A.; Patten, A.; Giles, E.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Voluntary exercise induces adult hippocampal neurogenesis and BDNF expression in a rodent model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1799–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Mohapel, J.; Boehme, F.; Patten, A.; Cox, A.; Kainer, L.; Giles, E.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Altered adult hippocampal neuronal maturation in a rat model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Brain Res. 2011, 1384, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintsova, A.Y.; Helfer, J.L.; Calizo, L.H.; Dong, W.K.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T. Persistent impairment of hippocampal neurogenesis in young adult rats following early postnatal alcohol exposure. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Job, J.; Kully-Martens, K.; Rasmussen, C. Executive function and memory in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Child Neuropsychol. 2011, 17, 290–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.; Soleimani, M.; Pei, J. Executive functioning and working memory deficits on the cantab among children with prenatal alcohol exposure. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 18, e44–e53. [Google Scholar]
- Streissguth, A.P.; Barr, H.M.; Kogan, J.; Bookstein, F.L. Understanding the Occurrence of Secondary Disabilities in Clients with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) and Fetal Alcohol Effects (FAE); Tech. Rep. No. 96-06; University of Washington Fetal Alcohol & Drug Unit: Seattle, DC, USA, August 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Parada, M.; Corral, M.; Mota, N.; Crego, A.; Rodríguez Holguín, S.; Cadaveira, F. Executive functioning and alcohol binge drinking in university students. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, C.; Gualano, B.; Takao, P.; Avakian, P.; Fernandes, R.; Morine, D.; Takito, M. Effects of acute physical exercise on executive functions: A comparison between aerobic and strength exercise. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2012, 34, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Tsai, C.; Hung, T.; So, E.; Chen, F.; Etnier, J. Effects of acute exercise on executive function: A study with a tower of london task. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2011, 33, 847–865. [Google Scholar]
- Kluding, P.M.; Tseng, B.Y.; Billinger, S.A. Exercise and executive function in individuals with chronic stroke: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2011, 35, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Brocardo, P.S.; Boehme, F.; Patten, A.; Cox, A.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Christie, B.R. Anxiety- and depression-like behaviors are accompanied by an increase in oxidative stress in a rat model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: Protective effects of voluntary physical exercise. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Maldonado, C.; Vidal-Infer, A.; Guerri, C.; Aguilar, M.; Miñarro, J. Intermittent ethanol exposure increases long-lasting behavioral and neurochemical effects of mdma in adolescent mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, R.; Sircar, D. Repeated ethanol treatment in adolescent rats alters cortical NMDA receptor. Alcohol 2006, 39, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, R.; Basak, A.K.; Sircar, D. Repeated ethanol exposure affects the acquisition of spatial memory in adolescent female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 202, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell, K.K.; Sheema, S.; Paz, R.D.; Samudio-Ruiz, S.L.; Laughlin, M.H.; Spence, N.E.; Roehlk, M.J.; Alcon, S.N.; Allan, A.M. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder-associated depression: Evidence for reductions in the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a mouse model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado-Devincci, A.M.; Badanich, K.A.; Kirstein, C.L. Alcohol during adolescence selectively alters immediate and long-term behavior and neurochemistry. Alcohol 2010, 44, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Do Couto, B.R.; Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Aguilar, M.A.; Rodriguez-Arias, M.; Guerri, C. Changes in histone acetylation in the prefrontal cortex of ethanol-exposed adolescent rats are associated with ethanol-induced place conditioning. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Klintsova, A.; Matthews, J.; Goodlett, C.; Napper, R.; Greenough, W. Therapeutic motor training increases parallel fiber synapse number per purkinje neuron in cerebellar cortex of rats given postnatal binge alcohol exposure: Preliminary report. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Klintsova, A.Y.; Scamra, C.; Hoffman, M.; Napper, R.M.A.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T. Therapeutic effects of complex motor training on motor performance deficits induced by neonatal binge-like alcohol exposure in rats: II. A quantitative stereological study of synaptic plasticity in female rat cerebellum. Brain Res. 2002, 937, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilg, W.; Synofzik, M.; Brötz, D.; Burkard, S.; Giese, M.; Schöls, L. Intensive coordinative trainingimproves motor performance in degenerative cerebellar disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgel, A.L.; Vitek, J.L.; Alberts, J.L. Forced, not voluntary, exercise improves motor function in Parkinson’s disease patients. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, V.S.; van Skike, C.E.; Berry, R.B.; Kirk, R.E.; Diaz-Granados, J.; Matthews, D.B. Effect of acute ethanol and acute allopregnanolone on spatial memory in adolescent and adult rats. Alcohol 2011, 45, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Skike, C.E.; Novier, A.; Diaz-Granados, J.L.; Matthews, D.B. The effect of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure on spatial memory in adolescent rats: The dissociation of metabolic and cognitive tolerances. Brain Res. 2012, 1453, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, É.W.; Mullally, S.; Foley, C.; Warmington, S.A.; O’Mara, S.M.; Kelly, Á.M. Aerobic exercise improves hippocampal function and increases BDNF in the serum of young adult males. Physiol. Behav. 2011, 104, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herting, M.M.; Nagel, B.J. Aerobic fitness relates to learning on a virtual morris water task and hippocampal volume in adolescents. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 233, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlatt, M.W.; Potter, M.C.; Lucassen, P.J.; van Praag, H. Running throughout middle-age improves memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and BDNF levels in female C57BL/6J mice. Dev. Neurobiol. 2012, 72, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhyu, I.J.; Bytheway, J.A.; Kohler, S.J.; Lange, H.; Lee, K.J.; Boklewski, J.; McCormick, K.; Williams, N.I.; Stanton, G.B.; Greenough, W.T.; et al. Effects of aerobic exercise training on cognitive function and cortical vascularity in monkeys. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaynman, S.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Hippocampal BDNF mediates the efficacy of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 20, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar]
- Kohman, R.A.; Clark, P.J.; DeYoung, E.K.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Venghaus, C.E.; Rhodes, J.S. Voluntary wheel running enhances contextual but not trace fear conditioning. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Green, J.T.; Chess, A.C.; Burns, M.; Schachinger, K.M.; Thanellou, A. The effects of two forms of physical activity on eyeblink classical conditioning. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 219, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffino, F.L.; Jablonski, S.A.; Hamilton, G.F.; St. Cyr, S.A.; Finamore, J.M.; Greenough, W.T.; Stanton, M.E.; Klintsova, A.Y. Voluntary Exercise Followed by Environmental Complexity Reverses Deficits in Trace Eyeblink Conditioning and Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Rat Model of Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder. In Presented at the Pavlovian Society Meeting, Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–17 October 2010.
- Varlinskaya, E.I.; Spear, L.P. Chronic tolerance to the social consequences of ethanol in adolescent and adult sprague-dawley rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2007, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Skike, C.E.; Botta, P.; Chin, V.S.; Tokunaga, S.; McDaniel, J.M.; Venard, J.; Diaz-Granados, J.L.; Valenzuela, C.F.; Matthews, D.B. Behavioral effects of ethanol in cerebellum are age dependent: Potential system and molecular mechanisms. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterness, A.K.; Wiebe, E.; Kwasnica, A.; Keyes, G.; Christie, B.R. Voluntary exercise does not enhance long-term potentiation in the adolescent female dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2011, 183, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ceccanti, M.; Mancinelli, R.; Tirassa, P.; Laviola, G.; Rossi, S.; Romeo, M.; Fiore, M. Early exposure to ethanol or red wine and long-lasting effects in aged mice. A study on nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattori, V.; Abe, S.-I.; Kobayashi, K.; Costa, L.G.; Tsuji, R. Effects of postnatal ethanol exposure on neurotrophic factors and signal transduction pathways in rat brain. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, M.B.; Mitchell, J.J.; Paiva, M.; Walker, D.W. Ethanol-induced alterations in the expression of neurotrophic factors in the developing rat central nervous system. Dev. Brain Res. 2000, 121, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, M.B.; Moore, D.B.; Paiva, M.; Madorsky, I.; Mayer, J.; Shaw, G. The role of neurotrophic factors, apoptosis-related proteins, and endogenous antioxidants in the differential temporal vulnerability of neonatal cerebellum to ethanol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2003, 27, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarny, V.V.; Wiest, N.E.; Marquez, C.P.; Nixon, S.C.; Valenzuela, C.F.; Perrone-Bizzozero, N.I. Opposite effects of acute ethanol exposure on gap-43 and BDNF expression in the hippocampus versus the cerebellum of juvenile rats. Alcohol 2011, 45, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, K.E.; Ge, Y.; Belcher, S.M. Early postnatal ethanol exposure selectively decreases BDNF and truncated TrkB-T2 receptor mRNA expression in the rat cerebellum. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 93, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Miki, T.; Kuma, H.; Yokoyama, T.; Sumitani, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kusaka, T.; Warita, K.; Wang, Z.; Hosomi, N.; Magawa, T.; et al. Early postnatal ethanol exposure induces fluctuation in the expression of BDNF mRNA in the developing rat hippocampus. Acta Neurobiol.Exp. (Wars) 2008, 68, 484–493. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Ying, Z.; Gómez-Pinilla, F. Exercise influences hippocampal plasticity by modulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor processing. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Gomes da Silva, S.; Unsain, N.; Mascó, D.H.; Toscano-Silva, M.; de Amorim, H.A.; Silva Araújo, B.H.; Simões, P.S.R.; da Graça Naffah-Mazzacoratti, M.; Mortara, R.A.; Scorza, F.A.; et al. Early exercise promotes positive hippocampal plasticity and improves spatial memory in the adult life of rats. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 347–358. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, P.; Brassard, P.; Adser, H.; Pedersen, M.V.; Leick, L.; Hart, E.; Secher, N.H.; Pedersen, B.K.; Pilegaard, H. Evidence for a release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from the brain during exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Kassow, M.; Schädle, S.; Otterbein, S.; Thiel, C.; Doehring, A.; Lötsch, J.; Kaiser, J. Kinetics of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor following low-intensity versus high-intensity exercise in men and women. Neuroreport 2012, 23, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, H.-S.; Kang, E.-B.; Koo, J.-H.; Kim, H.-T.; Jin, L.; Kim, E.-J.; Yang, C.-H.; An, G.-Y.; Cho, I.-H.; Cho, J.-Y. Treadmill exercise represses neuronal cell death in an aged transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 69, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, T.; Lee, H.; Mikami, T. Regular exercise cures depression-like behavior via VEGF-Flk-1 signaling in chronically stressed mice. Neuroscience 2012, 207, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, C.S.; Searcy, J.L.; Bridges, M.T.; Brewer, L.D.; Popović, J.; Blalock, E.M.; Landfield, P.W.; Thibault, O.; Porter, N.M. Reversal of glial and neurovascular markers of unhealthy brain aging by exercise in middle-aged female mice. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26812. [Google Scholar]
- Petkov, V.V.; Stoianovski, D.; Petkov, V.D.; Vyglenova, I. Lipid peroxidation changes in the brain in fetal alcohol syndrome. Bull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 1992, 113, 500–502. [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran, V.; Watts, L.T.; Maffi, S.K.; Chen, J.; Schenker, S.; Henderson, G. Ethanol-induced oxidative stress precedes mitochondrially mediated apoptotic death of cultured fetal cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 74, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olney, J.; Wozniak, D.; Jevtovic-Todorovic, V.; Farber, N.; Bittigau, P.; Ikonomidou, C. Drug-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing brain. Brain Pathol. 2002, 12, 488–498. [Google Scholar]
- Olney, J.W.; Tenkova, T.; Dikranian, K.; Muglia, L.J.; Jermakowicz, W.J.; D’Sa, C.; Roth, K.A. Ethanol-induced caspase-3 activation in the in vivo developing mouse brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2002, 9, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Shah, R.; Mao, R.-F.; Kumar, A.; Yang, D.-S.; Dobrenis, K.; Saito, M. Elevation of GM2 ganglioside during ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, V.; Chopra, K. Attenuation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis by curcumin prevents cognitive deficits in rats postnatally exposed to ethanol. Psychopharmacology 2012, 224, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, N.; Naseer, M.I.; Ullah, I.; Lee, H.Y.; Koh, P.O.; Kim, M.O. Protective effect of pyruvate against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.K.H.; Thomas, J.D.; Saski, C.A.; Xia, X.; Kelly, S.J. Choline supplementation and DNA methylation in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of rats exposed to alcohol during development. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Pinilla, F.; Zhuang, Y.; Feng, J.; Ying, Z.; Fan, G. Exercise impacts brain-derived neurotrophic factor plasticity by engaging mechanisms of epigenetic regulation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Chaddock, L.; Erickson, K.; Prakash, R.; VanPatter, M.; Voss, M.; Pontifex, M.; Raine, L.; Hillman, C.; Kramer, A. Basal ganglia volume is associated with aerobic fitness in preadolescent children. Dev. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes da Silva, S.; Doná, F.; da Silva Fernandes, M.J.; Scorza, F.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Arida, R.M. Physical exercise during the adolescent period of life increases hippocampal parvalbumin expression. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.F.; Whitcher, L.T.; Klintsova, A.Y. Postnatal binge-like alcohol exposure decreases dendritic complexity while increasing the density of mature spines in mpfc layer II/III pyramidal neurons. Synapse 2010, 64, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.C.; Otero, N.K.H.; Kelly, S.J. Selective effects of perinatal ethanol exposure in medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, B.D.; Redila, V.A.; Christie, B.R. Voluntary exercise alters the cytoarchitecture of the adult dentate gyrus by increasing cellular proliferation, dendritic complexity, and spine density. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 486, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redila, V.A.; Christie, B.R. Exercise-induced changes in dendritic structure and complexity in the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2006, 137, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcher, L.T.; Klintsova, A.Y. Postnatal binge-like alcohol exposure reduces spine density without affecting dendritic morphology in rat MPFC. Synapse 2008, 62, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.F.; Murawski, N.J.; St. Cyr, S.A.; Jablonski, S.A.; Schiffino, F.L.; Stanton, M.E.; Klintsova, A.Y. Neonatal alcohol exposure disrupts hippocampal neurogenesis and contextual fear conditioning in adult rats. Brain Res. 2011, 1412, 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Helfer, J.L.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T.; Klintsova, A.Y. The effects of exercise on adolescent hippocampal neurogenesis in a rat model of binge alcohol exposure during the brain growth spurt. Brain Res. 2009, 1294, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, J.A.; Hayes, D.M.; Morris, S.A.; Nixon, K. Adolescent binge alcohol exposure alters hippocampal progenitor cell proliferation in rats: Effects on cell cycle kinetics. J. Comp. Neurol. 2011, 519, 2697–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.F.; Boschen, K.E.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T.; Klintsova, A.Y. Housing in environmental complexity following wheel running augments survival of newly generated hippocampal neurons in a rat model of binge alcohol exposure during the third trimester equivalent. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Bake, S.; Tingling, J.D.; Miranda, R.C. Ethanol exposure during pregnancy persistently attenuates cranially directed blood flow in the developing fetus: Evidence from ultrasound imaging in a murine second trimester equivalent model. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatara, V.; Lovrein, F.; Kirkeby, J.; Swayze, V., II; Unruh, E.; Johnson, V. Brain function in fetal alcohol syndrome assessed by single photon emission computed tomography. S. D. J. Med. 2002, 55, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, P.; Leichter, J.; Lee, M. Placental blood flow in rats fed alcohol before and during gestation. Life Sci. 1981, 29, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riikonen, R.; Salonen, I.; Partanen, K.; Verho, S. Brain perfusion spect and MRI in foetal alcohol syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1999, 41, 652–659. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Ogoh, S.; Hirasawa, A.; Oue, A.; Sadamoto, T. The distribution of blood flow in the carotid and vertebral arteries during dynamic exercise in humans. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Borght, K.; Kóbor-Nyakas, D.É.; Klauke, K.; Eggen, B.J.L.; Nyakas, C.; van der Zee, E.A.; Meerlo, P. Physical exercise leads to rapid adaptations in hippocampal vasculature: Temporal dynamics and relationship to cell proliferation and neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 928–936. [Google Scholar]
- Vogiatzis, I.; Louvaris, Z.; Habazettl, H.; Athanasopoulos, D.; Andrianopoulos, V.; Cherouveim, E.; Wagner, H.; Roussos, C.; Wagner, P.D.; Zakynthinos, S. Frontal cerebral cortex blood flow, oxygen delivery and oxygenation during normoxic and hypoxic exercise in athletes. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 4027–4039. [Google Scholar]
- Odgers, C.; Caspi, A.; Nagin, D.; Piquero, A.; Slutske, W.; Milne, B.; Dickson, N.; Poulton, R.; Moffitt, T. Is it important to prevent early exposure to drugs and alcohol among adolescents? Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, V.S.; van Skike, C.E.; Matthews, D.B. Effects of ethanol on hippocampal function during adolescence: A look at the past and thoughts on the future. Alcohol 2010, 44, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Guerri, C.; Pascual, M. Mechanisms involved in the neurotoxic, cognitive, and neurobehavioral effects of alcohol consumption during adolescence. Alcohol 2010, 44, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, L.P. The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2000, 24, 417–463. [Google Scholar]
- McClain, J.A.; Morris, S.A.; Deeny, M.A.; Marshall, S.A.; Hayes, D.M.; Kiser, Z.M.; Nixon, K. Adolescent binge alcohol exposure induces long-lasting partial activation of microglia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25 Suppl. 1, S120–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koss, W.A.; Sadowski, R.N.; Sherrill, L.K.; Gulley, J.M.; Juraska, J.M. Effects of ethanol during adolescence on the number of neurons and glia in the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala of adult male and female rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1466, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sircar, R.; Sircar, D. Adolescent rats exposed to repeated ethanol treatment show lingering behavioral impairments. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, H.C.; McDonald, C.G.; Smith, R.F. Alcohol exposure during adolescence impairs auditory fear conditioning in adult long-evans rats. Physiol. Behav. 2006, 88, 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, B.A. Ethanol modulation of synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikonomidou, C.; Bittigau, P.; Koch, C.; Genz, K.; Hoerster, F.; Felderhoff-Mueser, U.; Tenkova, T.; Dikranian, K.; Olney, J.W. Neurotransmitters and apoptosis in the developing brain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001, 62, 401–405. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, C.L.; Criado, J.R.; Wills, D.N.; Liu, W.; Crews, F.T. Periadolescent ethanol exposure reduces adult forebrain chat+ir neurons: Correlation with behavioral pathology. Neuroscience 2011, 199, 333–345. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich, D.; Pirchl, M.; Humpel, C. Effects of long-term moderate ethanol and cholesterol on cognition, cholinergic neurons, inflammation, and vascular impairment in rats. Neuroscience 2012, 205, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bales, K.R.; Tzavara, E.T.; Wu, S.; Wade, M.R.; Bymaster, F.P.; Paul, S.M.; Nomikos, G.G. Cholinergic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease is reversed by an anti-aβ antibody. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.R.; Leslie, F.M.; Thomas, J.D. The effects of perinatal choline supplementation on hippocampal cholinergic development in rats exposed to alcohol during the brain growth spurt. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, E.-K.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, H.; Sim, Y.-J.; Shin, M.-S.; Lee, S.-J.; Yang, H.-Y.; Chang, H.-K.; Lee, T.-H.; Jang, M.-H.; et al. Maternal ethanol administration inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis and tryptophan hydroxylase expression in the dorsal raphe of rat offspring. Brain Dev. 2005, 27, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buske, C.; Gerlai, R. Early embryonic ethanol exposure impairs shoaling and the dopaminergic and serotoninergic systems in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 698–707. [Google Scholar]
- Molet, J.; Bouaziz, E.; Hamon, M.; Lanfumey, L. Early exposure to ethanol differentially affects ethanol preference at adult age in two inbred mouse strains. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, S.; Grisel, J.E.; Grisel, J.E. Locomotor sensitization to EtOH: Contribution of β-endorphin. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, B.E.; Whitaker, L.R.; Morikawa, H. Previous ethanol experience enhances synaptic plasticity of NMDA receptors in the ventral tegmental area. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5205–5212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.; Goudarzi, I.; Lashkarbolouki, T.; Ghorbanian, M.T.; Elahdadi Salmani, M.; Abrari, K. Neuroprotective effects of the 17β-estradiol against ethanol-induced neurotoxicity and oxidative stress in the developing male rat cerebellum: Biochemical, histological and behavioral changes. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 100, 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Gillespie, R.A.; Pak, T.R. 17β-estradiol is required for the sexually dimorphic effects of repeated binge-pattern alcohol exposure on the hpa axis during adolescence. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybycien-Szymanska, M.M.; Mott, N.N.; Paul, C.R.; Gillespie, R.A.; Pak, T.R. Binge-pattern alcohol exposure during puberty induces long-term changes in hpa axis reactivity. PLoS One 2011, 6, e18350. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, N.; Yamashita, F.; Halpert, A.G.; Sliwowska, J.H.; Viau, V.; Weinberg, J. Effects of prenatal ethanol exposure on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal function across the estrous cycle. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, S.; Cotman, C.; Cahill, L. Exercise-induced noradrenergic activation enhances memory consolidation in both normal aging and patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, B.N.; Foley, T.E.; Day, H.E.W.; Campisi, J.; Hammack, S.H.; Campeau, S.; Maier, S.F.; Fleshner, M. Freewheel running prevents learned helplessness/behavioral depression: Role of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2889–2898. [Google Scholar]
- Mabandla, M.; Kellaway, L.; Daniels, W.; Russell, V. Effect of exercise on dopamine neuron survival in prenatally stressed rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2009, 24, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Heo, H.-I.; Kim, D.-H.; Ko, I.-G.; Lee, S.-S.; Kim, S.-E.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, T.-W.; Ji, E.-S.; Kim, J.-D.; et al. Treadmill exercise and methylphenidate ameliorate symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder through enhancing dopamine synthesis and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in spontaneous hypertensive rats. Neurosci.Lett. 2011, 504, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoir, T.; Chevarin, C.; Lanfumey-Mongredien, L.; Hannan, A. Effect of enhanced voluntary physical exercise on brain levels of monoamines in huntington disease mice. PLoS Curr. 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Hopker, S.W. The effectiveness of exercise as an intervention in the management of depression: Systematic review and meta-regression analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2001, 322, 763. [Google Scholar]
- Sigwalt, A.R.; Budde, H.; Helmich, I.; Glaser, V.; Ghisoni, K.; Lanza, S.; Cadore, E.L.; Lhullier, F.L.R.; de Bem, A.F.; Hohl, A.; et al. Molecular aspects involved in swimming exercise training reducing anhedonia in a rat model of depression. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchtold, N.C.; Kesslak, J.P.; Pike, C.J.; Adlard, P.A.; Cotman, C.W. Estrogen and exercise interact to regulate brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA and protein expression in the hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 1992–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.I.; Colcombe, S.J.; Elavsky, S.; McAuley, E.; Korol, D.L.; Scalf, P.E.; Kramer, A.F. Interactive effects of fitness and hormone treatment on brain health in postmenopausal women. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.P.; Cordeira, J.; Calderon, G.A.; Iyer, L.K.; Rios, M. Depletion of central BDNF in mice impedes terminal differentiation of new granule neurons in the adult hippocampus. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 39, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, W.E.; Moser, H.W. Dendritic anomalies in disorders associated with mental retardation. Cereb. Cortex 2000, 10, 981–991. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, J.E.; Trettel, J.; Levine, E.S. BDNF enhancement of postsynaptic NMDA receptors is blocked by ethanol. Synapse 2005, 55, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Morozova, M.V.; Naumenko, V.S. Ameliorative effect of BDNF on prenatal ethanol and stress exposure-induced behavioral disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 505, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekinschtein, P.; Oomen, C.A.; Saksida, L.M.; Bussey, T.J. Effects of environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise on neurogenesis, learning and memory, and pattern separation: BDNF as a critical variable? Semi. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 536–542. [Google Scholar]
- Tolwani, R.J.; Buckmaster, P.S.; Varma, S.; Cosgaya, J.M.; Wu, Y.; Suri, C.; Shooter, E.M. BDNF overexpression increases dendrite complexity in hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 2002, 114, 795–805. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Z.; Yip, S.P.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.-X.; Tong, K.-Y. The effects of voluntary, involuntary, and forced exercises on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and motor function recovery: A rat brain ischemia model. PLoS One 2011, 6, e16643. [Google Scholar]
- Ploughman, M.; Windle, V.; MacLellan, C.L.; White, N.; Doré, J.J.; Corbett, D. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to recovery of skilled reaching after focal ischemia in rats. Stroke 2009, 40, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Davies, K.; Powers, C.; Bruggen, N.; Chopp, M. VEGF enhances angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the ischemic brain. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 829–838. [Google Scholar]
- Parnell, S.E.; Ramadoss, J.; Delp, M.D.; Ramsey, M.W.; Chen, W.-J.A.; West, J.R.; Cudd, T.A. Chronic ethanol increases fetal cerebral blood flow specific to the ethanol-sensitive cerebellum under normoxaemic, hypercapnic and acidaemic conditions: Ovine model. Exp. Physiol. 2007, 92, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhan, W.G. Responses of cerebral arterioles during chronic ethanol exposure. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 262, H787–H791. [Google Scholar]
- Gleason, C.A.; Iida, H.; Hotchkiss, K.J.; Northington, F.J.; Traystman, R.J. Newborn cerebrovascular responses after first trimester moderate maternal ethanol exposure in sheep. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 42, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Licht, T.; Goshen, I.; Avital, A.; Kreisel, T.; Zubedat, S.; Eavri, R.; Segal, M.; Yirmiya, R.; Keshet, E. Reversible modulations of neuronal plasticity by VEGF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5081–5086. [Google Scholar]
- Louboutin, J.-P.; Marusich, E.; Gao, E.; Agrawal, L.; Koch, W.J.; Strayer, D.S. Ethanol protects from injury due to ischemia and reperfusion by increasing vascularity via vascular endothelial growth factor. Alcohol 2012, 46, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Chen, Y.; James-Kracke, M.; Wixom, P.; Cheng, Y. Ethanol-induced cell death by lipid peroxidation in PC12 cells. Neurochem. Res. 1997, 22, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen-Soriano, S.; Bosch-Morell, F.; Miranda, M.; Asensio, S.; Barcia, J.M.; Romá, J.; Monfort, P.; Felipo, V.; Romero, F.J. Ebselen prevents chronic alcohol-induced rat hippocampal stress and functional impairment. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yeo, H.C.; Övervik-Douki, E.; Hagen, T.; Doniger, S.J.; Chu, D.W.; Brooks, G.A.; Ames, B.N. Chronically and acutely exercised rats: Biomarkers of oxidative stress and endogenous antioxidants. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Radak, Z.; Toldy, A.; Szabo, Z.; Siamilis, S.; Nyakas, C.; Silye, G.; Jakus, J.; Goto, S. The effects of training and detraining on memory, neurotrophins and oxidative stress markers in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 49, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ogonovszky, H.; Berkes, I.; Kumagai, S.; Kaneko, T.; Tahara, S.; Goto, S.; Radák, Z. The effects of moderate-, strenuous- and over-training on oxidative stress markers, DNA repair, and memory, in rat brain. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 46, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, D. Aging: A theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J. Gerontol. 1956, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.L. Aging and resistance to oxidative damage in caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8905–8909. [Google Scholar]
- Marosi, K.; Bori, Z.; Hart, N.; Sárga, L.; Koltai, E.; Radák, Z.; Nyakas, C. Long-term exercise treatment reduces oxidative stress in the hippocampus of aging rats. Neuroscience 2012, 226, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Hofer, T.; Rani, A.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Foster, T.C. Comparison of lifelong and late life exercise on oxidative stress in the cerebellum. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 903–909. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, A.; Gomez, C.; López-Cepero, J.M.; Boveris, A. Beneficial effects of moderate exercise on mice aging: Survival, behavior, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial electron transfer. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 286, R505–R511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Chakraborty, G.; Hegde, M.; Ohsie, J.; Paik, S.-M.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Involvement of ceramide in ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the neonatal mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2010, 115, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, G.; Saito, M.; Shah, R.; Mao, R.-F.; Vadasz, C.; Saito, M. Ethanol triggers sphingosine 1-phosphate elevation along with neuroapoptosis in the developing mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 806–817. [Google Scholar]
- VanDeMark, K.L.; Guizzetti, M.; Giordano, G.; Costa, L.G. Ethanol inhibits muscarinic receptor-induced axonal growth in rat hippocampal neurons. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar]
- Sharafi, H.; Rahimi, R. The effect of resistance exercise on p53, caspase-9, and caspase-3 in trained and untrained men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Ko, I.-G.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, T.-W.; Kim, S.-E.; Shin, M.-S.; Kim, C.-J.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.-M.; Baek, S.-S. Treadmill exercise inhibits traumatic brain injury-induced hippocampal apoptosis. Physiol. Behav. 2010, 101, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y.; Oh, S.D.; Kim, S.M.; Shim, Y.T.; Park, S.; Kim, W.K. Maternal exercise reduces hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in developing mouse brain. Int. J. Hyperthermia 2011, 27, 445–452. [Google Scholar]
- Snigdha, S.; Berchtold, N.; Astarita, G.; Saing, T.; Piomelli, D.; Cotman, C.W. Dietary and behavioral interventions protect against age related activation of caspase cascades in the canine brain. PLoS One 2011, 6, e24652. [Google Scholar]
- Borg, M.L.; Omran, S.F.; Weir, J.; Meikle, P.J.; Watt, M.J. Consumption of a high-fat diet, but not regular endurance exercise training, regulates hypothalamic lipid accumulation in mice. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.L.; Kang, H.Y. Effects of endurance exercise and high-fat diet on insulin resistance and ceramide contents of skeletal muscle in sprague-dawley rats. Korean Diabetes J. 2010, 34, 244–252. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, W.M.U.; Marais, L.; Stein, D.J.; Russell, V.A. Exercise normalizes altered expression of proteins in the ventral hippocampus of rats subjected to maternal separation. Exp. Physiol. 2012, 97, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Maniam, J.; Morris, M.J. Voluntary exercise and palatable high-fat diet both improve behavioural profile and stress responses in male rats exposed to early life stress: Role of hippocampus. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.; Shumsky, J.S.; Murray, M.; Moxon, K.A. Exercise induces cortical plasticity after neonatal spinal cord injury in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 7549–7557. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, M.; Aoo, N.; Harada, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Akitake, Y.; Irie, K.; Mishima, K.; Ikeda, T.; Fujiwara, M. Sex differences in the benefits of rehabilitative training during adolescence following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia in rats. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 226, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.; Shin, M.-S.; Chang, H.-K.; Shin, M.-C.; Ko, I.-G.; Kim, K.-J.; Kim, T.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Rhim, Y.-T.; et al. Effect of postnatal treadmill exercise on c-fos expression in the hippocampus of rat pups born from the alcohol-intoxicated mothers. Brain Dev. 2008, 30, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redila, V.A.; Olson, A.K.; Swann, S.E.; Mohades, G.; Webber, A.J.; Weinberg, J.; Christie, B.R. Hippocampal cell proliferation is reduced following prenatal ethanol exposure but can be rescued with voluntary exercise. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 305–311. [Google Scholar]
- Helfer, J.L.; Calizo, L.H.; Dong, W.K.; Goodlett, C.R.; Greenough, W.T.; Klintsova, A.Y. Binge-like postnatal alcohol exposure triggers cortical gliogenesis in adolescent rats. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 514, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, D.; Sabia, J. Exercise and adolescent mental health: New evidence from longitudinal data. J. Ment. Health Policy Econ. 2010, 13, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, S.; Gerber, M.; Beck, J.; Hatzinger, M.; Pühse, U.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E. High exercise levels are related to favorable sleep patterns and psychological functioning in adolescents: A comparison of athletes and controls. J. Adolesc. Health 2010, 46, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.E.; Nitecki, R.; Bucci, D.J. Physical exercise during adolescence versus adulthood: Differential effects on object recognition memory and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels. Neuroscience 2011, 194, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry-McElrath, Y.M.; O’Malley, P.M.; Johnston, L.D. Exercise and substance use among american youth, 1991–2009. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 40, 530–540. [Google Scholar]
- Buscemi, J.; Martens, M.P.; Murphy, J.G.; Yurasek, A.M.; Smith, A.E. Moderators of the relationship between physical activity and alcohol consumption in college students. J. Am. Coll. Health 2011, 59, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Kuhn, H.G.; Gage, F.H. Experience-induced neurogenesis in the senescent dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3206–3212. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, A.K.; Eadie, B.; Ernst, C.; Christie, B.R. Environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise massively increase neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus via dissociable pathways. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 250–260. [Google Scholar]
- Van Praag, H.; Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.J.; Kohman, R.A.; Miller, D.S.; Bhattacharya, T.K.; Haferkamp, E.H.; Rhodes, J.S. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and c-fos induction during escalation of voluntary wheel running in C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 213, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.S.; Glover, L.R.; Sanzone, K.M.; Kamhi, J.F.; Cameron, H.A. The effects of exercise and stress on the survival and maturation of adult-generated granule cells. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronenberg, G.; Bick-Sander, A.; Bunk, E.; Wolf, C.; Ehninger, D.; Kempermann, G. Physical exercise prevents age-related decline in precursor cell activity in the mouse dentate gyrus. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Fuss, J.; Ben Abdallah, N.M.B.; Vogt, M.A.; Touma, C.; Pacifici, P.G.; Palme, R.; Witzemann, V.; Hellweg, R.; Gass, P. Voluntary exercise induces anxiety-like behavior in adult C57BL/6J mice correlating with hippocampal neurogenesis. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 364–376. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig, M.; Bennett, E.; Krech, D. Cerebral effects of environmental complexity and training among adult rats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1964, 57, 438–439. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.M.; Greenough, W.T. Differential rearing effects on rat visual cortex synapses. I. Synaptic and neuronal density and synapses per neuron. Brain Res. 1985, 329, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, W.T.; Volkmar, F.R.; Juraska, J.M. Effects of rearing complexity on dendritic branching in frontolateral and temporal cortex of the rat. Exp. Neurol. 1973, 41, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustroph, M.L.; Chen, S.; Desai, S.C.; Cay, E.B.; DeYoung, E.K.; Rhodes, J.S. Aerobic exercise is the critical variable in an enriched environment that increases hippocampal neurogenesis and water maze learning in male C57BL/6J mice. Neuroscience 2012, 219, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobilo, T.; Liu, Q.-R.; Gandhi, K.; Mughal, M.; Shaham, Y.; van Praag, H. Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment. Learn. Mem. 2011, 18, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Black, J.E.; Isaacs, K.R.; Anderson, B.J.; Alcantara, A.A.; Greenough, W.T. Learning causes synaptogenesis, whereas motor activity causes angiogenesis, in cerebellar cortex of adult rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5568–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.A.; Lussnig, E.; Schwarz, E.R.; Comery, T.A.; Greenough, W.T. Synaptogenesis and fos expression in the motor cortex of the adult rat after motor skill learning. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 4529–4535. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Klintsova, A.Y.; Hamilton, G.F.; Boschen, K.E. Long-Term Consequences of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Brain Structure and Function: Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 1-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010001
Klintsova AY, Hamilton GF, Boschen KE. Long-Term Consequences of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Brain Structure and Function: Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity. Brain Sciences. 2013; 3(1):1-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlintsova, Anna Y., Gillian F. Hamilton, and Karen E. Boschen. 2013. "Long-Term Consequences of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Brain Structure and Function: Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity" Brain Sciences 3, no. 1: 1-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010001
APA StyleKlintsova, A. Y., Hamilton, G. F., & Boschen, K. E. (2013). Long-Term Consequences of Developmental Alcohol Exposure on Brain Structure and Function: Therapeutic Benefits of Physical Activity. Brain Sciences, 3(1), 1-38. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci3010001





