Neurological Manifestations of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of HUS and Neurological Involvement
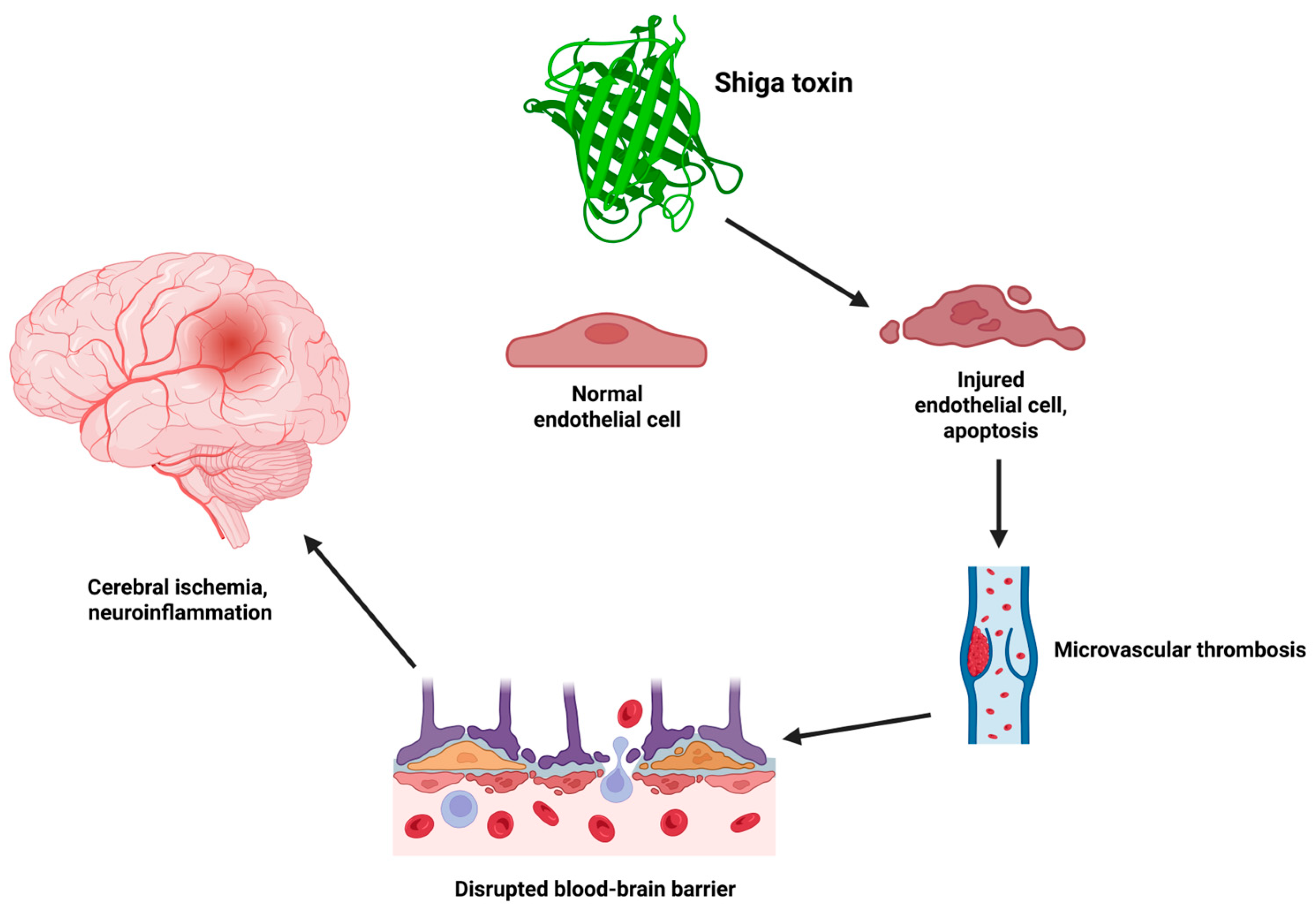
2.1. Shiga Toxin-Mediated Endothelial Injury and Microangiopathy
2.2. Complement Activation in Atypical HUS
2.3. Mechanisms of Central Nervous System Injury in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
2.3.1. Endothelial Injury
2.3.2. Microvascular Thrombosis
2.3.3. Metabolic Encephalopathy
3. Clinical Neurological Manifestations
3.1. Encephalopathy
3.2. Seizures and Status Epilepticus
3.3. Focal Neurologic Deficits
3.4. Movement Disorders
3.5. Cortical Blindness and PRES
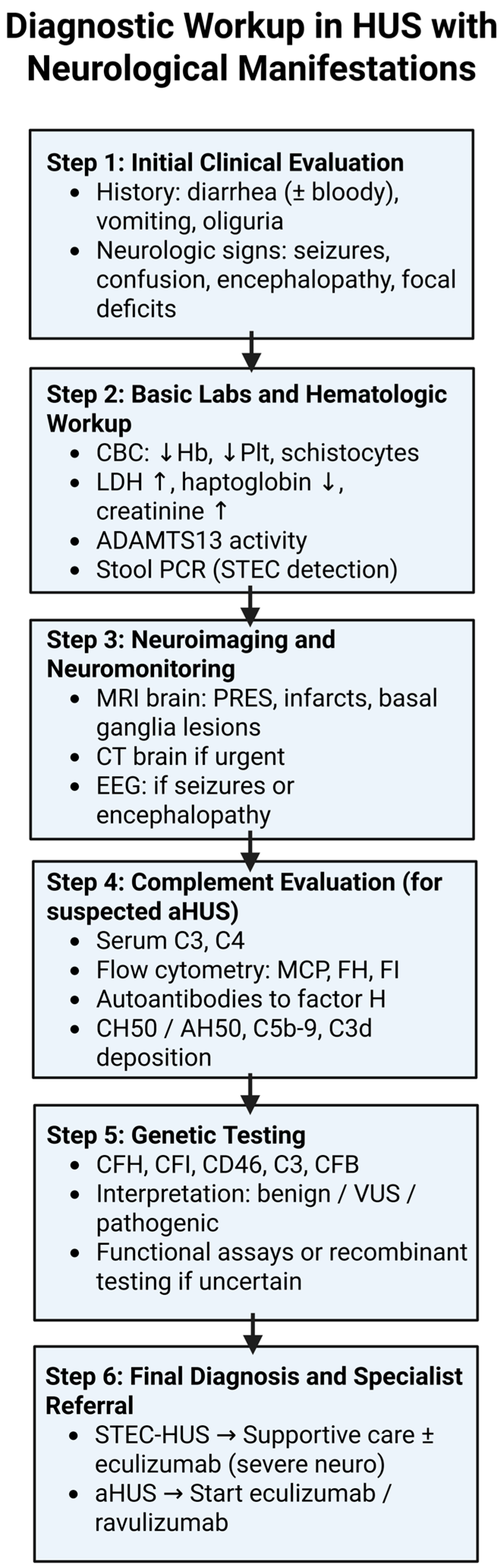
4. Diagnostic Workup
4.1. Laboratory Evaluation
4.2. Neuroimaging
4.3. EEG and Neurophysiology
5. Therapeutic Approaches
5.1. Supportive Care
5.2. Antimicrobial Agents
5.3. Plasma Exchange
5.4. Eculizumab and Complement Inhibitors
5.5. Neurologic Symptom Management
5.6. Neurorehabilitation and Follow-Up
6. Prognosis and Outcomes
6.1. Short-Term Neurological Outcomes
6.2. Long-Term Neurological Outcomes
7. Age-Related Differences in Neurological Involvement of HUS
7.1. Prevalence, Clinical Patterns and Imaging Differences
7.2. Therapeutic Implications and Outcomes by Age
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fakhouri, F.; Fila, M.; Provôt, F.; Delmas, Y.; Barbet, C.; Châtelet, V.; Rafat, C.; Cailliez, M.; Hogan, J.; Servais, A.; et al. Pathogenic Variants in Complement Genes and Risk of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Relapse after Eculizumab Discontinuation. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer, O.; Niaudet, P. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: New Developments in Pathogenesis and Treatment. Int. J. Nephrol. 2011, 2011, 908407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, H.; Denamur, E.; Dobrindt, U.; Finlay, B.B.; Hengge, R.; Johannes, L.; Ron, E.Z.; Tønjum, T.; Sansonetti, P.J.; Vicente, M. The Enemy Within Us: Lessons from the 2011 European Escherichia coli O104:H4 Outbreak. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtman, H.; Austin, C.; Lewinski, M.; Stahl, R.A.K. Renal and Neurological Involvement in Typical Shiga Toxin-Associated HUS. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costigan, C.; Raftery, T.; Carroll, A.G.; Wildes, D.; Reynolds, C.; Cunney, R.; Dolan, N.; Drew, R.J.; Lynch, B.J.; O’Rourke, D.J.; et al. Neurological Involvement in Children with Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R. Shiga Toxin (Stx) Classification, Structure, and Function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, EHEC-0024-2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlen, S.; Dersch, P. Anti-Virulence Strategies to Target Bacterial Infections. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2016, 398, 147–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpman, D.; Loos, S.; Tati, R.; Arvidsson, I. Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2017, 281, 123–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, A.L.; Arvidsson, I.; Johansson, K.E.; Chromek, M.; Rebetz, J.; Loos, S.; Kristoffersson, A.C.; Békássy, Z.D.; Mörgelin, M.; Karpman, D. A Novel Mechanism of Bacterial Toxin Transfer within Host Blood Cell-Derived Microvesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, A.L.; Sartz, L.; Nelsson, A.; Békássy, Z.D.; Karpman, D. Shiga Toxin and Lipopolysaccharide Induce Platelet-Leukocyte Aggregates and Tissue Factor Release, a Thrombotic Mechanism in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, A.L.; Sartz, L.; Karpman, D. Complement Activation on Platelet-Leukocyte Complexes and Microparticles in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-Induced Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Blood 2011, 117, 5503–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lämmle, B.; Kremer Hovinga, J.A.; Alberio, L. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1663–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggenenti, P.; Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G. Thrombotic Microangiopathy, Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome, and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, M.; Caprioli, J.; Bresin, E.; Mossali, C.; Pianetti, G.; Gamba, S.; Daina, E.; Fenili, C.; Castelletti, F.; Sorosina, A.; et al. Relative Role of Genetic Complement Abnormalities in Sporadic and Familial aHUS and Their Impact on Clinical Phenotype. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1844–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Fakhouri, F.; Garnier, A.; Bienaimé, F.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Ngo, S.; Moulin, B.; Servais, A.; Provot, F.; Rostaing, L.; et al. Genetics and Outcome of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Nationwide French Series Comparing Children and Adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewski, M.K.; Atkinson, J.P. Complement Regulator CD46: Genetic Variants and Disease Associations. Hum. Genom. 2015, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, J.; Rosales, A.; Fischer, C.; Giner, T. Extra-Renal Manifestations of Complement-Mediated Thrombotic Microangiopathies. Front. Pediatr. 2014, 2, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, M.; Moran, S.M.; Smith, R.J.; Ren, K.Y.M.; Smith, G.N.; Shamseddin, M.K.; Avila-Casado, C.; Garland, J.S. A Case-Based Narrative Review of Pregnancy-Associated Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome/Complement-Mediated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Journal of Neuroradiology. AJNR Case Collections: Diagnosis—Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. [Updated 2023]. Available online: https://www.ajnr.org/ajnr-case-collections-diagnosis/hemolytic-uremic-syndrome (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Malaki, M. Neurological Complications in Typical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Asian J. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 6, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinborn, M.; Leiz, S.; Rüdisser, K.; Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Schick, S.; Bonél, H.M. CT and MRI in Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome with Central Nervous System Involvement: Distribution of Lesions and Prognostic Value of Imaging Findings. Pediatr. Radiol. 2004, 34, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnus, T.; Röther, J.; Simova, O.; Meier-Cillien, M.; Repenthin, J.; Möller, F.; Gbadamosi, J.; Panzer, U.; Wengenroth, M.; Hagel, C.; et al. The Neurological Syndrome in Adults during the 2011 Northern German E. coli Serotype O104:H4 Outbreak. Brain 2012, 135, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, J.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kita, T.; Higure, A.; Takeda, T.; Tanaka, N.; Yoshida, S. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Histopathological Study of Brain Lesions in Rabbits Given Intravenous Verotoxin 2. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 5053–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzipori, S.; Chow, C.W.; Powell, H.R. Cerebral Infection with Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Humans and Gnotobiotic Piglets. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 1099–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, M.; Ichiyama, T.; Matsushige, T.; Iwaki, T.; Iyoda, K.; Fukuda, K.; Makata, H.; Matsubara, T.; Furukawa, S. Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 1 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-1 in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Encephalopathy. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 196, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, N.D.; Kaplan, A.M.; Bernes, S.M.; Cohen, M.L. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Particular Involvement of Basal Ganglia and Favorable Outcome. Pediatr. Neurol. 1995, 12, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Takaba, H.; Inoue, T.; Saku, Y.; Saito, F.; Ibayashi, S.; Fujishima, M. MRI Findings of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Encephalopathy: Widespread Symmetrical Distribution. J. Neuroimaging 2003, 13, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Gudinchet, F.; Meagher-Villemure, K.; Hanquinet, S.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Maeder, P.; Meuli, R. Brain Involvement in Haemolytic-Uraemic Syndrome: MRI Features of Coagulative Necrosis. Neuroradiology 2001, 43, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathanson, S.; Kwon, T.; Elmaleh, M.; Charbit, M.; Launay, E.A.; Harambat, J.; Brun, M.; Ranchin, B.; Bandin, F.; Cloarec, S.; et al. Acute Neurological Involvement in Diarrhea-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounier, S.; Gavotto, A.; Tenenbaum, J.; Meyer, P.; Fila, M.; Baleine, J. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Related to Shiga-like Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli with Encephalitis Hiding a Human Herpesvirus-6 Infection: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestracci, A.; Meni Battaglia, L.; Martin, S.M.; Toledo, I.; Puyol, I.; Beaudoin, L.; Robledo, N.L. Síndrome Urémico Hemolítico por Escherichia coli e Hipocomplementemia con Respuesta Favorable a Eculizumab: Comunicación de un Caso. Rev. Fac. Cien. Med. Univ. Nac. Córdoba 2021, 78, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasa, M.; Musgrave, J.; Abe, K.; Tanaka, L.; Xoinis, K.; Shiramizu, B.; Foskett, G.; Lau, R. A Case of Escherichia coli Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in a 10-Year-Old Male with Severe Neurologic Involvement Successfully Treated with Eculizumab. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2017, 5, 2324709617741144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.A.; Khalil, D.F.; Hasham, M.A.; Youssef, A.; Rashad, M.; Awadallah, M.; Ali, H. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Central Nervous System Manifestations: A Case Report and Literature Review. Radiol. Case Rep. 2023, 18, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.R.; Johnson, S. Eculizumab in the treatment of Shiga toxin haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montini, G.; Parodi, A.; Zauli, G.; Rizzoni, G.; Loi, B. Neurological Involvement in Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.J.; Boyd, S.G.; Tasker, R.C. Acute Neurology and Neurophysiology of Haemolytic-Uraemic Syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 84, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, T. Chronic Renal Failure and Guanidino Compounds. Yakugaku Zasshi 1997, 117, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, K.J.; Swick, H.M.; Haworth, N. Neurological involvement in hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1986, 19, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, T.A.; Schmook, M.T.; Brücke, C. Pearls & Oy-sters: Neurologic Involvement in Shiga Toxin-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Neurology 2024, 103, e209881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavasoli, A.; Zafaranloo, N.; Hoseini, R.; Otukesh, H.; Nakhaiee, S. Frequency of Neurological Involvement in Patients with/without Diarrhea Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2021, 35, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi Larijani, F.; Sayarifard, A.; Javadi Larijani, F.; Ataei, N.; Pajouhi, A. Typical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Diffused Brain Ischemia as a Complication: A Case Report of a Child in Iran. J. Ped. Nephrol. 2013, 2, 39–42. Available online: https://journals.sbmu.ac.ir/jpn/article/view/4979 (accessed on 30 May 2025).
- Lo Bianco, M.; Rinella, S.; D’Arco, F.; Caroli, F.; Massimino, M.; Faraci, M.; Morana, G. Isolated Cerebellar Stroke in a Paediatric Patient with Typical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review. Neuroradiology 2024, 66, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, A.; Ish-Horowitcz, M.; el-Peleg, O.; Mor, J.; Branski, D. Stroke in a patient with hemolytic-uremic syndrome with a good outcome. Brain Dev. 1986, 8, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travert, B.; Rafat, C.; Mariani, P.; Cointe, A.; Dossier, A.; Coppo, P.; Joseph, A. Shiga Toxin-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Specificities of Adult Patients and Implications for Critical Care Management. Toxins 2021, 13, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campistol, J.M.; Arias, M.; Ariceta, G.; Blasco, M.; Espinosa, L.; Espinosa, M.; Grinyó, J.M.; Macía, M.; Mendizábal, S.; Praga, M.; et al. An update for atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome: Diagnosis and treatment. A consensus document. Nefrologia 2015, 35, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Inui, T.; Yamada, M.; Kinoshita, Y.; Yamada, T.; Morikawa, T.; Ogawa, M.; Takano, T. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Complicated by Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis: A Case Report. Pediatr. Int. 2014, 56, e66–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, J.S.; Havens, P.L.; Higgins, J.J.; O’Rourke, P.P.; Estroff, J.A.; Strand, R. Neurological complications of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 1989, 4, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Children with Typical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A 10-Year Retrospective Study. Medicine 2019, 98, e15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, N.M.; Anastasopoulou, C.; Patel, G.; Badireddy, M. Hypercalcemia. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430900/ (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Zhao, H.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; He, D.; Shen, B. Acidosis leads to neurological disorders through overexciting cortical pyramidal neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 415, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.M. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). Clin. Lab. Med. 2010, 30, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Thaker, H.; Wang, C.; Xu, Z.; Dong, M. Diagnosis and Treatment for Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Toxins 2023, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasni Bouraoui, I.; Gamaoun, W.; Arifa, N.; Mama, N.; Kadri, K.; Harbi, A.; Tlili Graeiss, K. MRI and MR Spectroscopy Findings in a Case of Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome with Central Nervous System Involvement. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 40, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldo, I.; Manara, R.; Cogo, P.; Sartori, S.; Murer, L.; Battistella, P.A.; Laverda, A.M. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Findings in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome with Central Nervous System Involvement. J. Child Neurol. 2009, 24, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Loos, S.; Wehrmann, C.; Horstmann, D.; Donnerstag, F.; Lemke, J.; Hillebrand, G.; Löbel, U.; Pape, L.; Haffner, D.; et al. Neurological Involvement in Children with E. coli O104:H4-Induced Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014, 29, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenborn, K.; Donnerstag, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Heeren, M.; Worthmann, H.; Hecker, H.; Schmitt, R.; Schiffer, M.; Pasedag, T.; Schuppner, R.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of E. coli Infection-Induced Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome in Adults. Neurology 2012, 79, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.; Rashid, S.; Williams, M.T. A Unique Case of Neurological Manifestation of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Which Responded to the Treatment with Intravenous Magnesium Sulfate. Int. J. Case Rep. Images 2017, 8, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuppner, R.; Maehlmann, J.; Dirks, M.; Worthmann, H.; Tryc, A.B.; Sandorski, K.; Bahlmann, E.; Kielstein, J.T.; Giesemann, A.M.; Lanfermann, H.; et al. Neurological Sequelae in Adults After E. coli O104:H4 Infection-Induced Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome. Medicine 2016, 95, e2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilkis, M.D.; Bonany, P. Hydration in Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 2021, 119, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegler, R.L.; Pysher, T.J.; Tesh, V.L.; Taylor, F.B.; Krizanac-Bengez, L.; Kaplan, B.S. Prophylactic Heparinization Is Ineffective in a Primate Model of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2002, 17, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunathan, V.; Sethi, S.K.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Dhaliwal, M.; Raina, R.; Jha, P.; Bansal, S.B.; Kher, V. Targeting Renin-Angiotensin System in Malignant Hypertension in Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Indian J. Nephrol. 2017, 27, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harkins, V.J.; McAllister, D.A.; Reynolds, B.C. Shiga-Toxin E. coli Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Review of Management and Long-Term Outcome. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. 2020, 8, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, N.; Abe, T.; Ikeda, N.; Nagahiro, Y.; Kawano, S.; Tochigi, T.; Nakaike, T.; Yamashita, K.; Kubo, K.; Yamanaka, A.; et al. Clinical Features and Outcomes of Four Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Cases at a Single Institution in Miyazaki Prefecture from 2015 to 2019. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2022, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, T.; Warshaw, B.; Katzenstein, H.M. Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Responsive to Steroids and Intravenous Immune Globulin. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, R.K.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Scott, M.K.; Dunn, J.; Smith, K.; Tobin-D’Angelo, M.; Shiferaw, B.; Wymore, K.; Clogher, P.; Palmer, A.; et al. Risk of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Related to Treatment of Escherichia coli O157 Infection with Different Antimicrobial Classes. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakoullis, L.; Papachristodoulou, E.; Chra, P.; Panos, G. Shiga toxin-induced haemolytic uraemic syndrome and the role of antibiotics: A global overview. J. Infect. 2019, 79, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangaraju, S.; Khandelwal, P.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, M.; Puraswani, M.; Saini, R.; Hari, P.; Coshic, P.; Sinha, A.; Bagga, A. Abbreviated Protocol of Plasma Exchanges for Patients with Anti-Factor H Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 2091–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, P.; Thomas, C.C.; Rathi, B.S.; Hari, P.; Tiwari, A.N.; Sinha, A.; Bagga, A. Membrane-Filtration Based Plasma Exchanges for Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: Audit of Efficacy and Safety. J. Clin. Apher. 2019, 34, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wildes, D.M.; Harvey, S.; Costigan, C.S.; Hanisch, B.R.; Schmidt, A.G. Eculizumab in STEC-HUS: A Paradigm Shift in the Management of Pediatric Patients with Neurological Involvement. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percheron, L.; Gramada, R.; Tellier, S.; Salomon, R.; Harambat, J.; Llanas, B.; Fila, M.; Allain-Launay, E.; Lapeyraque, A.L.; Leroy, V.; et al. Eculizumab treatment in severe pediatric STEC-HUS: A multicenter retrospective study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnol, R.; Alfisi, A.; Moi, M.; Bonvecchio, I.; Bertazza Partigiani, N.; Vidal, E. Eculizumab in Severe Pediatric STEC-HUS and Its Impact on Neurological Prognosis—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2025, 184, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, Y.Y. Ravulizumab: A Review in Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Drugs 2021, 81, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, R.-G.; Anderco, P.; Ichim, C.; Cimpean, A.-M.; Todor, S.B.; Glaja-Iliescu, M.; Crainiceanu, Z.P.; Popa, M.L. Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Review of Complement Dysregulation, Genetic Susceptibility and Multiorgan Involvement. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaeyi, S.A.; Bozio, C.H.; Duffy, J.; Rubin, L.G.; Hariri, S.; Stephens, D.S.; MacNeil, J.R. Meningococcal Vaccination: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, United States, 2020. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2020, 69, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (CADTH). Ravulizumab (Ultomiris): CADTH Reimbursement Review: Therapeutic Area: Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder; CADTH: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2024; Report No. SR0785CL. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/39088679 (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Abou-Khalil, B.W. Antiepileptic Drugs. Continuum 2016, 22, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buder, K.; Latal, B.; Nef, S.; Neuhaus, T.J.; Laube, G.F.; Spartà, G. Neurodevelopmental Long-Term Outcome in Children after Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formeck, C.; Swiatecka-Urban, A. Extra-Renal Manifestations of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qamar, I.U.; Ohali, M.; MacGregor, D.L.; Wasson, C.; Krekewich, K.; Marcovitch, S.; Arbus, G.S. Long-Term Neurological Sequelae of Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome: A Preliminary Report. Pediatr. Nephrol. 1996, 10, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pundzienė, B.; Dobilienė, D.; Čerkauskienė, R.; Mitkienė, R.; Medzevičienė, A.; Darškuvienė, E.; Jankauskienė, A. Long-Term Follow-Up of Children with Typical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Medicina 2015, 51, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, H.; Buder, K.; Landolt, M.A.; Neuhaus, T.J.; Laube, G.F.; Spartà, G. Long-Term Health-Related Quality of Life and Psychological Adjustment in Children after Haemolytic-Uraemic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2017, 32, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwmeester, R.N.; Engel, L.J.; Altena, W.; Renette, C.; van Daelen, C.; van Kempen, E.; de Wildt, R.; van de Kar, N.C.A.J. Living with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in the Netherlands: Patient and Family Perspective. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 2189–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beczkiewicz, A.T.E.; Scharff, R.L.; Kowalcyk, B.B. Facilitating Evaluation of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Long-Term Health Outcomes through Social Media Support Groups. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 544154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.C.; Garcia, X.; Bhakta, R.T.; Sanders, E.; Prodhan, P. Severe Acute Neurologic Involvement in Children with Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020013631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, A.; Hofer, J.; Zimmerhackl, L.B.; Jungraithmayr, T.C.; Riedl, M.; Giner, T.; Strasak, A.; Orth-Höller, D.; Würzner, R.; Karch, H.; et al. Need for Long-Term Follow-Up in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli-Associated Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Due to Late-Emerging Sequelae. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.F., Jr.; Brasher, C.; Siegler, R.L. CNS Manifestations of the Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome: Relationship to Metabolic Alterations and Prognosis. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1980, 134, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlieper, A.; Orrbine, E.; Wells, G.A.; Clulow, M.; McLaine, P.N.; Rowe, P.C. Neuropsychological Sequelae of Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome. Arch. Dis. Child. 1999, 80, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simova, O.; Weineck, G.; Schuetze, T.; Wegscheider, K.; Panzer, U.; Stahl, R.A.; Gerloff, C.; Magnus, T. Neuropsychological Outcome after Complicated Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.K.; Kim, I.O.; Kim, W.S.; Hwang, Y.S.; Choi, Y.; Yeon, K.M. Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: MR Findings of CNS Complications. Pediatr. Radiol. 1994, 24, 585–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, A.; Staudt, M.; Klare, B.; von Einsiedel, H.G.; Krägeloh-Mann, I. Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome with Involvement of Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum. Neuropediatrics 1999, 30, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengenroth, M.; Hoeltje, J.; Repenthin, J.; Meyer, T.N.; Bonk, F.; Becker, H.; Faiss, S.; Stammel, O.; Urban, P.P.; Bruening, R. Central Nervous System Involvement in Adults with Epidemic Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, E.L.; Rabinstein, A.A. Neurological Manifestations of Thrombotic Microangiopathy Syndromes in Adult Patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, K.; Göknar, N.; Gülhan, B.; Melek, E.; Yıldırım, Z.Y.; Baskın, E.; Hayran, M.; Gülleroglu, K.; Özçakar, Z.B.; Ozaltin, F.; et al. Extra-Renal Manifestations of Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome in Children. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duneton, C.; Kwon, T.; Dossier, C.; Baudouin, V.; Fila, M.; Mariani-Kurkdijan, P.; Nel, I.; Boyer, O.; Hogan, J. IgG-Immunoadsorptions and Eculizumab Combination in STEC-Hemolytic and Uremic Syndrome Pediatric Patients with Neurological Involvement. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2025, 40, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinale, J.M.; Ruebner, R.L.; Copelovitch, L.; Kaplan, B.S. Long-Term Outcomes of Shiga Toxin Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Zwart, P.L.; Mueller, T.F.; Spartà, G.; Luyckx, V.A. Eculizumab in Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 1369–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, C.M.; Licht, C.; Muus, P.; Greenbaum, L.A.; Babu, S.; Bedrosian, C.; Bingham, C.; Cohen, D.J.; Delmas, Y.; Douglas, K.; et al. Terminal Complement Inhibitor Eculizumab in Atypical Hemolytic–Uremic Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2169–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, L.A.; Fila, M.; Ardissino, G.; Al-Akash, S.I.; Evans, J.; Henning, P.; Lieberman, K.V.; Maringhini, S.; Pape, L.; Rees, L.; et al. Eculizumab Is a Safe and Effective Treatment in Pediatric Patients with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulleroglu, K.; Fidan, K.; Hançer, V.S.; Bayrakci, U.; Baskin, E.; Soylemezoglu, O. Neurologic Involvement in Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and Successful Treatment with Eculizumab. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2013, 28, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohanian, M.; Cable, C.; Halka, K. Eculizumab Safely Reverses Neurologic Impairment and Eliminates Need for Dialysis in Severe Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonkovic, U.; Bogicevic, M.; Manzar, A.; Andrejic, N.; Sic, A.; Atanaskovic, M.; Gajić, S.; Bontić, A.; Ksiazek, S.H.; Mijušković, A.; et al. Neurological Manifestations of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070717
Tonkovic U, Bogicevic M, Manzar A, Andrejic N, Sic A, Atanaskovic M, Gajić S, Bontić A, Ksiazek SH, Mijušković A, et al. Neurological Manifestations of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(7):717. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070717
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonkovic, Una, Marko Bogicevic, Aarish Manzar, Nikola Andrejic, Aleksandar Sic, Marko Atanaskovic, Selena Gajić, Ana Bontić, Sara Helena Ksiazek, Ana Mijušković, and et al. 2025. "Neurological Manifestations of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review" Brain Sciences 15, no. 7: 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070717
APA StyleTonkovic, U., Bogicevic, M., Manzar, A., Andrejic, N., Sic, A., Atanaskovic, M., Gajić, S., Bontić, A., Ksiazek, S. H., Mijušković, A., Stojanović, N. M., & Baralić, M. (2025). Neurological Manifestations of Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Brain Sciences, 15(7), 717. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15070717












